PATHO EXAM 4- ACID/BASE AND RENAL STUFF
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
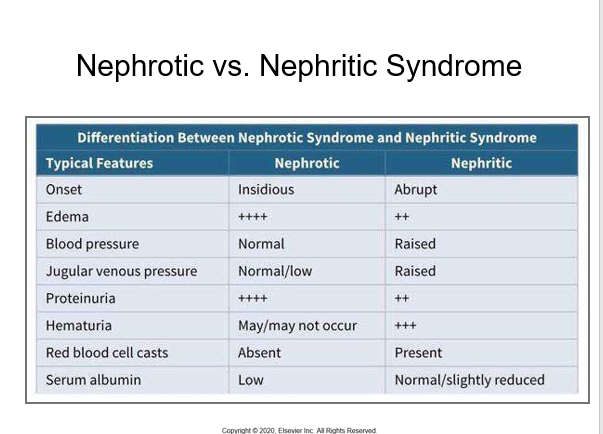
- Nephrotic and nephritic syndromes: clinical and Lab differences
nephrotic
what: glom/podocyte damage
s and s: lotta tein in urine, more edema, NO rbc cast, very low chance of hematuria , has lower serum albumin cuz the more edema
lab:
nephritic
what: ab-ag complex leading to damage to endothelial cells and basement mem
s and s: blood in urine (rbc casts), pyuria, water retention, less severe than rotic
fill out the table type yes if right
onset
edema
bp
jug venous pressure
proteinuria
hematoruira
rbc cast
serum albumin
yes
rotic or ritic is more seen in kids. parents may notice (insert adjective) urine. edema can become more pronounced with blank. breathing becomes hard because of blank. this part of body will see swelling. the skin will be blank and blank. the veins will be blank
rotic. frothy. acietis. pul effusion. scrotum/vag. shiny and pale. prominent
s and s of BOTH RITIC AND ROTIC HELP
edema (more in rotic)
proteinuria (more bad in rotic)
hypoproteinemia (more bad in rotic)
hyperlipdemia
lipiduria
vitamin d low
hypothyroidism
ritic or rotic: pore sizes lg enough due to increased perme of glom filter membrane so now blood can pass thru
ritic
rotic or ritic: glom filter of plasma teins esp albumin is getting reabs too much. now there is high or low oncotic P?
rotic. low.
- Define: GN,
two major symps if severe include blank and blank. other s and s include (these other 5)
what
what: I of glomerulus
s and s: edema, blood in pee, protein in pee, high bp, oliguria, rotic and ritic sediment
Cystitis (adult)
def
most common strain and second most
s and s
a kid will see the same smyps plus another one aka
I of the bladder
e coli and staph sapro
frequency, urgency, dysuria, low back pain, blood in urine, flank pain, urine reflux cuz of uvj distortion, high bp
kid will see enuresis
most common site of UTI is blank
cystitis
urethritis define
I of urethra
usually caused by sexy microO
s and s: tingling,itching,burning of urethral or freq/urgency
pyelonephritis acute
define
most cases in M or F
the most common risk factors include (2)
in kids acute can also lead to blank
infection of one or both upper urinary tracts such as ureter, renal pelvis and kidney interstitium
F
s and s: fever, chills, flank/groin pain, freq, dysuria, costovertebral tenderness
rf= urinary obstruction and reflux of urine
kids= edema
chronic pyelone may be asymtomatic in kids t or f
true
chronic pyelonephritis
def
persistent/recurrent infection of kidney that leads to scarring
the early symps of chronic pyelonephritis are often (maximal or minimal) and may include these four things. progression can lead to blank.
minimal. hypertension, flank pain, dysuria, freq. kidney failure
renal failure means blank. what percentage assc to end stage kidney disease will show a functioning kidney
Kidney failure refers to significant loss of renal function. When less than 10% of kidney function remains, this is termed end-stage kidney disease (ESKD).
- Acute GN: which germ?
usually will see group A β-hemolytic streptococci,
- UTIs: which germ? HELP
e coili
clinical symps of utis
t or f: fever will be seen here
freq, urgency, dysuria, pubic and low back pain
no fever or chills but this will be seen in pyelonephrisits
hydronephrosis complication is most seen in uti t or f
true
what is hydronephrosis
Dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces proximal to a blockage is referred to as hydronephrosis or ureterohydronephrosi
stages of UTI
urethretisi
cytistis
pyelooneprhtisi
pre-renal failure cause is generally due to lack of blank. insert the causes
perfusion issues.
Hypovolemia
Hemorrhagic blood loss (trauma, gastrointestinal bleeding, complications of childbirth)
Loss of plasma volume (burns, peritonitis)
Water and electrolyte losses causing dehydration (severe vomiting or diarrhea, intestinal obstruction, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, inappropriate use of diuretics)
Hypotension or hypoperfusion
Septic shock
Cardiac failure or shock
Massive pulmonary embolism/thrombosis
Stenosis or clamping of renal artery
which drug cate can lead to pre renal failure
NSAIDs
this disease that creates secondary hypertension is seen in (pre renal, intra renal or post renal)
bilateral renal artery stenosis
pre-renal
intra renal is mostly caused by blank. insert the other causes
acute tubular necrosis.
———————————-
Glomerulopathies
Acute interstitial necrosis (tumors or toxins)
Vascular damage like Malignant hypertension or vasculitis
Coagulation defects
Renal artery/vein occlusion
Bilateral acute pyelonephritis
post-renal is generally cuz of a blank. the causes include
urinary tract obstructions that must hut kidneys bilaterally.
kidney stones or clots or edema, benign prostatic hyperplasia, urethral stricture (where scarring causes narrow of urethra), neurogenic bladder, C of prostate cervix or colon
Kidney stones mean growth into a stone via blank. manifestation include blank. tx includes (lowering or increasing) fluid intake
crystallization/agglomeration. renal colic meaning pain due to dilation/spasm, vomming, blood in urine. higher.
1 renal colic with pain to lateral flank/lower abds
2 symps of urgency/frequency, voding, urge, incontinence
3 renal colic with pain starting in flank and going to groin
——————-
A obstruction in renal pelvis/proximal ureter
B miduter obsturction
C lower ureter/ureterovescial junction
1 and B
3 and C
2 and A
- Incontinence types: functional, urge, stress, overflow incontinence
A- sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine. connected to OAB and decreased bladder wall compliance. also seen with involuntary contractions of detrusor (neurogenic or non neuro sources)
B- when the bladder becomes overly distended and urine leaks out due to excessive fullness. dribbling. connected to neurologic lesions, polyneuropathes and urethral obsturction ie big ass prostate
C- combo of both stress and urge incontinence most common in older women
D- involuntary pee leakage but still have healthy normal urinary function. peeing on self because another condition makes it difficult to get to a bathroom in time or prevents you from recognizing that you need to pee aka dementia or immobility
E- invol loss of urine during cough, sneeze, laugh or something that increased abs pressure
1- urge
2- functional
3- stress
4- overflow
5- mixed
1a
b4
c5
2d
3e
- First sign of renal failure (urine output!) HELP
first sign of renal failure is oliguria
- Renal failure and GFR levels
normal =
mild=
moderate=
severe=
end stage=

pt A has 57 ml/min GFR
pt B has 125 ml.min GFR
pt C has 12 ml/min GFr
what stage is each one at
A is moderate
B is normal
C is
- Nephroblastoma: signs, diagnosis
what: embryonal tumor of kidney arising from undiffered mesoderm
signs: kid will be seen with large mass on abomin.
s and s: abd pain, high bp, hemauria, anridia, anemia, fever
when u see ph going into normal status that is very close to end points such as 7.47 or 7.36 this means that u see (blank). pay attn to the clinical story so you know exactly what had been causing the imbalnces in the first place.
compensation
steps of figuring out meta/rez alka or acid (four)
steps of figuring out meta/rez alka or acid
1- look at body ph. acidic or basic?
2- check in with clinical story. is it cuz of rez or meta reasons?
3- cross reference that with seeing what is going on with co2 and bicarb. what is high and low? what does this mean?
Rez acid
- caused by…
-ph levels
-paco2 levels
-compensation vs without compensation (TALK ABOUT BICARB LEVEL)
Rez acid caused by hypoventilation due to emphysema, COPD, pulmonary edema, asthma, monia, sleep apnea
PH= less than 7.38
PaCO2= more than 44 mmHg
compensation= the blood ph has dropped due to a lot of retention of co2. kidney steps in and does high hco3 reabs where we want to see bicarb at more than 24. H ions excreted into urine. you will also see ph level at normal.
uncomp= ph level still low. bicarb normal. this means kidneys have not yet had sufficient time to help out
Meta acidosis
- caused by…
-ph levels
-hco3 levels
-comp vs uncomp (TALK ABOUT PACO2 LEVELS FOR COMP)
caused by= dka, ckd or impairment acid excretion by kidneys, diarrhea, lactic acidosis
ph levels= less than 7.38
hco3 levels= less than 22 meq/L
comp= lungs come to help by breathing deeply and rapidly hyperventilation aka kussmaul breathing in order to get rid of co2 fast. ph level will be normal. co2 level will be at less than 40
umcomp= ph level still low. co2 levels are normal. lungs havent been helping quite yet
Meta alka
-caused by
-ph levels
-hco3 levels
-comp vs uncomp (TALK ABOUT PACO2 LEVELS FOR COMP)
-caused by: vomiting, antacids, pooping a lot, diuretics
-ph levels: more than 7.42
-hco3 levels: more than 26 meq/L
comp= lung help out by slower and shallower ventilation which helps retain co2 aka hypovent. paco2 will now be more than 40 mmhg. ph level will be normal.
uncomp= ph high. normal paco2. lungs havent quite helped out yet
Rez Alkalosis
- caused by…
-ph levels
-paco2 levels
-what happens to blood ph? what does it causes bicarb to do?
caused= stroke, pain, fever, panic attack
ph= more than 7.42
paco2= less than 38 mm hg
comp= kidneys will help by decreasing rate of H ions excreted into urine and reducing the reabs of bicarb ions into plasma. normal ph at fully comp. hco3 will be less than 24 meq/L
uncomp= normal hco3 levels with high ph
- DKA
what is going on?
what type of imbalance is this?
compensation: common early symp of dka is this type of breathing. what is it?
what type of scent will be smelled from breasth
what= formation of ketone bodies which increase blood acidity
type= metabolic acidosis cuz its affecting the body system itself, nothing to do w lungs
compensation= early symp aka kussmual breathing, a type of hyperventilation that is deep and rapid. fast breathing helps get co2 out even quicker in order to compensaste for acidosis since co2 is a type of acid.
breath= fruity
- Ions (cation and anion): which ones are in EC vs Intracellular.
extracell: sodium (cation) and chloride (anion)
intracell: potassium and phospahte (anion)
- Body fluid percentages
blank percent of total body water in adults
blank percent of intracell fluid
blank percent of extracell fluid
blank percent of interstit fluid
blank percent of plasma
60 cent
66 cent or 2.3 intracell
33 cent or 1/3 extracell
80 cent of interstit
20 cent of plasma
extracellular fluid is located (out or in) cell. this includes blank, blank, and blank
outside. includes plasma, interstit fluid, transcell fluid
- Aldosterone and ADH functions
aldosterone= leads Na and h20 back into reabsorption which goes into blood circ, secreting K which reduces loss of h2o in urine and increase BP
ADH= increase h20 (ONLY) reabs into plasma which reduce loss of h2o in urine
- Define: acidosis, alkalosis, hyper/hyponatremia, hyper/hypokalemia, uremia
acidosis= high concentration of H ions, esp co2 or bicarb is v low. ph is very low
alkalosis= a state of high concentration of OH ions like bicarb as well as v low H ions. ph is high
hypo/hyper natremia= low or high sodium levels
hyper/hypo kalemia= low or high K
- Signs of hypercalcemia
v tired
weak
naseous
constipation
impaired rneal func/0kidney stones
dysrhytmias
bone pain/osteoporosis