Unit 2: Atoms and The Periodic Table
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

53 Terms
atom
Smallest particle of an element
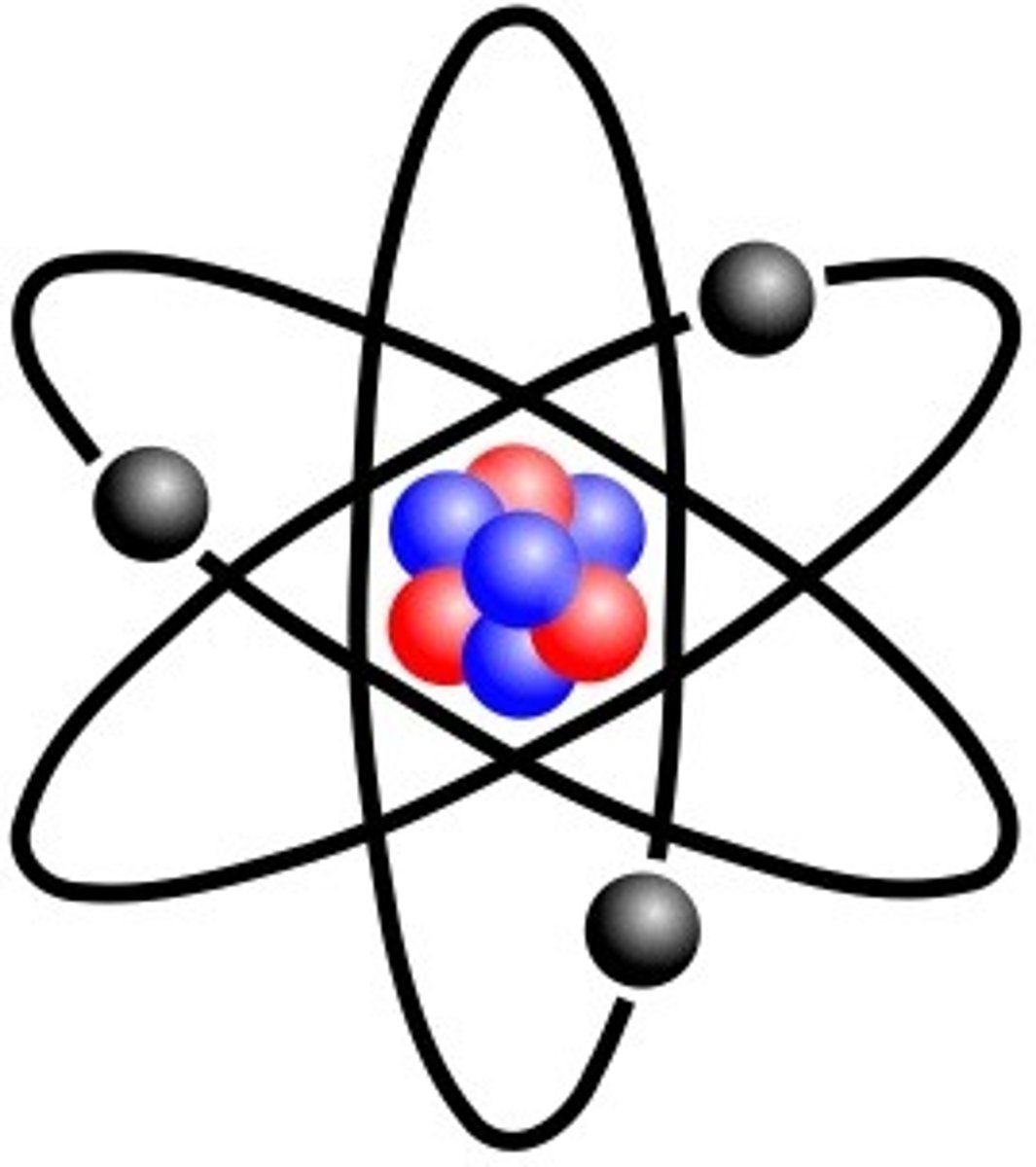
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
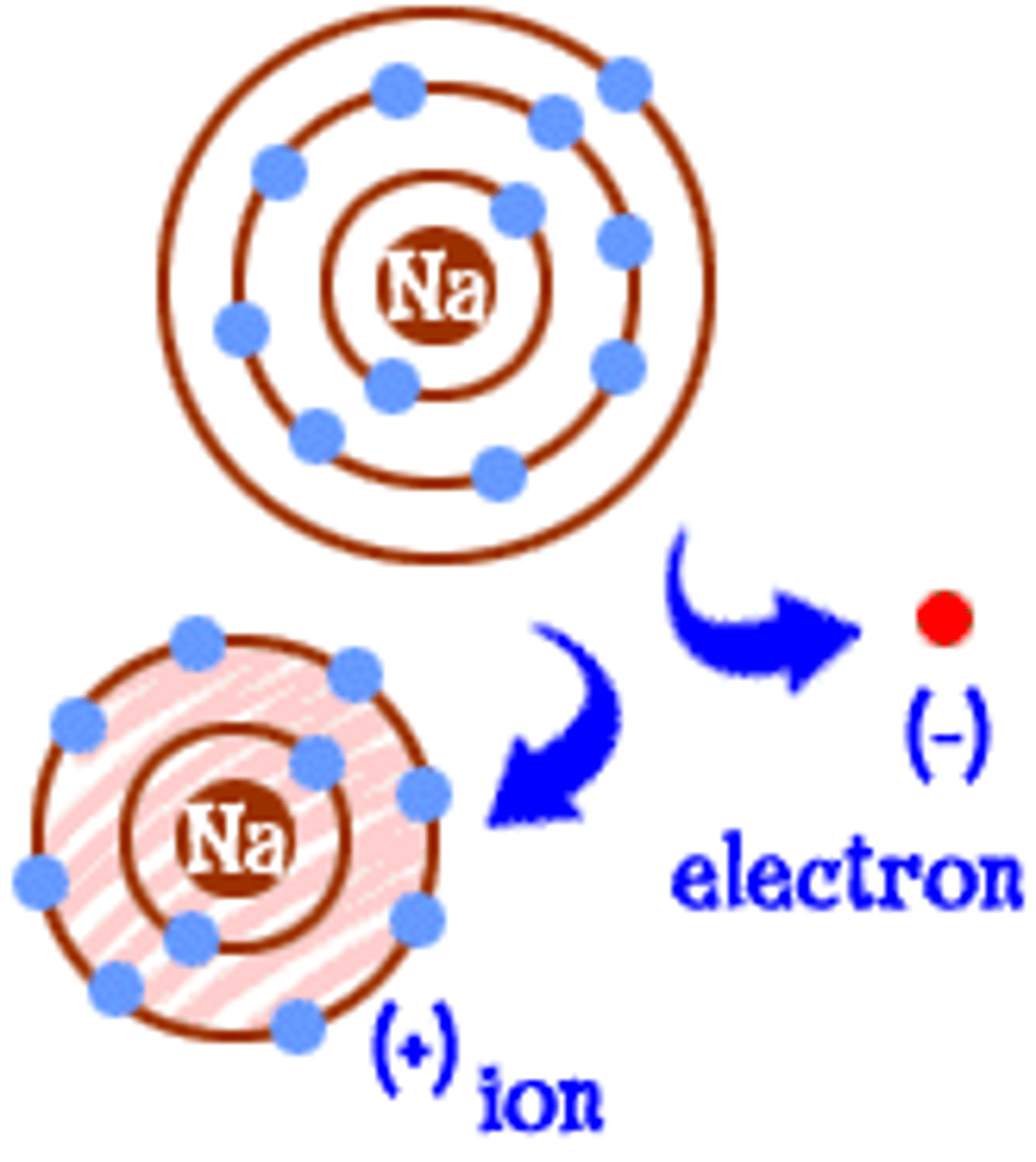
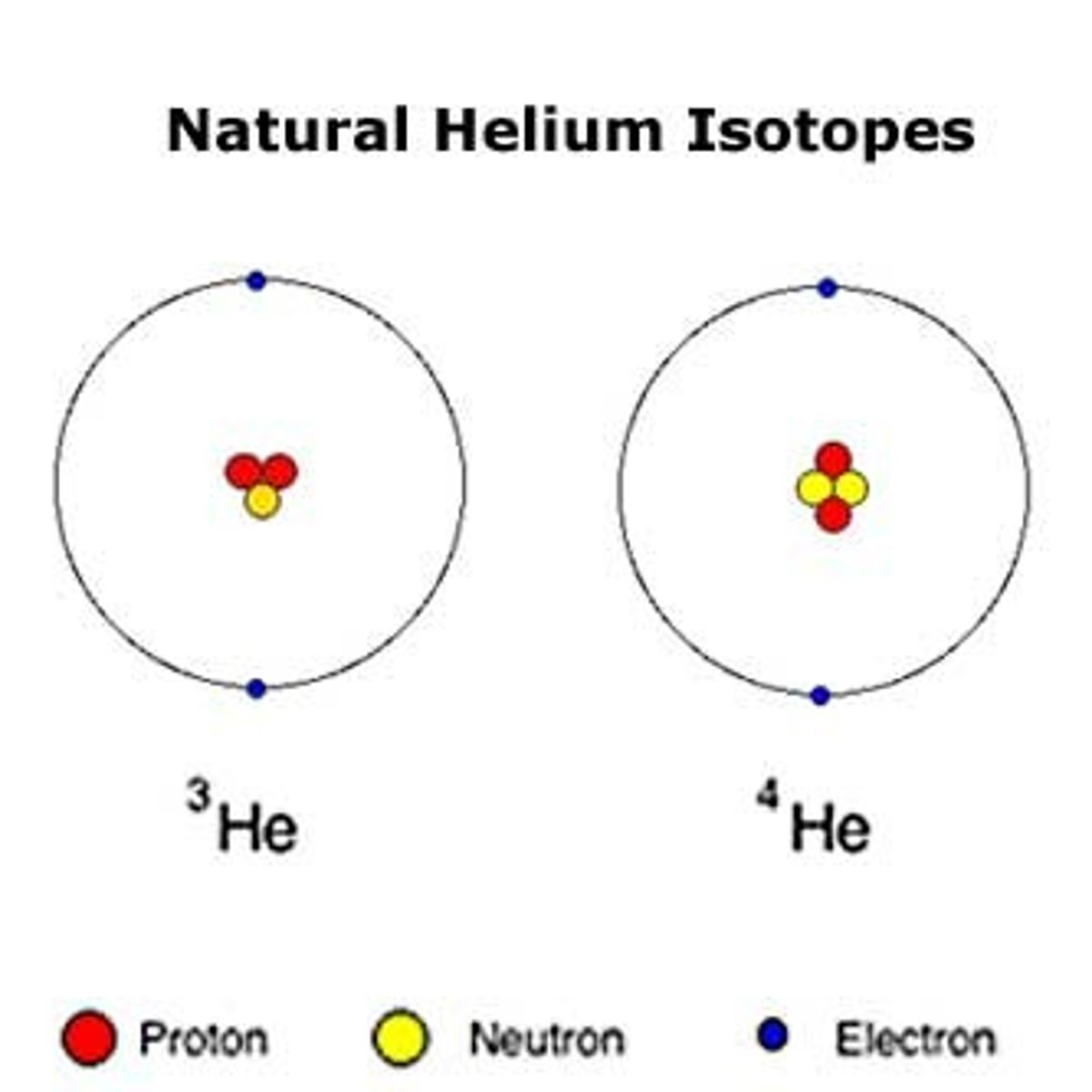
isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
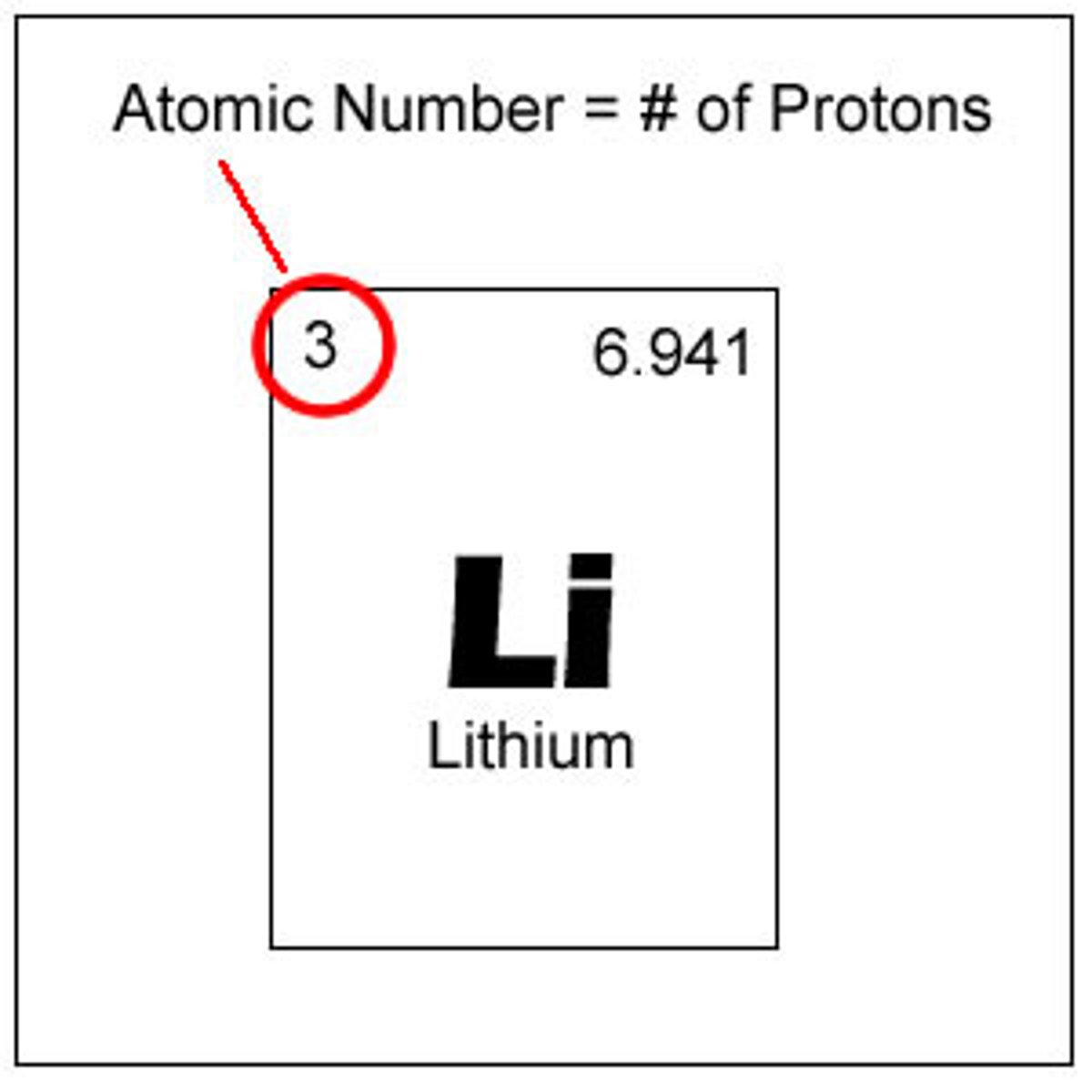
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
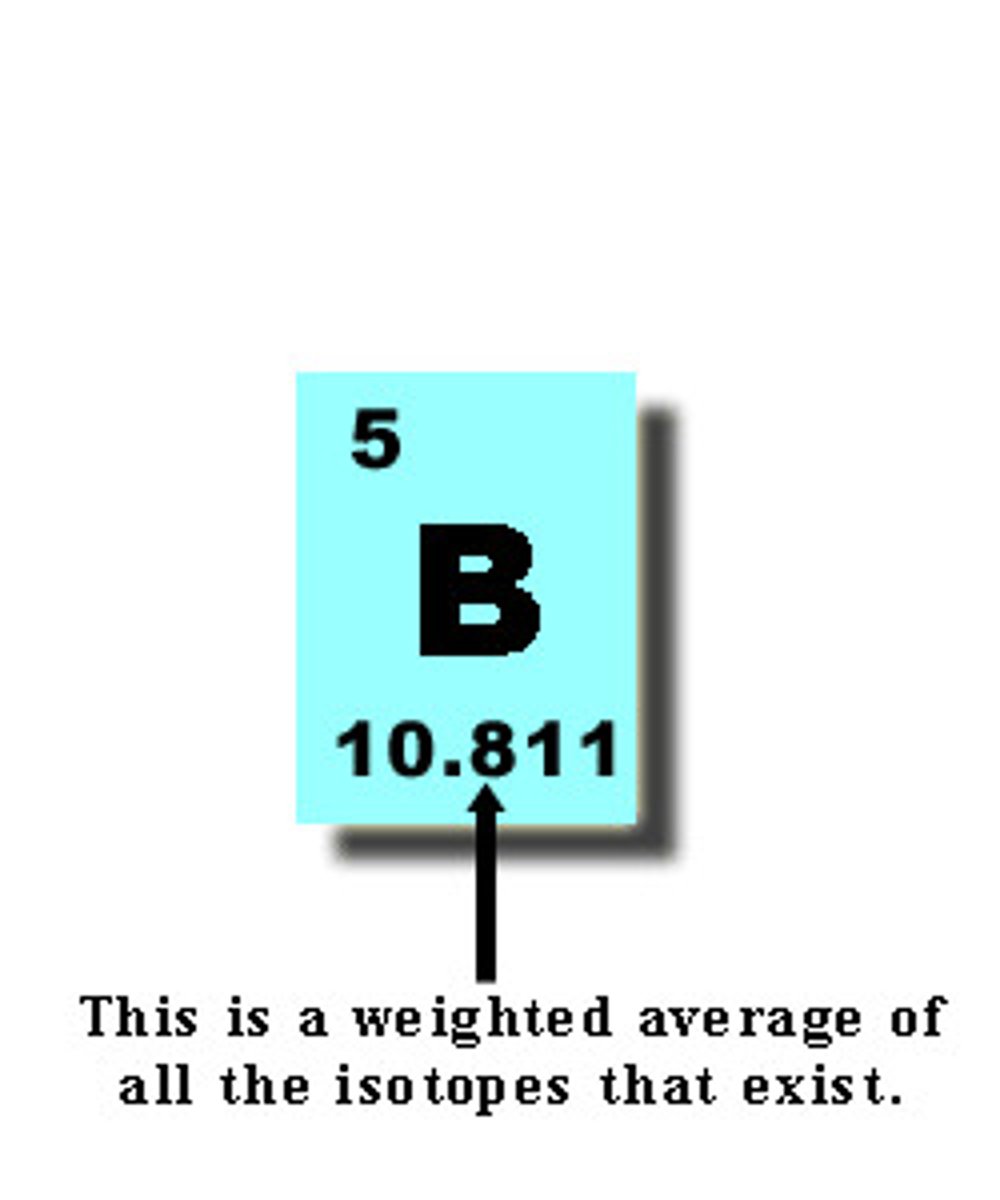
atomic mass
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element
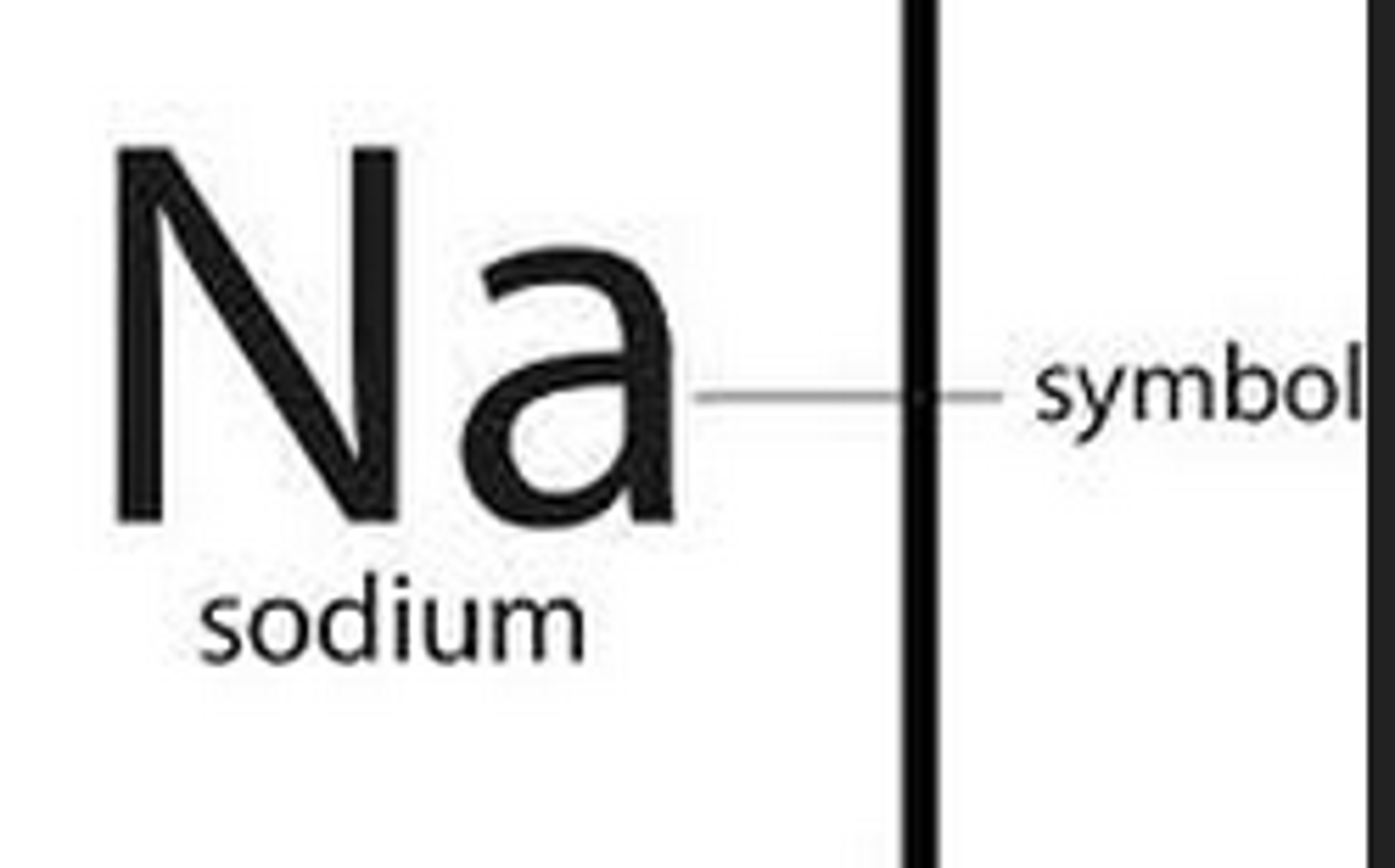
chemical symbol
A one or two letter representation of an element
Electron
negatively charged particle
electron cloud
a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found
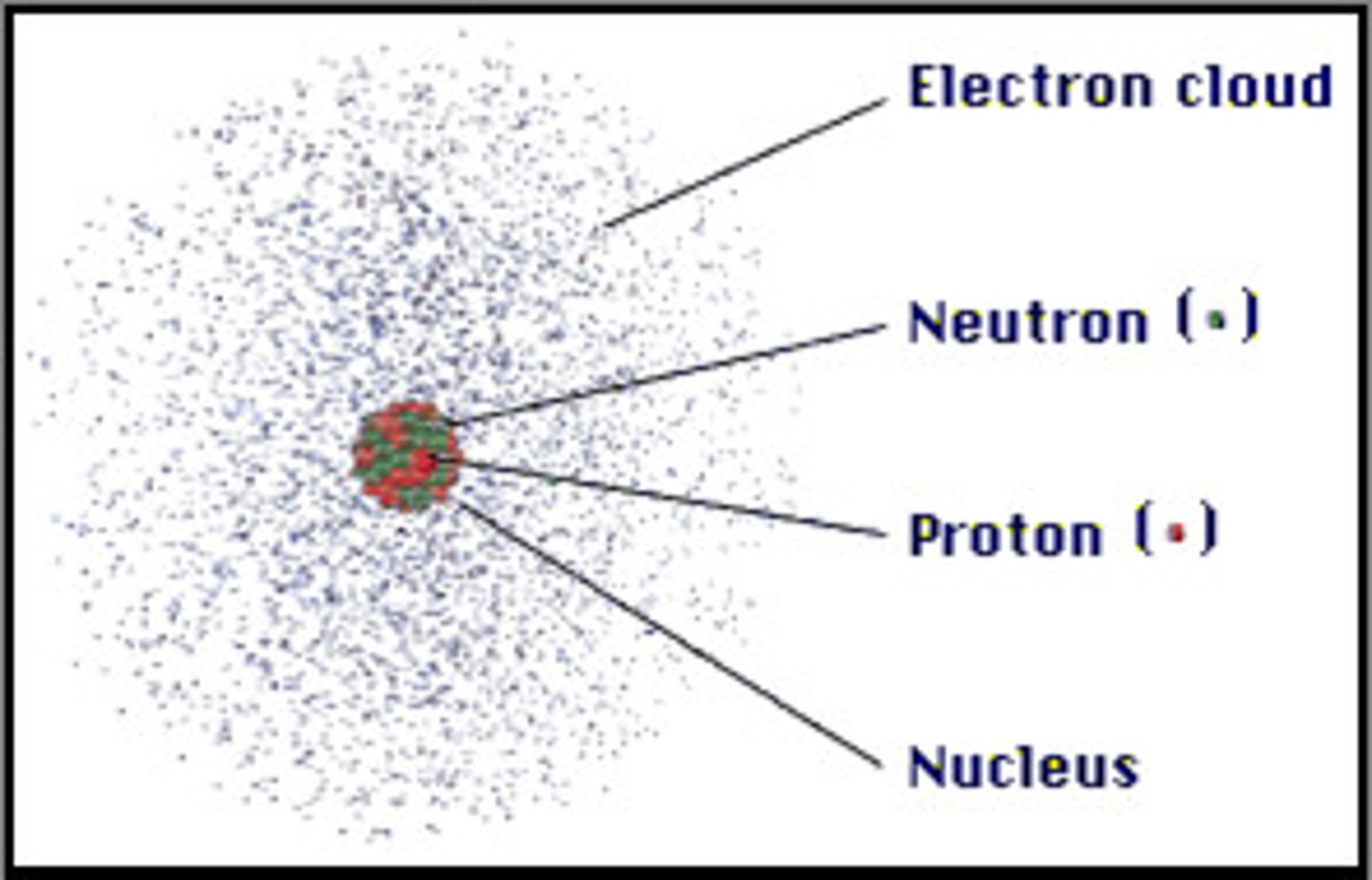
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
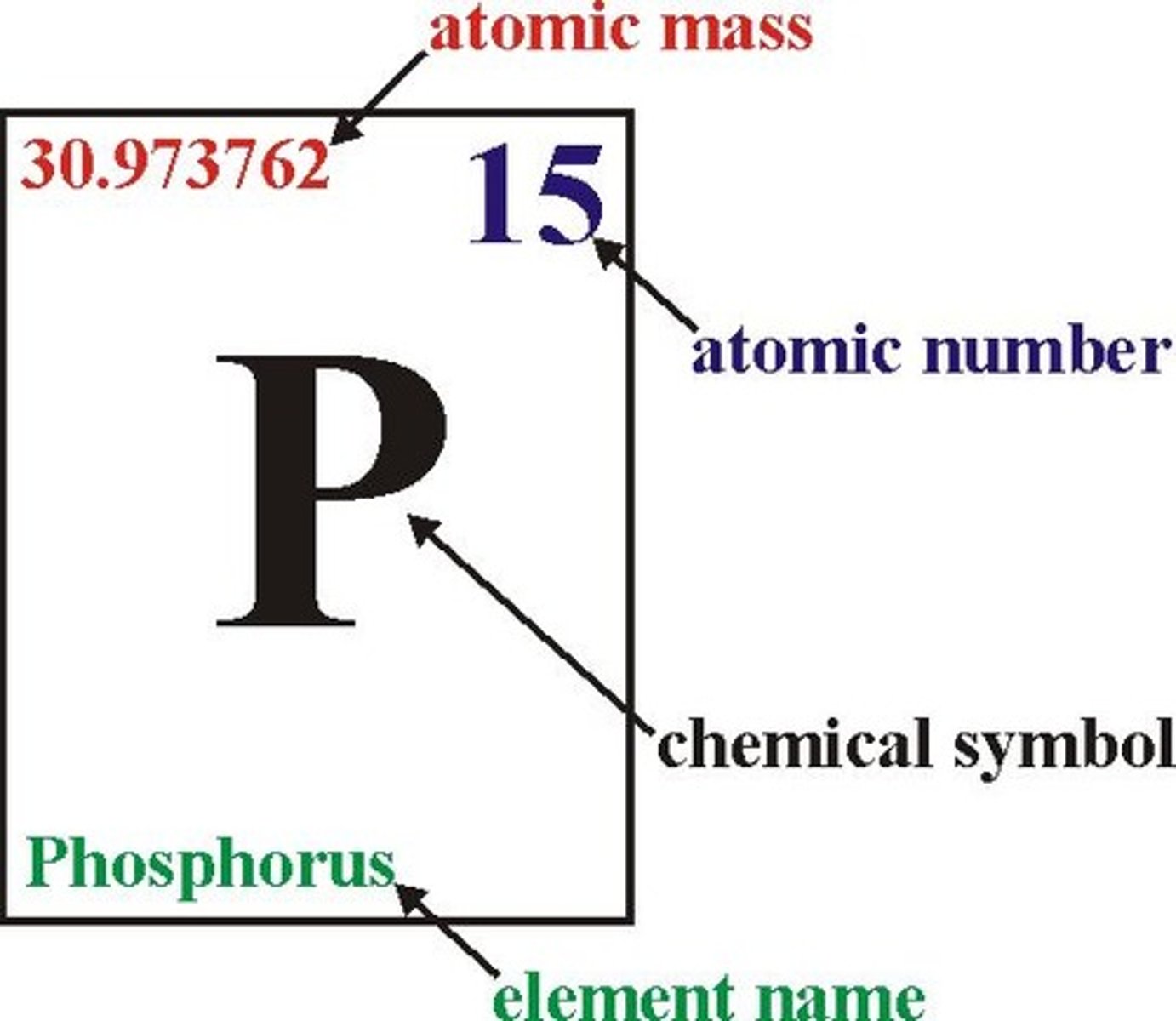
element key
shows the element's name, atomic number, chemical symbol, state of matter, and atomic mass
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus

neutron
A particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Nucleus
Center of an atom
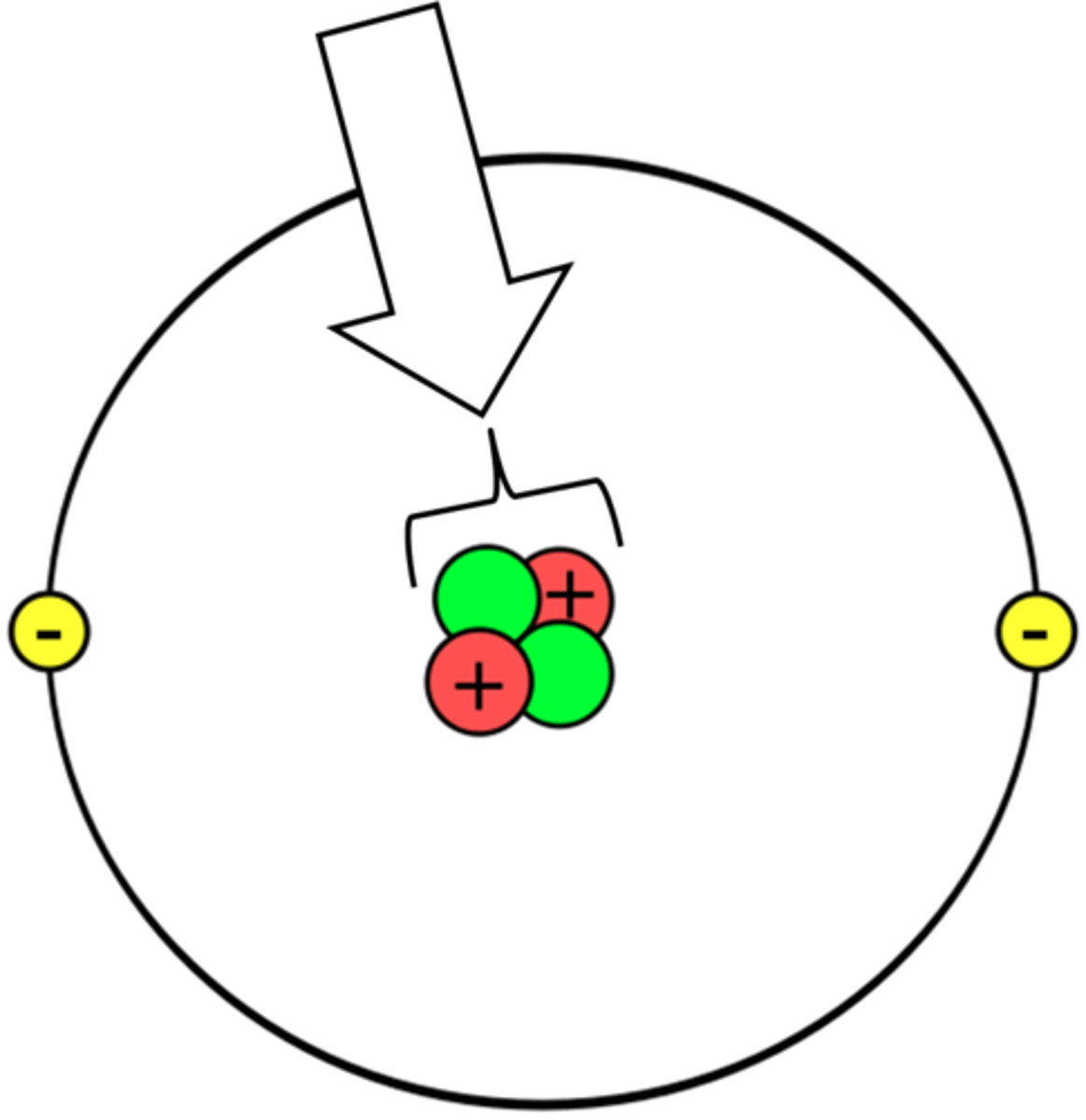
Proton
A particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
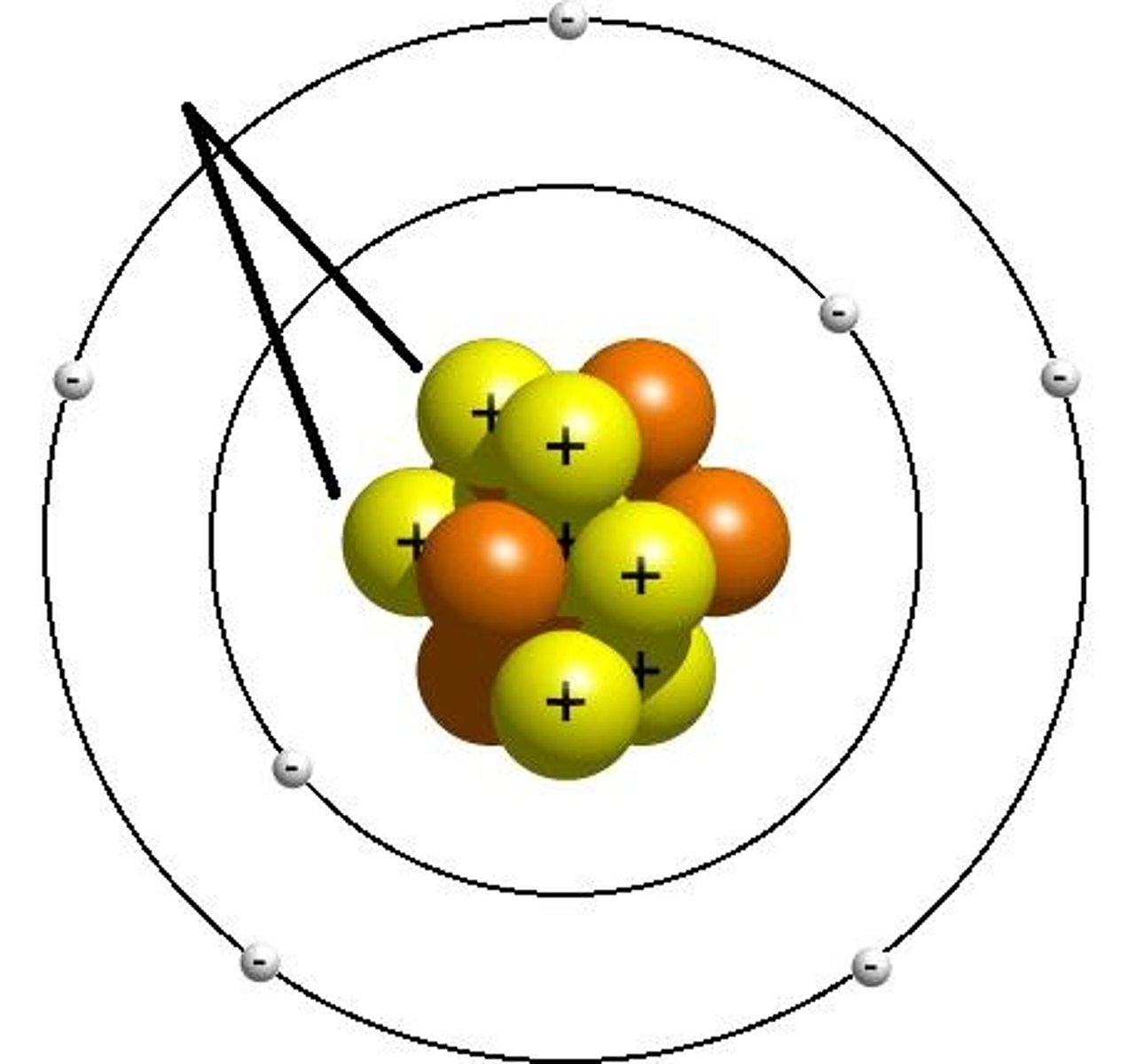
energy levels (shells)
Structures of an atom that contain electrons
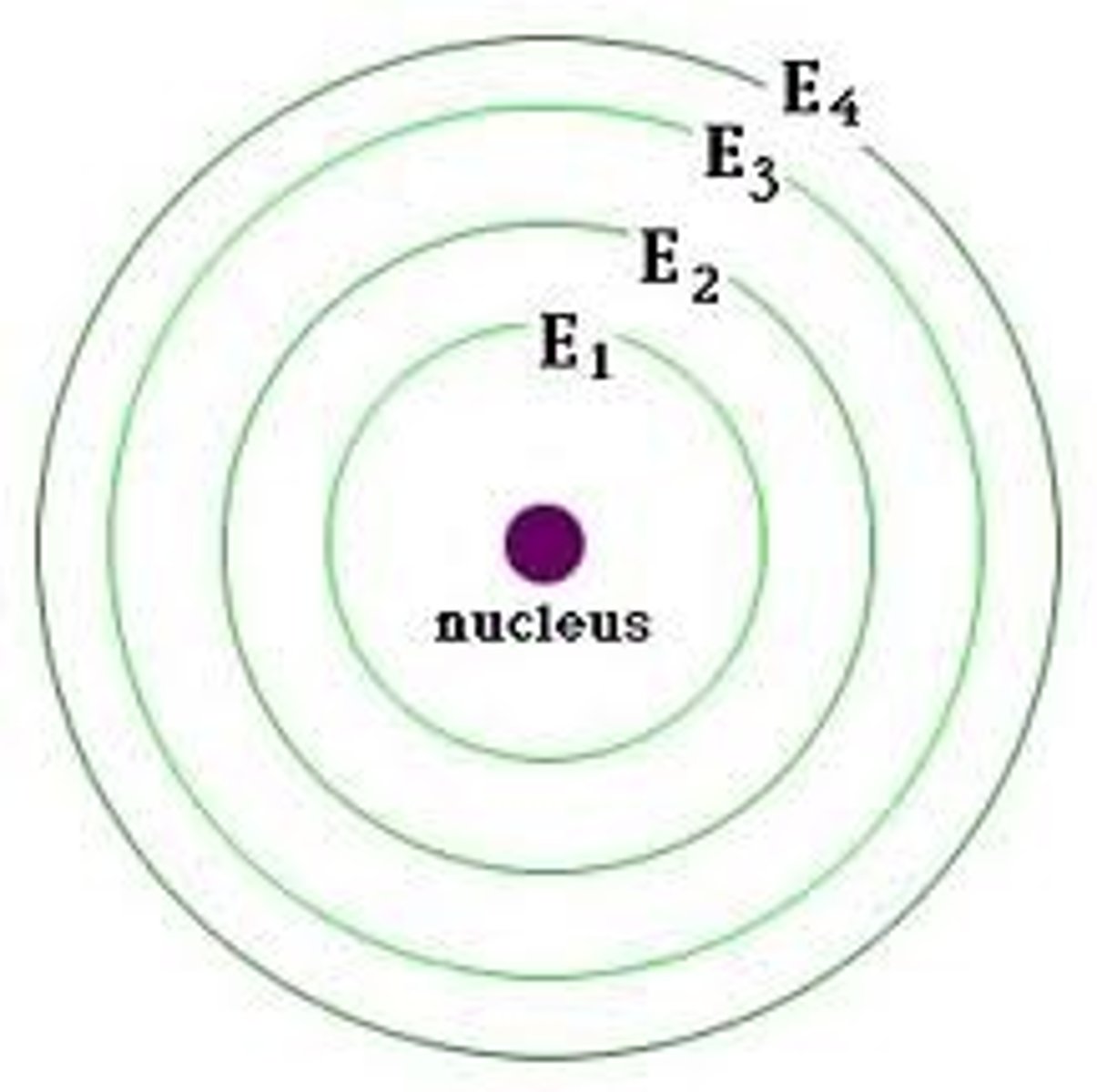
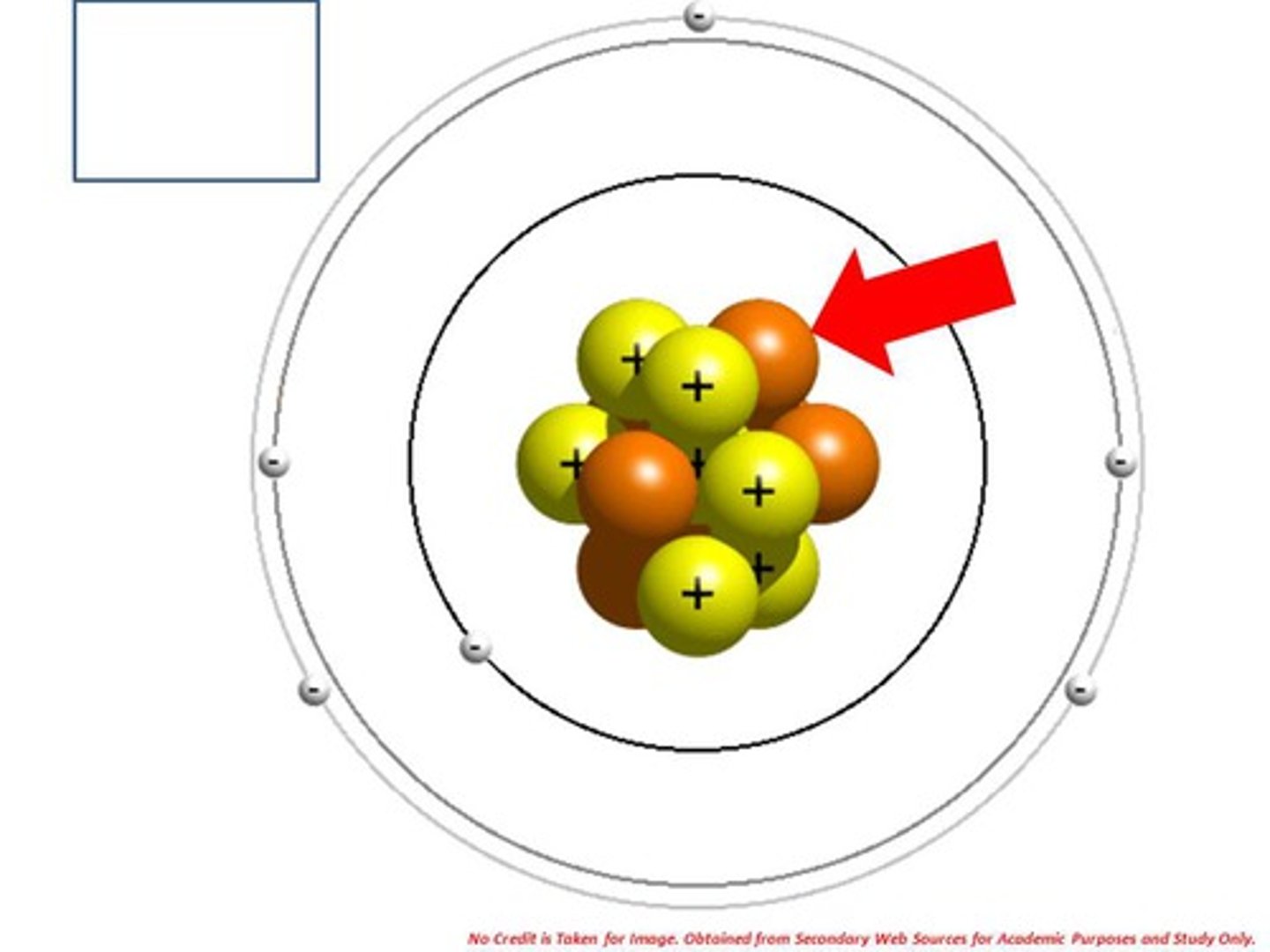
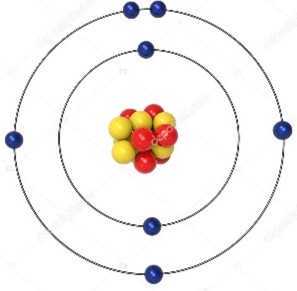
Bohr Diagram
a diagram that shows the arrangement of an element's subatomic particles and the number of electrons in each shell surrounding the nucleus of an atom
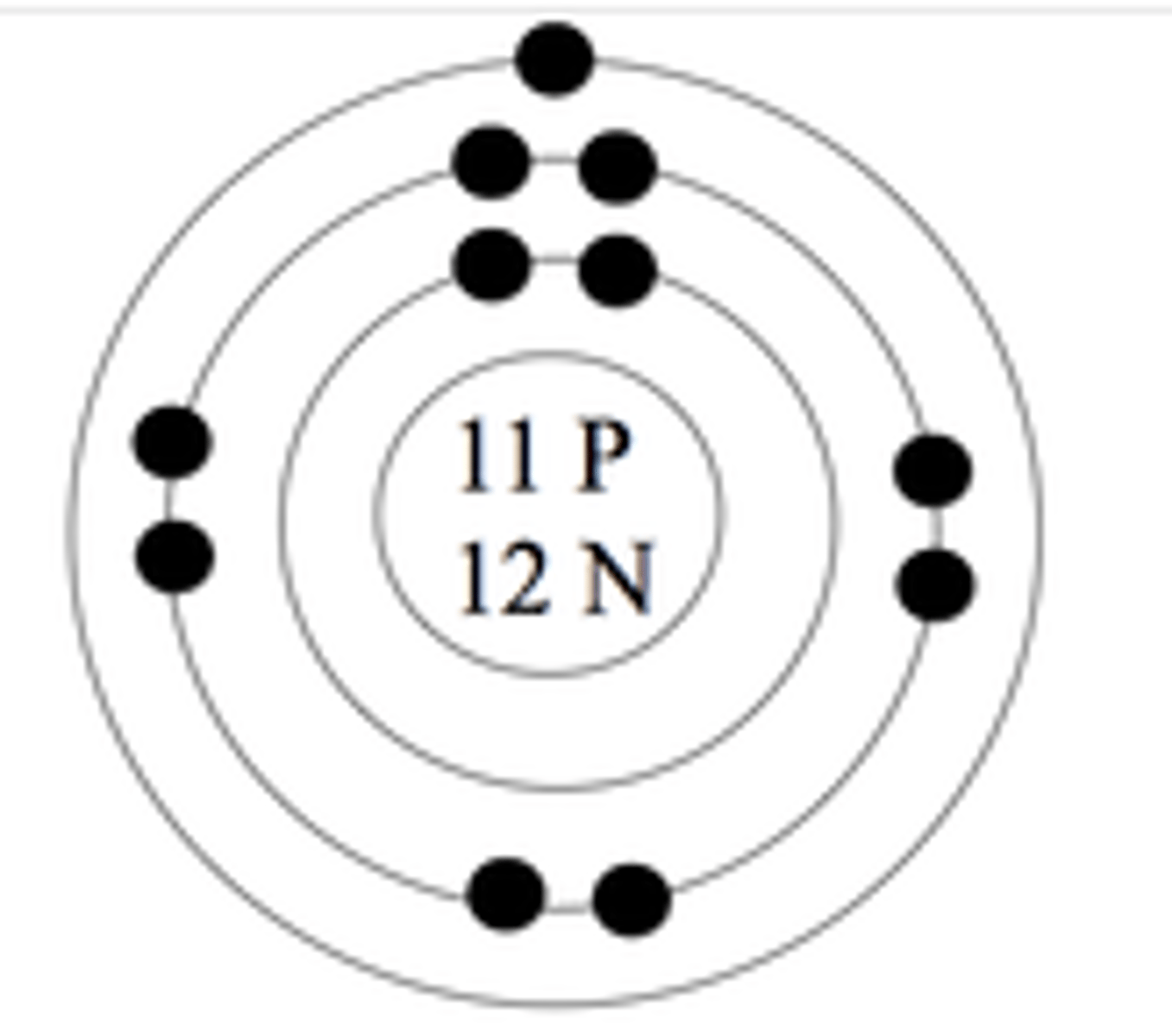
Bohr Model 1st energy level
maximum 2 electrons
Bohr Model 2nd energy level
maximum 8 electrons
Bohr Model 3rd energy level
maximum 18 electrons
Bohr Model 4th level
maximum 32 electrons
Mass Number - Atomic Number
Number of neutrons
Compound
A substance formed when two or more elements chemically bond together. Compounds have unique properties different from the elements that compose them.
MIxture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. Each component retains its individual properties and can be separated by physical means.

Homogenous Mixture
a mixture that has a uniform composition and appearance throughout, in which the individual components are indistinguishable.

Heterogenous Mixture
A mixture in which the individual components are visibly distinguishable and can be separated physically. The composition is not uniform throughout.

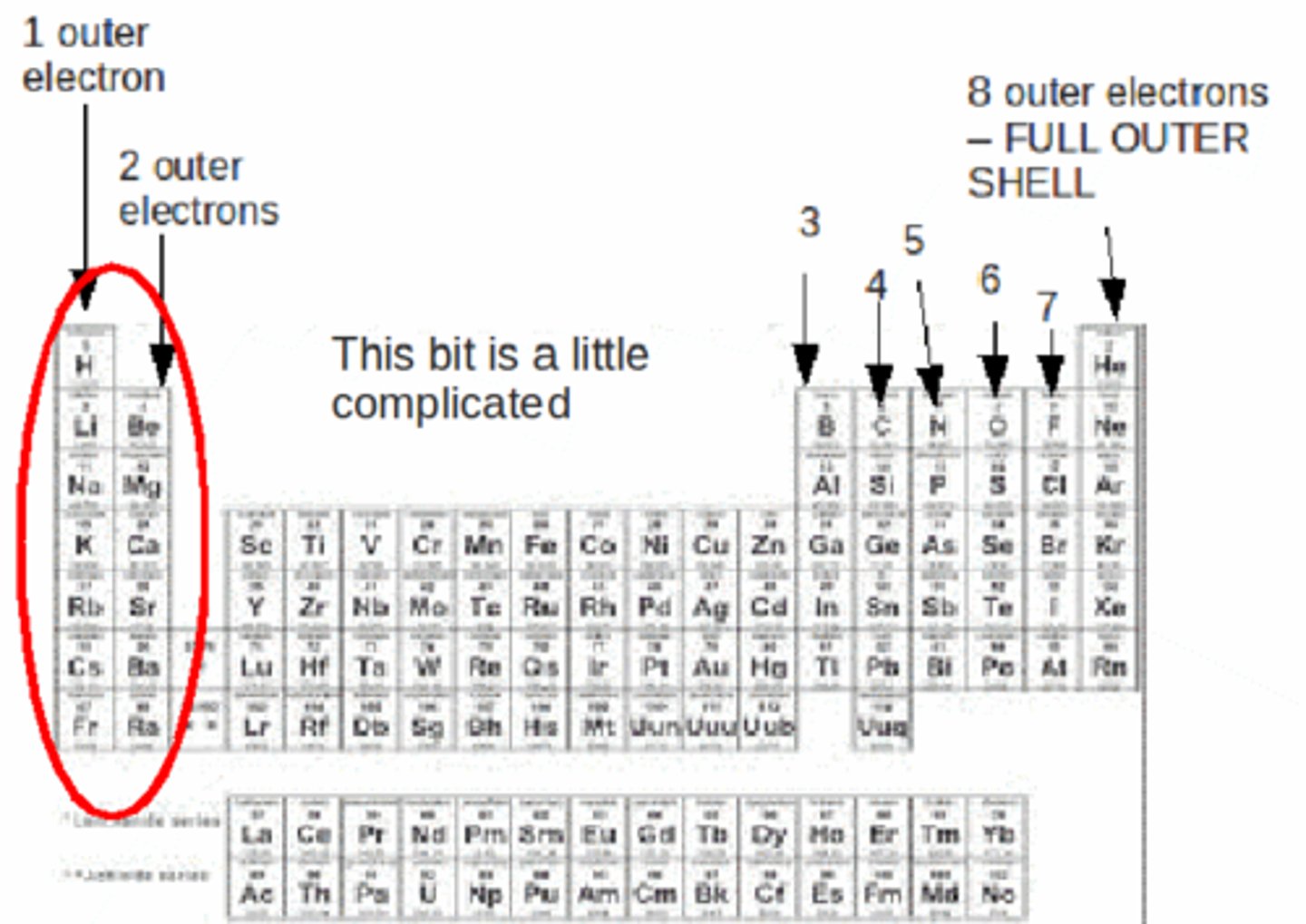
family on periodic table
columns, share chemical and physical properties and number of valence electrons
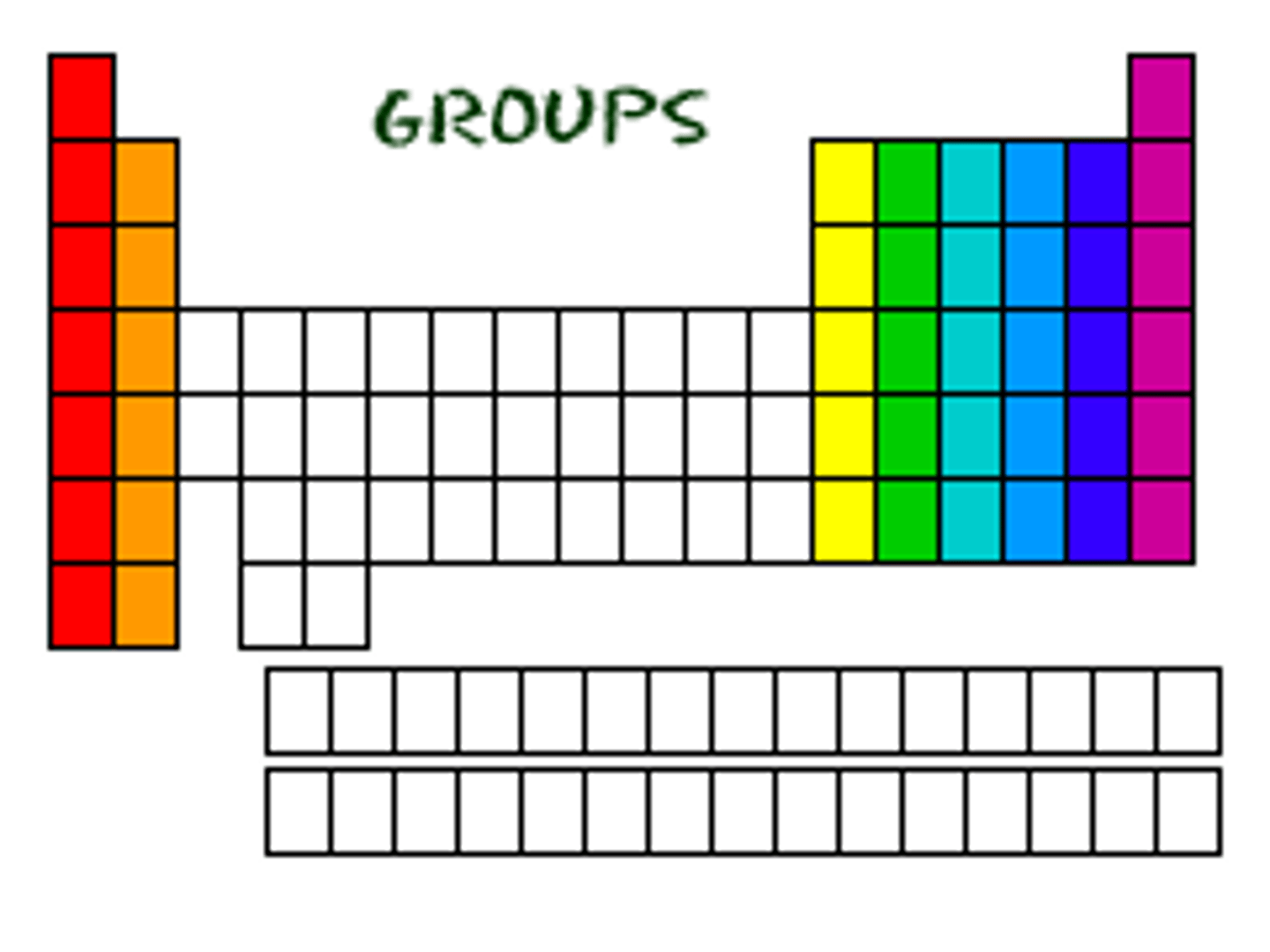
Group (periodic table)
vertical columns; also called families
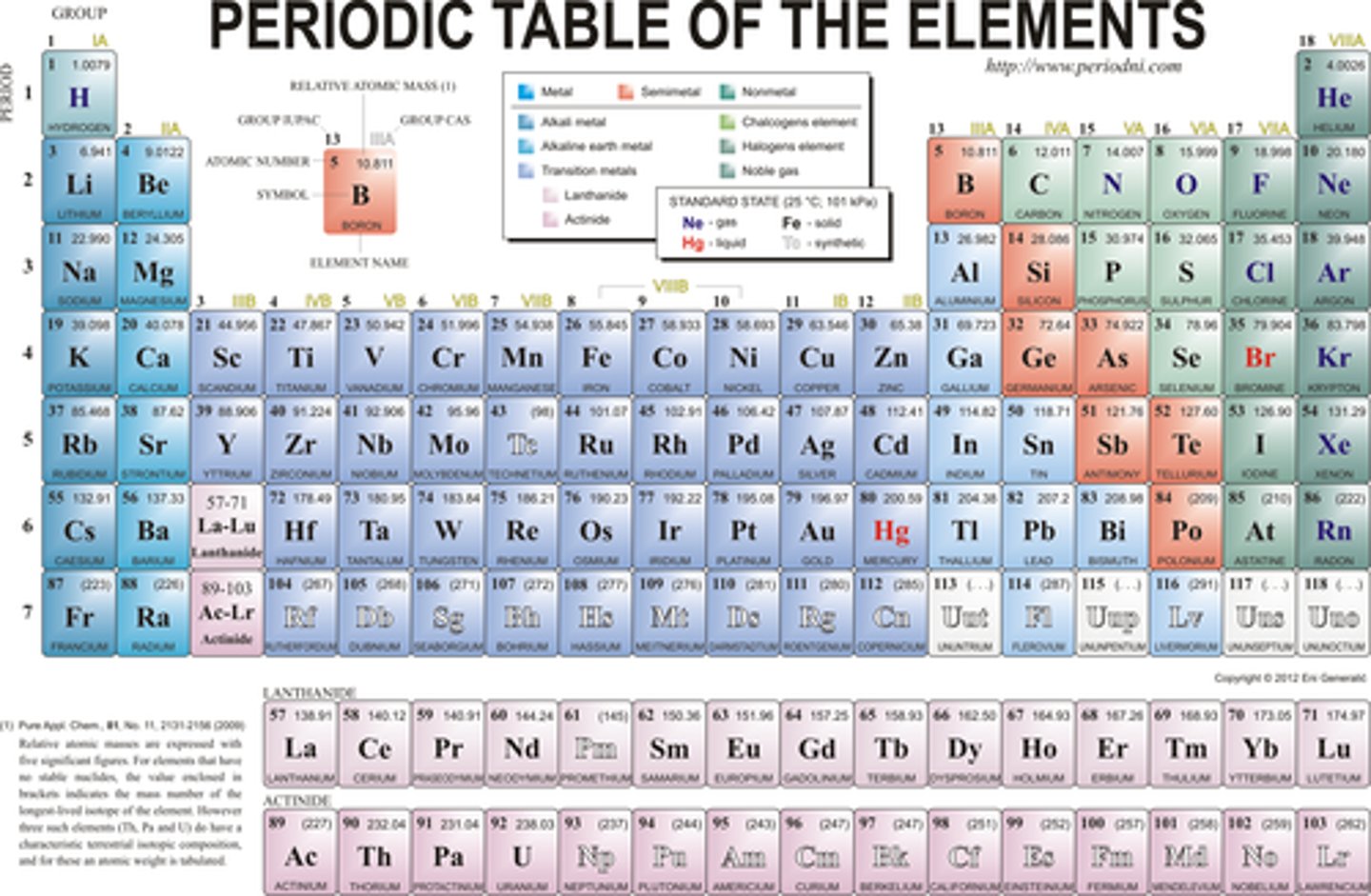
periodic table
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
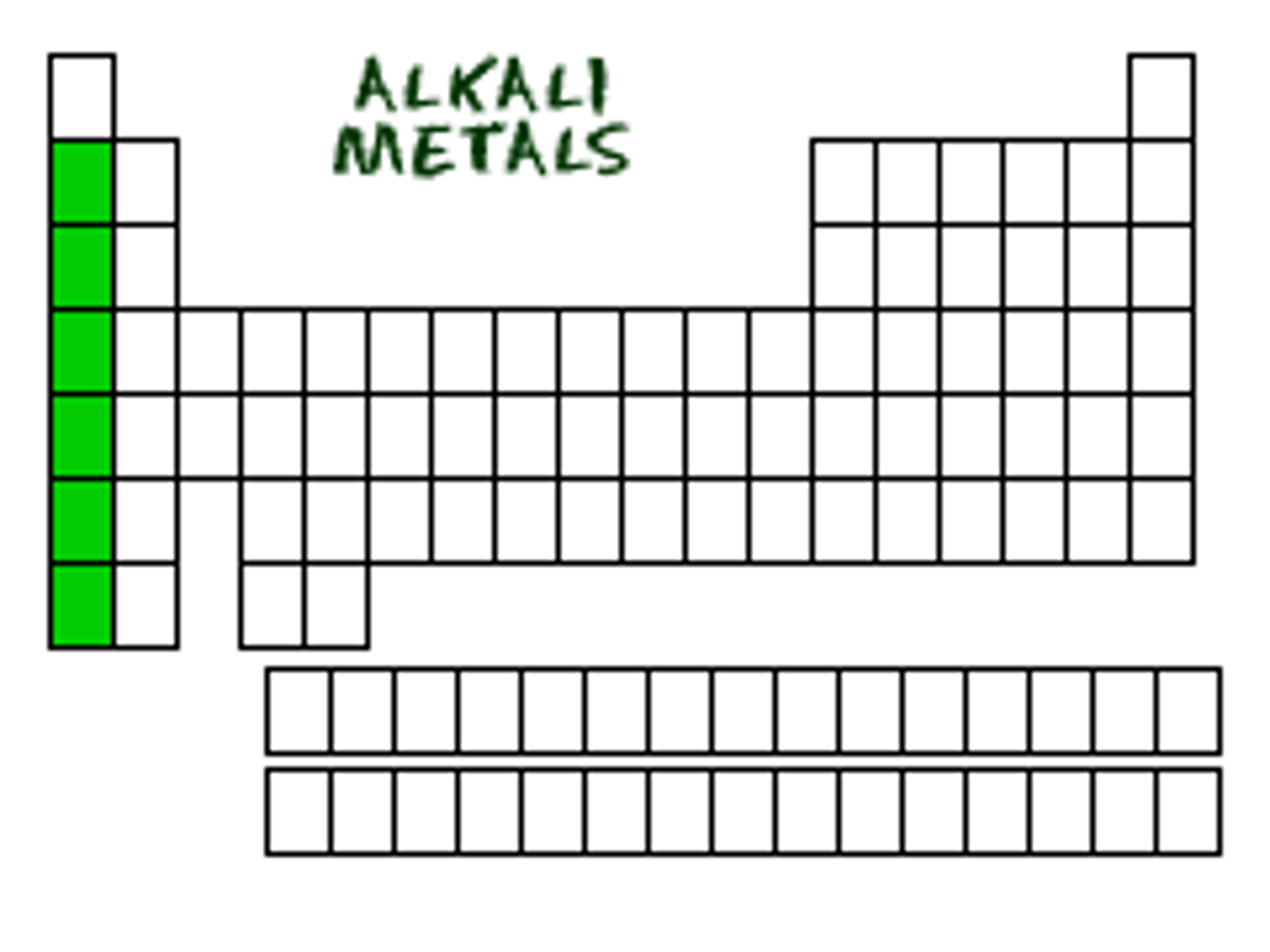
alkali metals (group 1)
Group 1, 1 electron in outer level, very reactive, soft, silver, shiny, low density; Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Francium
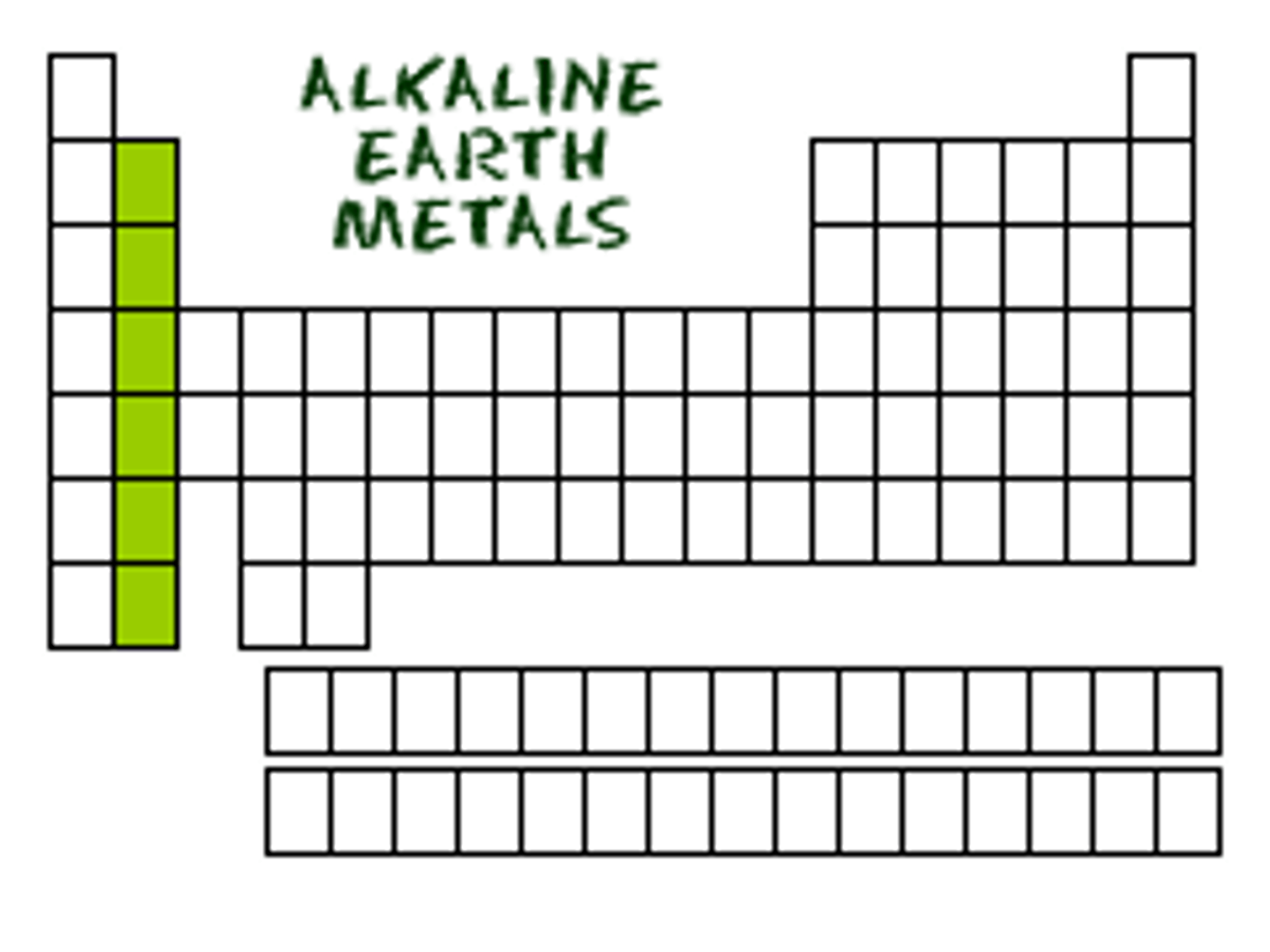
Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2)
metallic elements in group 2 of the periodic table which are harder than the alkali metals and are also less reactive
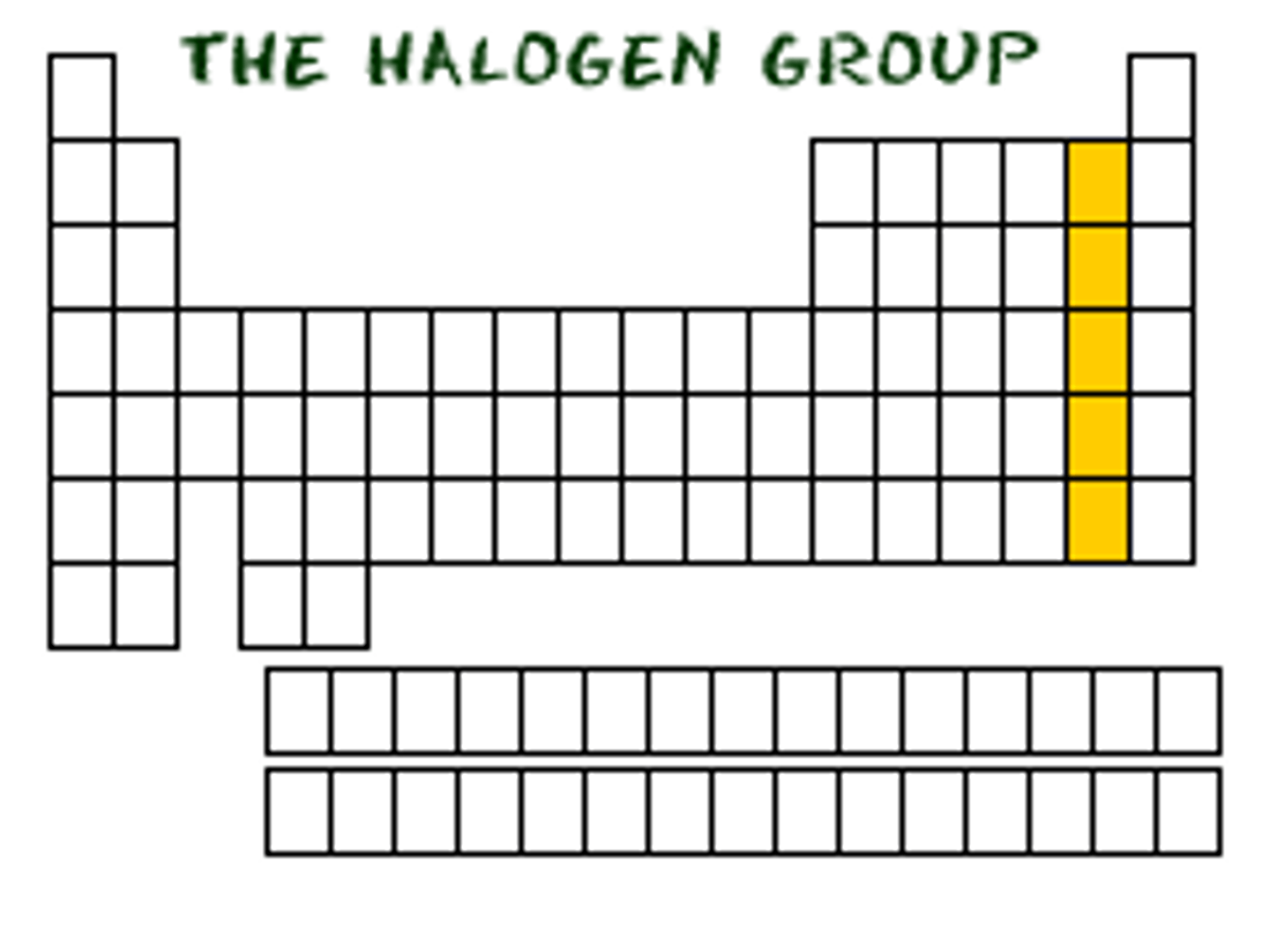
Halogens (Group 17)
Contains nonmetals, 7 valence electrons in it's outermost energy level. most reactive nonmetals
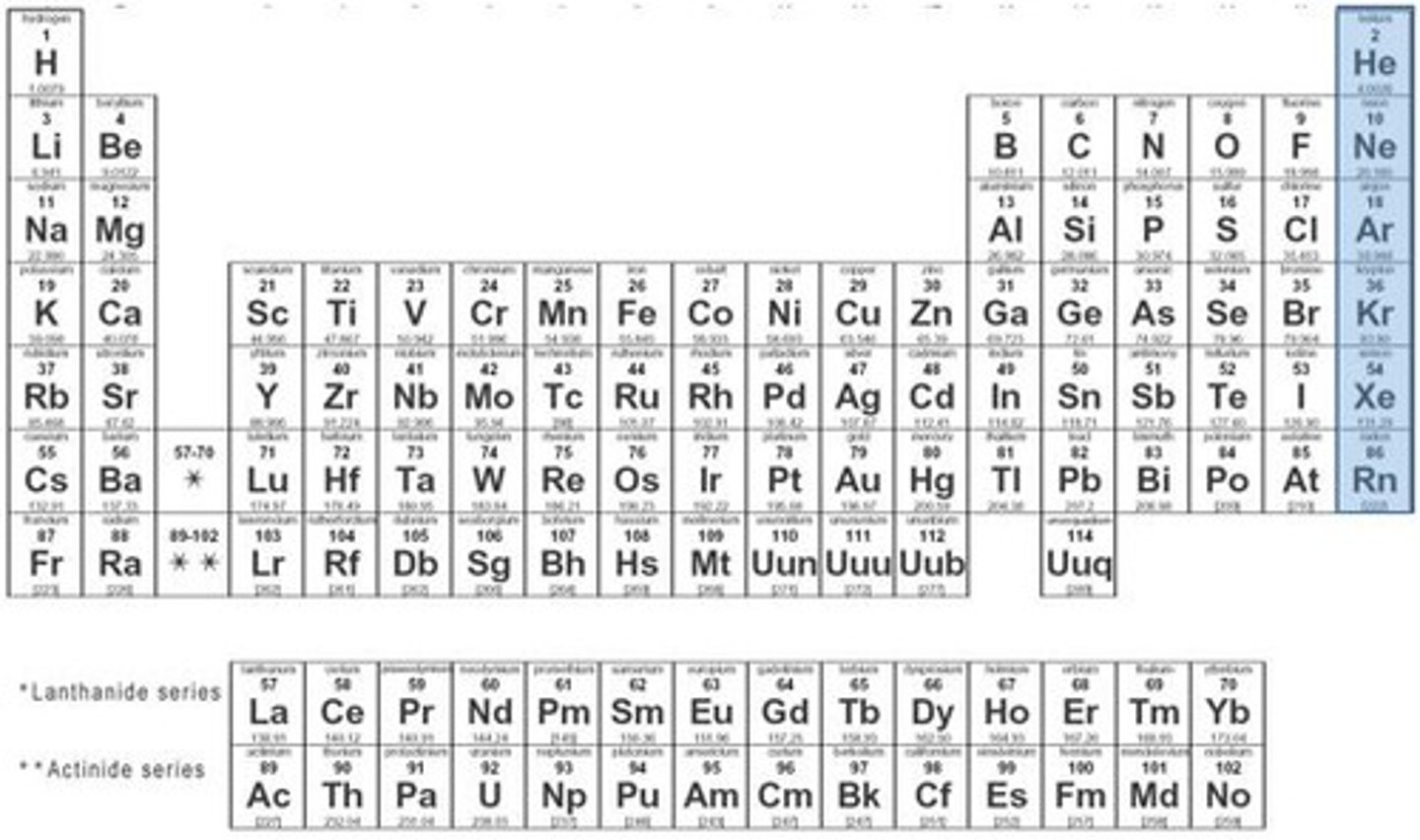
Noble Gases (Group 18)
have a full outer energy levels of 8 electrons and are stable
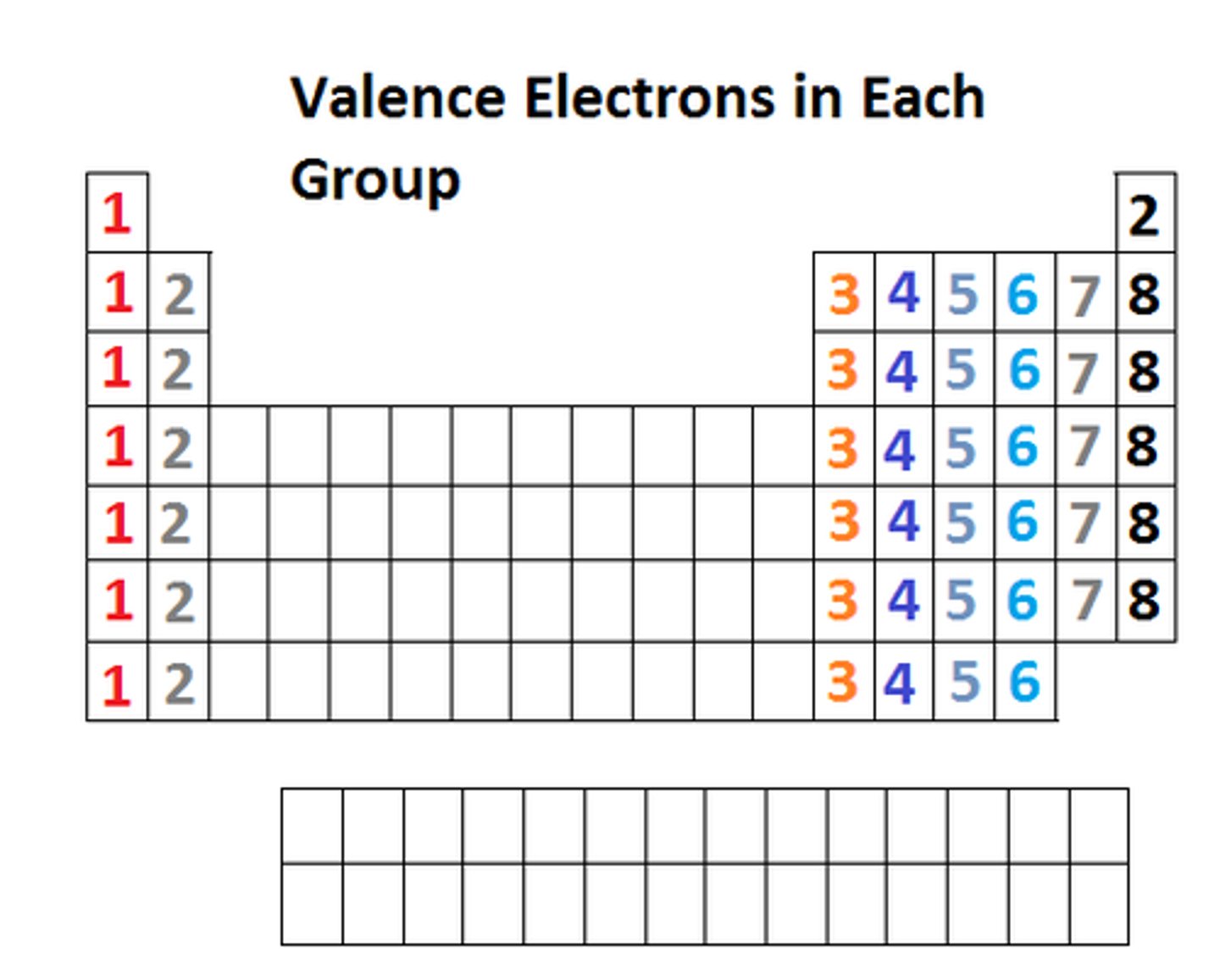
valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
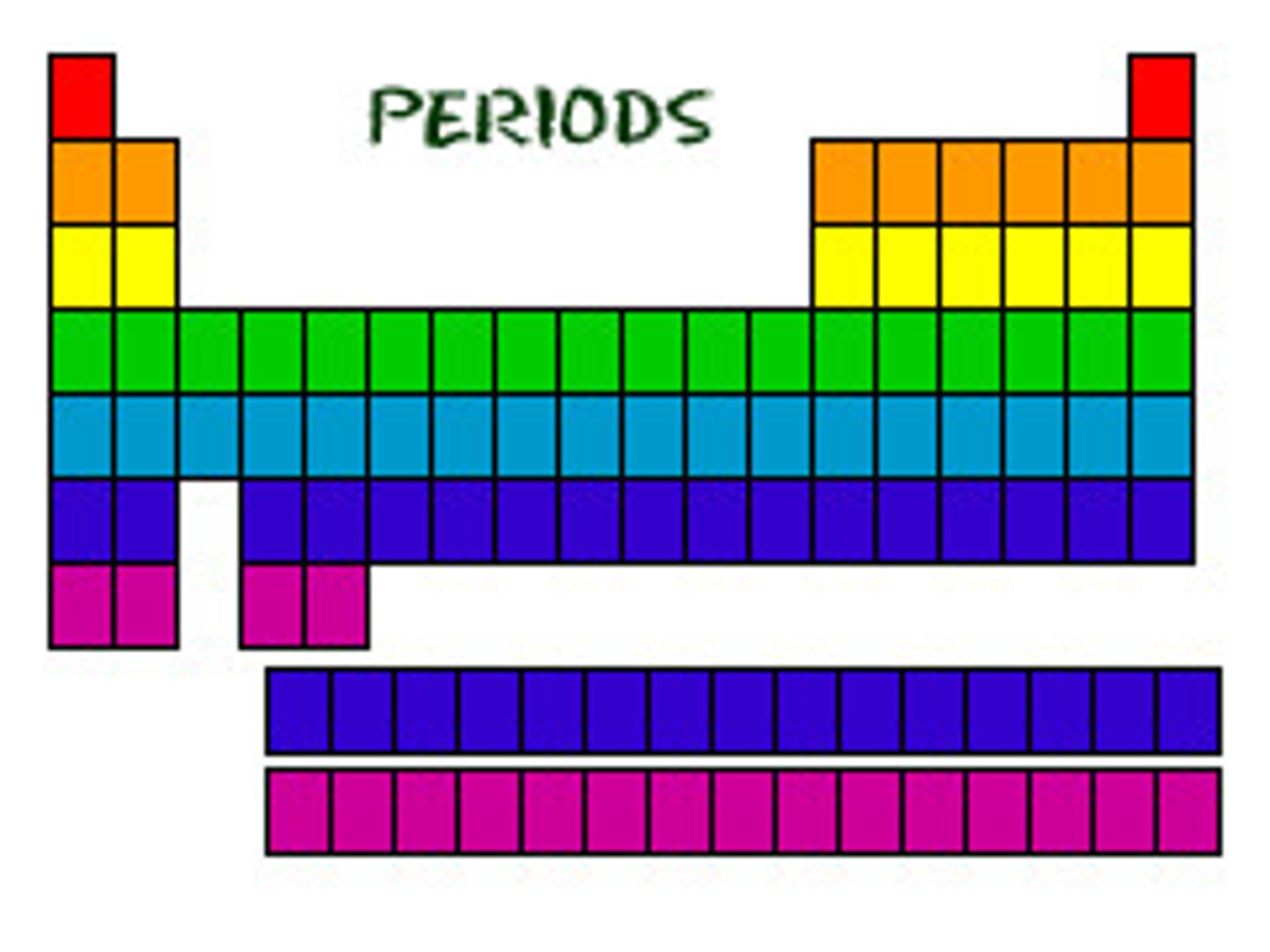
period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
Dimitri Mendeleev
Russian scientist that created the perodic table according to atomic mass

Henry Moseley
Arranged the periodic table by atomic number instead of mass number

Reactivity
The ease and speed with which an element combines, or reacts, with other elements and compounds.
Metals
good conductors of heat and electric current, solid (except Mercury), malleable, ductile

malleable
capable of being shaped
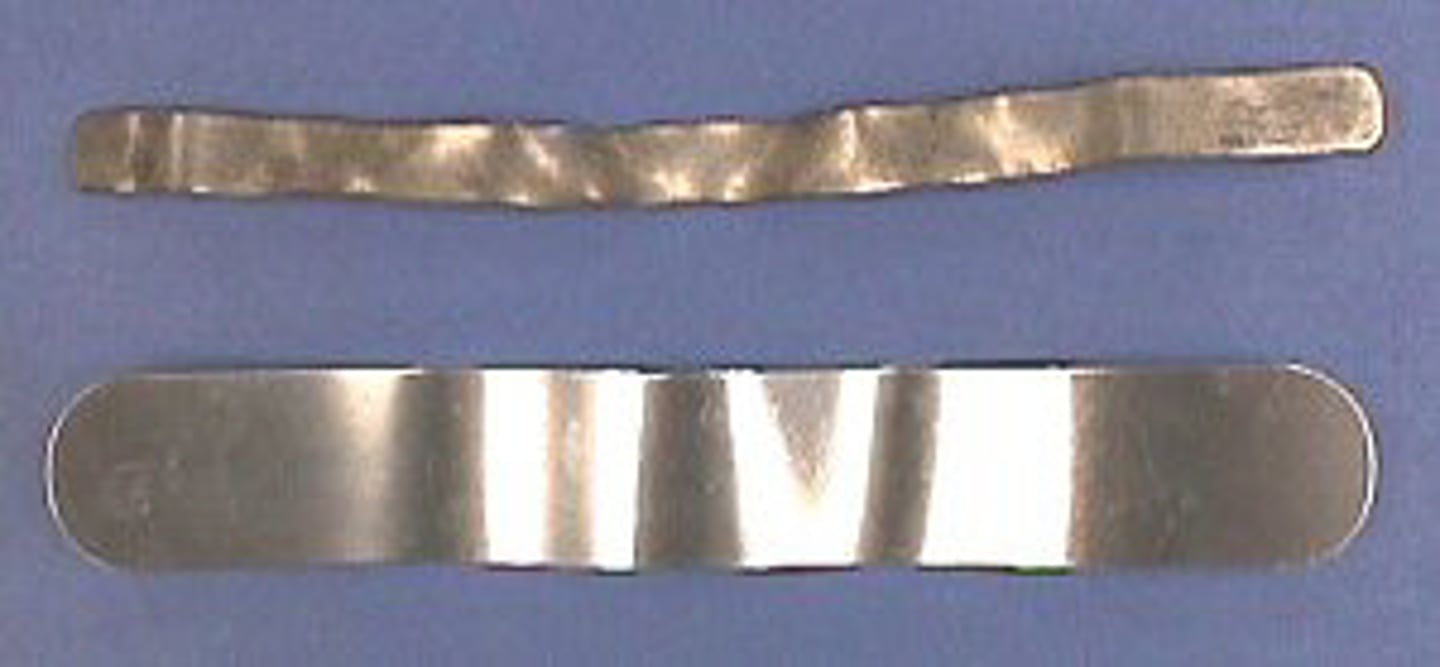

ductile
A term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a long wire.
Nonmetals
Elements that are poor conductors of heat and electric current; brittle solids, liquids, or gasses; insulators
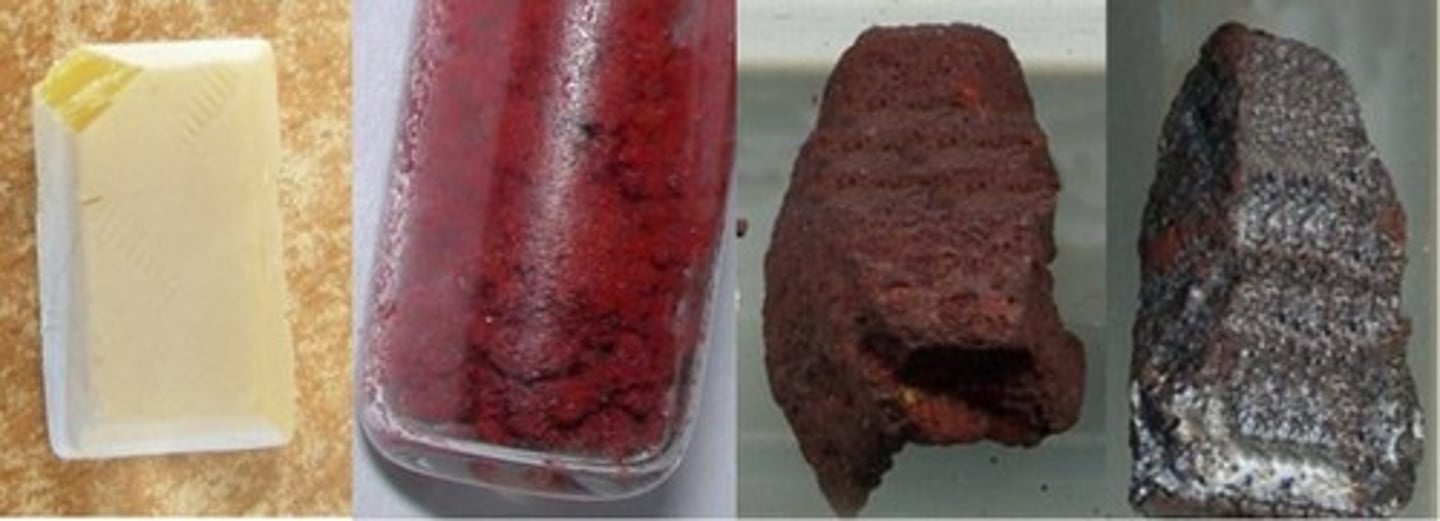

brittle
Easily broken; not flexible
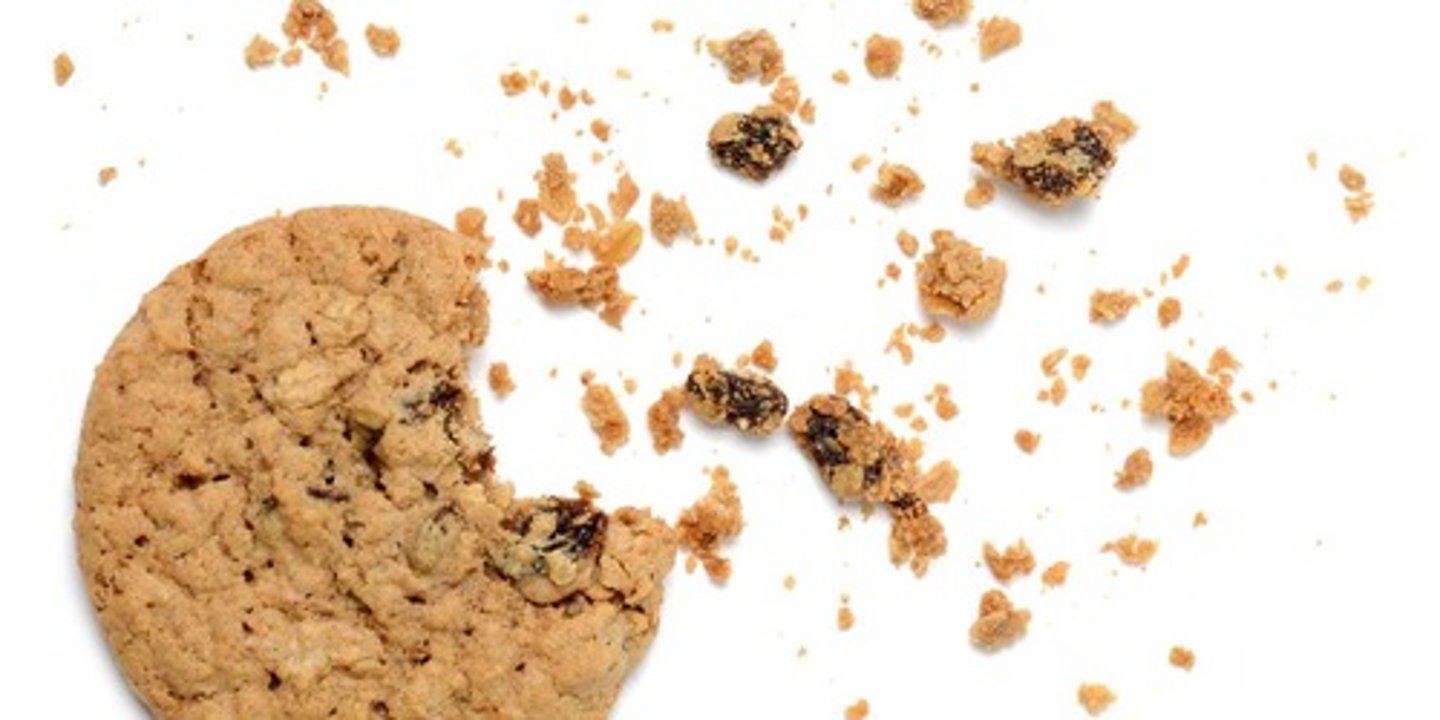

Metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals; semiconductors
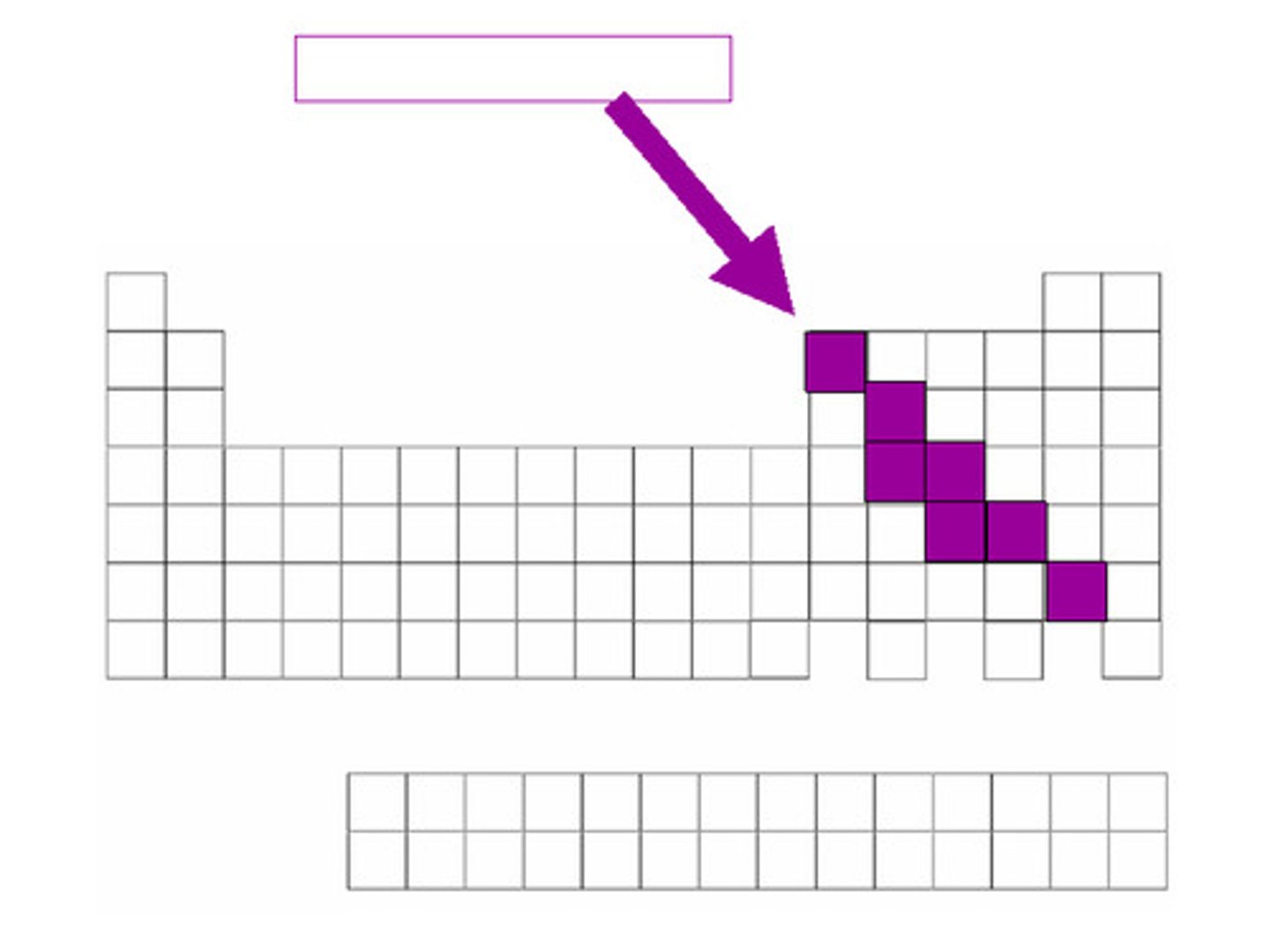
semiconductor
A substance that can conduct electricity under some conditions
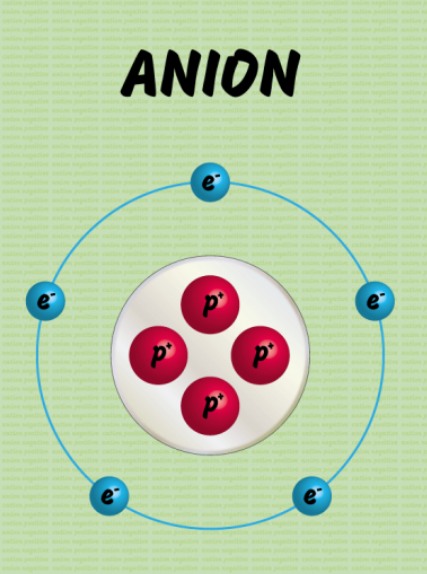
Anion
negatively charged atom formed from gaining or losing electrons
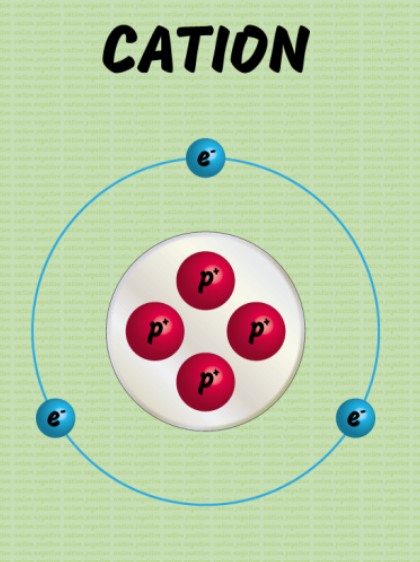
cation
positively charged atom formed from losing electrons
conductivity
The ability of a material to conduct energy

corrosion
the process of deterioration of metals due to chemical reactions, typically with oxygen and moisture.

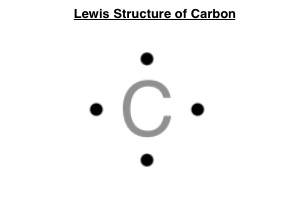
Lewis Dot Structure
a diagram that shows the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist.
luster
the way a surface reflects light, often associated with the shininess of metals.

matter
anything that has mass and occupies space, consisting of atoms and molecules.

subatomic particle
the smaller components that make up an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Transition Metal
a group of metallic elements that have partially filled d orbitals, known for their ability to conduct electricity, form colorful compounds, and exhibit variable oxidation states.