Unit 7: Organic chemistry
1/75
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
what is the general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
alkanes are … molecules because the carbon atoms are fully … to the … atoms
saturated
bonded
hydrogen
what is a hydrocarbon
a molecule made up of only carbon and hydrogen
features of crude oil
made over millions of years from remains of plankton in mud
found in rocks
mixture of hydrocarbons
as the size of hydrocarbon increases, the … the viscosity (runny/ …)
higher
thickness
as the size of hydrocarbon increases, the … the flammability
lower
as the size of hydrocarbon increases, the … the boiling point
higher
what do hydrocarbon fuels release when combusted (burned)
energy
are carbon and hydrogen atoms oxidised or reduced in combustion
oxidised
what happens if the oxygen supply is unlimited in the combustion of hydrocarbons and what is this reaction called
the reaction also produces CO2 and water which is called complete combustion
what are the steps to the fractional distillation of crude oil
crude oil is heated at very high temp causing it to boil
crude oil vapour is fed into the column
hydrocarbon vapours rise up the column
hydrocarbons condense when they reach their boiling point
liquid fractions are then removed
remaining hydrocarbon move up column
they condense when they reach their boiling points
what are some fractions used for in the fractional distillation of crude oil
feedstock which is a chemical used to make other chemicals
what is cracking
when a long-chain alkane is broken down to produce smaller molecules
what does cracking make
alkenes which have at least one carbon to carbon double bond
what are the conditions needed for cracking
high temperature
high pressure
what are alkenes useful for
to make polymers
used as a starting material for chemicals
how can we test for alkenes
shake alkene with bromine water
bromine turns colourless if alkene is present
what is the general formula for alkenes
CnH2n
alkenes are … because they have … fewer hydrogen atoms than the alkane with the same number of … atoms
unsaturated
two
carbon
what does ethene look like
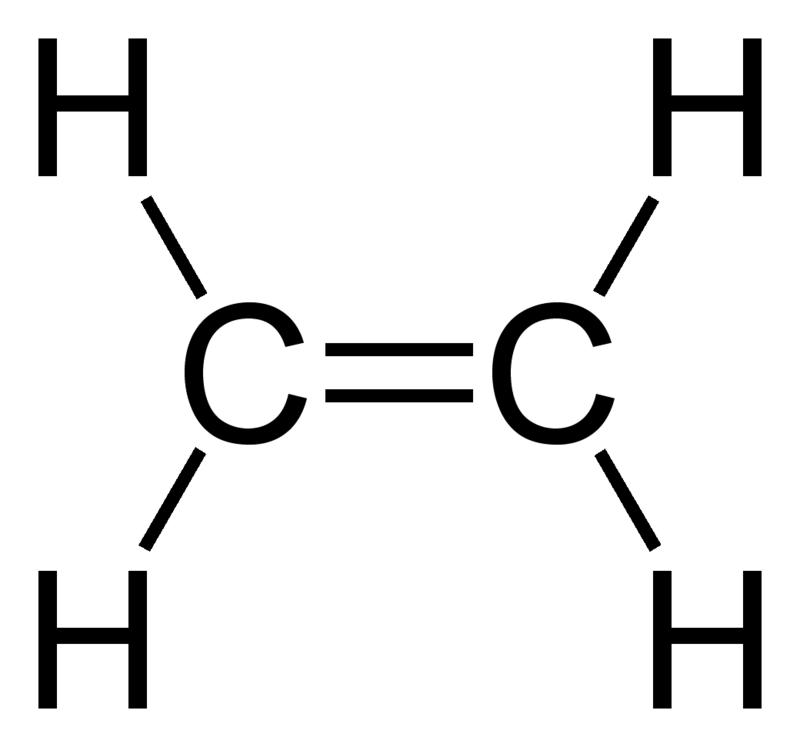
what does propene look like
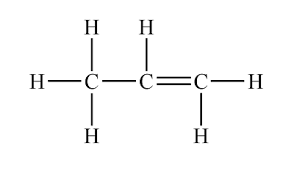
what does butene look like
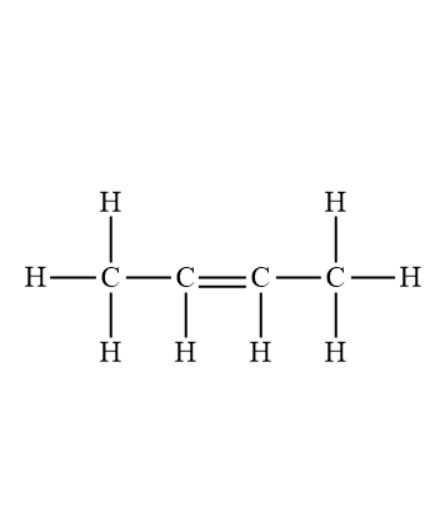
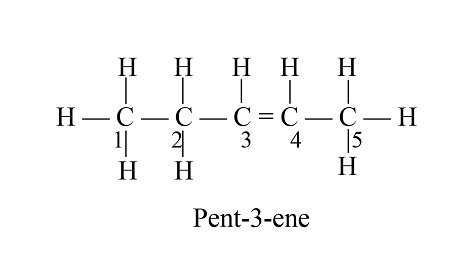
what does pentene look like
what is a functional group
part of a molecule that determines the way it reacts
what is a homologous group
members with the same functional group
what does combusting and alkene produce and what is this reaction called
CO2, water, unburnt carbon particles
incomplete combustion
what does reacting an alkene with hydrogen produce and what is this reaction called
an alkane
hydrogenation
what does reacting an alkene with water (in the form of steam) produce and what is this reaction called
an alcohol
hydration
what type of reaction is hydration
reversible reaction
what are the conditions of hydration
300 degrees Celsius
7 atm (pressure)
phosphoric acid catalyst
what does reacting an alkene with a halogen produce and give an example
di(start of halogen name)(alkane name)
e.g. dichloroethane
what does methanol look like
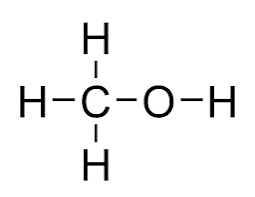
what does ethanol look like
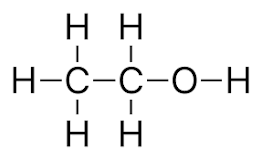
what does propanol look like
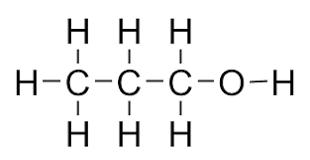
what does butanol look like
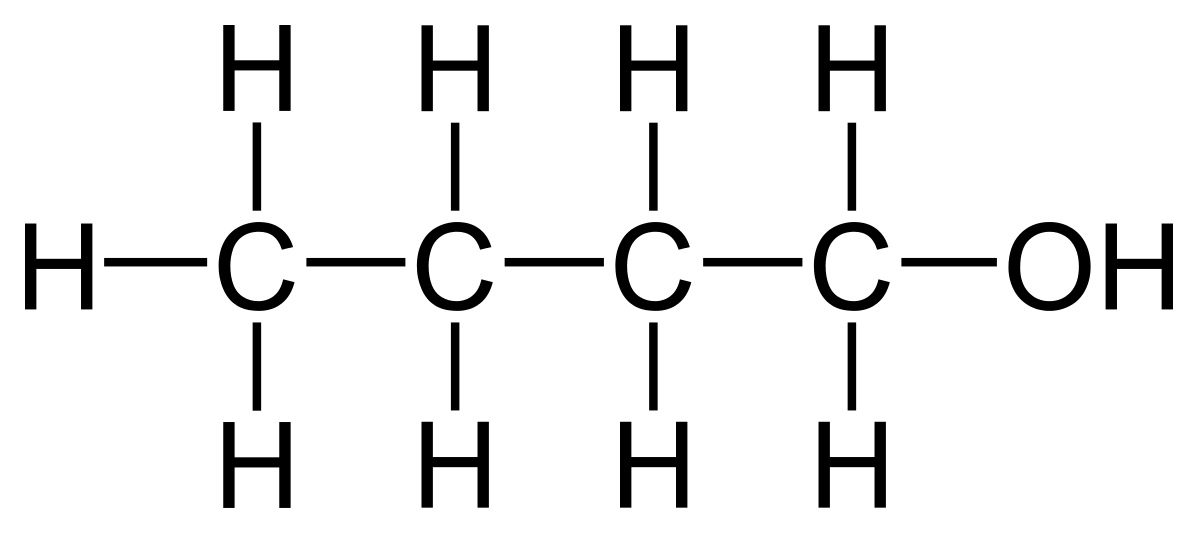
what is the functional group of alcohols
OH
what are the uses of alcohols
fuels
solvents
drinks
what are the advantage of the hydration of ethene
high yield of ethanol produced
what are the disadvantages of the hydration of ethene
requires lots of energy
ethene in the reaction comes from crude oil which is non-renewable
what is the equation for the fermentation of sugar and at what temperature should it be carried out at
30 degrees Celsius

what are the advantages of the fermentation of sugar
not a lot of energy required
reaction comes from plants so is renewable
what are the disadvantages of the fermentation of sugar
product is an aqueous solution
alcohols are … in water and form … solutions
soluble
neutral
as number of carbon atoms increase, solubility …
decreases
what is produced in the reaction between alcohols and sodium
bubbles of hydrogen and sodium ethoxide
what is produced in the reaction between alcohols and oxidising agents
carboxylic acid and water
what does the combustion of alcohol produce
CO2 and water
are carboxylic acids weak or strong acids in water
weak
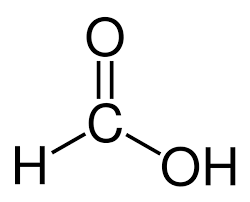
what does methanoic look like
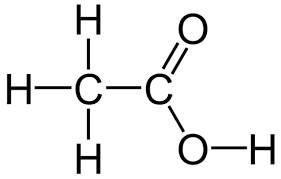
what does ethanoic look like
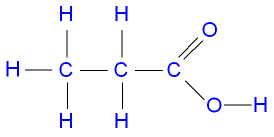
what does propanoic look like
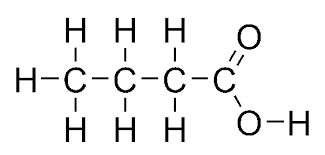
what does butanoic look like
what is the functional group of carboxylic acids
C=O
I
OH
what does the reaction between carboxylic acids and metal carbonates produce
a salt, water and CO2
what does the reaction between carboxylic acids and alcohols produce
an ester and water
what type of reaction is the reaction between carboxylic acids and alcohols
reversible reaction
what is required in the reaction between carboxylic acids and alcohols
sulfuric acid as a catalyst
what is a polymer
thousands of small, identical molecules
what is a monomer
the small, identical molecule in a polymer
are the monomers alkanes or alkenes in addition polymers
alkenes
addition polymers have the same … as the monomer
atoms
does a monomer have a double or single carbon to carbon bond
double
does a polymer have a double or single carbon to carbon bond
single
how do you name a polymer and give an example
poly(name of monomer/ alkene)
e.g. polyethene
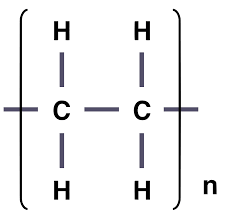
what does a repeating unit look like in addition polymers and does it contain a double bond
no
in condensation polymers, the monomers are not … . when the monomers react, we … small molecules such as …
alkenes
lose
water
with condensation polymers, we start with two different … . each monomer has to of the same …
monomers
functional groups
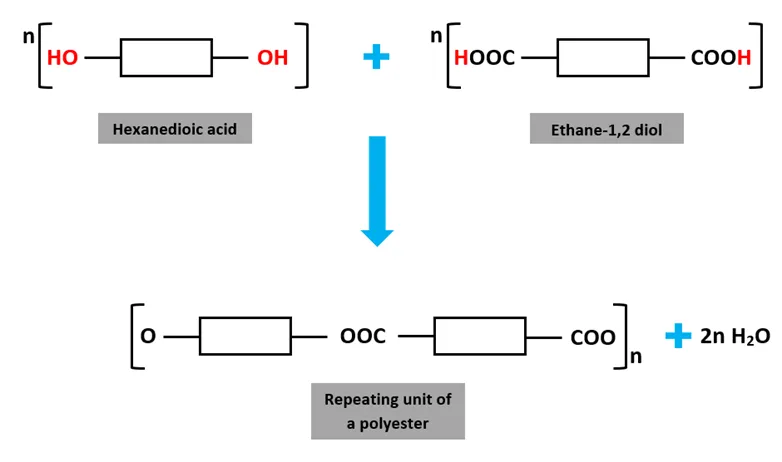
what is a polyester
a polymer with thousands of monomers
what does a repeating unit look like in condensation polymers
what can amino acids react to form
a condensation polymer and water
what is a polypeptide
a polymer made from one type of amino acid
what is a protein
a polymer made from different amino acids
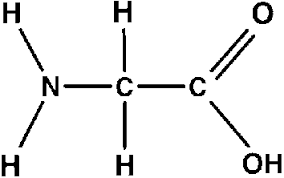
what does glycine look like
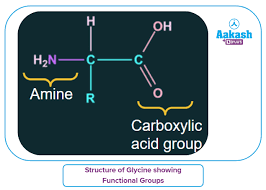
what are the functional groups of glycine
what does DNA consist of
two polymer chains made from monomers called nucleotides
what are the naturally occurring polymers and what are they polymers of
proteins → polymers of amino acids
starch → polymer of glucose
cellulose → polymer of glucose