ATI TEAS 7- Cardiovascular System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
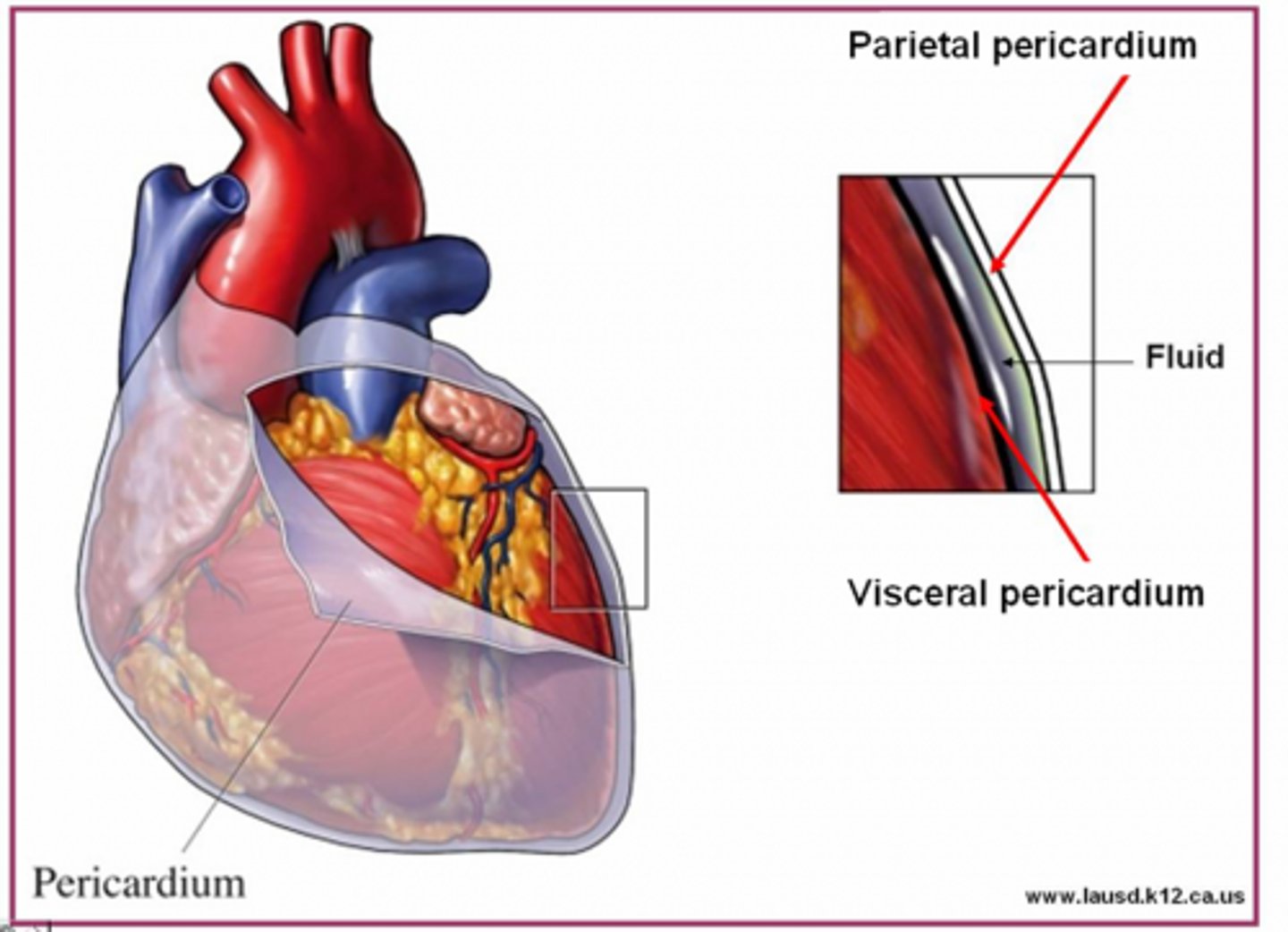
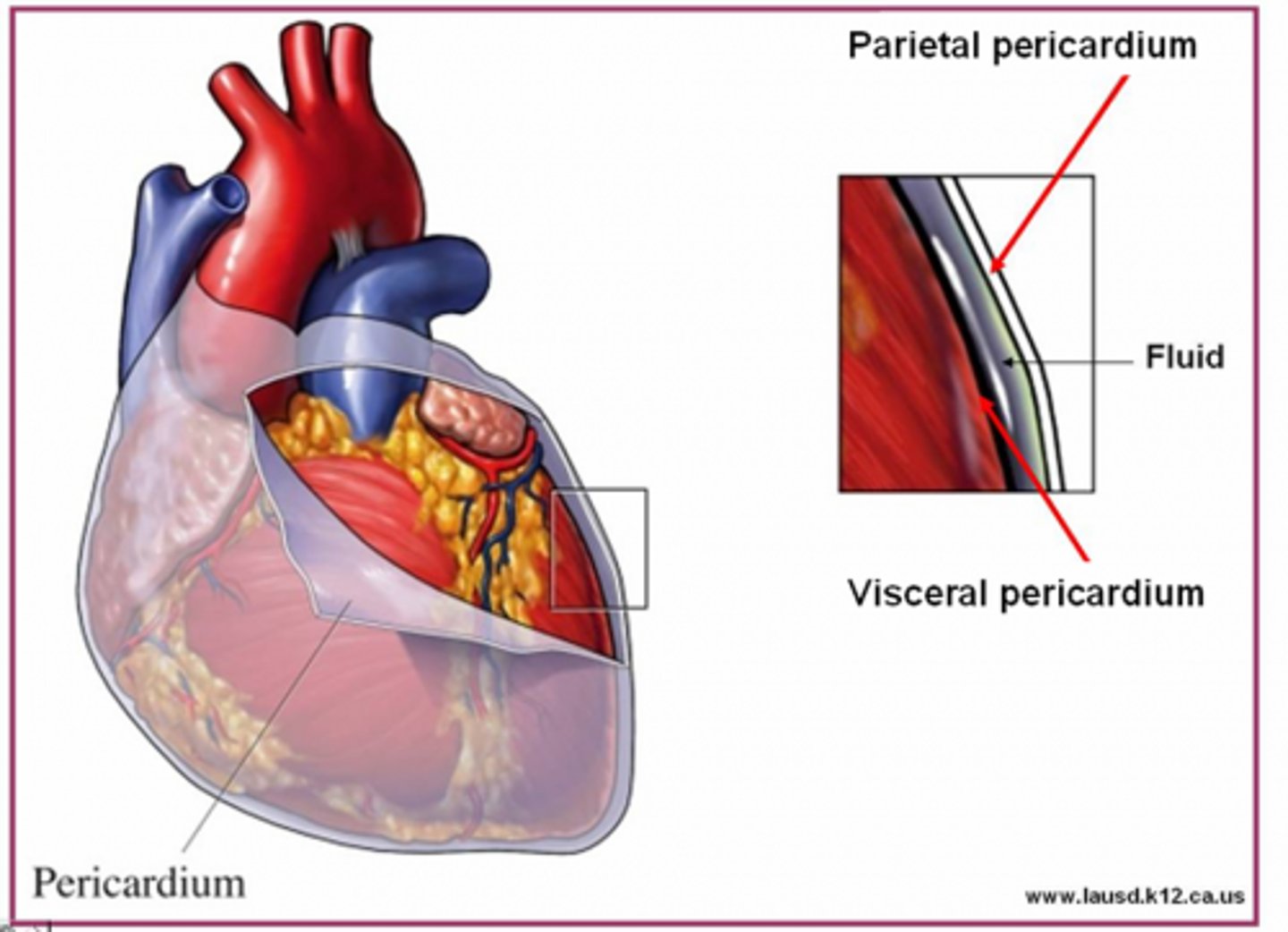
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
Myocardium
Middle Layer of the heart
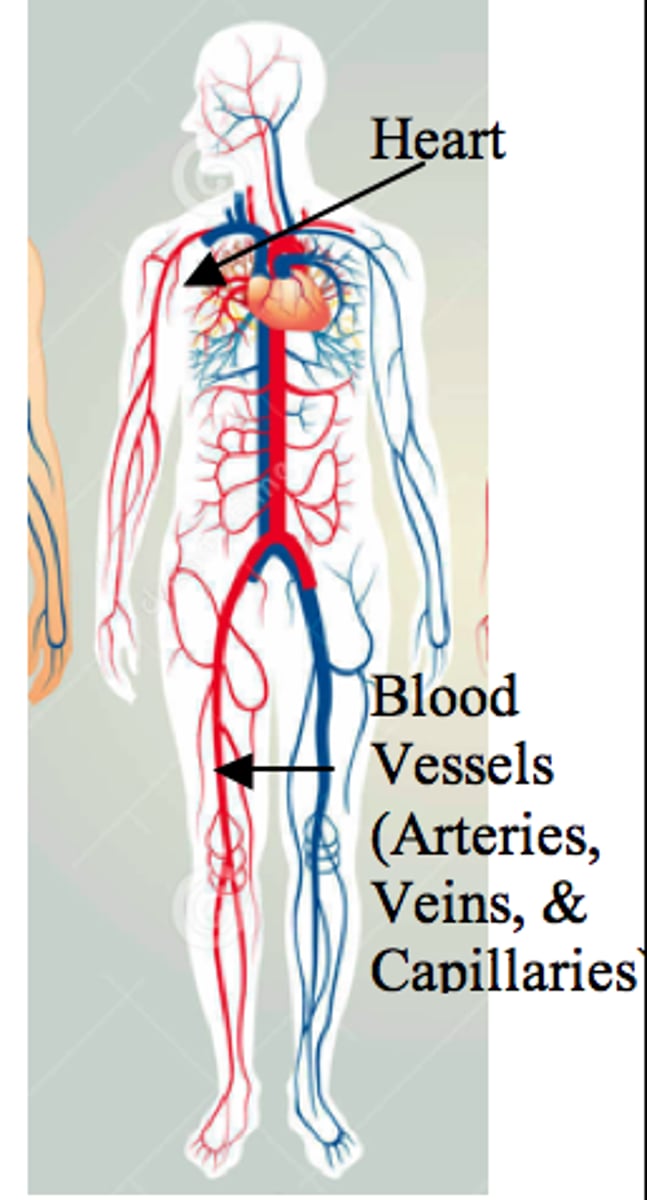
Circulatory System Function
To transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, ions, and fluids, throughout the body, as well as remove of metabolic wastes.
The Heart Function
Pumps blood throughout the body

The Three Layers of the Heart
Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
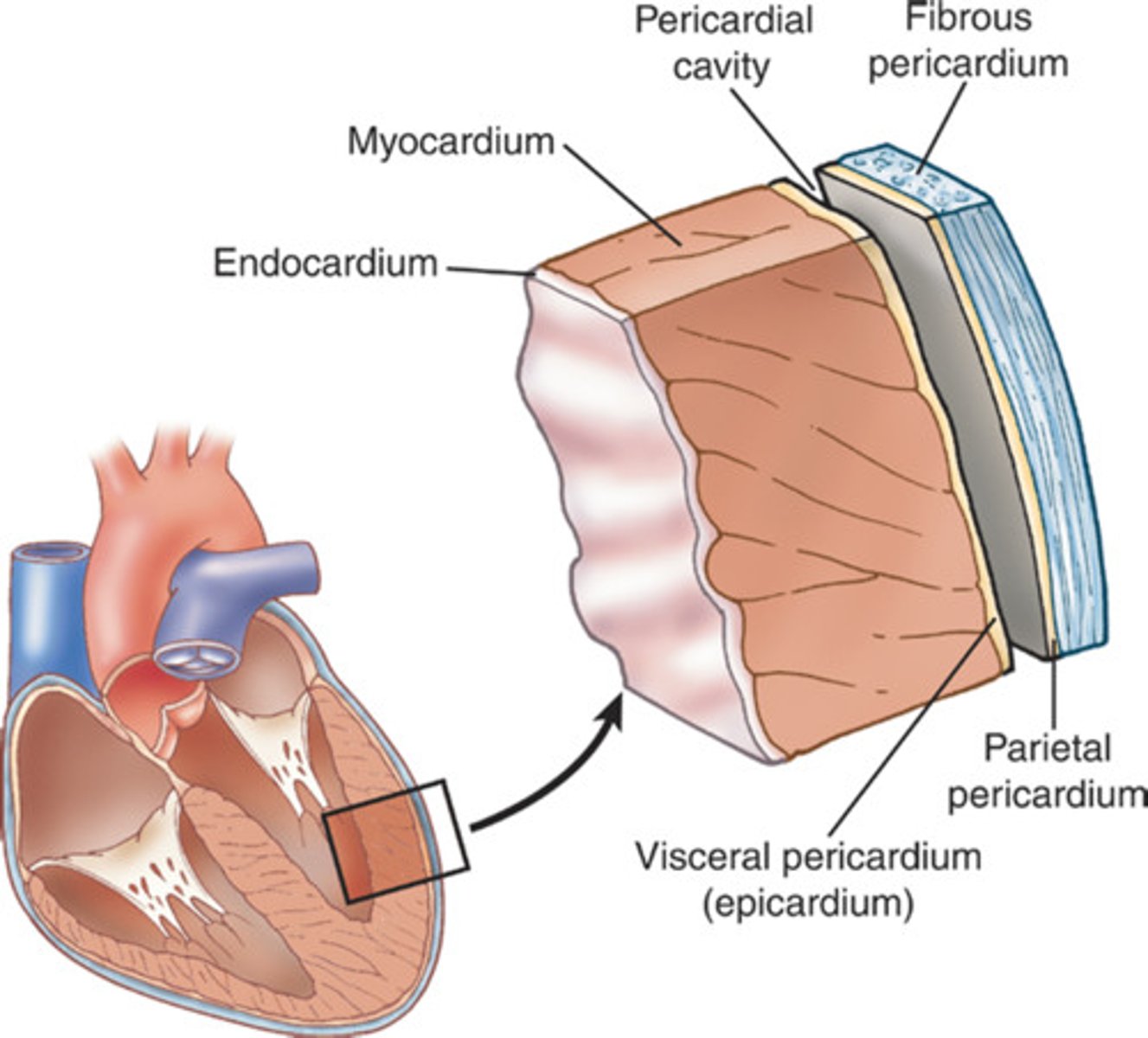
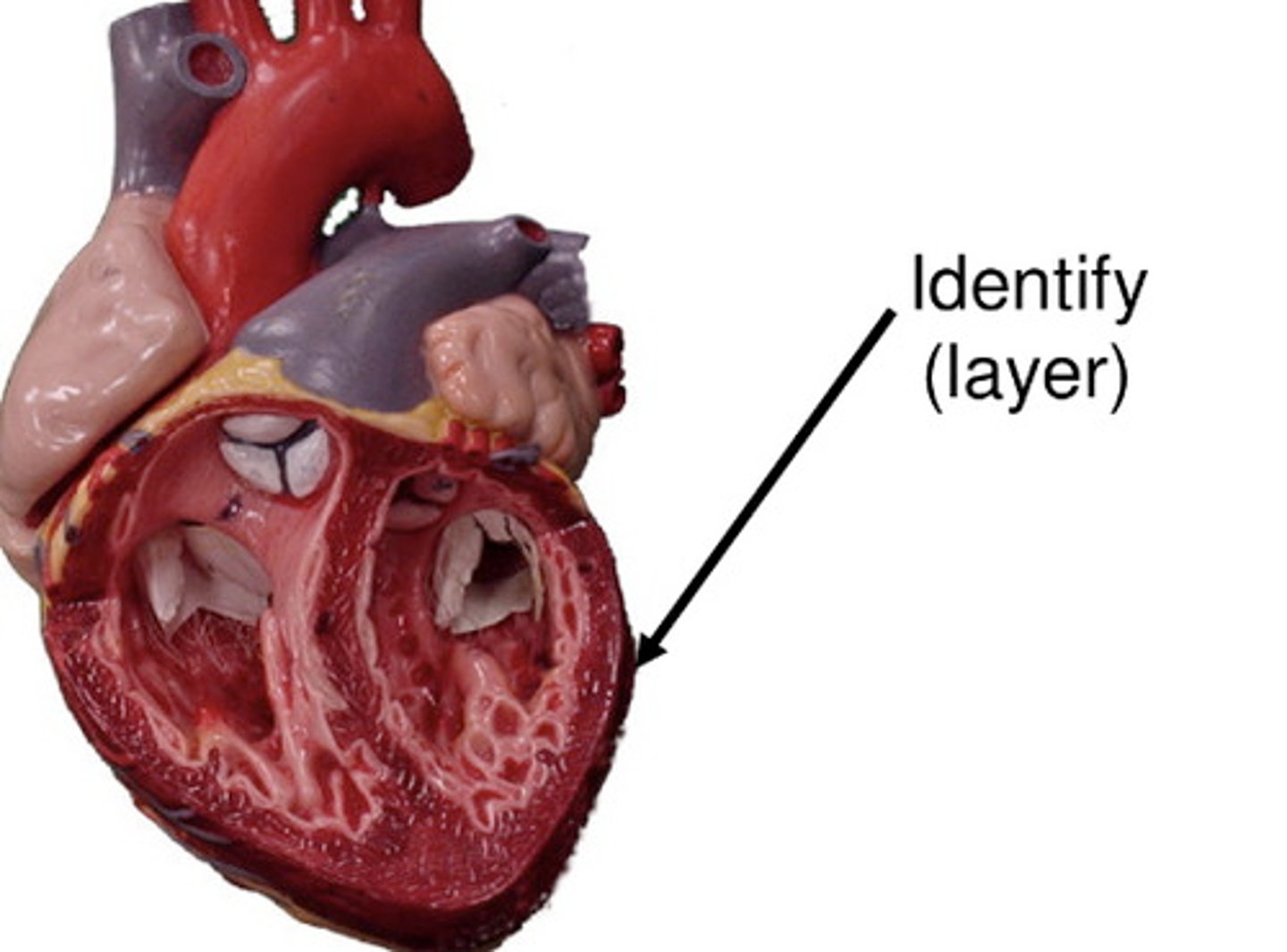
Epicardium
Outer layer of the heart
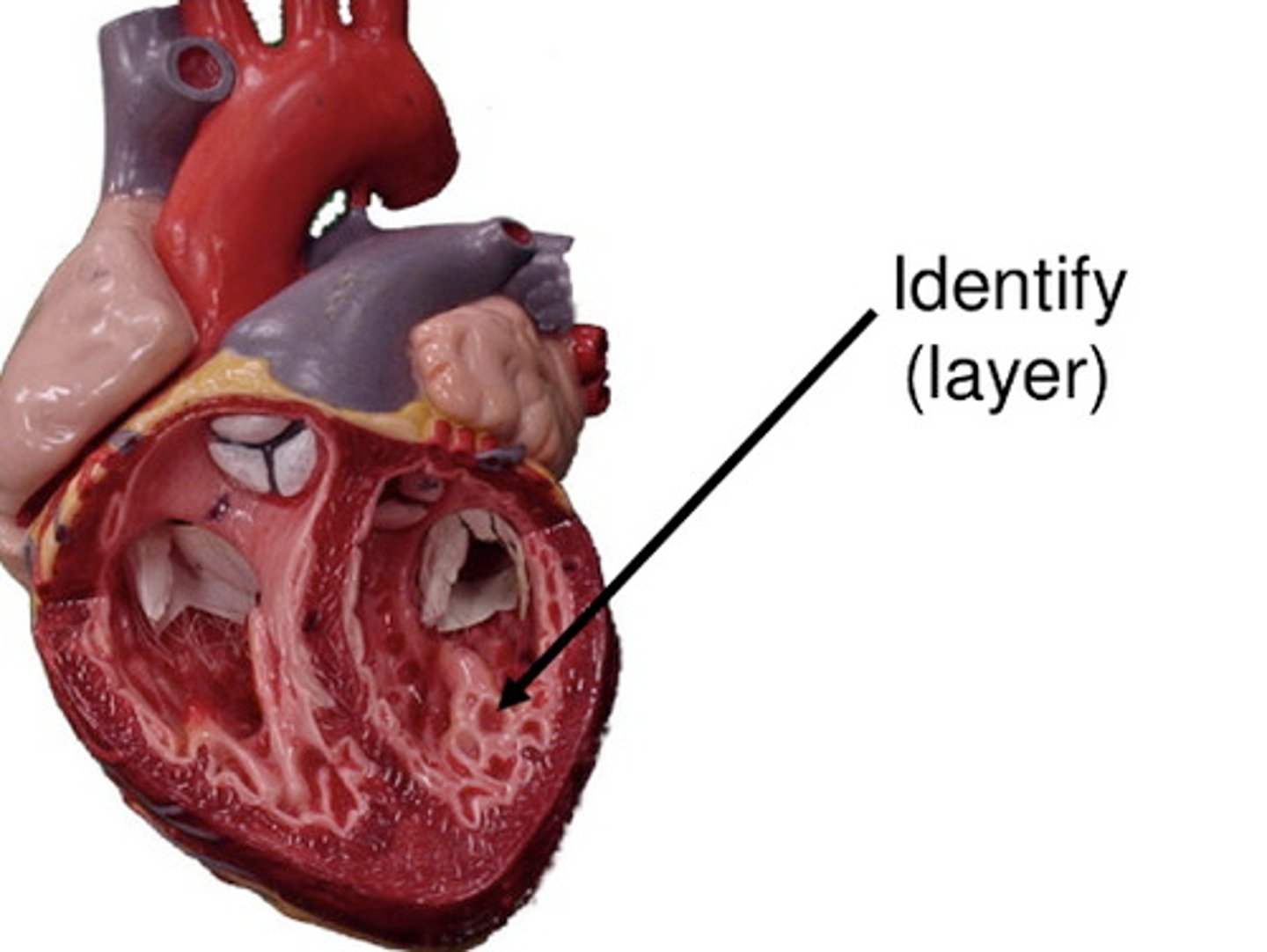
Endocardium
Inner layer of the heart; lines the heart chambers and valves.
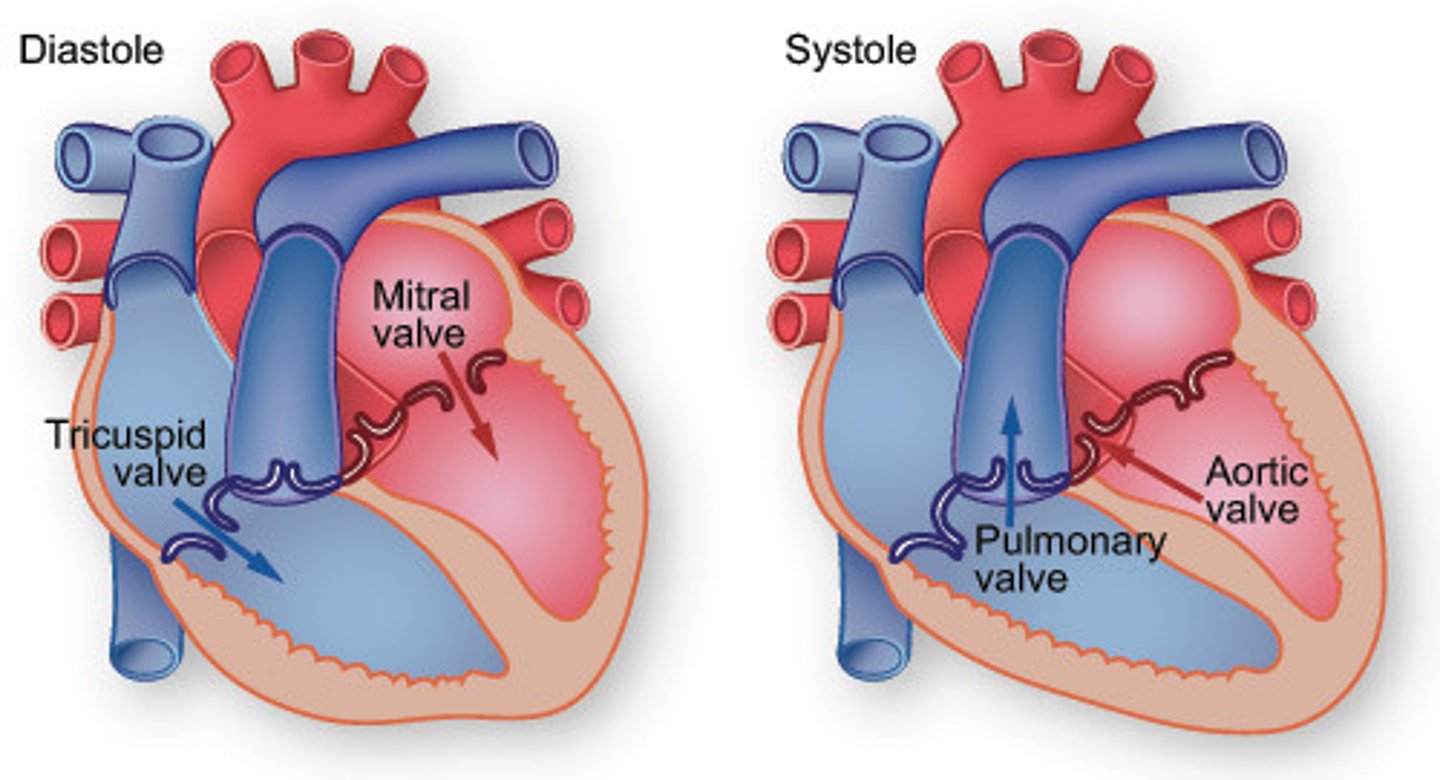
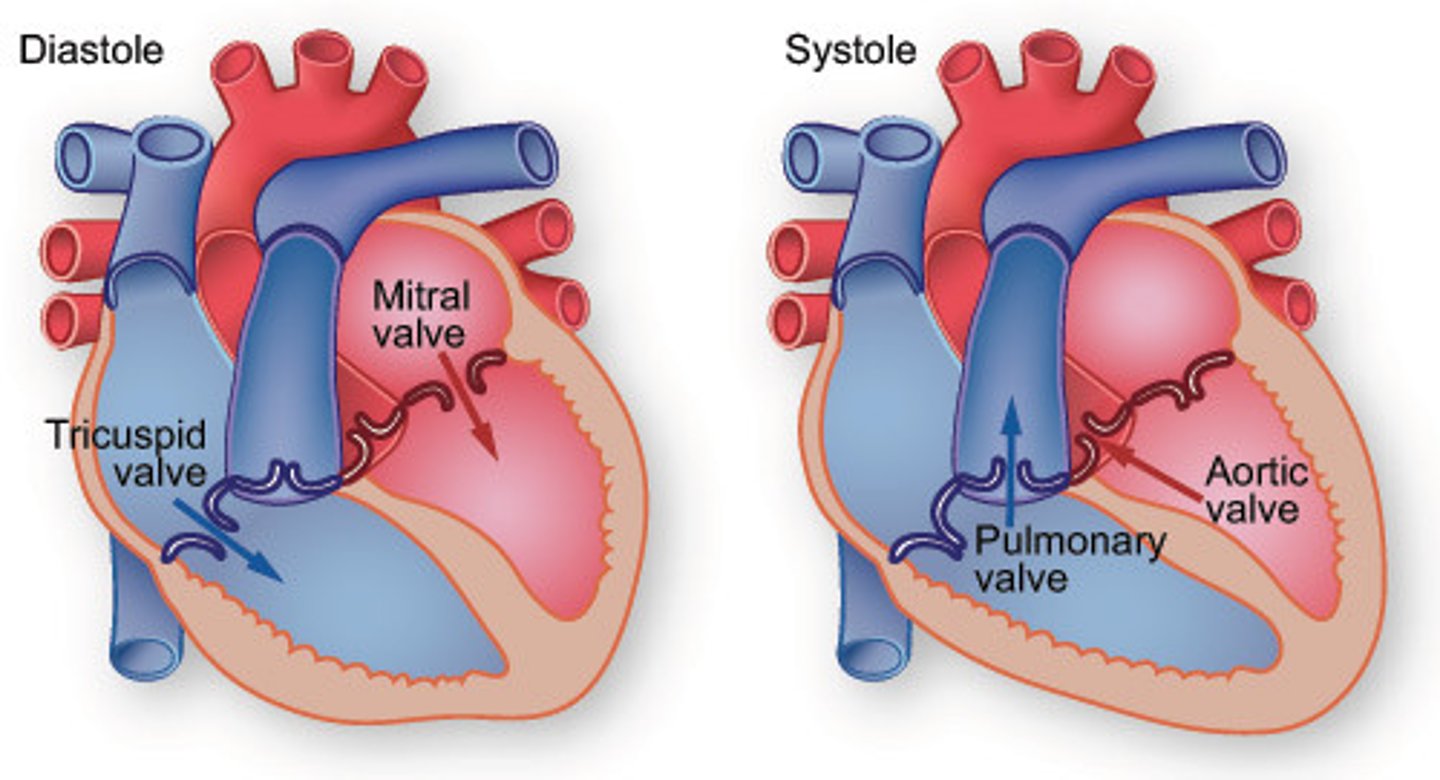
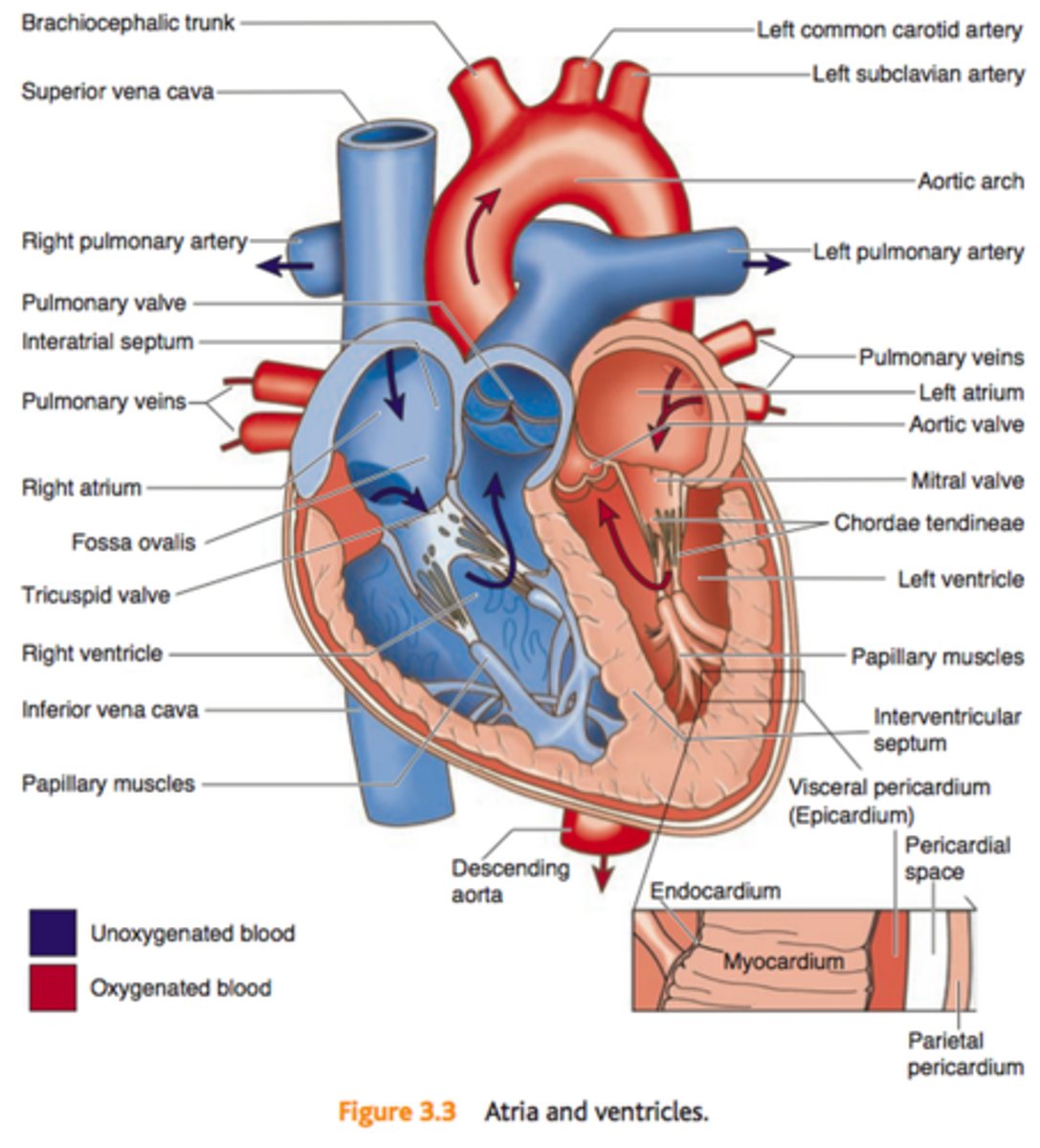
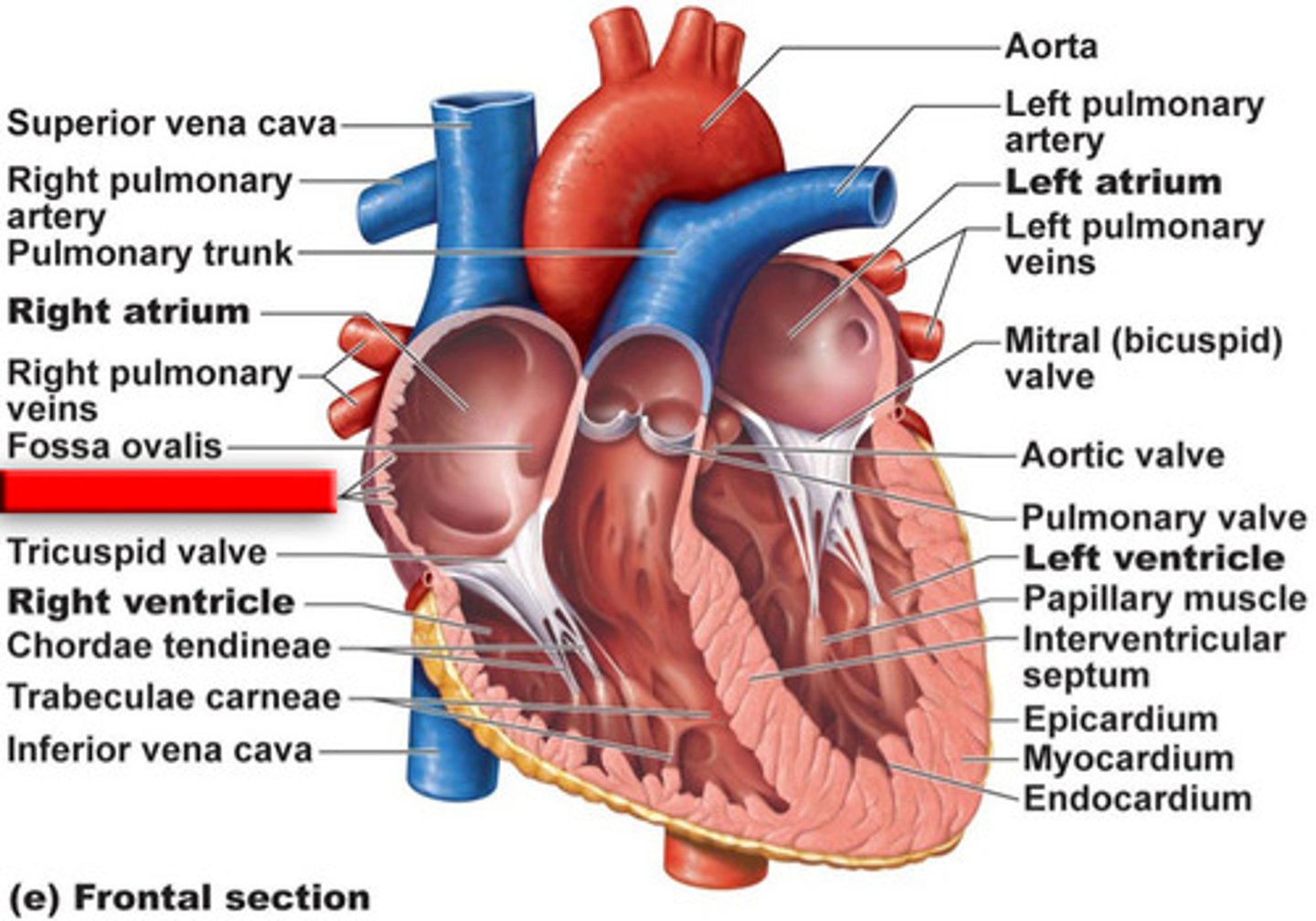
Flow of blood through the heart
1. Deoxygenated blood enters right atrium through Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
2. Blood enters right ventricle through tricuspid valve 3. Blood exits right ventricle through pulmonary valve and enters pulmonary artery
4. Left and right pulmonary arteries send blood to lungs, where gas exchange occurs
5. Oxygenated blood returns to heart via the pulmonary veins enters left atrium
6. Blood enters left ventricle through mitral valve
7. Blood exits left ventricle through aortic semilunar valve to enter aorta
8. Aorta distributes blood to body
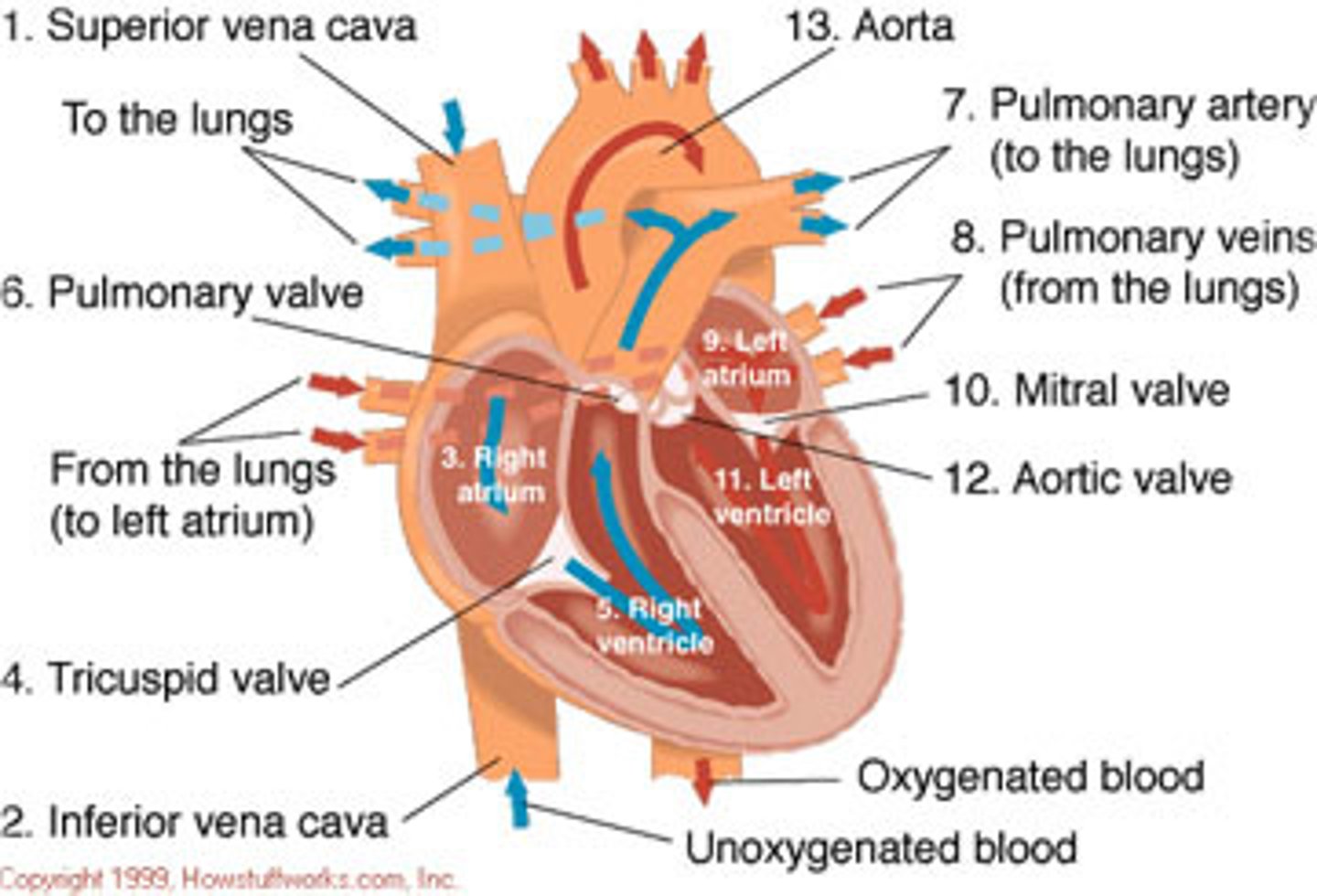
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
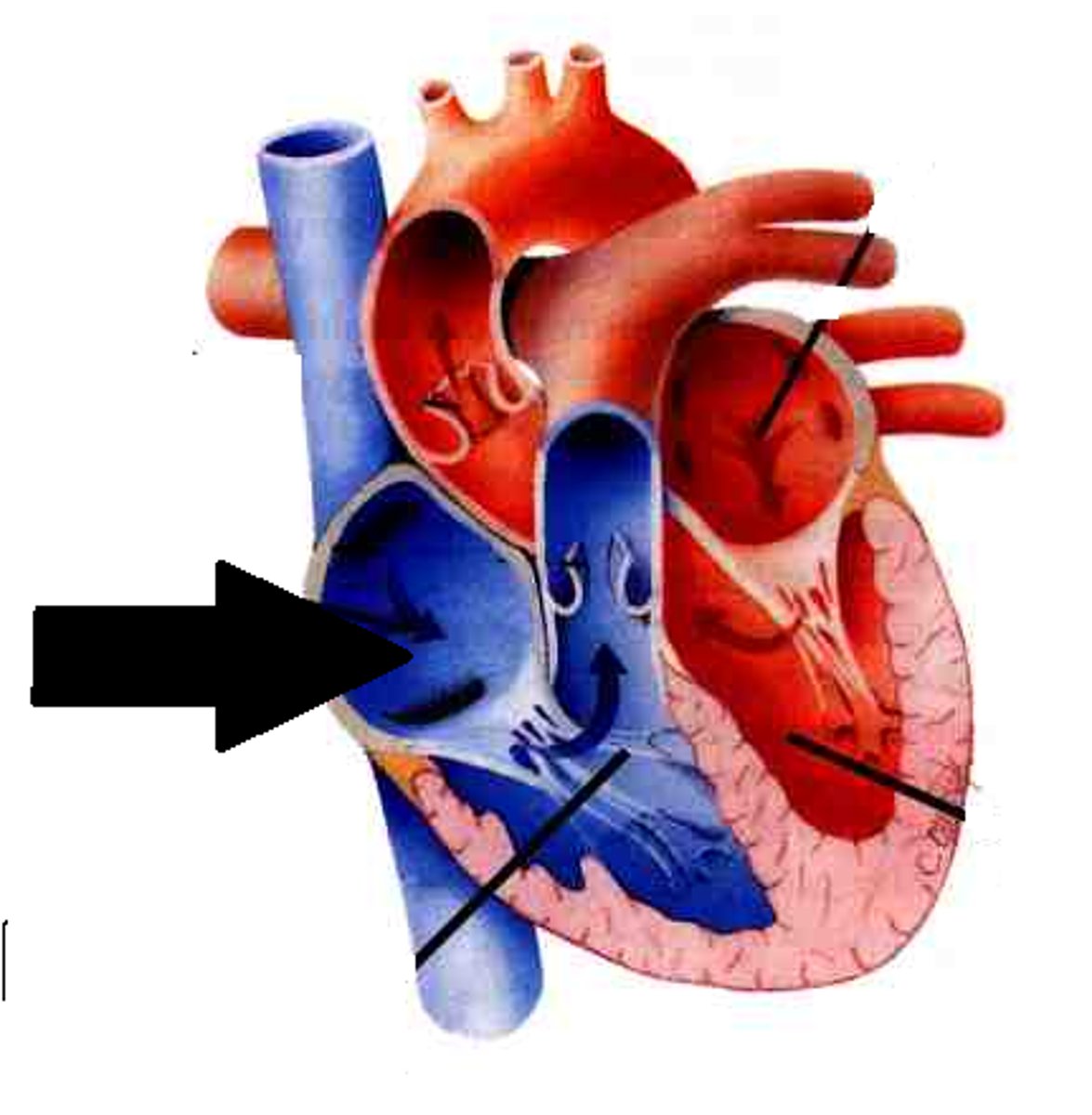
Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
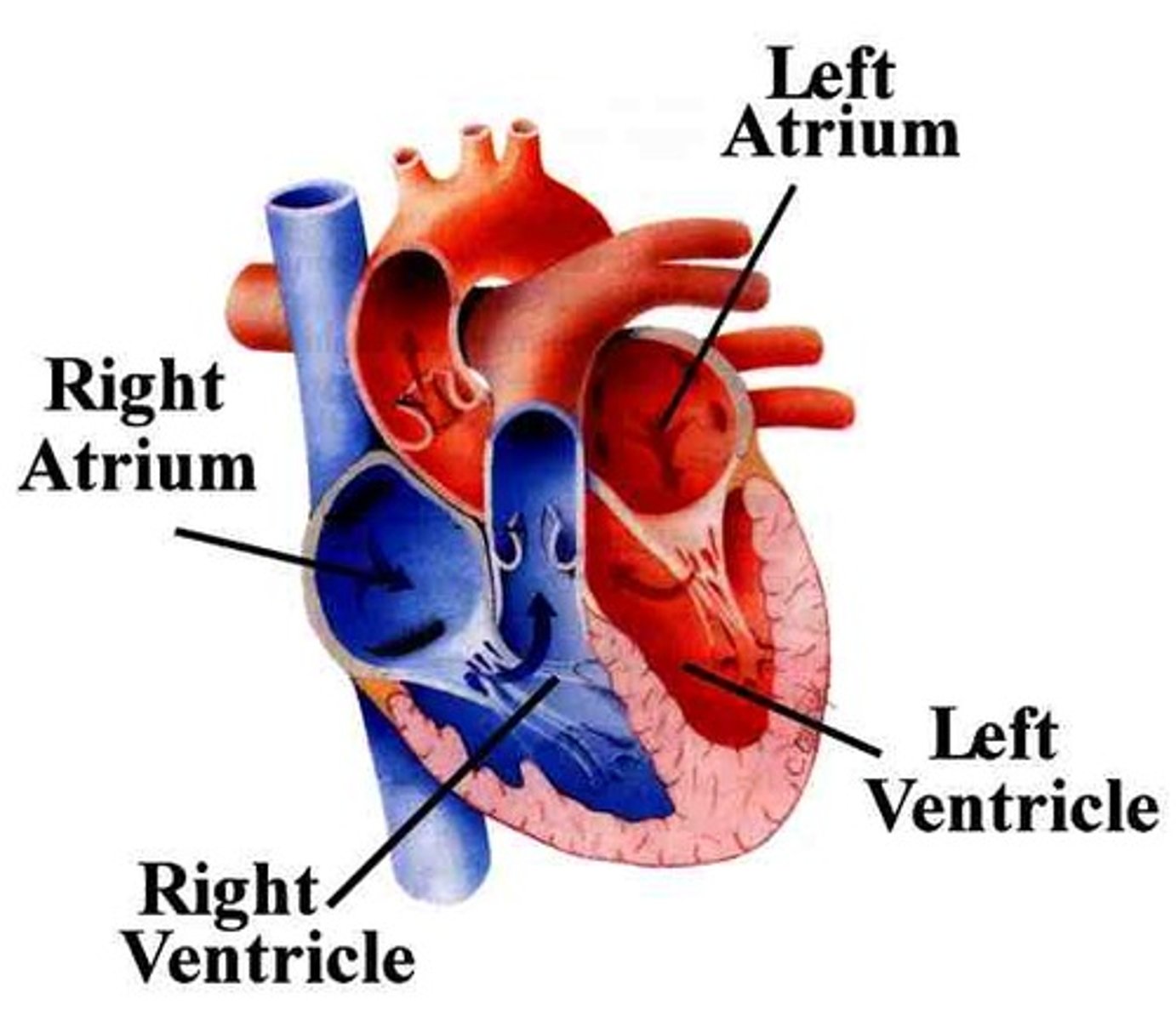
Left Atrium
Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins
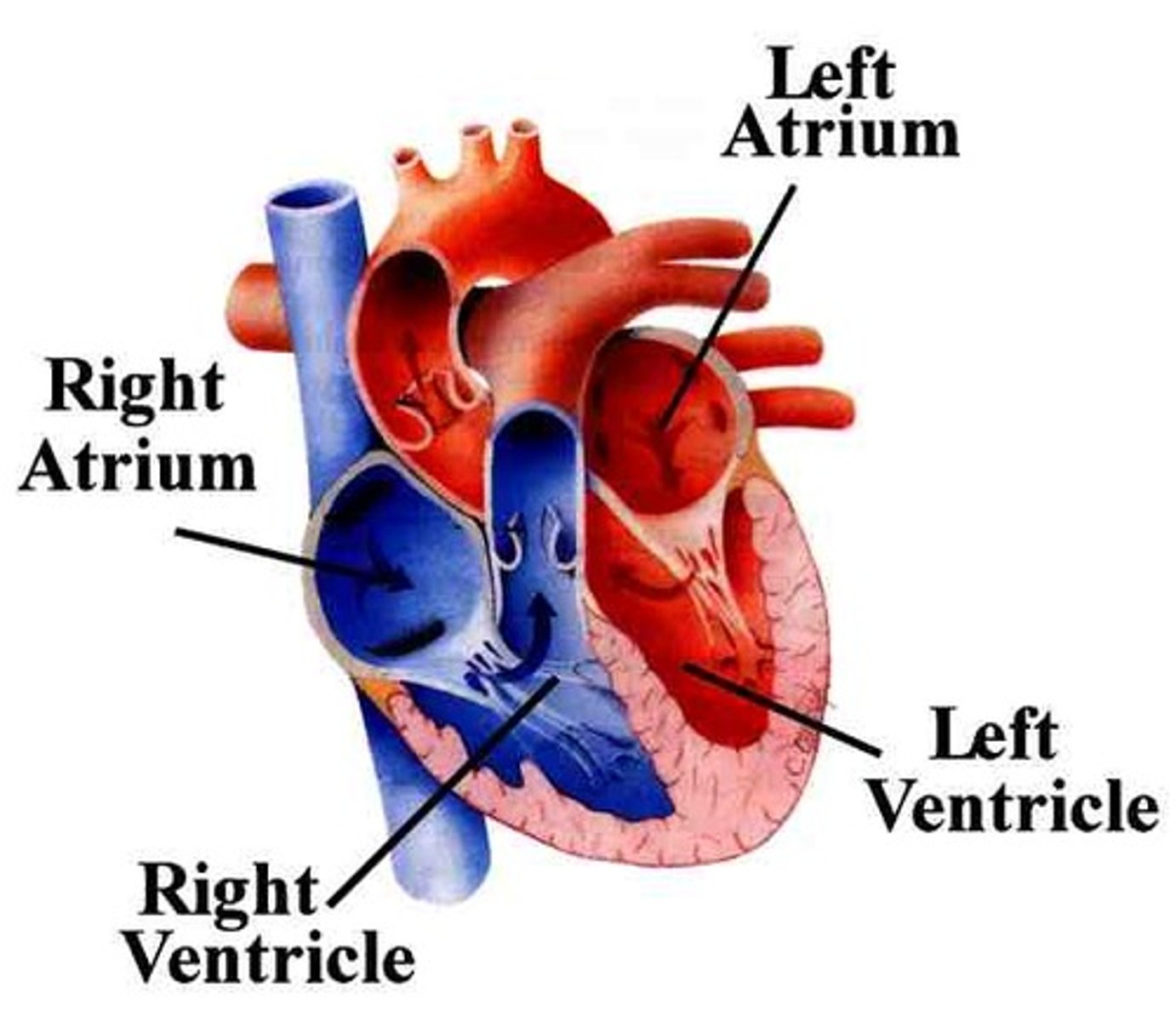
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body via the aorta
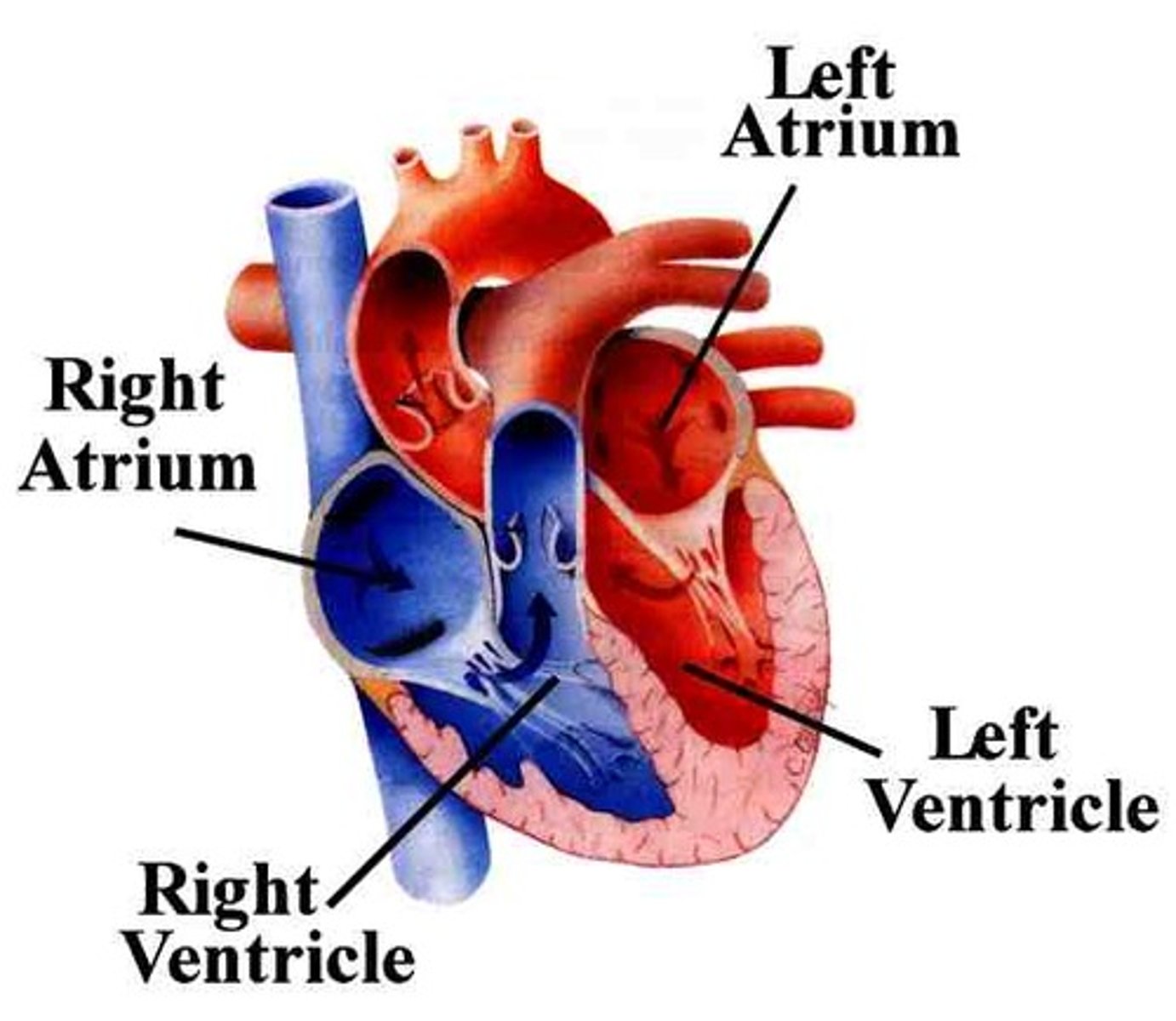
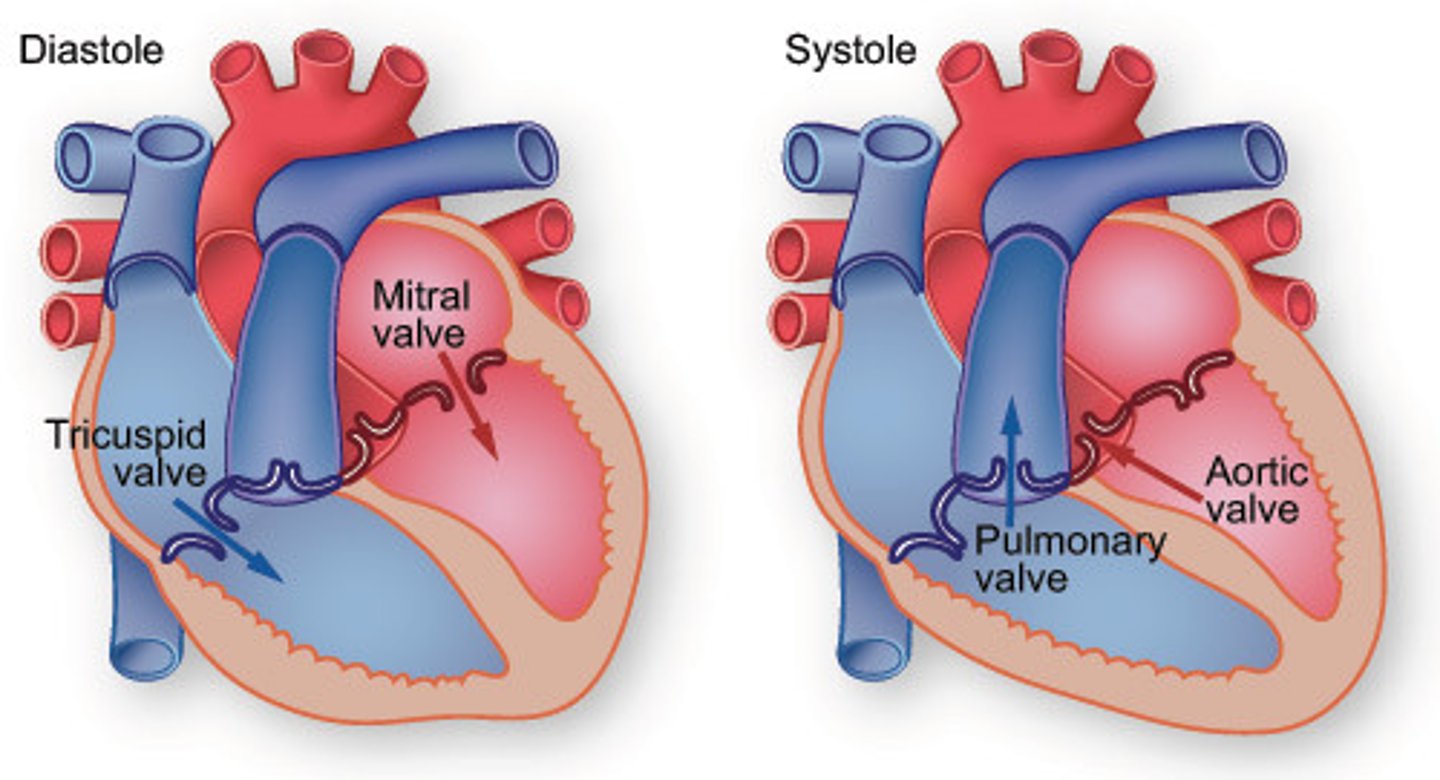
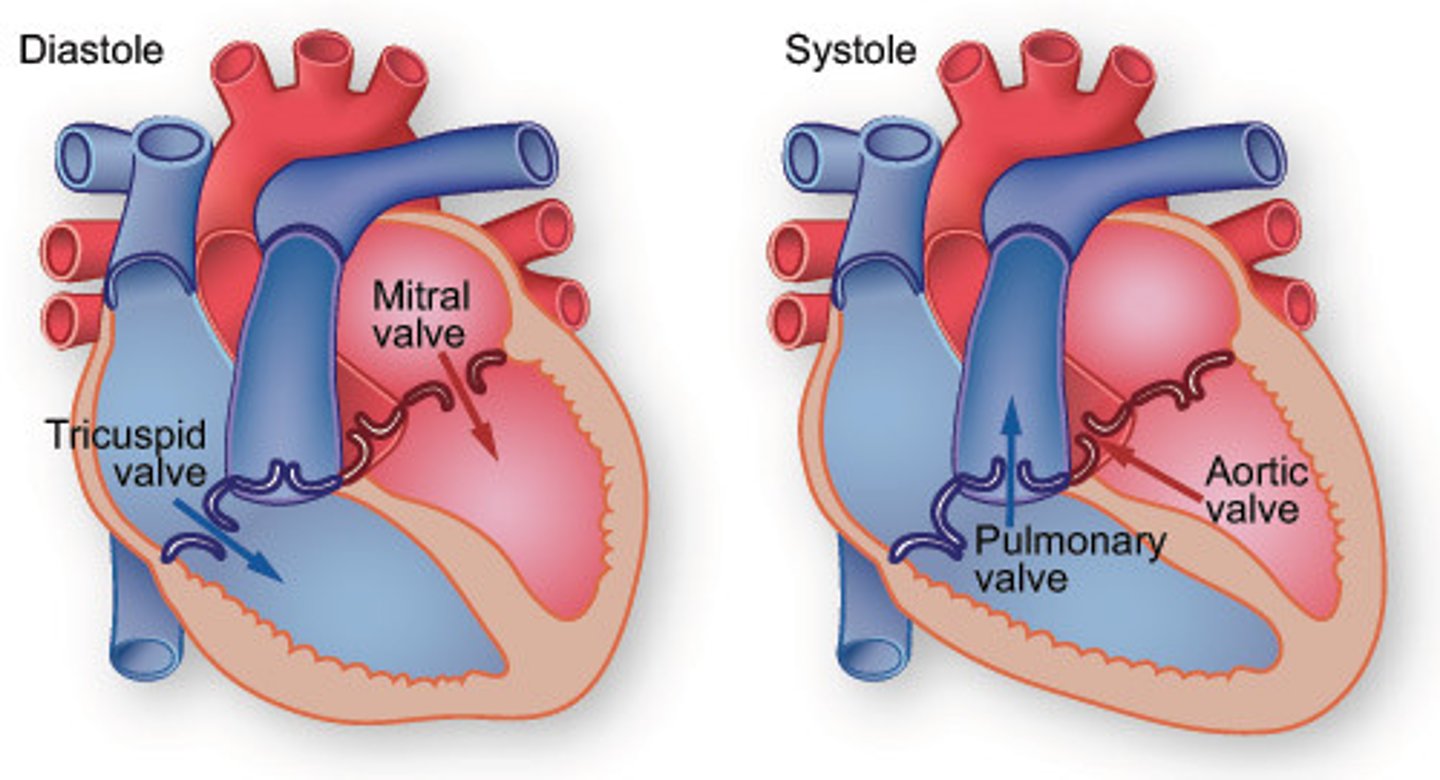
Pulmonary Valve
Valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Prevents the return of blood into the right ventricle.

Tricuspid Valve
Valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. Prevents the backflow into the atrium when the ventricle contracts.

Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve)
Valve between the left atrium and left ventricle. Prevents blood from entering the left atrium when the ventricle contracts.
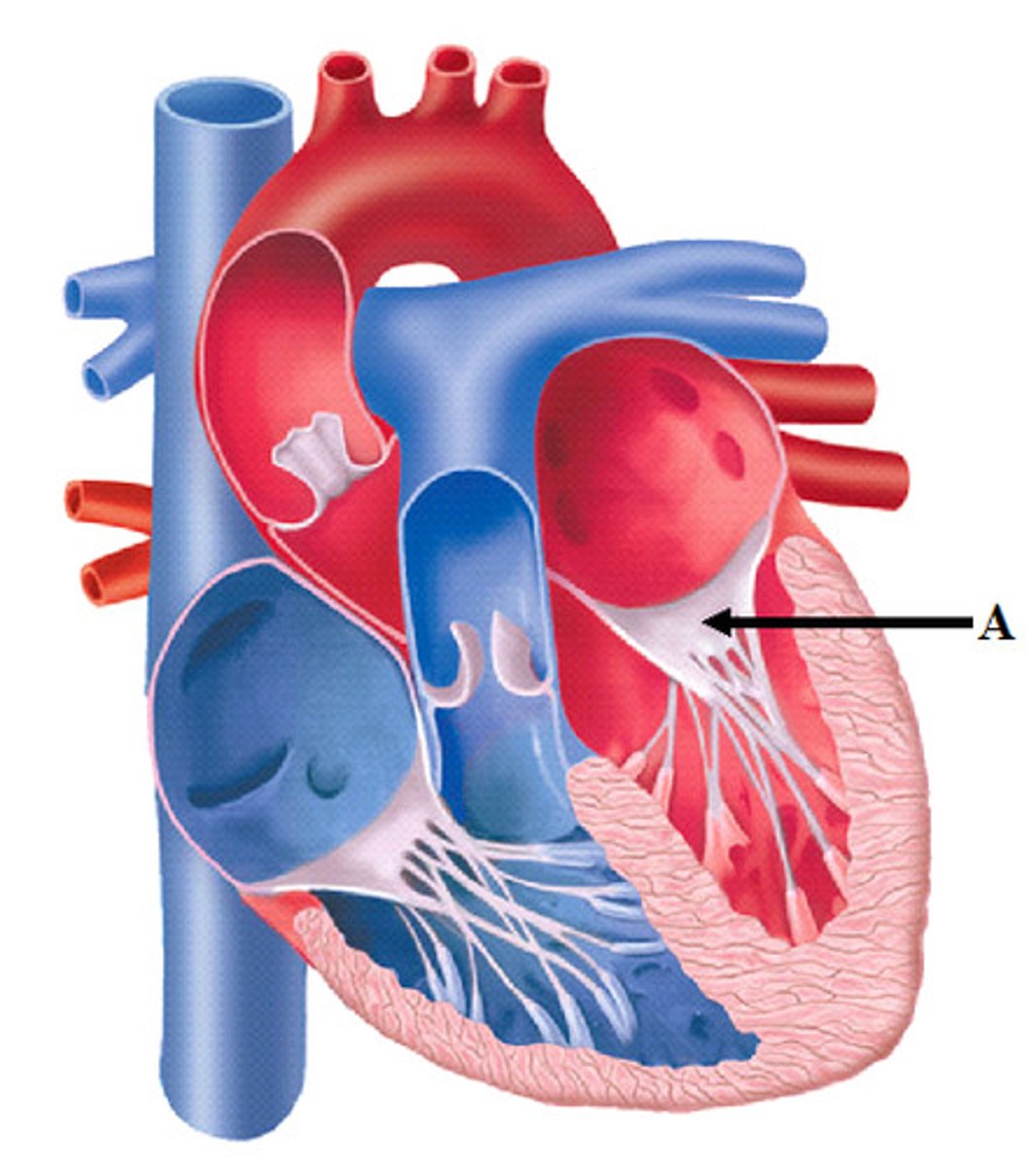
Aortic Valve
Heart valve between the left ventricle and the aorta. Stops the backflow of blood into the left ventricle as it leaves the aorta.

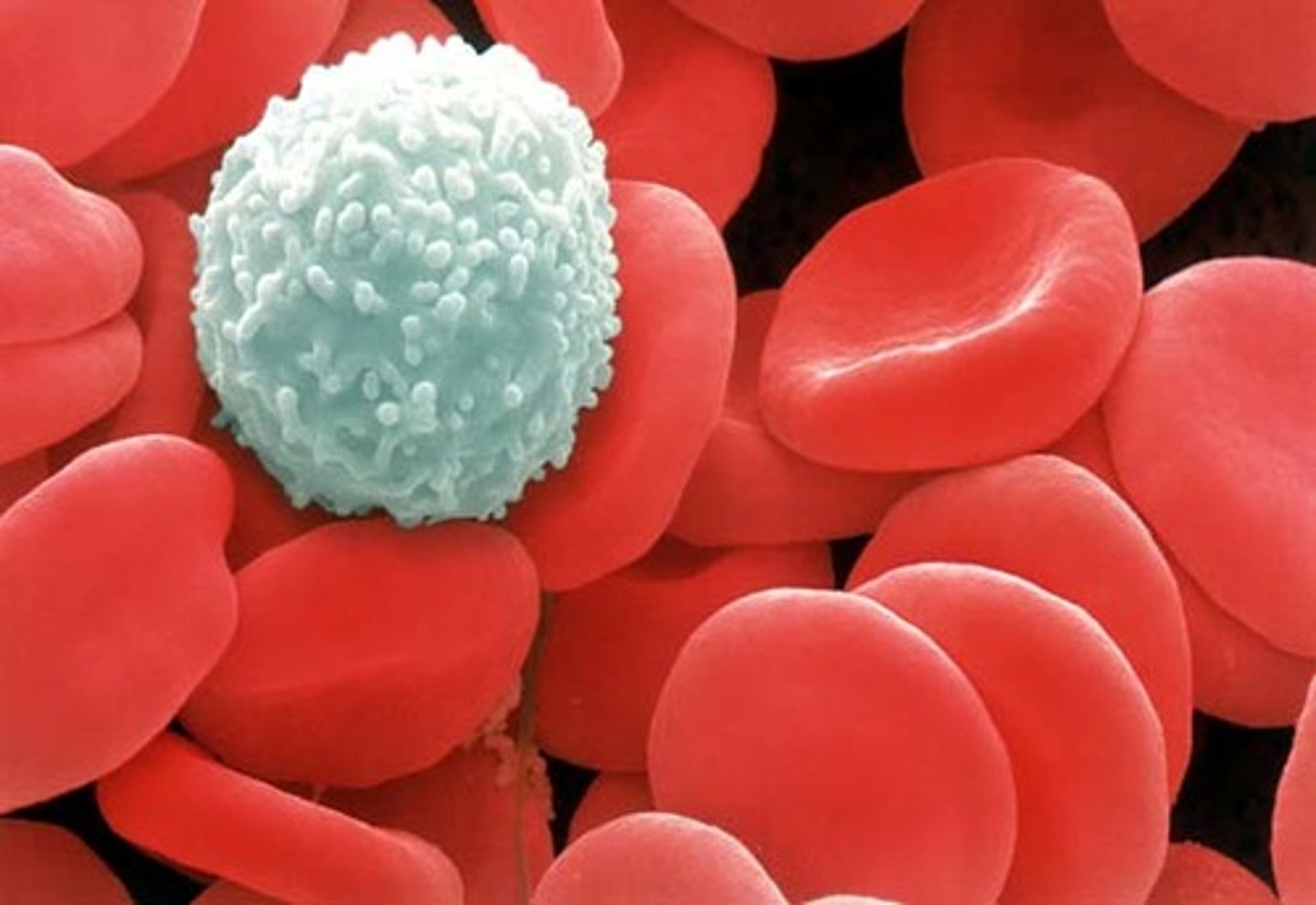
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
Fight infection
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding.
Elastic arteries
Includes the aorta, and major branches. Stretch when blood is forced out of the heart, and recoils under low pressure.
Systole
Contraction of the heart
Diastole
Relaxation of the heart
Systemic Circuit
Circuit of blood that carries blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
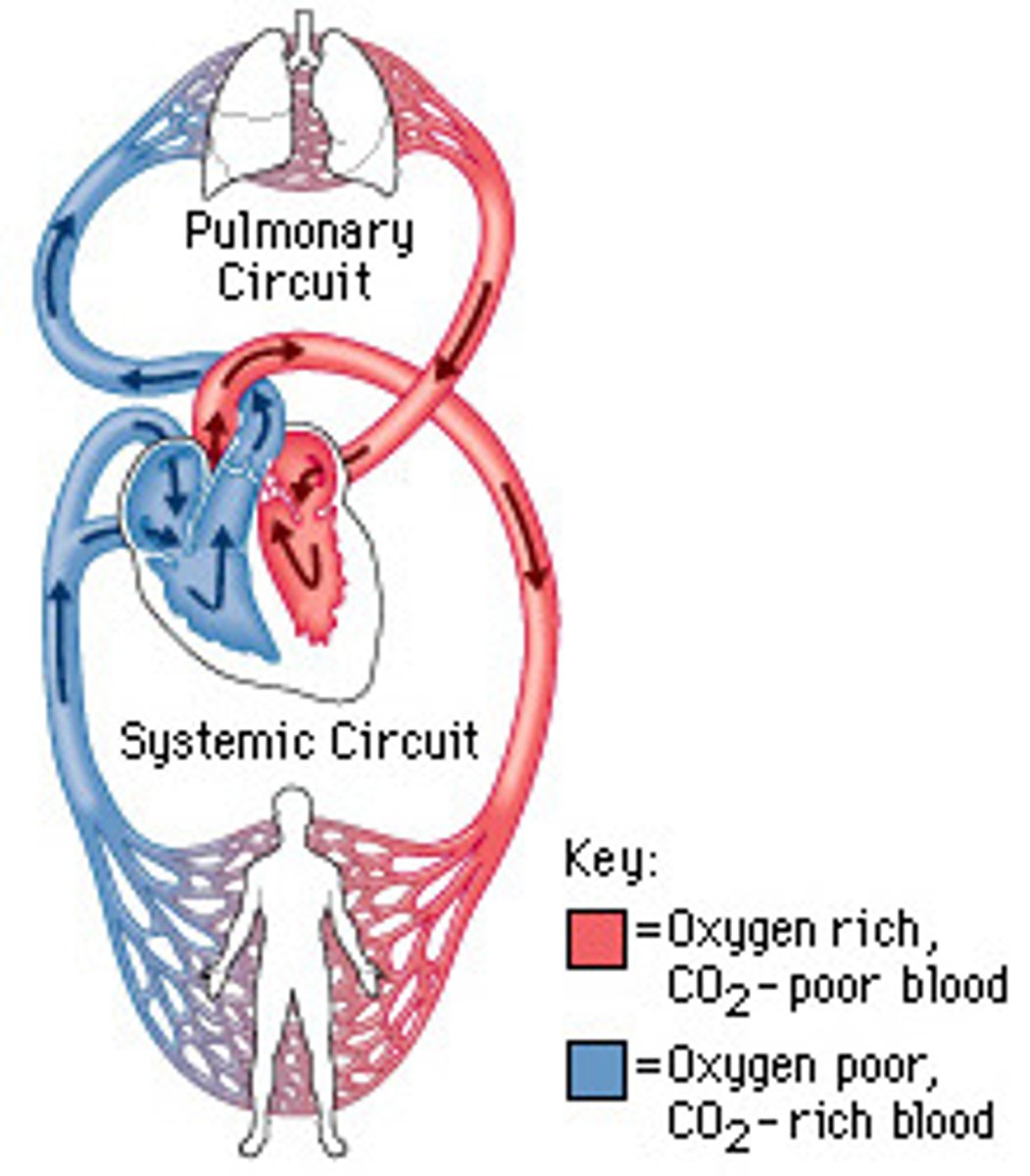
Pulmonary Circuit
Carries blood to and from gas exchange surfaces of lungs.

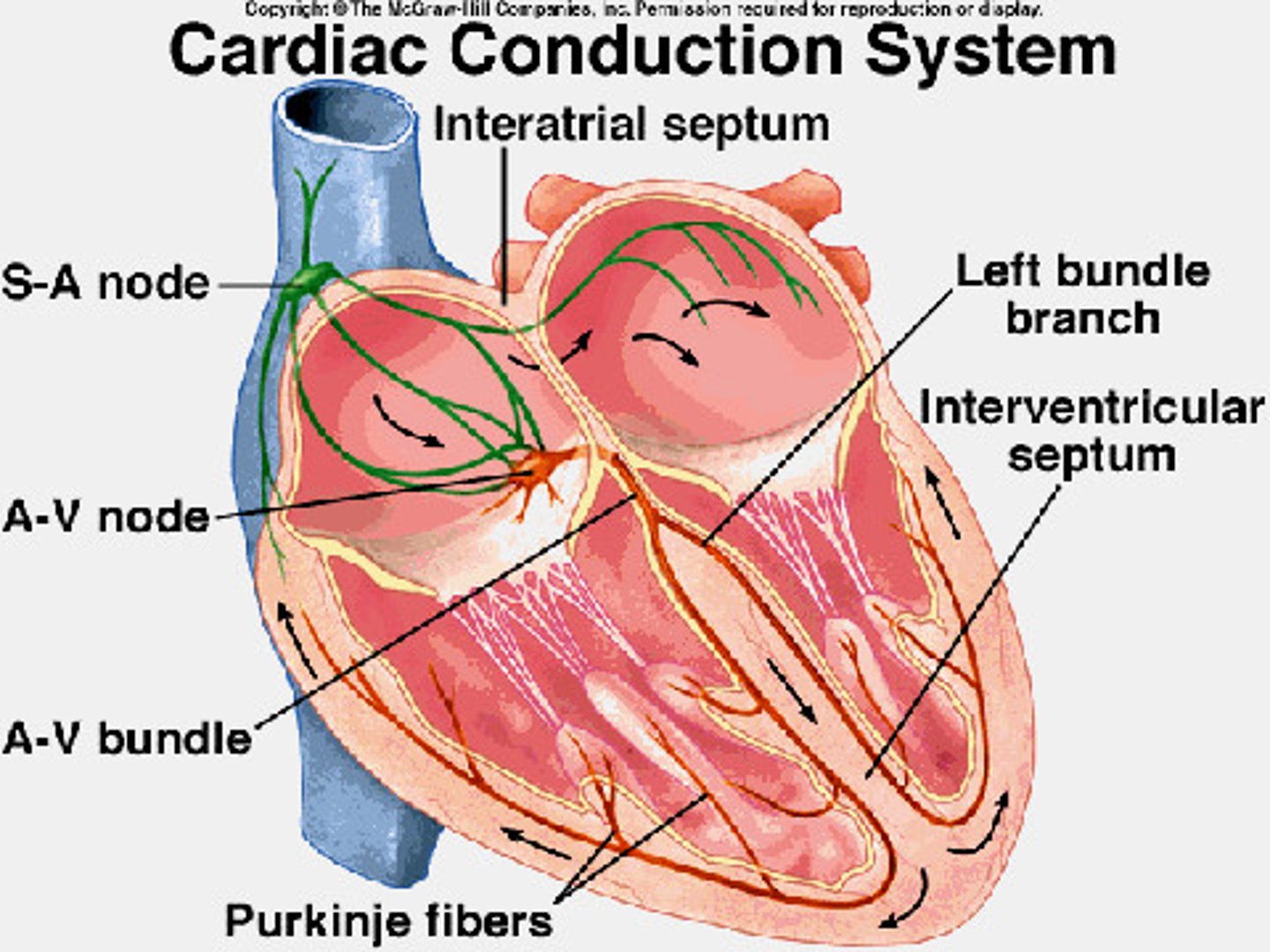
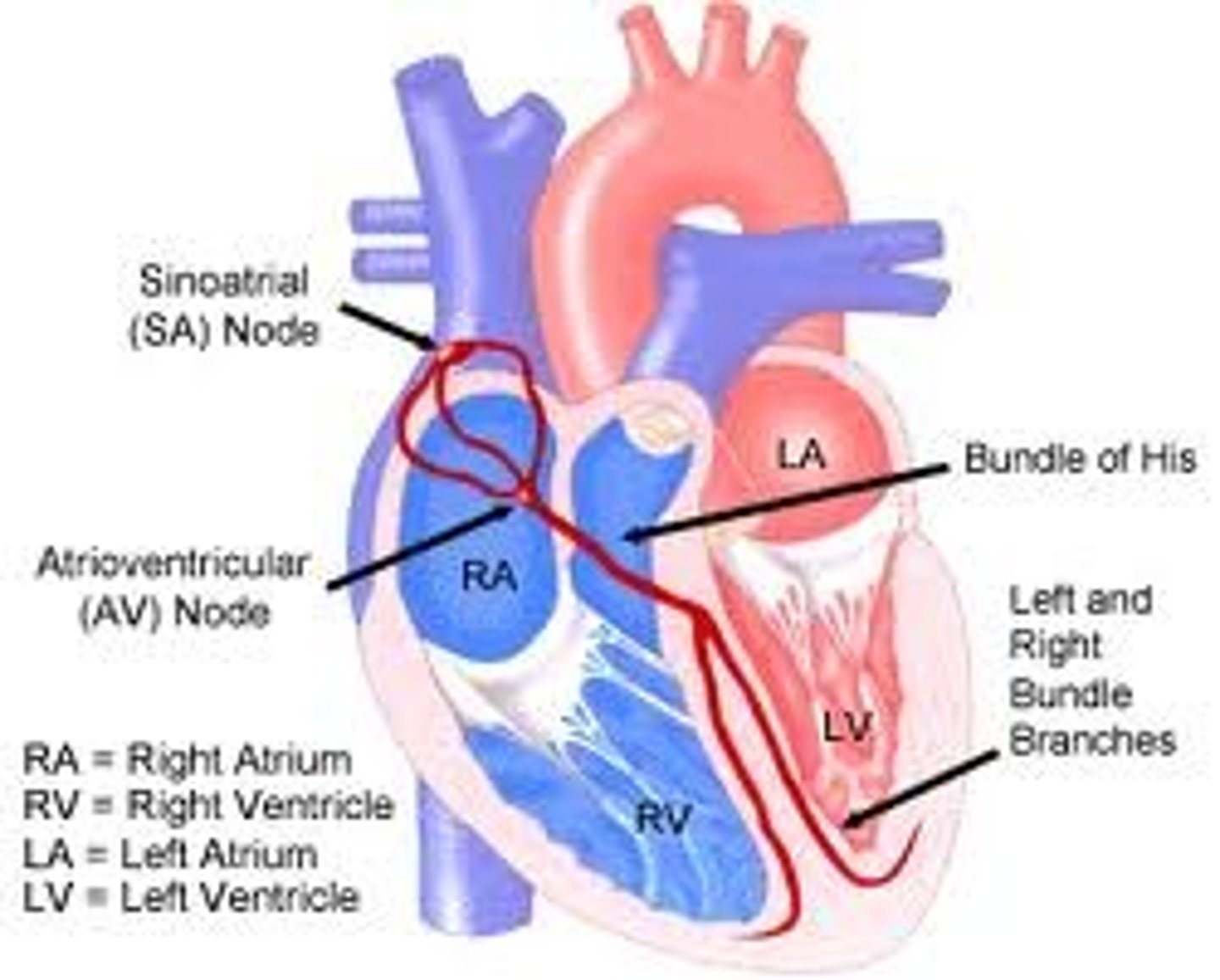
Electrical Conduction
Generates and propagates the electrical impulses that sustain the rhythmic electrical contractions of the heart.
Blood Pressure
The pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart. Thick walls
Veins
Carry blood back to the heart. Thin walls.
Muscular Arteries
Regulate blood flow by vasoconstriction/vasodilation
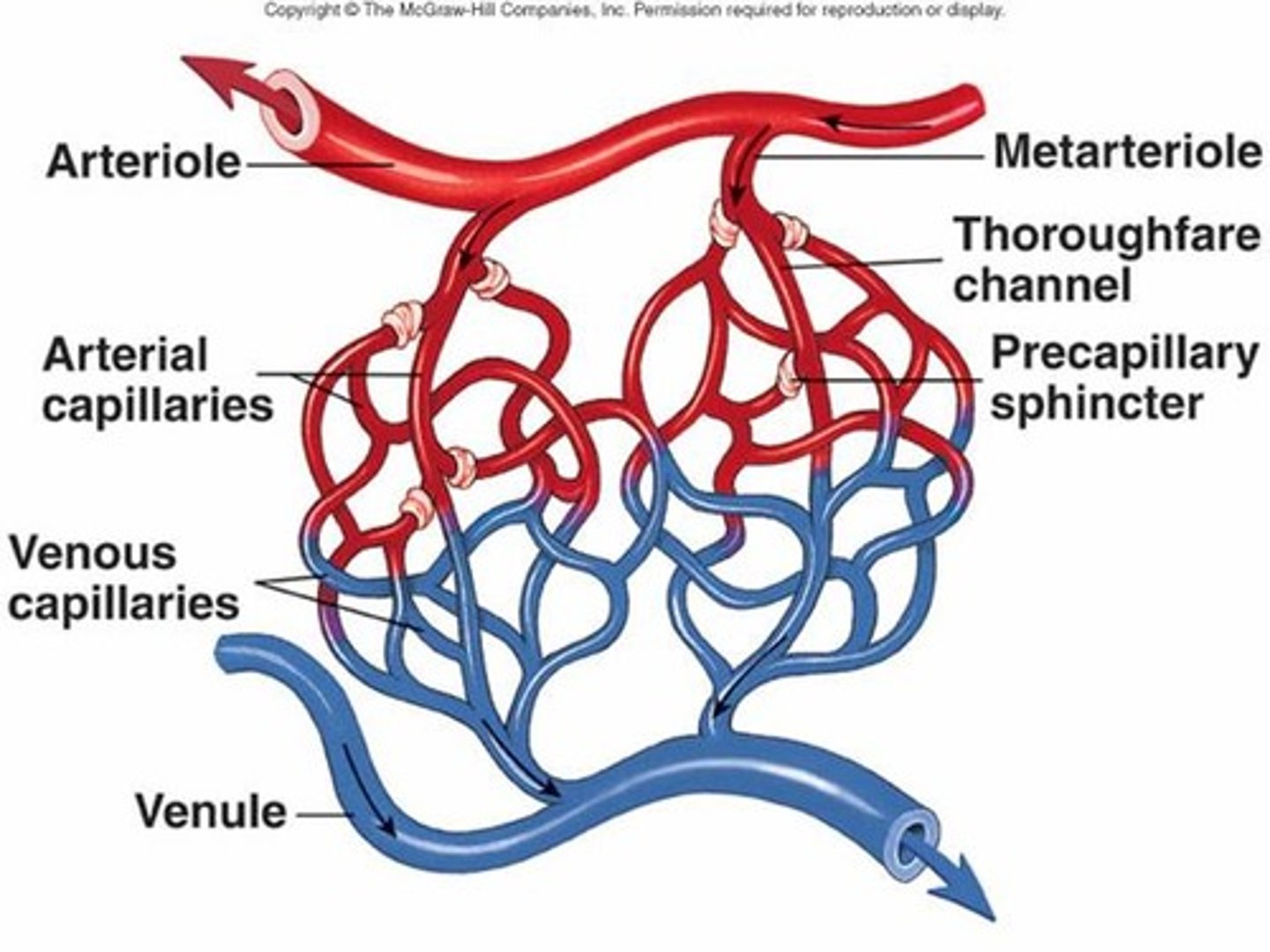
Arterioles
Primary vessels involved in vasoconstriction/vasodilation. Control blood flow to capillaries.
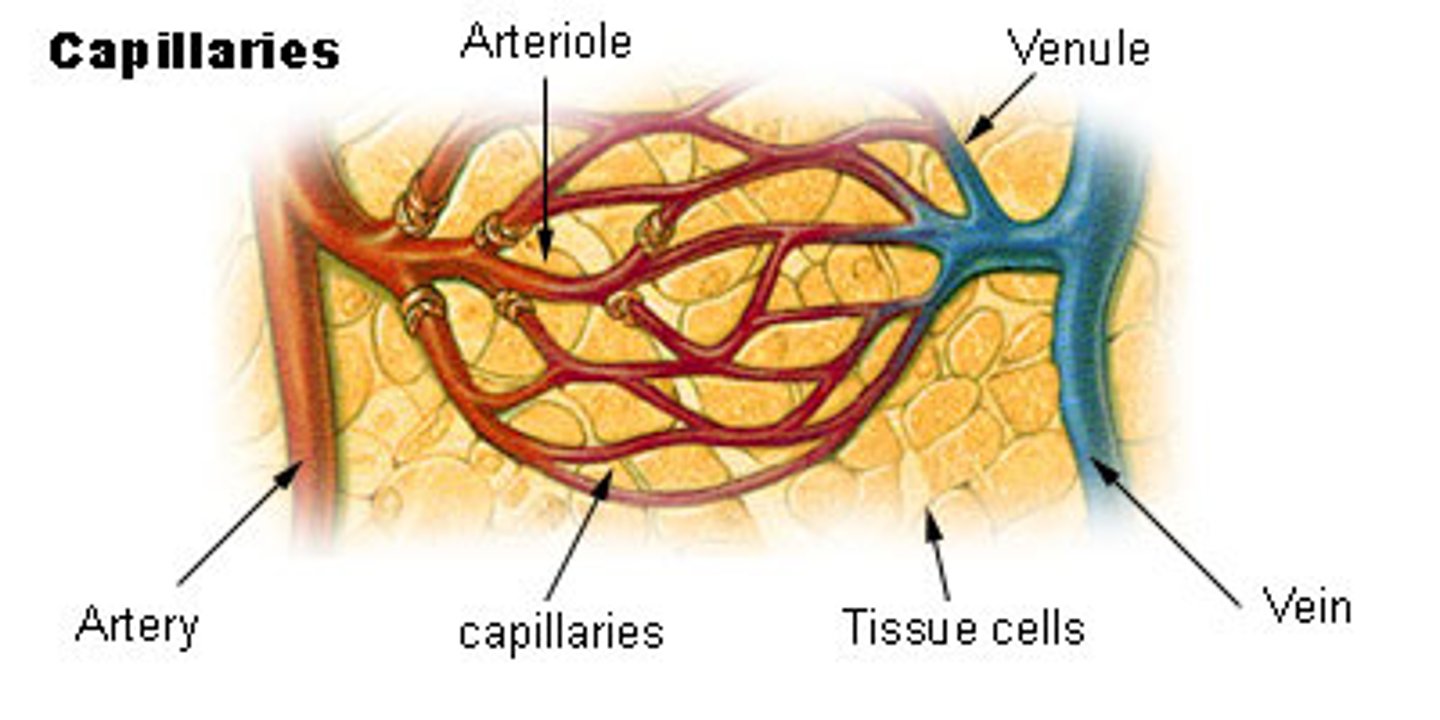
Venules
Empties blood into larger veins
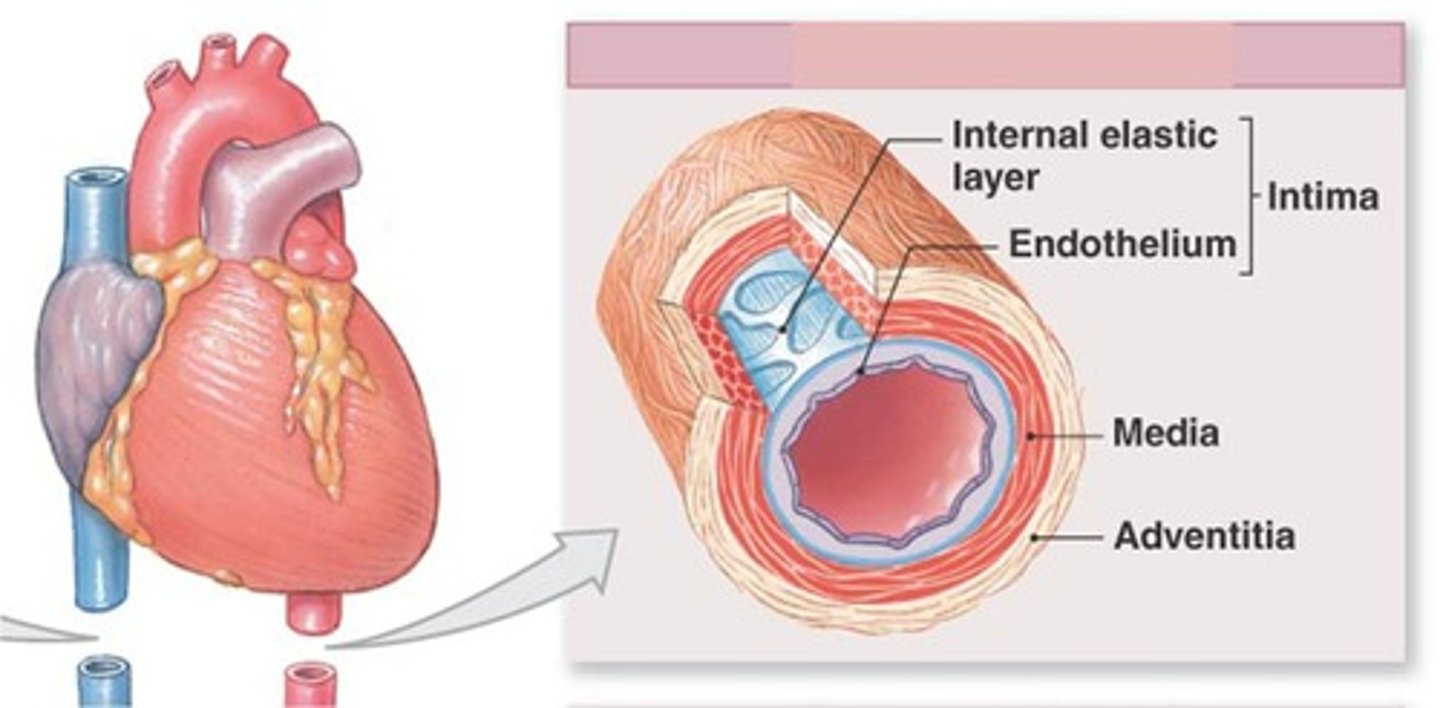
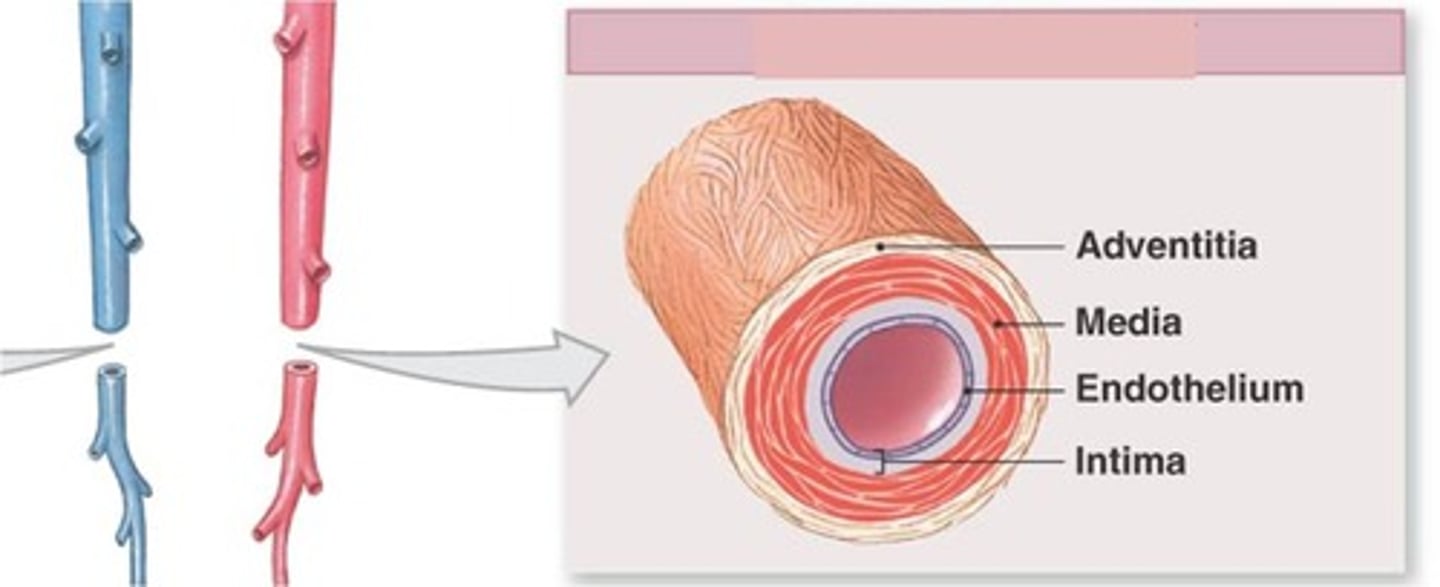
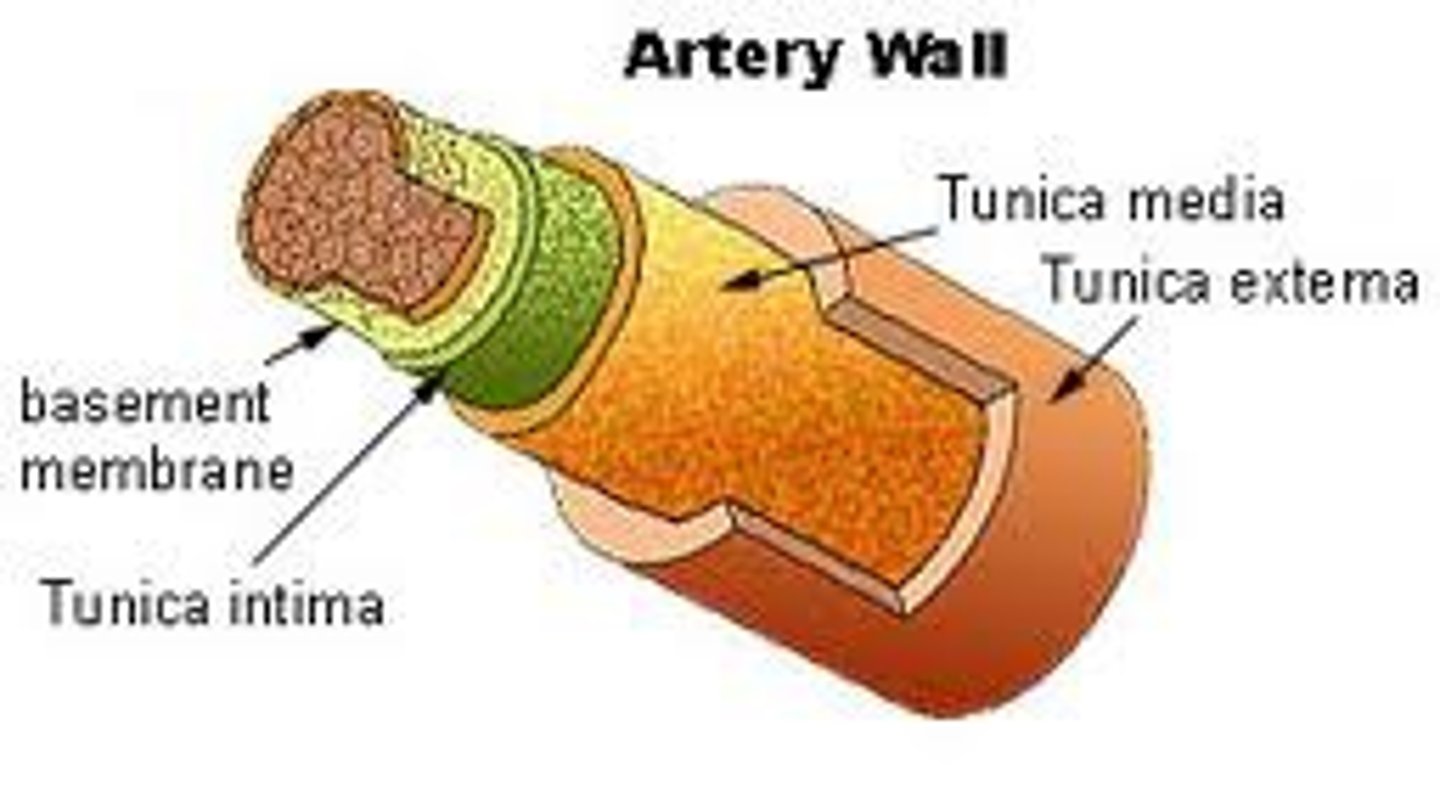
Tunica Intima
the innermost layer of a blood vessel
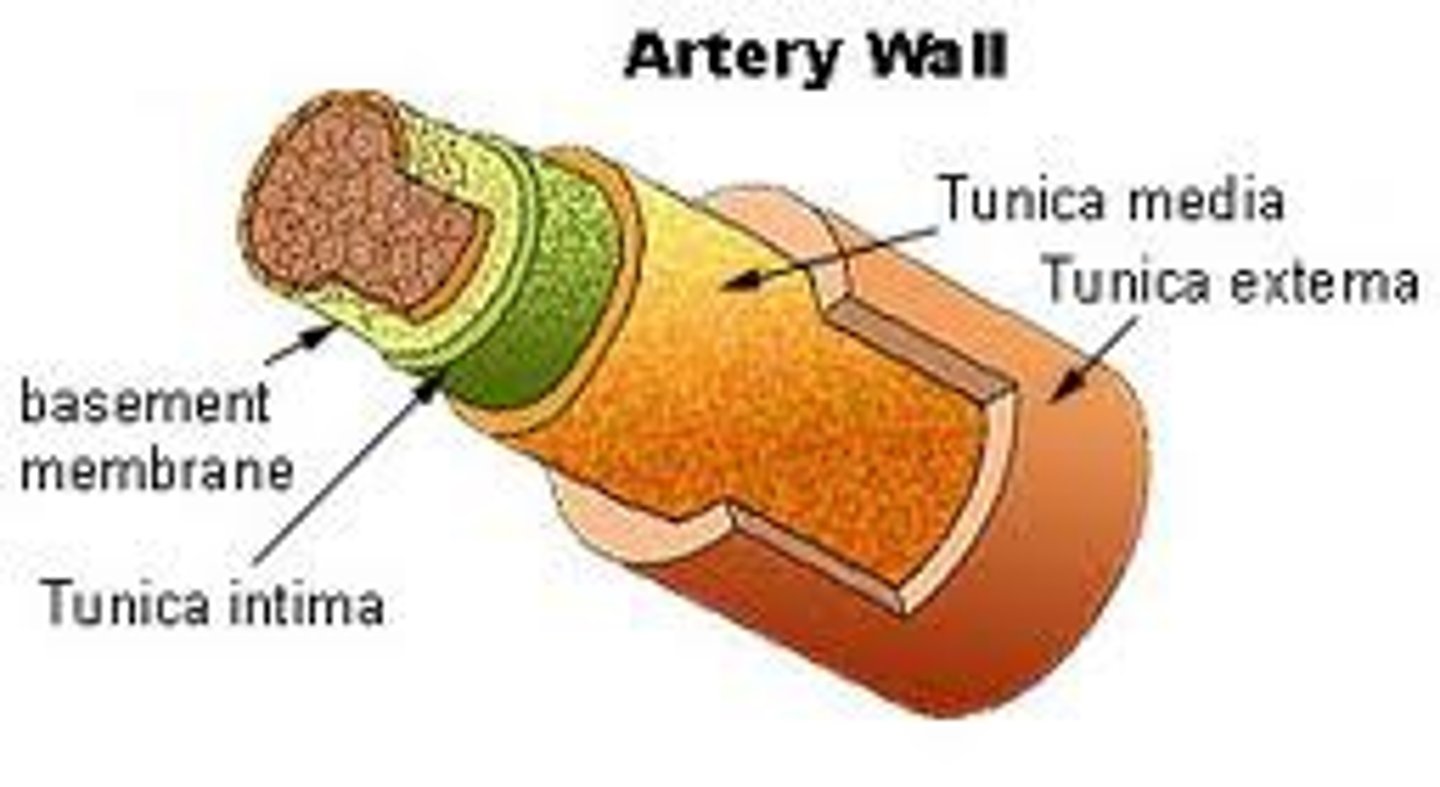
Tunica Media
The middle and thickest layer of tissue of a blood vessel wall, composed of elastic tissue and smooth muscle cells that allow the vessel to expand or contract in response to changes in blood pressure and tissue demand.

Tunica Adventitia
The outer layer of tissue of a blood vessel wall, composed of elastic and fibrous connective tissue.
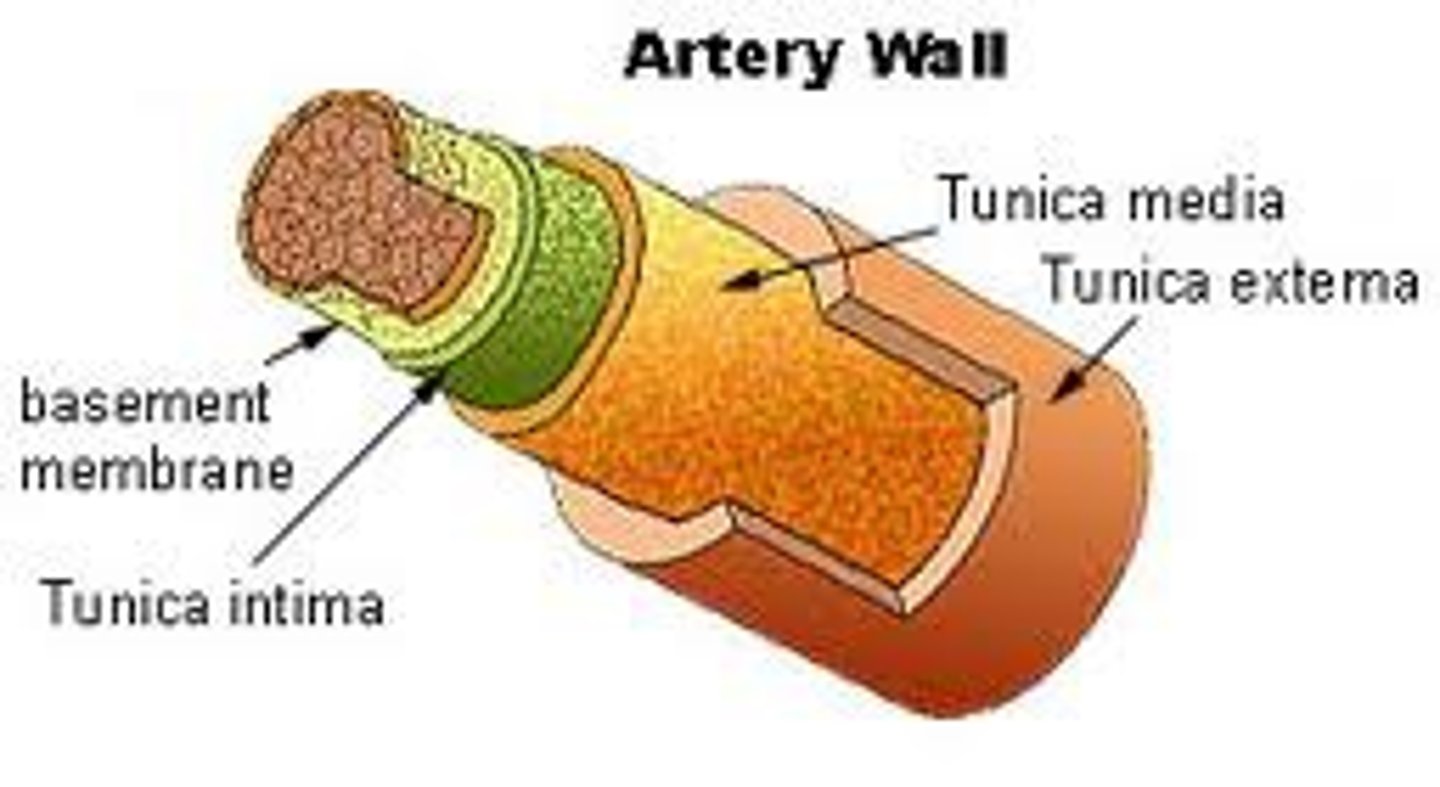
Blood Vessel Layers
Tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
Systolic Pressure
The peak pressure is produced by the contracting ventricles.
Diastolic Pressure
The pressure in your arteries when the ventricles are relaxed.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
The walls of the blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, heart failure, and stroke.
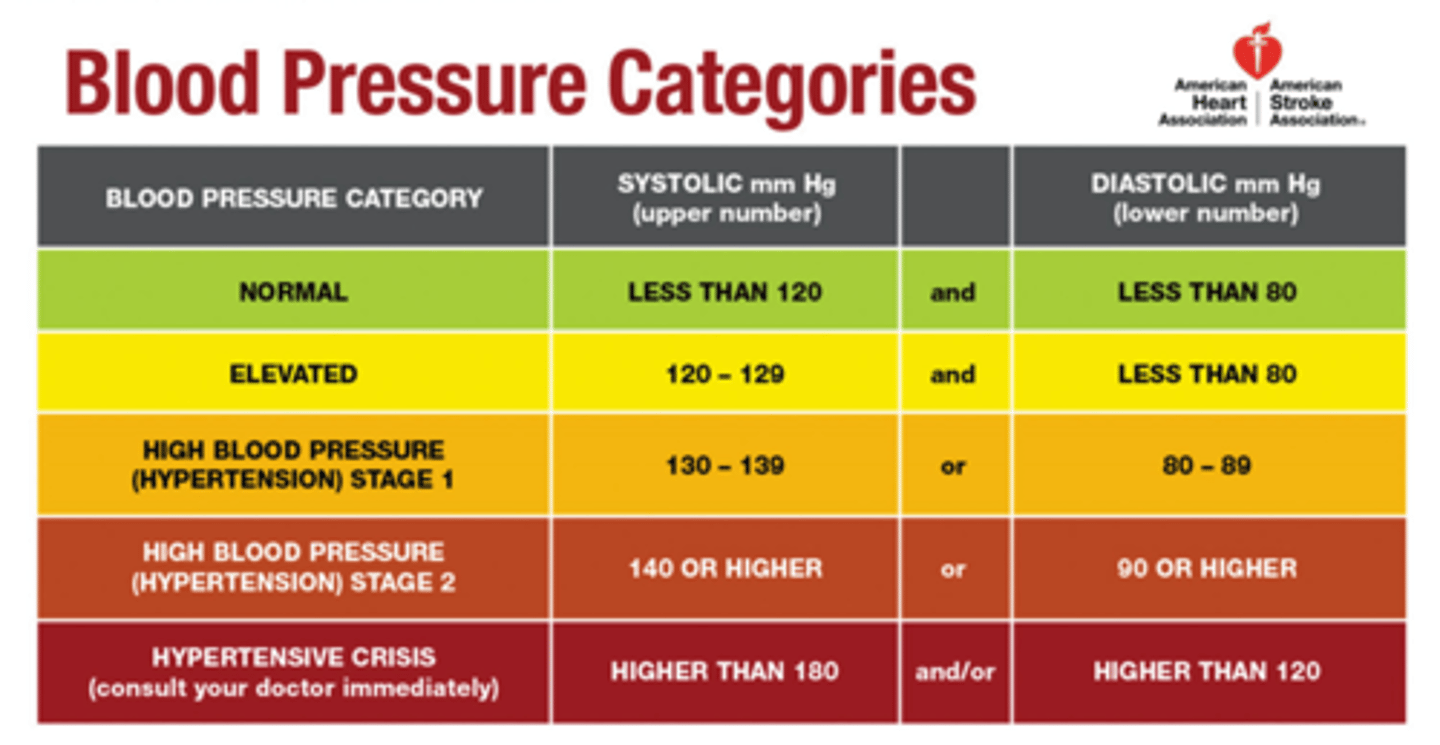
Low Blood Pressure (Low Blood Pressure)
Below 100/60. Symptoms include lightheadedness or fainting.
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Abnormal heart beats
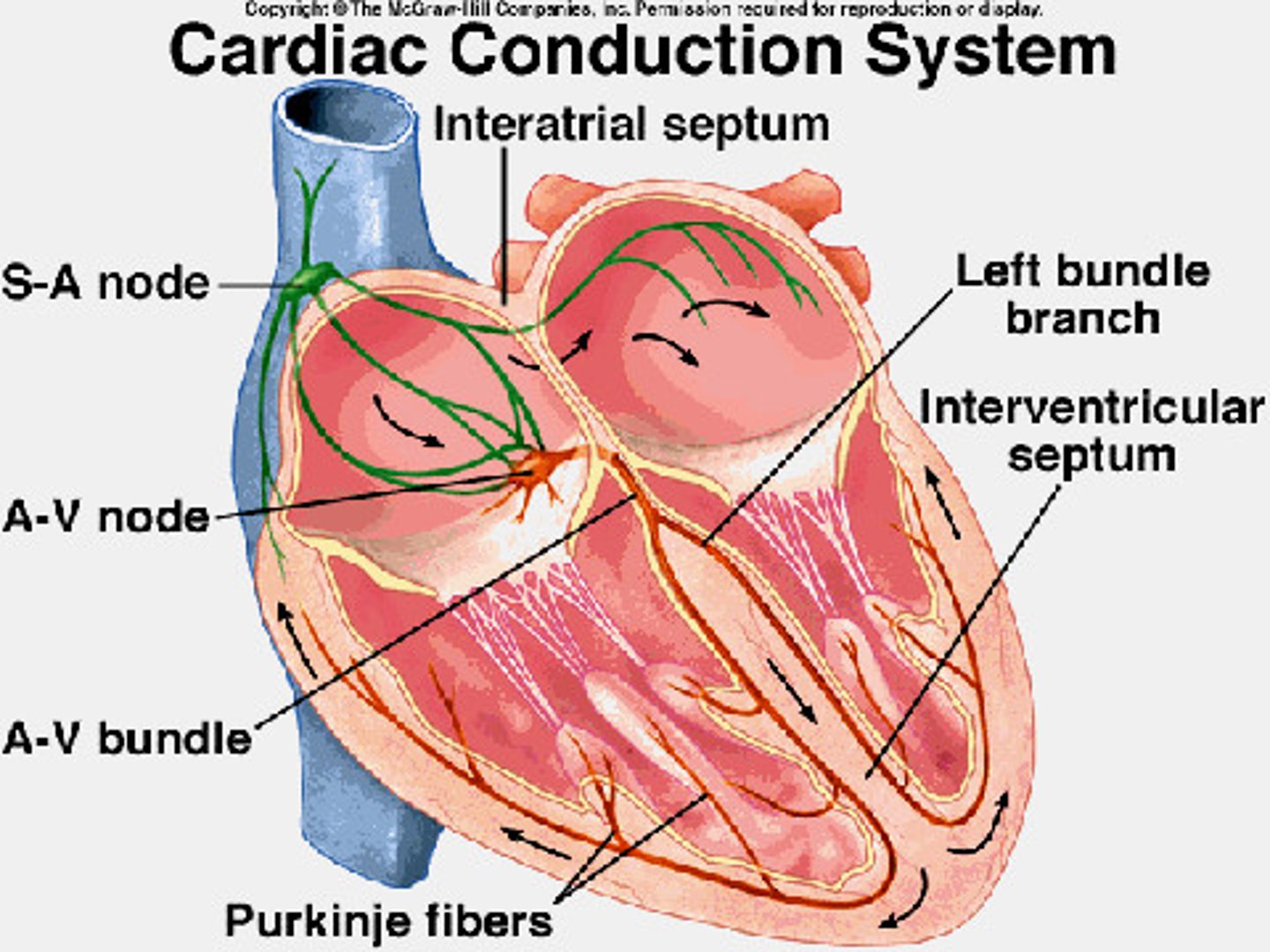
Sinoatrial Node
Pacemaker of the heart
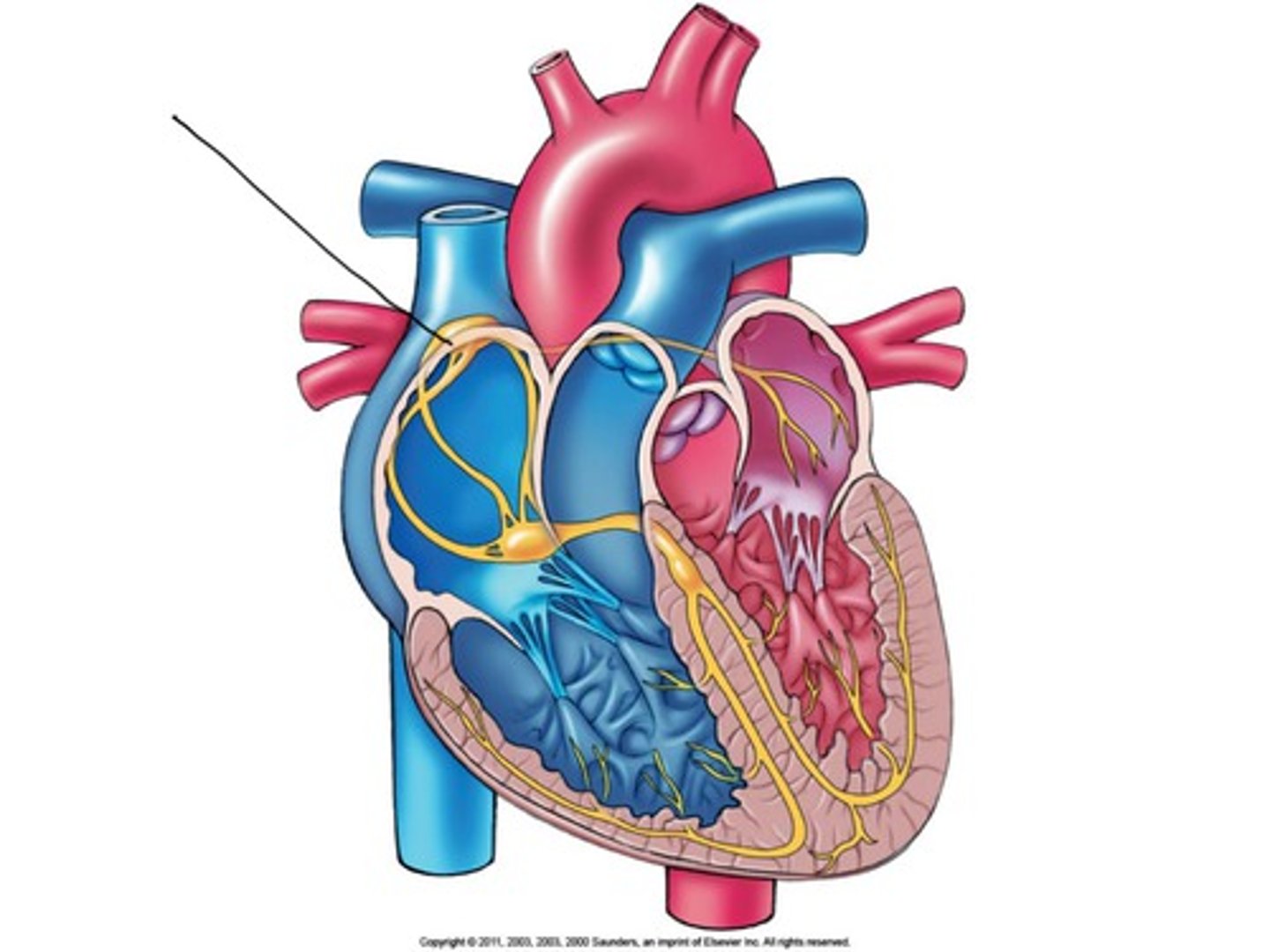
High Blood Pressure Causes
High salt diet, smoking, and lack of exercise.
Cardiac Arrest
Sudden, unexpected stoppage of heart action, often leads to sudden cardiac death. Takes place when the heart stops beating or goes into a dangerously abnormal rhythm.
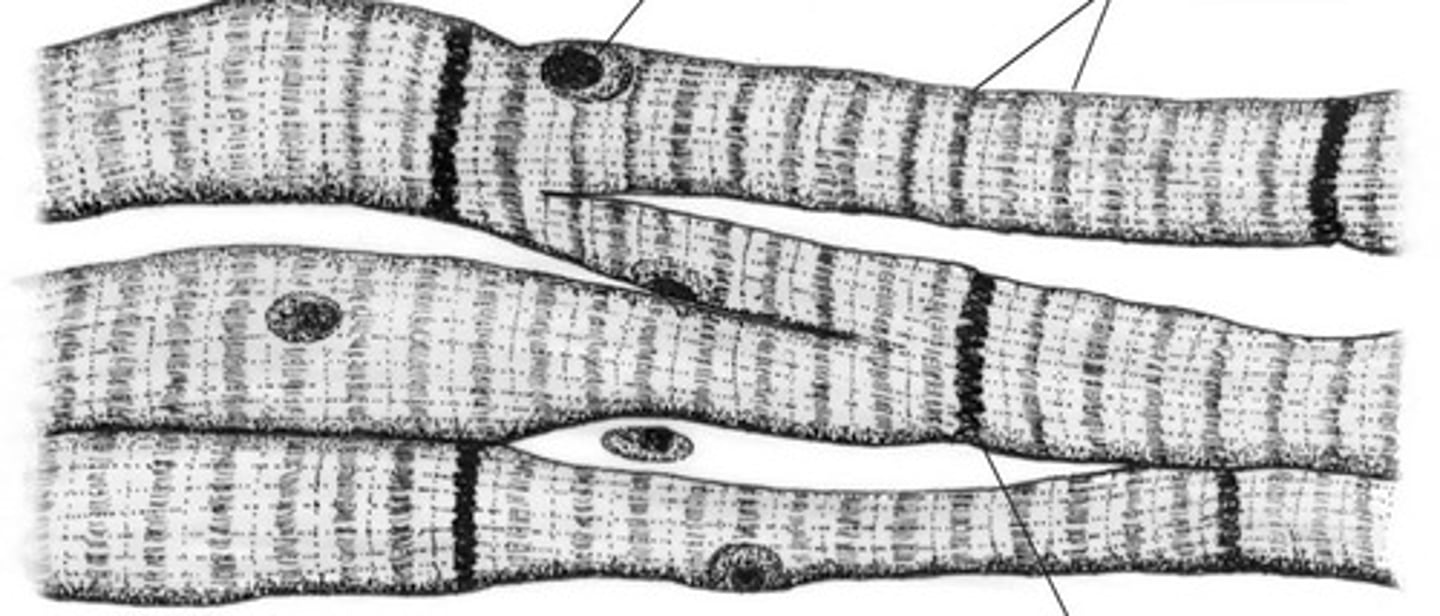
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue is found only in the heart. Has Striations, squat, branched out, and interconnected with one or two nuclei.
Atrioventricular Node
A specialized mass of conducting cells located at the atrioventricular junction in the heart.
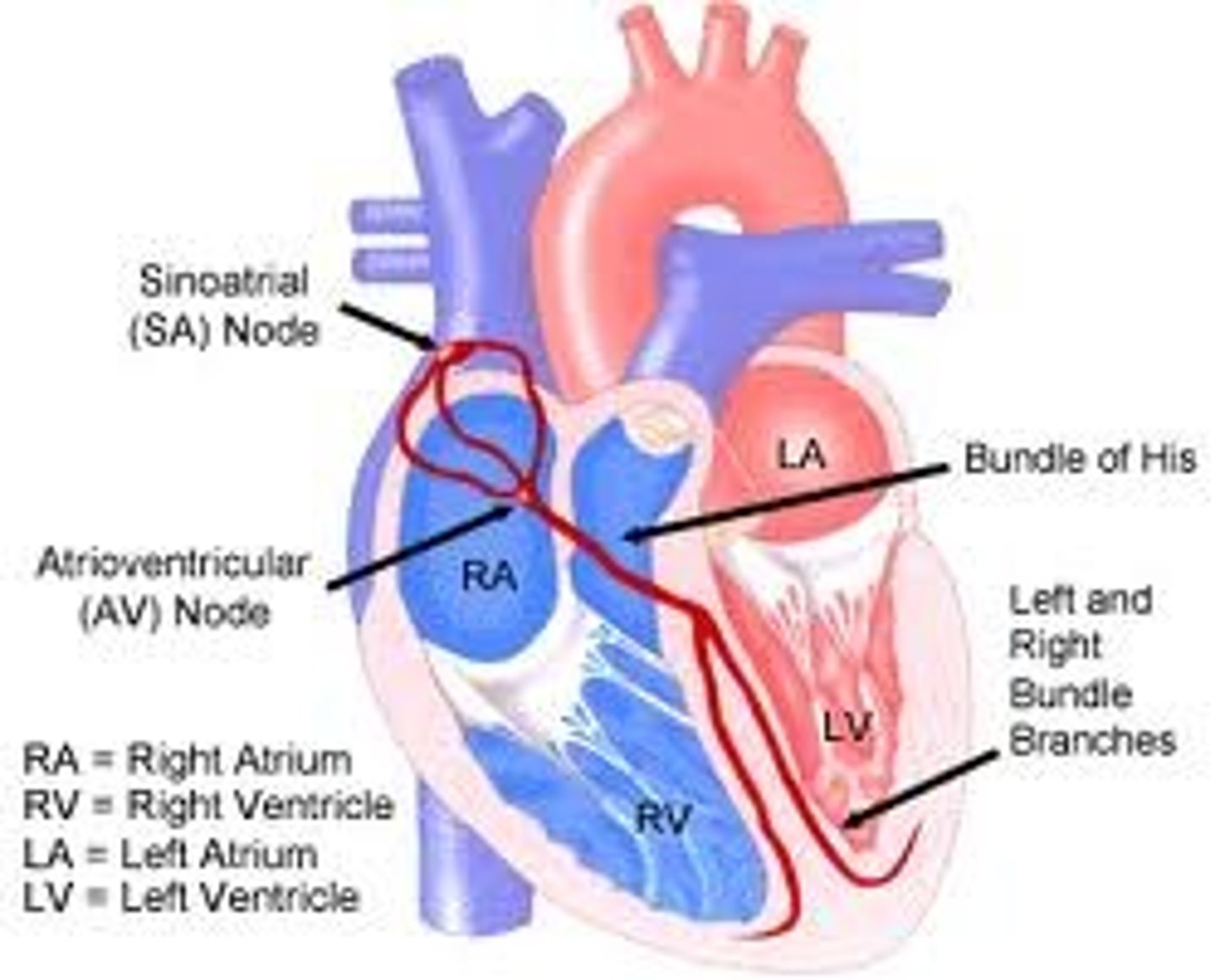
Bundle of His
Neurological fibers extending from the AV node to the right and left bundle branches that fire the impulse from the AV node to the Purkinje fibers
Monocytes
Another type of white blood cell. These cells are characterized by a well-defined nucleus. Play an important role in the body's immune response to pathogens. Produced in the bone marrow.
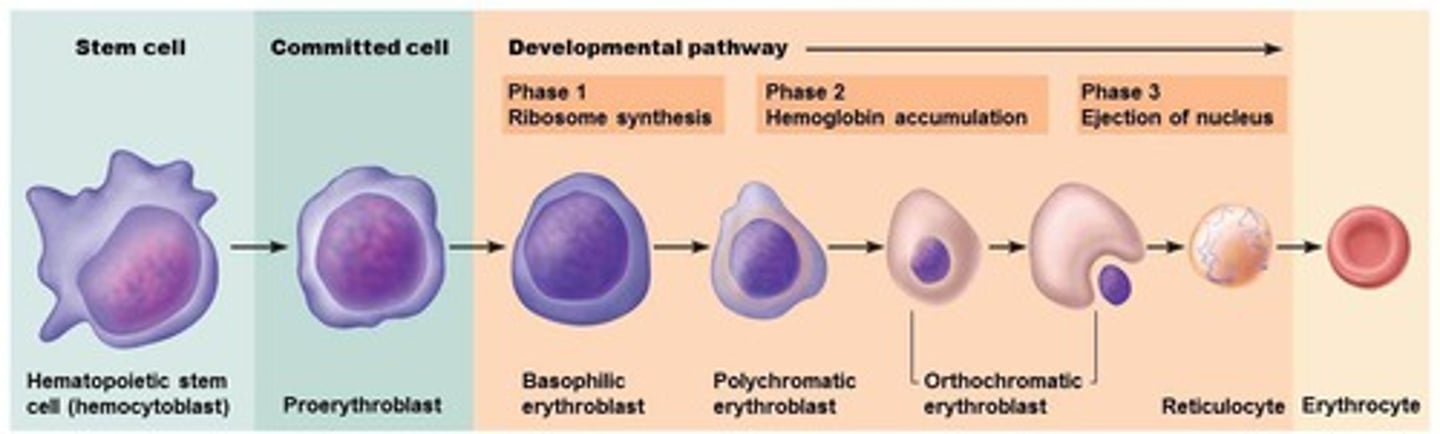
Erythropoiesis
The production of red blood cells
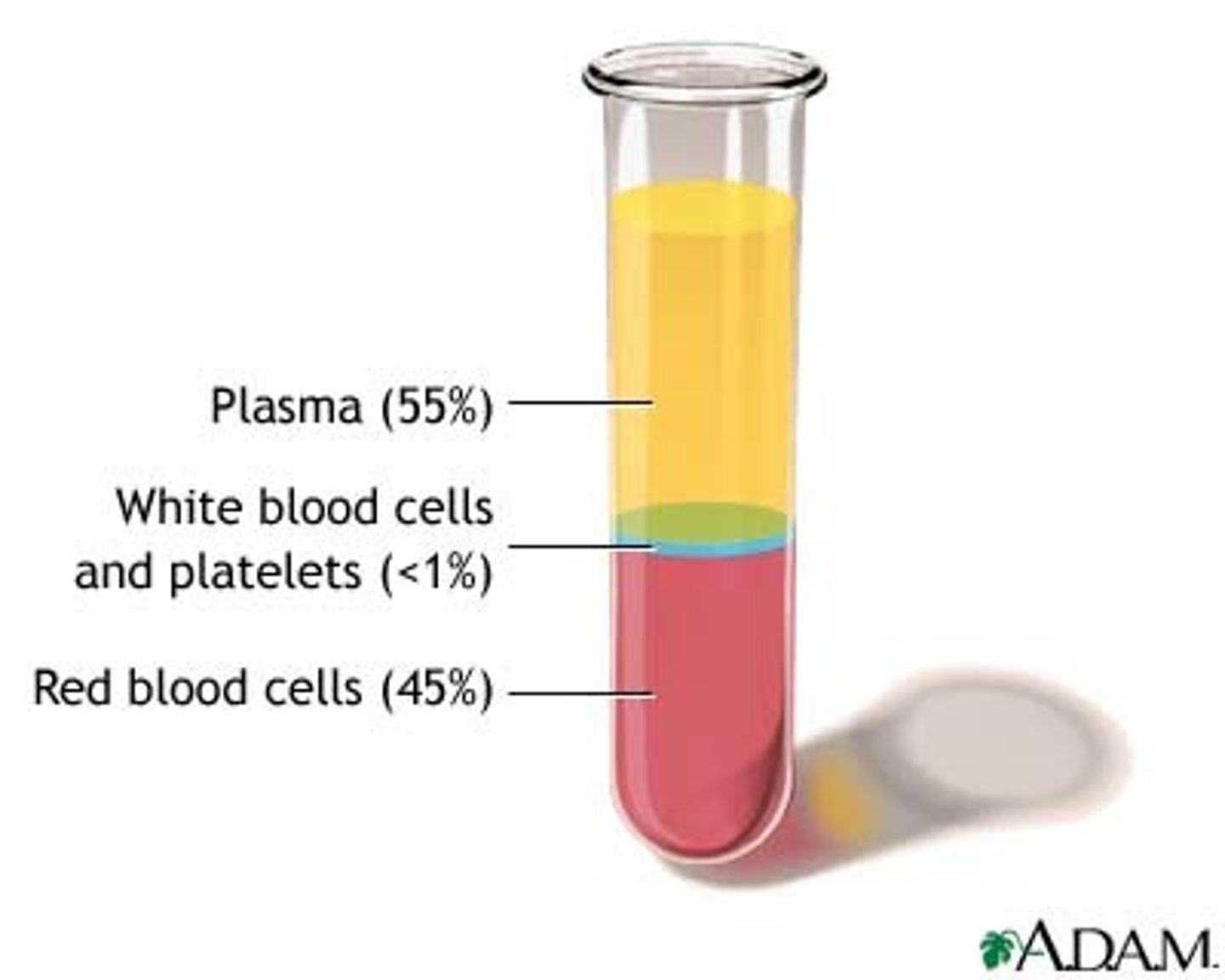
Blood
Connective tissue made of plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Plasma
A solution of water, plasma proteins (albumin, antibodies, clotting proteins), carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids, vitamins, salts, gases, hormones, and waste products.
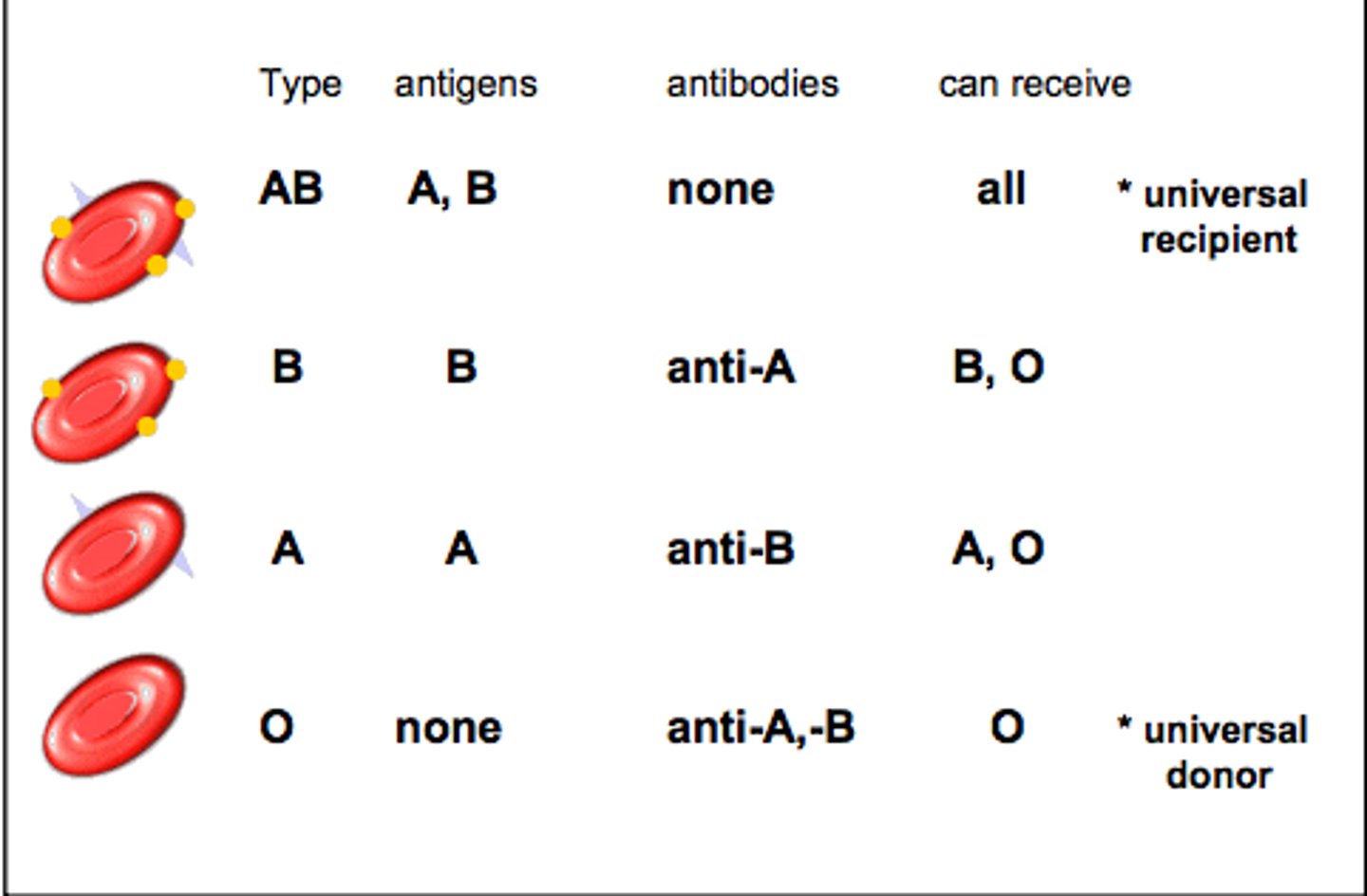
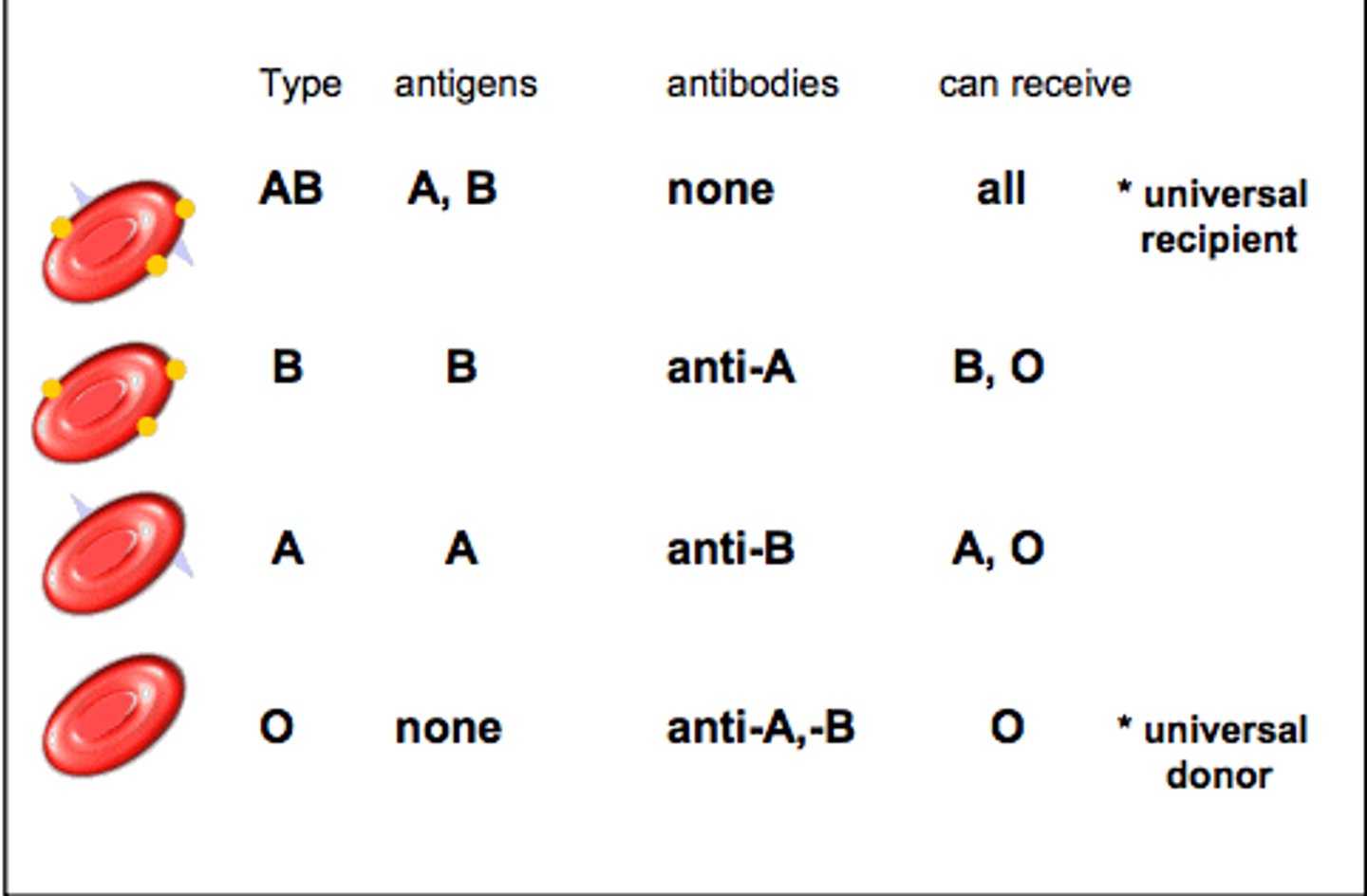
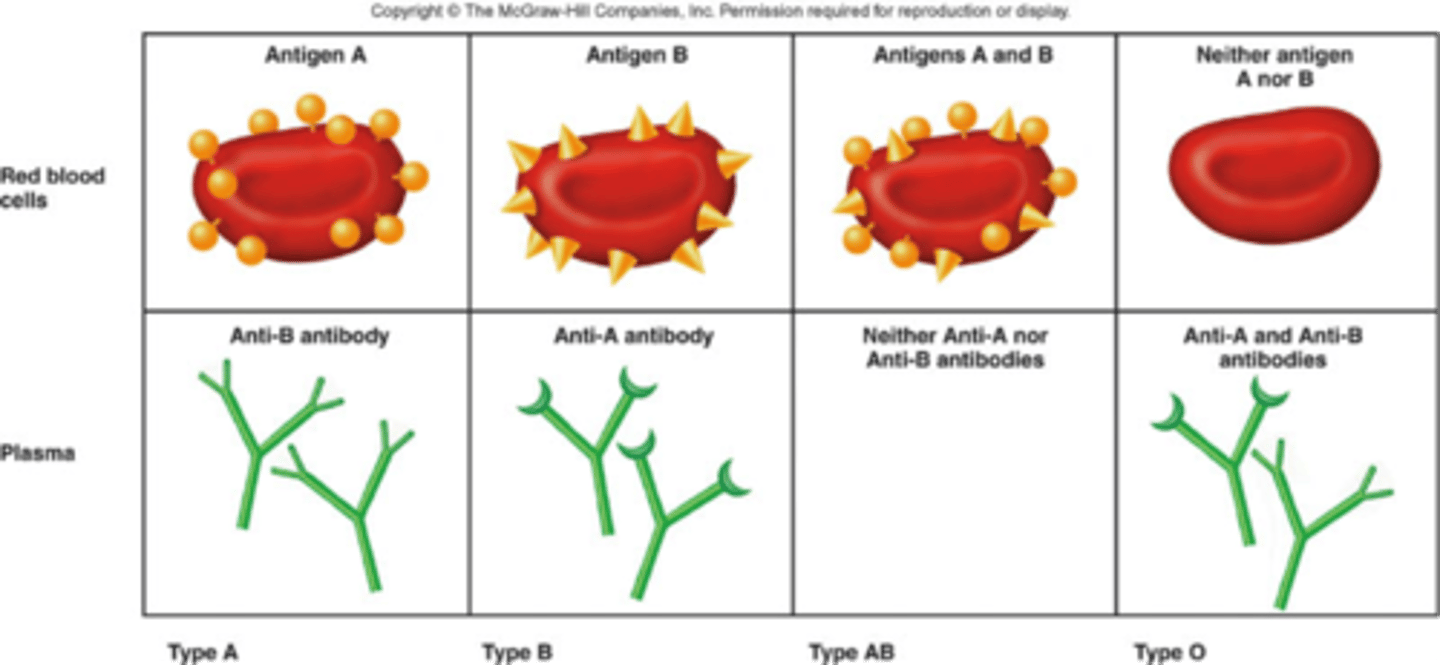
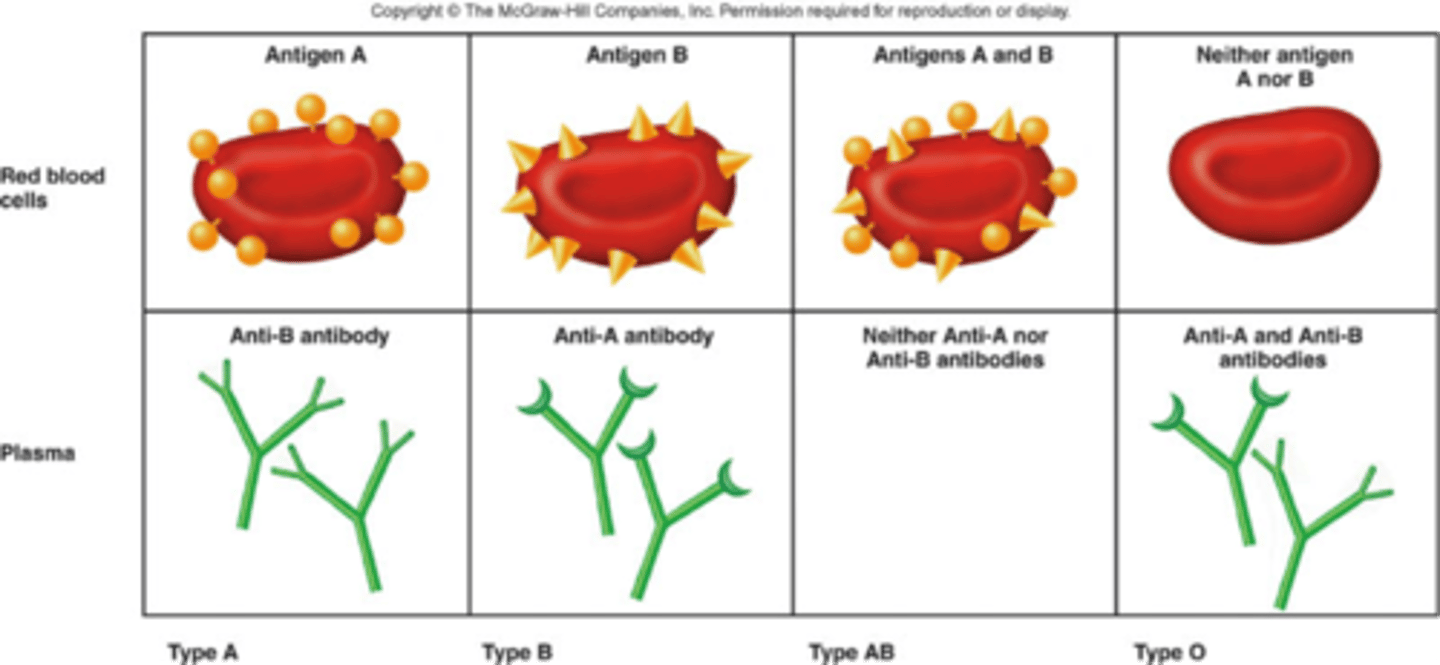
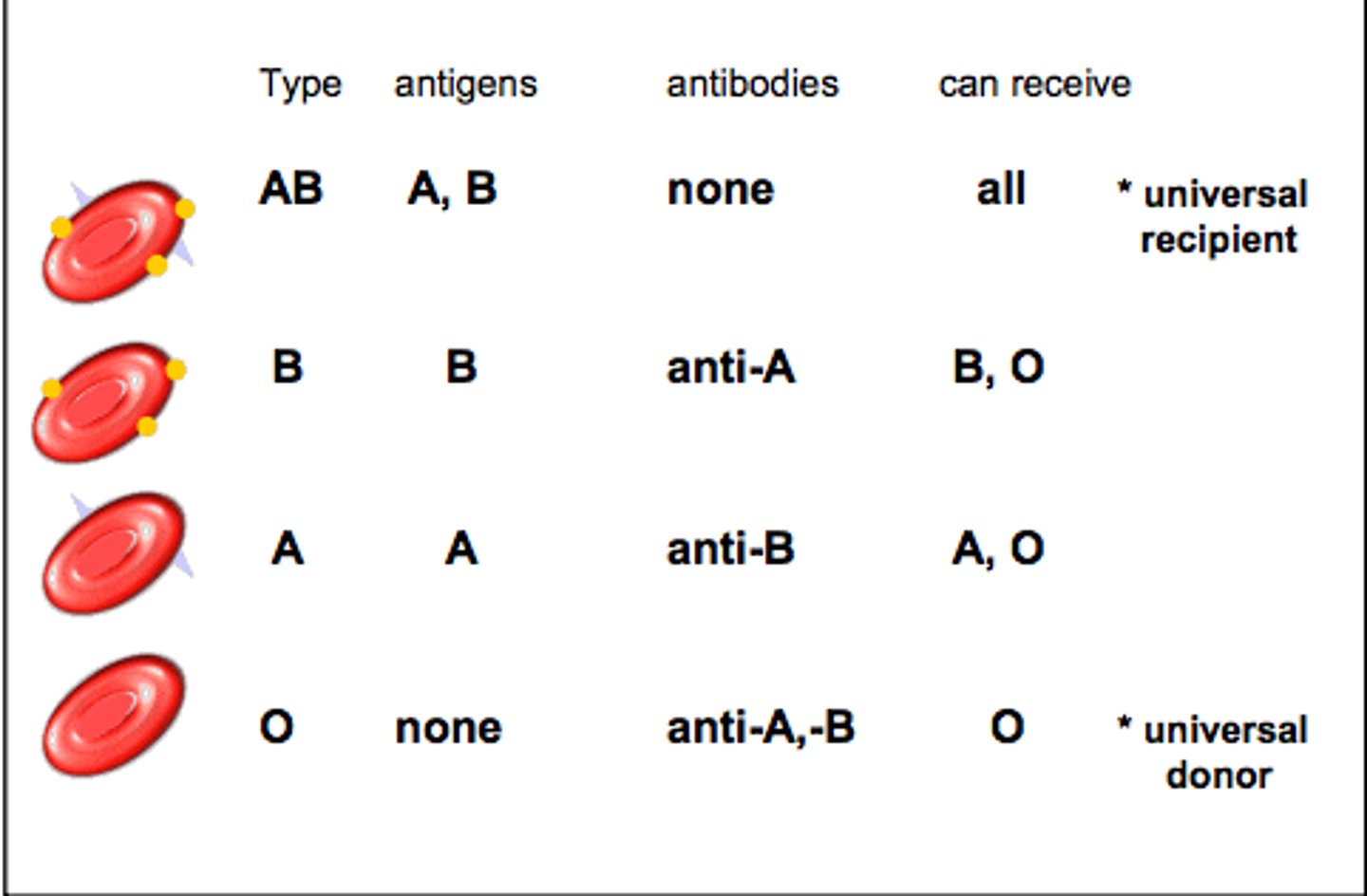
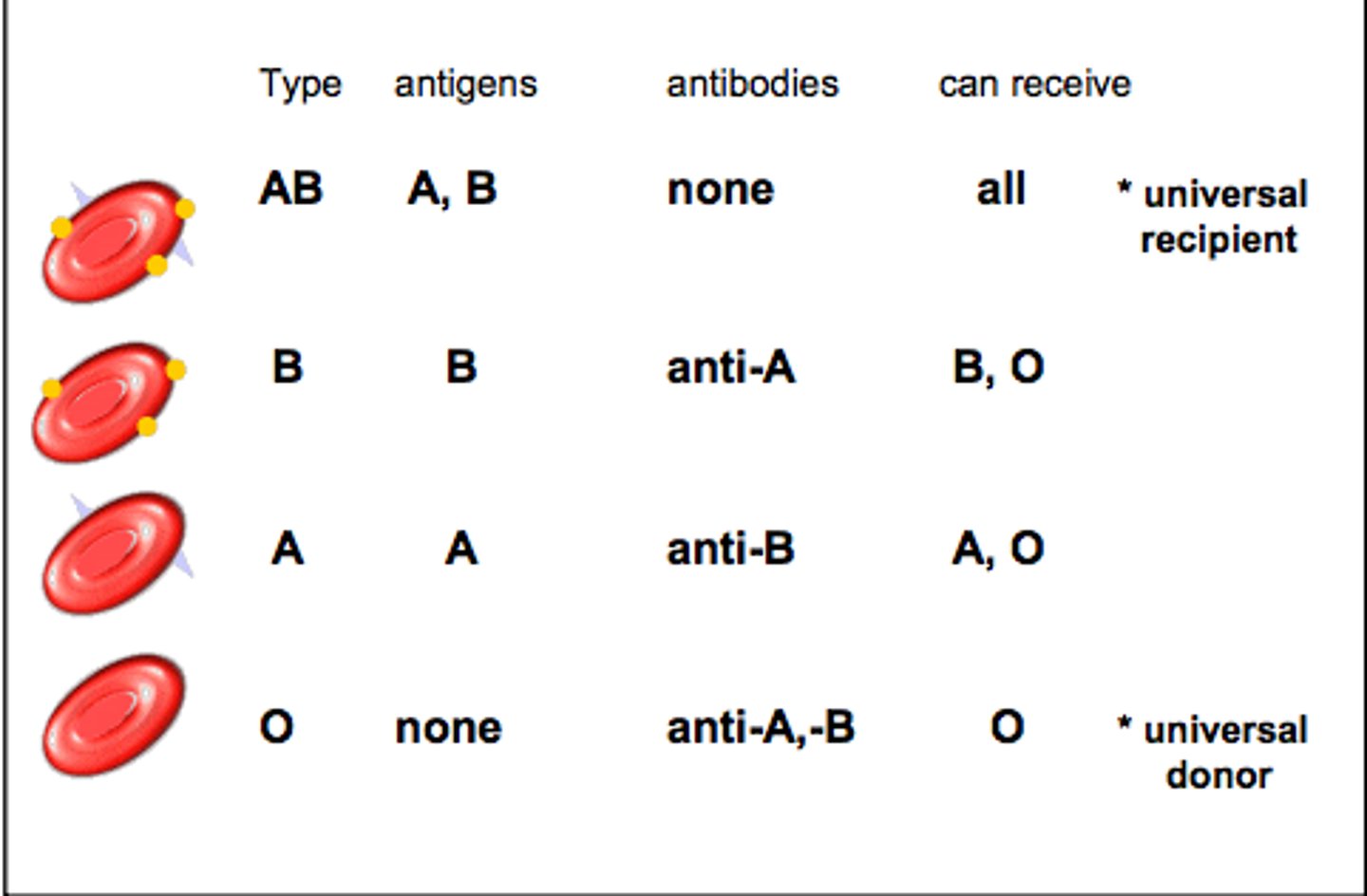
Blood Types
A, B, O, and AB
Do individuals with type A have A antigens?
Yes
Do individuals with type A have B antigens?
No
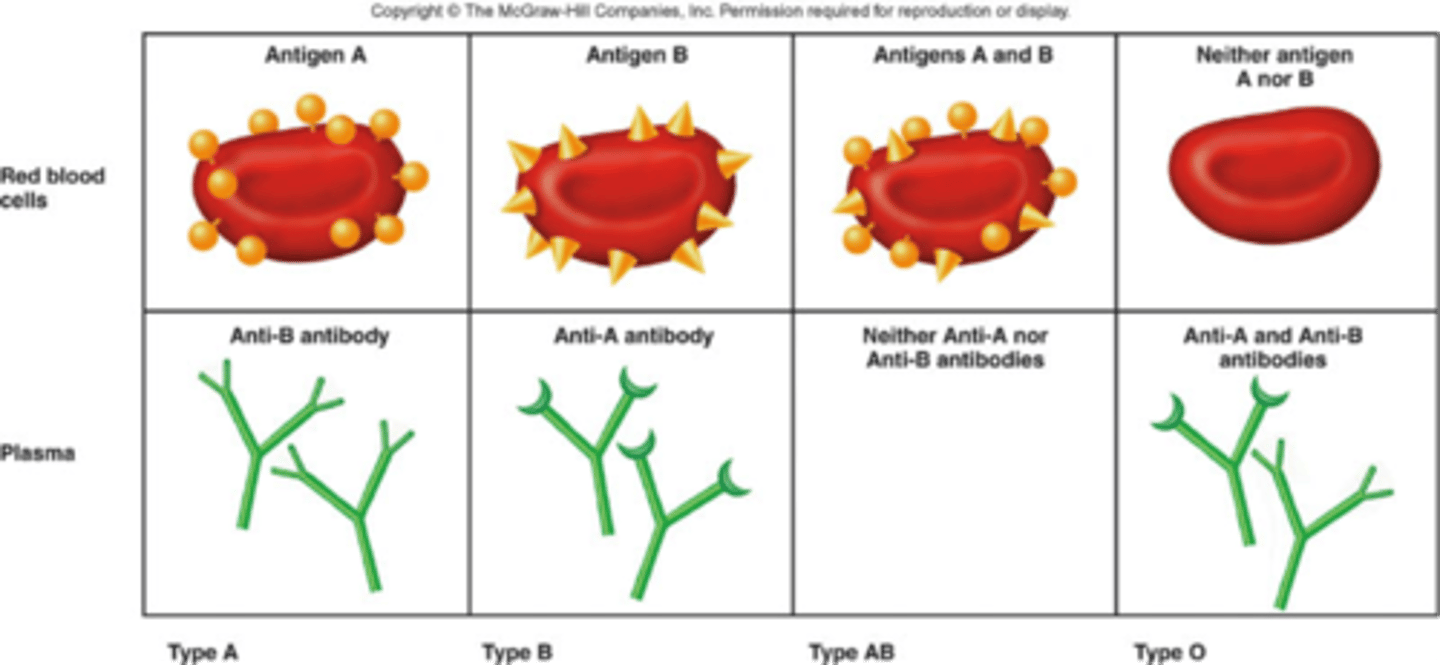
Do individuals with type A have AB antigens?
No
Do individuals with type B have A antigens?
No
Do individuals with type B have B antigens?
Yes
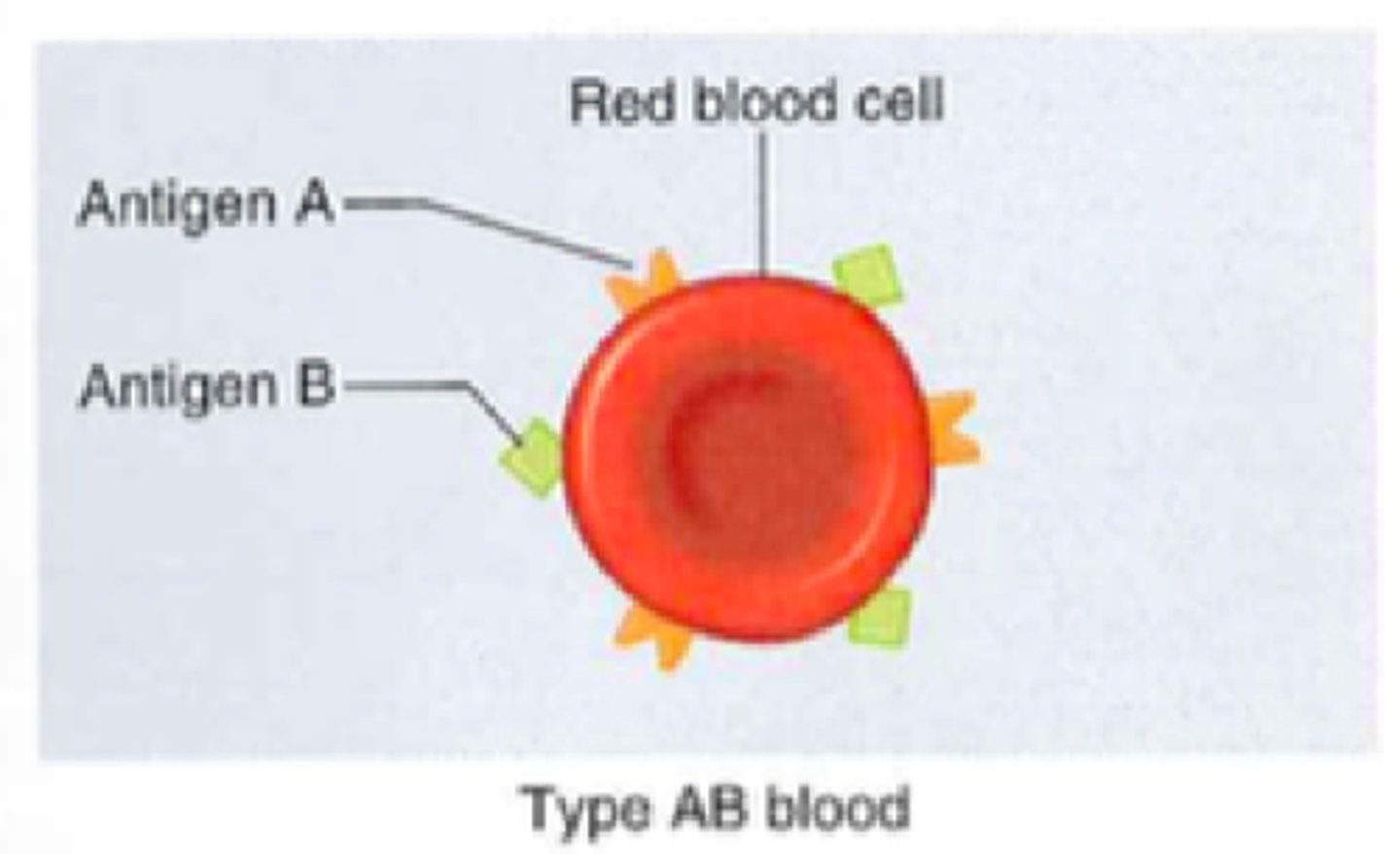
Do individuals with type AB have A antigens?
Yes
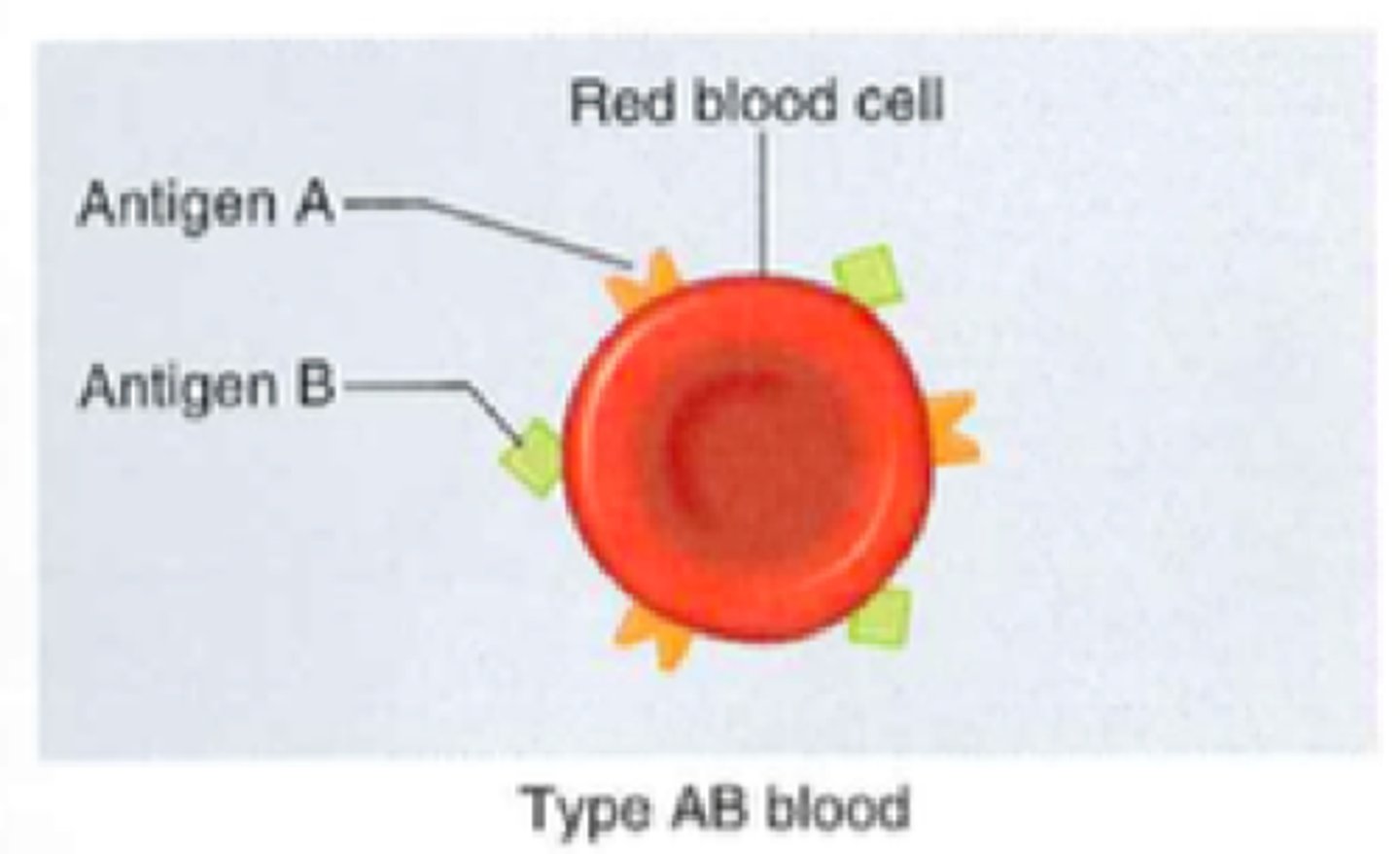
Do individuals with type AB have B antigens?
Yes
Do individuals with type O have A antigens?
No
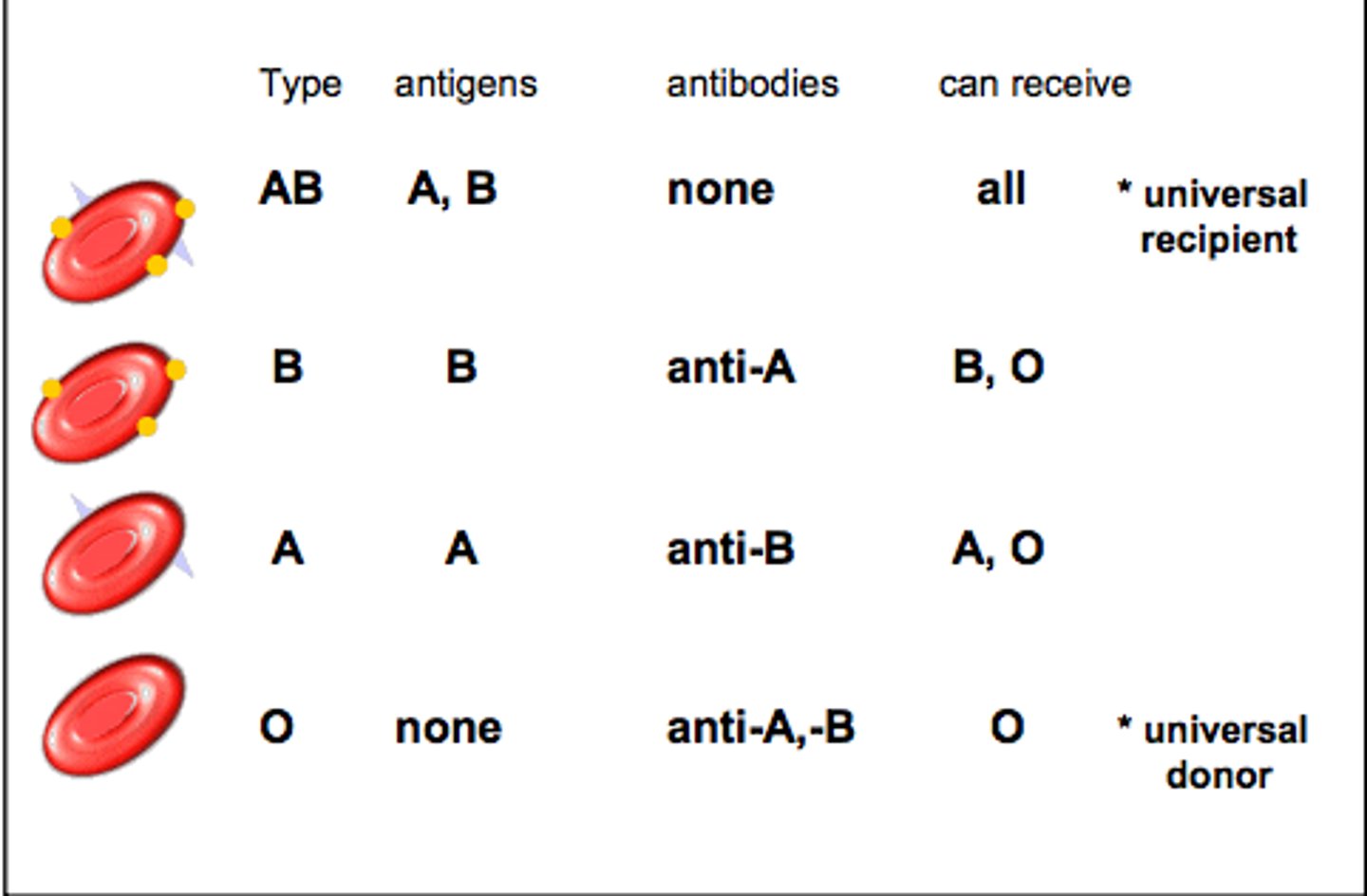
Do individuals with type O have B antigens?
No
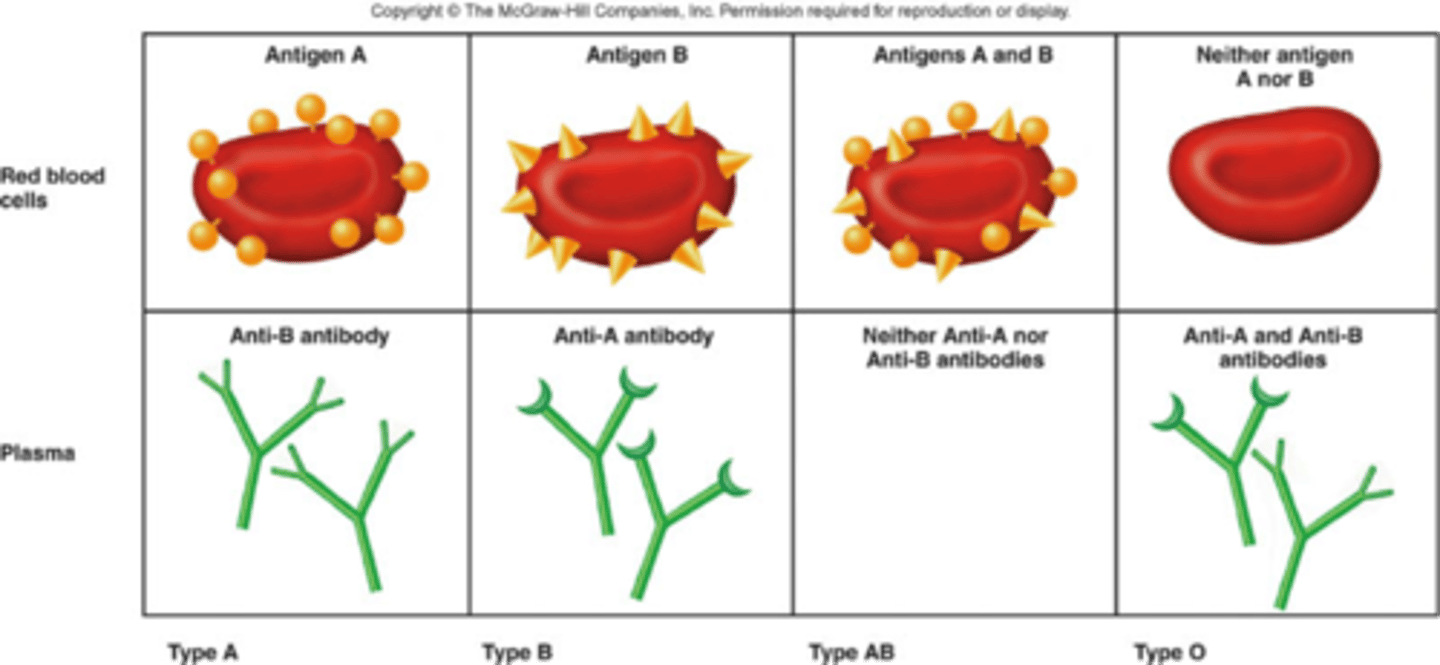
Type A Blood
A antigens and anti-B antibodies
Type B Blood
B antigens and anti-A antibodies
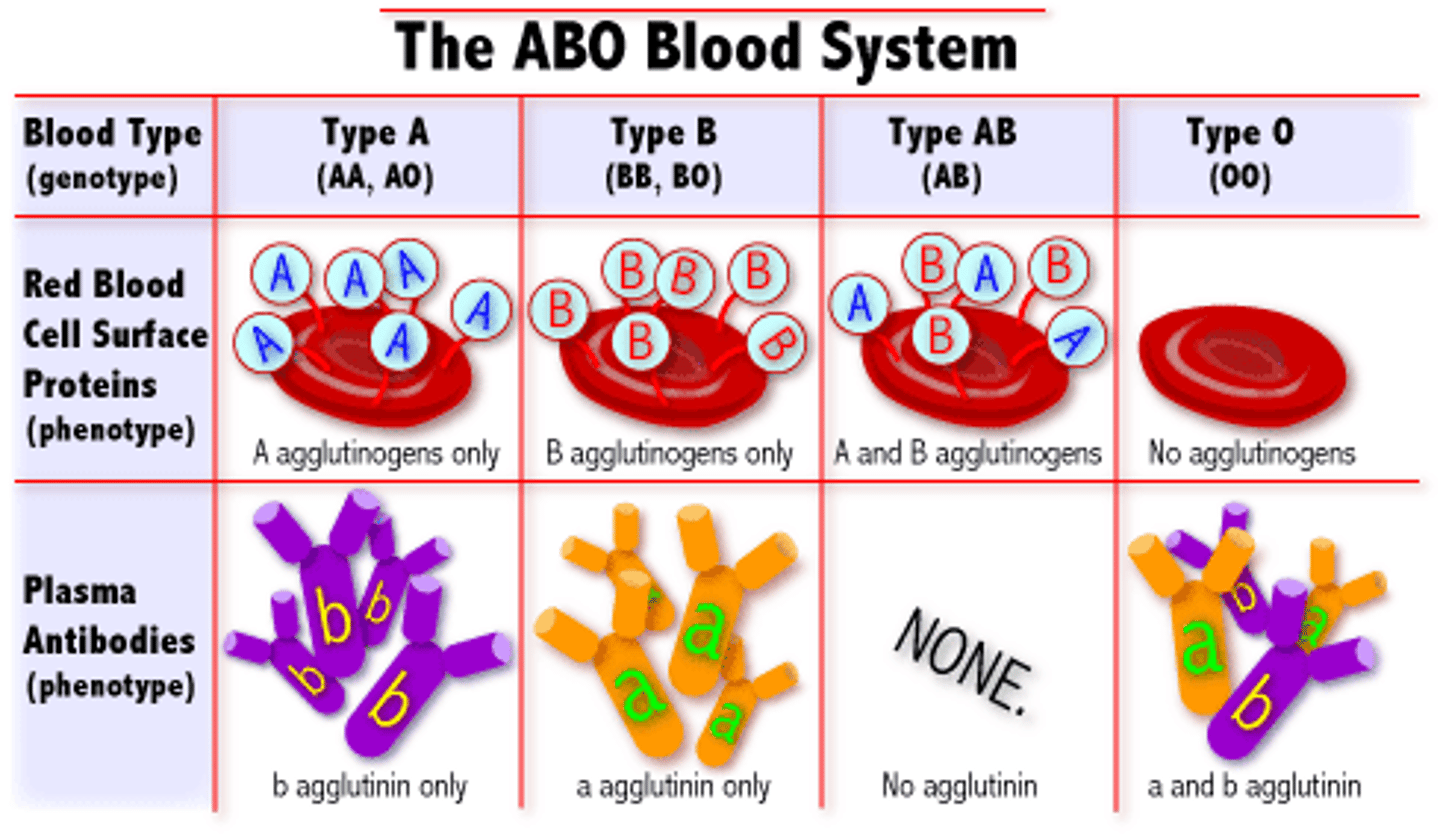
Type AB Blood
A and B antigens, no antibodies
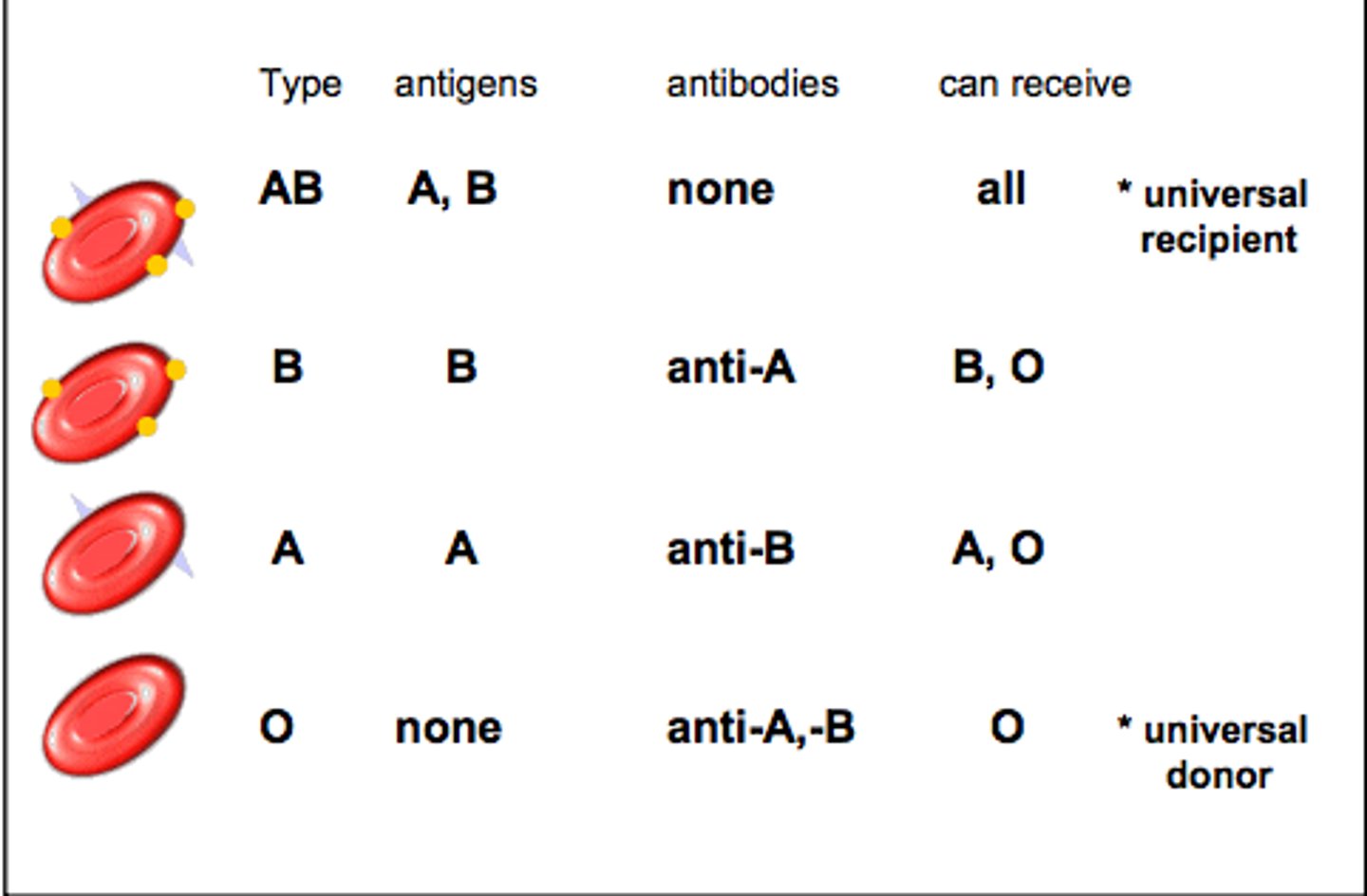
Type O Blood
no antigens, A and B antibodies
Pericardium Function
-Protects and anchors the heart
-Prevents overfilling of the heart with blood
-Allows for the heart to work in a relatively friction-free environment
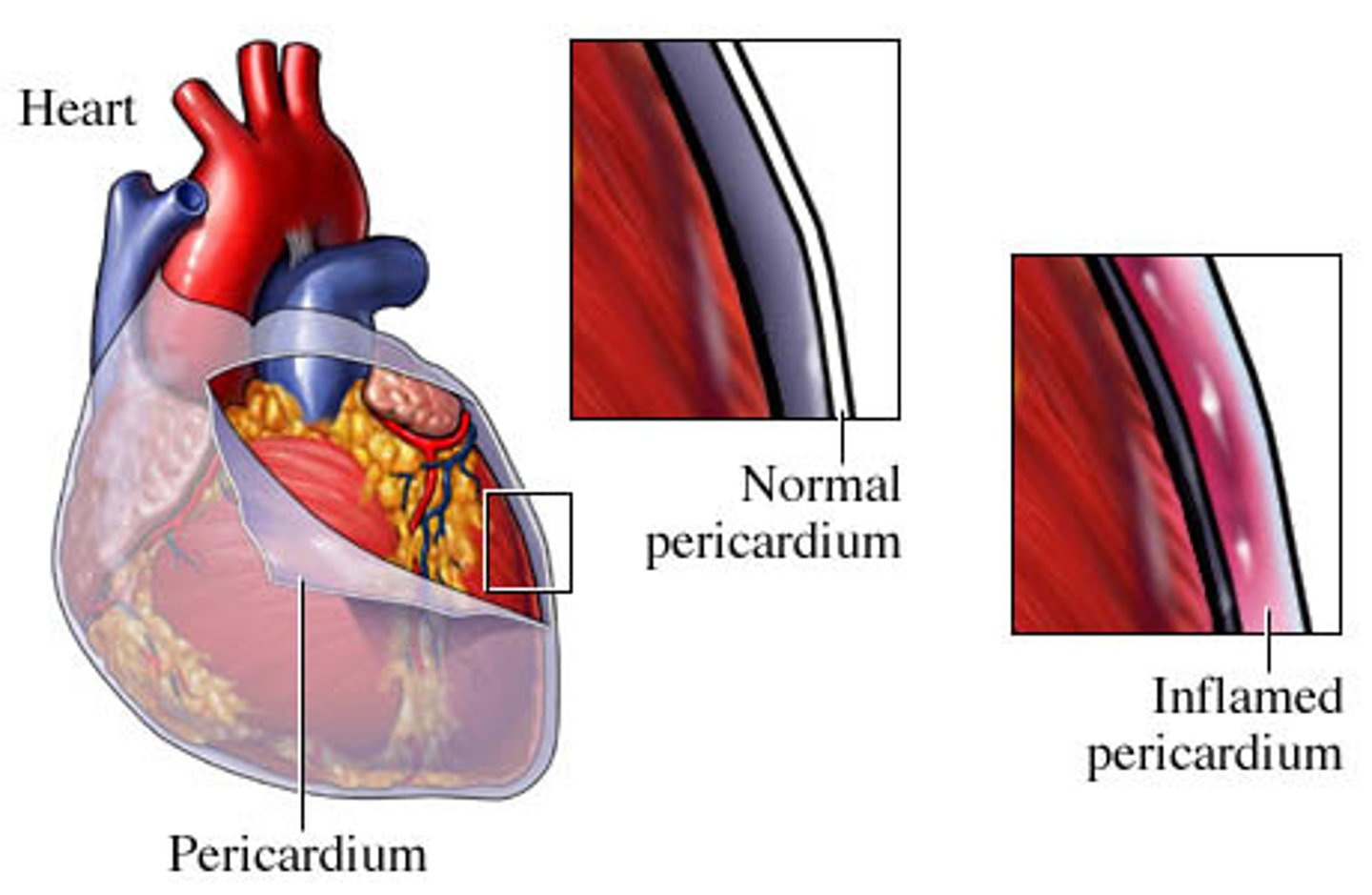
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the membrane surrounding the heart
Coronary sulcus
Separates atria from ventricles. Groove extending around the circumference of the heart
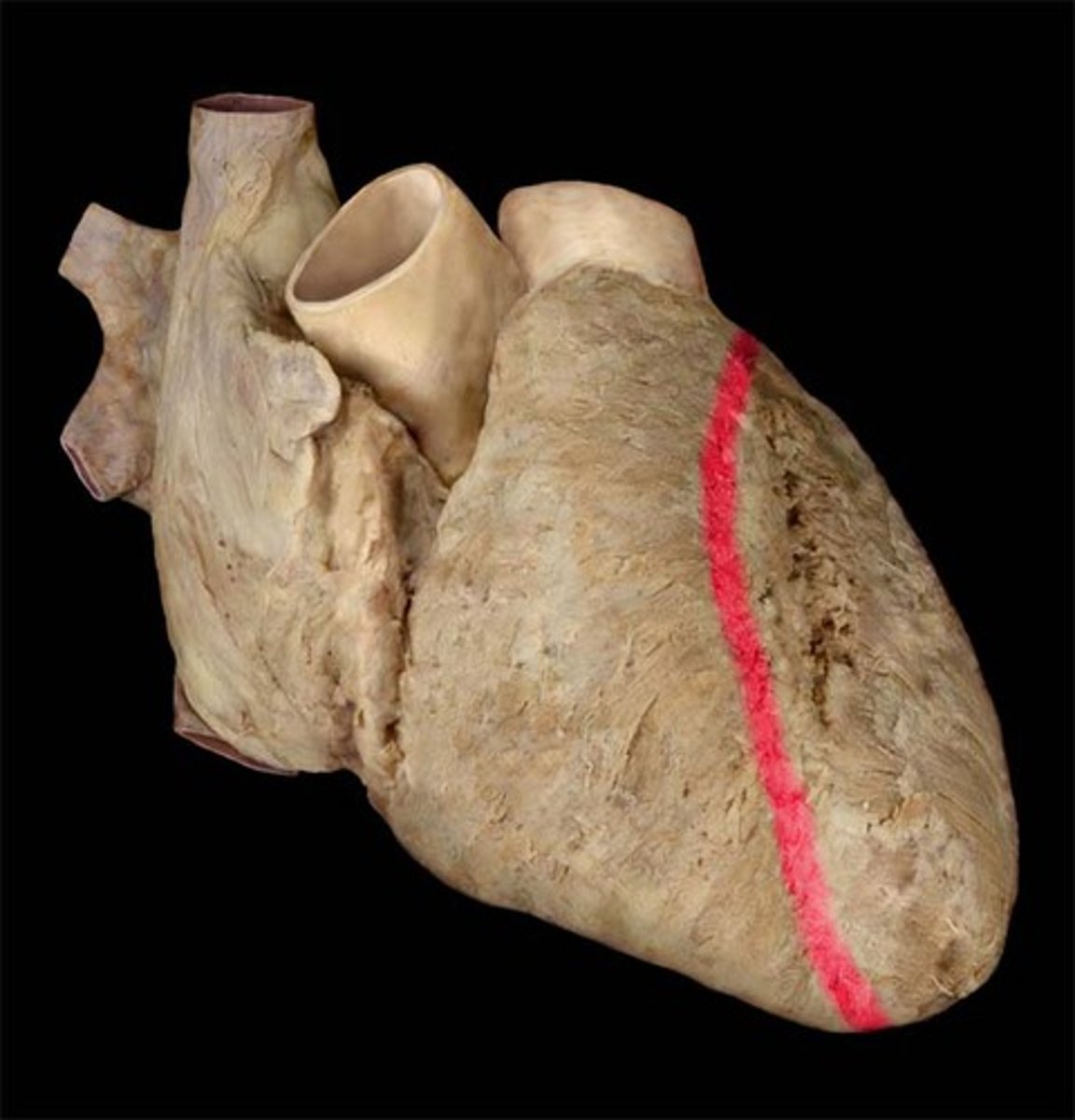
Interventricular sulci
Separates left from right ventricles
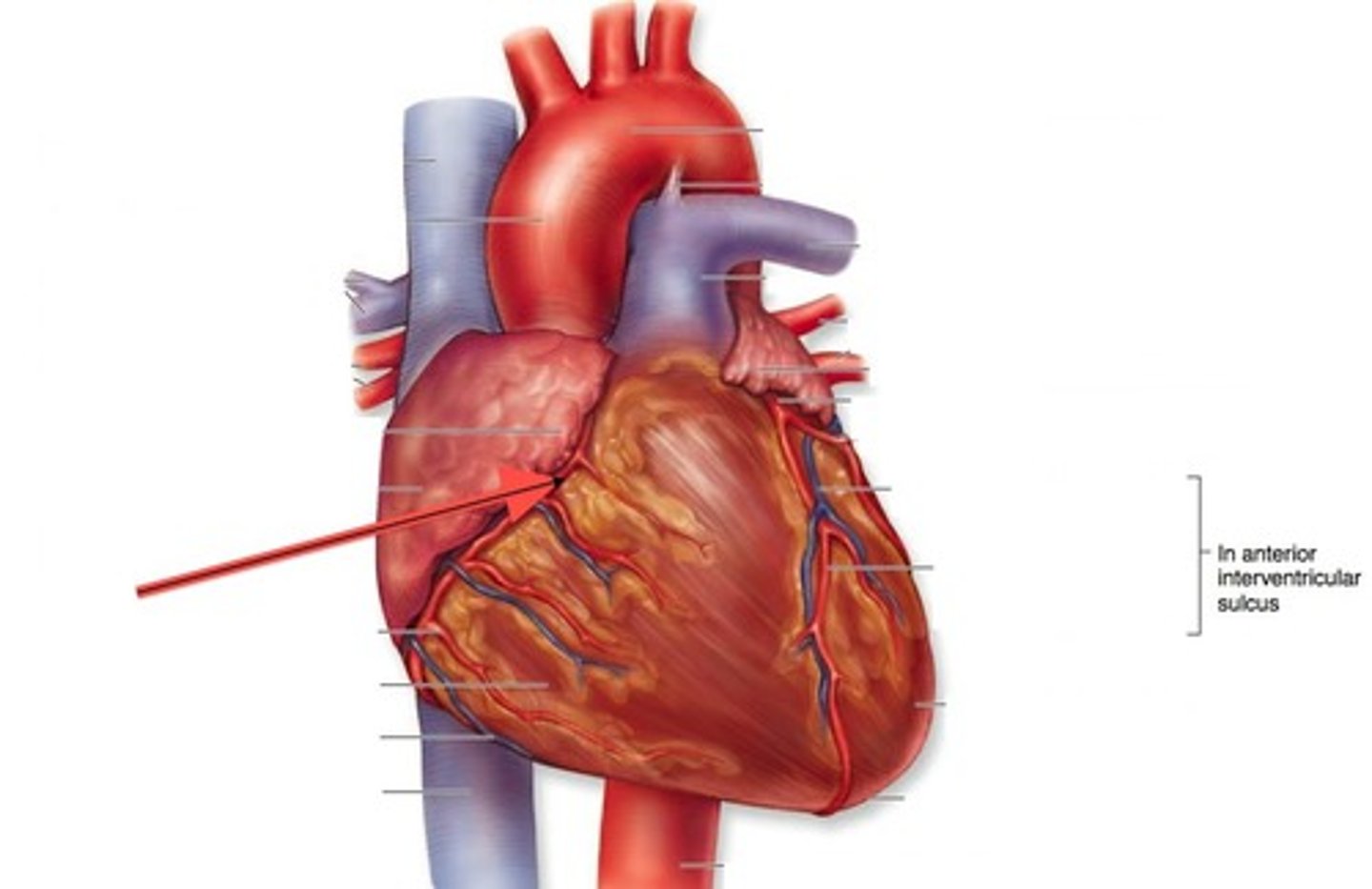
Anterior interventricular sulcus
Marks the boundary between the ventricles anteriorly.

Posterior interventricular sulcus
Marks the boundary between the ventricles posteriorly.
Heart Murmur
An abnormal sound from the heart produced by defects in the chambers or valves.
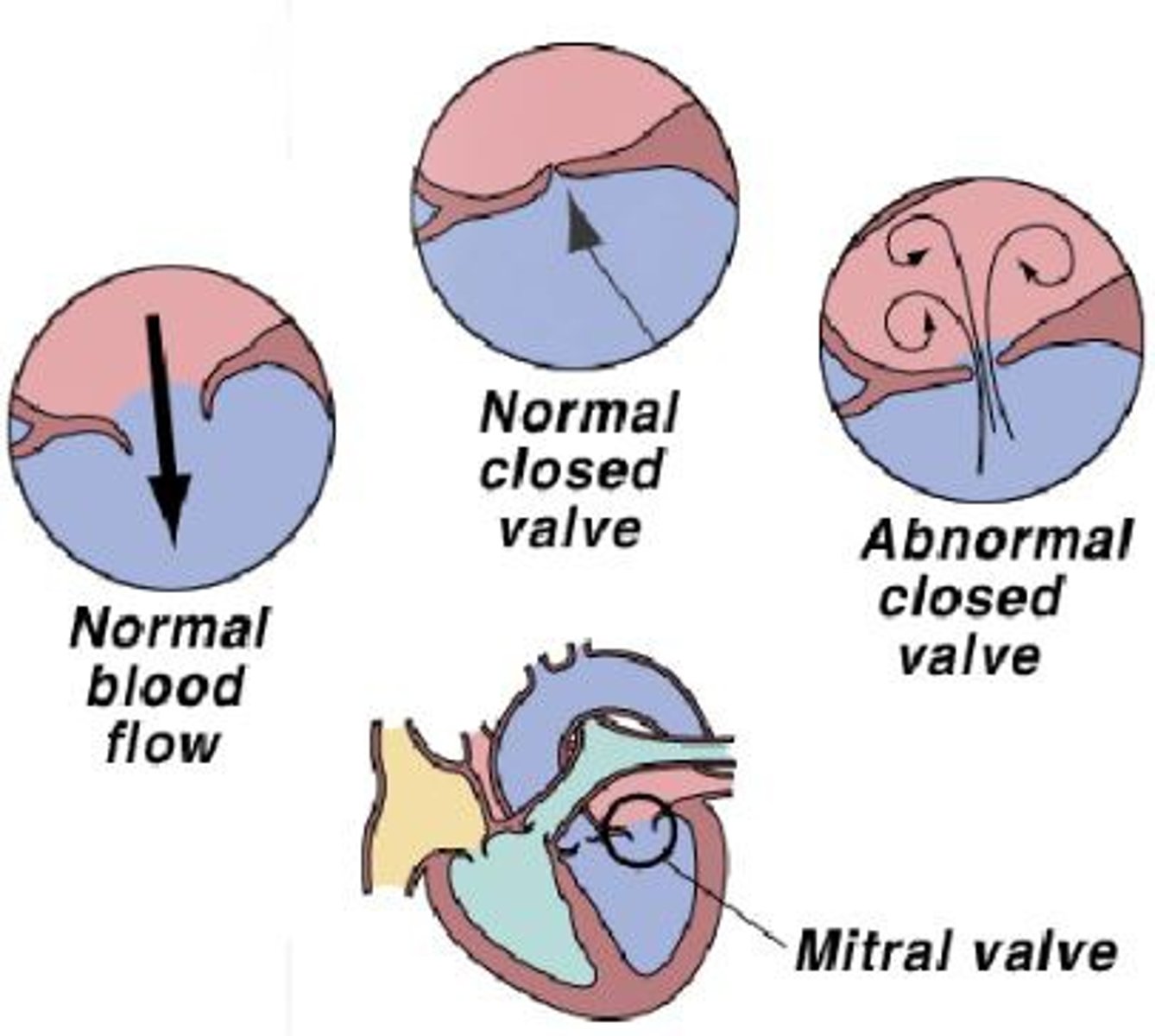
Valvular insufficiency
Any failure of a valve to prevent reflux, the backward flow of blood
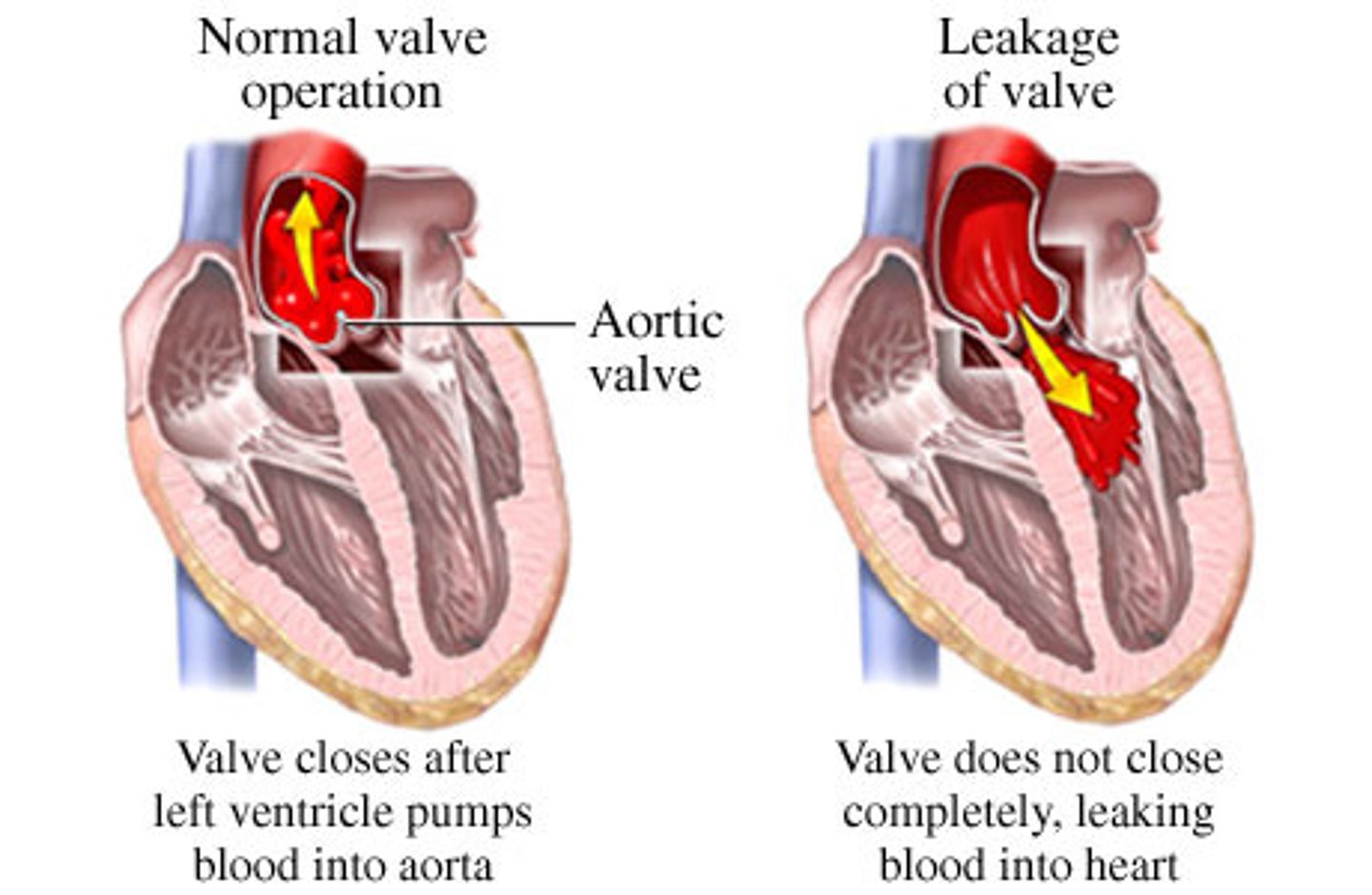
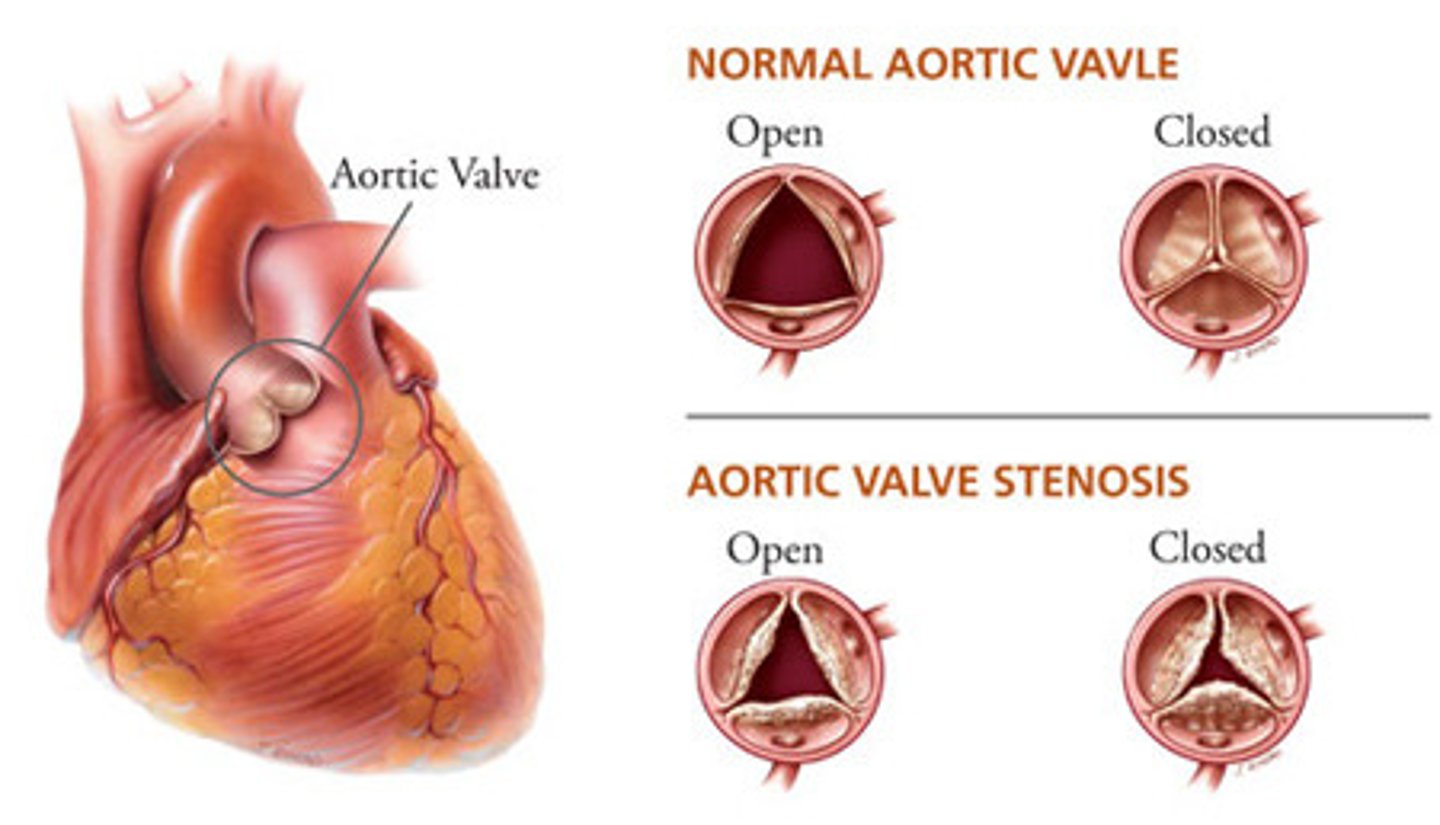
Valvular stenosis
A condition in which there is narrowing, stiffening, thickening, or blockage of one or more valves of the heart
Separation of chambers
Interatrial septum and interventricular septum
Interatrial septum
Separates left atrium from right atrium
Interventricular septum
Separates left ventricle from right ventricle
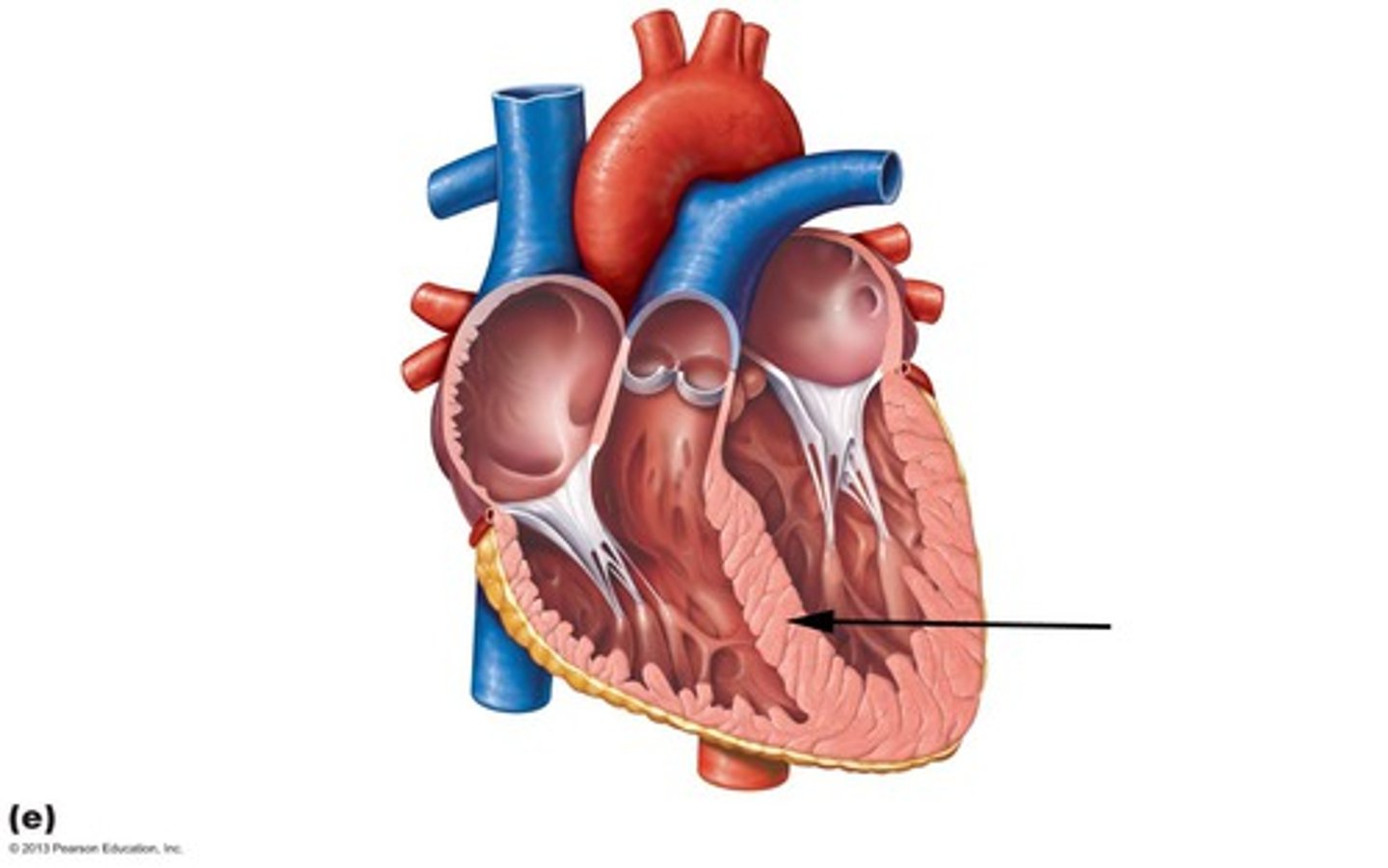
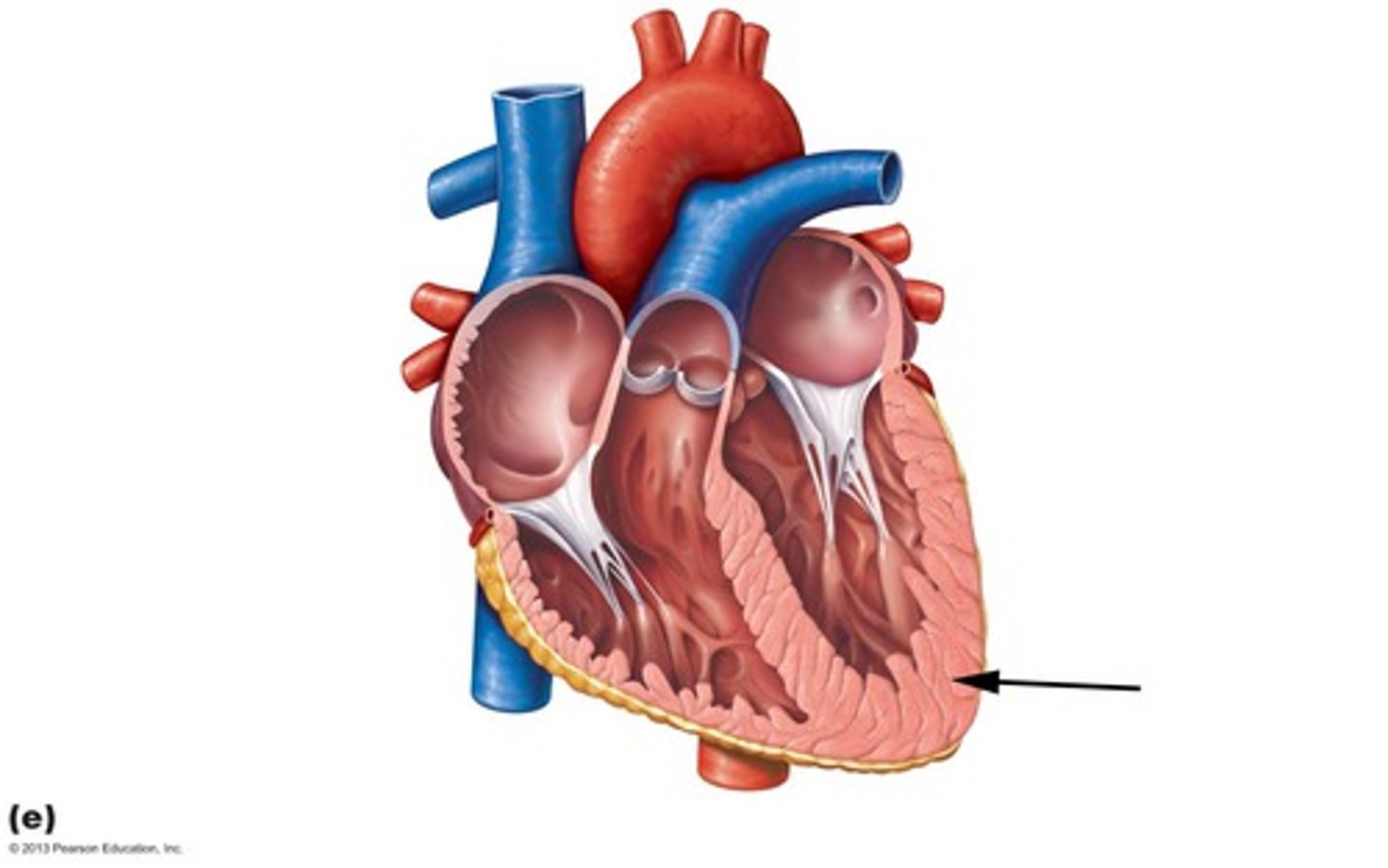
Pectinate muscles
Ridges on anterior wall and within auricle
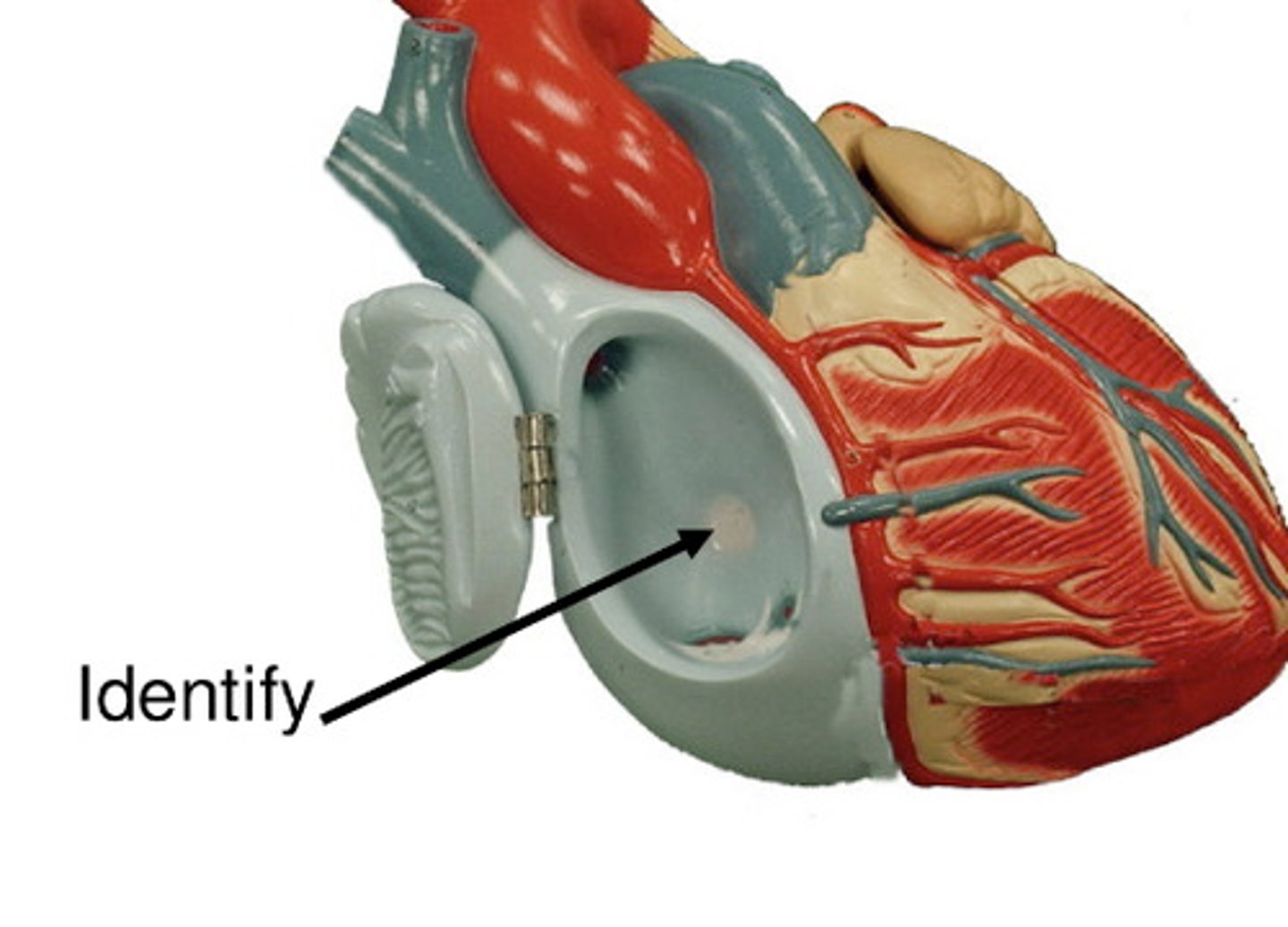
Fossa ovalis
Oval depression on interatrial septum
Pectinate Muscles and Fossa Ovalis
Right atrium
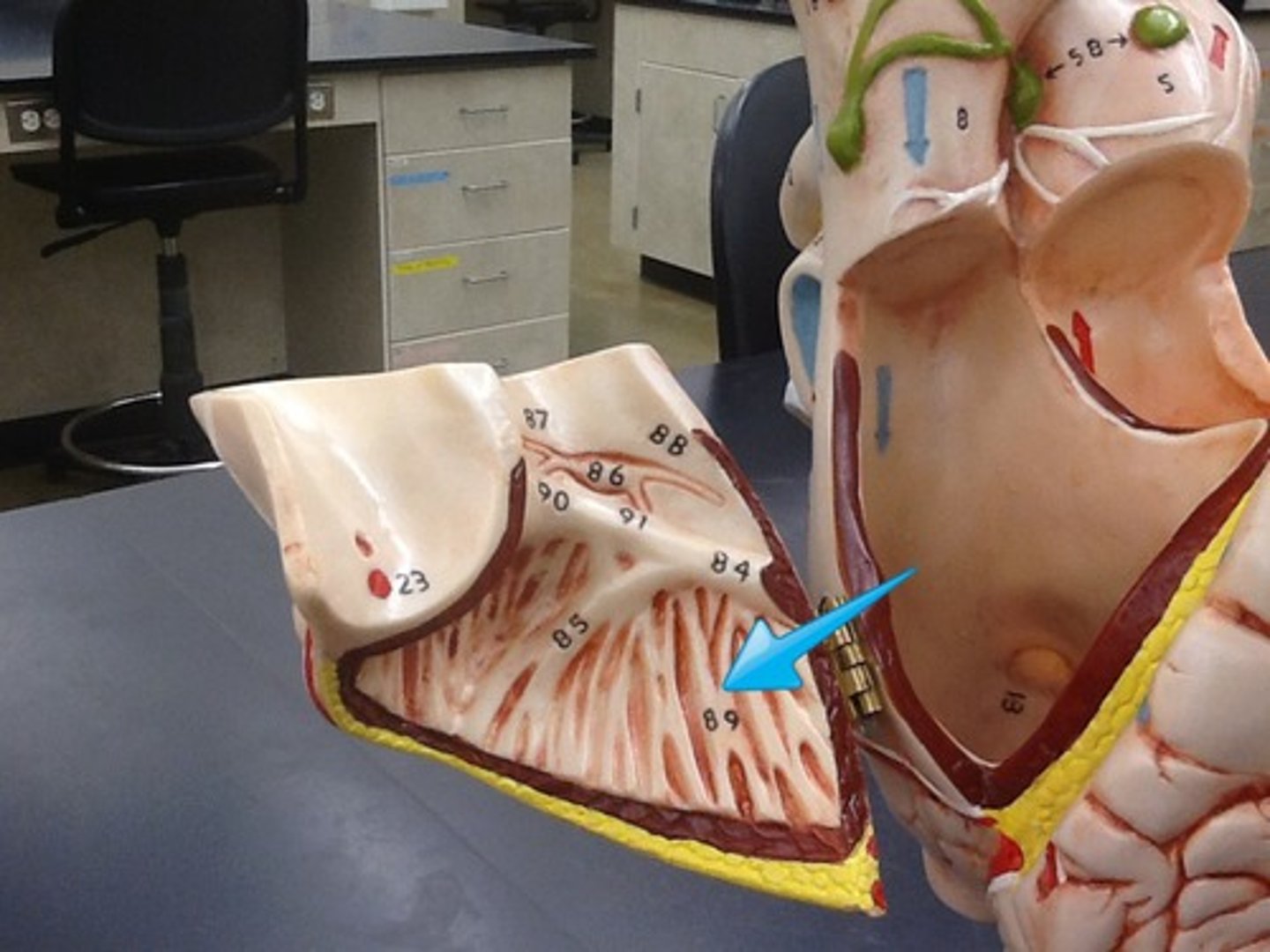
Trabeculae carnage
Irregular muscular ridges inside ventricle wall
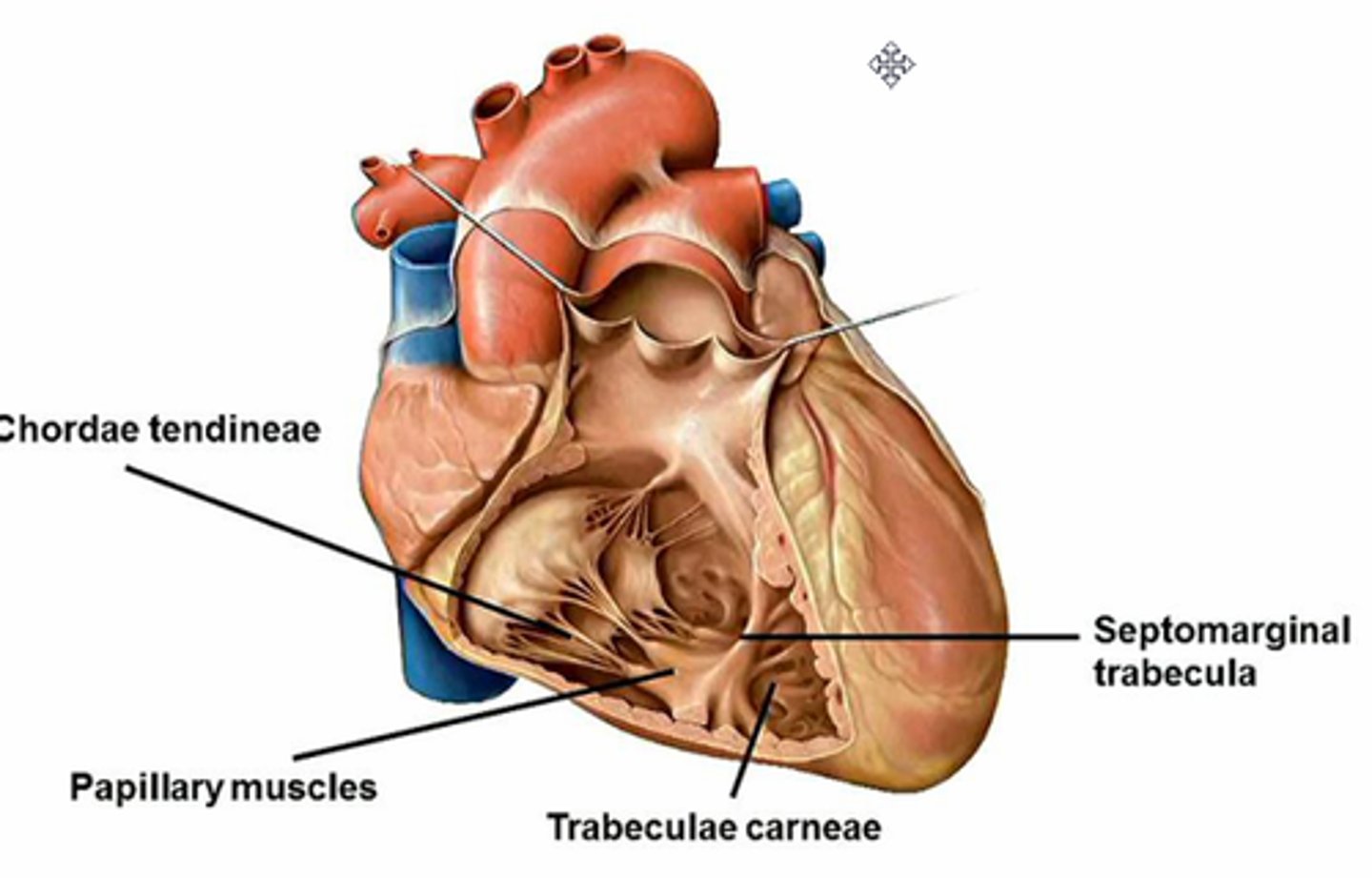
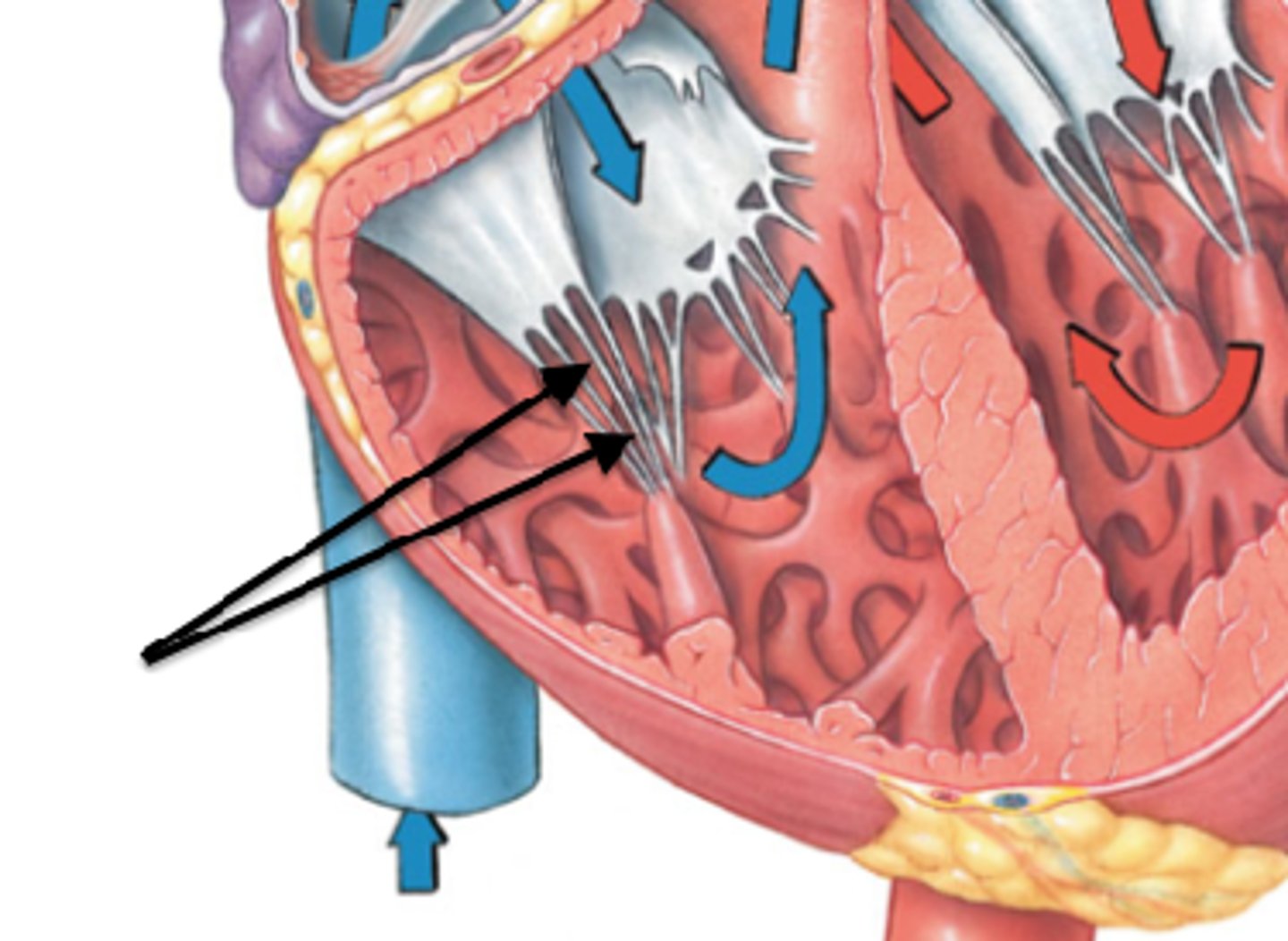
Papillary muscles
Cone-shaped projections extending from internal ventricle wall (right ventricle typically has 3 of them)
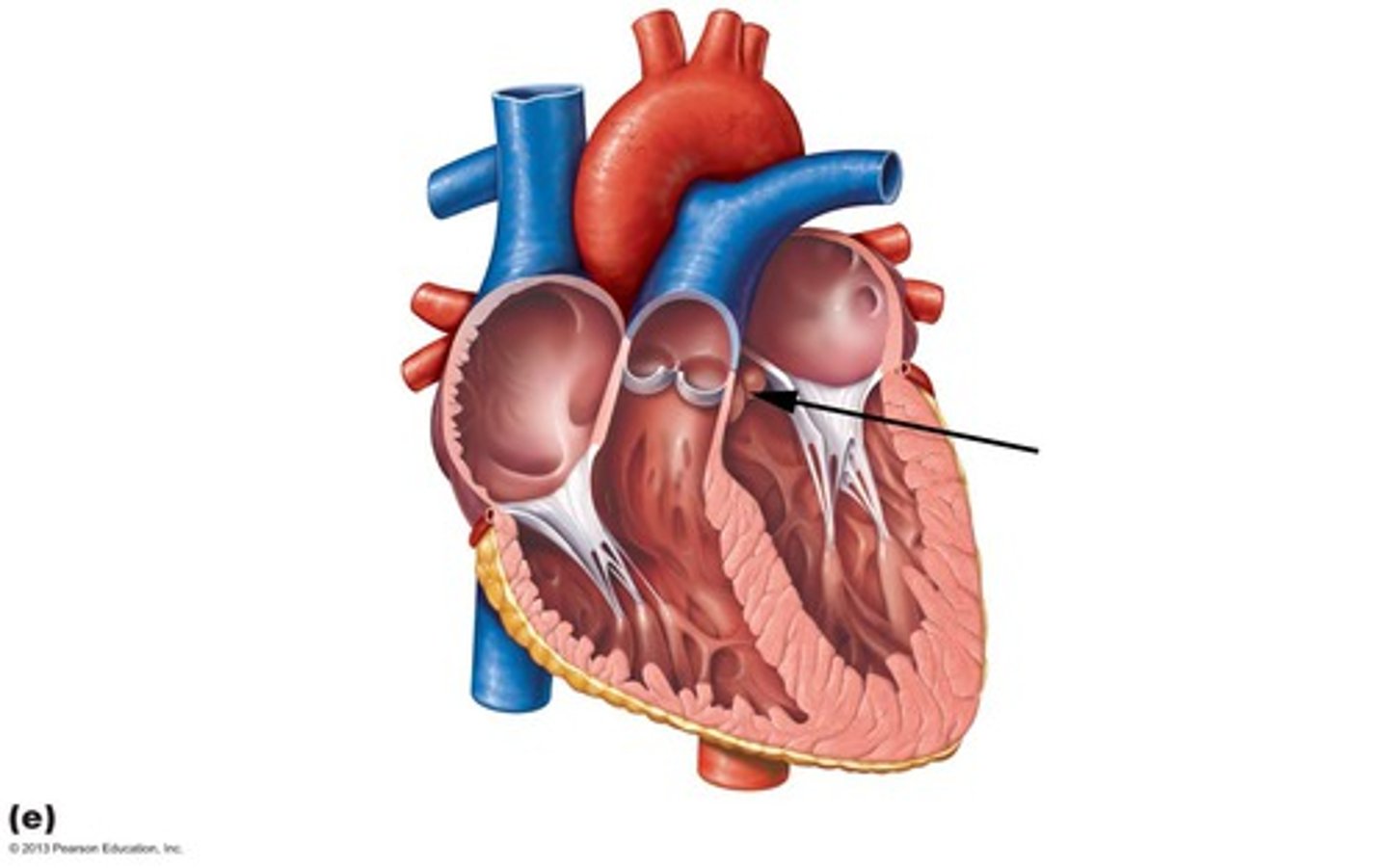
Chordae tendineae (tendinous cords):
–heartstrings
- Thin strands of collagen fibers attaching to AV valve
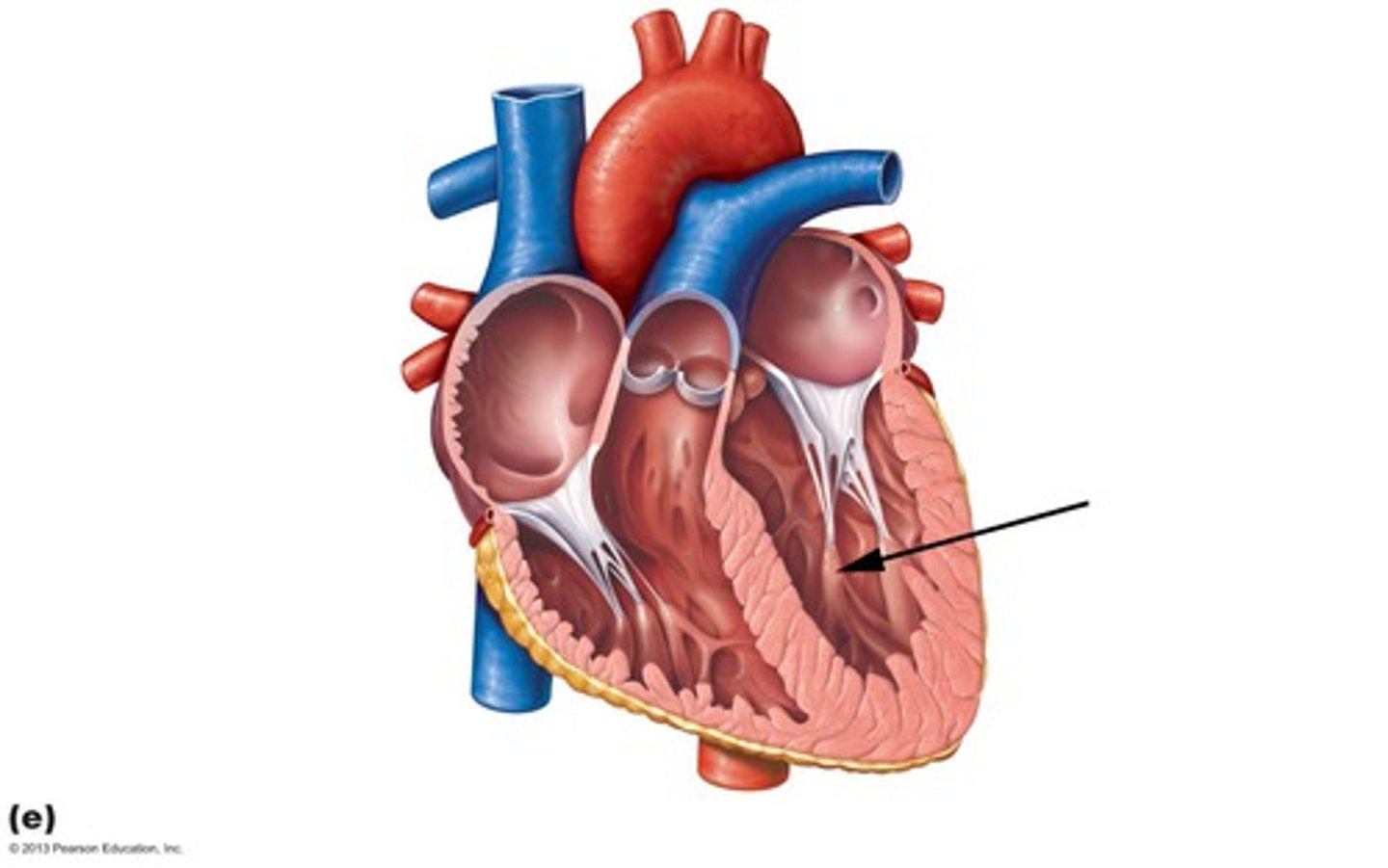
Valves
Prevent back flow of blood
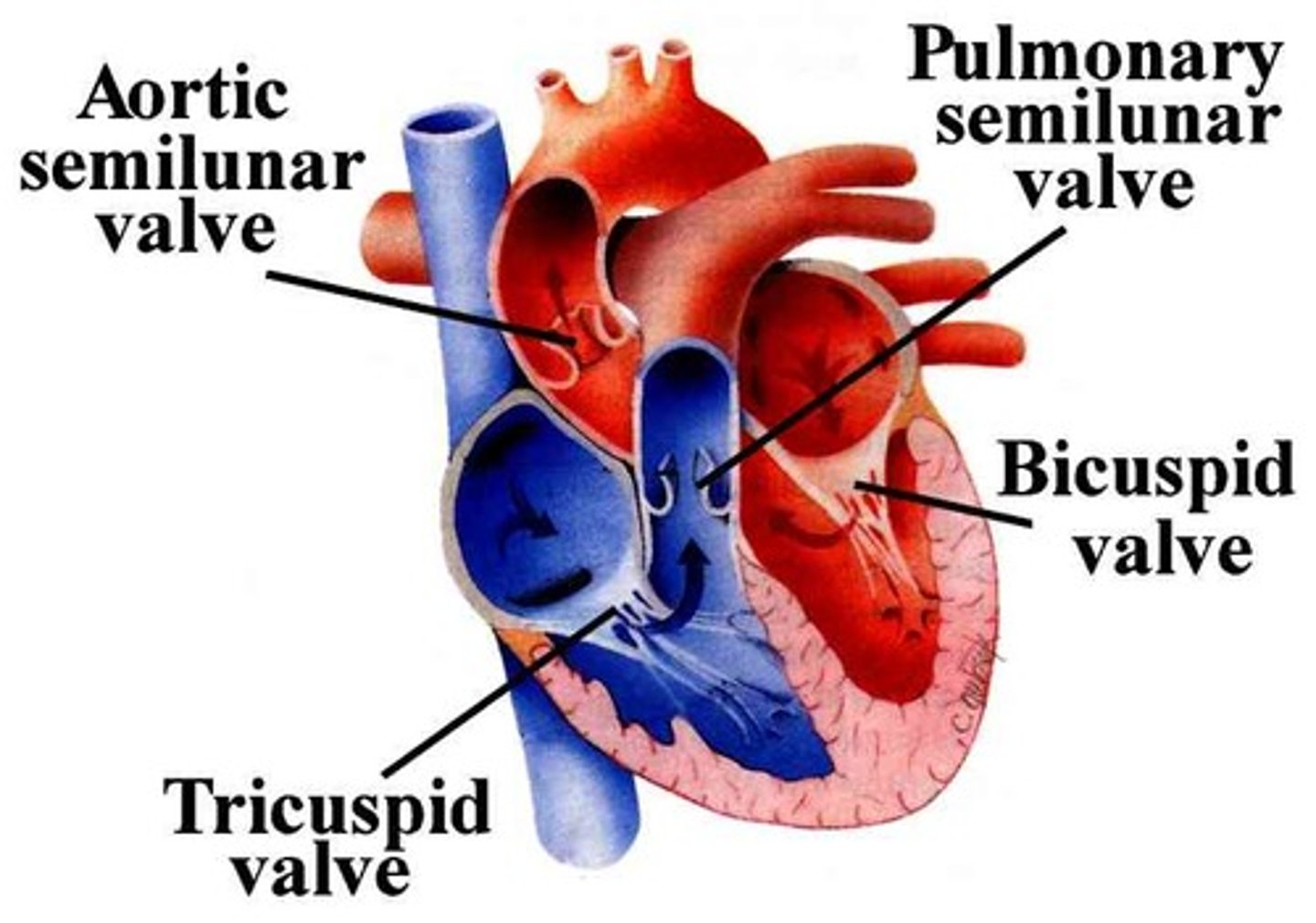
Semilunar Valves
Prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles
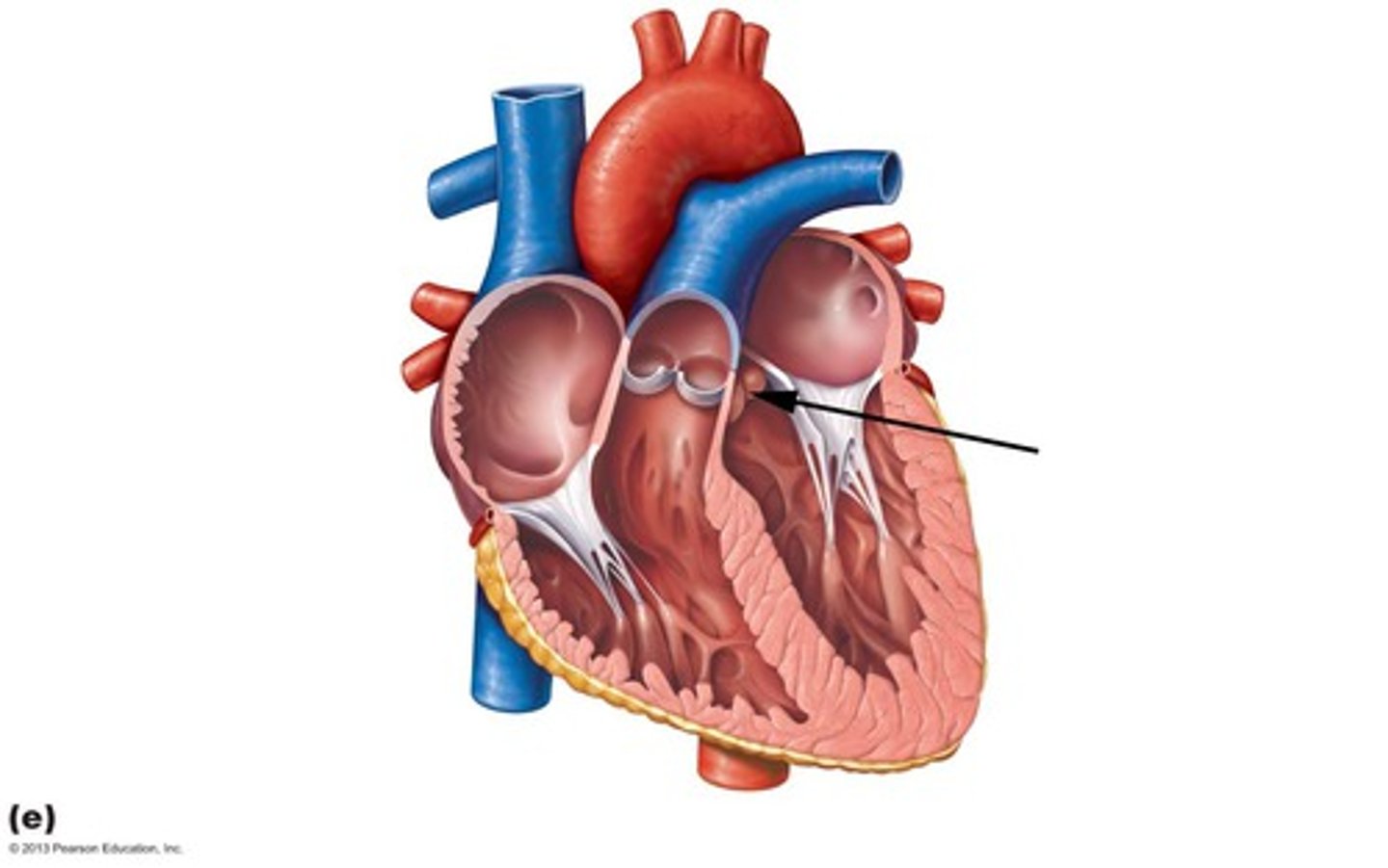
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Located between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
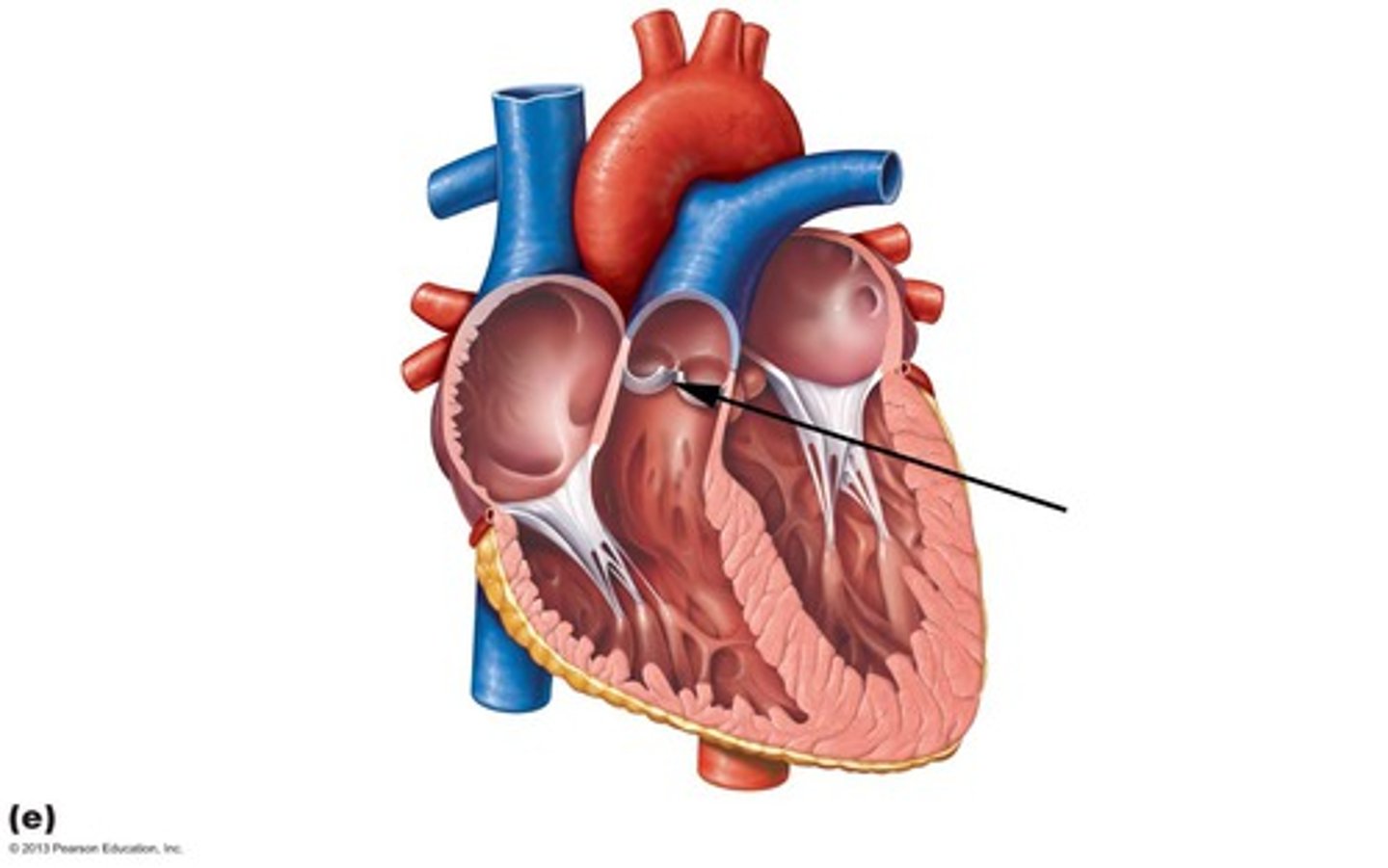
Aortic semilunar valve
Located between left ventricle and the aorta