APHuG - Unit 04 Vocab Summative Study
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
contagious diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population. Viral videos blues music spreading northward from southern USA
sociofacts
ways people organize their society and relate to one another. Family, school/education, land use, religion
Creole language
a language that began as a pidgin language but was later adopted as the mother tongue by a people in a place of the mother tongue; the Haitian language is an example
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group. Viewing others by means of stereotypes leading to violence and discrimination.
Stimulus Diffusion
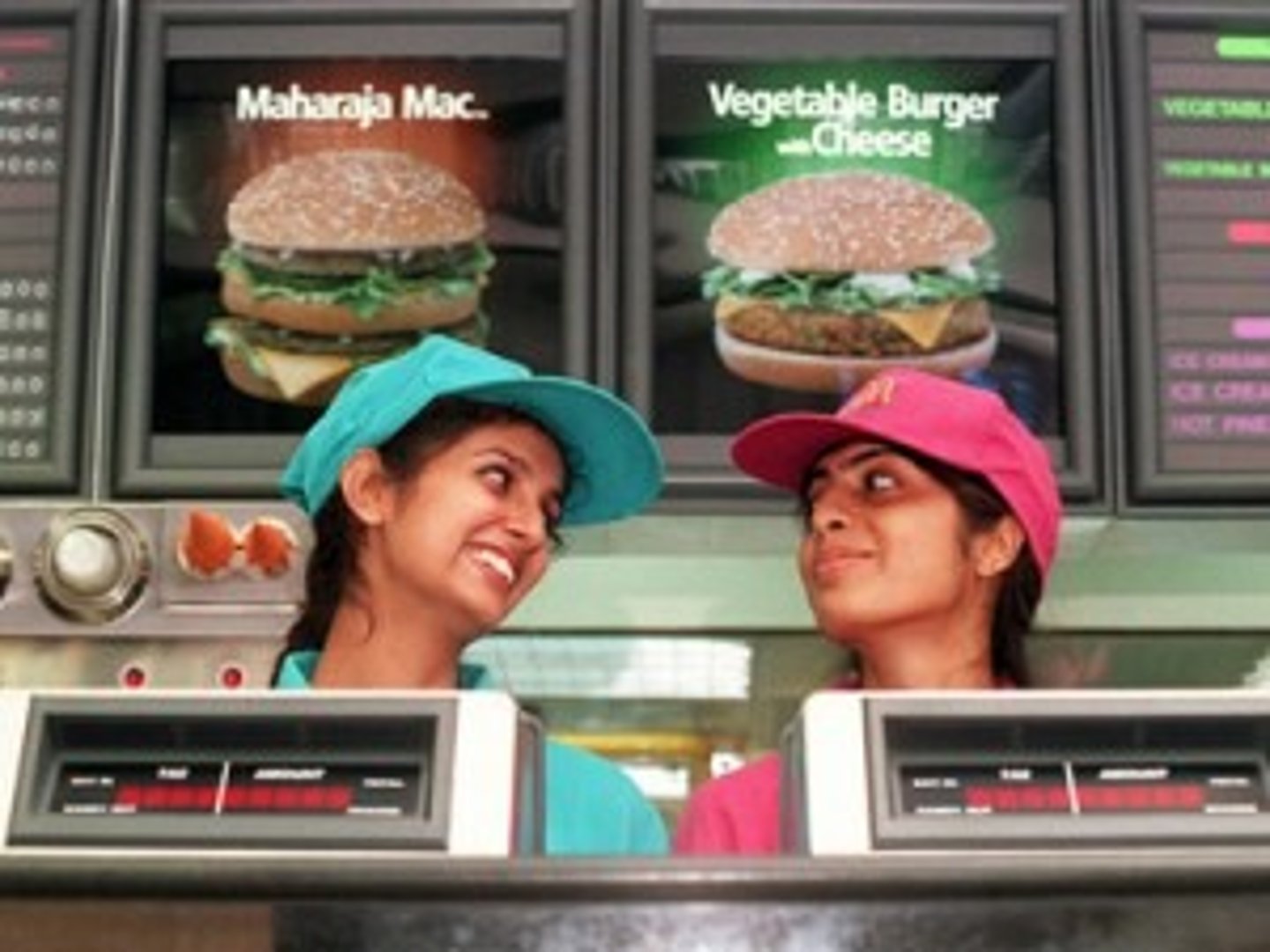
a form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place. McDonald’s diffusing to India adapting to offer veggie burgers to due eating beef being a taboo.

Traditional Architecture
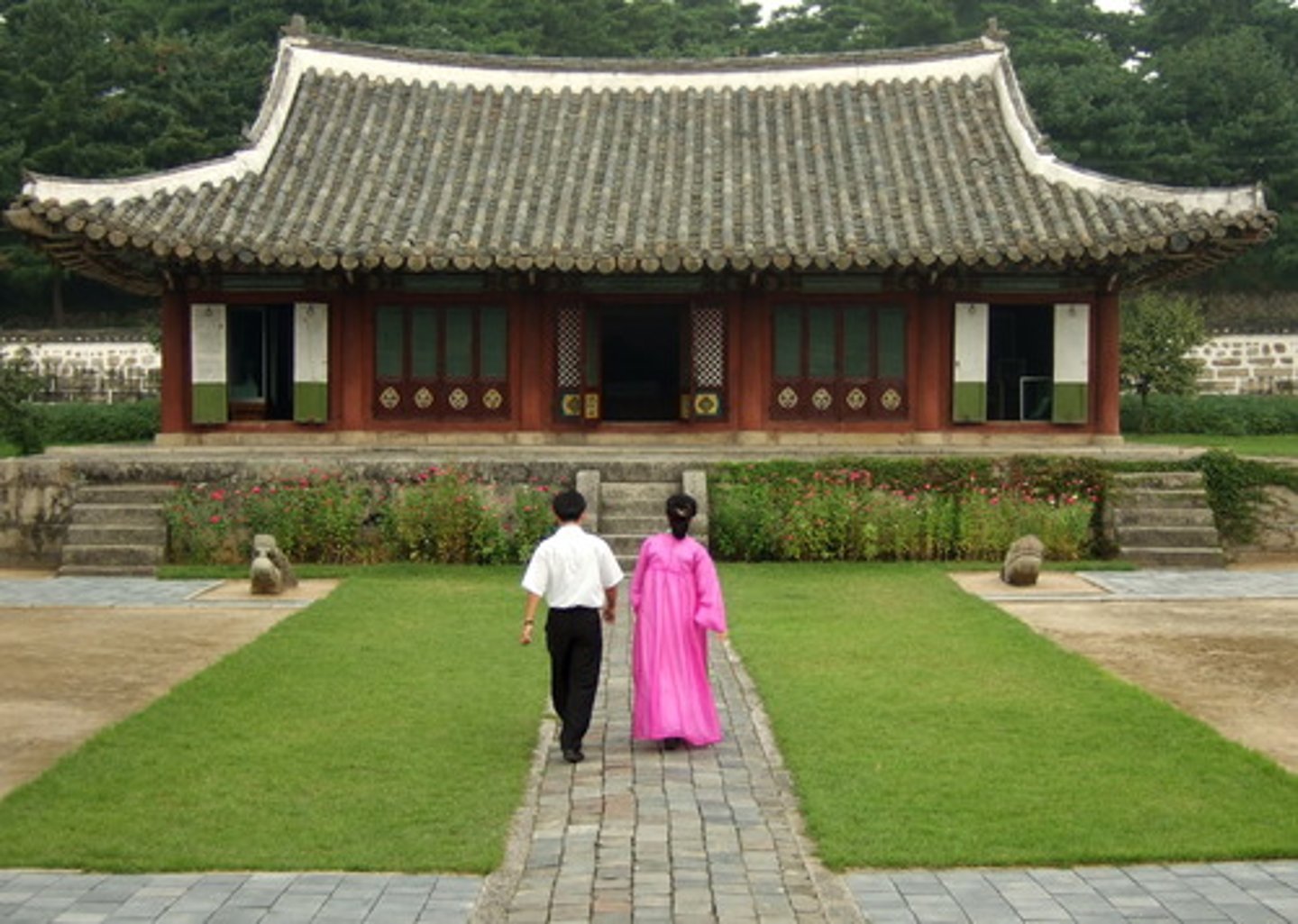
traditional building styles of different cultures, religions, and places. Stone and clay houses in rural Nepal, Spanish adobe mud homes in SW USA.

Isogloss
a map indicating language boundaries. The boundary where the term dry creek bed is replaced by the spanish word arroyo.
Post Modern Architecture
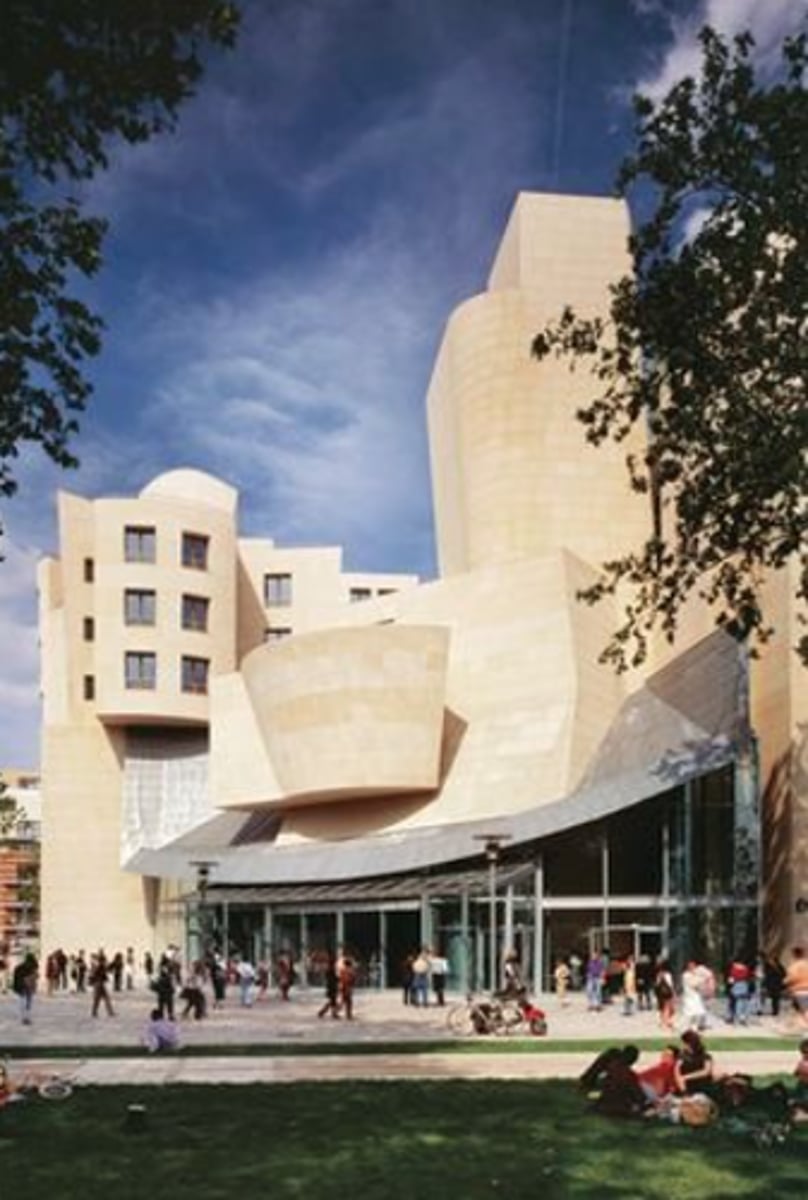
an architectural style that emphasized breaking the rules of the rigid style of modern architecture. frank lloyd wright’s fallingwater, skyscrapes, 1983 bank of america center.

Ethnicity
Identity with a group of people that share distinct physical and mental traits as a product of common heredity and cultural traditions. Ethnic enclaves like chinatown
Cultural Divergence
The likelihood or tendency for cultures to become increasingly dissimilar with the passage of time. Amish culture is distinct due to isolation from mainstream US culture and modern tech rejections.

Lingua Franca
a language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different for business purposes. English is world lingua franca.
Indo-European Language Families
A large group of languages that might all have descended from a language spoken around 6,000 years ago. Includes branch of romance languages and germanic branch.
Pidgin Language
A form of speech that adopts a simplified grammar and limited vocabulary of a lingua franca, used for communication among speakers of two different languages.
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another is a snowballing process.
Centrifugal Forces
Forces that tend to divide a country. multiple competing ethnicities or languages or religions
Cultural Landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape. a skyscraper or a cleared field. names changing from anglo words to spanish names and wood buildings being replaced by adobe buildings alone interstate 25.

Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places. cell phones were first only owned by wealthy elites and slowly diffused to lower class.
Sequent Occupance
the notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape. Waterbury, CT hsd hosted many different cultures that left their imprint over time. The Pyramids, Harlem NYC.

Cultural Realms
A large area of the world that shares a similar cultural traits and characteristics. Anglo-American christianity shared history with Latin America.
Pop Culture
Culture is found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics; it is highly contagious and always changing. K-pop, bollywood movies, anime, european soccer.
Relocation Diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend through the bodily movement of people from one place to another. Migration of Europeans to the Americas resulting in spread of Christianity and European languages. Spread of pizza by Italy to USA.

Dialects
Local or regional characteristics of a language. While accent refers to the pronunciation differences of a standard language, a dialect, in addition to pronunciation variation, has distinctive grammar and vocabulary. Difference pronunciations of same language. British vs American English.
Cultural Hearth
The start of a trait. Classical greece of democracy and NYC for rap music in the 70s.
Romance Languages
Any of the languages derived from Latin including Italian, Spanish, French, and Romanian.
Cultural Appropriation
The adoption of cultural elements belonging to an oppressed group by members of the dominant group, without permission and often for the dominant group's gain

Polythestic
Belief in many gods. Hinduism
Syncretism
a blending of beliefs and practices from different religions into one faith. Santeria developed through influence of African Yoruban and Roman Catholicism. Snowboarding blends skateboarding and surfing
Universalizing Religions
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location. Typically has a prophet. Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, and Sikhism.
Judaism
Hearth is Israel, prophet is Abraham. Monotheistic. Large numbers of Jews were forced out of Israel during the Roman Empire’s reign.

Folk Culture
Culture is traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation from other groups. Festival celebrating Kutubu Foe and Faso people. Amish people of Pennsylvania.
Multiculturalism
A perspective recognizing the cultural diversity of the United States and promoting equal standing for all cultural traditions. In 1971 Canada government established as a fundamental right. Foods eaten in the USA such as corn from indigenous americans and bagels from eastern jews.

Mentifacts
the ideas, beliefs, values, and knowledge of a culture. religious beliefs, language, food preferences, taboos, belief in a god.
Centripetal Forces
Forces that tend to unite or bind a country together. Holiday season in the US from November through December. Common language or ethnicity
Cultural Convergence
The tendency for cultures to become more alike as they increasingly share technology and organizational structures in a modern world united by improved transportation and communication. World sports People around the world wearing jeans and t shirts on a daily basis.
Taboos
Behaviors are heavily discouraged by a culture. taboo in hindu culture to eat beef.
Buddhism
The teaching of Buddha that life is permeated with suffering caused by desire, that suffering ceases when desire ceases, and that enlightenment obtained through right conduct and wisdom and meditation releases one from desire and suffering and rebirth. Spread along water trading routes in SE Asia.
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms. Adherents make a pilgrimage to the Ganges River
Acculturation
The adoption of cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another.
Cultural Relativism
the practice of judging a culture by its own standards even if different from ones own beliefs.
Time-space convergence
The idea that the distance between some places is actually shrinking as technology enables more rapid communication and increased interaction among those places. Time taken to cross Atlantic ocean has decreasing from 36 days to 7 hours today.
Official Language
The language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents. Zimbabwe has 16 official languages. English is most common official language around the world.
Assimilation
the social process of absorbing one cultural group with another; Native American cultures forced to become "White Americans" during the reservation system. Native American Boarding Schools where native americans were forced to learn english and completely change how they looked.

Artifacts
object made by human beings. Houses, clothing, architecture, toys, tools.
Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior. Emperor Theodosius declared Christianity the official religion of Roman Empire.
Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), Paradise and Hell, and a body of law written in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims. Followers make pilgrimage to Mecca.
Universalizing Religion
a belief system that aims to be global, appealing to all people regardless of their culture or location; Islam, Christianity, and Buddhism
Ethnic Religion
A religion with a relatively concentrated spatial distribution whose principles are likely to be based on the physical characteristics of the particular location in which its adherents are concentrated. Hinduism, Judaism. Global migration of Hindus from India or the Jewish diaspora.

Culture
All of a group's learned behaviors, actions, beliefs, and objects. It is a visible force seen in a group's actions, possessions, and influence on the landscape, and an invisible force guiding people through shared belief systems, customs, and traditions.The bison was central to the religious beliefs of the Lakota. |
Cultural Traits
Visible and invisible elements learned by children and adults that are passed down. |
Material Culture
Consists of tangible things, or those that can be experienced by the senses. | Art, clothing, food, music, sports, and housing types. |
Nonmaterial Culture
Consists of intangible concepts, or those not having a physical presence. | Beliefs, values, practices, and aesthetics. |
Diffusion
The spread of information, ideas, behaviors, and other aspects of culture from their hearths to wider areas. | The influenza outbreak of 1918-1919. |
Social Constructs
Ideas, concepts, or perceptions that have been created and accepted by people in a society or social group and are not created by nature. | (No specific examples provided in the sources for the definition itself.) |
Sikhism
A relatively new universalizing monotheistic faith, founded by Guru Nanak in the Punjab region (India/Pakistan) during the 16th century. | The practice of men adding the name Singh and women adding the name Kaur to create a more equal society. |