Life Science Ch 6
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What disease occurs when cells replicate even though they should not be dividing?
A) anthrax
B) cancer
C) influenza
D) tuberculosis
B) cancer
What is a benign tumor?
A) a fluid-filled sac under the skin
B) fluids that travel to other locations
C) a mass of cells that invades other tissues
D) a mass of cells that remains in one area
D) a mass of cells that remains in one area
What happens when a tumor becomes metastatic?
A) Tumor cells attack invading bacteria.
B) Tumor cells begin to die off.
C) Tumor cells break away to start a new tumor.
D) Tumor cells fill with excess fluid.
C) tumor breaks away to start a new tumor
What are synergistic substances?
A) substances controlling how enzymes function
B) substances with a much greater effect when combined
C) substances producing large amounts of energy
D) substances reducing the harmful effects of certain chemicals
B) substances with a much greater effect when combined
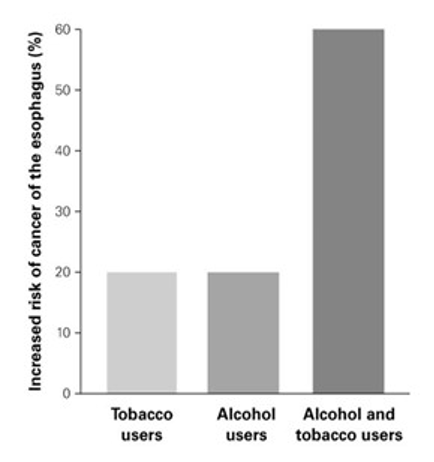
How does the use of tobacco and alcohol affect the risk of esophageal cancer?
A) Esophageal cancer risk is doubled for people who only use tobacco.
B) Esophageal cancer risk is reduced for people who only use alcohol.
C) Esophageal cancer risk is three times as high for people who use both tobacco and alcohol.
D) Esophageal cancer risk is six times as high for people who use both tobacco and alcohol.
C) esophageal cancer risk is three times as high for people who use both tobacco and alcohol
Which organ may be surgically removed and analyzed to determine if metastasis has occurred?
A) appendix
B) gall bladder
C) lymph node
D) salivary gland
C) lymph node
Which type of cancer is most common?
A) esophageal
B) liver
C) pancreatic
D) skin
D) skin
What are sister chromatids??
A) the matched set of two chromosomes
B) the middle region of a replicated chromosome
C) the protein structures moving the chromosomes
D) the two identical copies of one chromosome
D) the two identical copes of one chromosome
Consider a strand of DNA with the sequence AGTTCGATT. What is the sequence of the complementary strand?
A) AGTTCGATT
B) CTGGATCGG
C) GACCTAGCC
D) TCAAGCTAA
D) TCAAGCTAA
Which description is characteristic of DNA?
A) Thymine (T) forms a base pair with guanine (G).
B) The backbone of DNA strands contains nitrogenous bases.
C) Complementary nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.
D) DNA constantly maintains a compressed linear structure.
C) Complementary nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds
A eukaryotic cell has DNA with 26% of the bases as T. What percentage of the bases are G?
A) 24%
B) 26%
C) 48%
D) 52%
A) 24%
In a bacterial species, 45% of the bases in its DNA are A. What percentage of the bases are T?
A) 25
B) 35
C) 45
D) 55
C) 45
What term describes nucleotides in opposing strands of DNA that bind to each other?
A) semiconservative
B) complementary
C) conjoined
D) sister chromatids
B) complementary
What type of reproduction do single-celled amoeba use to produce genetically identical daughter cells?
A) asexual reproduction
B) fertilization
C) meiosis
D) sexual reproduction
A) asexual reproduction
The double-stranded DNA molecule can be described as a twisted rope ladder. What component of DNA would be like the steps of the ladder?
A) DNA polymerase
B) nitrogenous bases
C) phosphate groups
D) sugar (deoxyribose) molecules
B) nitrogenous bases
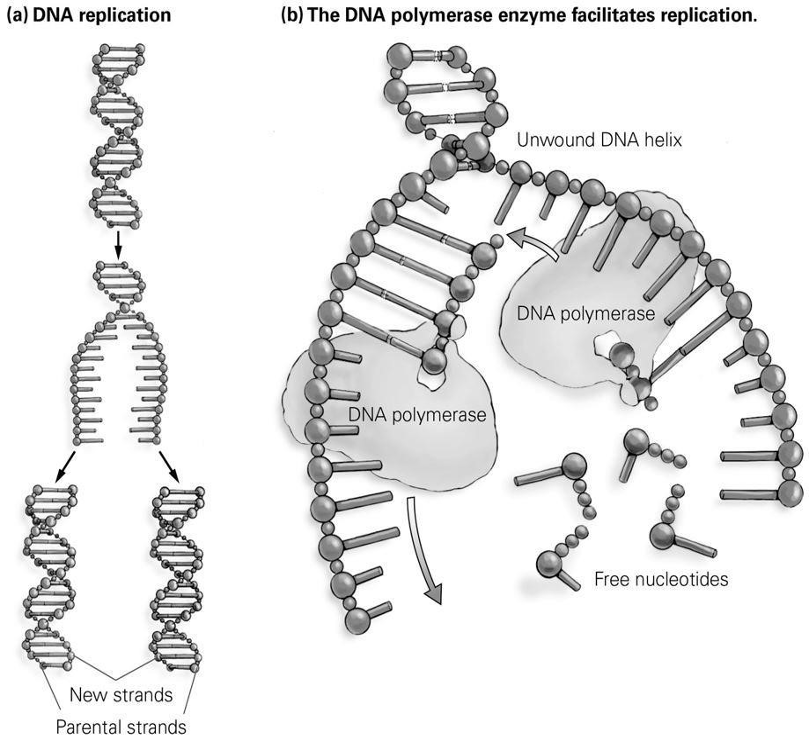
According to this figure, what is the purpose of DNA polymerase?
A) to ensure that nucleotides are only added to one parental strand
B) to help the sugars in DNA break apart from the phosphates
C) to help the free nucleotides bond to the unwound DNA strands
D) to prevent mutations in the complementary base pairs
C) to help the free nucleotides bond to the unwound DNA strands
Which phase occurs during mitosis?
A) first gap phase
B) metaphase
C) second gap phase
D) S phase
B) metaphase
What is the correct order of events in the cell cycle?
A) G1, G2, S, mitosis, cytokinesis
B) G1, S, G2, mitosis, cytokinesis
C) S, G1, G2, cytokinesis, mitosis
D) S, G1, G2, mitosis, cytokinesis
B) G1, S, G2, mitosis, cytokinesis
During which part of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down?
A) anaphase
B) metaphase
C) prophase
D) telophase
C) prophase
What is the correct order of events in mitosis?
A) anaphase, metaphase, prophase, telophase
B) anaphase, prophase, metaphase, telophase
C) metaphase, prophase, telophase, anaphase
D) prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
D) prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
What would result if a cell underwent mitosis but did not complete cytokinesis?
A) one cell with one nucleus containing twice the normal number of chromosomes
B) one cell with two nuclei
C) two daughter cells with no nucleus
D) two daughter cells with too few chromosomes
B) one cell with two nuclei
During which process would a cell plate form?
A) cytokinesis in an animal cell
B) cytokinesis in a plant cell
C) mitosis in an animal cell
D) mitosis in a plant cell
B) cytokinesis in a plant cell
Which carbohydrate forms the cell wall during cytokinesis in plant cells?
A) cellulose
B) sucrose
C) glucose
D) lactose
A) cellulose
During which phase of mitosis are the replicated chromosome aligned in the middle of the cell?
A) prophase
B) anaphase
C) metaphase
D) telophase
C) metaphase
During which phase of the cell cycle does the cytoplasm divide?
A) cytokinesis
B) G1 phase
C) M phase
D) S phase
A) cytokinesis
During which phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate to opposite poles of the cell?
A) telophase
B) prophase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
D) anaphase
In which phase of the cell cycle are cells most often found?
A) anaphase
B) interphase
C) metaphase
D) prophase
B) interphase
Which cells may spend the most time in interphase?
A) epithelial cells lining the stomach
B) hair follicles
C) motor neurons in the spine
D) skin cells on the hands
C) motor neurons in the spine
Why do chromosomes resemble the letter X when viewed during metaphase?
A) Because they all appear and function as X chromosomes at that stage.
B) Because there are two sister chromatids joined at a point in the middle (the centromere).
C) Because microtubules encircle and attach pairs of chromosomes to each other at the centromere.
D) Because each X-shaped structure is actually four chromosomes joined at the centromere.
B) because there are two sister chromatids joined at a point in the middle (the centromere)
During which phase of the cell cycle do most organelles duplicate?
A) prophase of mitosis
B) telophase of mitosis
C) the S phase of interphase
D) the G1 phase of interphase
D) the G1 phase of interphase
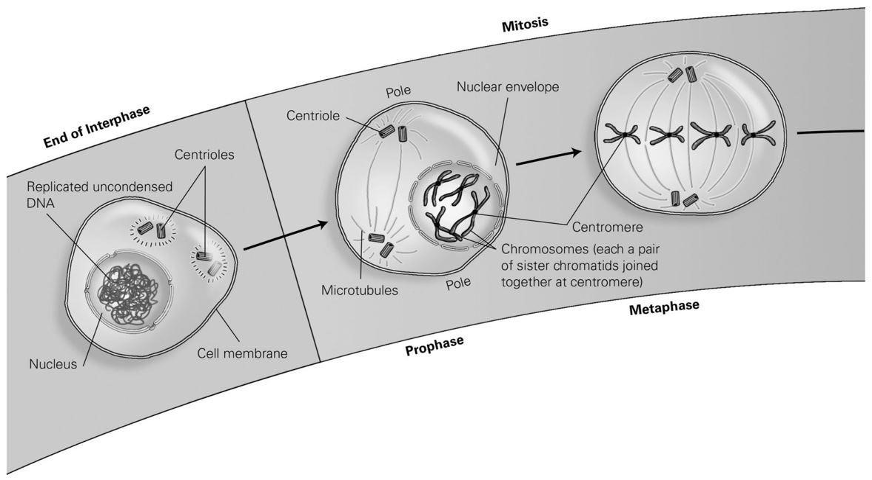
According to the diagram, what structures are connected to the microtubules during mitosis?
A) the nuclear envelope
B) uncondensed DNA
C) cytoplasm
D) centromeres
D) centromeres
During the metaphase checkpoint, what conditions are being checked by the cell proteins?
A) if the cell is large enough to divide
B) if the chromosomes are attached to microtubules
C) if the DNA has been replicated correctly
D) if sufficient nutrients are available
B) if the chromosomes are attached to microtubules
What gene encodes a protein that will inhibit cell division?
A) angiogenesis inhibitor
B) growth factor
C) oncogene
D) tumor-suppressor gene
D) tumor-suppressor gene
Which characteristic indicates a cancer cell?
A) fluid-filled
B) metastasis
C) not moving
D) stopping at checkpoints
B) metastasis
Why might chemotherapy be used on cancer cells?
A) Tumors are close to the body surface.
B) Cancer cells remain in one area of the body.
C) Surgery to remove the tumor would be difficult.
D) Cells lining the stomach cannot be damaged.
C) surgery to remove the tumor would be difficult
Why might cancer patients suffer from nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea after receiving chemotherapy?
A) Cancer patients have restrictive diets that affect their digestion.
B) Cancer patients may have tumors that affect their nutrient absorption.
C) Chemotherapy contains high-energy particles that are aimed at internal organs.
D) Chemotherapy attacks rapidly dividing cells like those lining the stomach and intestine.
D) Chemotherapy attacks rapidly dividing cells like those lining the stomach and intestine
When might radiation therapy be used?
A) Tumors are found deep inside body organs.
B) Tumors are still metastasizing within the blood.
C) Tumors are located close to the body surface.
D) Tumors were completely removed by surgery.
C) tumors are located close to the body surface
What conclusion can be made if the cell margins of a biopsy are clear when observed under a microscope?
A) The cancer cells are transparent.
B) The body cells are filled with extra fluid.
C) The body cells have formed a protective layer.
D) The cancer has not invaded other tissues.
D) the cancer has not invaded other tissues
What is immunotherapy?
A) antibiotics that fight infections in weakened immune systems
B) substances that attack cancer cells having specific cell markers
C) techniques that increase the circulation of chemotherapy drugs
D) therapy to decrease the production of immune system cells
B) substances that attack cancer cells having specific cell markers
What carcinogens may be targeted by a cancer vaccine?
A) alcohol and tobacco
B) cigarette smoke
C) human papilloma virus (HPV)
D) ultraviolet (UV) light
C) human papilloma virus (HPV)
Why is immunotherapy a promising cancer treatment?
A) Chemotherapy or radiation cannot be used for all cancer types.
B) Fewer healthy cells are attacked resulting in better patient health.
C) Less laboratory work is required for application of this treatment.
D) Medical costs are greatly reduced compared to other treatments.
B) fewer healthy cells are attacked resulting in better patient health