Cornea 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the major concepts regarding the Cornea?
Part of fibrous tunic
Transparent
Tough
Highly innervated
Avascular
Major REFRACTIVE component of the Eye
What are the dimensions of the cornea?
Anterior 1/6th of the eye
Area: 1.3 cm²
Steeper curvature vs Sclera
What is the External Scleral Sulcus?
Where the cornea and sclera meet
What is the anterior dimensions of the corneal?
Horizontal: 11.7-12.6 mm
Vertical: 10.6-11.7 mm
What are the dimensions for Posterior Cornea?
Horizontal/Vertical: 11.7 mm
What is the overall dioptric power of the WHOLE cornea?
+43.00 D
What are the Radius of curvature for the Cornea?
Anterior: 7.8 mm
Posterior: 6.5 mm
What is the refractive index of the Cornea?
1.376
What type of refractive error is most common?
Axial
What is Astigmatism?
Unequal curvature of refractive structures
Multiple focal points, can’t be focused as one on the retina
What is WTR, ATR, and Oblique Astigmatism?
WTR— Steeper in Vertical meridian (power is in the horizontal)
ATR— Steeper in the Horizontal meridian (power is in the vertical)
Oblique— Steeper curvature in oblique axis (neither 90 or 180 and outside the range)
What is Irregular and Lenticular Astigmatism?
Irregular— Steepest and flattest meridians are NOT 90 degrees apart
Lenticular— Unequal curvature of the lens.
What is the Average Central Corneal Thickness?
520-550 um
What is the average Peripheral Corneal thickness?
670 um
What happens if there are thick or thin corneas to IOP?
Thick— Artificially high IOP
Thin— Artificially low IOP
****Thin central corneas are a risk for Glaucoma
African Americans generally have thinner corneas
What is a Pachymeter?
Measures central corneal thickness with ULTRASOUND
What is the Bulbar Limbus?
Fascia Bulbi (Tenon’s capsule)— Green
Strongly adheres to episclera and conjunctiva
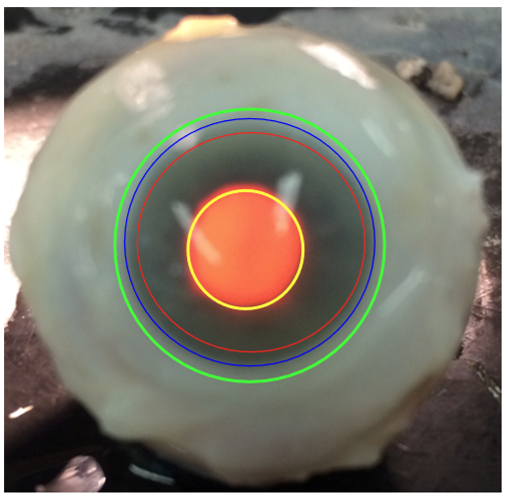
What is the Corneoscleral Limbus?
Juncture of cornea and sclera, 1-2 mm wide —Blue
***You shouldn’t see blood vessels grow past the Corneoscleral Limbus
What is the Conjunctival Limbus?
Conjunctiva extends 1 mm beyond corneoscleral limbus —Red
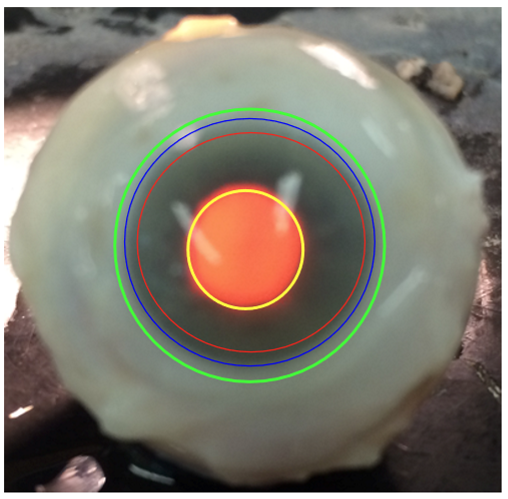
What is the optical zone?
Central 4mm of cornea —yellow
What are some characteristics of the Corneal Tear Film?
3 microns thick
3 layers
Volume of 6.2 microliters
Rate of production 1.2 microliters/sec
What makes up the lipid layer?
Secreted by Meibomian glands
What makes the aqueous layer?
Lacrimal gland
What makes the mucous layer?
Goble cells in Conjunctiva.
Is the tear film distinct layers?
No, form a colloidal matrix
What is glycocalyx?
Secreted by epithelial cells
Includes trans membranous mucins
What are the characteristics of Corneal Histology?
Predominantly Extracellular material
Sheet of cells
Anterior epithelium has 5-7 layers
Endothelium is MONOlayer
Attach via basement membranes
What are the layers of the Cornea?
Epithelium
Bowman’s layer
Stroma
Descemet’s membrane
Endothelium
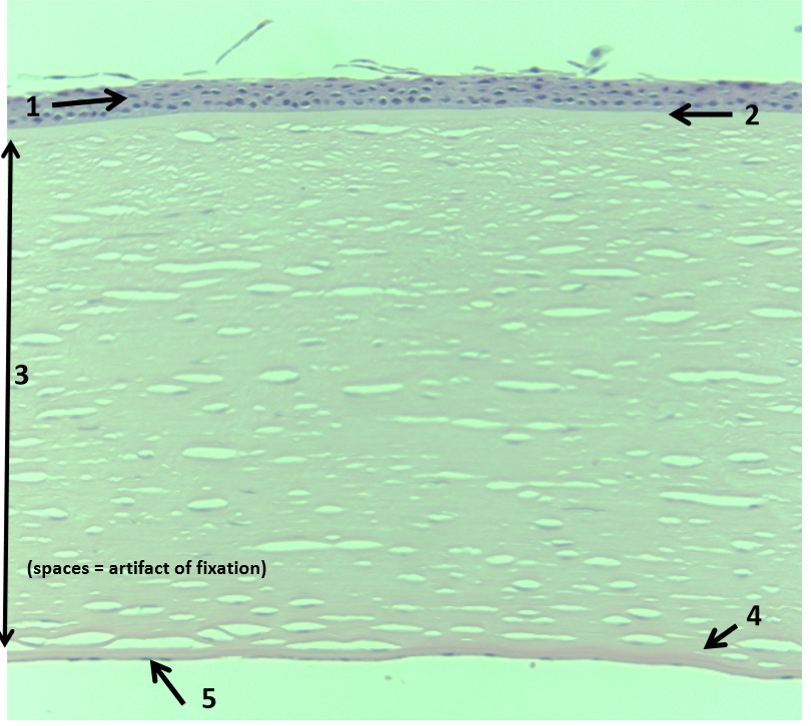
What are the characteristics of Corneal Epithelium?
Non-keratinized Stratified squamous epithelium
50-60 um in thickness
Continuous with bulbar conj. epithelium
Melanocytes and Langerhann’s cells
ANCHORS TO basement membrane
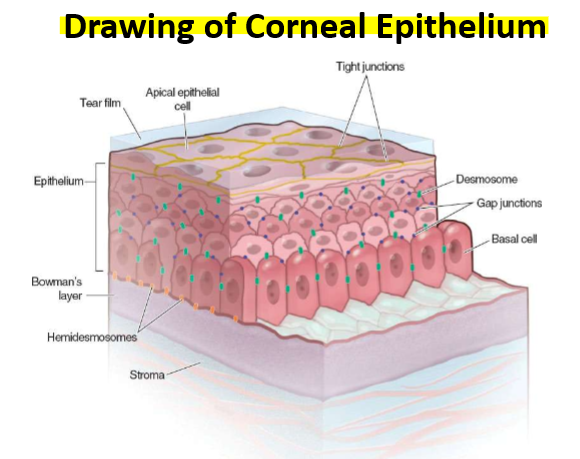
How many layers make up the Epithelium?
5-7
What cell types make up the Epithelium?
Apical (superficial layer), 1-2 layers
Wing cells, 2-3 layers, Desmosomes/gap junctions
Columnar basal cells, held to Bowman’s layer by hemidesmosomes.
Why is Microplicae important?
Helps maintain mucoid layer
Loss of these “ridges” can lead to dry eye symptoms.
What is found between Apical cells?
TIGHT JUNCTIONS
Zona Occludens take 1 hr to reform
What are the characteristics of Wing Cells?
Attached to adjacent cells via desmosomes
Gap junctions
Become flatter the higher they move to surface
What are some characteristics of Basal Cells?
Attached via desmosomes
Gap Junction
Mitotic division
What is the Lamina Lucida?
Translucent layer of Basement Membrane
What is Lamina Densa?
Dark layer composed of collagen
Below Lamina Lucida
What are the two layers of the Basement Membrane?
Lamina Lucida, Densa
How long does it take to replace corneal epithelim?
7-10 days
If the basement membrane gets damaged, how long does it take to repair?
Months
Why is Adhesion Complexes important?
It keeps epithelium from sloughing off
Be able to know where gap junctions and Hemidesmosomes are at
Draw
Where are Langerhan’s Cells found?
Peripheral cornea
Antigen recognition and processing
Where are Melanocytes found?
Peripheral cornea
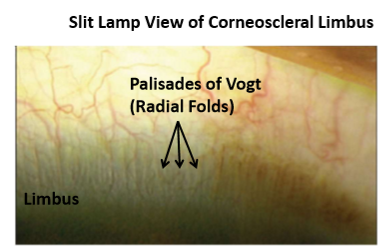
What are Palisades of Vogt?
Limbal stem cell population
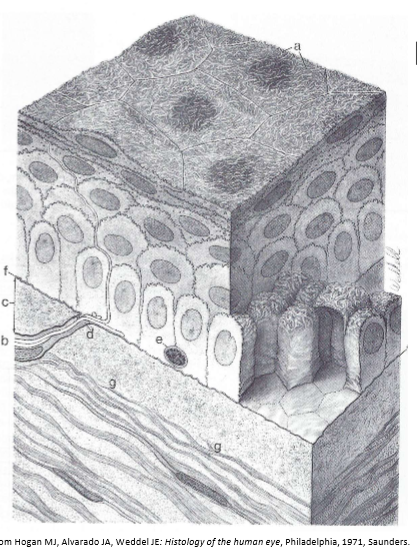
What are these structures?
A. microplicae
B. Corneal nerve
C. Bowman’s layer
D. Naked nerve
E. Lymphocyte
F. Basement membrane
G. Anterior Stromal lamellae
What is a corneal abrasion?
Scratch on the cornea
Painful, but not usually severe
Symptoms of Corneal Abrasion
Pain
Foreign body sensation
Tearing
Discomfort when blinking
What do you do with a Corneal Abrasion?
Rinse with clean water/saline
DO NOT RUB
Aggressive lubrication, antibiotic ointment or drops.
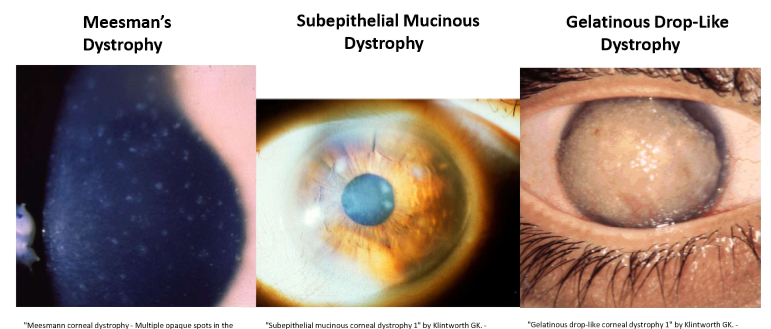
What are some Epithelial Dystrophies?
Meesman’s Dystrophy
Subepithelial Mucinous Dystrophy
Gelatinous Drop-like Dystrophy
What are some characteristics of Bowman’s Layer?
Structural support
Oriented collagen fibers
NO KERATOCYTES
8-12 um thick
Pores for passage of corneal nerve fibers
DOS NOT REGENERATE
If damaged, replaced by thickened epithelium
Is Bowman’s membrane a true basement membrane?
NOPE
Characteristics of the Stroma?
90% of Corneal thickness
450-500 um
Collagen, Keratocytes, ground substance
Collagen organized in layers (lamellae)
GAGS pull aqueous humor into cornea
Keratocytes interspersed between lamella (maintains collagen/ground substance)
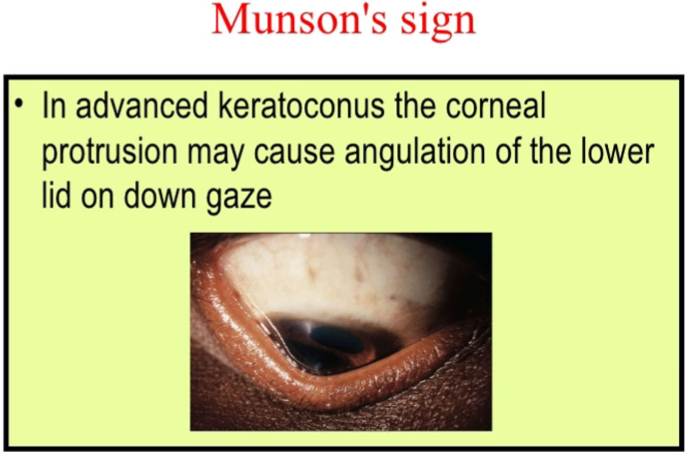
What is Munson’s sign?
You can see Keratoconus corneal protrusion when pt. looks at down gaze
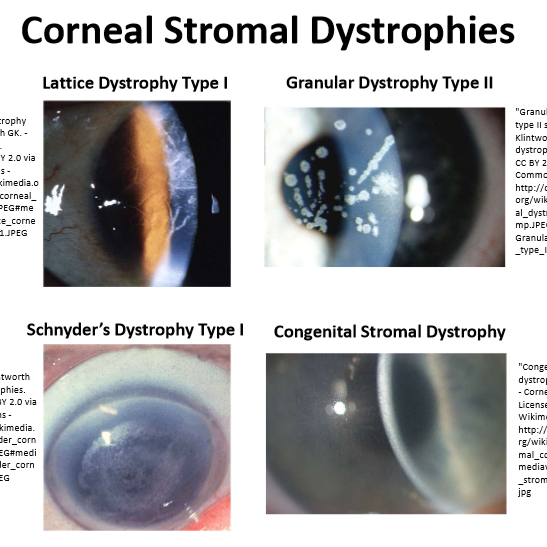
What are some Stromal Dystrophies?
Lattice Dystrophy Type 1
Granular Dystrophy Type 2
Schnyder’s Dystrophy Type 1
Congenital Stromal Dystrophy