Marine Ecosystems 1
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
ocean’s earliest navigators
pacific islanders
considered to be the first marine biologist
aristotle - described 117 fish species
james cook
first to make scientific observations, went on 3 voyages, first to use a chronometer, killed by native hawaiians (1779)
charles darwin and sms beagle
proposed theory of evolution, theory of how coral atolls form
edward forbes
malacologist (clams and snails), found animals density and diversity decreases with depth
challenger deep
deepest known point of seabed (mariana trench)
d/v glomar challenger
continental drift and seafloor spreading evidence, age of seafloor determined
d/v/ joides resolution
drills into ocean core, shamar was on it i think
d/v chikyu
drill to mantle/seismogenic zone
sonar (sound navigation and ranging)
developed for growing threat of submarine warfare
SCUBA (self-contained underwater breathing apparatus)
developed for automobiles to run on compressed natural gas
alfred wegener
first to identify pangea and theory of continental drift
clues to plate tectonics
fit of continents separated by ocean
matching structures across present oceans
distribution of fossil organisms with limited geographic ranges
volcano distribution
theory of the geodynamo
mechanism by which a celestial body generates a magnetic field
magnetic poles
point of compass needle, slightly offset of geographic poles
earth rotation
geographic north and south poles
paleomagnetism
magnetic polarity preserved in igneous rock, determines when rocks formed
magnetic reversals
176 reversals in the past 76 million yrs, unpredictable
marie tharp
discovery of the mid atlantic ridge
3 types of plate boundaries
divergent, convergent, transform
divergent boundaries
within continental crust: continental rifting, formation of new ocean
within oceanic crust: seafloor spreading
ocean-ocean divergent land forms
mid ocean ridges, rift valleys, seafloor spreading, ocean basins, hydrothermal vents
continental-continental divergent land forms
rift valleys, new oceans
driving forces for divergent motion
mantle plumes
ocean crust density
as it gets older, contracts and gets denser
ocean-ocean convergent boundary
ocean trench (subduction), accretionary wedge, volcanic island arc
accretionary wedge
pile of deformed ocean sediment scraped off subducting plate
volcanic island arc
partial melting of subducting slab
ocean-continental convergent plate boundary
ocean crust denser, always subducts under continental
island arcs
curvature of the Earth, the subduction zone, and the chain of islands, is arc-shaped
tall oceanic volcanos
grow tall enough, become islands
continental-continental convergent
mountains
3 growth stages of an ocean
embryonic: uplift
juvenile: divergence, narrow seas
mature: divergence, ocean basin w continental margins
growth of an ocean
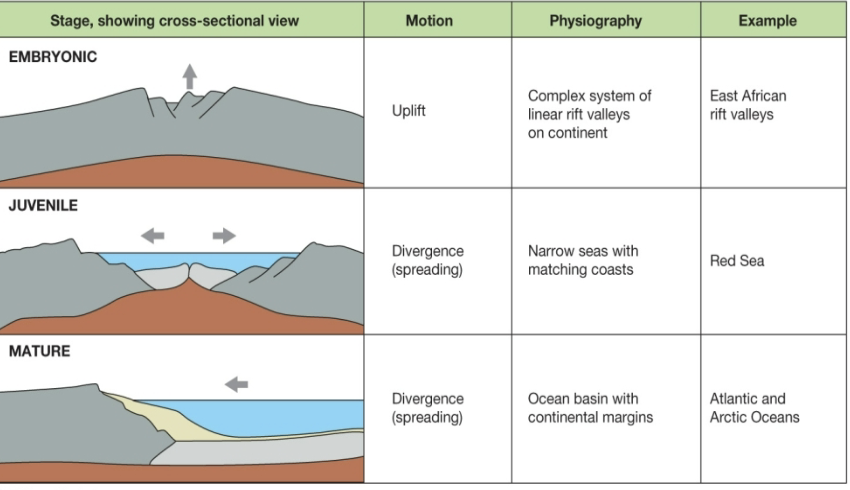
3 destruction phases of an ocean
declining: convergence (subduction)
terminal: convergence (collision) and uplift
suturing: convergence and uplift
destruction of an ocean
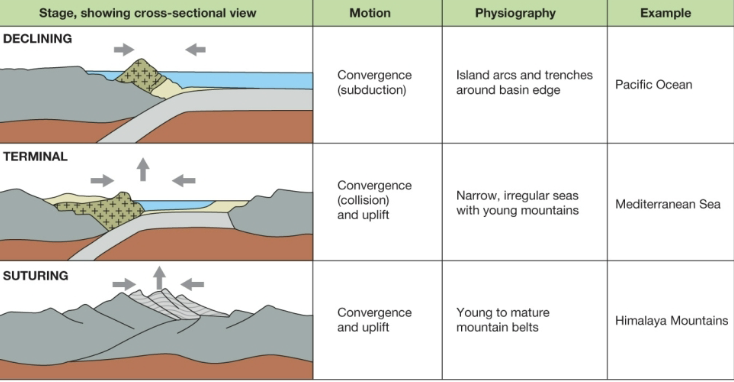
ocean life cycle
made at mid ocean ridges, consumed at subduction zones
hotspots
isolated plumes in the mantle, melted lithosphere rises through crust, forms a seafloor volcano, stationary so as plate moves forms island arc chain
atoll
ring shaped coral reef system w central lagoon rising from deep water
seamount
mountain rising from ocean seafloor, does not reach surface (underwater mountain)
guyot
flat topped seamount
formation of atolls
volcano acquires fringing coral reef
volcano becomes inactive begins to erode and subside (sink)
reef continues to grow upwards at a rate faster than
rate of volcano sinking
only growing fringing reef remains with deep central
lagoon
oldest to youngest
guyot, seamount, island, hotspot
properties of water
high heat capacity, high heat of evaporation, high dissolving power, high transparency (absorbs infrared, ultraviolet), high latent heat of melting
thermocline
transitional layer between warmer mixed water and cooler deep water
salinity
grams of dissolved salt per 1000 g seawater
salinity controlled by
evaporation, sea ice formation, precipitation, river runoff
seawater important elements
chlorine, sodium, magnesium, sulfur, calcium, potassium, bromine, carbon
principle of constant element ratios
ratios are constant even with varying salinity
coriolis effect
movement of fluids in relation to earth beneath results in deflections.
right in NHem, left in SHem
upwelling
coastal winds + coriolis effect (
thermohaline circulation controlled by
location of formation of water, density, coriolis (to a degree)
global ocean conveyor belt
origin: high lat surface waters
high salinity + low temp = high density
circulation types and effects
coriolis: upwelling, deflection of currents
surface: gyres, eastern boundary currents
thermohaline: water masses (density determined)
fetch
amount of open water a wind blows over
larger fetch = bigger waves
waves
Highest point of a wave is the crest, the lowest point is the trough.
Distance between two crests is the wavelength
Time is takes for a wave to pass by a set point is the wave period.
tides
waters on the side of the earth that are closer to the moon cause a high tide
waters on the side of the earth further away from the moon cause a low tide
tides are usually higher at night and lower during the daytime
tidal range = diff between high and low tides
diurnal tide cycle
one high tide one low tide every lunar day
semidiurnal tide cycle
two high tides and two low tides per lunar day, approx equal in size
mixed semidiurnal tide cycle
two high tides and two low tides per lunar day, diff in size
four organic molecules
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acid
made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
carbohydrates examples
cellulose, chitin
proteins examples
enzymes, hormones, structural
lipids uses
insulating layer, buoyancy, energy storage
levels of organization
Population: group of organisms of the same species
living in the same habitat
Community: all of the species that live in a particular habitat
Ecosystem: a combination of the community and the physical environment
diffusion vs osmosis
diffusion = mvmt of solutes
osmosis = mvmt of water
osmoconformers
internal concentration varies as the salinity in the water around them changes
tolerate narrow range of salinities
osmoregulators
control their internal concentrations of solutes and water
tolerate wider range of salinities
ectotherms
generate body heat metabolically, heat is
rapidly lost so organisms cannot maintain a constant internal body temp; matches that of the surrounding
environment
endotherms
retain most metabolic heat, and body temp stays higher that that of the surrounding environment
poikilotherms
body temp varies with the temp of the surrounding environment
homeotherms
regulates body temp
asexual reproduction examples
fission: two of equal size
budding: small buds form and break off
vegetative reproduction: underground stem sent sideways, new plants sprout from it
colonial reproduction
genetically identical, compose a module if connected
natural vs sexual selection
natural: increase fitness
sexual: increase mating success
two types of sexuality
gonochoristic: separate sexes
hermaphroditism: can have male or female function (simultaneous or sequential)
cyanobacteria
photosynthetic bacteria most
important in the marine enviro
stromatolites
massive calcareous mounds formed by cyanobacteria
marine bacteria role
break down dead organic matter forming detritus
chemosynthetic
energy from chemical compounds
heterotrophs
energy from organic matter by means of respiration
marine diatoms
photosynthetic, yellow brown in color, silica shell, reproduce by cellular division
marine dinoflagellates
shape enforced by cellulose, two flagella, some are bioluminescent
zooxanthellae
dinoflagellates have symbiotic relationship with
many organisms
foraminiferans
exclusively marine, non photosynthetic (are heterotrophs), shells of calcium carbonate, pseudopods
radiolarians
planktonic, shell of silica, pseudopods
silicoflagellates
star shaped silica skeleton, two flagella of varying lengths
coccolithophores
exclusively marine, photosynthetic, shells of calcium carbonate, annual blooming events
ciliates
hair like cilia, most live as solitary cells
biological classifications
Dear – Domain
King – Kingdom
Philip – Phylum
Come – Class
Over – Order
For – Family
Great – Genus
Spaghetti – Species
species
individuals that have many characteristics in
common and the ability to breed successfully with each other.
3 cell layers
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
coelem
cavity that develops in embryo within mesoderm
deuterostome
symmetrical/radial cleavage
protostome
asymmetric/spiral cleavage
sponges
all are sessile (attached), filter feeders through pores, asymmetrical body plan, asexual budding and sexual reproduction
cnidarians
radial symmetry, free swimming or attached forms, nerve net
arthropods
phylum with largest number of species
chitin exoskeleton, must be shed to grow
crustaceans: dominant marine arthropods, open circulatory system, internal fertilization
planktonic organisms
microscopic organisms that cannot propel themselves/are weak swimmers
drifters or floaters that are carried along by tides or currents
copepods
eat phytoplankton by filter feeding
are primary consumers