PSYC 132 Quiz 1 ( Chapter 1-3 )
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
Behavioral Endocrinology
The study of interactions among hormones, brain, and behavior
Hormone
An organic chemical messenger released from endocrine cells that travels through the blood systems to interact with cells that travels through the blood system to interact with cells at some distance away and causes a biological response
Endocrine Gland
A ductless gland from which hormones are released into the blood system in response to specific physiological signals
ductless → not specific targeting
Testes
The male gonads, which produce steroids hormones and sperm
Castration
The surgical removal of the gonads
Eunuch
A man who has been castrated (testes removed)
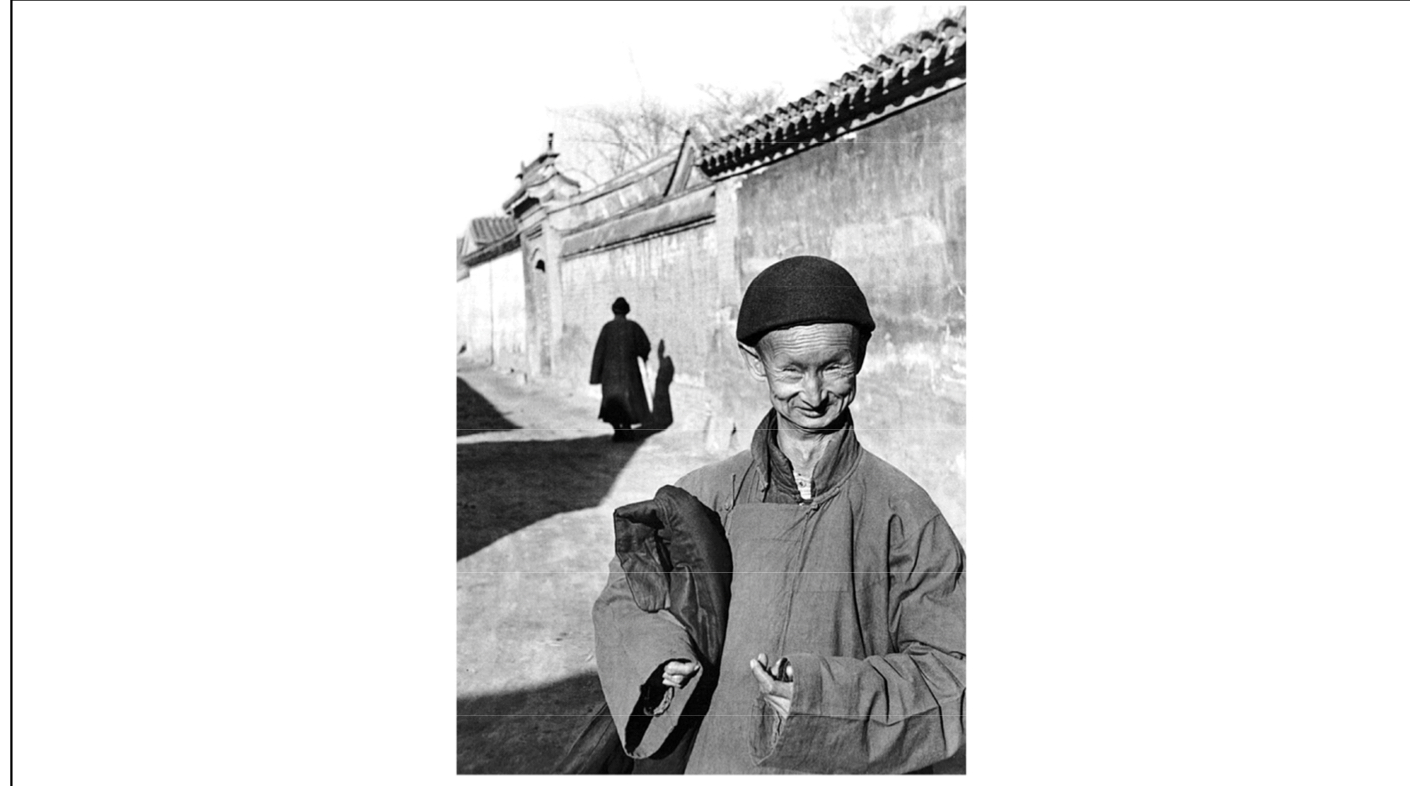

Eunuch from the Last Imperial Court of China
Characterized by his lack of facial hair and long arms
Lack of testes before maturation causes differences in appearance

Arnold Adolph Berthold
University of Göttingen
Published in 1894 what is now recognized as the first formal experiment endocrinology
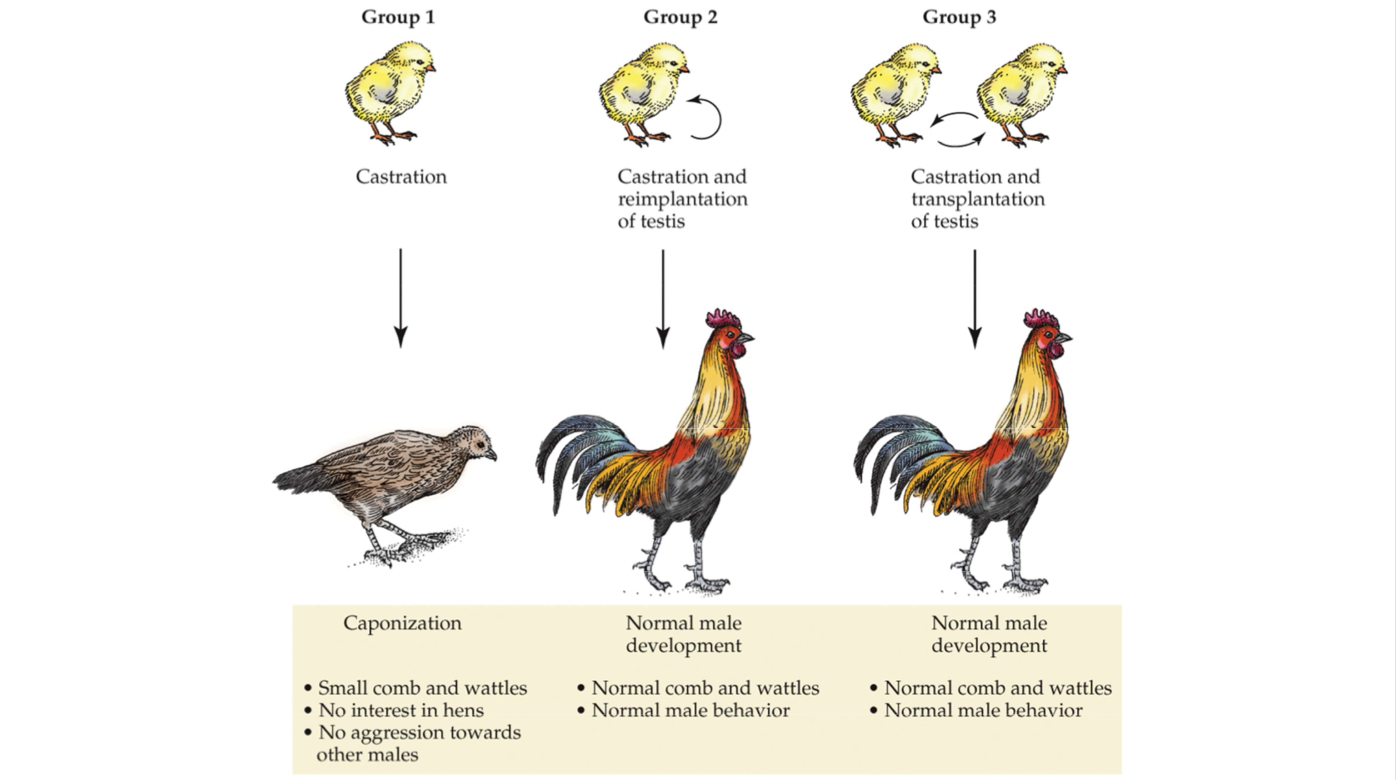
Berthold’s experiment on rosters and different conditions for castration
Shows the developmental differences between roosters who have no testes vs. had testes removed and reimplanted

Frank Beach
Published Hormones and Behavior in 1948
Beginning of the formal study of behavioral endocrinology
Regarded as the father of behavioral endocrinology
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that communicate between nerve cells (neurons)
Similarities between neurotransmitters and hormones
both are chemicals
They are messengers for action → meaning they tell parts of the body to initiate some kind of action/response
Released and received by cells in similar ways (work in similar ways)
Differences between neurotransmitters and hormones
Neurotransmitters: shorter travel distances, rapid onset/offset (meaning they work fast and leave fast), more voluntary control (e.g., moving your arm causes the release of a neurotransmitter)
Hormones: longer travel distances, long lasting effects, less voluntary control

Dark-eyed Junco
Have been used to understand the role of testosterone in behavior and physiology

Zebra Finches
Used in the study of the hormonal and neural bases of birdsong
Only the male zebra finches sing in nature
Levels of Analysis
The set of overlapping and interacting questions about behavior that span different types of approaches, including mechanistic, developmental, phylogenetic, and adaptive
Mechanistic Level
The physiological mechanism(s) underlying behavior
Behavior is explained in terms of genes, neurotransmitters, hormones, etc.
Developmental level
The role of experience in individual behavior
Behavior explained in terms of maturation, aging, learning, etc.
Phylogenetic level
The perspective(s) adopted by biologists who assume that evolutionary processes are central to issues in ecology, systematics, and behavior
Behavior is explained in terms of its presence in closely related species and ancestral species
Adaptive level
The role of any structural, physiological, or behavioral process that increases an individual’s fitness to survive and reproduce as compared with other conspecifics
Behavior is explained terms of how it helps survival and reproduction
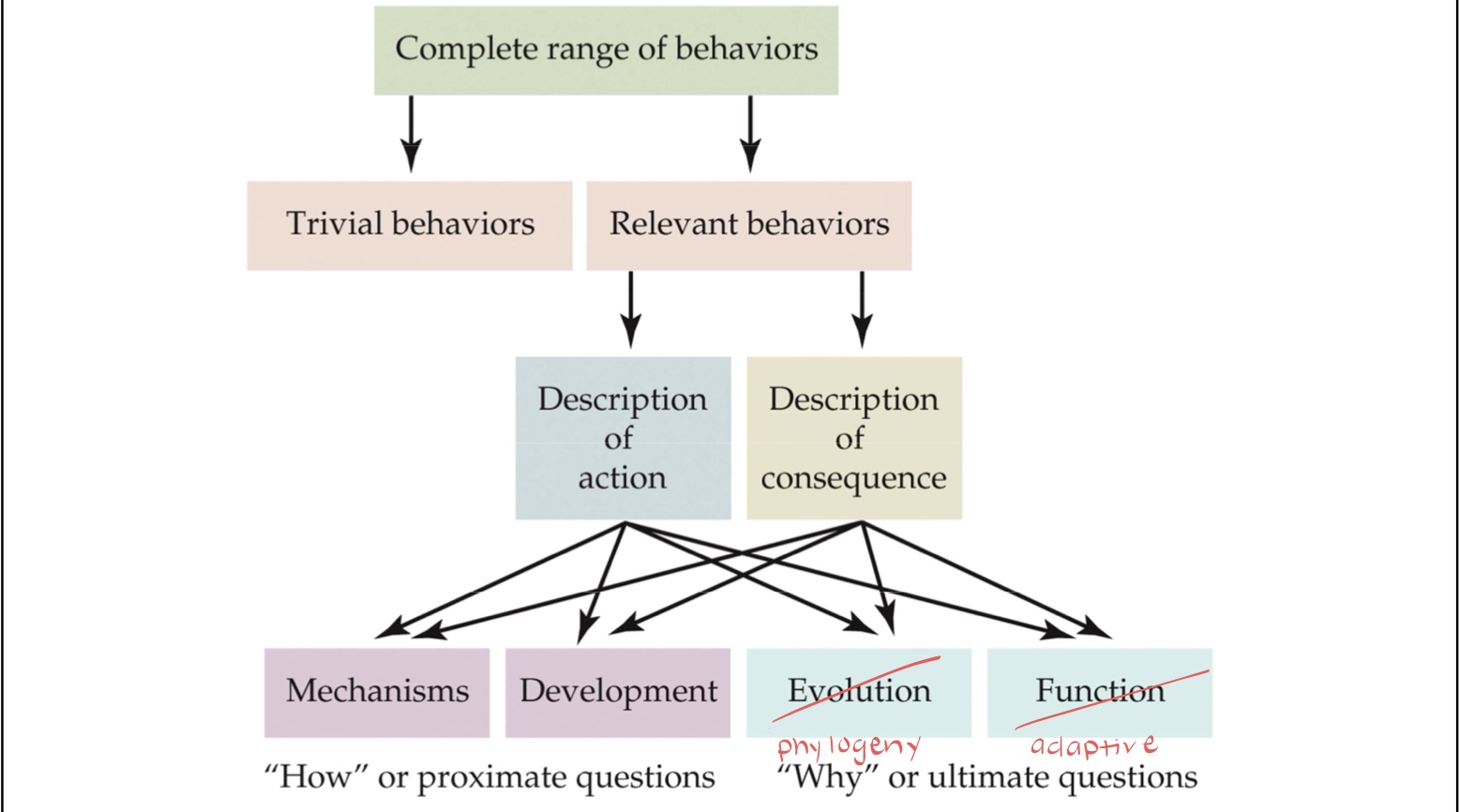
Stages of Behavioral Research
Examines the levels of analysis that addresses either proximate (“How”) or ultimate (“Why”) questions
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
An enzyme immunoassay that is used to detect small amounts of specific proteins and other biological substances such as hormones or other chemical messengers
A type of assay → used to study hormone measurements since hormones are too small and hard to measure on their own
Ablation
Removal, especially by cutting
Lesion
Damage to an area, such as a brain region, that is caused by accident, disease, or experimental procedure
Agonist (hormone)
A chemical substance that binds to receptors for a hormone or neurotransmitter and causes a biological response that is indistinguishable from the response elicited by the natural hormone or neurotransmitter
produces a biological response
Antagonist (hormone)
A chemical substance that binds to receptors for a hormone or neurotransmitter, but does not cause a biological response
Have opposing effects on a bodily function → used to maintain homeostasis
Cannulation
A technique in which hollow electrodes or fine tubes (cannulas) are inserted into specific brain regions or into specific blood vessels, so that substances can be introduces precisely into a particular place or a blood sample can be obtained from a specific location
E.g., _____ may be used to administer hormones or drugs, or to have blood samples drawn form which hormones can be measured
Transgenic
Relating to an animal in which a gene has been inserted, altered, or deleted
Knockout
An individual, usually a mouse, in which a specific gene has been inactivated
Chimera
An animal whose tissues are composed of two or more genetically distinct cell types; also calles a mosaic
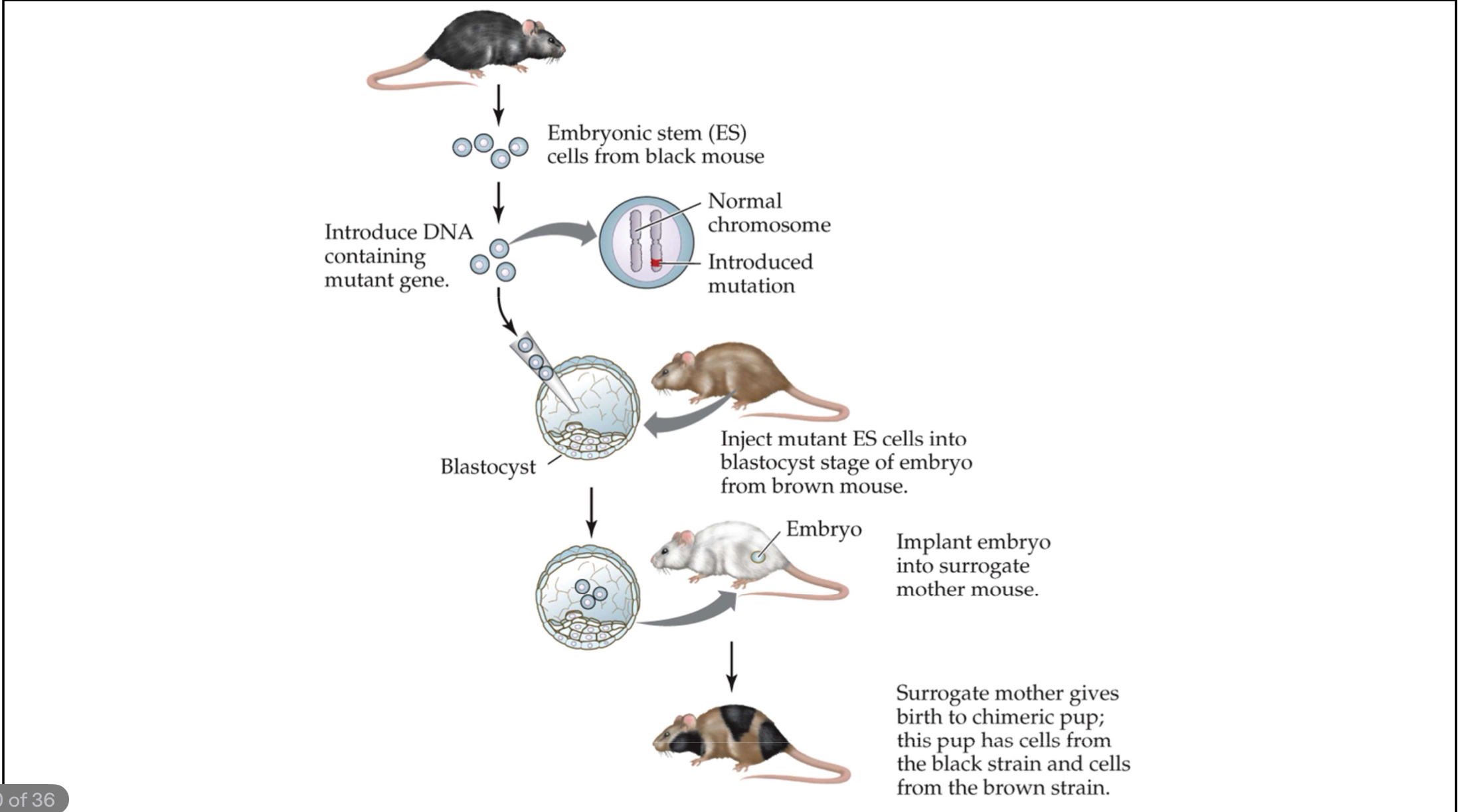
we examine the relationship between gene and behavior by examining the behaviors of mice with different gene types
behaviors of mice with (+/+) vs. (+/-) vs. (-/-)
H-B principle #1
Hormones don’t cause behavior per se
They instead increase the probability that a behavior will occur
For example, lower the threshold for the hormone to cause a certain behavior
H-B principle #2
The hormone-behavior relationship is bidirectional and multi factorial
hormones affect behavior just as much as behaviors accept hormones
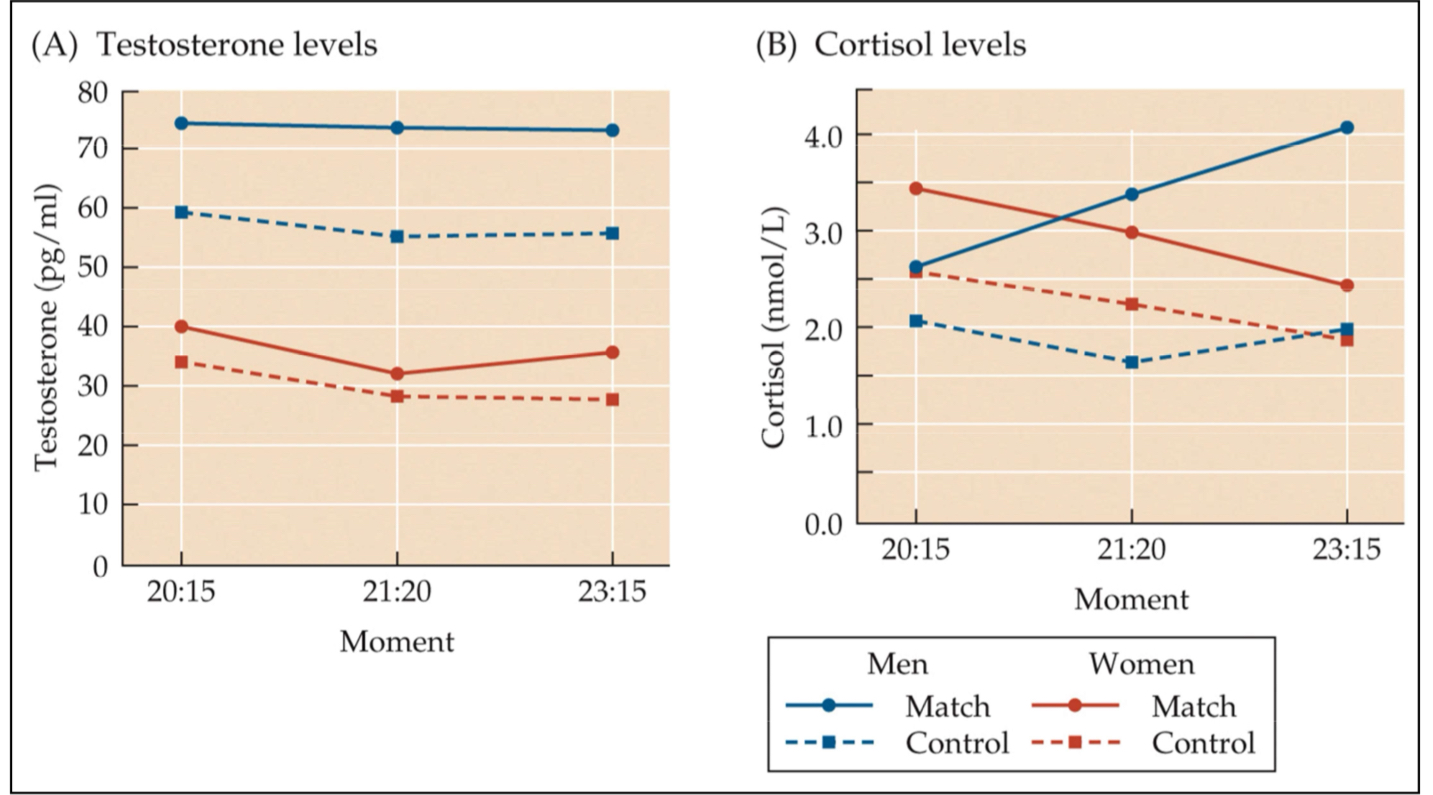
Hormonal responses to viewing a soccer match: men vs. womeN
Men: elevated testosterone and cortisol levels
Women: some change but not as much as male
H-B principles #3
Hormone-behavior relationships are nonlinear
consistent changes to one doesn’t mean consistent changes (changes in quantity) in the other
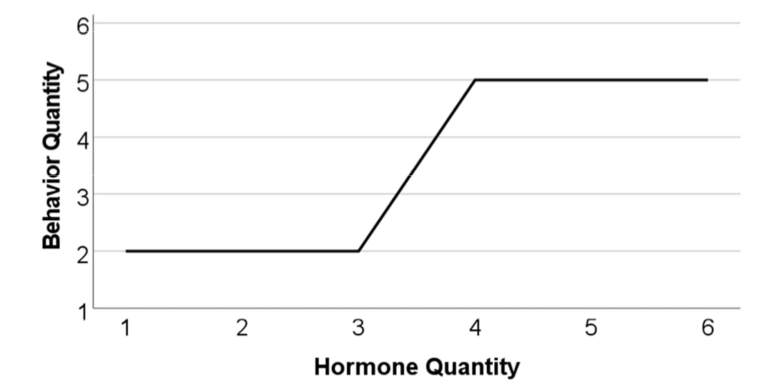
H-B principle #4
Hormones are less predictive of behavior in humans than in nonhumans
humans don’t just rely on their hormone-influenced reflexes as nonhumans do → humans think, plan, and resist impulses
H-B principle #5
Hormone functions are evolving more than hormone structures
the structure of hormones are the same but the functions can change
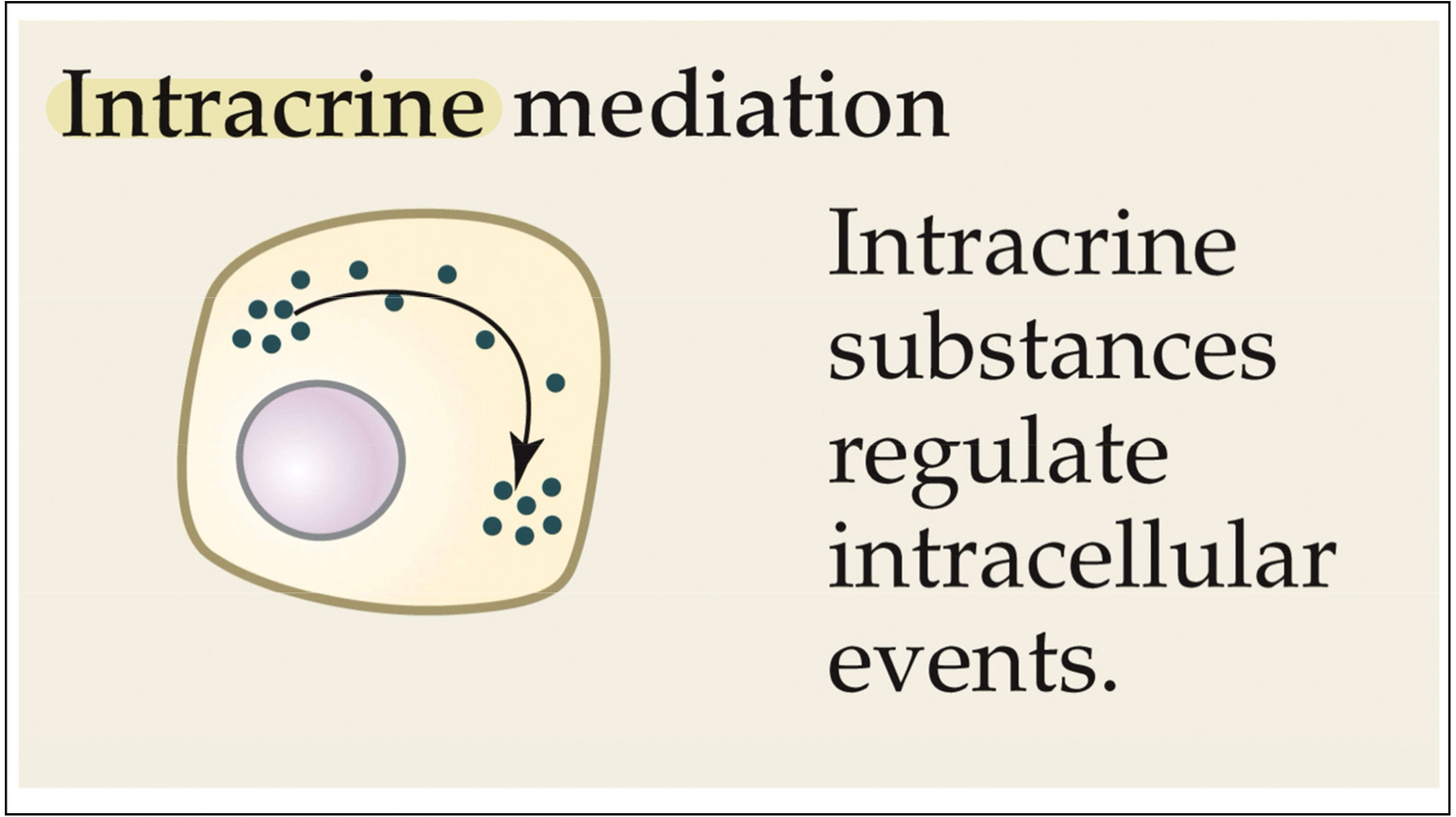
Intracrine
Peptide hormones or growth factors that bind and act inside cells either after internalization by the cells or retention in their cells of synthesis
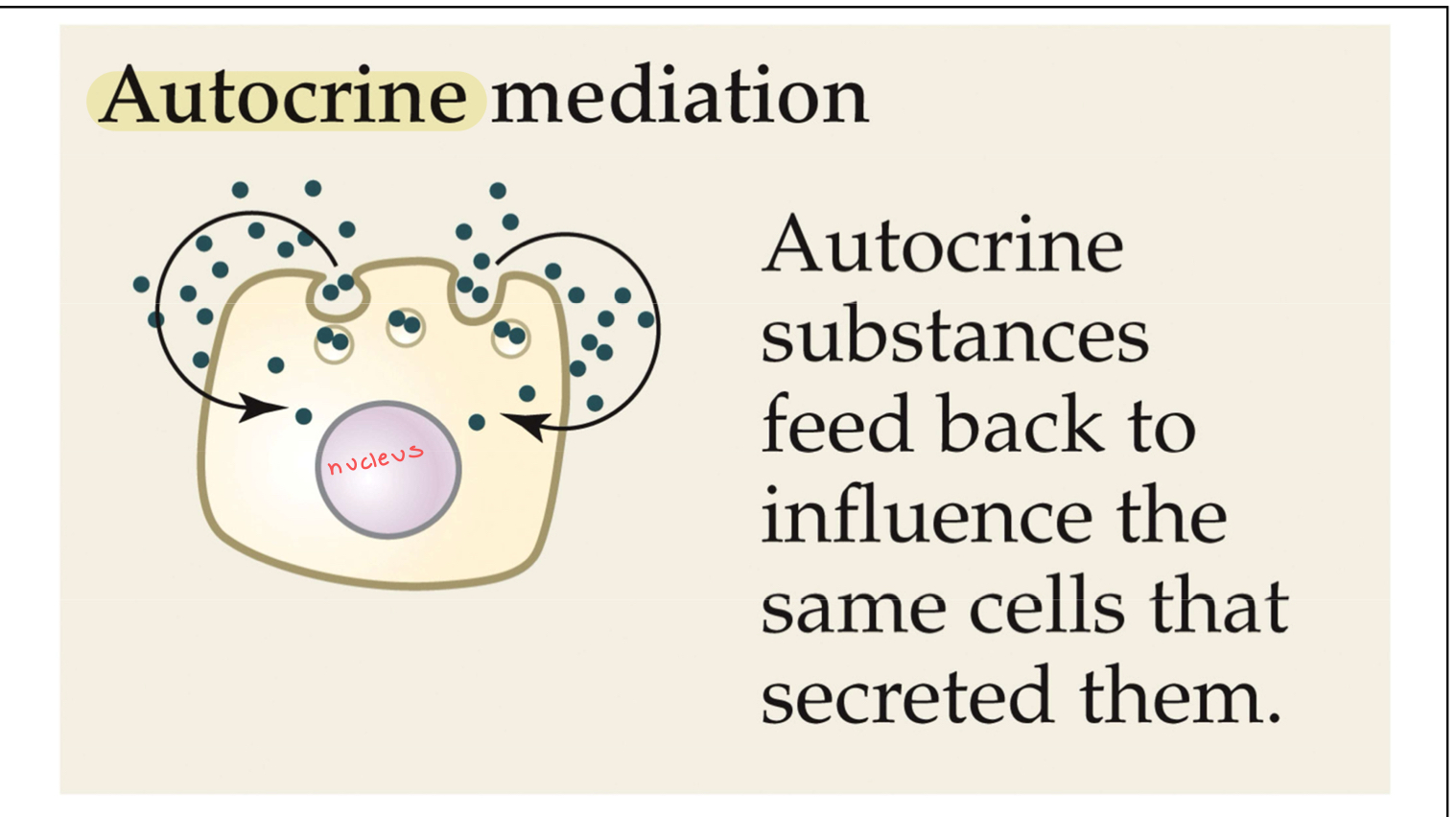
Autocrine
Pertaining to a signal secreted by a cell into the environment that affects the transmitting cell
Paracrine
A form of cellular communication in which a cell releases a product that induces changes in a nearby cell
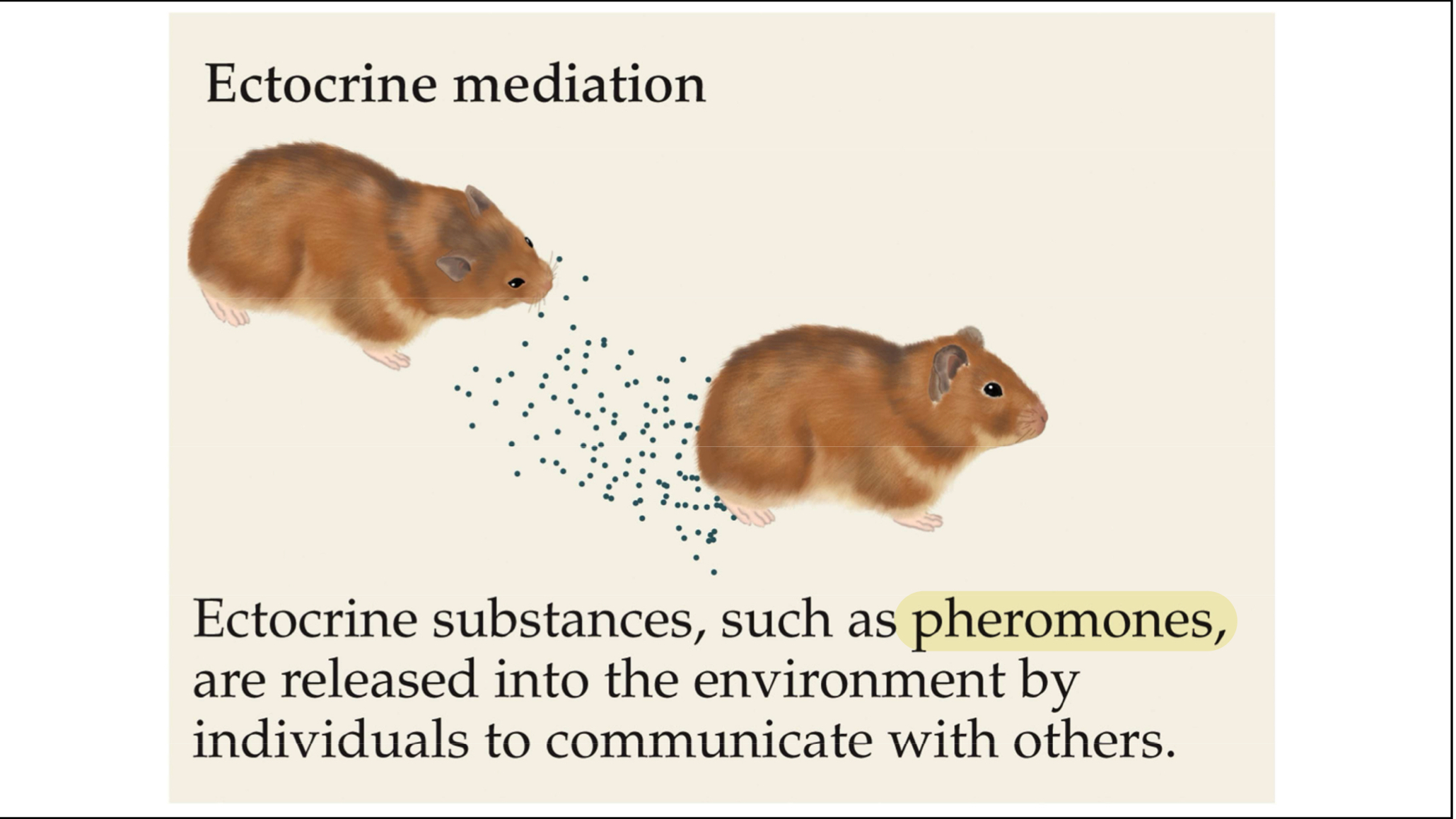
Ectocrine
A parahormonal chemical substance that is secreted (usually by an invertebrate organism) into its immediate environment (air or water) which alters physiology or behavior of the recipient individual
Outside of body → like pheromones
Exocrine gland
A gland that has a duct through which its product is secreted into adjacent organs or the environment
has a duct → specific targeting
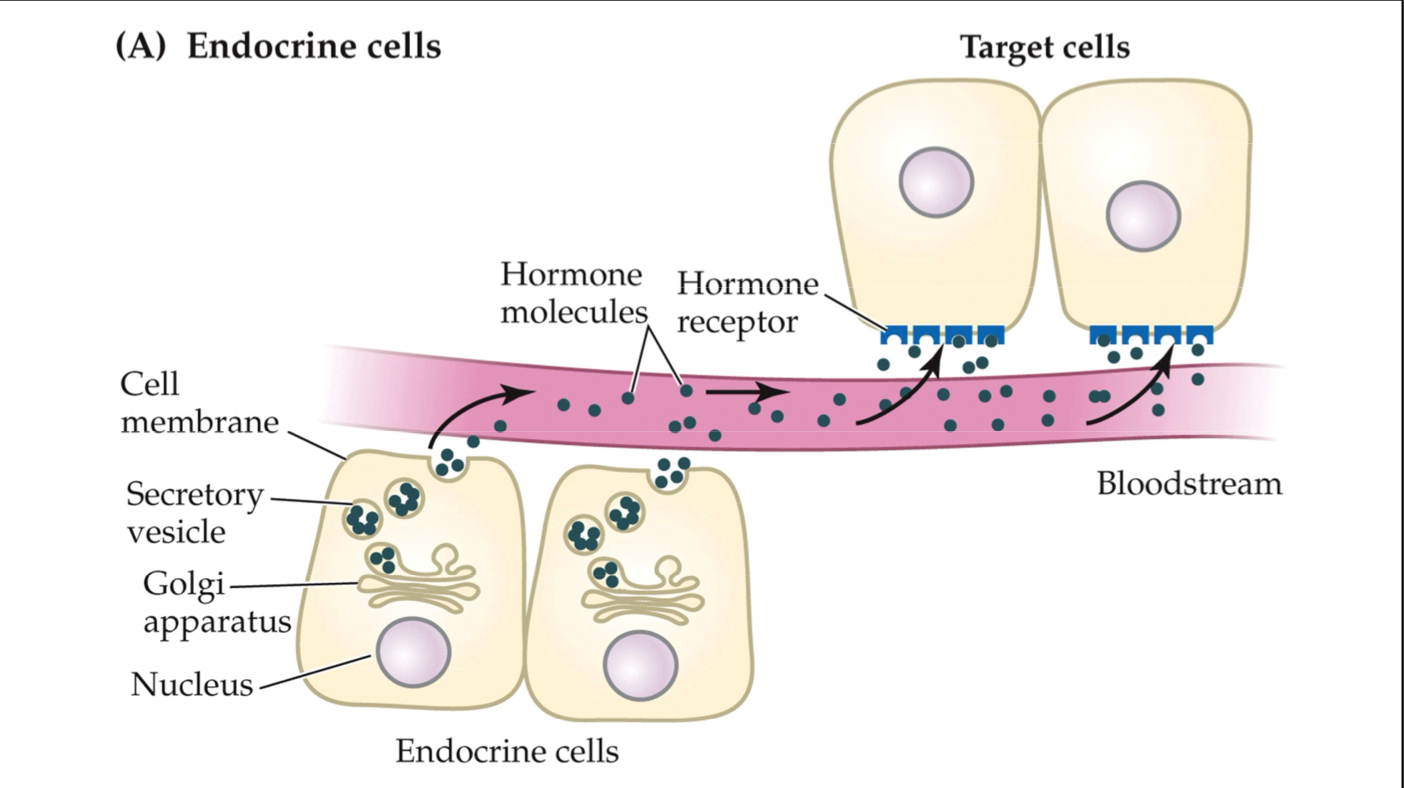
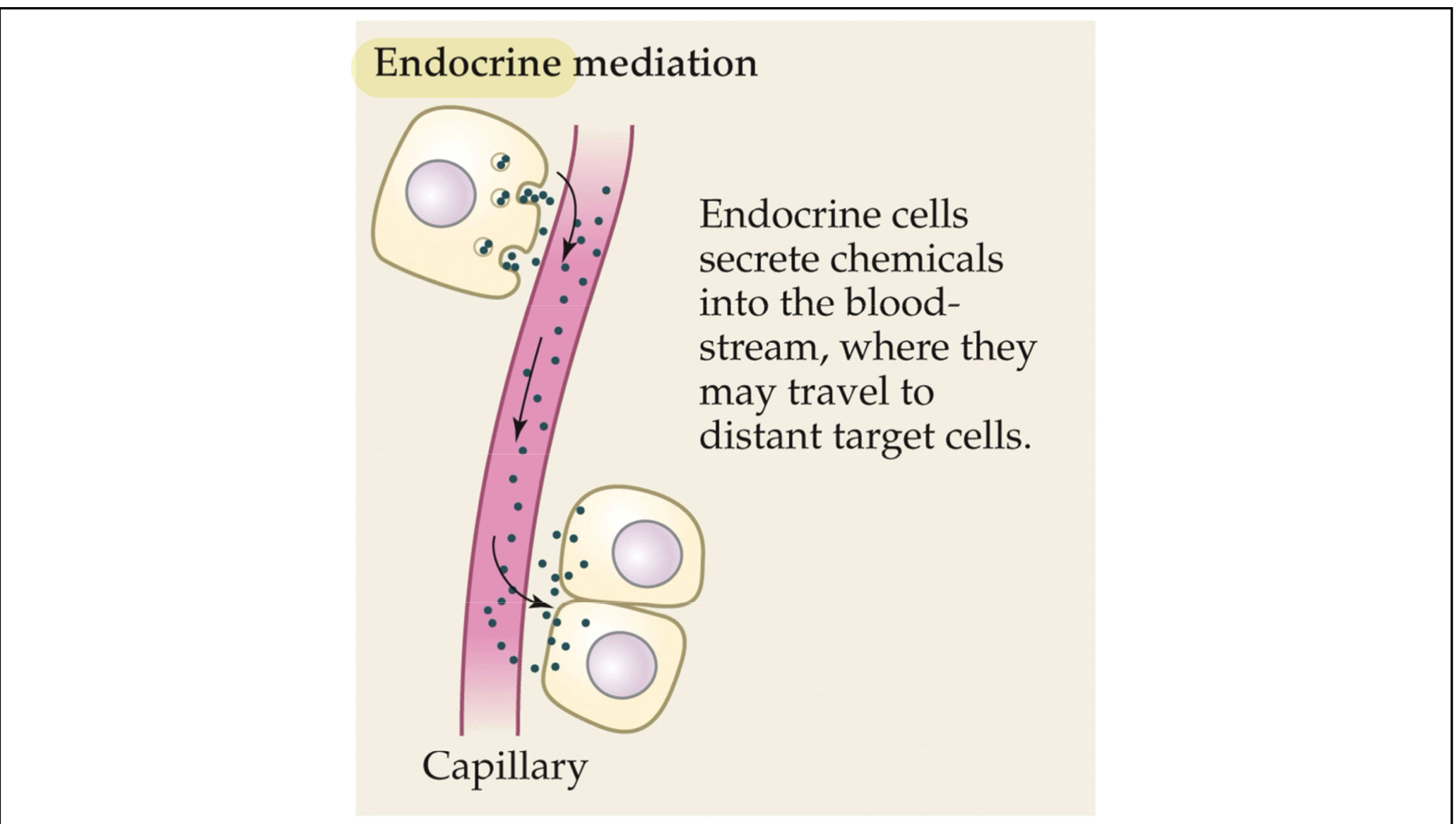
Another visual of how endocrine cells release hormones into the blood stream → the hormones FREELY travel to target cells and bind to cause some kind of affect (does not have a target cell)
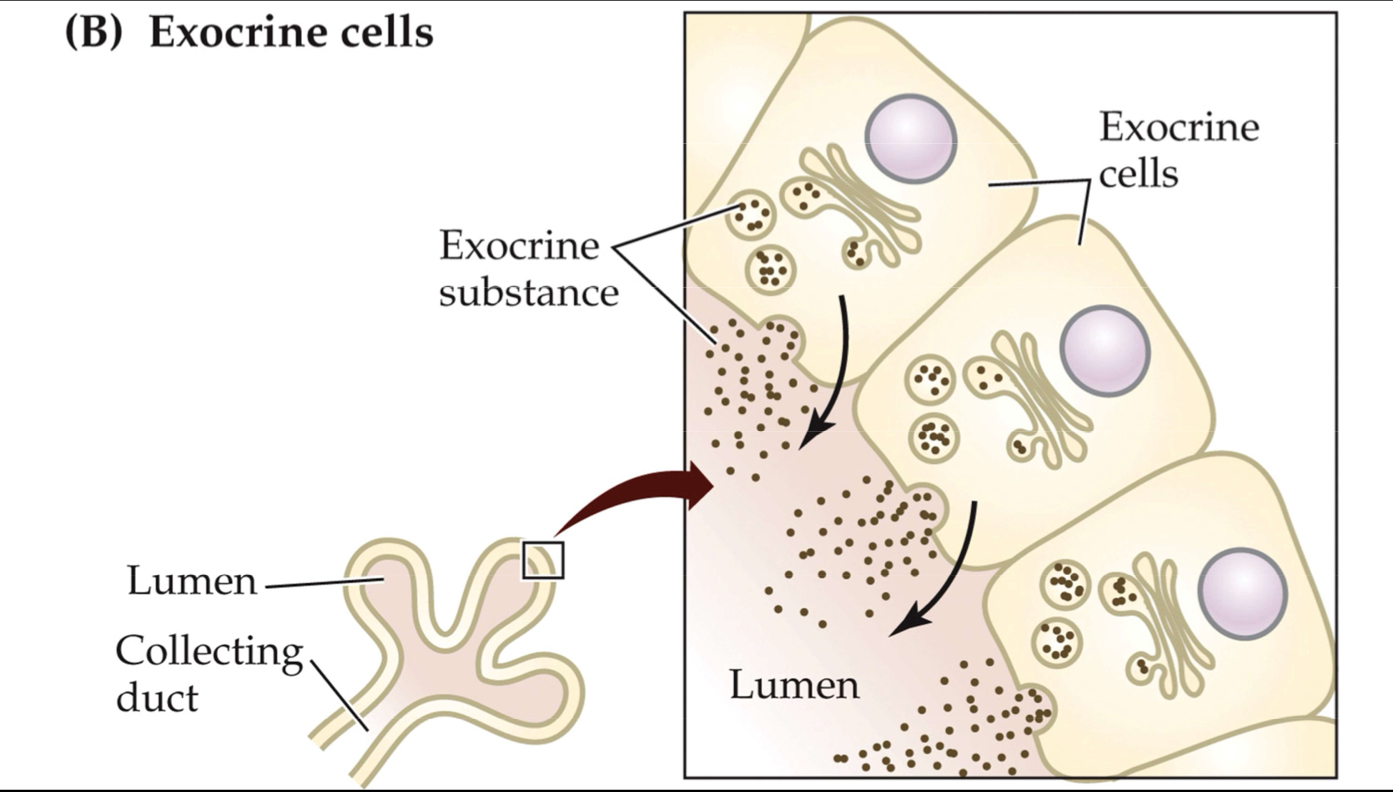
Another visual of how exocrine cells release hormones → releases some hormone from its gland (organ) onto adjacent organs/ environment to cause some kind of change
Carrier protein
One of several different plasma proteins that bind to hormones of low solubility (primarily thyroid and steroid hormones), providing a transport system for them
a protein that binds to steroids to transport them
Vesicle
A secretory granule or sac within a cell in which hormone or neurotransmitter molecules are stored
Exocytosis
The extrusion or secretion of substances from a cell by the fusion of a vesicle membrane with the cell membrane
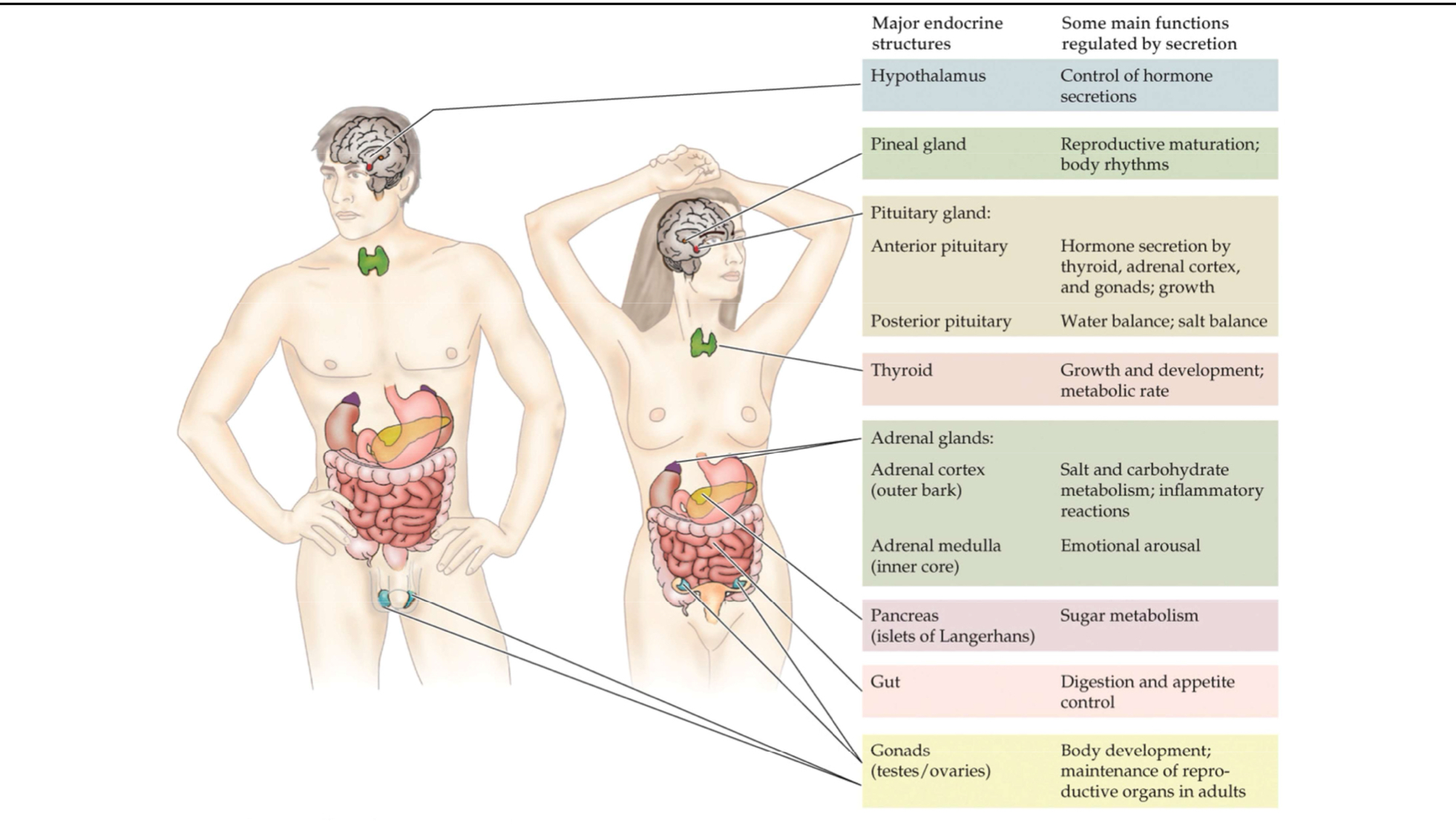
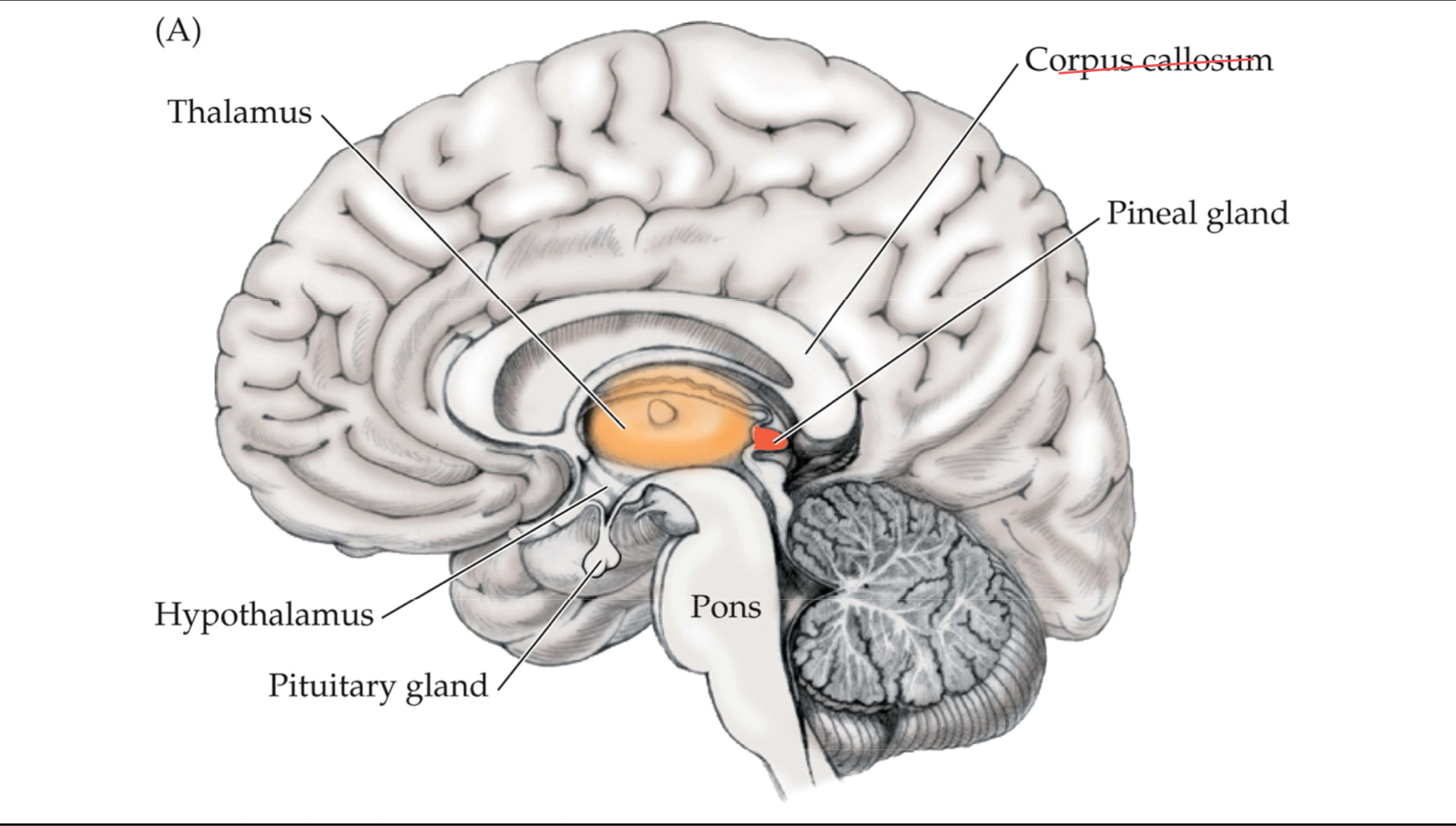
Hypothalamus
An endocrine structure that controls the release of pituitary hormones by secreting ‘releasing’ and ‘inhibitory’ hormones, all of which are called releasing hormones
below the thalamus
Releasing hormones
One of several polypeptides released from the hypothalamus that increase or decrease the release of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and beta-endorphins from the anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
Stimulates releas of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Stimulates release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic hormone
Gonadotropin inhibitory hormone (GnIH)
Inhibits release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH) from the anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic hormone
Prolactin inhibitory hormone (PIH)
Inhibits prolactin release from the anterior pituitary
Hypothalamic hormone
Anterior pituitary
The front part of the endocrine gland that extends from the base of the brain and secretes a number of tropic hormones in response to hormonal signals from the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus secretes peptide hormones to anterior pituitary → anterior pituitary reacts and produces & releases tropic hormones
Communication via blood vessels
Posterior pituitary
The rear part of the endocrine gland that extends from the base of the brain and stores and releases oxytocin and vasopressin, which are produced in the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus produces & stores hormones in posterior pituitary
Communication via neurons
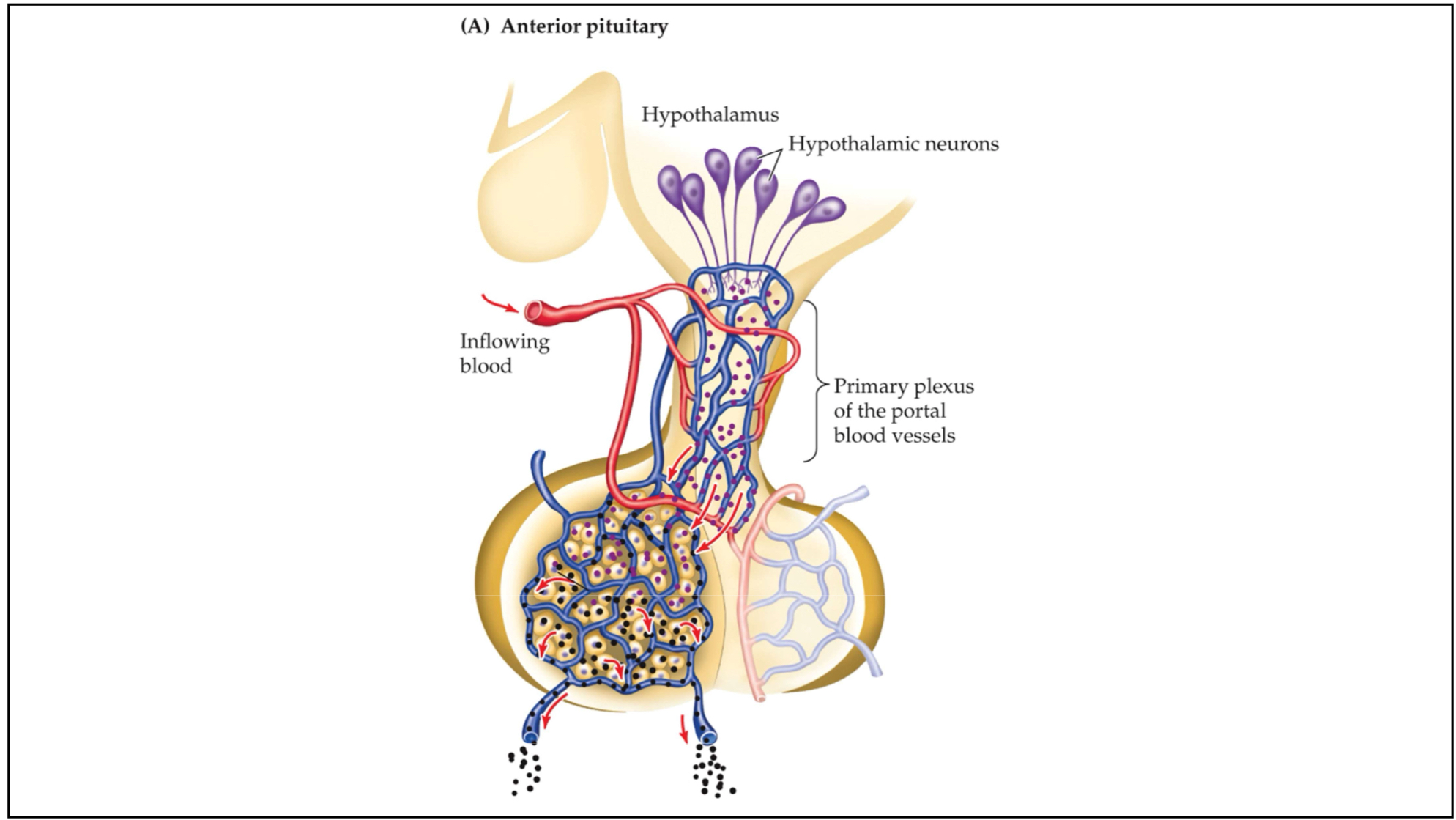
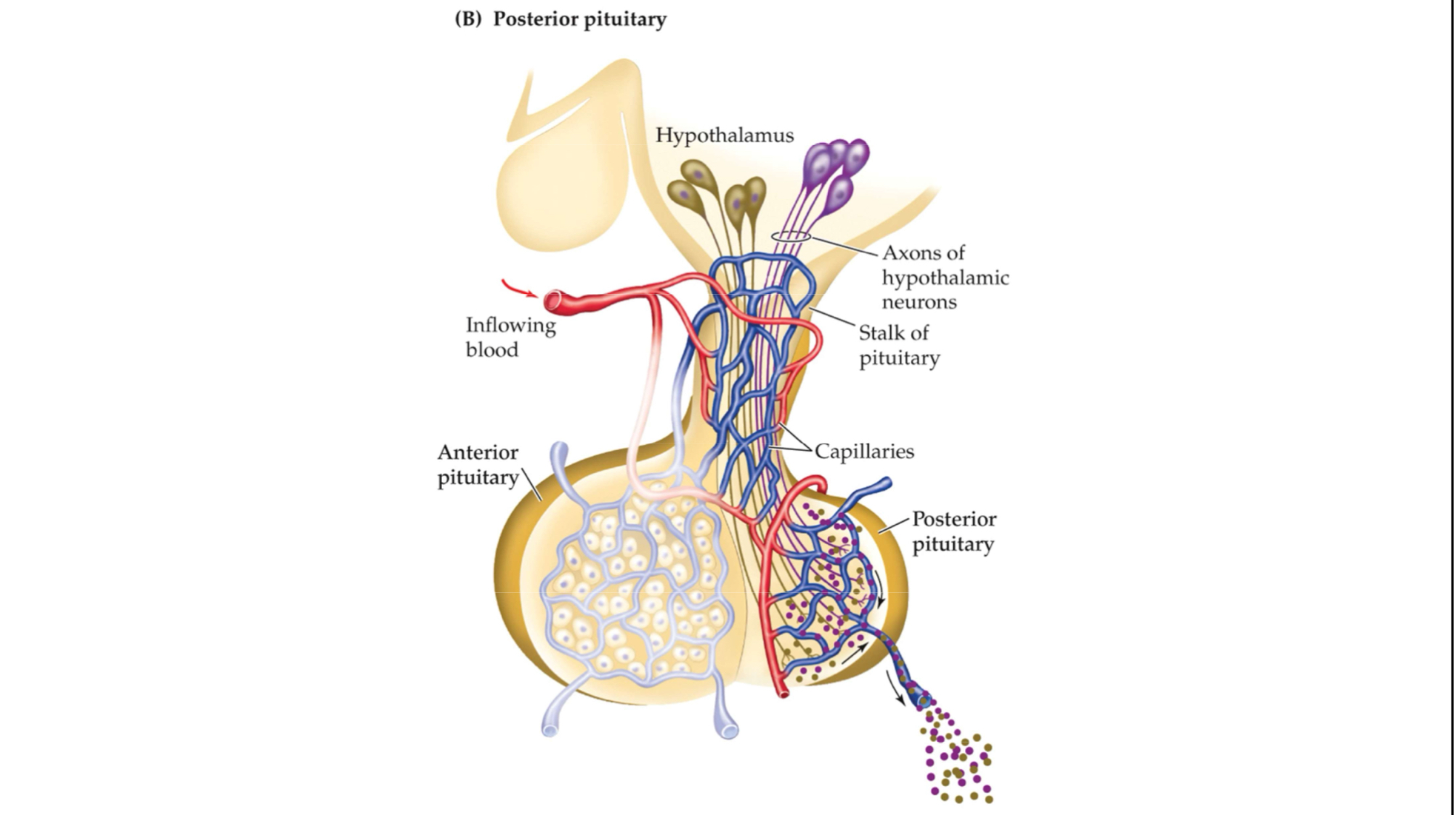
Tropic hormones
Hormones from the anterior pituitary that simulate various physiological processes, either by acting directly on target tissues or by causing other endocrine glands to release hormones
____ ____ trigger endocrine glands to release more hormones
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates release of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex
Anterior pituitary hormone
Beta-endorphins
Stimulates analgesic (pain killing) effects
Anterior pituitary hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates release of thyroid hormones
Anterior pituitary hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulates Leydig cell development and testosterone release in males; stimulates corpus luteum development and progesterone release in females
Anterior pituitary hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Stimulates spermatogenesis in males; stimulates ovarian follicle development and estrogen release in females
Anterior pituitary hormone
Growth hormone (GH)
Stimulates cell growth
Anterior pituitary hormone
Prolactin
Stimulates lactation
Anterior pituitary hormone
Oxytocin
Stimulates milk letdown and uterine contractions during birth
Posterior pituitary hormone
Vasopressin
Increases kidney water absorption; increases blood pressure during serious blood loss
Posterior pituitary hormone
Pineal gland
An endocrine gland that secretes melatonin, a hormone important in the regulation of daily seasonal cycles
Melatonin affects reproductive functions, e.g., timing of puberty
Thyroid gland
A double-lobed endocrine gland located on or near the trachea or esophagus in vertebrates that secretes several hormones important in metabolism, including thyroxine and triiodothyronine
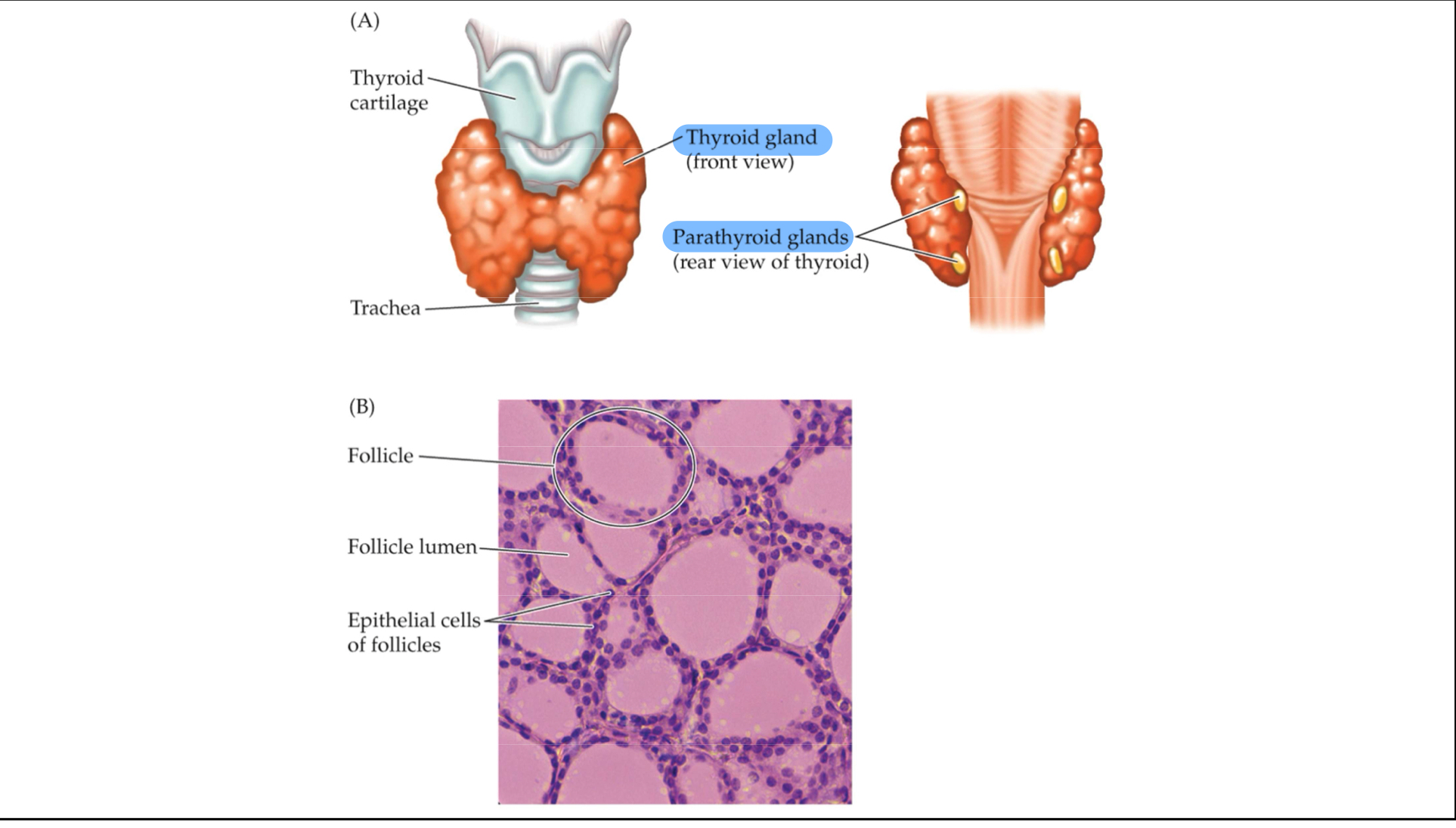
Know the location of the thyroid and parathyroid glands
Thyroxine (T4)
Increases oxidation rates in tissues
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Increases oxidation rates in tissues
Parathyroid gland
Separate endocrine tissues associated with the thyroid gland; produces hormones involved in calcium metabolism
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Regulates blood calcium levels
PTH increases blood calcium when its low
Thymus gland
An endocrine and lymph gland located in the thorax
The ___ ___ increases in size and activity until puberty and then begins in atrophy (decrease in size) and be replaced by fatty tissue
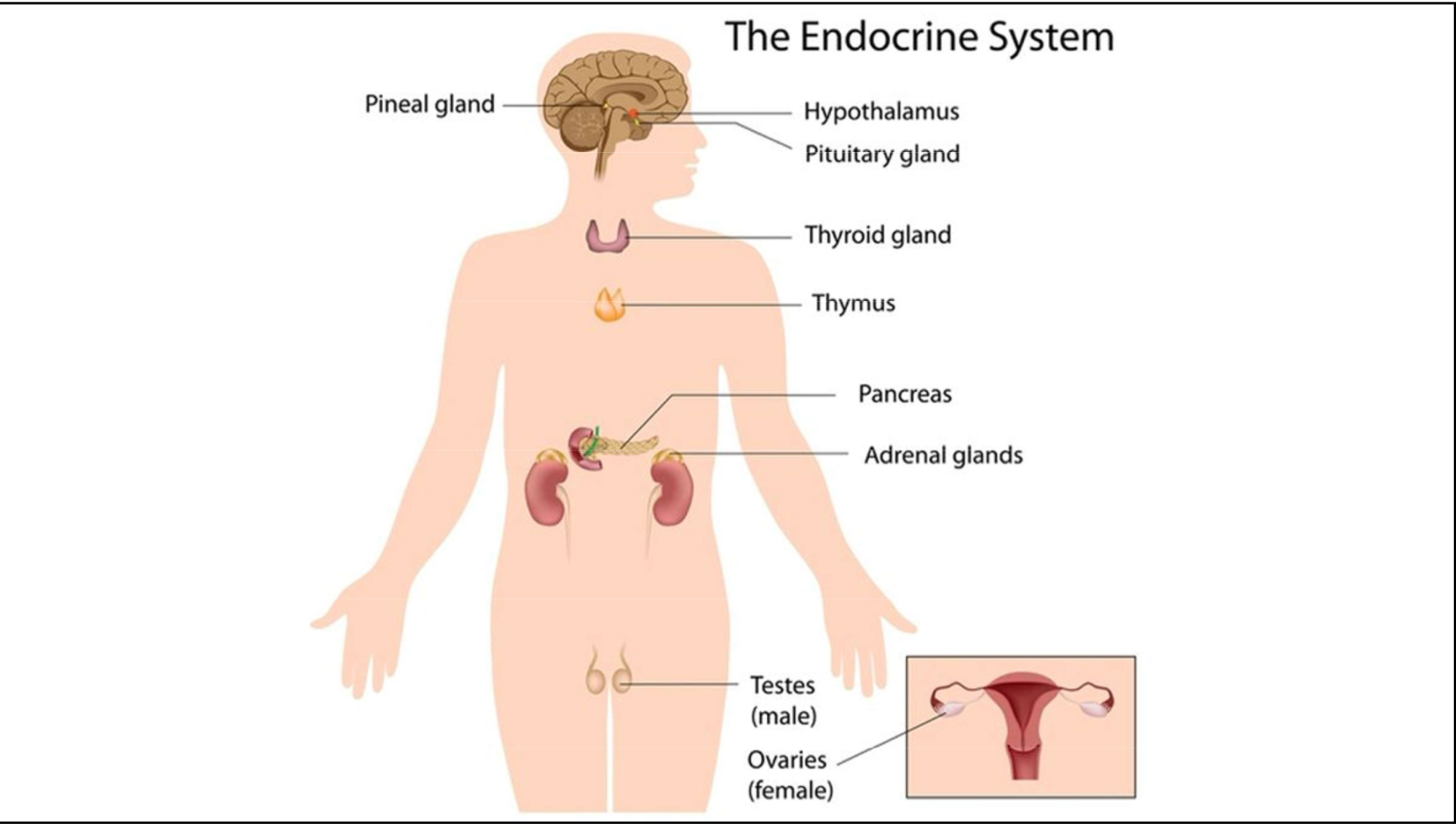
Endocrine system
Thymosin
Stimulates lymphocyte development
Lymphocyte = a type of white blood cell → this hormone is important in immune system functioning
Thymostatin
Stimulates lymphocyte development
Lymphocyte = a type of white blood cell → this hormone is important in immune system functioning
Pancreas
A composite vertebrate gland composed of both endocrine and exocrine functions
Islets of Langerhans
Islands of endocrine tissues nested throughout the exocrine tissue of the pancreas
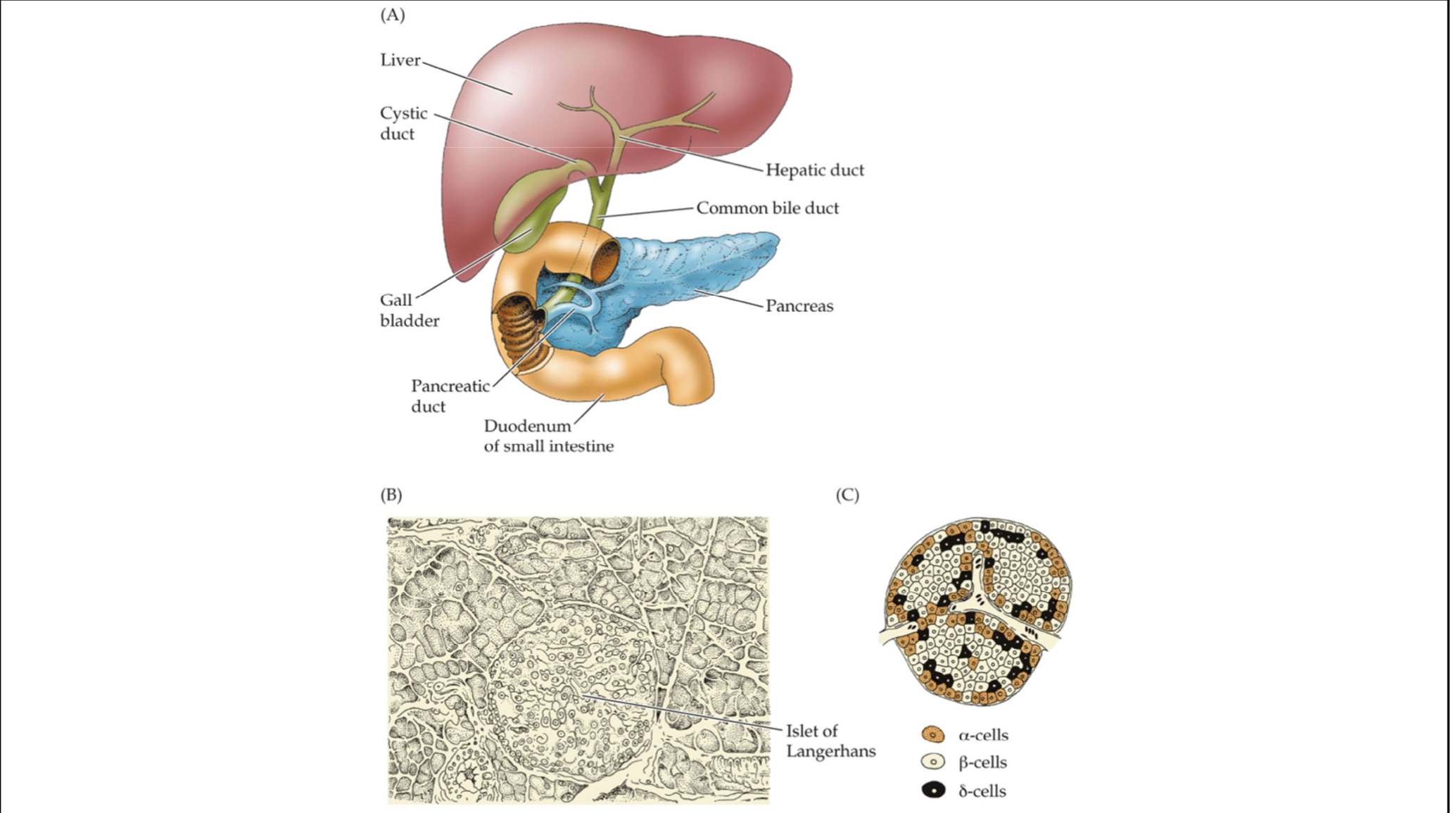
Note the location of the pancreas
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose
pancreatic hormone
Glucagon
Raises blood glucose
pancreatic hormone
Growth hormone inhibitory hormone (GHIH)
Also known as somatostatin, inhibits release of growth hormone form the anterior pituitary, and inhibits pancreatic release of insulin and glucagon
pancreatic hormone
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Moderated food intake
CCK decreases hunger and good intake when you’ve eaten
GI Tract hormone
Ghrelin
Moderated food intake
Ghrelin increases hunger and food intake when you’ve not eaten
GI Tract hormone
Adrenal glands
Paired, dual-compartment endocrine glands in vertebrates consisting of a medulla and a cortex
Adrenal cortex
The outer layer(s) of the endocrine organ that sits above the kidneys in vertebrates and secretes steroid hormones
Adrenal medulla
The inner portion of the endocrine organ that sits above the kidneys in vertebrates and secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
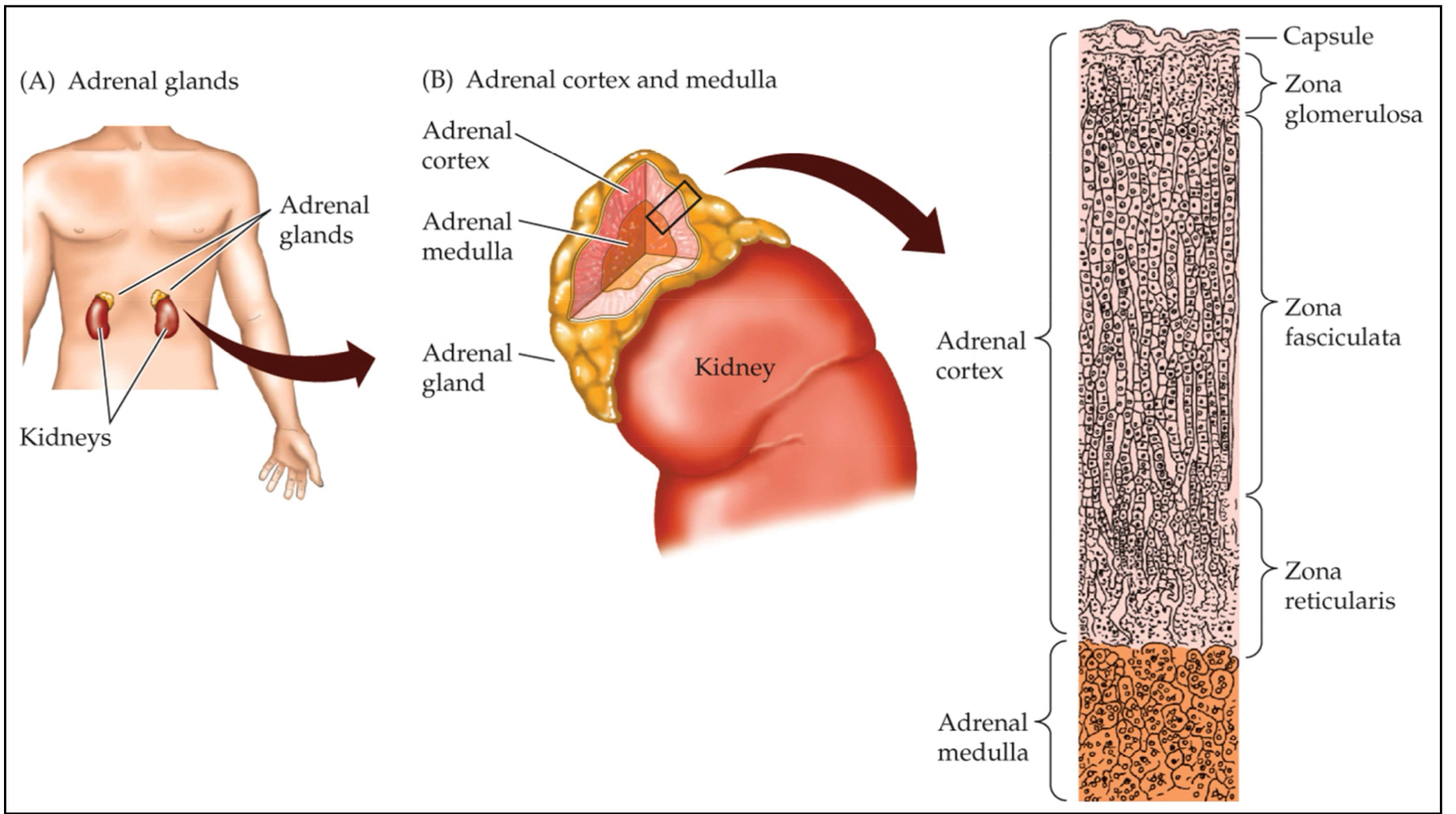
Know the structure/ orientation of the adrenal gland, adrenal cortex, and adrenal medulla in respect to each other
In order from outside to inside:
Adrenal gland → Adrenal cortex → Adrenal medulla
Epinephrine
Mediates the physiological response to stress
Also called adrenaline
Adrenal medulla hormone
Norepinephrine
Mediates the physiological response to stress
Adrenal medulla hormone
Glucocorticoids
Increase carbohydrate metabolism
The primary glucocorticoid in humans is cortisol; in reptiles, birds, and rodents it’s corticosterone
Adrenal cortex hormone
Gonad
An endocrine organ that produces sex steroids and gametes; the ovaries and testes are gonads
Ovaries
The female gonads, which produce estrogens, progestins, and ova
Placenta
A specialized organ produced by the mammalian embryo that is attached to the uterine wall and serves to provide nutrients, hormones, and energy to the fetus
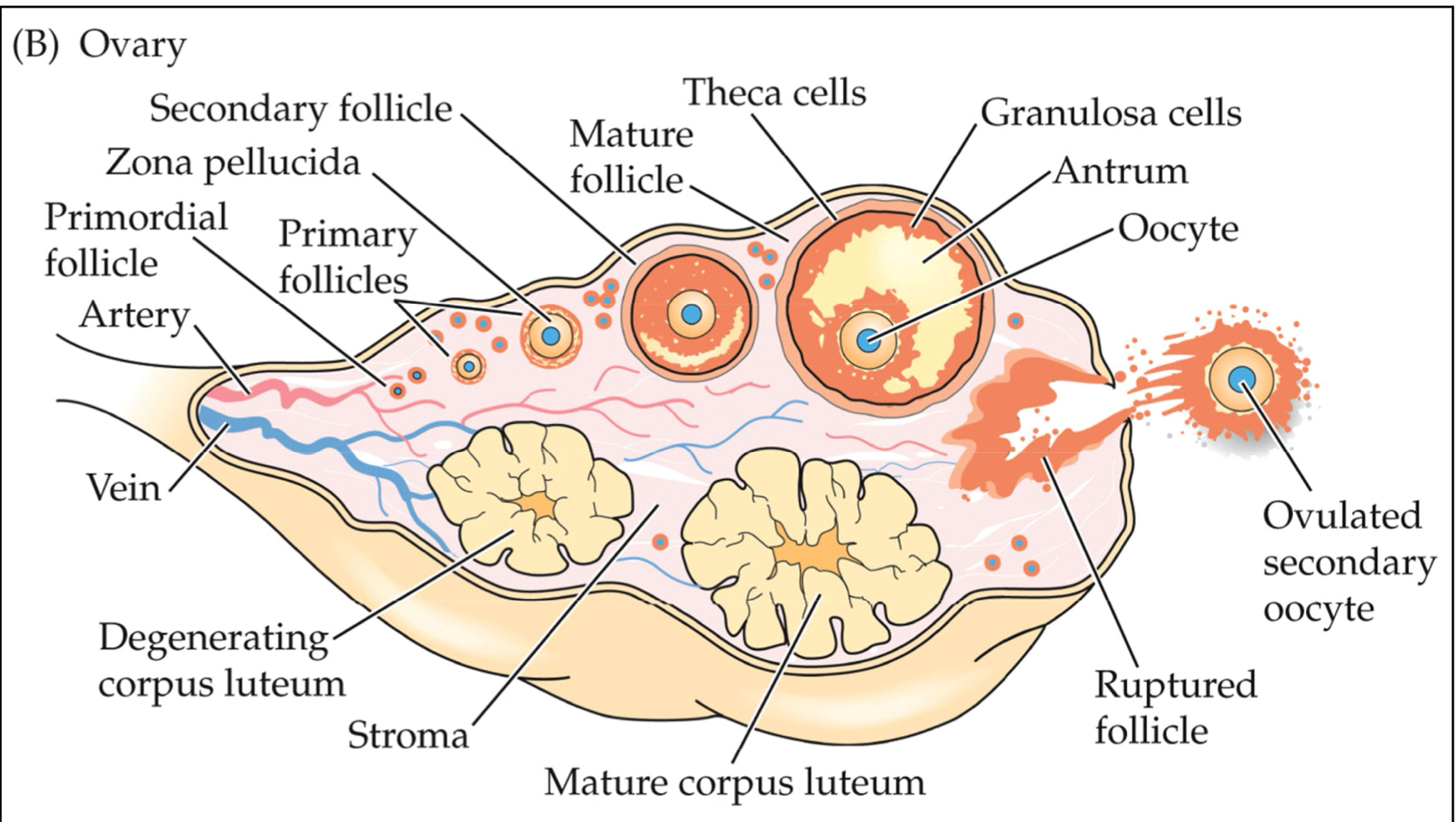
Ovum is released from the ovary
Note that the ruptured follicle stays in the ovary and develops into the corpus luteum