Respiratory Exam in 80hrs shit
1/275
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
276 Terms
RA Clinical
Physical changes to the joint space (3)
BPH
Pannus formation
Bone erosion (metalloproteinases degrading the matrix and Osteoclasts)
Hyperplasia (Fibroblasts)
Cells involved in RA
Th1 cells! (Not His related=> not Th2—>IgE—-> IL-4)
MTX MOA
Folate Synthesis
Adenosine
Polyamine (Spermine and Spermidine)
CK profile alteration
Adhesin (VCAM-1)
ROS (reduce T cell numbers)
Folate Metabolism
Folate—> Dihydrofolate —> Tetrahydrofolate—> dUMP—> dTMP
first two steps cat by dihydrofolate reductase
fx of THF
Methyl Donor
Adenosine Pathway Intracellular
MTX—-| AICAR Transformylase
AICAR build up inside the cell
AICAR—-| Adenosine deaminase
Adenosine enters the extracellular space via ENT1 transporters
Adenosine acts as a signalling molecule by binding to a GPCR A2A receptor
M1—> M2
CK decrease
TCR inhibition
Overdose of MTX
Leucovorin

What enzyme needs Me donor THF
thymidylate synthetase
Exraceullar Adenosine Pathway
ATP—>ADP—AMP—>A—> I
transmembrane CD39 ×2 (multiple by 2 steps get seventy something)
transmembrane CD73
Polyamine examples
Spermine and Spermidine are v. high in RA
Polyamine Pathway
Dihydrofolate Reductase inhibition leads to lowered number of THF which acts as a Methyl donor not only for dUMP but also METHIONINE AND S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
Action of ROS
increased apoptosis of T cells (Th1 cells mediate RA)
Which Adhesion molecules are affected
VCAM
ICAM-1
Leukocyte adhesion: ICAM-1 is expressed on endothelial cells (which line blood vessels) and binds to integrins (like LFA-1) on leukocytes.
Which pro-inf CK are affected by MTX
IL-4
IL-3
TNF
INFy
Effects of Sulfasalazine
—-| LOX 5-amino-salicyclic acid
—-|COX 5-amino-salicyclic acid
—-| NFKB ((nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells upregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α)
—- decreases O * made by neutrophils (radicals have no chanrge us)
—-| T and B cell proliferation
Sulfasalazine s/e
Photosensitivity
Myelosupression
Hypoglycaemia in DM
Orange discoluration of lenses and bodily fluids
Thromboyctopenia
GIT issues
Tinnitus
Gold Compound Example
Au-thio-glucose
Au MOA
Phagocytosed by macrophages which decreases antigen processing
—-| NFKB as well
Au s/e
Priutus
Nephtotoxic (fat fed macrophages block tubules)
Ulcerations of the mouth
Leflomide MOA
decreased pyridine synthesis
Pencillamine MOA
Decreases the response in IL-1 (1st antibiotic)
Role of TNF-a
chemokine production
prostaglandin production
neutrophil activation
B cell activation
pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-1, IL-6)
upregulates adhesion molecules like ICAM-1
TNF-α promotes synovial fibroblast proliferation, matrix metalloproteinase
Two types of TNFa and two receptors
TNFa: membrane bound and soluble
TNFAR: 1 in all cells 2 in immune cells
TNFaR2 role
Survival of Tcells
Etanercept
Fc of IgG1
p75 tnfa receptor that binds both TNF alpha and beta (beta=its special power)
Infliximab
IgG1- antiTNF a a/b
will bind soluble and membrane bound TNF a
Adalimumab
anti-TNF antibody
s/e of using TNFa inhibitors
Immunosupression (malignancy/ invasive infection/ opportunistic pathogens)
Heart Failure
Congenital Abnormalities
Lupus-like disease
Infusion reactions
Anakinra
(IL-1R) antagonist that inhibits the binding of both IL-1α and IL-1β to the IL-1R
Juvenille
also used for gout along with canaki and rilonacept
Tocilizumab
binds the membrane bound and soluble IL-6 RECEPTOR
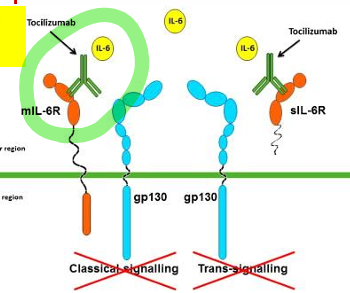
Abatacept
CD28 competition —> no full T cell activation
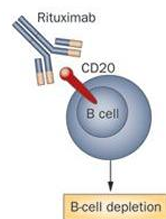
Rituximab
Anti-CD20 on B cells
Needs a MTX Rx
TNF used preferentially though
Ocelizumab
anti CD20 mab
(CD-20 B cell antigen) • Flags the B cells for destruction by body’s own immune system
Signs of RA
Tiredness/ more than 3 joints/ fever/ deformation of the joint/ anaemia/ loss of appetite
→ very much systemic effect!!
DX of RA
Squeeze test
Tender along joint line
Synovitis
+3 affected
Rheumatoid Factor (every immune disease has its bloodmarker!)
When to start a DMARD
3/12 of symptoms => then start ASAP
Why bridging therapy is needed?
Onset of action can be three months!!
When to taper CS
repeated courses
short course after a long course
nocte
3 weeks
more than 7 days of 40mg
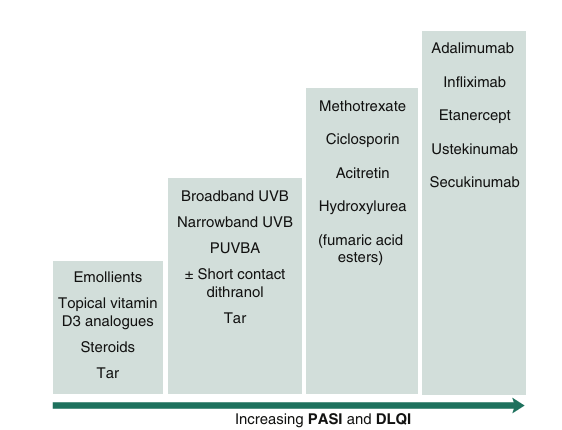
What is first line
MTX and Leflumide/ Sulphasalazine/Hydroxylchlorquine
we want a combination!
Monitoring needed for MTX
weekly—> monthly—→ quaterly
eGFR (Clrenal) LFT and full blood count (due to myelosupression!!!)
Tests for Sulfasalazine
Well kind of none because you take it with MTX as first line and both require the same tests of LFT /GFR/ FBC every month/ quarterly when stabilised
Hydroxychloroquine caution
ocular toxicity (annual and pretreatment exam)
DDI with hydroxylcholoroquine
Antaacids!
s/e of Hydrochloroquine
Malaria—> mosquito bites—> rash
Etanocept:
TNFa 25mg twice weekly
TNFb 50mg once weekly
Rituximab dosing
2 infusions given that are two weeks apart (CD20)
Can be repeated 6 months later
Abatacept
Loading dose of an Infusion every 2 weeks three times
Then once monthly IV
or
Once weekly SC
Tests to be done before immunusupressants
Tuberculin skin test and X-ray for latent TB
When are biologics contraindicated
NYHA III
Before surgery
Baby making (congenital defects especially heart) O
OA
Primary and Seconcary Arth
1*= idiopathic
2+= trauma/ congenital disease/iflammatory
Risks
high bmi
female
sport
occupation
trauma
family hx
Why do a blood test
to exlude RA (rheumatoid factor)
Physical presentation
Heberden’s Nodes
Worsens with activity
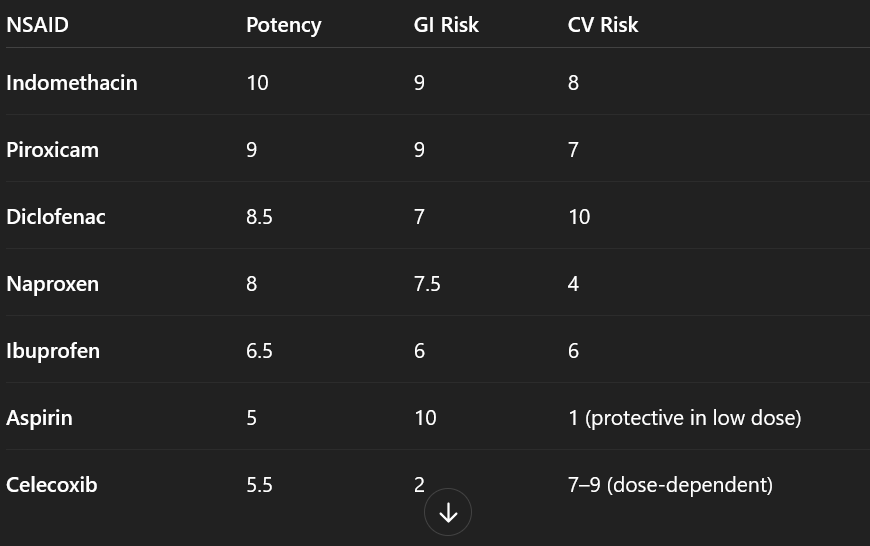
Piroxicam
CAMERA DOWN YOUR MOUTH CUZ YA GOT ULCERS
Ketoprofen s/e
photosensitivity
Naproxen
least side effectsD
Diclofenac
CV event risk increased but more potent than ibuprofen
What is stronger than diclofenac
indomethacin
stronger=forteit mucosa as you burn holes in it
NSAID s/e
hyperkaelmia
ulceration
thromobosis
oedema —>HF decomp
renal insufficiency
Who is more predisposed to NSAID induced athma
female
middle age
chromic congestion
polyps
What are the NSAID Stopp Criteria (10 of them, think renal, heart, GIT)
with warfarin or a DOAC
antiplatelet w/o PPI
history or predisposition of PUD or GIT bleeds unless with concurrent PPI or H2-receptor
concurrent corticosteroids without PPI
older people
eGFR less than 50 mL
hypertension or severe heart failure
longer than 3 months symptom relief of osteoarthritis pain where paracetamol has not been tried
for chronic treatment of gout where there is no contraindication to a xanthine-oxidase inhibitor •
COX-2 selective NSAID in concurrent cardiovascular disease - increased risk of myocardial infarction and stroke
SSRI risk
increase bleeding risk
NSAIDs and MTX
Renal Insuffiency——extrapolate—— MTX clearance
Paracetamol in OA
4g/24 hrs max
change dose in hepatic impairment
Desperate Attempts at making it better:
Glucosamine
Chondrioitin
Intra-art inf once weekly for 5 weeks (help for about 2 weeks but invasive)
Joint replacent if you promise to DOAC :)
Keratin
Strong fibrous protein that keeps keratinocytes from getting destroyed
Epidermis cells:
Melanocytes
Langerhans cells
Dead keratinocytes on top
Fx of skin
acidic pH protection
adipocytes in hypodermis for protection
excretion
D3
nerves
blood reservoir in the dermis
social and sexual signalling
Fitzpatrick Skin Scale
type I —> risk of skin cancer, never tans
Type VI —> rare skin cancers and less sensitivive
Two melanins
Eumelanin (black)
Pheomelanin
How is eumelanin produced
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone stimulates the melanoCORTIN TYPE 1 RECEPTOR
increases cAMP levels and PKA is activated
UVC rays
shortest but filtered out by the ozone (100-290)
Effect of UVA
AGING
some reaches the epidermis
UVA= ROS
ROS damage DNA
decreaces Cells of Langerhans and APC (immunosupression= psoriasis and carcinogensis)
increases dermal inflammatory cells
Chromophores in cells
Melanin
Cellular DNA
Aromatic AA
= these absorb ultraviolet light
Effect of UVB
some reaches the upper dermis
direct DNA damage PYRIMIDINE DIMERS FORM)
stimulates vitamin D
What is PUVA
PUVA (psoralen and UVA)
Inorganic Suncreen
TiO2 scatters UV light (some UVA as well)
Range of Protection 290-350 (some UVA as well clearly)
Chemical UV filters
Ethyl hexyl salicytate 2(6)asp
Absorb UV
Emit IR
Atopic Eczema Treatments
Severe (cyclosporine, dupilumab: atopic dermatitis (eczema) and severe asthma. It works by blocking the IL-4 and IL-13 mycophenolate mofetil)
Moderate (topical tacrolimus)
Mild (topical calcineurin inh)
Baseline (emollients)
Topical Calcineurin inh
Pimecrolimus
Tacrolimus
acrolimus ointment (Protopic® 0.03% and 0.1%) and pimecrolimus
When to use topical vs systemic
Topical: mild to moderate when CS not recommended, low systemic absorption
Systemic: rescue therapy, metabolism by CYP3A4
Lipophillic= long t/12
Side effects of Calcineurin INH
alcohol intolerance
infections
discolaration
papilloma:benign, non-cancerous tumor that grows on an epithelial surface
premature delivery (lipophillic=> crosses the barrier)
hyperkalaemia
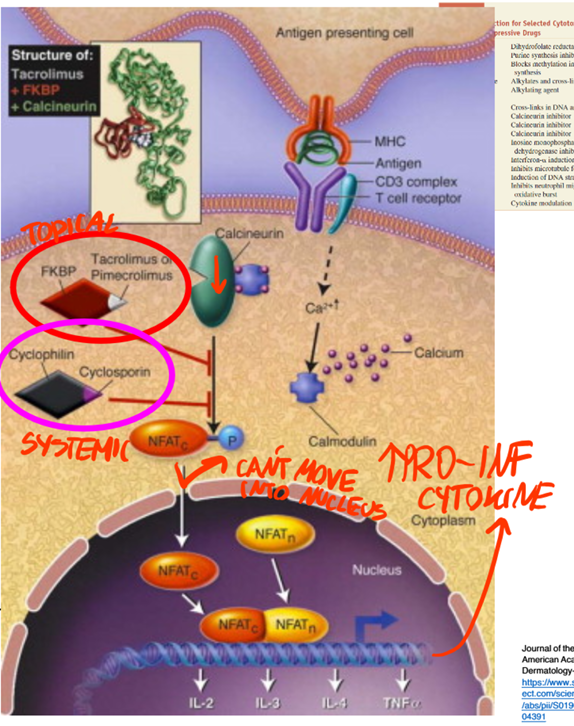
Calcineurin INH MOA
Systemic ❤ Cyclophillin
Topical ❤ FKBP12 (isomerases)
Drug–FKBP-12 complex forms inside T cells.
This complex inhibits calcineurin, a calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphatase.
As a result, NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) stays phosphorylated and cannot enter the nucleus.
Cytokine gene transcription (e.g. IL-2) is blocked → reduced T-cell activation and inflammation
Usual pathway for Il-2/3/4/tnf a transcription
APC presents an antigen via MHC to a TCR
Increase in Ca++
Activation of Calmodulin
Calmodulin activates Calcineurin
Calcinuerin dephosphorylates NFATc
NFAT enters the nucleus
Trans
What is Mycophenolate Mofetil used for
Lupus erythematosus
Pyoderma Gangrenosum
Severe Atopic Dermatitis
Mycophenolate Mofetil Activation
Esterases cleave it to mycophenolic acid M
ALL THESE QUESTIONS ARE FOR ATOPIC DERMATISIIS AND NOT PSORIASIS YET
MOA of Mycophenolic Acid
—-| inosine monophosphatase dehydrogeanse
less GMP avaible for T and B cell proliferation
Type I and Type II IMPDH
inosine monophosphatase dehydrogenase type II found in activated B and T cells
s/e of Mycophenolate Mofetil
sepsis
leucopenia
infections
malignancies
Dupilumab
Binds to IL-4R at the alpha subunit
(used for asthma and atopic derm both are TH2 mediated and IL-4)
IL-4 involved in a feedback loop that generates IL-13 and IL-4
DECREASES activation eosinphilcs and mast cells and basophils and B cell and T cells S

s/e of Dupilumab
Eye inflammation
Eye itchiness
Herpes
Vasculitis
CUM IN UR EYES
Pathophysiology of Psoriasis
epidermal hyperproliferation :differentiation of cells through the epider mis normally takes approximately 40 days, but in psoriatic skin may be as rapid as 7 days
increased epidermal turnover
thickened upper horny layer (hyperkeratosis)
increased DNA synth
keratin 6 and 16 increased
keratin 1 and 10 delayed
neutrophils in the epidermis
CD8+ cells in the dermis
f TH1- and TH17-mediated immune responses
(TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17
MOA of Glucocorticosteroids
bind to glucocorticoids receptor complex
release of chaperones
dimerisation
nucleus translocation
bidning to glucorticoids response elements
transcription of genes
Vitamin D use
1. reduction in keratinocyte proliferation
2. induces keratinocyte differentiation
3. immunomodulator function
What is combination therapy in Psoriasis
Calcipotriol acts on keratinocytes Vit D receptors
→ less IL-36-a and IL-36 y expressed
CS supress IL-17 (made by TH17 cells ) and IL-23 (made by dendritic cells)
IL-36aIL-36y and IL-17 and IL-23 are in a positive feedback loop
SYNERGISM BABY
Phototherapy in Psoriasis
PUVA = psoralen acts as a chromophore
Alone= chromophores in the skin absorb UV
When is Psoralne given
2 hours before UVA
Interactions with Psoralen
ACDH
FPNTT
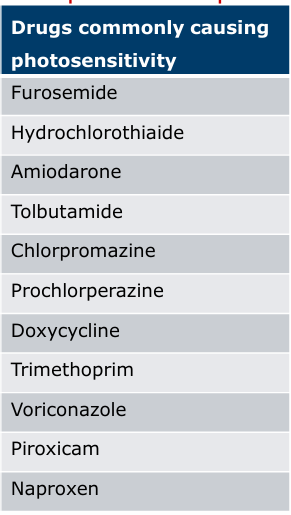
Effect of PUVA
Type I reaction: O2 independent addition of psoralens to pyrimidine bases of DNA.
Type II reactions involve the transfer of energy to O2, creating a ROS.
Both reactions stimulate melanocytes and induce anti-proliferative, immune suppressive and anti-inflammatory effects.
Risk of interaction with photosensitizing meds: phenothiazines, thiazides, sulfonamides, NSAIDS, sulfonylureas, tetracyclines, and benzodiazepines