Power and Authority: Post-WWI Treaties and Dictatorships
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Purpose of the Paris Peace Conference?
To discuss peace moving forward and punishments for certain countries after World War I.
Who participated in the Paris Peace Conference?
USA (Woodrow Wilson), Britiain (Lloyd George), France (Georges Clemanceu), Italy (Vittorio Orlando)
What did the Paris Peace Conference focus on?
Reviewing and finalising the treaties that concluded World War I and their outcomes.
Woodrow Wilson goals regarding post-WWI treaties?
Sought minor or greatly diminished repercussions for Germany to ensure no further conflicts, embodying an idealist approach to peace.
Lloyd George's approach to post-WWI treaties?
A pragmatic stance, advocating for balanced penalties while prioritizing his nation's strategic advantages.
Georges Clemenceau's stance on Germany after WWI?
An unyielding demand for severe and complete reparations from Germany.
What were the key terms imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles?
Full blame for WW1
Reparations
Limited military forces
What were the main consequences of the Treaty of St Germain for Austria?
The Treaty of St Germain involved major land redistributions and the creation of a land-locked state.
What were the main characteristics of dictatorships that emerged after WWI?
Dictatorships featured a single leader with full control, a radical program for change, a cult of personality, and control over the economy and military.
Name two notable dictators of WWII.
Benito Mussolini and Adolf Hitler.
What political conditions contributed to the rise of dictatorships after WWI?
Post-war peace treaties, ineffective democracies, and political instability contributed to the rise of dictatorships.
How did economic conditions after WWI facilitate the rise of dictatorships?
Countries faced large debts, paying reparations, and economic crises, leading to instability and discontent.
What social factors contributed to the rise of dictatorships after WWI?
The rise of nationalism, scapegoating of minority groups, and poor living conditions during and after the war contributed to the rise of dictatorships.
What was unique about the dictatorship that emerged in Russia?
Russia faced difficulties with Nicholas II and the Provisional Government, leading to the rise of the Bolsheviks and a Marxist ideology.
What were the main challenges Italy faced after WWI?
Italy was not given promised territories from the Treaty of Versailles, suffered from inflation, high unemployment, and a strong Mafia presence.
What role did Japan's military play in its post-WWI government?
The military gained popularity after the Great Depression, leading to a strong relationship with the emperor and aggressive policies.
What were the main features of Stalinism in Russia?
Stalinism included censorship, use of terror against political opposition, a centralized one-party system, and a cult of personality.
What characterized Mussolini's regime in Italy?
Mussolini's regime was a totalitarian dictatorship that maintained good relations with the Catholic Church, rejected communism, and promoted imperial expansion.
How did Japan's nationalism influence its government after WWI?
Japan's wounded nationalism and economic crisis from the Great Depression led to a desire for independence from the West and aggressive military policies.
What was the Weimar Republic?
The Weimar Republic was the democratic government established in Germany after WWI, lasting from 1919 to 1933.
What were the main phases of the Weimar Republic?
The phases included: 1918-1919: The Beginning, 1919-1923: The Crisis Years, 1923-1928: The Golden Years, and 1929-1933: End of Weimar.
What was Article 48 in the Weimar Constitution?
Article 48 allowed the German president to bypass the Reichstag to pass laws in a state of emergency.
What was the Stab in the Back Myth?
The Stab in the Back Myth was the belief that the Weimar Republic betrayed Germany by signing the Treaty of Versailles, leading to a loss of trust.
What was the significance of the Kapp Putsch in 1920?
The Kapp Putsch was a failed coup where the army refused to protect the Weimar Republic, highlighting the government's instability.
What were the economic conditions that led to the collapse of the Weimar Republic?
The naval blockade after the armistice, hyperinflation, high unemployment, and the Great Depression contributed to the collapse.
What was the Beer Hall Putsch and its outcome?
The Beer Hall Putsch was a failed coup led by Hitler in 1923 that resulted in his imprisonment, during which he wrote Mein Kampf.
How did Hitler consolidate power in the early 1930s?
Hitler called for new elections, prevented communist campaigning, and exploited the Reichstag fire to gain more power.
What incident was a Dutch communist blamed for, which Hitler used to promote communism negatively?
The Reichstag Fire.
What was the purpose of the Reichstag Fire Decree?
To prevent personal freedom and provide Hitler with a legal boost for his dictatorship.
What strategy did the NSDAP use despite not winning a majority in elections?
They formed coalitions with other parties to gain control over industries and businesses.
What was the Enabling Act and what power did it grant?
It allowed the government to make laws without the Reichstag for 4 years, consolidating Nazi power.
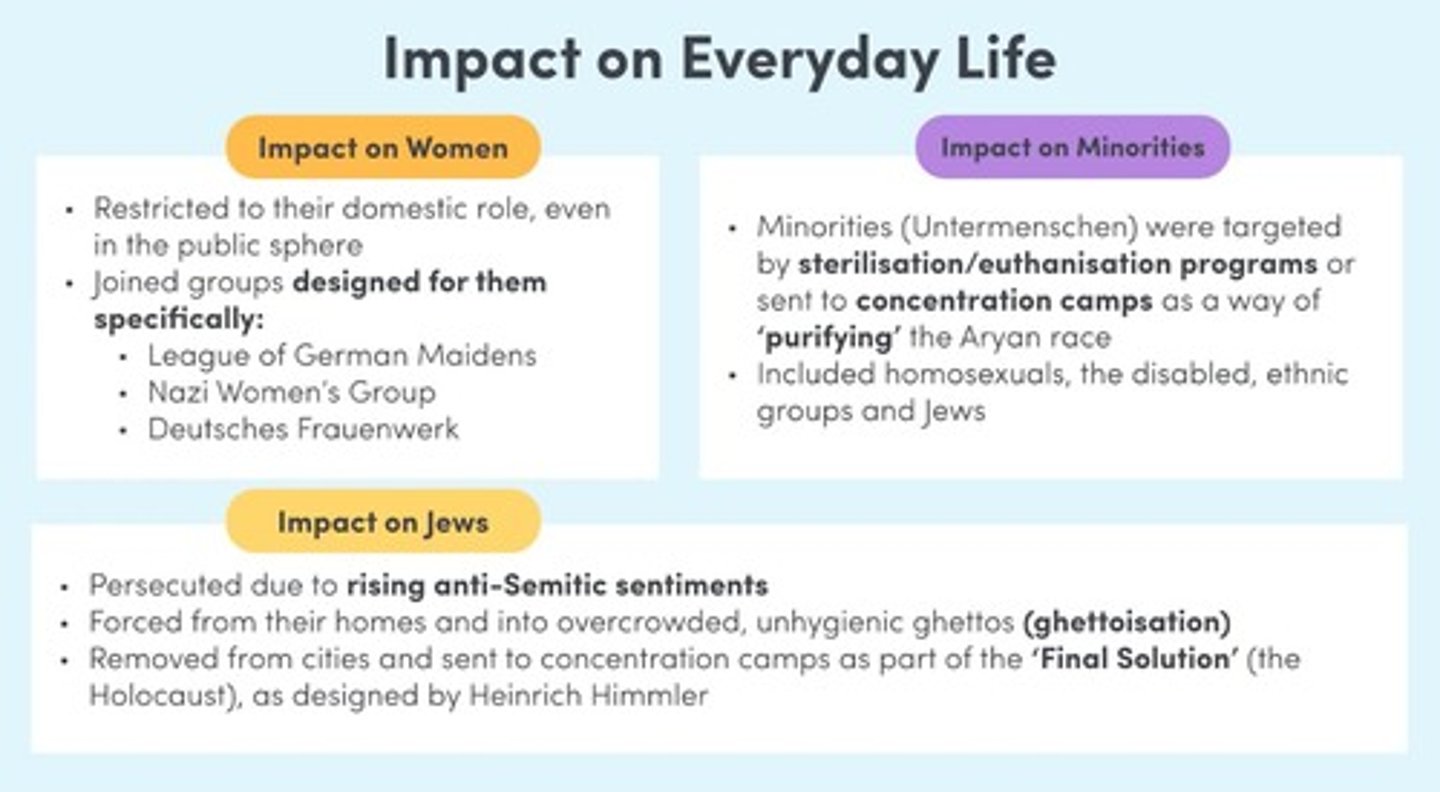
What actions did the Nazis take against Jewish people and other undesirables?
They boycotted Jewish businesses and removed Jews from civil jobs, highlighted by the Book Burnings.
What laws did the Nazis pass to eliminate their political opponents?
They removed opponents from civil service, banned strikes and trade unions, and prohibited new political parties.
What does Gleichschaltung refer to in Nazi Germany?
The process of nazification of German society affecting all aspects of life.
What was the Night of Long Knives?
A purge ordered by Hitler to eliminate SA leaders and consolidate power, resulting in the execution of 400 opponents.
What happened after President Hindenburg's death?
Hitler combined the roles of President and Chancellor, declaring himself Fuhrer and making the army swear loyalty to him.
What is an ideology?
A system of ideas that shape the values, attitudes, and policies of a society.
What is Aryanism and its significance in Nazi ideology?
A belief in the superiority of the Aryan race, justifying imperialism and conquest of 'lesser' races.
What does GrossDeutschland mean and what was its goal?
It means 'Greater Germany' and aimed to expand Germany against the Treaty of Versailles.
What is Volksgemeinschaft and its implications?
Meaning 'Racial Community', it aimed to unite Aryan Germans while excluding those with 'lesser' racial backgrounds.
What principle emphasizes the importance of the state over the individual in Nazi ideology?
Volksgemeinschaft highlights that individual existence should be dedicated to the preservation of the state.
What is Volkish Nationalism?
The belief that one must struggle and sacrifice for the strength of the greater community.
How did the Nazis view full-blooded Germans in relation to benefits?
Full-blooded Germans were entitled to benefits, while those mixed with 'lesser' races were excluded.
What was the role of the SS during the Night of Long Knives?
The SS executed SA leaders as part of Hitler's consolidation of power.
What was the significance of the Enabling Act in establishing Hitler's dictatorship?
It allowed the Nazis to legislate without parliamentary approval, solidifying their control.
What was the impact of the Reichstag Fire on the political landscape in Germany?
It allowed Hitler to frame communism as a threat, justifying his authoritarian measures.
What was the outcome of the coalition formed by the NSDAP?
It enabled Hitler to gain control over industries and further his military ambitions.
How did the Nazis aim to create a master race?
Through the concept of Herrenvolk and the promotion of Aryan supremacy.
What was the effect of the laws banning strikes and trade unions?
They suppressed workers' rights and eliminated opposition to Nazi policies.
What are the three methods by which individuals can contribute to society according to the notes?
Working, Serving, Procreating.
What does Social Darwinism suggest about social hierarchies?
It posits that those at the top are entitled to their position due to innate superiority based on the theory of 'survival of the fittest'.
What is eugenics in the context of Social Darwinism?
Eugenics suggested that the racial purity of superior races should be preserved by purging lesser races.
List the groups ranked lower in the human hierarchy created by Social Darwinism.
Women, Non-whites, Jews, The poor.
What is antisemitism?
Hostility or prejudice against Jewish people.
How were Jews perceived in Nazi ideology?
They were considered a lesser race and a major threat to Aryan racial purity.
What conspiracy theory was associated with Jews during WWI?
The belief that Jews colluded against Germany to secure control over banks and businesses.
What does Lebensraum translate to and what did it signify for the Nazis?
Living Space; it signified the belief that Nazis were entitled to imperialism in Eastern Europe to spread their 'superior' Aryan race.
What significant event started WWII according to the notes?
The invasion of Poland in 1939.
What was the Führerprinzip?
It was the idea that Hitler was the center of the entire Nazi system, responsible for unifying Germans and expanding the Nazi regime.
What role did Adolf Hitler play in the Nazi Party?
He was the center of the Nazi Party, wrote the 25 point programme, and authored Mein Kampf.
What was Joseph Goebbels' role in the Nazi regime?
He was responsible for organizing events that reflected Nazi ideology and was involved in the 1933 book burnings.
What did Hermann Goering do to help Germany become self-sufficient?
He gained access to numerous agencies and was responsible for giving German citizens confiscated Jewish property.
What was Heinrich Himmler's responsibility in the Nazi regime?
He was responsible for exterminating racial undesirables and civilian enemies in Nazi-occupied Eastern Europe.
What was Reinhard Heydrich's role in the Nazi regime?
He controlled the Central Immigration and Resettlement Office and removed non-Germans from German territories.
What was Robert Ley's contribution to Nazi ideology?
He focused on employer control over workers and created 'Strength Through Joy' for leisure activities.
What was the Reichstag Fire Decree of 1933?
It limited civil rights by allowing the regime to arrest political opponents without charge, dissolve political organizations, suppress publications, and overrule state laws.
What was the purpose of censorship under the Nazi regime?
To regulate all forms of media to only exhibit Nazi-approved content.
What types of media were heavily regulated by the Nazis?
Newspapers, radio, cinema, and theatre.
What was the significance of the Nuremberg Laws?
They were laws that institutionalized racial discrimination against Jews.
What was the Beer Hall Putsch?
An attempted coup by Hitler to overthrow the government before he became Chancellor.
What was the role of propaganda in the Nazi regime?
To promote Nazi ideology and maintain control over the populace.
Who was appointed the Minister of Enlightenment and Propaganda in March 1933?
Joseph Goebbels
What principles were the propaganda created by the Nazi party founded upon?
Simplicity, Repetition, Emotion, Lying, Marginalisation, Single Views.
What does the principle of 'Simplicity' in Nazi propaganda entail?
Aiming at a low intellectual level.
How did Nazi propaganda utilize 'Repetition'?
By using slogans.
What was the goal of the 'Emotion' principle in Nazi propaganda?
To make the people feel, not think.
What does the principle of 'Lying' suggest in the context of Nazi propaganda?
The bigger the lie, the better.
What groups were marginalized in Nazi propaganda?
Jews and Communists.
What was the purpose of Nazi propaganda?
To promote the party, denounce other political parties, spread nationalism, build hate for enemies, and build the image of Hitler as Germany's saviour.
What mediums did the Nazis use to spread propaganda?
Newspapers, Press, Music, Radio, Literature, Cinema, Major events.
What is the 'Fuhrer myth'?
The representation of Hitler as the saviour of Germany.
How was Hitler portrayed in the media according to the Cult of Personality?
As extraordinary but relatable, modest, and a man of the people.
What achievements were credited to Hitler in the Cult of Personality?
Ending the Depression in Germany, anti-Marxist stance against communism, tearing up the Treaty of Versailles, and taking strong action against enemies.
What was the SA (Sturmabteilung)?
The Nazi paramilitary force that existed from the early 1920s, fought street battles, and ran camps from 1933-1934.
What was the role of the SS (Schutzstaffel)?
Initially Hitler's bodyguard, it became an elitist force responsible for running the camps.
Who led the SS and emphasized its elite character?
Heinrich Himmler.
What was the Gestapo and when was it set up?
The Gestapo was established in November 1933 to protect the regime against its enemies.
Under whose control was the Gestapo first established?
Initially under Hermann Göring, then under Heinrich Himmler.
What was the primary responsibility of the Gestapo?
Internal security.
How effective was the Gestapo in its operations?
Their effectiveness was undeniable.
What was the fate of the SA after June 30, 1934?
Their real power ended.
What characterized the SS by the early 1940s?
It became a mass organization with its own factories, courts, and army units.
What were the first concentration camps set up by the Nazi regime?
The first concentration camp was established in 1933 at Dachau.
What was the initial target of the Nazi concentration camps?
The initial target was political opponents, but later it expanded to socially undesirable groups and eventually Jews.
What was the main goal of the League of Nations?
To resolve international disputes, administer global justice, and prevent future conflicts.
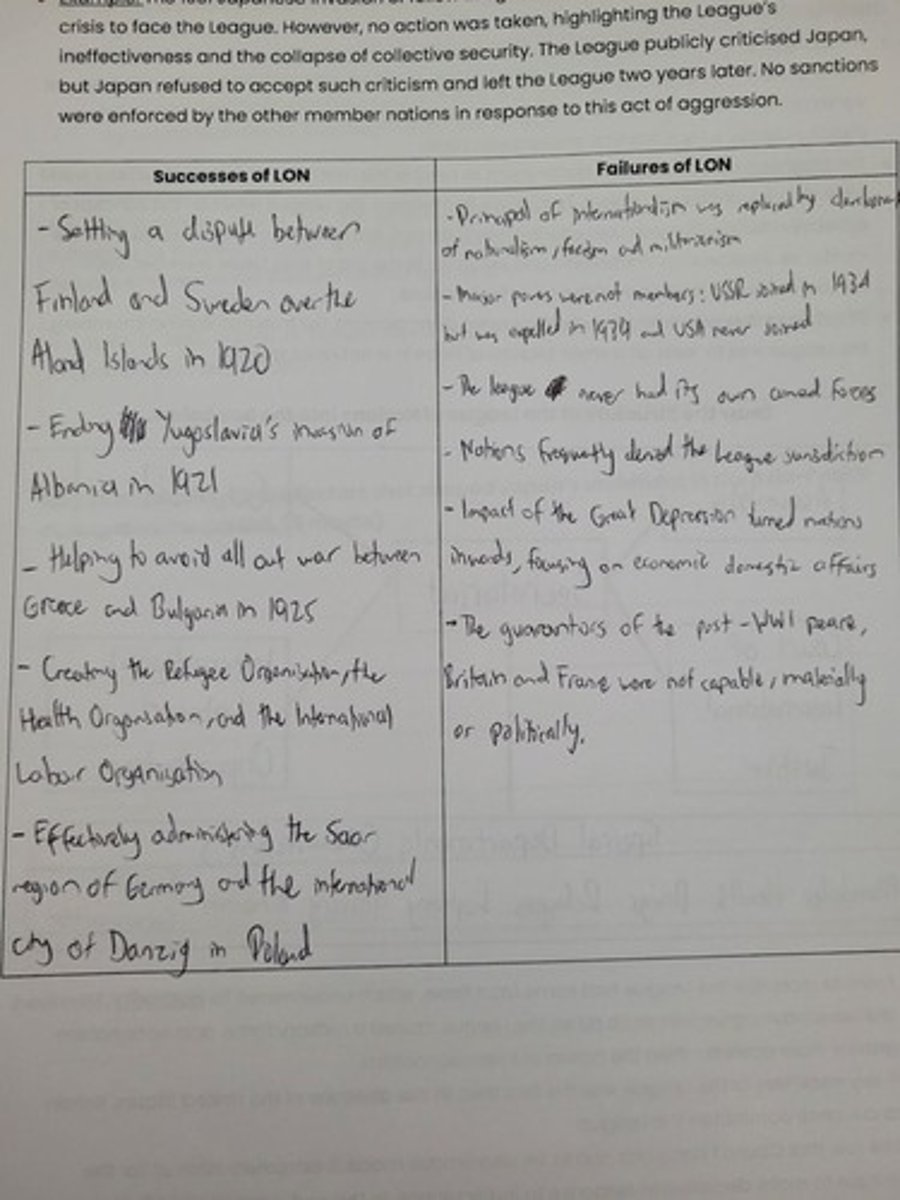
Who proposed the League of Nations and in which treaty was it included?
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson proposed the League of Nations, and it was included in the Treaty of Versailles.
What principle did the League of Nations rely on for collective security?
An attack on one member was treated as an attack on all members.
What was a key principle emphasized by the League of Nations?
Universal disarmament.
What was the significance of the Moscow Declaration in 1943?
It called for the creation of an international organization to maintain peace and security.
What are the main objectives of the United Nations?
To maintain global peace and security, foster friendly relations among nations, improve living conditions, combat hunger, disease, and promote human rights.