NUTR250 - CH1 & CH2
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Diet
food and beverage you regularly choose
Factors that influence food choice
preference, habits, culture, social interactions, economy, emotions, values, body image, nutrition, and negative/positive associations
nutrient composition of foods
– Water, carbohydrates, fibers, lipids, protein
– Vitamins, minerals
– Phytochemicals
nutrient composition of the body
– Water (~60%), CHO, fat, protein, major minerals
– Vitamins and trace minerals (< 1#)
Organic (contain carbon = “alive”)
carbohydrates, lipids, protein, vitamins
Inorganic
minerals and water
Calorie
very small unit of measure of the energy in food
Macronutrients
– Contain energy (kcals)
– Organic (contain carbon)
– All macronutrients provide raw material for
building tissue and regulating body activities
Carbs, Proteins, Lipids (fats)
Carbs - kcals per gram
4 kcals/gram
Proteins - kcals per gram
4 kcals/gram
Lipids - kcals per gram
9 kcals/gram
Alcohol - kcals per gram
7 kcals/gram
How is energy released in the body?
When the body uses macronutrients, the bonds
between the nutrients’ atoms break
– Energy is released as heat or electrical impulses
Can be used or stored
All three macronutrients (carb, protein, and fat) can be stored as fat in the body (adipose tissue)
Body’s preferred fuel source
Carbs and lipids
Proteins
regulate digestion and energy
metabolism—not used as frequently for energy
Minerals
– Simplest nutrient
– Inorganic (do not contain carbon)
– 16 essential minerals
– Found in bones, teeth, and body fluids
Water
– Inorganic: hydrogen and oxygen
– Environment for nearly all body processes
Micronurtients
Vitamins and minerals
don’t contain energy
facilitate energy release
Dietary Reference Intake (DRIs)
collab between Canada and USA
defines standards for energy, nutrients, etc
recommendations for healthy people
Estimated Average Requirements (EAR)
Average amount of a required nutrient that meets the needs of 50% of the healthy population
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA)
Recommendation that meets the needs of 98% of healthy people
Adequate Intakes (AI)
Reflects the average amount of a nutrient that a healthy population consumes
Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (UL)
The point after which toxicity is likely
Estimated Energy Requirement (EER)
– No upper limit
– The EER is the average energy intake to maintain
energy balance (kcals in vs. kcals out)
– Usually based on the following:
Healthy body weight
Physical activity level
Age
Pregnancy status
Sex
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution (AMDR)
Provided a person consumes adequate calories,
they should meet their daily macronutrient needs
if they follow the AMDR guidelines
– The sum of all three categories must equal
100%
Carbohydrate = 45-65%
Protein = 10-35%
Fat = 20-35%
Registered Dietitians (RD)
RDs are healthcare providers that specialize in nutrition and food to help people maintain optimal health and manage disease
Assessment Tools for RDs
1. Historical information
– Health status, socioeconomic status (SES),
pharmaceutical/street drug use and alcohol use
– Diet history—intake over several days; portion sizes;
computer analysis (can also cover alcohol use here)
2. Anthropometric measurements
– Height, length, circumference, and weight—track to
identify trends
3. Physical examinations
– Hair, skin, eyes, tongue, fingernails
4. Laboratory tests
– Blood and urine
– Sometimes stool and hair
Malnutrition
Deficiency or excess over time leads to malnutrition
– Undernutrition and overnutrition
Symptoms of Malnutrtion
– Diarrhea
– Skin rashes
– Fatigue
– Low blood pressure
– Low heart rate
– Obesity
– Hair loss
Common Chronic Disease Risk Factors
smoking, poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol intake, high blood pressure, obesity, high cholesterol
Top 10 causes of Morality in US
1. Heart disease
2. Cancer
3. Unintentional injuries
4. Stroke
5. Chronic lower respiratory diseases
6. Alzheimer’s
7. Diabetes
8. Chronic kidney disease
9. Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis
10. COVID-19
Six Principles and Guidelines of a Nutritious Diet
1) Adequacy
2) Balance
3) kcal (energy) control
4) Nutrient density—promotes adequacy and kcal control
5) Moderation—contributes to adequacy, balance, and kcal control
6) Variety
Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGAs)
• Evidence-based
• Translate nutrient recommendations (DRI) into food recommendations
• Reviewed and revised every 5 years
2020 - 2025 DGAs Key Guidelines
1. Follow a healthy dietary pattern at every life stage
2. Customize and enjoy food and beverage choices to reflect personal
preferences, cultural traditions, and budget
3. Focus on meeting food group needs with nutrient-dense foods and
beverages, and stay within calorie limits
4. Limit foods and beverages higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and
sodium, and limit alcoholic beverages
2020 - 2025 DGAs Key Recs for More
Adopt a healthy eating pattern that accounts for all foods and beverages w/in an appropriate kcal level and meet the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
• Include more:
• Vegetables from all subgroups: dark green, red and orange, legumes, starchy,
and other
• Fruits, esp. whole
• Grains: ½ of which are whole
• FF or LF dairy and/or fortified soy beverages
• Variety of animal and plant protein
• Healthy plant oils
2020 - 2025 DGAs Key Recs for Less
Adopt a healthy eating pattern that accounts for all foods and beverages w/in an appropriate kcal level
• Limit:
• Saturated and trans fats to < 10% of daily kcal
• Added sugars to < 10% of daily kcal
• Sodium (NaCl) to < 2300 mg/day
• Consume alcohol in moderation—1 drink/day for women, 2 drinks/day for men, or abstain
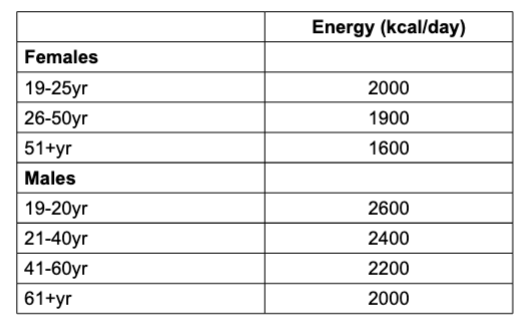
Estimated Energy Needs for Sedentary Adults
Five Major Food Groups
Fruits, vegetables, grains, protein foods, milk and milk products (dairy)
Recommended Daily Amounts per Food Group for 14+
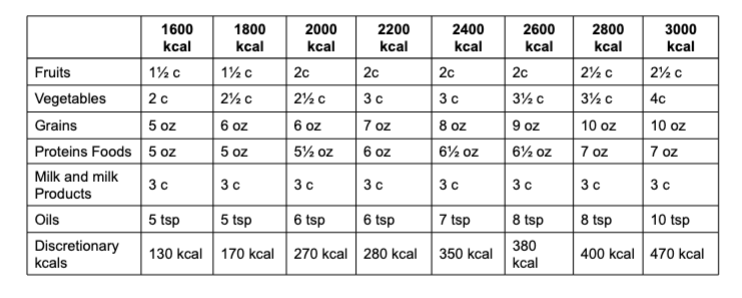
Which food groups are measured in cups?
Fruits, Veggies, and milk
Which food groups are measured in ounces (cooked)?
grains and proteins
MyPlate

Educational tool illustrating 5 food groups - size
indicates relative proportion required in diet
MyPlate Shortcomings
Lack of detail and distinction between healthier choices within food groups
Food Lists
Sometimes called Exchange Lists
• Help achieve dietary adequacy, balance, variety
• Originally used in diabetes care, for weight mgmt, and general diet
planning
• Sorted by energy-nutrient content
• Foods with similar nutrient profiles like kcals/serving, grouped together
• Ex:
Protein: meats, cheeses, meat substitutes
Starchy vegetables and grains
Fats: oils, nuts, olives, bacon, cream cheese
Ultra-processed
deliver few nutrients and abundance of
sugar, fat, salt
Fortified
the addition of nutrients that weren’t originally
present, or present in small amounts
Refined
process by which coarse parts of a food are removed
Enriched
addition of nutrients removed during processing
Whole Grain
a grain that maintains the same relative
proportions of endosperm, bran, and germ (but not husk); not refined
Nutrition Facts Label
The Nutrition Facts label breaks down the amount of calories, carbs, fat,
fiber, protein, and vitamins per serving of the food
appear on nearly all packaged foods
Exceptions: plain coffee, tea, spices; food produced by small businesses;
food prepared and sold in same place; alcoholic beverages
Required for restaurants with >20 locations
The Ingredient List
All packaged foods must list all ingredients—including additives
Ingredients listed in descending order by weight
Must list common allergens in plain language
Must also list possibilities of allergen cross-contamination
Serving Sizes
standardized by FDA for each food category
Reflect typical eating habits, not recommended portion sizes
Daily Values for Nutrition Facts Label
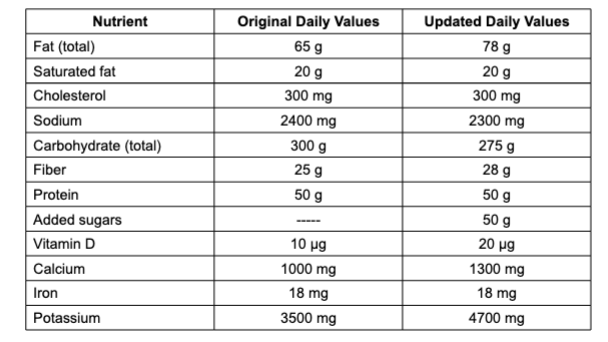
derived from 2000 kcals/day diet
Health Claims
describe a relationship between a food or
nutrient and a disease state
Evidence-based: “Diets low in sodium may reduce the risk of high blood pressure”
Emerging evidence requires qualified health claims: “Very limited and preliminary research suggests that eating one-half to one cup of tomatoes and/or tomato sauce may reduce the risk of prostate cancer”
Structure-Function Claims
do not require FDA approval
Only criteria: must NOT mention a disease or symptom
Less/reduced
at least 25% less than the reference food
Free
nutritionally trivial amount per serving
Low
an amount that allows frequent consumption w/o exceeding daily value for the nutrient
Good Source of
10-15% of daily value per serving
High
20% or more of daily value per serving
kcal-free or calorie-free
< 5 kcals per serving
High Fiber
5 g or more of Fiber per serving
Sugar-free or fat-free
< 0.5 g/serving
Low Sodium
< 140 mg/serving