Sensation and Perception
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Sensation
Process of receiving and representing stimulus energies from environment
Sensory receptors
Nerve endings that respond to stimuli
Perception
Process of organizing and interpreting sensory information
Bottom-up processing
Analysis starting with sensory receptors and integrating sensory information
Top-down processing
Information processing guided by higher-level mental processes
Selective attention
Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
Inattentional blindness
Failing to see visible objects when attention is directed elsewhere
Change blindness
Failing to notice changes in the environment
Transduction
Conversion of stimulus energies into neural impulses
Psychophysics
Study of relationships between physical characteristics of stimuli and psychological experience
Absolute thresholds
Minimum stimulus needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
Signal detection theory
Theory predicting how and when we detect faint stimuli amid background stimulation
Subliminal
Below threshold for conscious awareness
Difference thresholds
Minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time
aka just noticeable difference (JND)
Priming
Activation of certain associations, predisposing perception, memory, or response
Weber's Law
Principle that two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage to be perceived as different
Sensory adaptation
Diminished sensitivity due to constant stimulation
Perceptual set**
Mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
Extrasensory perception (ESP)**
Controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input
Parapsychology**
Study of paranormal phenomena, including ESP and psychokinesis
Wavelength
Distance from peak of one light or sound wave to the peak of the next
Hue
Dimension of color determined by wavelength of light
Intensity
Amount of energy in a light or sound wave
Cornea
Eye's clear, protective outer layer
Pupil
Adjustable opening in the center of the eye
Iris
Ring of muscle tissue that controls the size of the pupil opening
Lens
Transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to focus images on the retina
Retina
Light-sensitive inner surface of the eye
Accommodation
Process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus on near or far objects
Rods
Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray
Cones
Retinal receptors that detect fine detail and color
Fovea
Central focal point in the retina
Optic nerve
Nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
Blind spot
Point where optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a blind spot
Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory
Theory that the retina contains three different types of color receptors
Opponent-process theory
Theory that opposing retinal processes enable color vision
Feature detectors
Nerve cells in the brain's visual cortex that respond to specific features of the stimulus
Parallel processing
Processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously
Gestalt
An organized whole
Figure-ground
Organization of the visual field into objects and their surroundings
Grouping
Perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups
Depth perception
Ability to see objects in three dimensions
Visual cliff
Laboratory device for testing depth perception
Binocular cues
Depth cues that depend on the use of two eyes
Retinal disparity
Binocular cue for perceiving depth
Monocular cues
Depth cues available to either eye alone
Phi phenomenon
Illusion of movement created by blinking lights
Perceptual constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging despite changing retinal images
Color constancy
Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color
Perceptual adaptation
Ability to adjust to changed sensory input
Audition**
Sense of hearing
Frequency**
Number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
Pitch**
Experienced highness or lowness of a tone
Middle ear**
Chamber between the eardrum and cochlea
Cochlea**
Coiled, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear
Inner ear**
Innermost part of the ear
Sensorineural hearing loss**
Hearing loss due to damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or auditory nerves
Conduction hearing loss**
Hearing loss due to damage to the mechanical system conducting sound waves
Cochlear implant**
Device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve
Place theory**
Theory linking pitch with the place where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated
Frequency theory**
Theory linking pitch with the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve
Gate-control theory
Theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that blocks pain signals
Olfaction
Sense of smell
Kinesthesia
Sense of movement and position of individual body parts
Vestibular sense
Sense of body movement and position for balance
Sensory interaction
Principle that one sense may influence another
Embodied cognition
Influence of bodily sensations on cognitive preferences and judgments
anosmia
the complete loss of smell
closure
tendency to overlook completeness to perceive the whole

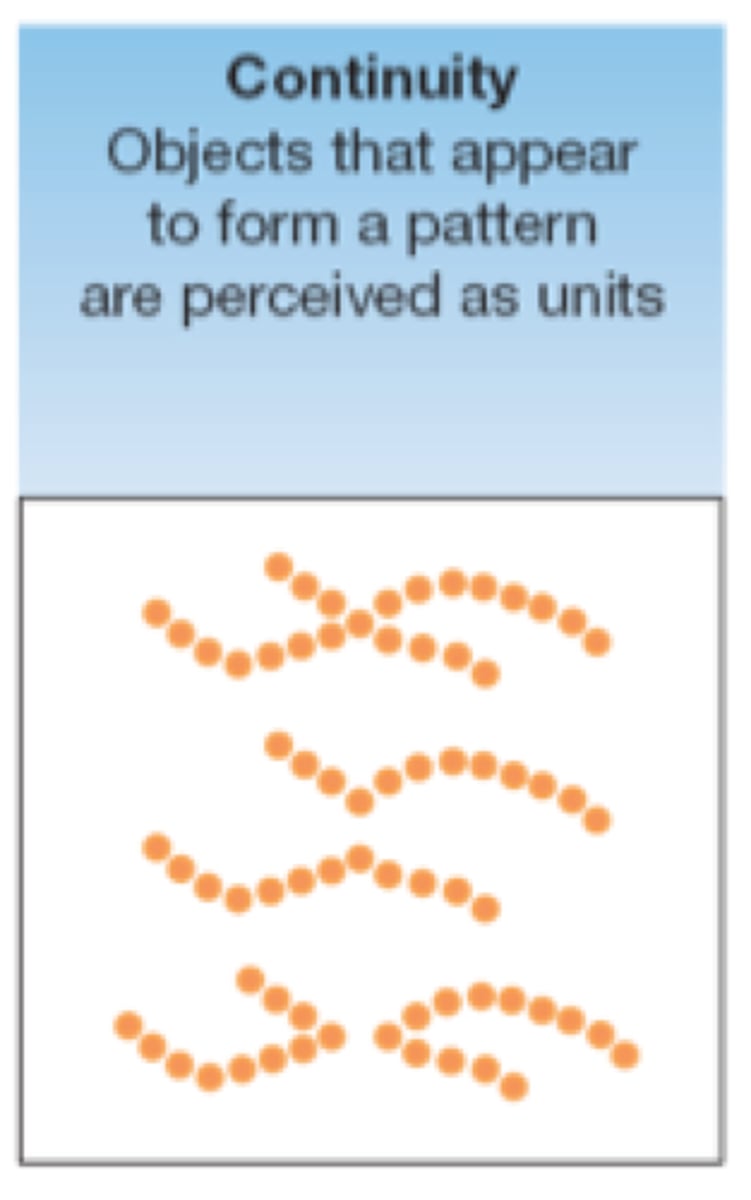
continuity
items that continue a pattern or direction are grouped as a pattern
proximity
when objects are close to each other, we group them together
dichromacy
a form of color blindness