LAB PRACTICAL #1
1/190
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
Define a hormone
A chemical messenger that regulates specific body functions
Define a target cell
A tissue cell that has a receptor protein on its plasma membrane or in its interior for a hormone to bind to
Define a receptor
A protein that binds specifically with other molecules
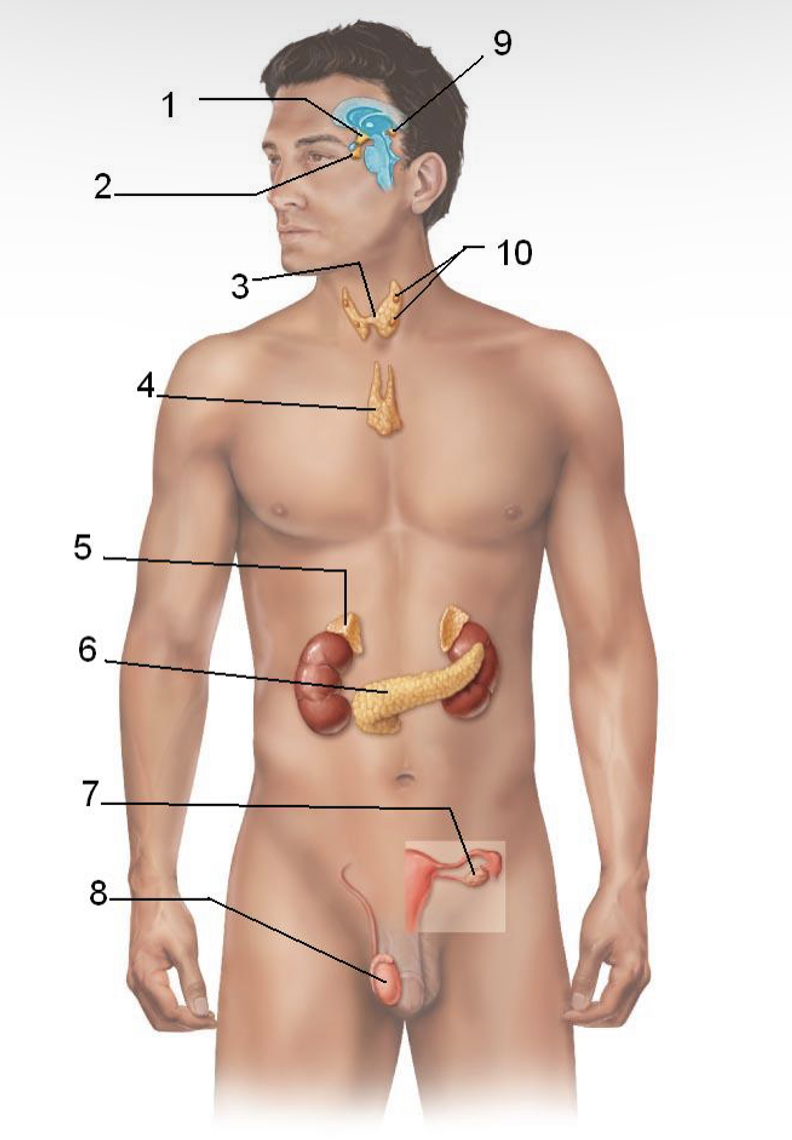
Identify and name the major endocrine glands & tissues of the human body
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Thymus
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Ovary
Testes
Pineal gland
Parathyroid gland
Name the hormone:
GH
Growth hormone
Name the hormone:
TSH
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Name the hormone:
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Name the hormone:
FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone
Name the hormone:
LH
Luteinizing hormone
Name the hormone:
PRL
Prolactin
Name the hormone:
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone
Name the hormone:
OT
Oxytocin
Name the hormone:
CT
Calcitonin
Name the hormone:
NE
Norepinephrine
Name the hormone:
EPI
Epinephrine
Name the hormone:
ICSH
Interstitial-cell stimulating hormone
Name the hormone:
TH
Thyroid hormone
Name the hormone:
PTH
Parathyroid hormone
What hormone(s) do the anterior pituitary gland create & secrete?
FSH
LH
ACTH
PRL
GH
TSH
What hormone(s) do the posterior pituitary gland secrete?
ADH
OT
What hormone(s) do the hypothalamus gland create, but don’t secrete?
ADH
OT
What hormone(s) do the hypothalamus gland create & secrete?
Releasing/Inhibiting hormones
What hormone(s) do the pineal gland create & secrete?
Melatonin
What hormone(s) do the thyroid gland create & secrete?
TH
T3 - Triiodothyronine
T4 - Thyroxine
What hormone(s) do the thymus gland create & secrete?
Thymosin
What hormone(s) do the adrenal medulla create & secrete?
EPI
NE
collectively know as adrenaline
What hormone(s) do the adrenal cortex gland create & secrete?
Zona glomerulosa - mineralocorticoids, primarily aldosterone
Zona fasciculata - glucocorticoids, primarily cortisol
Zona reticularis - gonadocorticoids, primarily androgens
What hormone(s) do the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans gland create & secrete?
Glucagon
What hormone(s) do the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans gland create & secrete?
Insulin
What hormone(s) do the ovaries gland create & secrete?
Estrogen
Progesterone
What hormone(s) do the testes gland create & secrete?
Testosterone
What hormone(s) do the heart create & secrete?
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
What hormone(s) do the kidneys create & secrete?
Renin
Erythropoietin
Calcitrol
What is the function of FSH?
Causes the secretion of estrogen (regulates menstrual cycle) in females & causes sperm production in males
What is the function of LH?
Triggers ovulation in females, causes the endocrine cells of the testis to produce testosterone in males
What is the function of ACTH?
stimulates the production of adrenal glucocorticoids (cortisol)
What is the function of PRL?
Stimulates milk production in females
What is the function GH?
Stimulates growth of all body tissues, especially skeletal muscle & bone; mobilizes fat
What is the function of TSH?
Stimulates thyroid hormone production
What is the function of ADH?
Stimulates kidneys to reabsorb water
What is the function of OT?
Stimulates contraction of the uterus during childbirth and the ejection milk after delivery
What is the function of melatonin?
Helps set sleep-wake cycle
What is the function of TH?
Accelerates cellular metabolic rate; involved in glucose oxidation (breakdown of glucose into ATP & NADH)
What is the function calcitonin?
Regulates calcium by lowering absorption (released in response to high calcium levels)
What is the function of thymosin?
Involved in t-cell development & important for immune response
What is the function of EPI?
Adrenaline; chief adrenal medulla hormone
What is the function of NE?
Adrenaline; 20-25% of medulla secretion
What is the function of cortisol?
Assists the body to resist stress; depresses inflammatory & immune response; promotes gluconeogenesis (formation of glucose); mobilizes fat for energy; stimulates protein catabolism (break down)
What is the function of aldosterone?
Increase levels of Na+ & decrease levels of K+; blood volume and pressure rise
What is the function of androgens?
Controls male secondary sex characteristics
What is the function of glucagon?
Raises glucose level of blood
What is the function of insulin?
Decreases glucose level of blood
What is the function of estrogen?
Stimulates female secondary sex hormones
What is the function of testosterone?
Necessary for normal sperm production
What is the function of ANP?
Decreases Na+ in blood, thereby reducing blood volume/pressure
What is the function of EPO?
Signals to red bone marrow to increase RBC produces
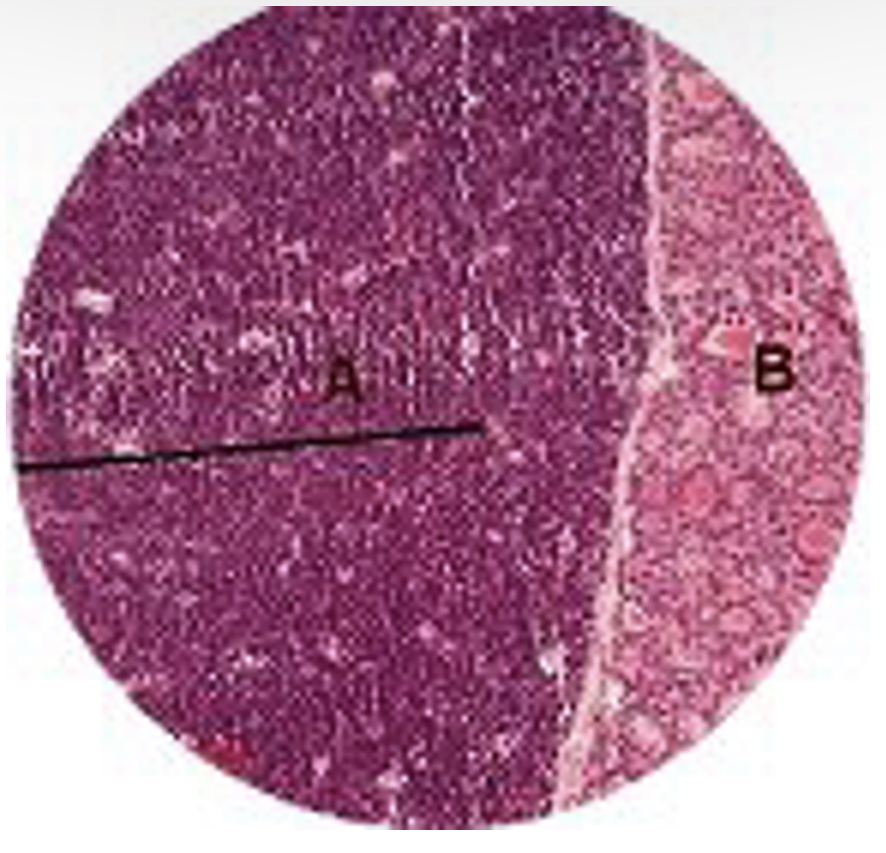
Name glands A & B
A: Parathyroid gland
B: Thyroid gland
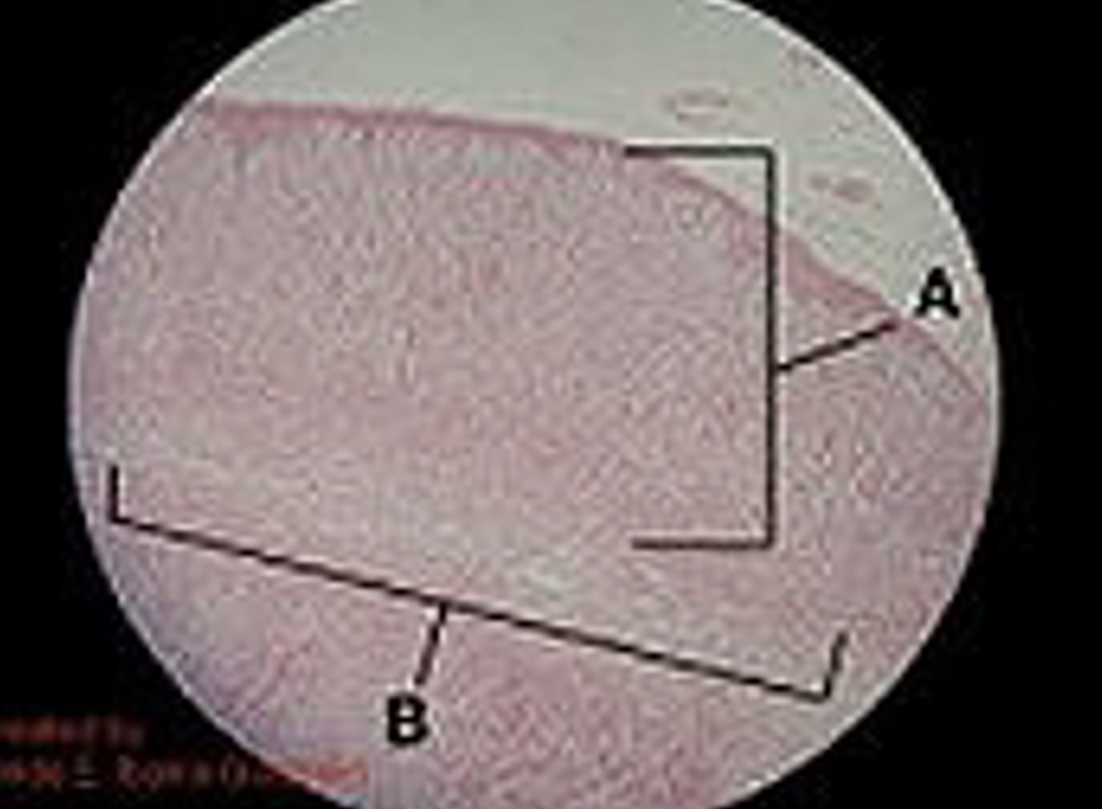
Name glands A & B
A: Adrenal cortex
B: Adrenal medulla
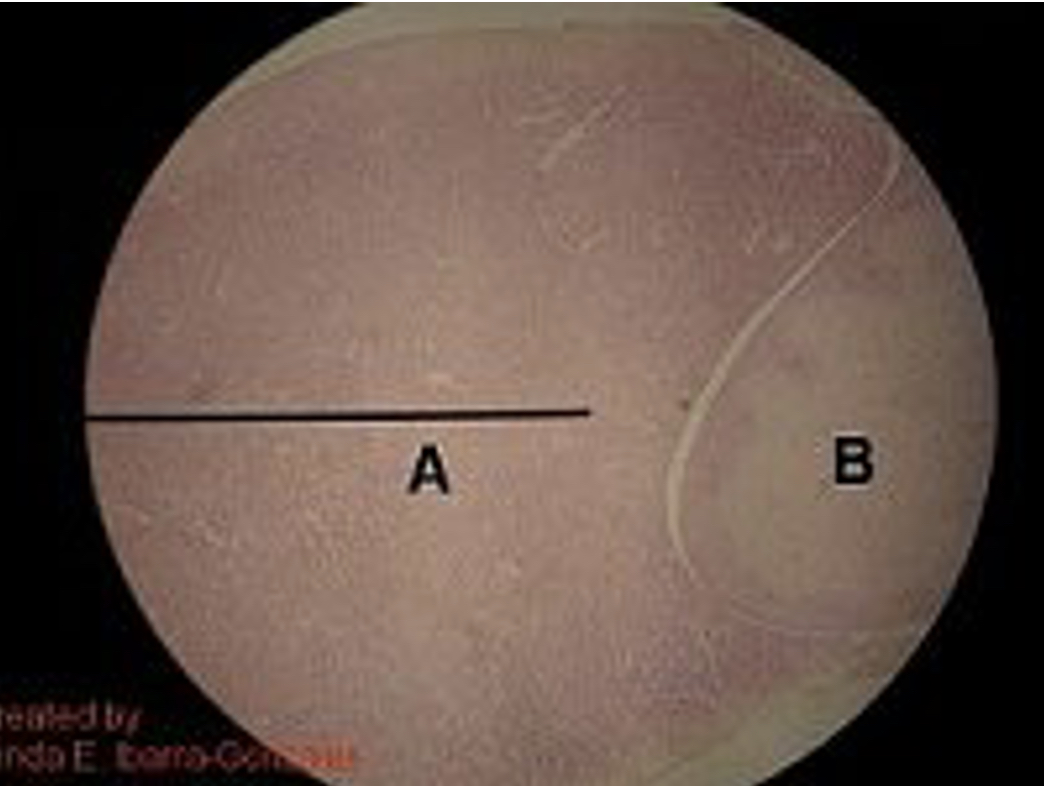
Name glands A & B
A: A. pituitary
B: P. pituitary
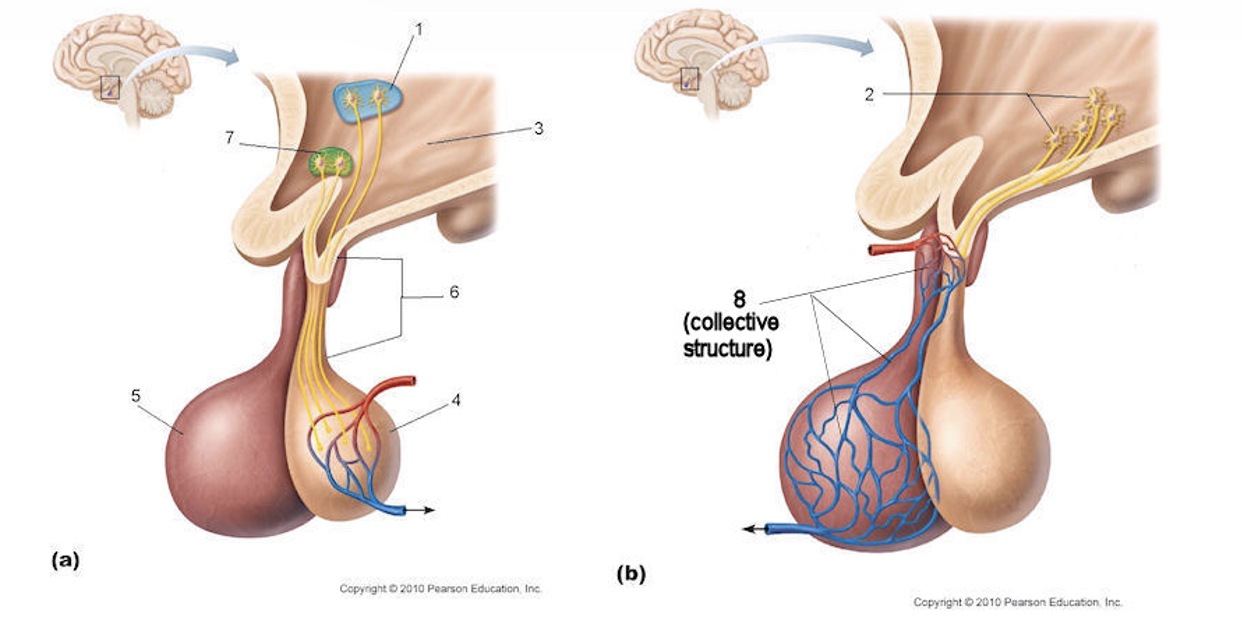
Identify anatomical structures of the hypothalamus & pituitary gland
Paraventricular nucleus
Hypothalamic neuron
Hypothalamus
Posterior lobe
Anterior lobe
Infundibulum
Supraoptic nucleus
Hypophyseal portal system
Describe the anatomical relationship between the hypothalamus and a. pituitary gland
The anterior lobe, composed of epithelial tissue, is connected to the hypothalamus vascularly, via the hypophyseal portal system. Releasing/inhibiting hormones are secreted by the hypothalamus and circulate to the a. pituitary via the portal system.
Describe the anatomical relationship between the hypothalamus and p. pituitary gland
The posterior gland is connected to the hypothalamus via the infundibulum and is neural/hypothalamic tissue that grows downward, maintaining a neural connection via the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract.
Name the two major components of blood and state their average percentages in whole blood
Erythrocytes - 45%
Plasma - 55%
Describe the composition and functional importance of plasma
Water – 90%, acts as the dissolving solvent of blood & absorbs heat
Electrolytes – most abundant solute, helps maintain normal blood pH
Plasma proteins- 8%, help maintain water balance in blood & tissues
Other substances (nutrients, gases, waste) are transported through the plasma
Describe RBCs, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Biconcave, anucleate disc
4-6 million
Transports oxygen and CO2
Describe WBCs and list the number of cells/mm3
Spherical, nucleate cells
4,800-10,800
Describe neutrophils, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Multilobed nucleus; inconspicuous cytoplasmic granules
3000-7000
Phagocytize bacteria
Describe eosinophils, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Bilobed nucleus; red cytoplasmic granules
100-400
Kill parasitic worms; complex role in allergies/asthma
Describe basophils, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Bilobed nucleus; large purplish-black cytoplasmic granules
20-50
Releases histamine, a mediator of inflammation; contains heparin, an anticoagulant
Describe lymphocytes, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Spherical or indented nucleus; pale blue cytoplasm
1500-3000
Mount immune response by direct cell attack or via antibodies (t-cells & b-cells)
Describe monocytes, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
U-shaped nucleus; gray-blue cytoplasm
100-700
Phagocytosis; develop into macrophages in the tissues
Describe thrombocytes, list the number of cells/mm3; and function.
Discoid cytoplasmic fragments containing granules; stain deep purple
150,000-400,000
Blood clotting; seals small tears in blood vessels
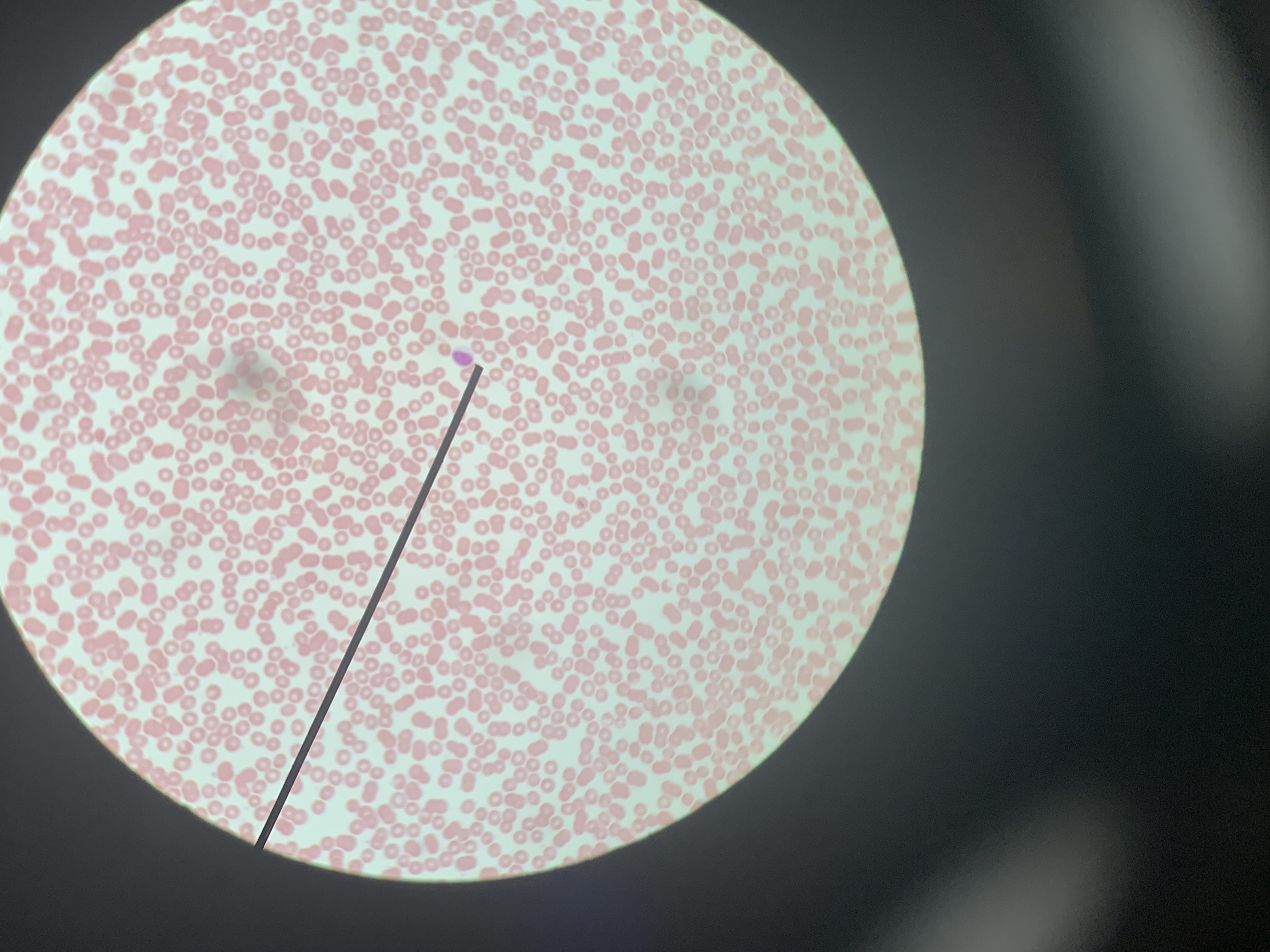
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Monocyte
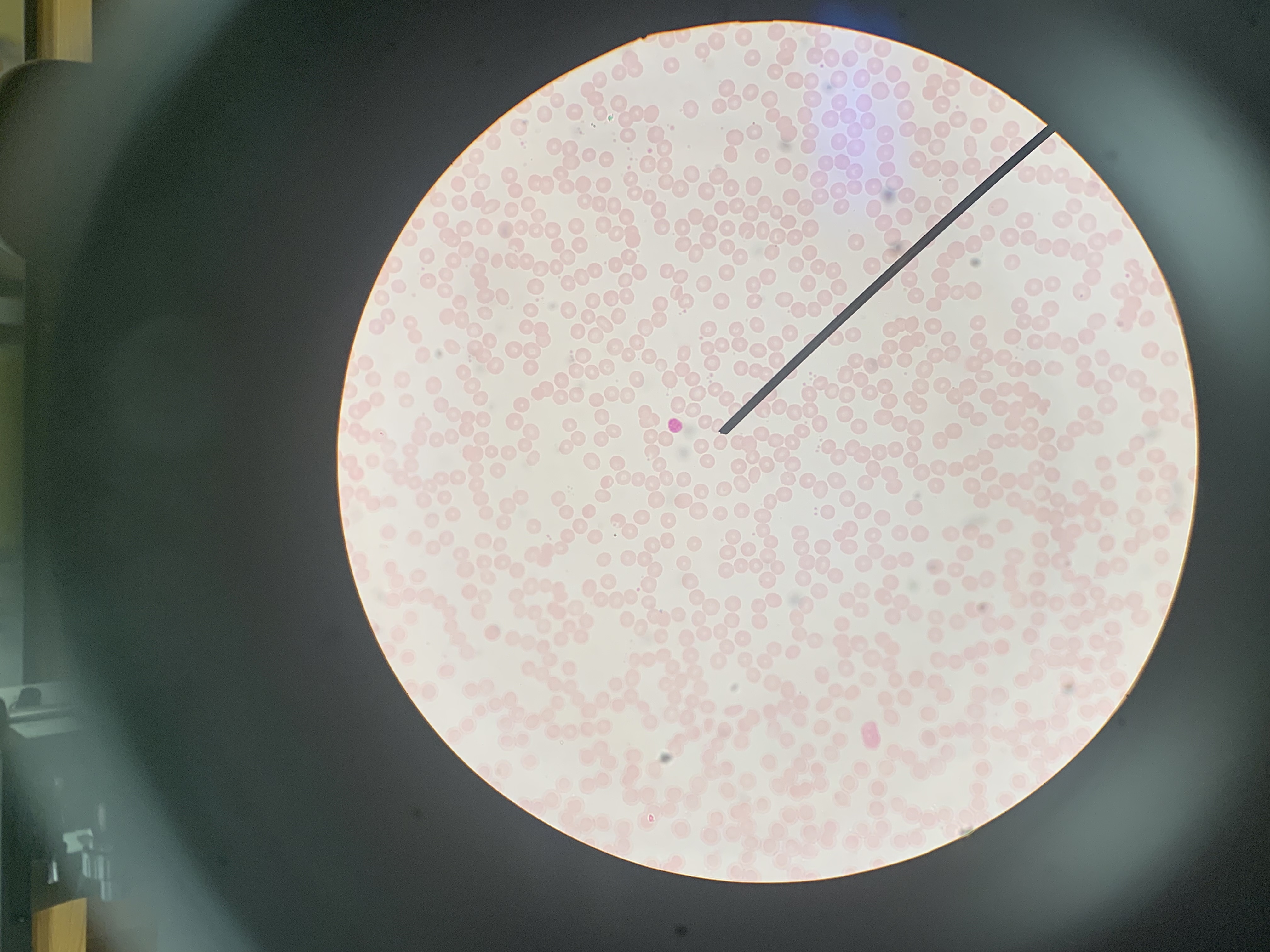
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Platelets
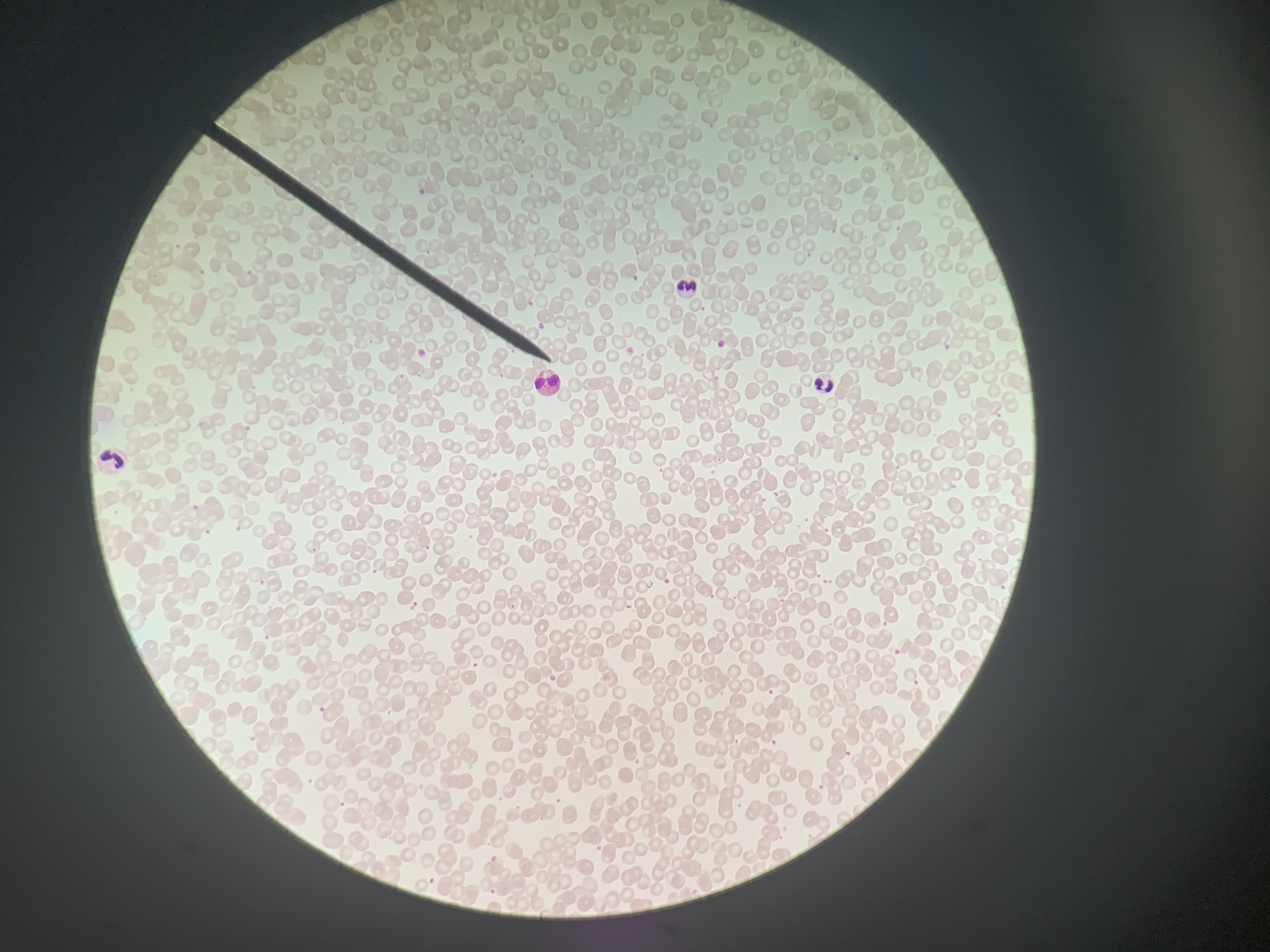
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Eosinophil
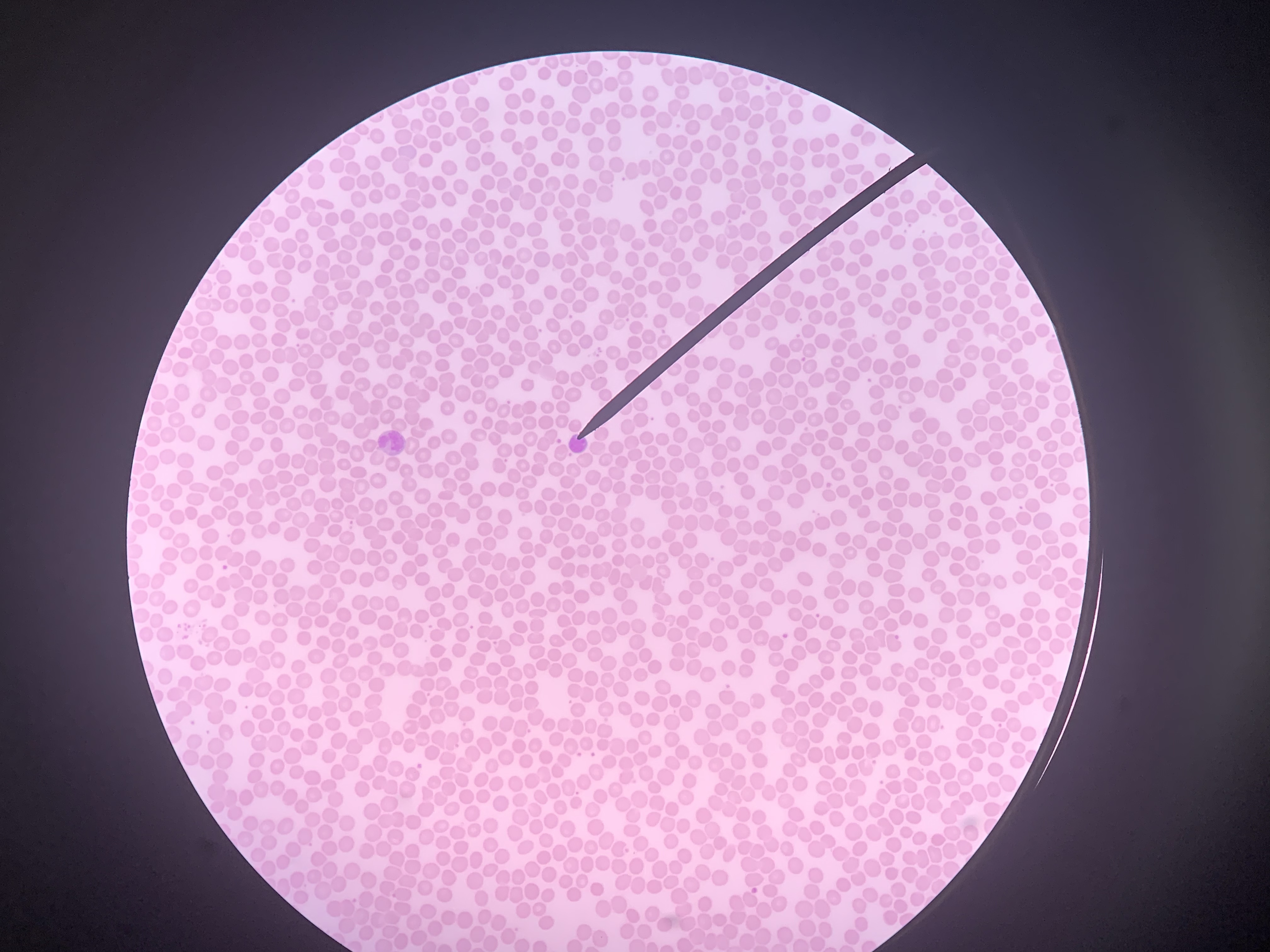
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Lymphocyte
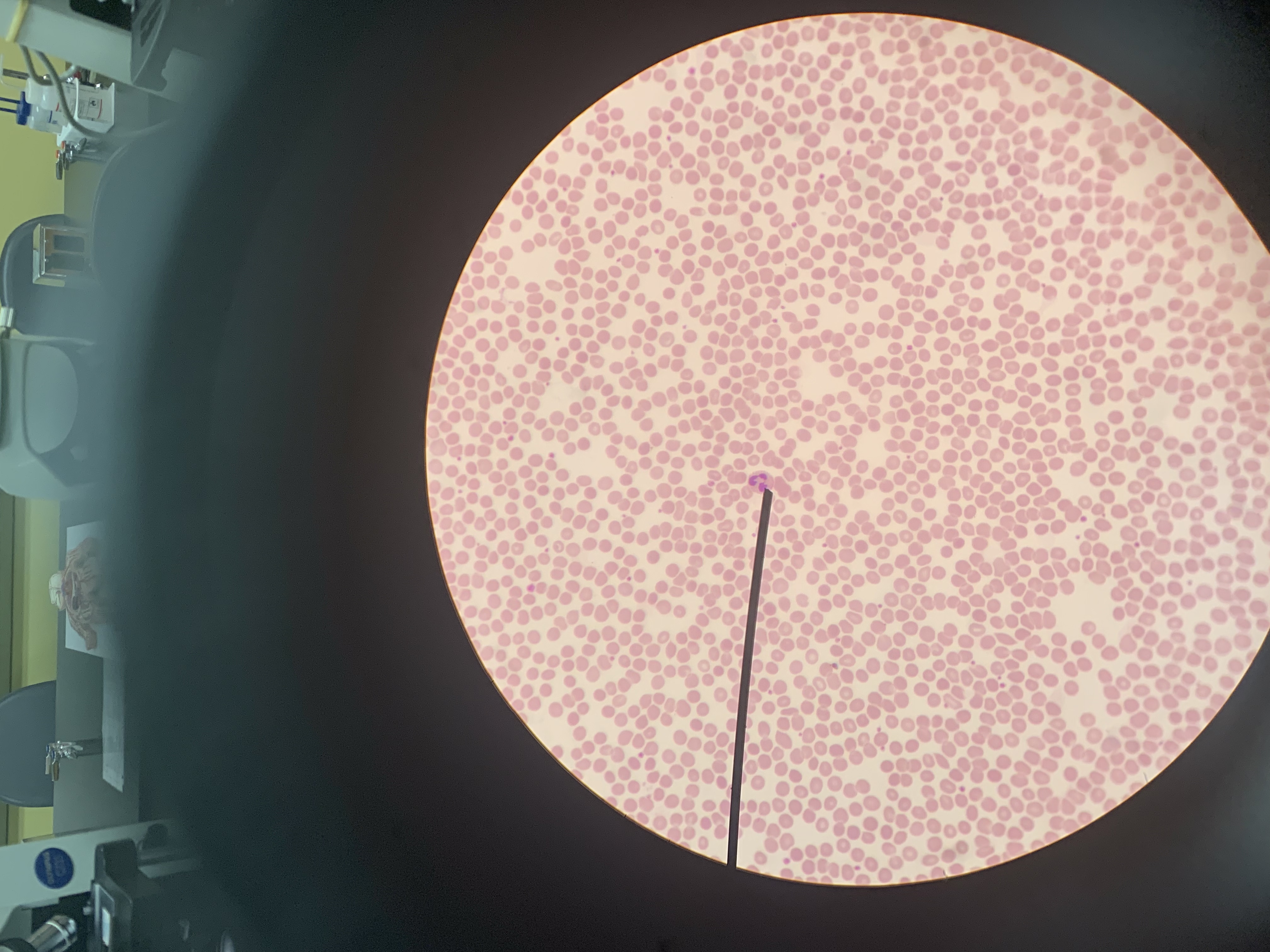
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Neutrophil
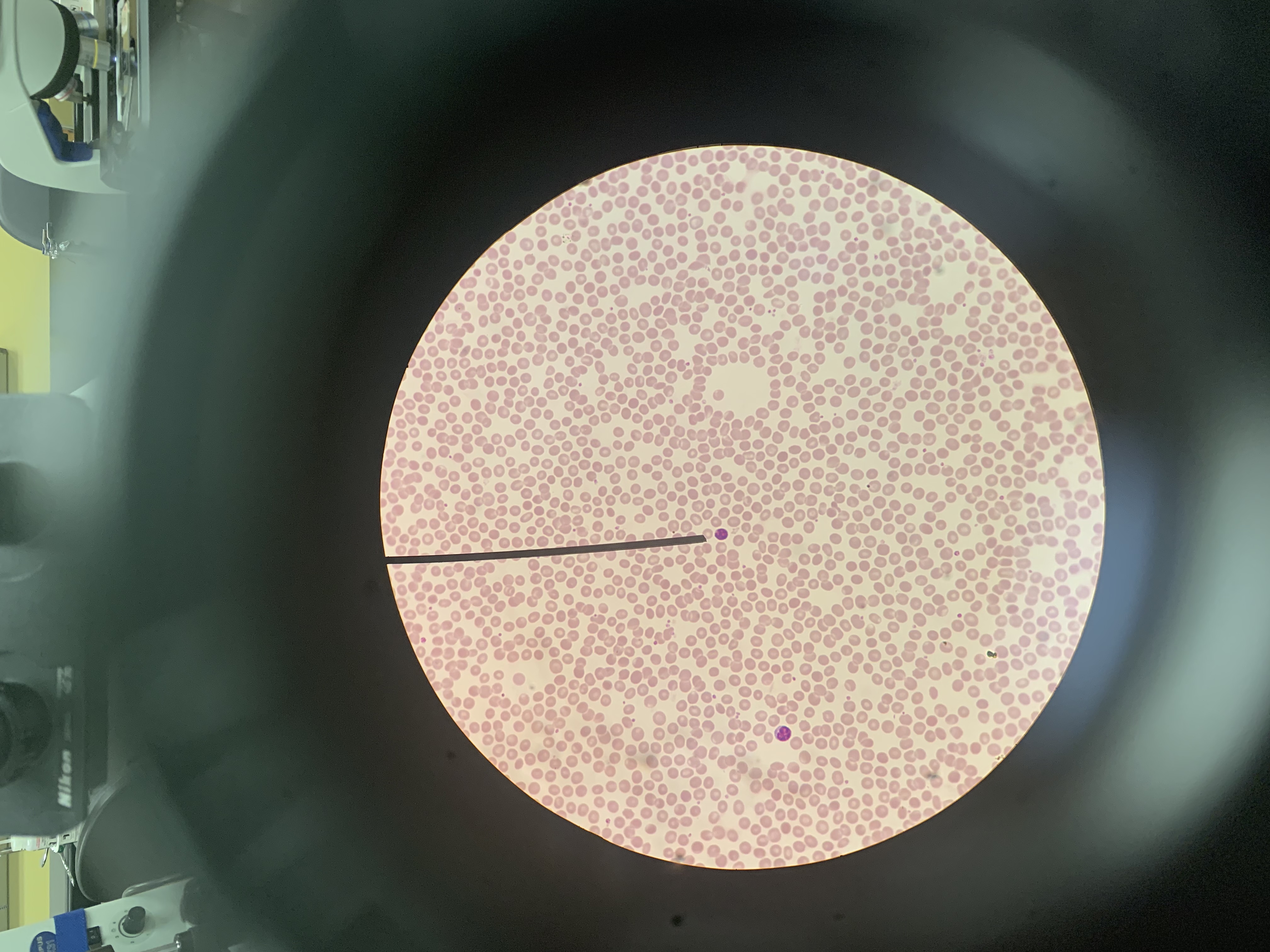
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Basophil
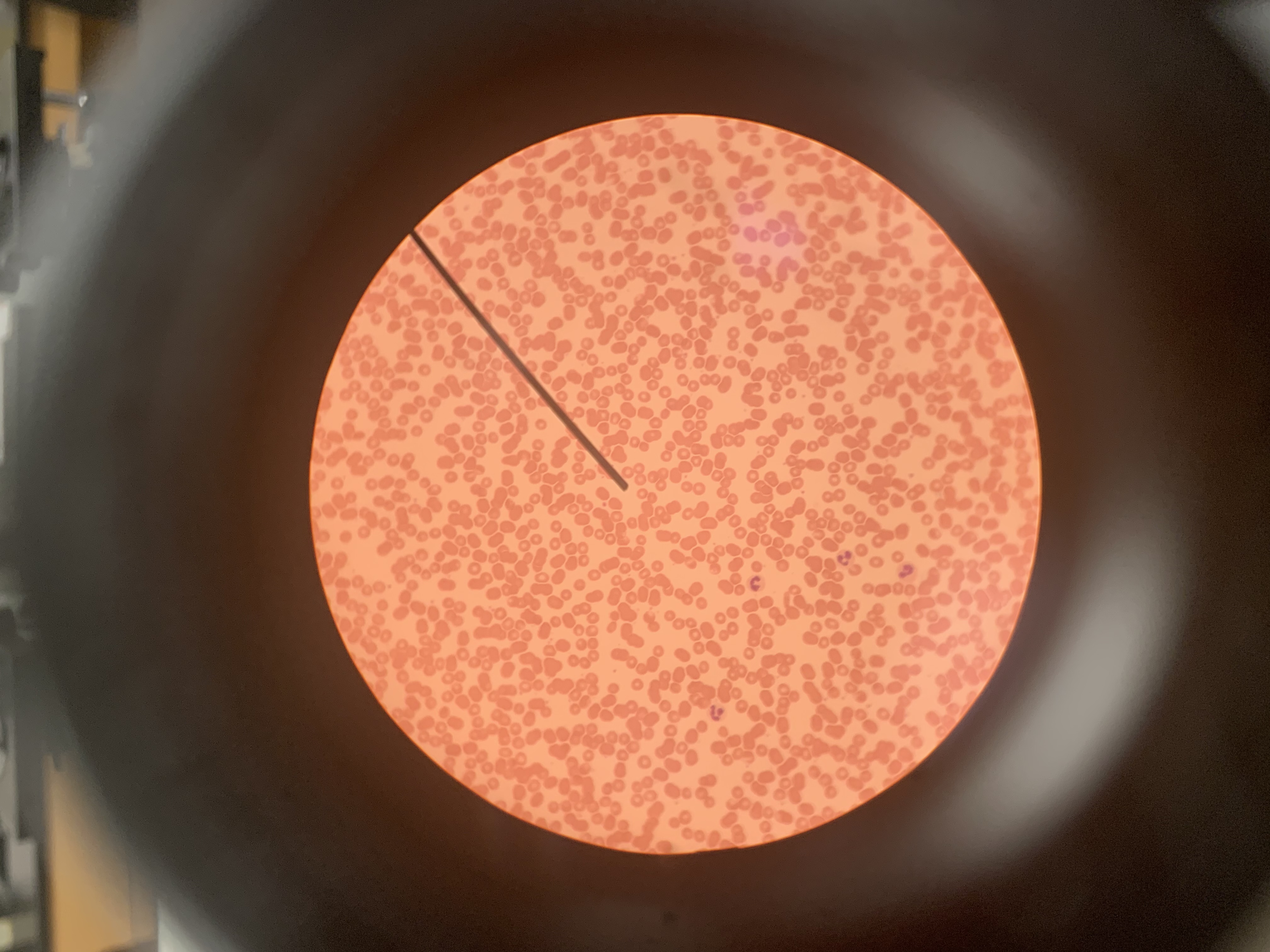
Identify the blood cell at the tip of the pointer:
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Define hematocrit and describe what information it provides when performed as a medical test.
Hematocrit is the percentage of RBCs in total blood volume. As a medical test it determines the amount of RBCs in the blood and can aid in the diagnosis of anemia or polycythemia.
Describe the structure and function of hemoglobin
Structure - consists of globin and four heme groups.
Function - a protein that makes RBCs red, binds & carries oxygen through the body
Describe the A blood type:
A antigen
B antibody
Can receive A & O blood
Can donate to A & AB types
Describe the B blood type:
B antigen
A antibody
Can receive B & O blood
Can donate to B & AB types
Describe the AB blood type:
A & B antigens
No antibodies
Universal recipient
Can only donate to AB types
Describe O blood type:
No antigens
A & B antibodies
Can receive O blood
Universal donor
Describe what is meant by Rh factor when typing blood
Those who carry the D Rh antigen are Rh+, those who do not are considered Rh-. This must be considered when typing blood because Rh- blood types can only receive from other Rh- types.
What is the reason for transfusion reactions resulting from the administration of mismatched blood?
Plasma antibodies attack & destroy the donor’s RBCs
What causes hemolytic disease of the newborn (Erythroblastosis fetalis) and what can be done to prevent it.
A woman who is Rh- becomes pregnant with a Rh+ baby. During delivery, the baby’s Rh+ antigens can enter the mother’s bloodstream, creating anti-Rh antibodies. This can be prevented by treating the mother with RhoGAM during the pregnancy and delivery of her first baby. If she is left untreated and becomes pregnant again with another Rh+ baby, the anti-Rh antibodies can cross through the placenta and destroy the baby’s RBCs, thereby causing Erythroblastosis fetalis in the newborn
Describe polycythemia & cite the reason for this condition
An abnormally high number of erythrocytes, may occur when less oxygen is available or EPO production increases
Describe leukocytosis & cite the reason for this condition
An increase in the number of leukocytes, results from a pathogen attack and may signal severe infection
Describe leukopenia & cite the reason for this condition
Abnormally low WBC count, is typically induced by drugs
Describe leukemia & cite the reason for this condition
A group of cancerous conditions involving the overproduction of abnormal WBCs
Describe the hematocrit test & its significance
Determines the percentage of RBC to the total blood volume; can help identify anemia or polycythemia
Describe the hemoglobin test & its significance
Determines the amount of hemoglobin, an oxygen-carrying protein, present in the blood; can help identify anemia
Describe the differential WBC count test & its significance
Determines the relative proportion of individual leukocyte types present in blood; can help identify abnormal white blood cell populations
Describe ABO blood typing & its significance
Used to identify A & B antigens present on RBCs; prevents transfusion reactions from occurring
Describe Rh typing & its significance
Used to identify if a specific Rh antigen is present in the blood; prevents transfusion reaction from occurring
Describe the size & location of the heart
The heart is about the size of a first and weighs less than a pound. It is located in the mediastinum and 2/3 of its weight lies left of the midsternal line. Its apex points towards the left hip & the base points toward the right shoulder. It rests upon the diaphragm.
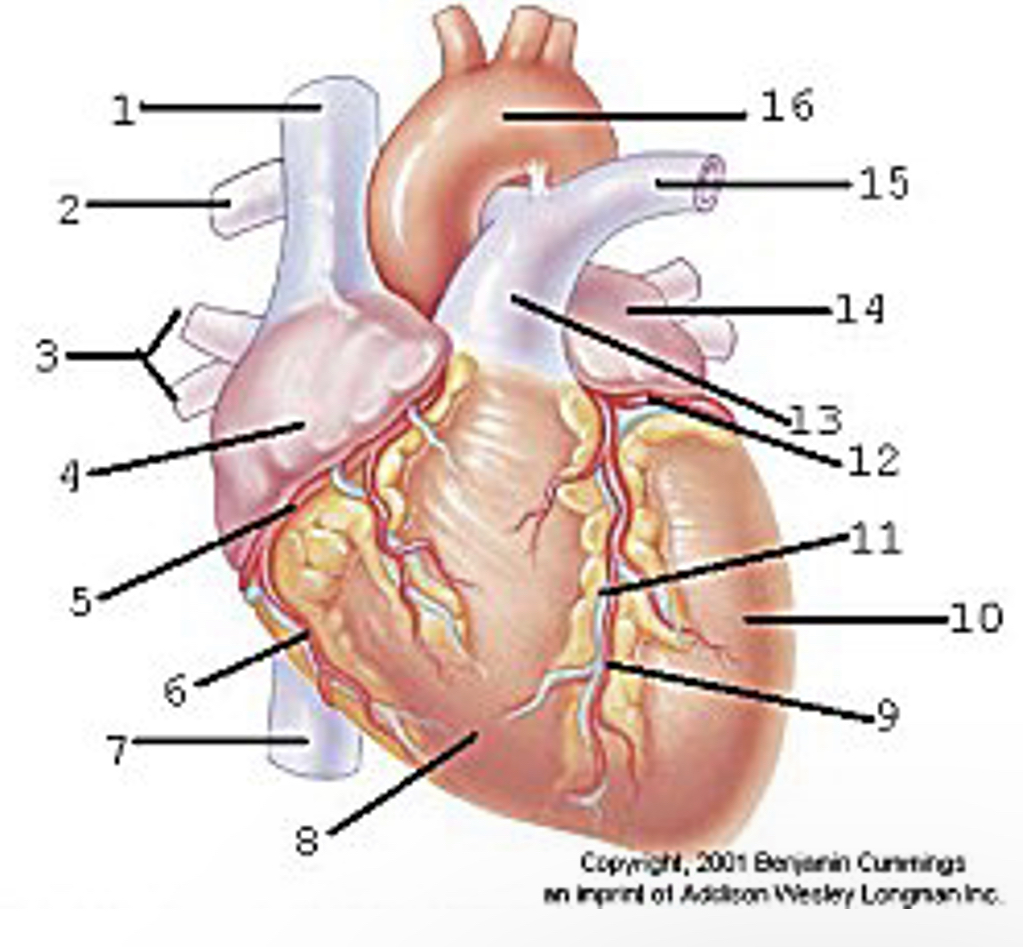
Locate the major anatomical areas and structures of the anterior view of the heart
Superior vena cava
Right pulmonary artery
Right pulmonary veins
Right atrium
Right coronary artery
Right marginal artery
Inferior vena cava
Right ventricle
Anterior interventricular artery
Left ventricle
Great cardiac vein
Left coronary artery
Pulmonary trunk
Left atrium
Left pulmonary artery
Aortic arch
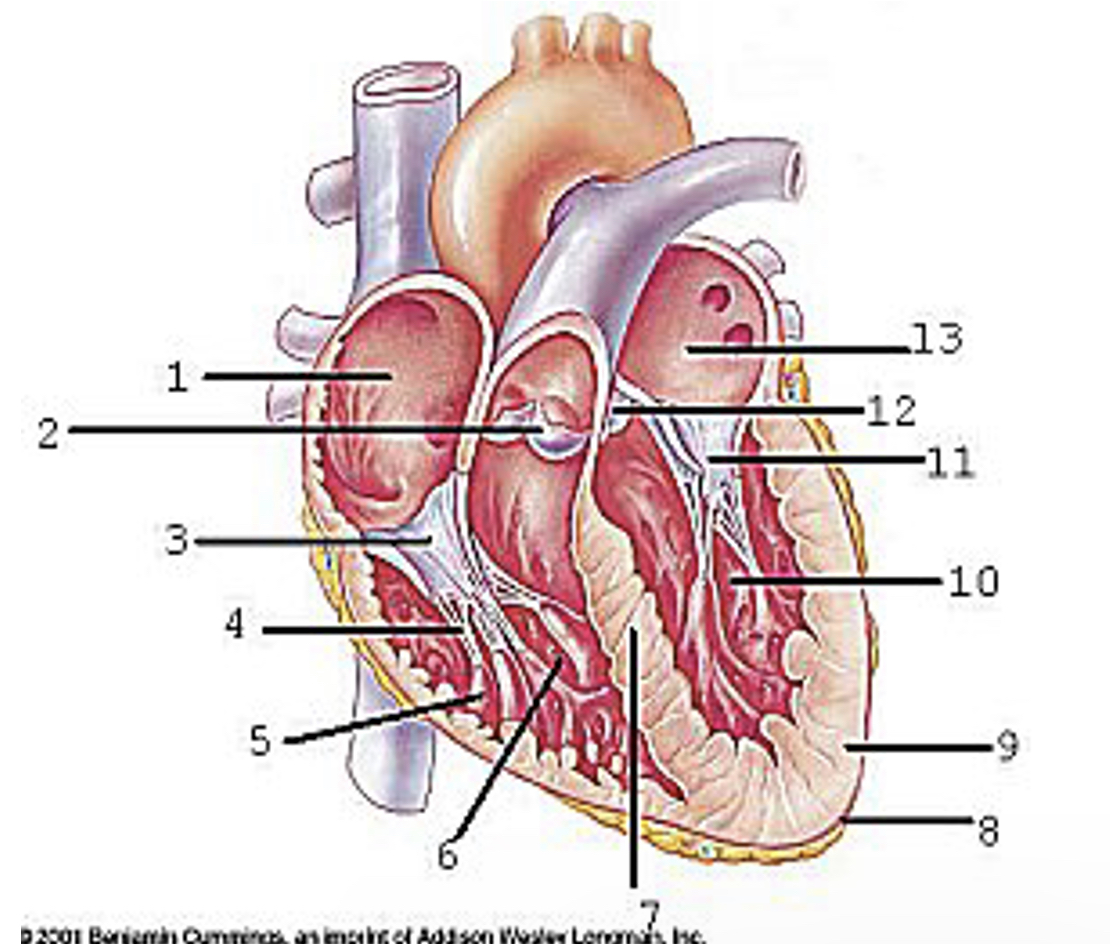
Locate the major anatomical areas and structures of the interior view of the heart
Right atrium
Pulmonary valve
Tricuspid valve
Chordae tendineae
Papillary muscle
Right ventricle
Interventricular septum
Epicardium
Myocardium
Left ventricle
Mitral valve
Aortic valve
Left atrium