Chemistry 11: Balancing Equations and Reaction Types
1/189
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Coefficient
The number in front of a chemical formula that indicates the number of molecules or formula units.
Subscript
A small number inside the chemical formula that indicates the number of atoms in a molecule or number of ions in a formula unit.
Reactants and Products State Notation
's' for solid, 'l' for liquid, 'g' for gas and 'aq' for aqueous.
Balancing Equations
To balance the equation, multiply the coefficients in front of the reactants and/or products without changing the subscripts.

Oxygen Molecules in Reaction
There are 2 oxygen molecules in the reaction.
Hydrogen Atoms in Methane
There are 4 hydrogen atoms in a molecule of methane, CH4.
Carbon Dioxide Molecules in Reaction
There is 1 carbon dioxide molecule in the reaction.
Water Molecules in Reaction
There are 2 water molecules in the reaction.
Hydrogen Atoms in Two Water Molecules
There are 4 hydrogen atoms in two molecules of water, H2O.
Synthesis Reaction
A chemical reaction where two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex product.

Example of Synthesis Reaction
Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
Decomposition Reaction
A chemical reaction where a single compound breaks down into two or more elements or new compounds.
Example of Decomposition Reaction
2 H2O2(l) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g)
Decomposition of a Base
A decomposition of a base produces a metal oxide and water.
Decomposition of an Acid
A decomposition of an acid produces a non-metal oxide and water.
Carbonate Decomposition
Carbonates decompose to carbon dioxide and a metal oxide.
Chlorate Decomposition
Chlorates decompose to oxygen gas and a metal chloride.
Combustion Reaction
A chemical reaction where a compound reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water, and energy (exothermic).

Single Displacement
A chemical reaction where an element takes the place of another element in the compound.
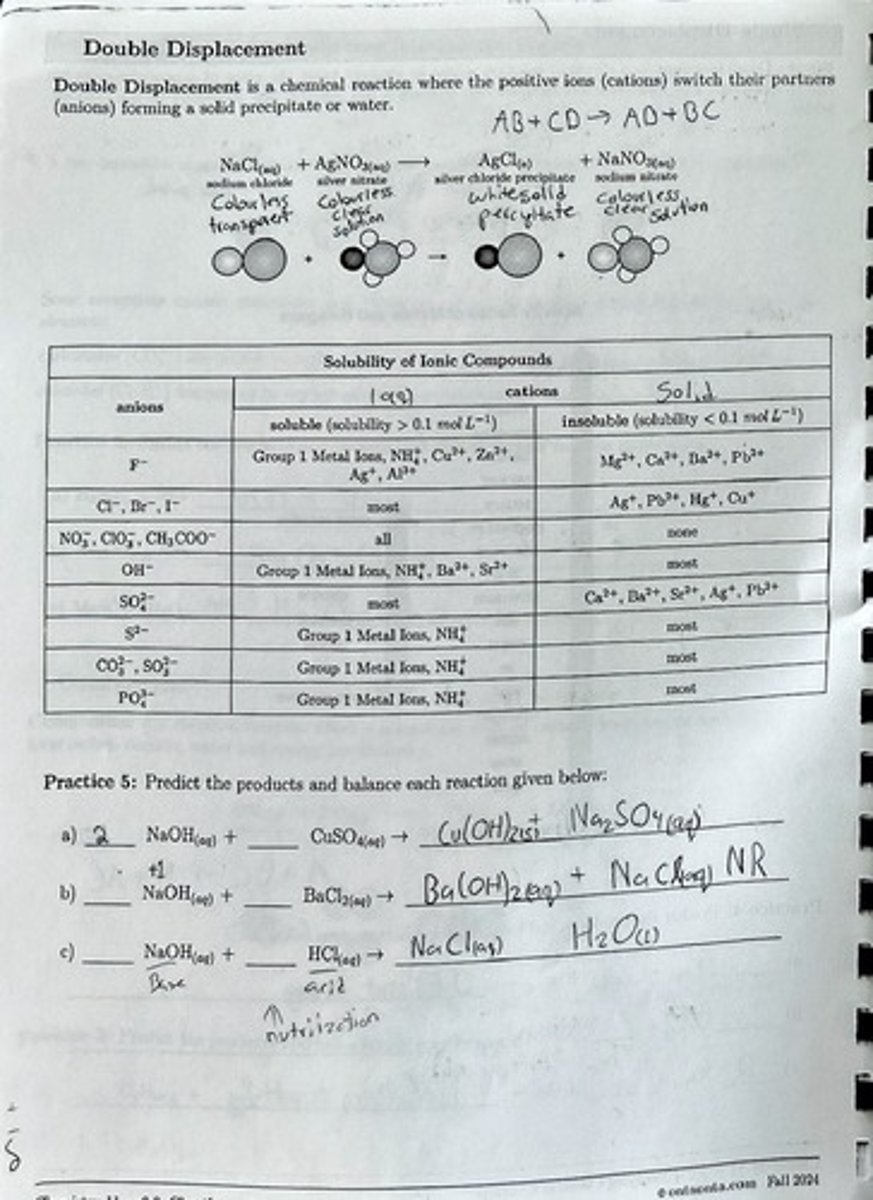
Double Displacement
A chemical reaction where the positive ions (cations) switch their partners (anions) forming a solid precipitate or water.
Activity Series of Metals and Halogens
A list that ranks metals and halogens based on their reactivity.
Solubility of Ionic Compounds
A classification of ionic compounds based on their solubility in water.
Magnesium Metal Reaction with Hydrochloric Acid
Produces hydrogen gas and magnesium chloride.
Sodium Metal Reaction with Oxygen Gas
Produces sodium oxide.
Lithium Metal Reaction with Copper(II) Chloride
Yields aqueous lithium chloride and copper metal.
Sodium Sulfate Reaction with Barium Nitrate
Gives sodium nitrate and barium sulfate.
Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Heating
When heated, water escapes as vapor leaving the anhydrous salt.
Barium Hydroxide Reaction with Nitric Acid
Produces water and barium nitrate.
Magnesium
A metal that can displace copper in a single displacement reaction.
Copper(II) Chloride
A compound that reacts with magnesium in a single displacement reaction.
Sodium Chloride
A compound that reacts with silver nitrate in a double displacement reaction.
Silver Nitrate
A compound that reacts with sodium chloride in a double displacement reaction.
Silver Chloride Precipitate
Formed as a result of the double displacement reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate.
Sodium Nitrate
A product formed in the double displacement reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate.
Cations
Positively charged ions that can switch partners in double displacement reactions.
Anions
Negatively charged ions that can switch partners in double displacement reactions.
Soluble Compounds
Compounds with solubility greater than 0.1 mol L-1.
Insoluble Compounds
Compounds with solubility less than 0.1 mol L-1.
Group 1 Metal Ions
Ions that are generally soluble in water.
Aqueous solution
An ionic salt dissolved in water, designated as aqueous (aq).
Precipitate
An insoluble solid that does not dissociate back into ions.
Spectator ions
Dissociated ions that do not participate in the reaction.
Total Ionic Equation (TIE)
An equation that shows all the ions present in a solution.
Net Ionic Equation (NIE)
An equation that shows only the ions that participate in the reaction.
Double Displacement Reaction
A reaction where two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.

Single Displacement Reaction
A reaction where one element displaces another in a compound.

Dissociation
The process of ionic compounds separating into their ions in water.
Copper(II) sulfate
A chemical compound that can react with sodium hydroxide.
Sodium hydroxide
A strong base that can react with acids to form water and a salt.
Sulfuric acid
A strong acid that can react with bases to form water and a salt.
Balanced Equation
An equation where the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides.

Ionic compound
A compound composed of ions held together by electrostatic forces.
Copper metal
A metal that can displace silver from silver nitrate solution.
Lead(II) nitrate
An ionic compound that can react with sodium carbonate.
Sodium carbonate
An ionic compound that can react with lead(II) nitrate.
Hydrogen gas
A product formed in reactions involving acids and metals.
Copper(II) nitrate
An ionic compound that can be formed in displacement reactions.
Silver chloride
A precipitate formed when sodium chloride and silver nitrate are mixed.
Chemical reaction
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.

Ionic equation
An equation that represents the dissociation of ionic compounds in solution.
Aqueous copper(II) chloride
A solution that reacts with lead(II) nitrate.
Balanced Equation for copper(II) chloride and lead(II) nitrate
CuCl2(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) → PbCl2(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq)
A piece of magnesium metal in hydrochloric acid
A reaction that produces magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas.
Balanced Equation for magnesium and hydrochloric acid
Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
A piece of magnesium metal in copper(II) nitrate
A reaction that produces copper and magnesium nitrate.
Balanced Equation for magnesium and copper(II) nitrate
Mg(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) → Cu(s) + Mg(NO3)2(aq)
A piece of copper metal in hydrochloric acid
A reaction that does not produce any reaction.
Predicting products and balancing reactions
The process of determining the products of a reaction and ensuring the equation is balanced.
Sodium sulfate reacts with strontium nitrate
A reaction that produces sodium nitrate and strontium sulfate.
Balanced Equation for sodium sulfate and strontium nitrate
Na2SO4(aq) + Sr(NO3)2(aq) → SrSO4(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq)
Type of reaction for sodium sulfate and strontium nitrate
Double Displacement (DD)
Barium hydroxide neutralized with hydrochloric acid
A reaction that produces barium chloride and water.
Balanced Equation for barium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
Ba(OH)2(aq) + 2 HCl(aq) → BaCl2(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
Type of reaction for barium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
Double Displacement (DD)
Ethane gas burns in oxygen gas
A combustion reaction producing carbon dioxide and water.
Balanced Equation for ethane combustion
2 C2H6(g) + 7 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g)
Type of reaction for ethane combustion
Combustion (C)
Magnesium metal burns in oxygen
A synthesis reaction producing magnesium oxide.
Balanced Equation for magnesium burning in oxygen
2 Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2 MgO(s)
Type of reaction for magnesium burning in oxygen
Synthesis (S)
Calcium metal placed in hydrochloric acid
A single displacement reaction producing calcium chloride and hydrogen.
Balanced Equation for calcium and hydrochloric acid
Ca(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Type of reaction for calcium and hydrochloric acid
Single Displacement (SD)
Aqueous sodium hydroxide added to magnesium sulfate
A reaction producing magnesium hydroxide and sodium sulfate.
Balanced Equation for sodium hydroxide and magnesium sulfate
2 NaOH(aq) + MgSO4(aq) → Mg(OH)2(s) + Na2SO4(aq)
Mole
The unit of measurement for an amount of substance, containing 6.02 x 10^23 of atoms, molecules, ions, or other particles.
Avogadro Number (NAV)
Represents the number of atoms, molecules or ions in one mole of substance, equal to 6.02 x 10^23 atoms/molecules/particles.

Water Molecules Calculation Example
Calculate the number of water molecules in 22 moles of water: 22 mol H₂O x (6.02 x 10^23 H₂O molecules/1 mol H₂O) = 1.3 x 10^25 H₂O molecules.
Silver Atoms Calculation Practice
Calculate the number of silver atoms in 0.12 moles of silver metal: 0.12 moles Ag x (6.02 x 10^23 Ag atoms/1 mol Ag) = 7.2 x 10^22 Ag atoms.
Oxygen Mole Calculation Example
Calculate the moles of 8.8 x 10^23 oxygen molecules, O₂: 8.8 x 10^23 O₂ molecules x (1 mol/6.02 x 10^23 O₂ molecules) = 1.5 mol O₂.
Carbon Dioxide Moles Calculation Practice
Calculate the amount (number of moles) of carbon dioxide for 1.2 x 10^22 CO₂ molecules: 1.2 x 10^22 CO₂ molecules x (1 mol/6.02 x 10^23 CO₂ molecules) = 0.020 mol CO₂.
Water Molecules Calculation Practice
Calculate the number of water molecules in 14 moles of water: 14 mol H₂O x (6.02 x 10^23 H₂O molecules/1 mol H₂O) = 8.4 x 10^24 H₂O molecules.
Silver Atoms Calculation Practice 2
Calculate the number of atoms in 0.33 moles of silver: 0.33 moles Ag x (6.02 x 10^23 Ag atoms/1 mol Ag) = 2.0 x 10^23 Ag atoms.
Formula Units Calculation Practice
Calculate the number of formula units in 56 moles of magnesium hydroxide: 56 moles Mg(OH)₂ x (6.02 x 10^23 Mg(OH)₂ formula units/1 mol Mg(OH)₂) = 3.4 x 10^25 Mg(OH)₂ formula units.
Iron (II) Nitrate Formula Units Calculation Practice
Calculate the number of formula units in 1.4 moles of iron (II) nitrate: 1.4 moles Fe₂(NO₃)₂ x (6.02 x 10^23 Fe₂(NO₃)₂ formula units/1 mol Fe₂(NO₃)₂) = 8.4 x 10^23 Fe₂(NO₃)₂ formula units.
Water Mole Calculation Practice 2
Calculate the amount (number of moles) of 1.5 x 10^22 water molecules: 1.5 x 10^22 H₂O molecules x (1 mol/6.02 x 10^23 H₂O molecules) = 0.025 mol H₂O.
Oxygen Mole Calculation Practice
Calculate the amount of 4.3 x 10^25 oxygen molecules: 4.3 x 10^25 O₂ molecules x (1 mol/6.02 x 10^23 O₂ molecules) = 71 mol O₂.
Molar Mass
The mass in grams of 1 mole of a substance.

Molar Mass of Water Calculation Example
Calculate the Molar Mass of water, H₂O: MMH₂O = 2(MMH) + 1(MMO) = 2(1.01 g) + 16.00 g = 18.02 g.

Molar Mass of Magnesium Phosphate Calculation Practice
Calculate the Molar Mass of magnesium phosphate: MMMg₃(PO₄)₂ = 3(MMmg) + 2(MMP) + 8(MMO) = 3(24.36 g) + 2(30.975 g) + 8(16.00 g) = 262.879 g.