Chapter 11 Regulation of Cellular Processes BIOL 3340
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Regulation of Gene Expression
Control of gene activity in cells.
Transcription Initiation
First step in gene expression process.
Transcription Elongation
Process of RNA strand lengthening.
Translation
Synthesis of proteins from mRNA.
Posttranslational Modification
Chemical changes to proteins after synthesis.
Constitutive Genes
Genes expressed continuously for basic functions.
Inducible Genes
Genes activated under specific environmental conditions.
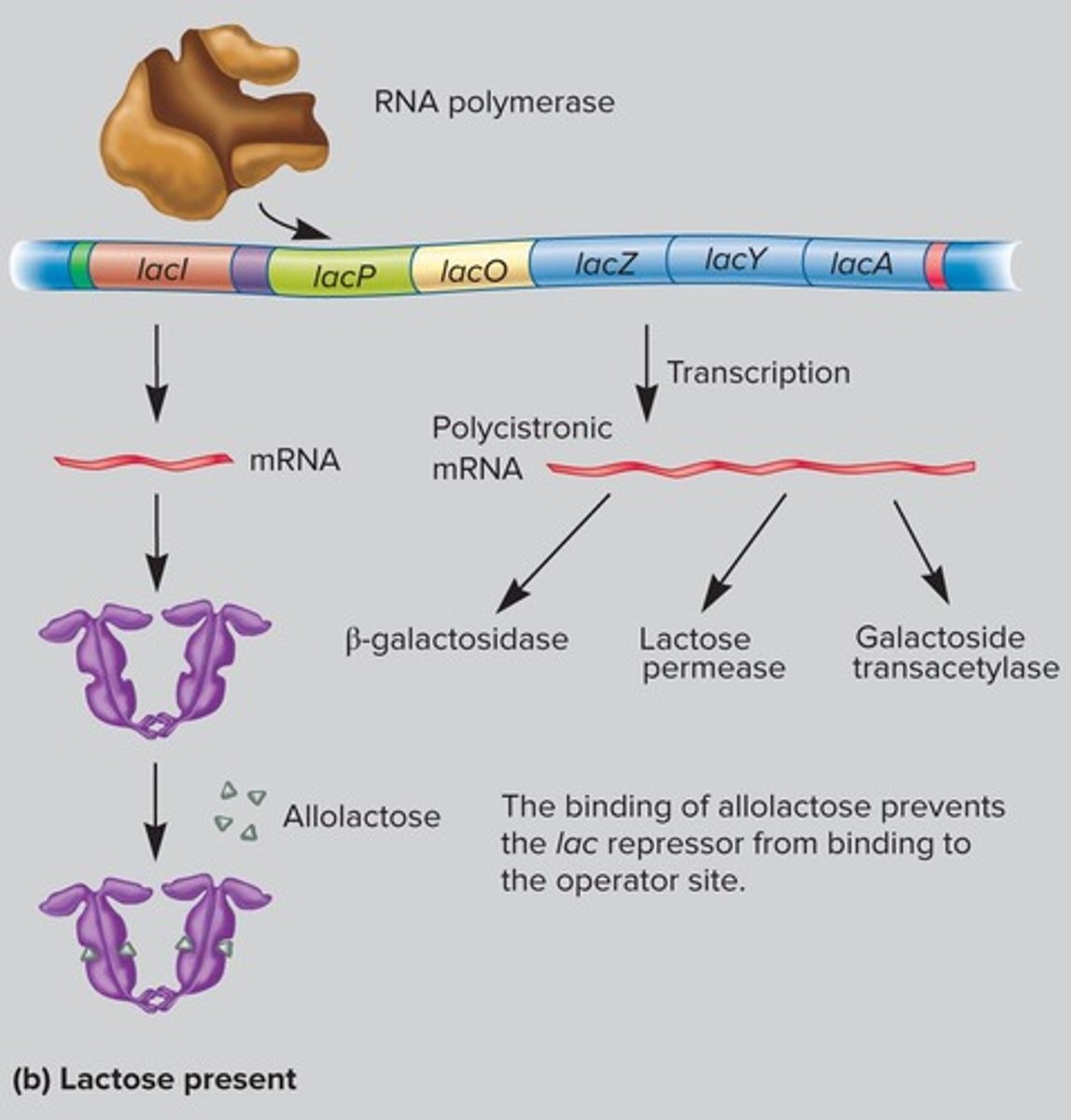
β-Galactosidase
Enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose into glucose.
Inducible Enzymes
Enzymes present only when substrates are available.
Repressible Genes
Genes that are usually active unless inhibited.
Biosynthetic Pathways
Metabolic routes for synthesizing cellular components.
Transcriptional Regulatory Proteins
Proteins that control gene transcription by binding DNA.
DNA-Binding Domain
Region of protein that attaches to DNA.
Allosteric Site
Site on protein that interacts with effectors.
Negative Control
Regulatory mechanism that inhibits gene expression.
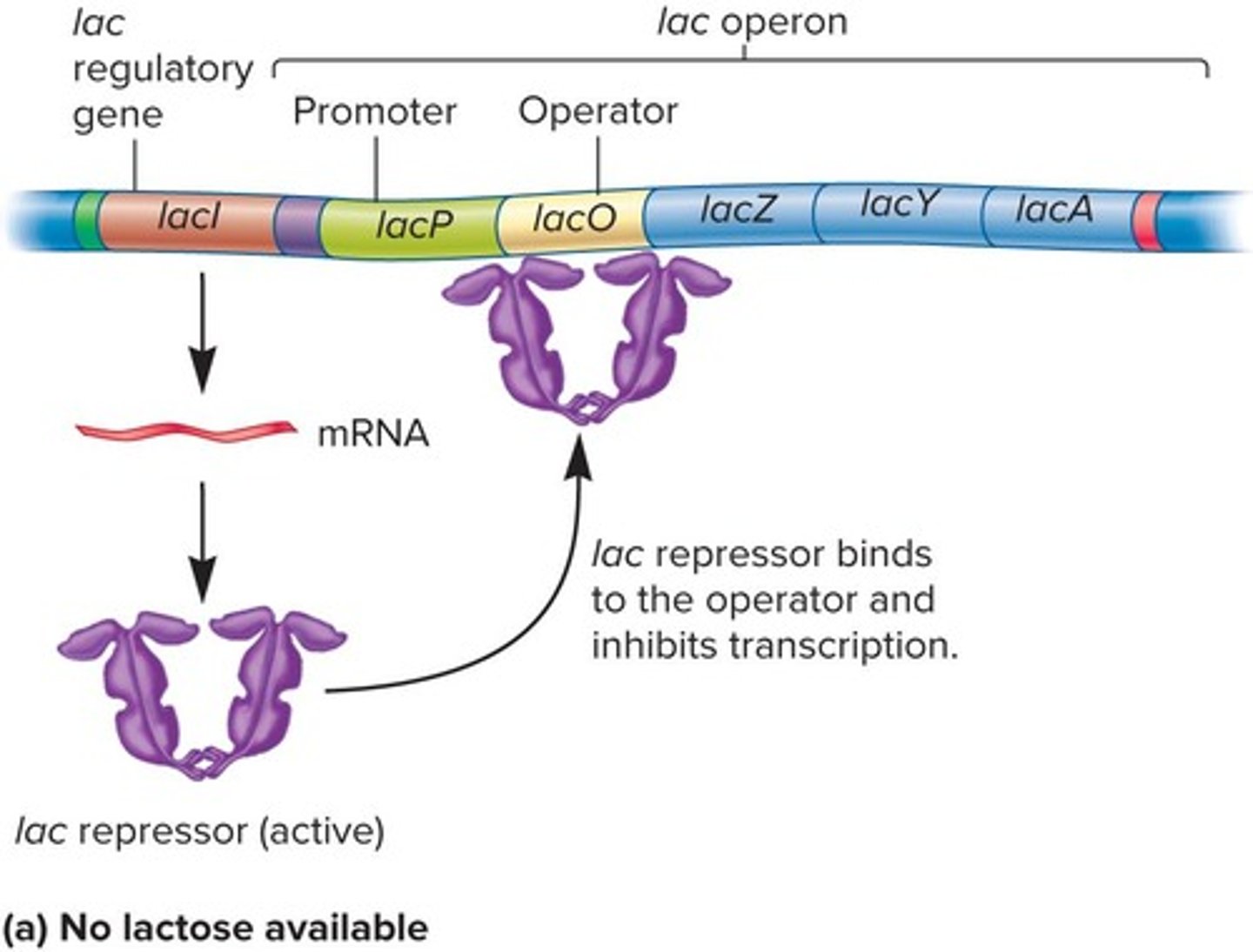
Repressor Proteins
Proteins that prevent transcription when bound to DNA.
Inducers
Molecules that activate repressor proteins.
Positive Control
Regulatory mechanism that promotes gene expression.
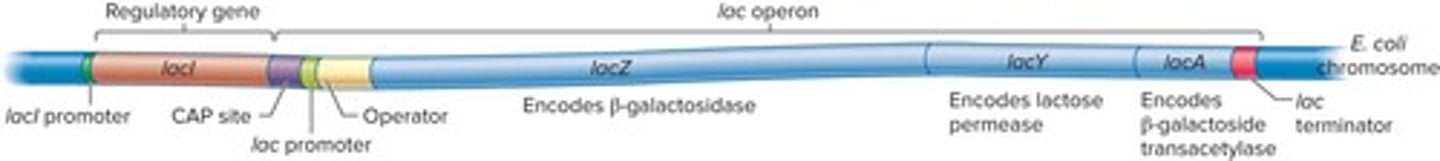
Operon
DNA sequence controlling gene expression with promoter.
Lactose Operon
Operon regulating lactose metabolism in bacteria.
lac Repressor
Protein that inhibits transcription in lactose operon.
Tetramers of Repressor
Four subunit complexes that bind operator sites.
Operator Sites
DNA regions where repressor proteins bind.
lac Operon
Regulated by lac repressor and CAP.
Allolactose
Binds repressor, allowing transcription.
CAP
Regulates operon based on glucose levels.
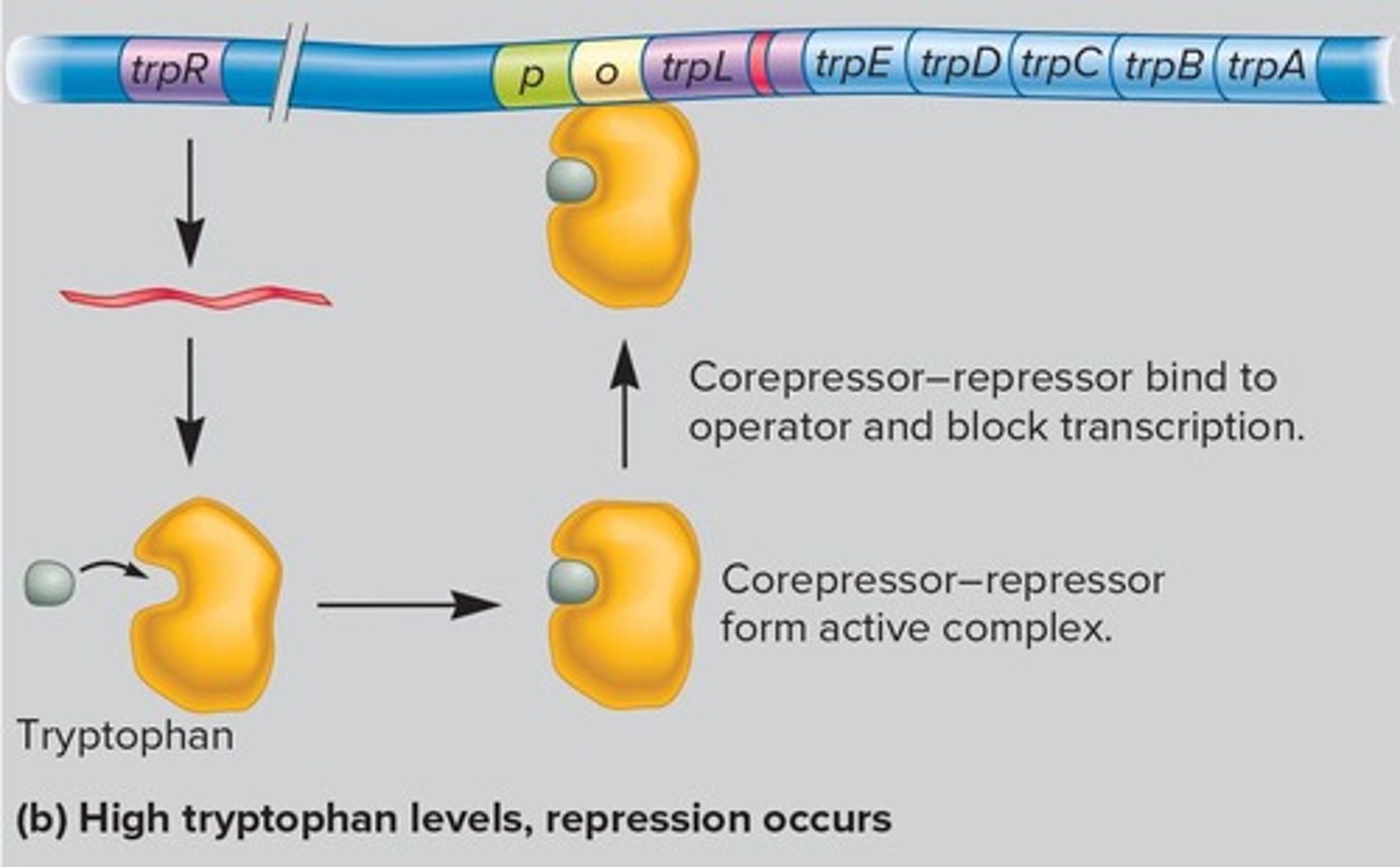
Tryptophan Operon
Contains genes for tryptophan synthesis.
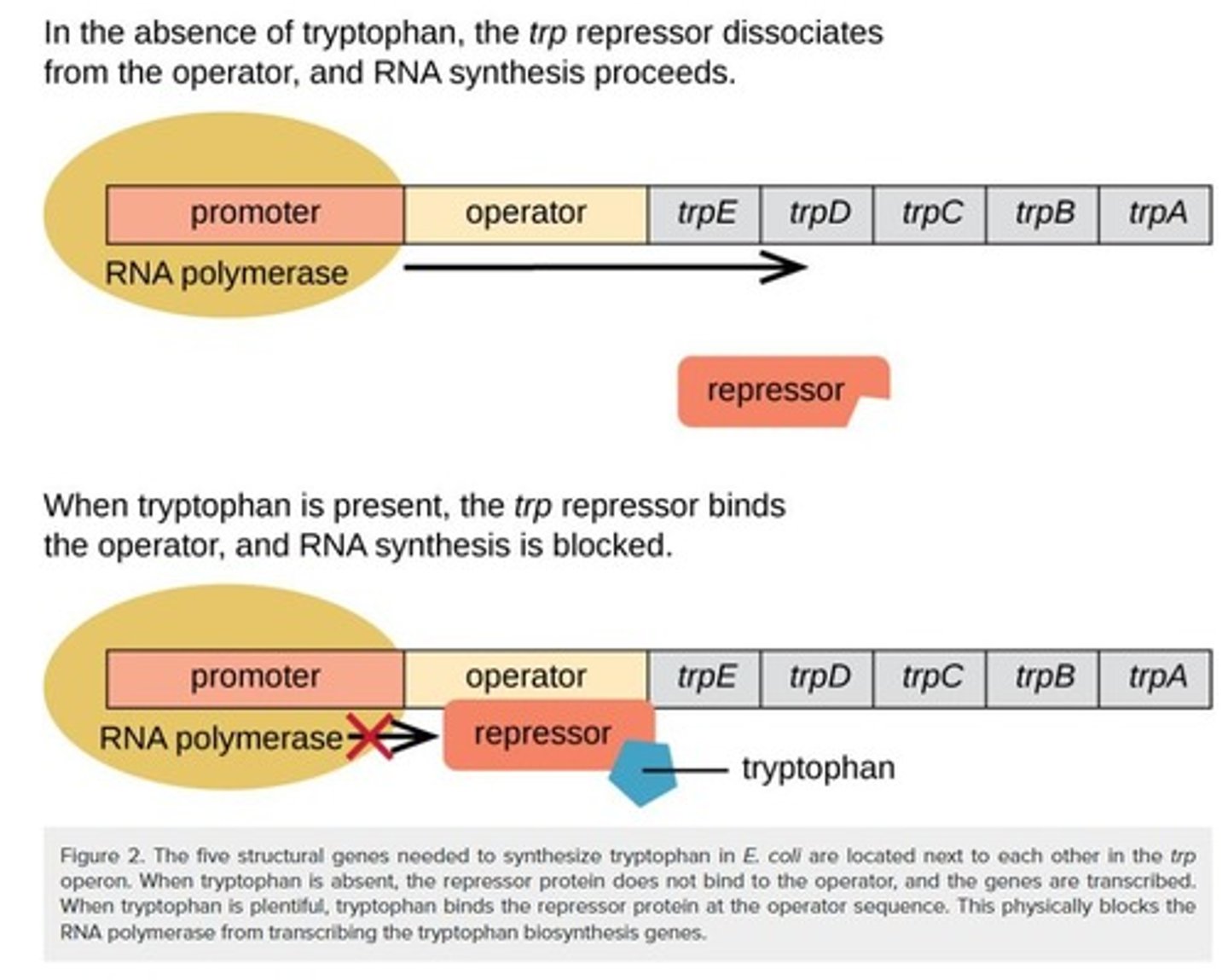
trp Repressor
Inhibits transcription when tryptophan is present.
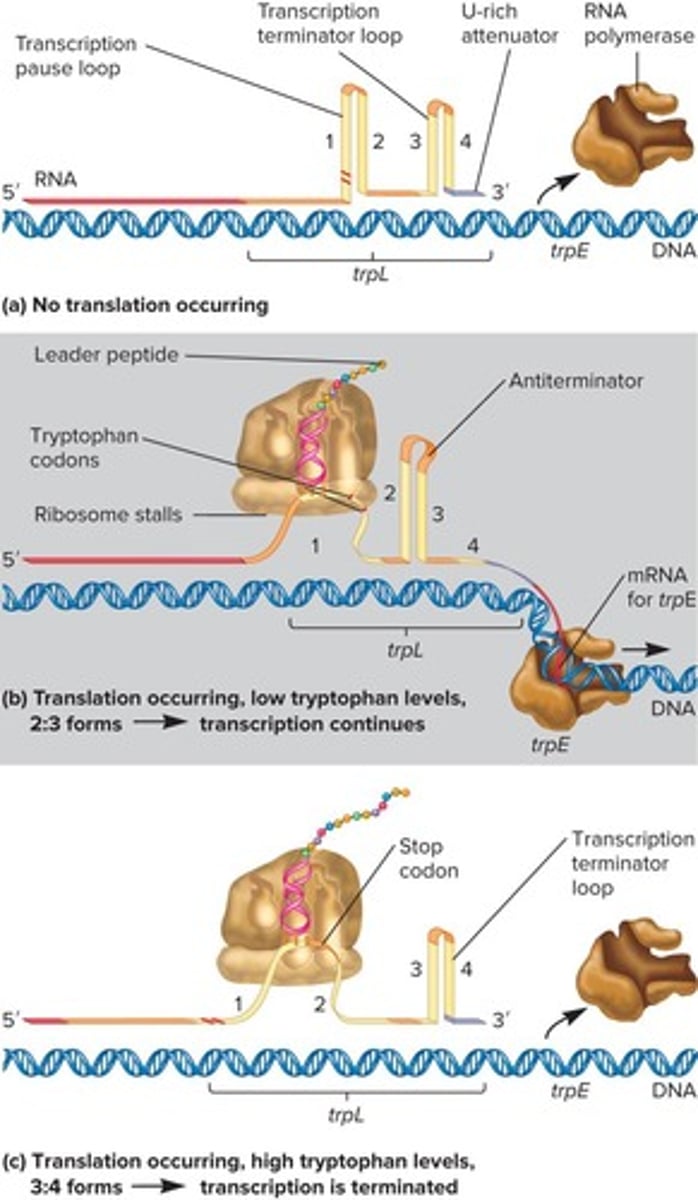
Attenuation
Regulation of transcription termination during elongation.
Riboswitches
mRNA structures that regulate transcription termination.
Arabinose Operon
Controlled by AraC protein, responds to arabinose.
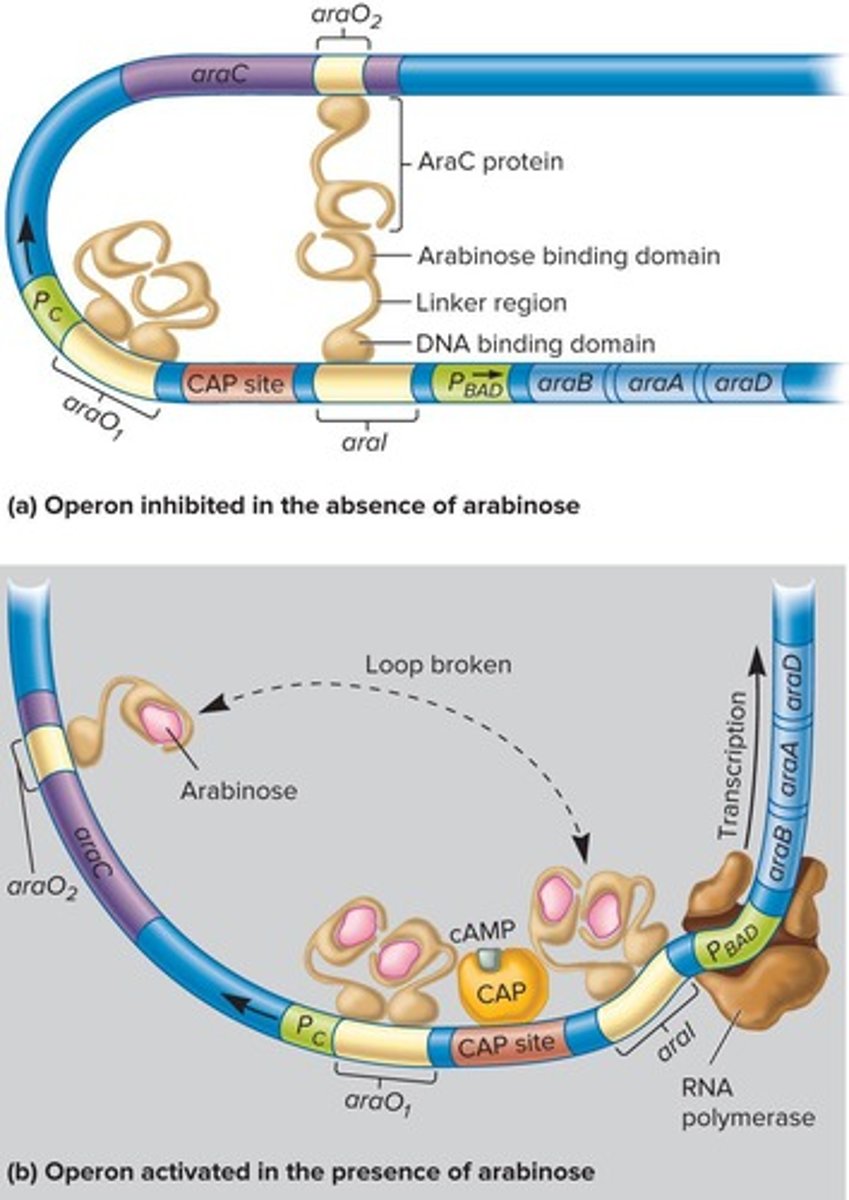
AraC Protein
Acts positively or negatively based on arabinose.
Transcription Elongation Regulation
Controlled by termination mechanisms like attenuation.
Leader Region
Site for transcription termination in trp operon.
Stem-loop Structures
Form in mRNA, affecting transcription based on trp.
Gram-positive Riboswitches
Regulate transcriptional termination in bacteria.
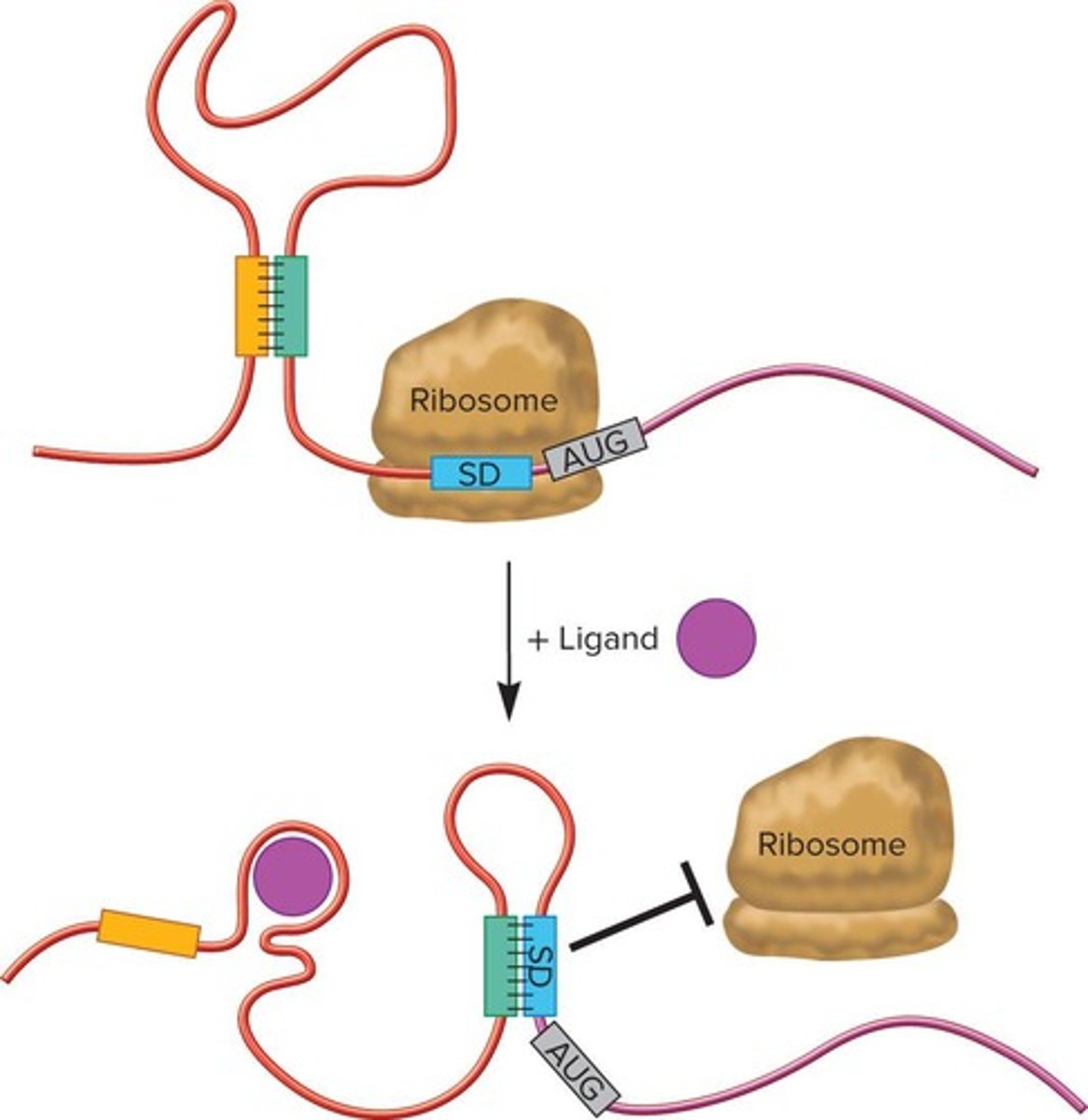
Gram-negative Riboswitches
Regulate translation of mRNA in bacteria.
Effector Molecule
Binds riboswitch, altering mRNA folding.
Small RNA Molecules
Regulate translation by binding to mRNA.
Cis-acting sRNAs
Control a single gene, synthesized from sense strand.
Trans-acting sRNAs
Control multiple genes, synthesized from distinct templates.
Translation Initiation
Can be regulated by small RNA molecules.
Negative Transcriptional Control
Repression of gene expression by repressor proteins.
Global Regulatory Systems
Regulatory systems affecting multiple genes and pathways.
Regulon
Genes or operons controlled by a common regulator.
Two-Component Signal System
Links external events to gene expression regulation.
Sensor Kinase
Extracellular receptor for metabolites in signaling.
Response Regulator
Activated by sensor kinase to regulate transcription.
Phosphorelay System
Signal transduction involving phosphorylation events.
Env Z
Sensor kinase that autophosphorylates in high osmolarity.
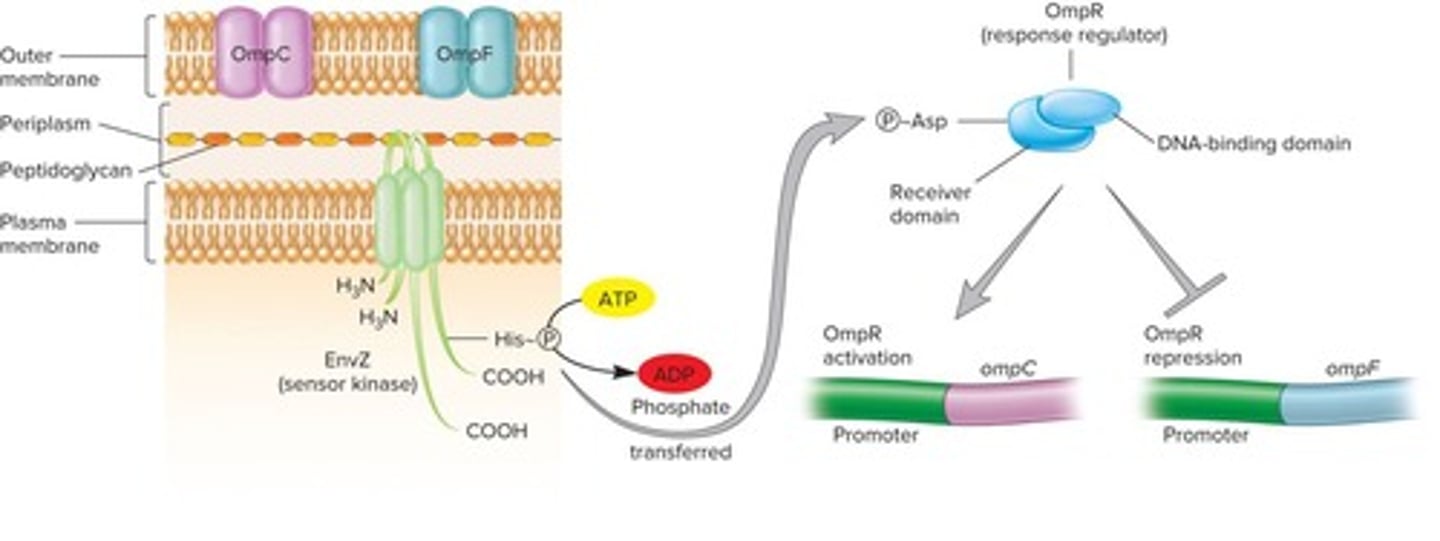
OmpR
Response regulator that controls porin gene expression.
OmpF
Larger porin protein allowing high solute diffusion.
OmpC
Smaller porin protein with lower diffusion capacity.
Sigma Factor
Protein directing RNA polymerase to specific genes.
σ70
Transcribes genes needed during exponential growth.
σ54
Transcribes genes involved in nitrogen metabolism.
σ38
Transcribes genes for stationary phase and stress response.
σ32
Transcribes genes protecting against heat shock.
σ28
Transcribes genes for flagellum assembly.
σ24
Transcribes genes for membrane protein folding.
σ19
Transcribes genes responding to iron starvation.
Second Messengers
Small molecules responding to external signals.
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a second messenger.
Diauxic Growth
Biphasic growth using preferred carbon source first.
Catabolite Repression
Inhibition of less preferred sugar metabolism.
Lag Phase
Growth pause after preferred substrate is exhausted.
CAP Binding Site
Site where CAP binds to regulate operons.
Catabolite Activator Protein (CAP)
Regulates catabolite operons based on cAMP levels.
cAMP Active Form
When bound to CAP, promoting transcription.
cAMP Inactive Form
Free of cAMP, CAP cannot activate transcription.
Adenyl Cyclase
Enzyme converting ATP to cAMP and PPi.
Glucose Presence
Inhibits adenyl cyclase activity, lowering cAMP.
Transcription Promotion
CAP binding allows RNA polymerase to initiate transcription.
Phosphotransferase System
Regulates cAMP levels via phosphate transfer.
Methyl-Accepting Chemotaxis Proteins (MCPs)
Chemoreceptors that bind environmental chemicals.
CheA Kinase
Sensor kinase that autophosphorylates upon activation.
CheY Response Regulator
Controls flagellar rotation based on phosphorylation.
Flagellar Rotation CCW
Occurs when attractant concentration is high.
Flagellar Rotation CW
Occurs when attractant concentration decreases.
MCP Methylation
Methylation by CheR affects MCP activity.
MCP Demethylation
Demethylation by CheB leads to CheA inactivity.
Quorum Sensing
Cell communication regulating gene expression based on density.
N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL)
Signaling molecule in quorum sensing.
LuxR Regulator
Transcriptional regulator activated by AHL in V. fischeri.
Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis
Global regulatory system responding to starvation signals.
Alternative Sigma Factors
Proteins that initiate transcription during sporulation.
pppGpp Production
Downregulates tRNA and rRNA synthesis during amino acid starvation.
Stringent Response
Cellular adaptation to amino acid starvation.
Restriction-modification
Microbes modify DNA bases to combat viruses.
Methylases
Enzymes that add methyl groups to DNA.
Restriction endonucleases
Enzymes that cut unmethylated DNA.
CRISPR/Cas system
Adaptive immune system in bacteria against viruses.
Adaptation stage
Viral genome pieces added to CRISPR array.
Expression stage
CRISPR region transcribed into large RNA.
Cas proteins
Proteins that process CRISPR RNA into crRNAs.
Interference stage
Cas-crRNAs destroy viral DNA or mRNA.
Chromatin remodeling
Rearranging chromatin structure to facilitate transcription.
Nucleosome-free core promoter
Region where transcription factors assemble.
Upstream activating sequences
Binding sites for transcriptional activators.
Enhancers
Regulatory sites that boost transcription rates.