posc201 jmu exam 2 hammond
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Overall Epicurus and epicureanism
-you shouldn't worry about things beyond your control
-ataraxia: psych tranquility
-focus on your inner tranquility
-he talks about reputation and appearances(one's own integrity is more important than reputation)
Epicurus first innate good
-pleasure
-enjoy the pleasures of life
-pleasure is the starting point and goal of living blessedly
-pleasures are neutral, no pleasure is better than another
Epicurus on self-sufficiency
-self-sufficiency is a great good
-those who least need extravagance, enjoy it the most
-all pain from want is removed
-when we say pleasure, we do not mean pleasure of consumption, but rather lack of pain and disturbance in the body + soul
Epicurus on prudence
-prudence is the greatest good
-prudence is more valuable than philosophy
-source of all other virtues
-it's impossible to live pleasantly without living prudently, honorably, and justly
Epicurus on politics
-our politics often cause pain + disturbance
-cannot focus on inner-tranquility if society is in turmoil
-a person can achieve self-sufficiency outside the polis
-the wise person avoids politics, but we still need politics
Epicurus on justice
-the just life for him is most free from disturbance in the body and soul
-justice is more like a contract(about neither harming each other or being harmed)
Epicurus on injustice
-if you succumb to injustice, it will damage your soul
-injustice is not a bad thing in its own right
-it's only bad because it's not pleasure
-Epicurus allows the possibility of being unjust
-injustice is only bad if you get caught
Main thinkers of stoicism
-Epictetus
-Seneca
-Marcus Aurelius
-Panaetius
-Cicero
what is stoicism?
-most of stoicism is trying to understand the boundary between fate and freedom
-in spite of fate, there is possibility of free will
-we have to cultivate the virtues to encounter difficulties of life
-thinks politics is essential
-argues you should be loyal to the universe and your country
-cynics influenced early stoics
-stoics say we all belong to the cosmopolis
Cynics
-they think politics should be avoided completely, we need to turn back to nature
-we should become citizens to the world(cosmopolis)
-the cynics were anti-politics and only some are part of cosmopolis
What does Epictetus think?
-somethings are up to us and can be controlled, somethings aren't up to us and can't be controlled
-emotions, opinions, and appetites can be controlled
-bodies possessions, etc. are beyond our control, but we can control our thoughts about them
-we are free in what we can control
-you gain what you desire, so be careful of what you desire
-for the time being, eliminate desire completely
What does Seneca think?
-Seneca says we are all chained to fortune, fate, and necessity. Much of what happens to us is beyond our control
-no situation is so harsh that a dispassionate mind cannot find tranquility
-apatheia: dispassionate
-maintain an even temper, no matter what happens to you
-avoid luxury
-all excesses are luxurious, but modern prosperity is most dangerous of all
What does Marcus Aurelius think?
What does Panaetius think?
jus naturale
natural law
just civile
-civil law
-human law
-positive law
jus gentium
law of human beings
lex
law
Cicero's thoughts on law
-Law is the highest reason in nature
-natural Law is not a product of human thought, but civil law is
-natural Law is the primal and ultimate mind of God
-We are not God, but we share reason with the divine
-those who share Law, must also share natural justice
-Law as right reason -> reason shared by all
-he see's his duty to Rome
-says there's a natural inclination to love our fellow humans
-Cicero adds a quote from Carneades
Carneades
-Carneades is opposed to the ideas of Cicero
-laws are obeyed because of the penalty's they would inflict, not because laws of our own justice
-men are not just by virtue
-there is no natural law, humans are led by their own self-interest
Polybius's typology of regimes
-only solution to not have regimes deviate is to mix regimes
-if you combine elements of the good regimes, that will reduce the chances of the regime becoming corrupt
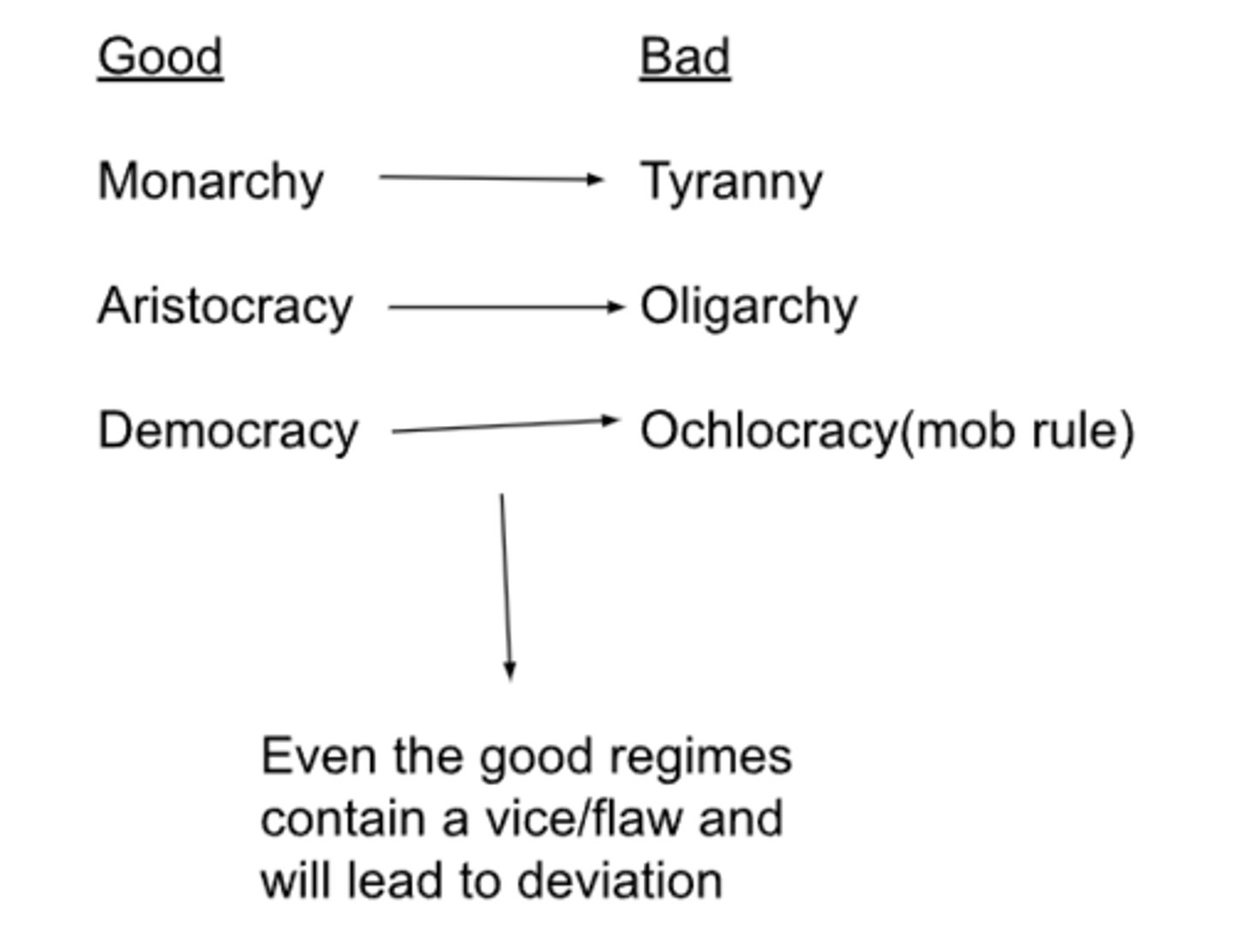
Cicero's thoughts on regimes
-a composite/mixed regime
-monarchy is the best of the 3 good regimes, but a mixed regime is the best
-Rome is an example of the best city
Jerusalem and Athens
St. Augustine
-influenced by the Christian faith
-influenced by Cicero and Plato
-two cities: there are 2 kinds of human societies, 2 cities
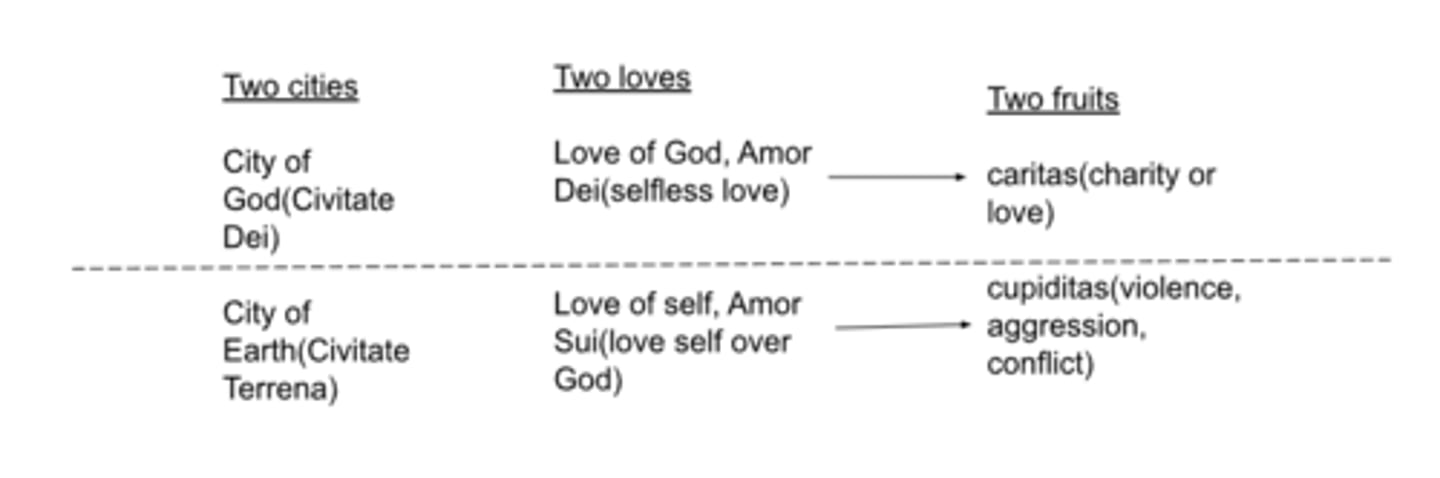
St. Augustine two cities
-any city that is not the city of god is not perfect and will have a hard time being just
-sin has not obliterated our original goodness, our inner goodness is a gift from god and will always remain
-the only truly just city is the city of god
-the rulers of the earthly city are covetous but also have impunity
-emperors and pirates are both covetous, unjust, etc.
-even benevolent cities contain injustice
Alfarabi
-heavily influenced by plato
-the virtuous city
-aims at encouraging virtue of citizens
-understand principles of being itself
-even if we never achieve the virtuous city, we must aim for it
Plato vs St. Augustine vs Alfarabi in terms of cities
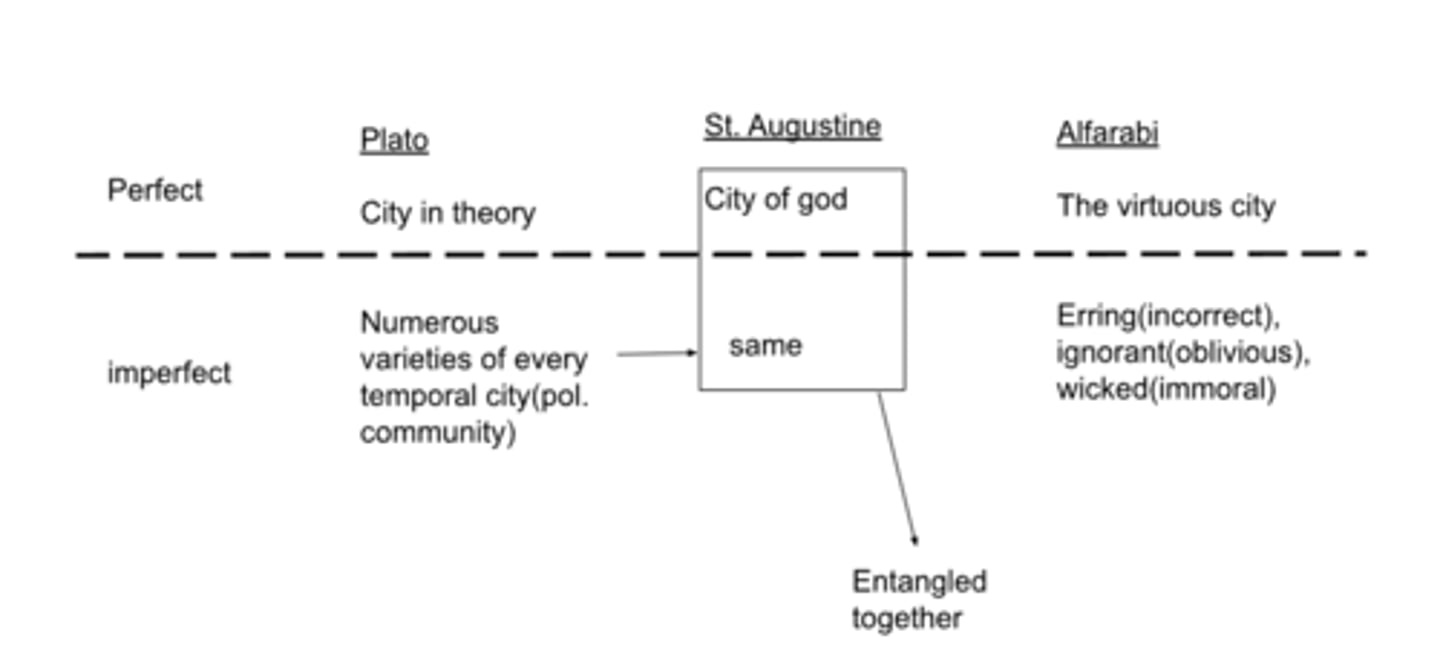
Plato vs Alfarabi
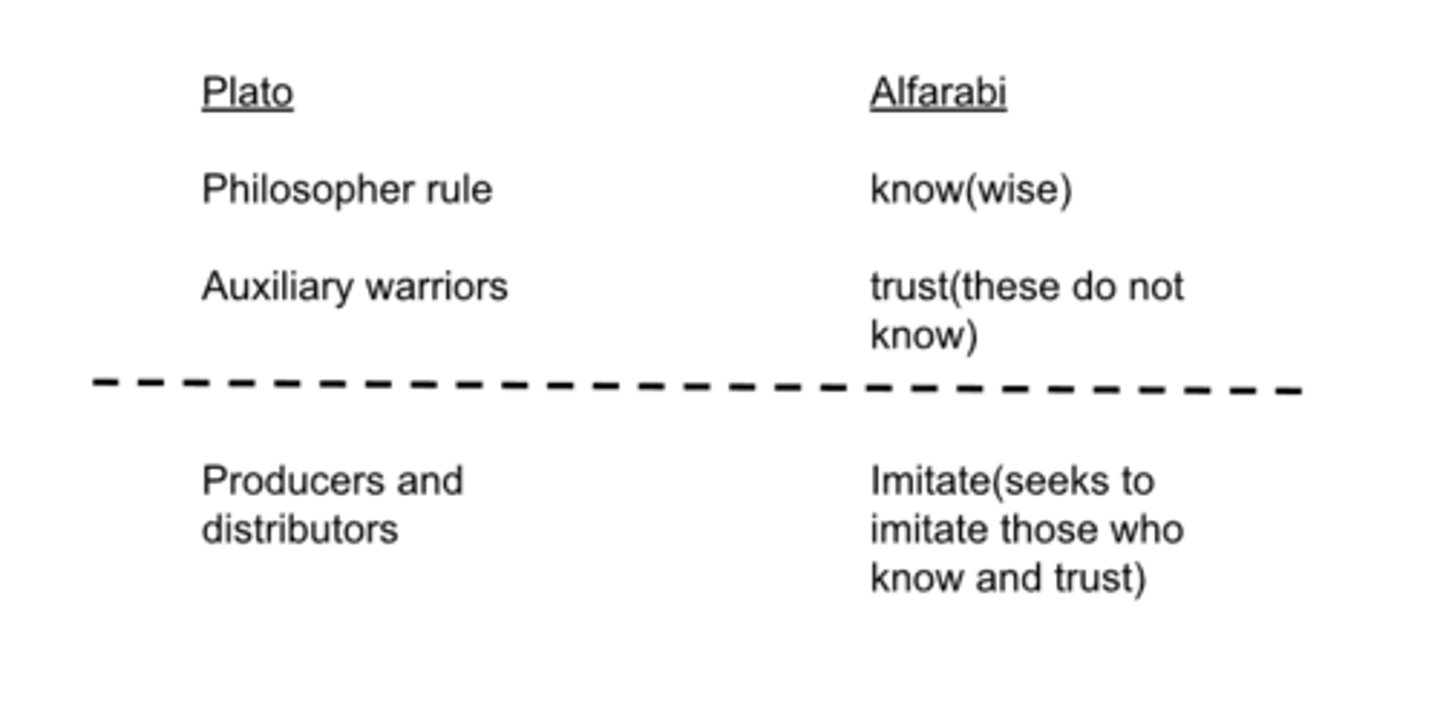
what are the 4 cities for Alfarabi?
-virtuous city(goal is virtue)
-erring(incorrect)(a kind of happiness that is not true happiness is established for, and represented to, them; and actions and opinions are prescribed for them by none of which true happiness can be attained.)
-ignorant(oblivious)(doesn't know, innocent, doesn't know better)
-wicked(immoral)(understands but doesn't care)
what are the goals of the imperfect cities?
-indispensable(necessity)
-vile(like an oligarchy)(goal is wealth)
-base(pleasure)
-timocratic(honor + victory)
-tyranny(power + domination over others)
-corporate association(democracy)(liberty + equality)(includes all types of people)
There are 2 ways to reach a virtuous regime, move toward:
-indispensable
-democracy(mixture of best and worst)
what does St. Thomas Aquinas believe about justice?
-influenced by St. Augustine and Aristotle
-each human being contains the light of reason
-human beings by nature are social and political
-the political community community is the perfect community, therefore we can talk about justice in our political communities
-it is possible to have justice in our cities(perfect, not flawless)
St. Thomas Aquinas and laws
-the whole purpose of law is to coerce virtue and lead human beings to virtue
-laws enable us to exercise the habits that will lead us to virtue, laws will not automatically make us virtuous. Gradually over time, it will lead us to virtue
Thinkers and their virtues
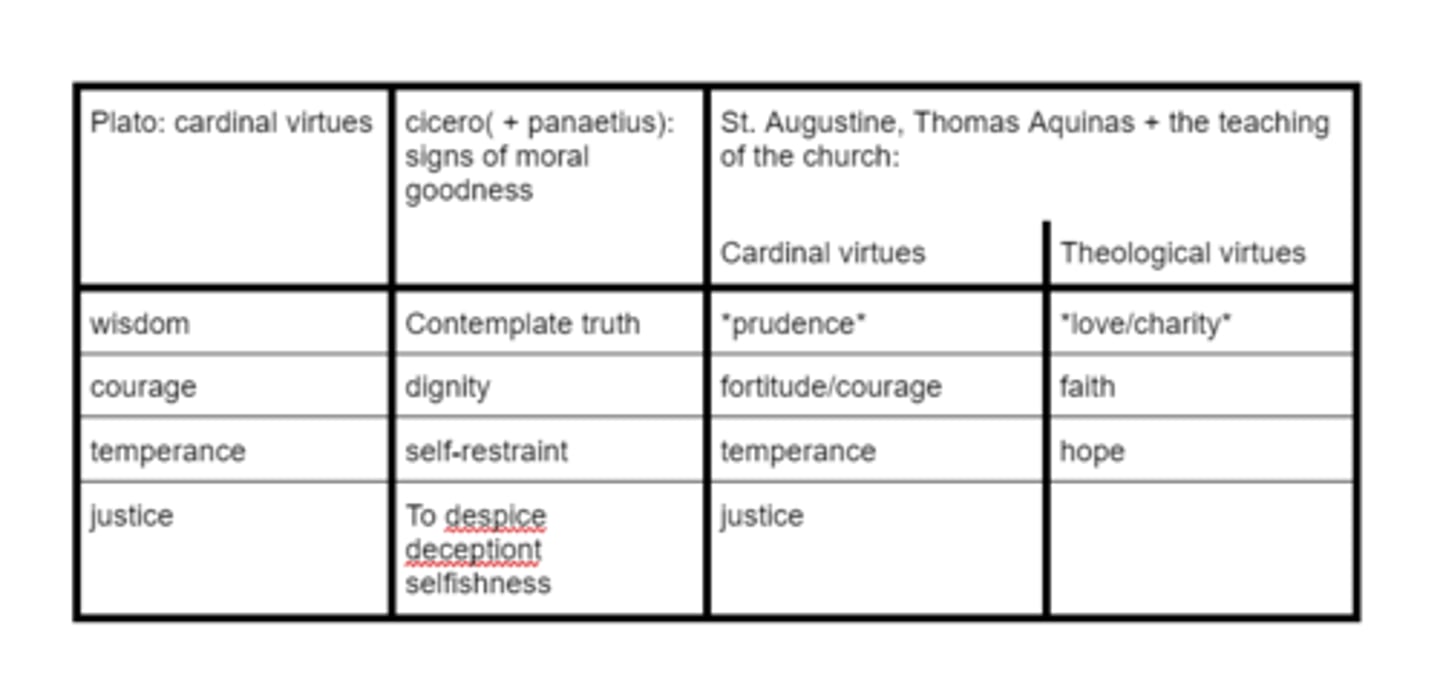
Sophia
contemplative wisdom
phronesis(prudence/prudentra)
-practical wisdom
-a habit must also perfect practical wisdom
what are the most important virtues for st. Augustine and thomas aquinas
-all virtues are important but prudence and love/charity are more primary
-prudence is right reason about what we can do
-who ever has charity/love, must have all other virtues
thomas aquinas's 4 kinds of laws
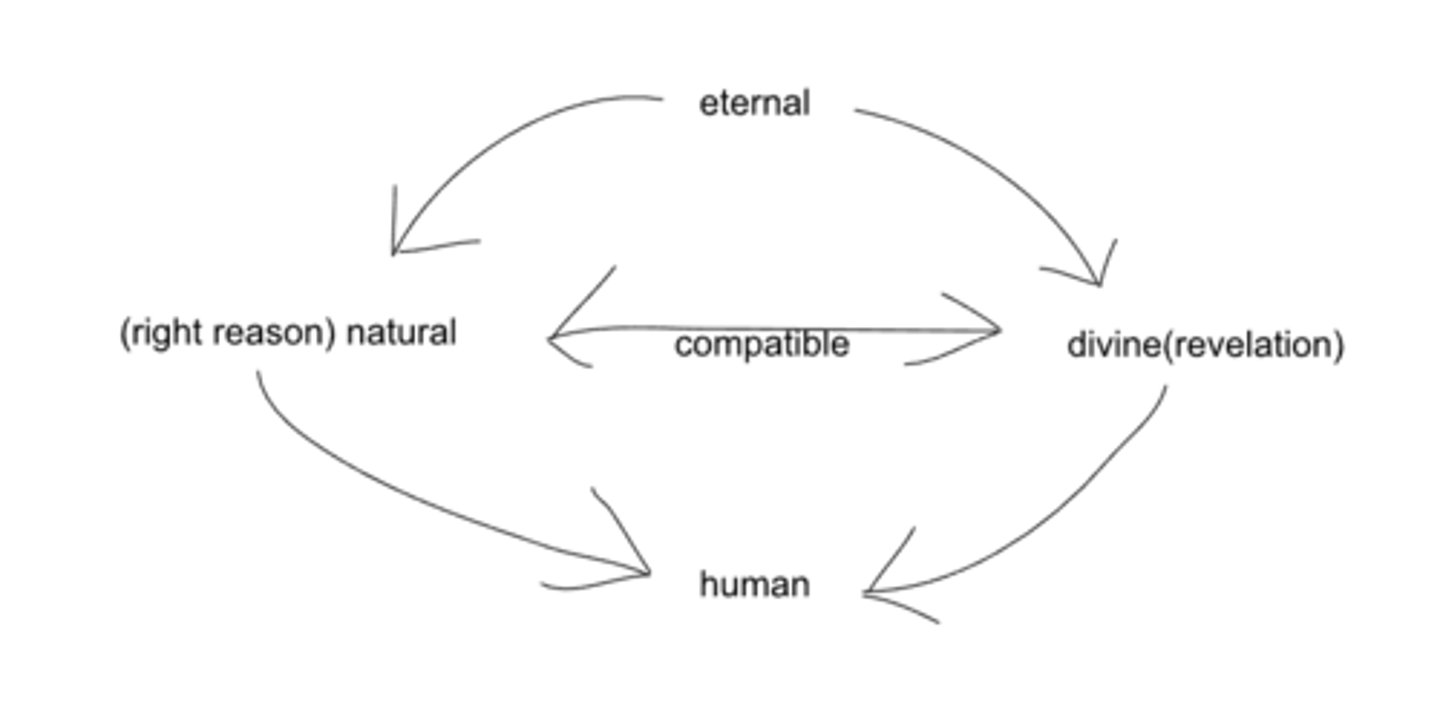
eternal law
-gods law that governs universe
-imprinted in our being
-even though our nature has been distorted by sin, we are innately good because the eternal law is imprinted on us
natural law
-right reason
-rational principle
-discerned through intellect
-natural law is contain in divine law
divine law
-revealed through scriptures
-divine law is contained in natural law
human law
-laws that humans enact
-human law cannot contradict higher law
thomas aquinas first precept of natural law, natural inclinations, and natural primary principles
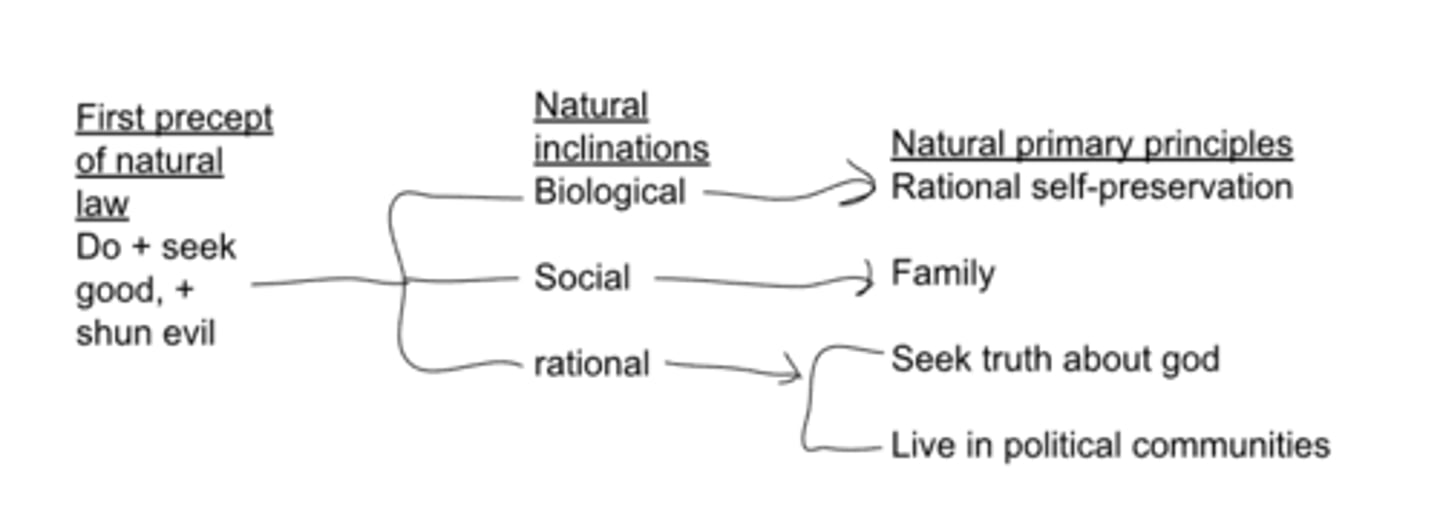
synderesis
-conscious
-the law of our intellect
-contains the habits of the natural law
-we understand intutivly
4 ways in which laws are just
-ends(goals)
-authority
-form
-aligned with the higher good(divine good)
ends(goals)
-ordained for the common good
-does no serve only private interests
authority
-enacted under legitimate power of lawmakers
-laws must not pass the authority of the lawmakers
form
-any burdens imposed must be fair to all(common good)
-ex: taxes are a burden to all, but you need to makes sure it's not more of a burden to a certain group. Some may argue taxes are more burdensome to the poor
When are laws unjust?
-laws are unjust if they violate any of the criteria(ends, authority, form, divine good)
-unjust laws don't have obligatory force(we aren't obligated to follow it)
-the primary rule of reason is natural law
-unjust laws aren't even laws
the best regime according to thomas aquinas
-monarchy(says this is the best in one place)
-example we find in nature(god is almighty king)(animals have a king)
-mixed regime(says this is the best in more than one place)
-judicious combination of monarchy, Aristocracy, and democracy(natural law and divine law)
3 problems raise in a Christian polity
-on private property
-on war
-on obedience and rebellion
on private property
-scriptures says people share resources/revenue
-3 ways to justify private property(reality of political world)
1.human beings are more careful for things that are their private property
2.helps human conduct their affairs in an orderly fashion
3.in private property we live in our own peace
on war
-we should seek peace, but sometimes thats not possible
-if you do resort to war, you should engage in war justly
-war should be last resort
-3 criteria to be met for war to be conducted justly
1. have to have legitimate political authority to declare war
2.must be a just cause to wage war(to defend yourself or an ally)
3.the intent must be right
on obedience and rebellion
-rebellion by nature is a mortal sin
-tyranny is unjust(they only seek their own good)
-to resist a tyrant does not count as rebellion
-tyrants insight discontent and rebellion
-the tyrants have rebelled against us, so to rebel against them is ok
what did Machiavelli think of human appetite
-human being are naturally envious
-human appetites are insatiable, but our circumstances only allow us to realize only some of those desires
-men are constantly dissatisfied and wanting more
-he refused to be intimidated by his critics and he believed he is exploring uncharted territories
comparing Machiavelli to the "mirror of princes"
-Christine de Pizan
1.a young prince must be taught by a tutor what is good and virtue
2.a good prince ought to be loved by his people
-john of salisbury
1. a prince performs ministry faithfully
2.a prince doesn't owe his life to himself, but rather to others
3. a prince is father + husband to his subjects
-Machiavelli
1.it is safer to be feared rather than loved. make sure you are not hated (some say Machiavelli is a teacher of evil)
Machiavelli's: the prince central teachings
- a ruler must learn how NOT to be good(to do this they should read Machiavelli's book intelligently)
-a ruler must maintain the appearance of being good
-a ruler's primary concern must be war
-a ruler must lay good foundations for power (good laws/good armies)
-"si guarda al fini"
1.the end justifies the means
2.people judge by the outcomes
fortuna(fate)
we do have free will, but a lot of what happens to us is beyond our control
Who is Machiavelli's prince examples?
-cesare borgia
-virtu(ideal ruler)
-NOT julius caesar
-moses, cyrus, Marcus Aurelious
-tutor of Achilles
-a princes needs to be prepared to do vicious things, but appear to be virtuous
-the rational must guide the irrational, but Machiavelli puts the irrational on the same level as rational(and maybe even higher)
Cesare Borgia
-he put one of his liutenits(Remiro d' orco)
-Borgia is the true power, but he steps away and gives d' orco power
- d' orco was cruel and the people hated him(even though Borgia was the one behind him)
-Borgia let d'orco do his dirty work and then Borgia killed him
-Borgia knew the importance of appearance. he knew how not to be good
virtu
-skill(those who hold office must be able to get things done)
-excellence(don't want the ruler to be incompetent)
-ingenuity(cleverness)
-boldness, strength, manliness
tutor of Achilles
-his tutor was a centaur(half man, half horse)
-a good ruler must know how to make good use of beastly qualities
Who is Machiavelli's prince analogy?
-a prince must be a fox and a lion
-detect traps like a fox
-lion has the strength to chase away the wolves
Machiavelli's typology of regimes
-good regimes(monarchy, aristocracy, democracy)
-bad regimes(tyranny, oligarchy, ochlocracy)
-the 3 good ones don't last long and the 3 bad ones are evil
-avoid the simple types and make a mixed regime(it would have checks and balances)
-have a prince or have a republic
-free cities are wealthy and powerful(ex: Rome and Athens)
-not just deposing tyrants but also deposing kings
Machiavelli ideal city
-ideal city is Republican Rome
-a republic is better than a prince
-people participate in republic
-the people could be unstable, but so could the ruler
-people are more prudent, stable, and are better than a prince
-good institutions + good laws will be good or better than a prince
Machiavelli on religion
-religion is good because it's useful( could be used to maintain power), not good because it's true
-Christianity only cares about appearance in the afterlife(he rejects it, he worries about this life)
-he praises savagery(they care about this life)
-says princes can't be christian
-if you are a ruler, how can you be a good christian?
-a ruler can appear to be a good christian, but can't afford to actually be it
-machiavelli focuses on what there is, not what there ought to be