Oncology + Obesity + Transplant + Dialysis
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
General Principles of Chemotherapy
Antineoplastics generally have ________ therapeutic ranges
The presence of tumor may _________ of drugs
Must know …. → blood/serum conc not always same as conc in tissues
Drug ______ are common
narrow
alter PK
drug conc where tumor is located
interxns
Chemo drugs
Unique AUC based dosing →
Therapeutic drug monitoring →
Clinical condition may affect PK of →
carboplatin
high dose MTX, busulfan
third space MTX
Pharmacogenomic Considerations
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency →
UGT1A1*28 homozygosity →
Thiopurine S-methyltransferase deficiency →
CYP2D6 alterations/drug interxns →
fluorouracil
irinotecan
6MP, 6-thioguanine
tamoxifen
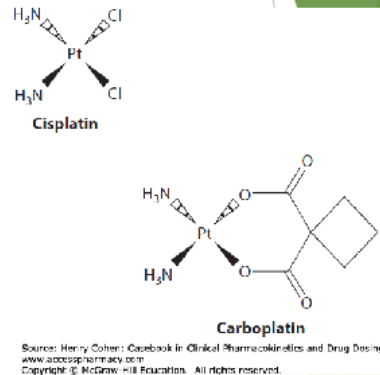
PLATINUM COORDINATION COMPLEXES
Cisplatin, Carboplatin
Platinum-based _________ agents
_______ binds DNA → produce _____ DNA cross links
Targets which phase of CC?
alkylating
covalently, interstrand
Mitosis
CARBOPLATIN
_____ BASED DOSING
Metabolism: ___________ metab to aquated & hydroxylated compounds
Excretion:
t1/2 NORMAL renal fx:
Protein binding:
Vd: 16L → penetrates … (4)
What does higher AUC mean?
AUC
minimal hepatic
urine (70% unchanged)
2.6-5.9h, Pt 5+ days
carbo 0%, Pt yes
liver, kidney, skin, CNS
+TC
CARBOPLATIN: Calvert Formula
Cap CrCL at ______
If SCr …
Weight consideration
Dose (mg) = target AUC x (GFR + 25)
125 mL/min
<0.7 → round to 0.7
use TBW, if 20-30%>IBW use ABW
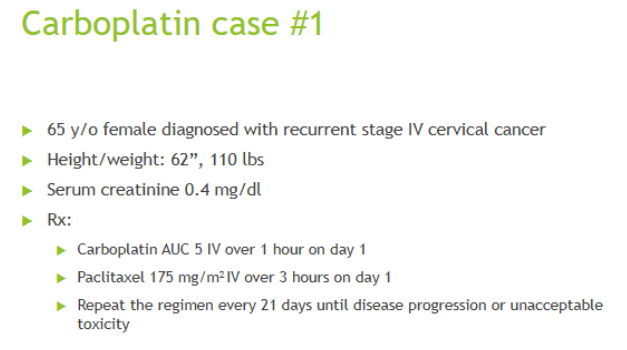
CrCL =
Dose =
63 mL/min
440 mg
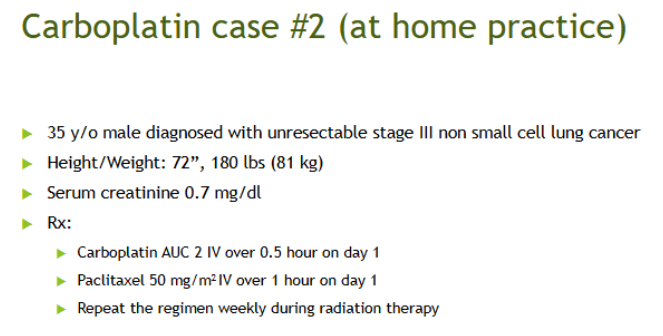
CrCL =
Dose =
168 mL/min
300 mg (cap CrCL at 125)
METHOTREXATE
MOA:
Oral abs:
Distribution: penetrates _______ fluids and exits them slowly
Excretion
inhib DHFR → prevent tetrahydrofolate FH4 to dihydrofolate FH2
variable, -abs w HIGHER doses → use IV
third space
80-90% urine, <10% feces (unchanged)
THIRD SPACING OF MTX
________ clearance of MTX
^ extends t1/2 by ____ times
*Must __________________ prior to MTX infusion!!
prolongs
3
drain third space fluids
HIGH-DOSE METHOTREXATE
Dose _______ gram/m² IV
Used for (3)
Why high dose? → allows MTX to enter cell by _____________ rather than through RFC
Required hospital admission and ____________
^ Purpose:
*RESCUE/REVERSAL AGENT REQUIRED FOR ALL PTS RECEIVING HD-MTX + site of action
Agent 2 + site of action (really expensive!!!)
>/= 0.5
leukemia, lymphoma, osteosarcoma
passive diffusion
monitoring of levels
predict/minimize toxicity
leucovorin/folinic acid → intracell → does NOT -MTX
Glucarpidase → extracell → use when kidney injury → will -MTX, given w leucovorin+hydration
PRIOR TO MTX INFUSION
Check for drug interxns: 7 examples
Give ________ to achieve adequate urine output to promote excretion of drug
Use ____________-based IV fluids to ensure alkalinization of urine BEFORE infusion → why?
Ensure _______
When to start leucovorin? + typical starting dose
^ dosage form?
^ Monitoring → 2
Continue IV fluids + leucovorin until MTX level is ____ micromolar (~3-4 days)
PPIs, NSAIDs, PCNs, phenytoin, cipro, amiodarone, probenecid
IV fluids
sodium bicarb → prevent precipitation
no third spacing
~24h after inf complete → 25-50 mg q 6h
oral saturable → use IV >25 mg
daily serum MTX + SCr
<0.1

What monitoring and supportive care is required for this patient’s high dose
methotrexate? (5)
drug interxns
urine alkalinity + regular urine pH
adequate urine output
daily SCr/MTX
leucovorin
BUSULFAN
Alkylating agent that reacts with ___________ and interferes w DNA rep + RNA transcription
Oral abs →
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
HIGH DOSE BUSULFAN USE →
Goals of busulfan therapeutic drug monitoring →
N7 pos of guanine
rapid + complete
plasma = CSF (readily crosses BBB)
HEPATIC → glutathione then oxidation
25-60% urine as METABs, <2% unchanged
stem cell txp
minimize tox AND maximize efficacy
HIGH DOSE BUSULFAN : IV busulfan PK procedures
Step 1: After 1st dose, draw levels at …
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
Typical targets =
at end, 15 min, 2h, 3h, 4h, 6h after EOI
calc AUC/Css with ^
calc CL → CL = dose/AUC
calc dose → dose = CL x target AUC
Css 600-900, AUC 900-1500
Obese classification
underweight
normal
overweight
pre-obese
Obese
obese class I
obese class II / severely
obese class III / morbidly
super obese
super super obese
<18.5
18.5-25
25+
25-30
30+
30-35
35-40
40+
50+
60+
PK CHANGES IN OBESITY: Absorption
-
-
IM injections may inadvertently be administered as ______
High Vd drug → tissues → which weight dosing?
Low Vd drug → plasma → which weight dosing?
Factors that impact drug distribution → 3
delayed GE → lower Cmax (peak)
+abs of some oral meds w fatty meal → higher Cmax
deep SQ → unknown impact on abs
lipophilic → TBW
hydrophilic → IBW/ABW
hydro/lipophilicity, plasma protein binding, Mw
PK CHANGES IN OBESITY: Metabolism
largely ________
hepatic volume ______ but most likely due to _________ rather than +metabolic activity
SOME data show +CYP2E1, 1A2, 2C9 and decreased _____
ELIMINATION → Bi directional, generally +CL but higher incidence of renal dysfx w _____ or _____
unknown
inc, fatty infiltration
-3A4
HTN, diabetes
What is the most accurate (but most expensive) CrCL equation for obesity?
Can also use Cockroft & Gault using _____
24h urine collection + measured CrCL eqn
LBW
AMINOGLYCOSIDES ADME
A - poor PO
D - small
E - renal
VANCOMYCIN ADME
A - poor PO
D - large
E - renal
100 kg 5’4” female patient
BMI
IBW
ABW
38
55
73
32 yo female, 270 lbs, 5’8, needs to be initiated on Tobramycin for pneumonia. CrCl is approx. 100 ml/min/m²
Assume traditional dosing
What questions would you ask?
Which body weight to use? + calculate weight
2.5 mg/kg/dose q 8-12h →
renal fx? comorbidities?
ABW = 87.4
~220 mg
END STAGE KIDNEY DISEASE (ESRD) PK
Impair in gut wall barrier function →
+Vd →
__________ through kidneys
DIALYSIS → removes ______ _______ molecules in ______
+abs
excess fluid retention (affects hydrophilic drugs), hypoalbumin, -protein binding
-CL
small unbound, bloodstream (SMALL VD)
LIVER FAILURE PK
3 main factors affecting hepatic clearance
Hepatic blood flow →
Hepatocytes ability to metabolize a medication →
Fraction of unbound medication →
Also, ________ affecting the assessment of renal fx (SCr, CrCL)
+BA for meds w high 1st pass metab
-CYP450 fx
+free drug (-proteins like albumin, CFs)
low muscle mass
Goals of Organ Transplant
_______ “disease”
Improve patient and graft __________
Improve ________
replace
survival
quality of life
TRANSPLANT REJECTION: immune system activation
Signal 1:
Signal 2
Signal 3
antigen activation → antigen + MHC + TCR
COSTIM → CD80/86 + CD28
cytokine signaling → interleukins
INDUCTION immunosuppressants
“Depleting agents” → ________ → 2 agents
“Non depleting agents” → _________ → 1 agent
T cell lysis → thymoglobulin, alemtuzumab
inhib T cells → basiliximab
MAINTENANCE IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
primary immunosuppressants →
adjuvant agents →
CNI, antimetabolites, corticosteroids
mTORi, costim blocker
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS
Agents = 2
MOA: Inhibit calcineurin, __________ is inhibited →
*Dose medications based on _________!
Very ______ therapeutic index
______ levels are markers for AUC
tacrolimus, cyclosporine
inhib IL2 synth → inhib T cell proliferation
levels
narrow
TR
Which brand name of cyclosporine is the NON MODIFIED form and is NOT interchangeable?
Sandimmune
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS ADES
Tacrolimus (3)
BOTH (4)
Cyclosporine (4)
hyperglycemia, alopecia, neurotox
NEPHROTOX, HTN, infxns, EL abnormalities
gingival hyperplasia, hyperlipidemia, hirsutism, gout
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS
Absorption: BA ______ →
Distribution:
t1/2 _____ (2-36h)
Metabolism
variable → tacrolimus -abs w food, Sandimmune dependent on bile, diurnal variation
large Vd, highly protein bound
varies
CYP3A4, Pgp
Based on pharmacokinetic parameters, would dialysis impact tacrolimus levels?
Tacrolimus = High Vd, highly protein bound
A. Yes
B. No
B (small Vd, unbound are affected by dialysis)
CNI DRUG INTERXNS:
CYP3A4 inhibitors = (6)
Effect?
clarithro/erythromycin, azole, nondihydro CCB, protease inhib (-navir), grapefruit juice, CBD prod
+
CNI DRUG INTERXNS:
CYP3A4 inducers / Pgp inducers = 4
Effect?
rifampin, phenytoin, St john wort, carbamazepine
-
CNI DRUG INTERXNS:
Pgp inhibitors = 7
Effect?
amiodarone, dronedarone, propafenone, carvedilol, clarithro/erythromycin, azole, verapamil
+
ANTIMETABOLITES
inhib cell cycle proliferation
Agents 1 + moa
Agent 2 + moa
*Dose based on ________!, NOT levels
mycophenolate → inhib IMPDH
azathioprine → inhib purine synth
side effects
ANTIMETABOLITES
Abs
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
good abs
large Vd
hepatic → MPA to MPAG (inactive) back to MPA, azathioprine prodrug to 6MP
urine as metabs
MYCOPHENOLATE metabolism
undergoes _____________
DDI → Inhibited by ________
DDI → ______ inhibit glucuronidase activity of gut flora → -enterohepatic recirculation → -[MPA]
ADEs → 5
Major DDI
enterohepatic recirculation
cyclosporine
ABs
GI, leukopenia, anemia, TC, teratogenic
birth control
AZATHIOPRINE metabolism
Recommended to test for _________ prior to allopurinol initiation
Xanthine Oxidase inhibitors lead to ________ and _________
ADEs (6)
Major DDI
TPMT deficiency
MS, hepatotox
leukopenia, anemia, TC, pancreatitis, hepatotox, squamous skin cell CA
XO inhib
CORTICOSTEROIDS
MOA:
________ at high doses
-IL2 prod
cytotoxic to T cells
mTOR INHIBITORS
Inhibits cell cycle in all rapidly dividing cells
Agents = 2
MOA: inhib a protein kinase mTOR, _____________
*Dose medications based on __________
sirolimus, everolimus
mammalian target of rapamycin
TR levels
mTOR INHIBITORS
Abs
Distribution
Metabolism
Half life
Excretion
BA 30%, -abs w fatty meals
large Vd
CYP3A4, Pgp
prolonged (adjust doses slowly)
feces
mTOR INHIBITORS
Sirolimus, Everolimus
ADEs → 6
BBW →
^ DONT use within 1st month of tx, consider alternative prior to surgery
TC, anemia, proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, -wound healing, peripheral edema
+risk hepatic/renal artery thrombosis in first 30 days post tx
COSTIMULATION BLOCKER
Agent =
MOA =
May be used in ________ patients ONLY!
BBW →
Belatacept
bind CD80/86
EBV+
lymphomas, malignancies, other infxns
COMMON MAINTENANCE IMMUNOSUPPRESSION REGIMEN =
-
-
-
____ tablets/capsules per day
tacrolimus → goal FK 8-10
mycophenolate
prednisone
15
Someone calls you in the pharmacy to tell you a tacrolimus level returned at 15 and asks what they need to do.
What is your response? (5)
is this a true TR?
What is the goal level is the transplant team going for?
Any recent rejections? infections?
Liver fx?
When was their transplant?
Kidney transplant recipient presents to your pharmacy with a prescription for Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir) for recent diagnosis of COVID.
What do you do?
patient should call txp center → RITONAVIR CYP INHIBITOR
You are reviewing a patient’s medication list and notice an interaction between sirolimus and diltiazem.
What do you do?
If it is new or +dose, they should call txp center
Mneumonic for need of DIALYSIS
A acidosis
E EL abnormalities
I intoxication
O overload
U uremia
Most common types of dialysis
Inpatient/outpatient
exclusively INPATIENT (ICU, etc)
iHD, PD
CVVH, CVVHD
IRRT vs CRRT
(intermed renal replacement therapy vs continuous)
IRRT advantages
IRRT disadvantages
CRRT advantages
CRRT disadvantages
rapid removal, simpler, no anticoagulation
hypotension, rapid V/EL changes
hemodynamics, adjustable
complex, anticoagulation, hypothermia, limited evidence on med dosing
DRUG CHARACTERISTICS THAT IMPACT DIALYSIS REMOVAL
Molecular weight
Vd
Protein binding
Renal vs nonrenal clearance → if drug _____ renal CL, then kidney failure unlikely to have much impact
relative to pore size of filter → small <500, mod 500-1000, large >1000
small Vd removed (ex AGs, theophylline)
unbound
<25%
Factors impacting FREE FRACTION of drug (4)
critical illness
drug interxns
uremia
pH
DIALYSIS CHARACTERISTICS that effect drug removal
__________ of filter/semipermeable membrane
__________ of semipermeable membrane
______ of dialysis
pore size
surface area
type
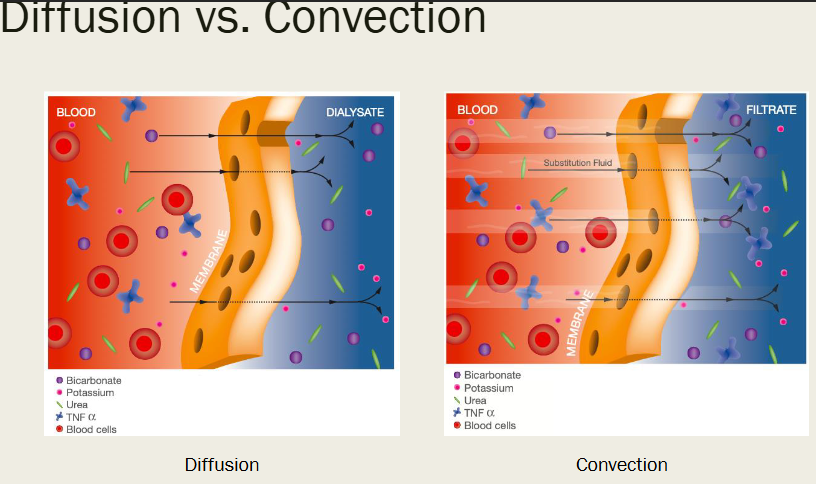
DIALYSIS MEMBRANES
Low vs high flux membranes
Diffusion → used by …
+MW, -CL
Dialysis saturation (capacity of drug to diffuse)
low = smaller pores, high = large
iHD, CVVHD, PIRRT
conc in dialysate / plasma conc
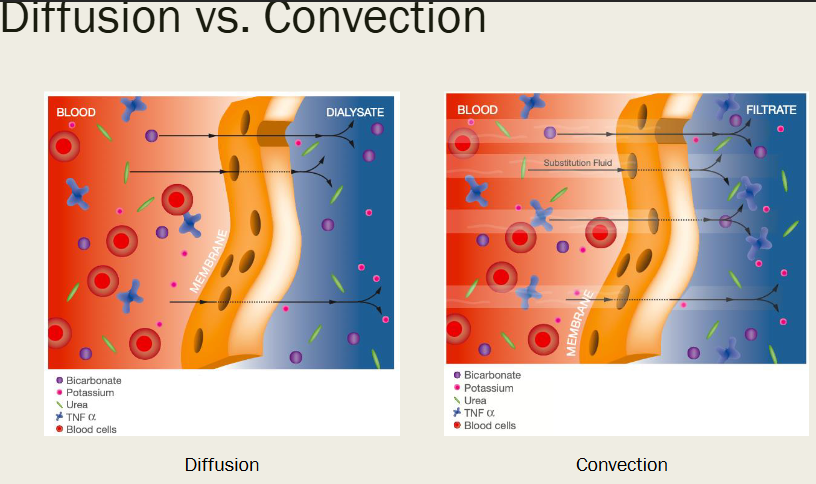
CONVECTION / HEMOFILTRATION
pumped through a filter
Used by _______
Better removal of _____ solutes
*Sieving coefficient =
Dependent on _________ and ______
CVVH
large
drug conc in ultrafiltrate / drug plasma conc
age of memb, filtration fraction
FDA requires drug manufacturers to complete __________ for renally eliminated drugs in patients on chronic hemodialysis
PK studies

Which medication may have decreased dialysis clearance due to increased protein binding?
A. Cefepime
B. Vancomycin
C. Tobramycin
D. Phenytoin
D (95% protein bound)
Which medication may have increased dialysis clearance due to its Vd?
A. Cefepime
B. Vancomycin
C. Tobramycin
D. Phenytoin
C (small Vd)
Which medication may have decreased dialysis clearance due to its molecular weight?
A. Cefepime
B. Vancomycin
C. Tobramycin
D. Phenytoin
B (large Mw)
DIALYSIS THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING
____________ is helpful/necessary
Ensure sufficient time has lapsed after HD is complete to allow for _____ to occur before drawing levels
serum conc
rebound
TACROLIMUS Goal TR levels
Days post-transplant (UAMS Kidney transplant protocol)
1-90
90-365
>365
8-10
6-8
5-7
Recall: Dosing based on …
CNIs (tacrolimus, cyclosporine)
Antimetabolites (MPA, azathioprine)
mTOR inhibitors (sirolimus, everolimus)
levels
side effects
TR levels
Which transplant meds are CYP3A4 + Pgp substrates?
CNIs
mTORi
Order of efficient drug removal via dialysis
CVVHDF > CVVHD > CVVH > PIRRT >/= iHD
Drug characteristics that impact dialysis removal (4)
mw
Vd
Protein binding
Renal vs non renal CL
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
_____ efficient at drug removal
______ need replacement or increased doses
May add _____ to dialysate
Less
Rarely
Meds
If the half-life of sirolimus is 60 hours, when should you plan to get a steady state TR level after starting the medication or switching doses?
A. 1 day after starting sirolimus
B. 10 days after starting sirolimus
C. Before the 4th dose of sirolimus
D. Sirolimus is not dosed based on TR levels
B (steady state 3-5 half lives)
Which statement is true comparing the PK/PD differences between an 80 yo grandmother GM (5’4” and 200 lbs) and her 7 yo grand daughter GD if giving phenytoin to both patients?
A. Based on age GM would require a larger dose than GD due to faster metabolism
B. Based on age GM will have decreased muscle mass requiring a larger dose than GD
C. Both can be treated the same
D. Based on age GD would require a larger dose than GM based on better renal function
E. Based on age GD will have more albumin and will require a larger dose than GM
E