Bio 1114 Ch 9 - Conquest of Land Plants
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Plant
Multicellular eukaryotic organism that is photosynthetic, generally lives on land, and adapted to terrestrial environments. Classified in the Kingdom Plantae.
Streptophyte Algae
The green algae that are closely related to land plants.
Apical meristems
A group of actively dividing cells at a growing tip.
Spores
Tough-walled reproductive cells that allow dispersal through dry air.
Bryophytes
Liverworts, mosses, and hornworts are informally known as the Bryophytes.
Zygotic life cycle
The zygote is the only cell that undergoes meiosis.
Sporic life cycle
Meiosis results in the formation of spores (alternation of generations).
Alternation of generations
Life cycle that alternates between a diploid organism (sporophyte) and haploid organism (gametophyte).
Sporophyte
Diploid, multicellular spore-producing generation.
Gametophyte
Haploid, multicellular gamete-producing generation.
Gametangia
Structures that produce the gametophytes.
Archegonia
Flask-shaped gametangia that enclose a single egg.
Antheridia
Elongate or spherical gametangia that produce many sperm.
Matrotrophy
Zygotes are enclosed in gametophyte tissue where they are sheltered and fed. (Critical innovation!)
Sporangia
Structures that produce and disperse spores.
Sporopollenin
Tough material that composes the walls of plant spores; helps to prevent damage during air travel.
Bryophytes lack Vascular tissues, which are..
Tissues that provide structural support and serve in conduction.
Tracheophytes
Group of vascular plants that includes Lycophytes, Pteridophytes, and seed-producing plants.
Tracheids
Specialized vascular cell that conducts water and minerals; provides structural support.
Stems
Branching structures that contain vascular tissue and produce leaves and sporangia.
Phloem
Specialized conducting tissue that carries organic nutrients.
Xylem
Specialized conducting tissue that carries water, minerals, and provides the structural support.
Lignin
Adds strength to and decay resistance to cell walls of tracheids, vessels, and other cells of plants.
Roots
Organs specialized for uptake of water and mineral from the soil.
Leaves
Flattened plant organs that emerge from stems and function in photosynthesis.
Waxy cuticle
A polyester layer on plants that prevents the plant from desiccation; protects against pathogens.
Stomata
Pores that are able to open and close on plants and allows plants to let in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
Gymnosperm
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits. Ex: Cycads, gingkos, conifers, and gnetophytes.
Seeds
Complex structures having specialized tissues that protectively enclose embryos and contain stores of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein.
Angiosperms
A flowering plant; seeds are enclosed in a fruit.
Flower
Short stems bearing organs that are specialized in ways that enhance seed production.
Fruits
Structures that develop from flower organs, enclose seeds, and foster seed dispersal.
Endosperm
Nutritive seed tissue that increases the efficiency with which food is stored in the seeds of flowering plants.
Placental transfer tissues
Nutritive tissues that aid in the transfer of nutrients from mother to embryo.
Lcyophylls
Tiny leaves with one single, unbranched vein.
Euphylls
Leaves that have extensively branched veins.
Ovule
A megaspore producing megasporangium and an integument.
Pollen
Tiny male gametophytes enclosed by sporopollenin-containing microscope walls.
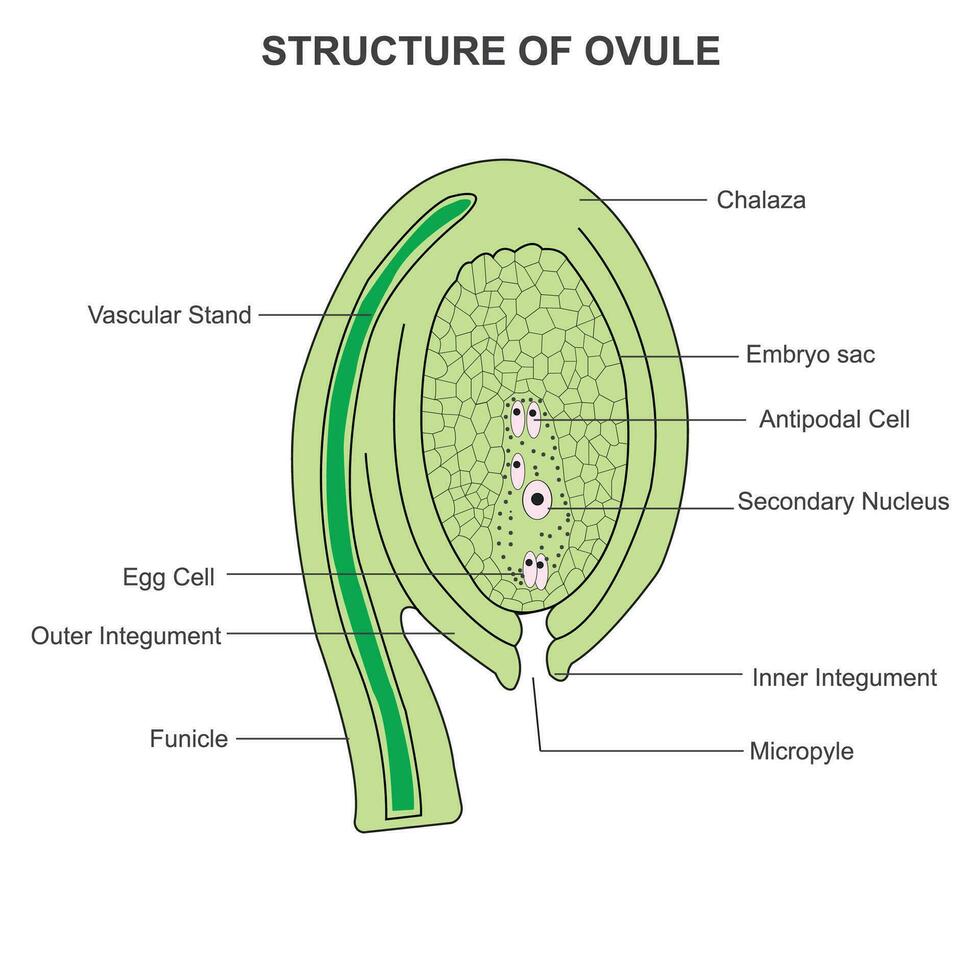
Integument
Structure that encloses the megasporangium.
Heterospory
Two distinct types of spores in two different types of sporangia.
Microspores
Spores that develop into the male gametophyte; develop into pollen.
Megaspores
Spores that develop into the female gametophyte, develop into eggs while enclosed by the megaspore's protective walls.
Ecological advantages of seeds
Many seeds are able to stay dormant, Seed coats can adapt to improve dispersal, Store a large amount of food for embryo, Pollen does not need water for transport to egg.