Art and History of Madrid Exam II
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
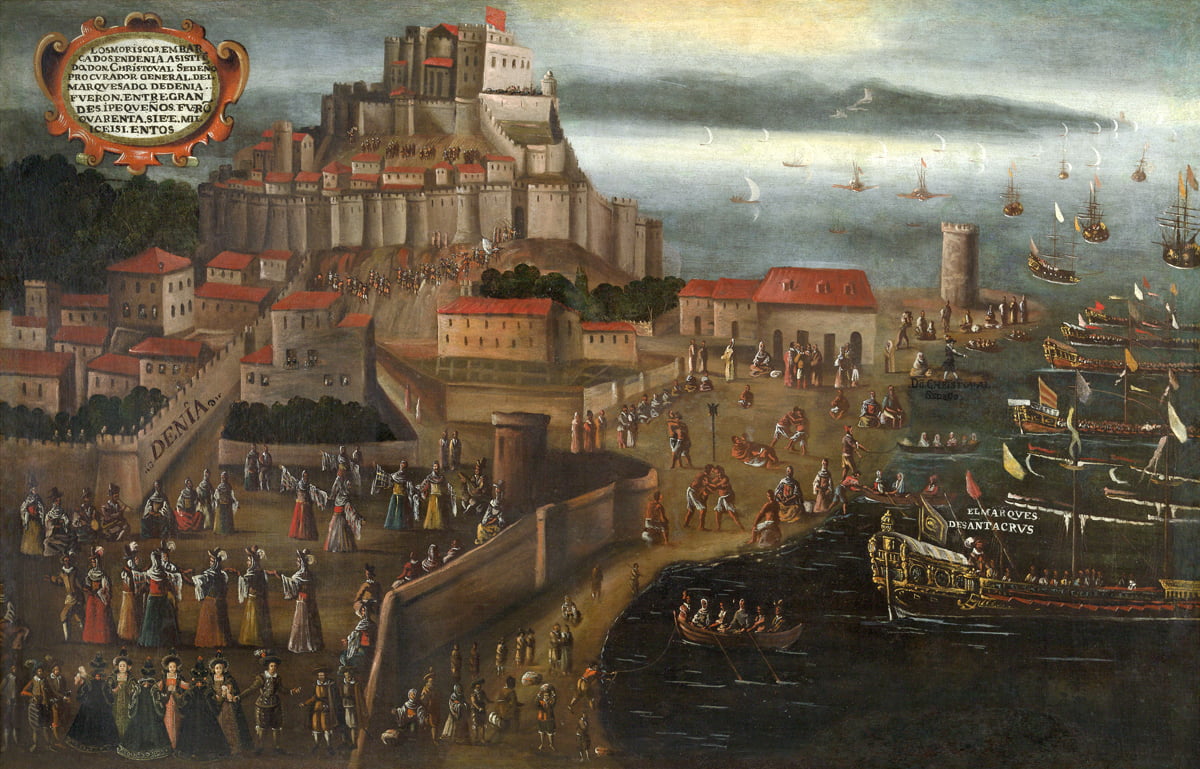
Expulsion of the Moriscos at the Port of Denia by Vicente Mostre, 1613, Baroque art

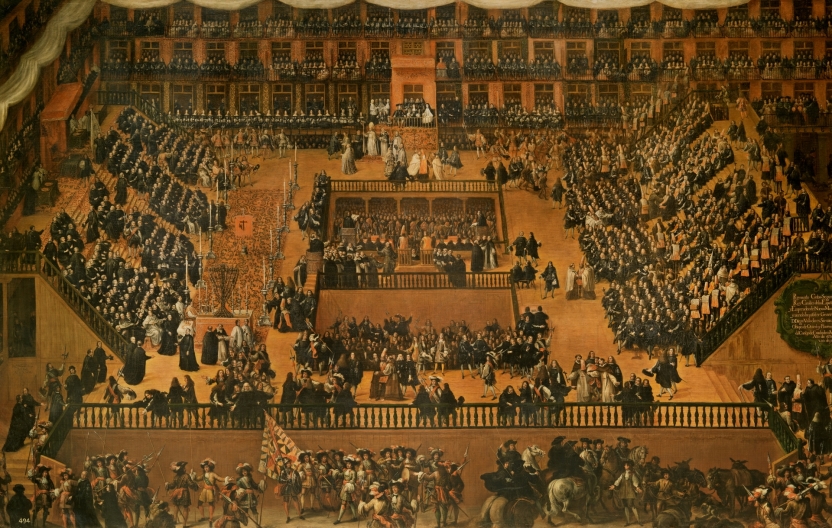
Francisco Rizi, Auto-da-fe in the Plaza of Madrid, 1683, oil on canvas, Prado Museum.
Charles II, his queen and the queen mother attending the auto-de-fe.
Baroque.

Peter Paul Rubens, Duke of Lerma, 1603. Prado Museum.
Favorite royal counselor.
King’s personal representative.

Peter Paul Rubens, The Judgement of Paris, 1639, Prado Museum.
Not a strong vanishing point, no focal point.
Idealism.
Busy background.
Lighting.
Different textures, fabrics, armor.
Moment frozen in time, action.

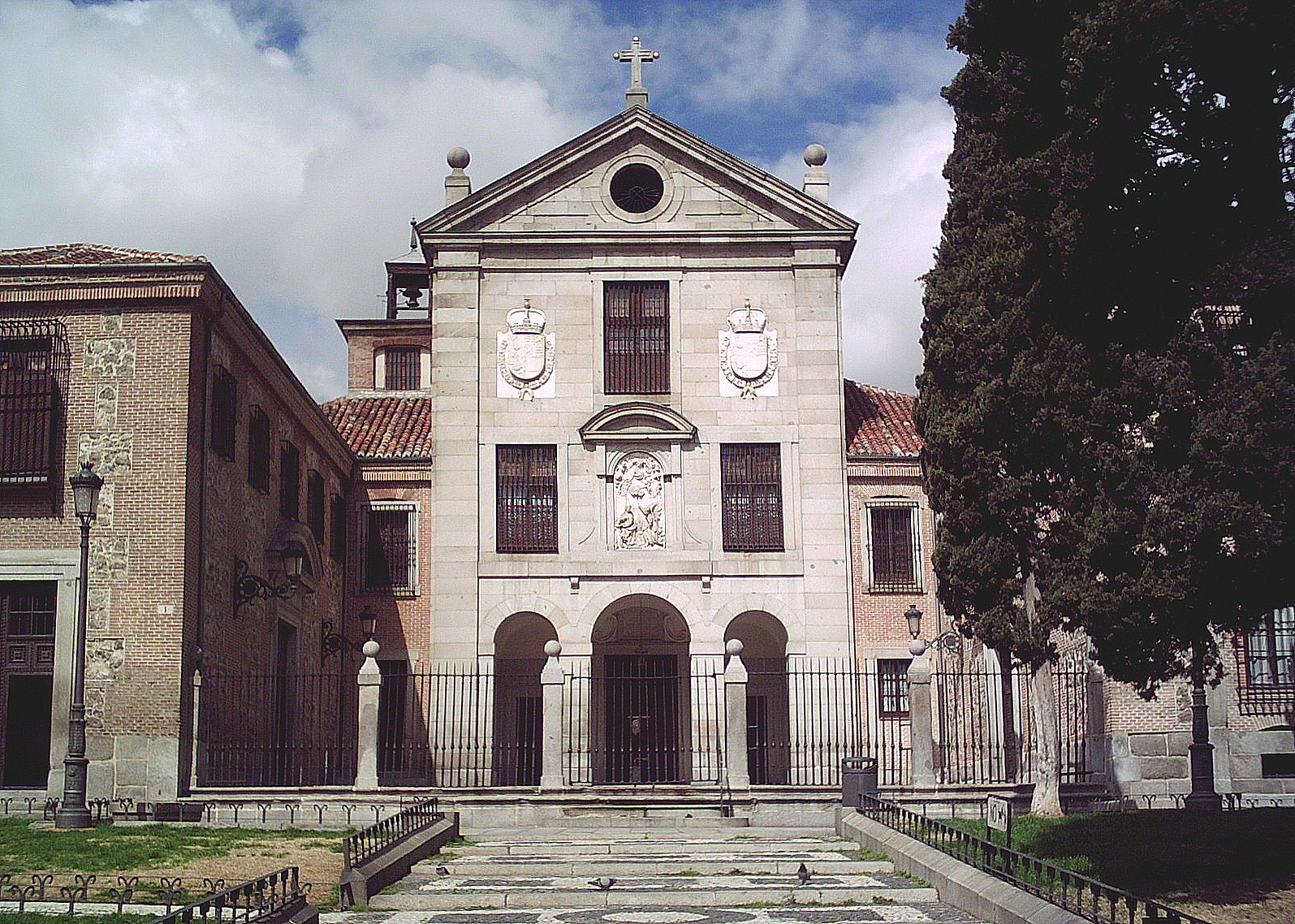
Royal Monastery of La Encarnación, early 17th century.
One relief, two coat of arms, church founded by Spanish kings
Round arches, pediments
Anti-classicist element: rounded pediment
Spheres on top, similar to El Escorial: Herrerian architecture, architect: Juan de Herrera
Founded by Queen Margaret of Austria to “celebrate” Philip III expulsion of the Moriscos
Adjacent to the Real Alcazar with direct access through a pass way

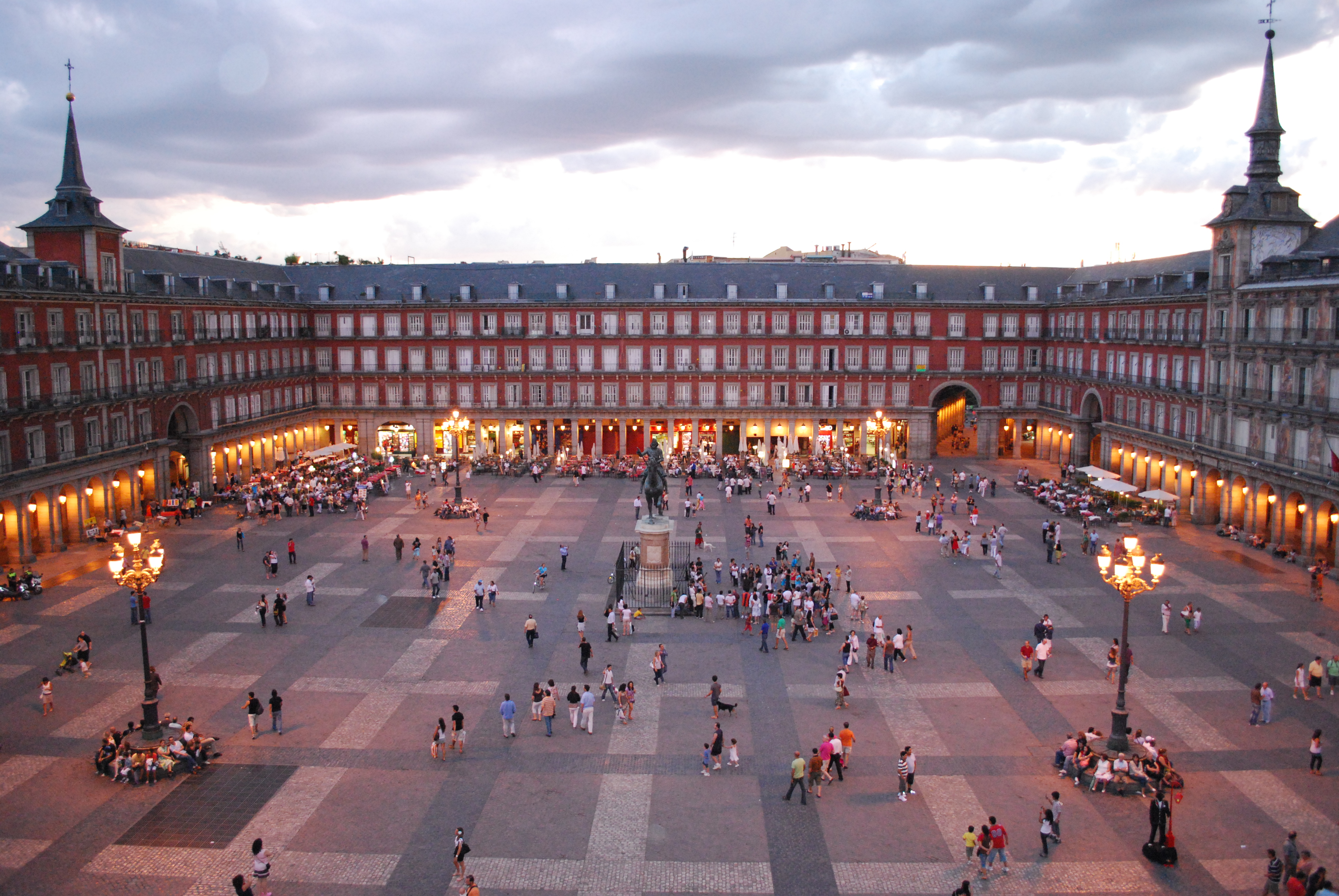
Plaza Mayor de Madrid.
Remodeled in 1760 after many fires, but originally conceived under Philip II (Juan de Herrera) and built under Philip III (Gomez de Mora).
Slate on roof
Round arch
Spheres on top of spires

José Ribera, St. Andrew, 1631
Dies by cruxifixction, X shape
Head of fish, fisherman before disciple
Painterly technique, can tell direction by brush texture
Realism, veins, bone structure, gray hair

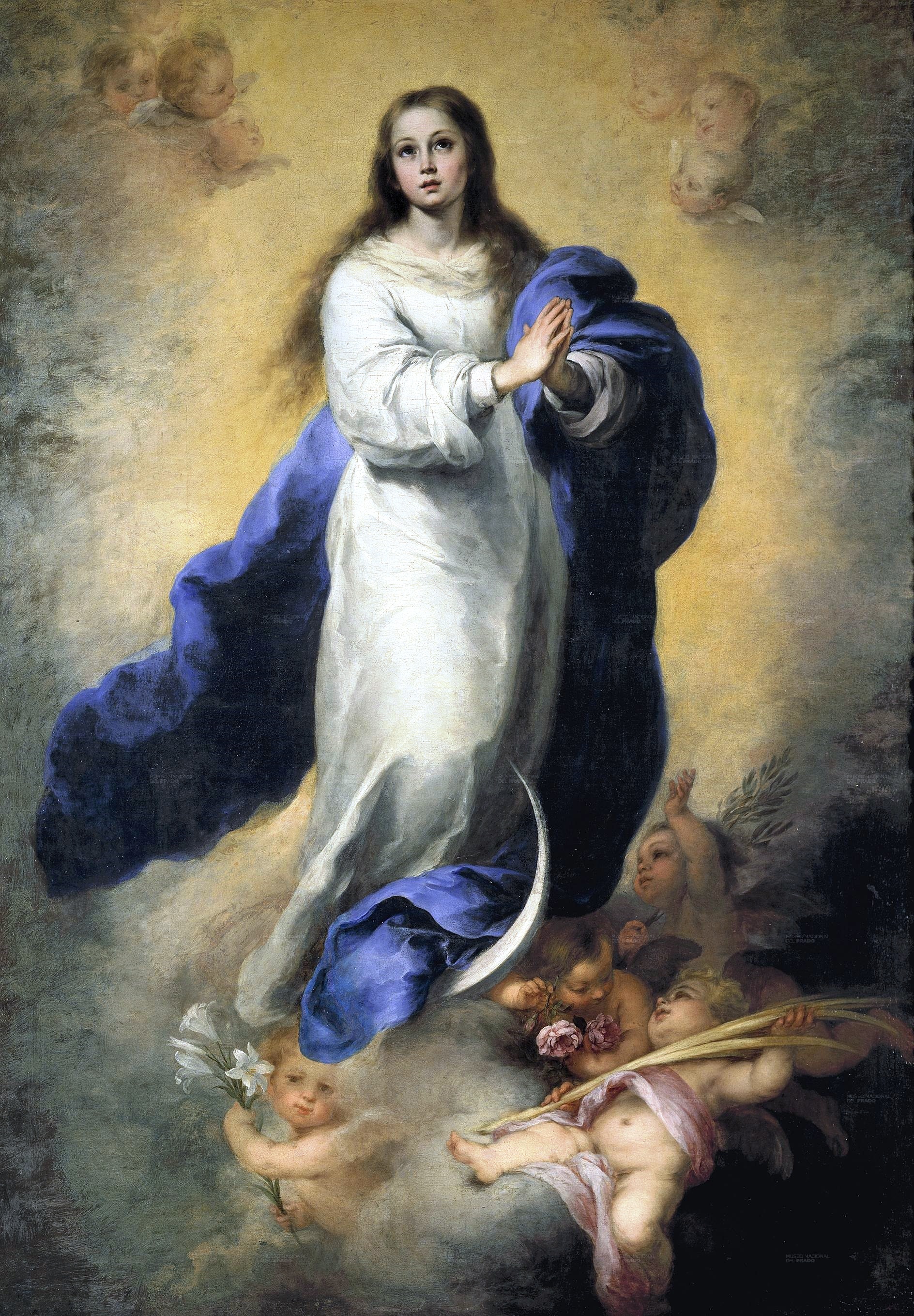
Bartolomé Murillo, The Inmaculate Conception, c. 1660-65, oil on canvas, Prado Museum.
Mary was conceived without sin, her birth was a miracle, not in Bible but Spanish people believed, used art to popularize this idea, propaganda
Mary is dressed in white, white flowers, light makes her floating
Crescent moon, associated with the immaculate conception, from story in Bible

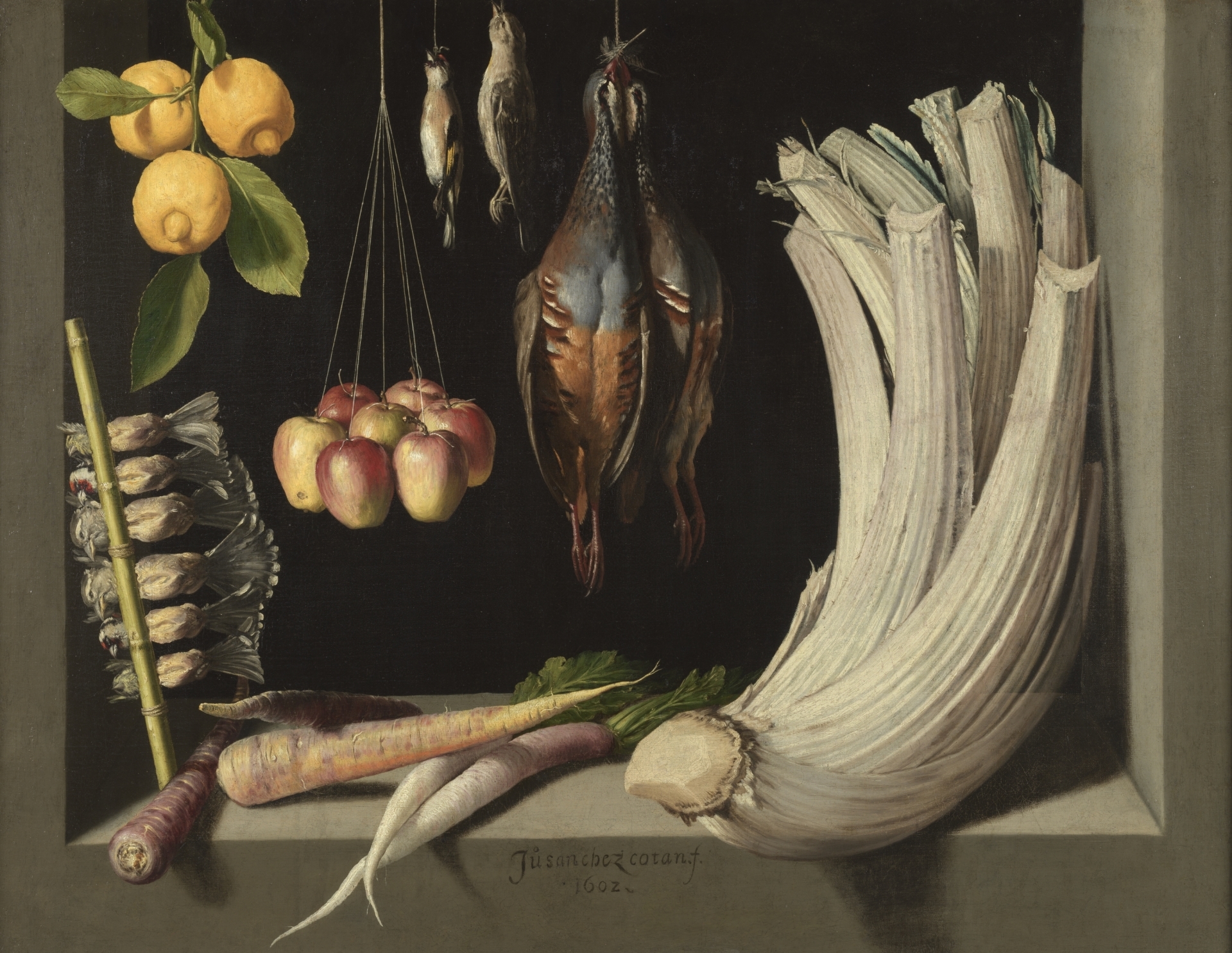
Juan Sanchez Cotán, Still Life with Game Fowl, fruit and Vegetables, 1602, oil on canvas, Prado Museum.
Visual parallel with mystic literature, Santa Teresa’s especially
“Still life” in Spanish is Bodegon, has religious connotations

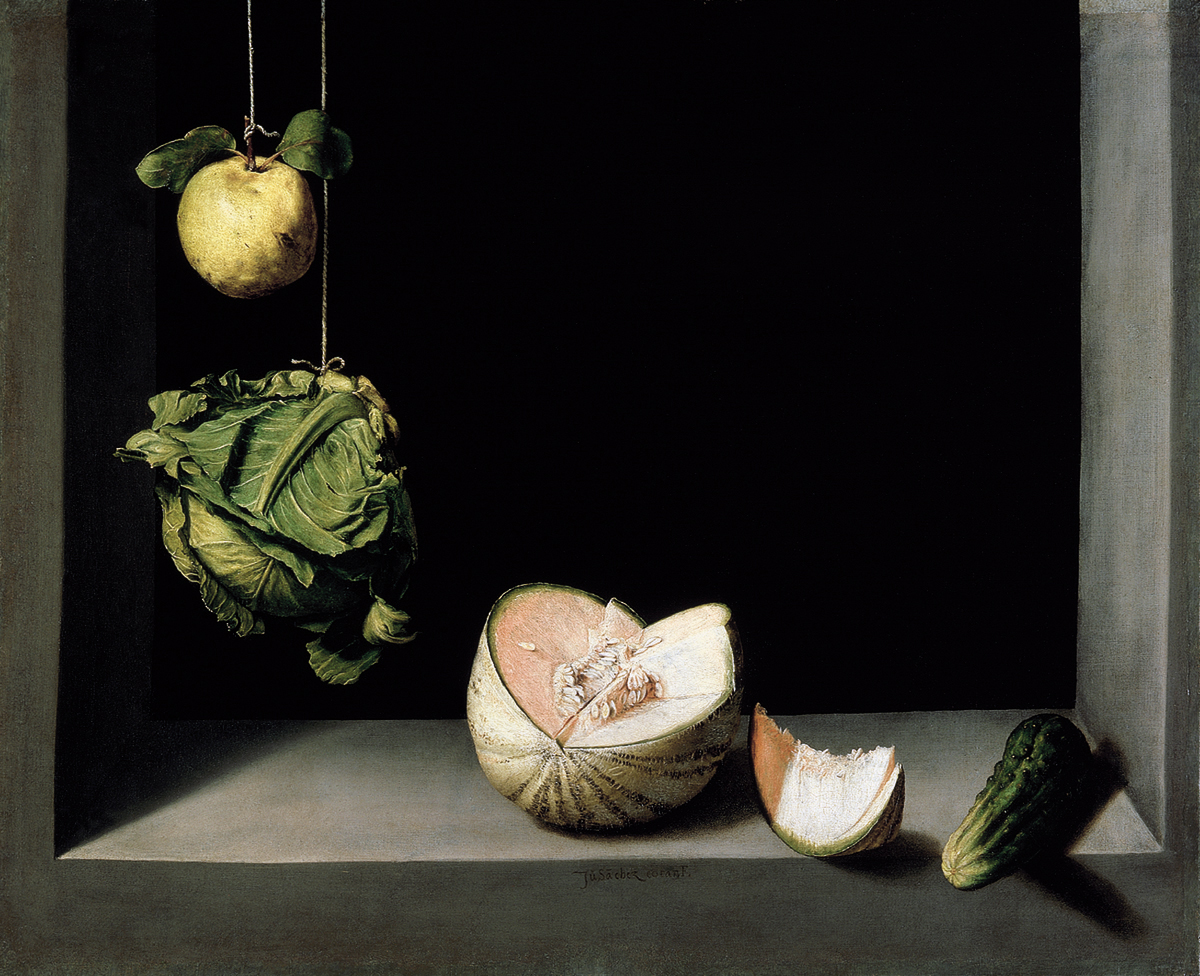
Juan Sánchez Cotán, Still Life with Cabbage, Melon and Cucumber, c. 1602, Fine Arts Museum in San Diego
Different interpretations, warning against gluttony
Shows off wealth during moment of crisis, others are starving, not really in Spain but other European countries
Santa Teresa started ideology that God is everywhere
Artists using illusionism, objects shown on edge of table or window to show off

Claudio Coello, The Adoration of the Holy Host, Sacristy of El Escorial, 1685-1690.
Baroque art
Sacristy of El Escorial, action takes place
Unity of the monarchy and the church
Scene of workshop and group portrait
Linear perspective
People attending mass, communion
Charles II, kneeling, last Hapsburg in Spain, dies without heir, lots of health problems, King can only kneel down in front of God
Keeling in front of relic, the host, found in Germany, vandalized Eucharist located behind painting, once a year it can be seen
Decoration, theatricality, painting as a curtain, bronze and tortoise shell materials, movement
Art symbolizes connection between church and crown
Philip VI, first king to choose own wife

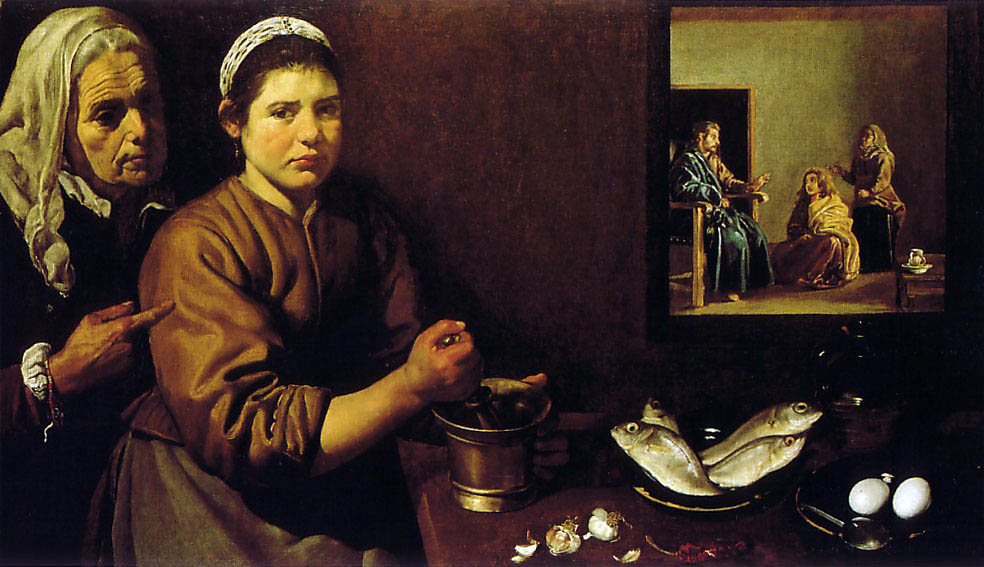
Velázquez, Christ in the House of Martha and Mary, 1618, National Gallery of London
Scene from the Bible and genre painting
Earthly tones / color palette
One sister making food, other sister listening to Christ which is the right thing to do
Creating double image, mixing genres, still life and religion
Velázquez 19 years old
Jesus in the background, food in foreground, anti-classical

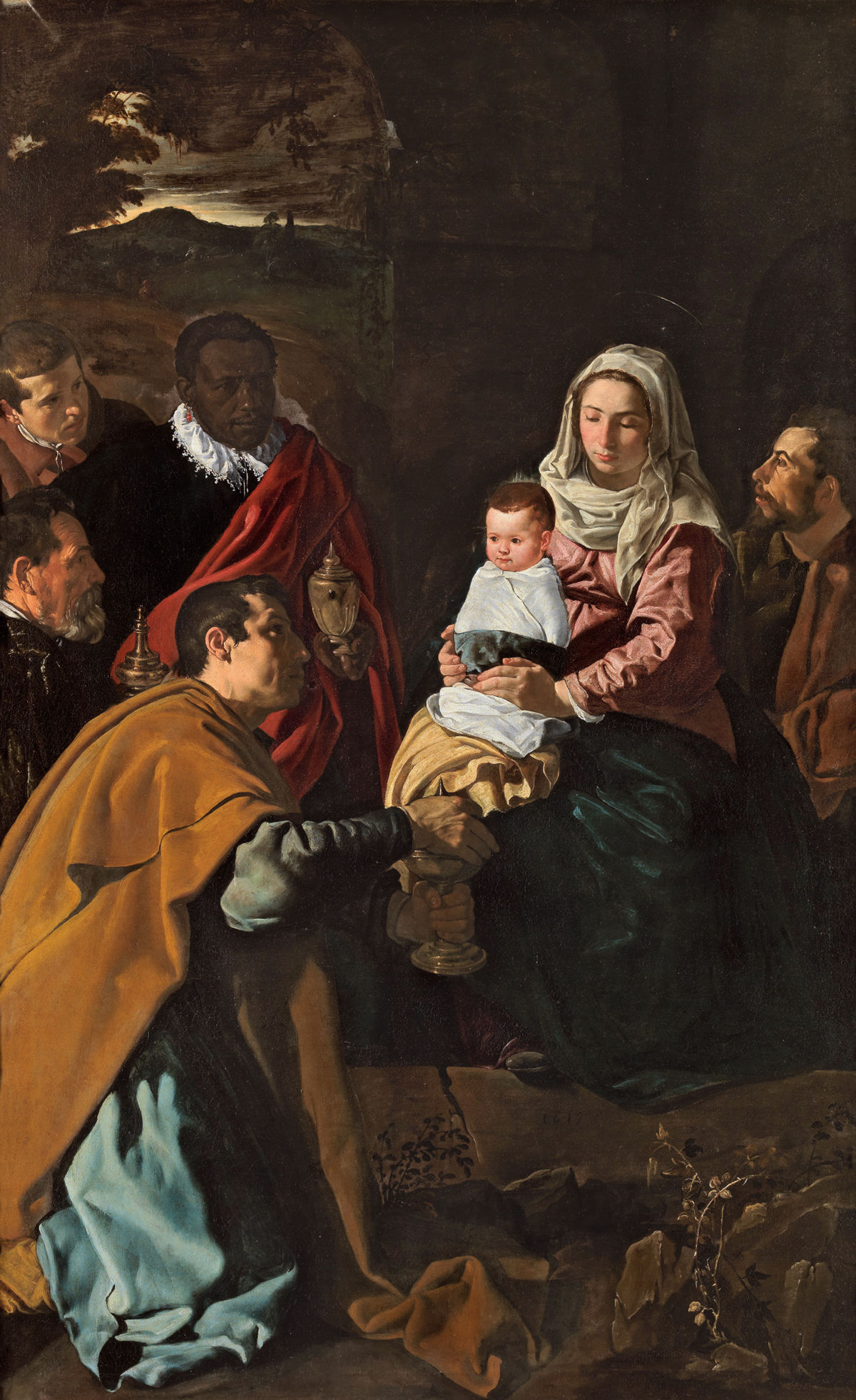
Velázquez, The Adoration of the Magi, 1619, Prado Museum
Married, had daughter, used wife and daughter as models
Three wise men visiting Jesus and bringing gifts
Includes more colors yet dark palette
Two sources of light from left and sunrise
Heaviness of fabric
Awkward composition, crowded, people not interacting with each other

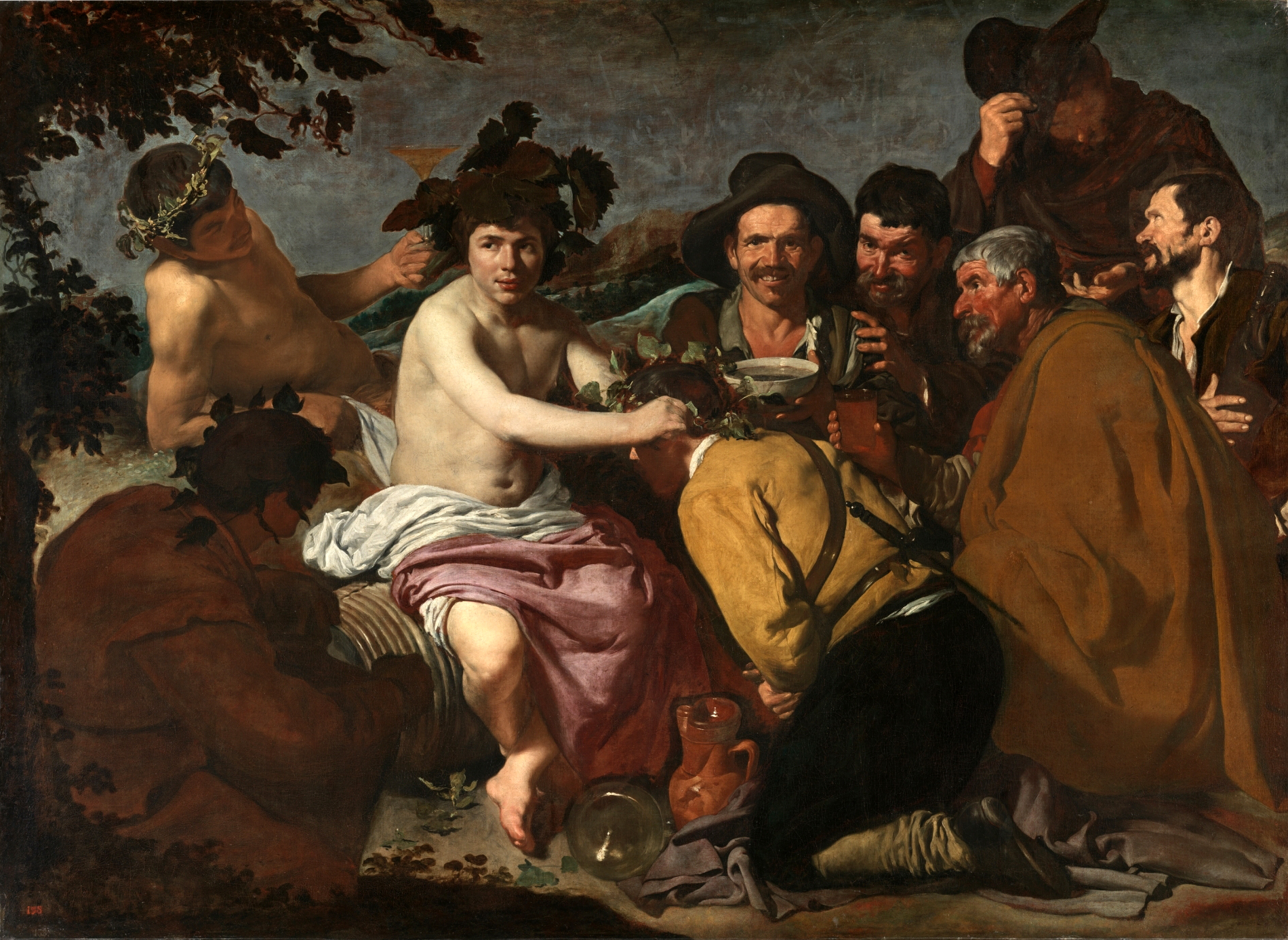
Velázquez, The Triumph of Bacchus, 1628-29
One of Velázquez’s first paintings in Madrid
Velázquez brought to royal palace to work for king, subject matters change, surrounded by royal palace artwork (Titian, Ruben), learning from the masters
Figure is paler, younger, wearing different (no) clothes, light on him, not as thin
Other figures dressed as contemporary figures
Brings commoners into mythology, not just for wealthy, giving people who are not usually represented a voice while working for the court

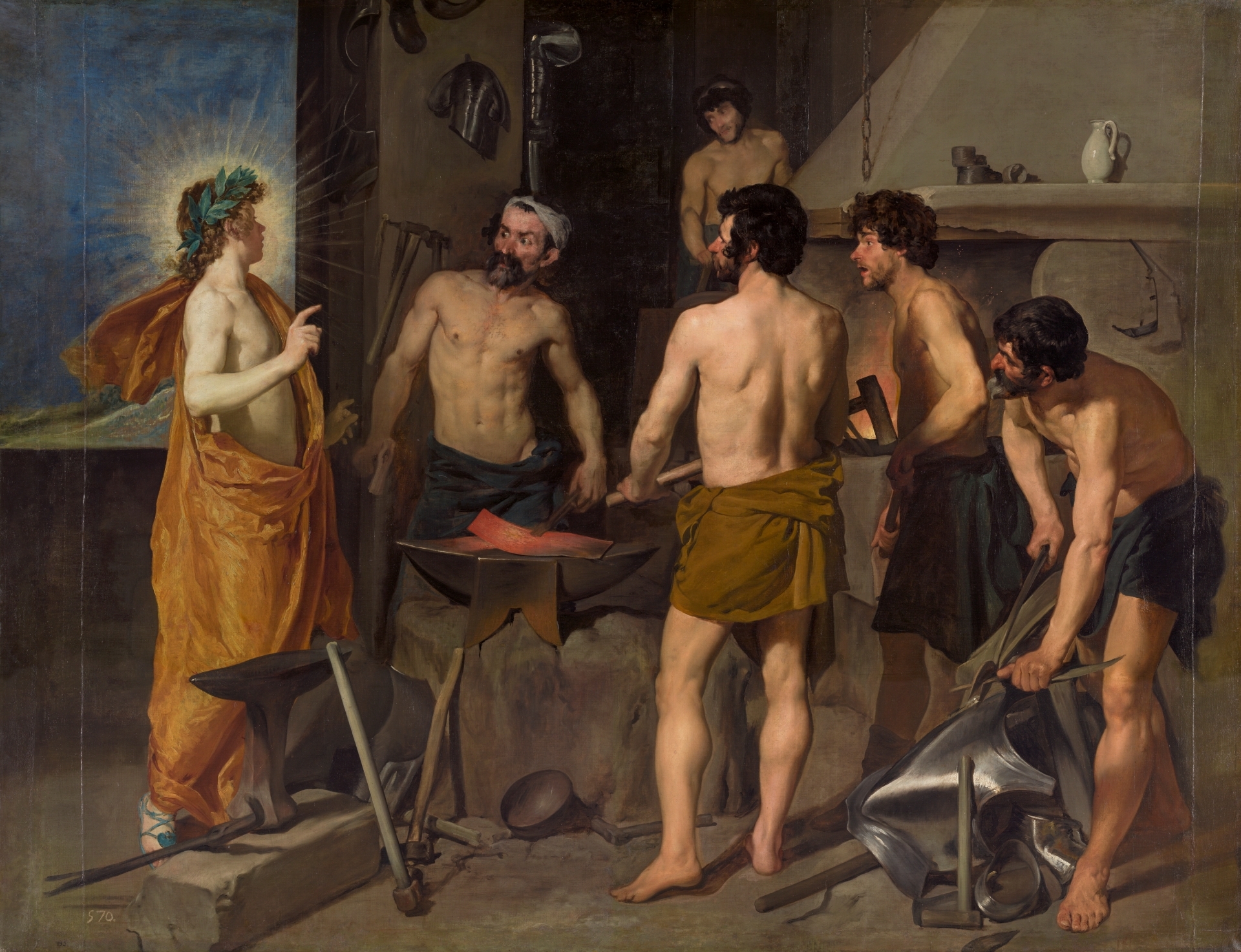
Velázquez, Apollo in the Forge of Vulcan, 1630.
Three dimensional, feels like you can walk through
Can read emotions, shock
Saint is off centered
Luminous (halo, fire, window)
Blacksmiths, muscular and fit, idealism, same proportions, studying classical sculptures
Created after traveling to Italy for first time, studied Renaissance art and classical sculptures
Hermes (Mercury) messenger of the Gods, talking to Vulcan (one of 12 main Gods, son of Zeus, result of affair, Zeus punished Aphrodite to marry Vulcan).
Hermes is telling Vulcan that Aphrodite is having an affair with Aries
Velázquez technique (painterly) will be greatly associated with the school


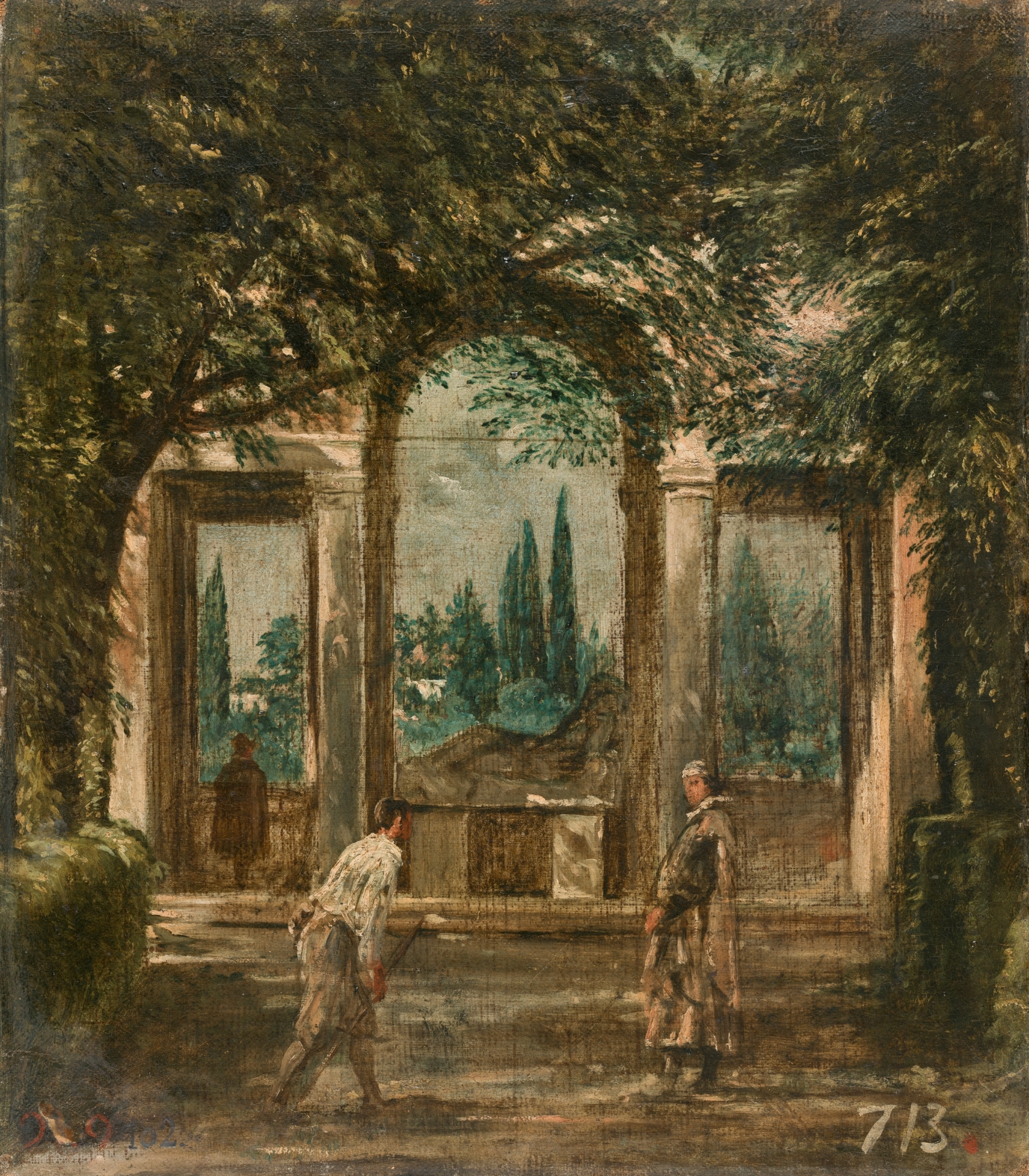
Velázquez, The Gardens of the Medici Gardens -both- 1630.
Velázquez did not have freedom to create whatever he wanted
Took care of party decorations, bought art in Italy because the king wanted to expand his collection
Two paintings, a pair, tiny
Kind of work he did without a commission
Among the first landscapes in the Spanish paintings
Figures are just occupying space, don’t tell / add to story
Interest in color and light, representing the outdoors

Velázquez, Christ Crucified, 1632.
Convent commission, church in Madrid
Dark background, attention on figure
Three dimensional, feels like sculpture
Hebrew, Greek, and Latin written
Four nails instead of three, his teacher wrote about using four nails because it looks more classical, three creates a different composition, people argued
Jesus’ face isn’t well defined
Goya paints similar work, wanted to please commissioner

Velázquez, Portrait of Martínez Montañés, 1635.
A portrait of an artist, sculpture
Came to Madrid to create sculpture of Philip III
Wearing fancy outfit, like a suit in todays time
Background is very neutral
Similar to painting of Titian, self-portrait (fancy clothing, paintbrush in hand)
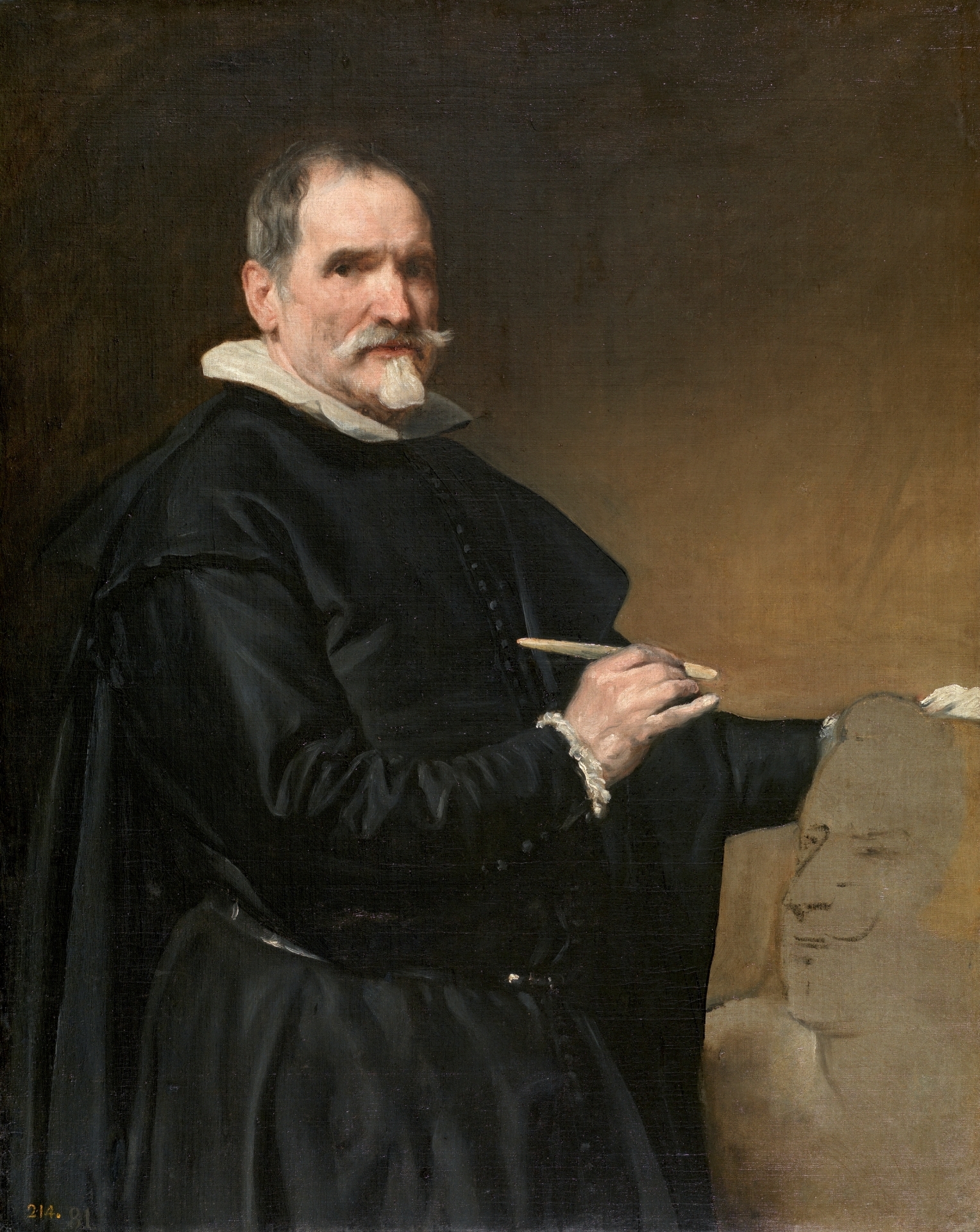

Velázquez, Portrait of Calabacillas, 1635-39
Someone the royal family hired for entertainment or administrative work
A physical or intellectual characteristic, entertainers (dwarfism)
Calabacillas: little pumpkin, has intellectual disability
Taking care of people who wouldn’t have an easy life outside the castle

Velázquez, Portrait of Pablo de Valladolid, ca. 1635
No background, painted space by shadow
Inspired by impressionists
Someone the royal family hired for entertainment or administrative work
A physical characteristic, entertainer (taller, fatter)
Taking care of people who wouldn’t have an easy life outside the castle
Actor, stance

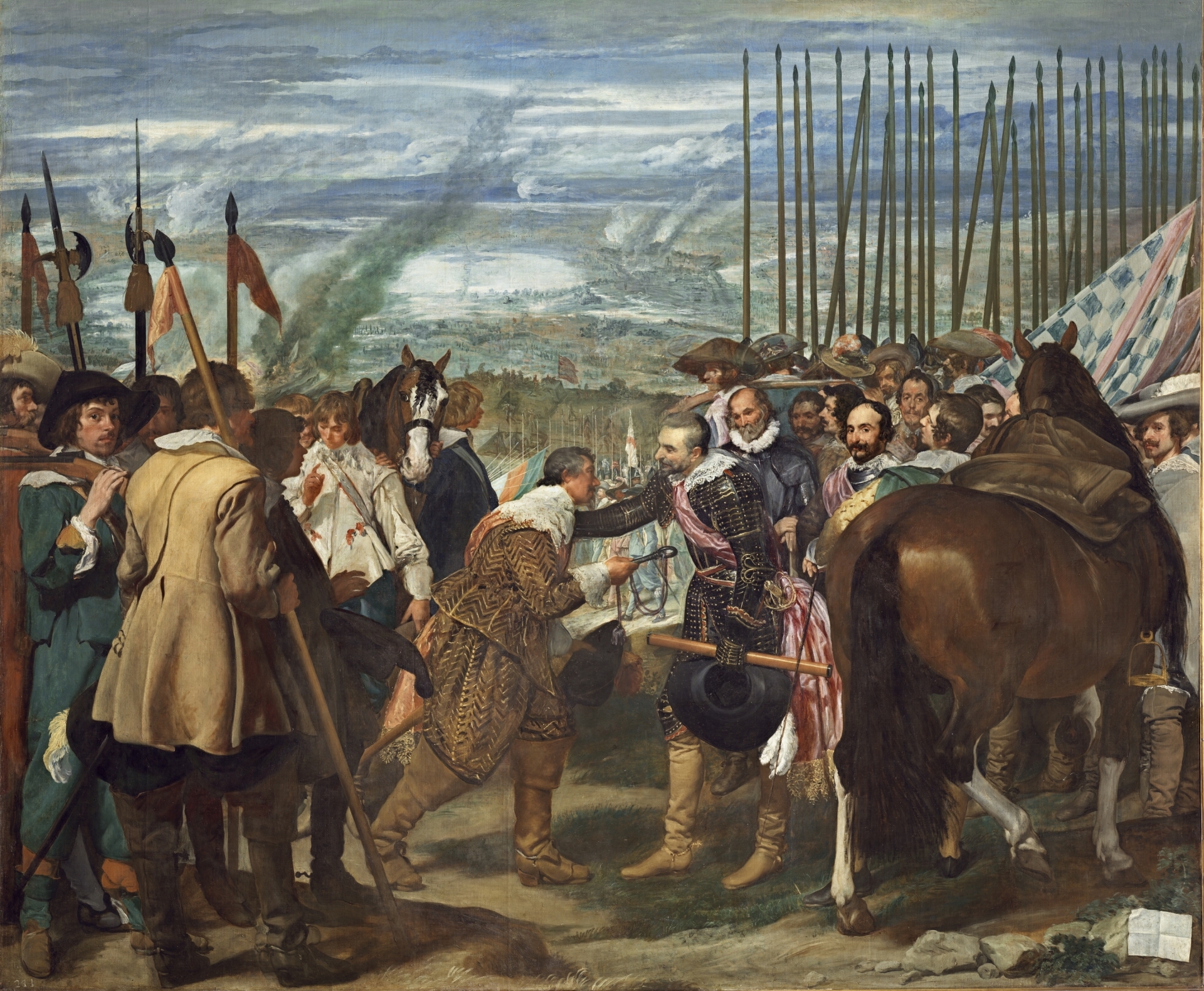
Velázquez, The Surrender of Breda, 1634-35.
Anti-classical, back of horse and man
No blood, artificial representation of war
Whoever won battle will be on a horse, person who lost in lower position
Propaganda piece to remember battle and Spaniards behaved like Christians, did the right thing

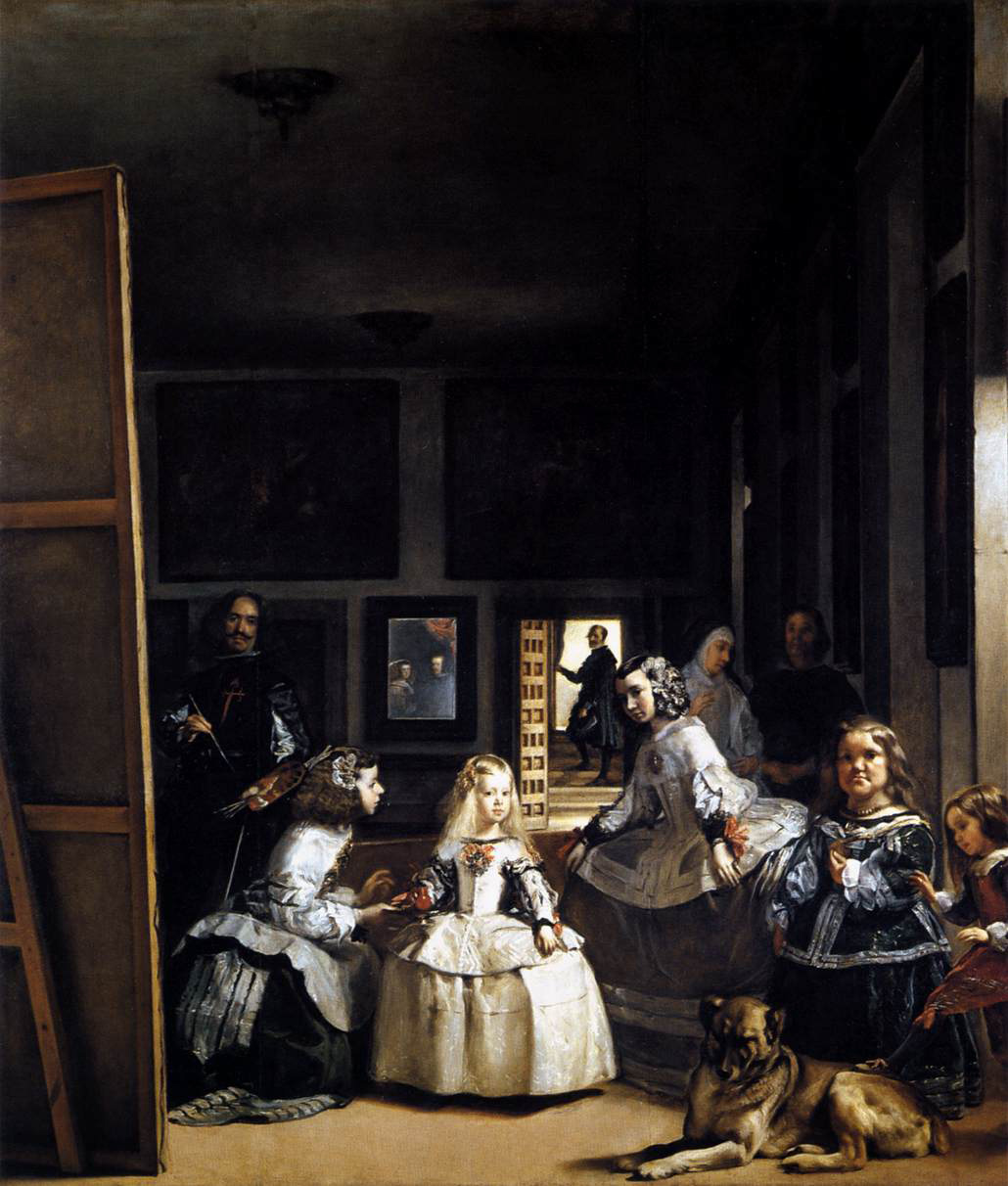
Velázquez, Las Meninas (The Maids of Honor) — My Girls, 1656
Group portrait, two ladies in waiting taking care of Princess Margaret, self portrait of Velázquez, two adults with dwarfism, two mentors of princess, one is widow, butler opening door for king
In royal palace
Might be painting princess, painting the painting we are looking at
Mirror of royal couple, Philip IV
How he got himself in portrait with royal family, others who have been invisible
Viewer has an active role, modern, not propaganda
Margaret, Infanta (daughter of king, won’t inherit the throne)
Breaking protocol
Painted an idealized version of himself, nobleman
Red cross, highest nobility / after king: old Christian, enough money to survive
Color, use of light, perfect harmony
Use of space, can walk among figures
Inspired Picasso style painting

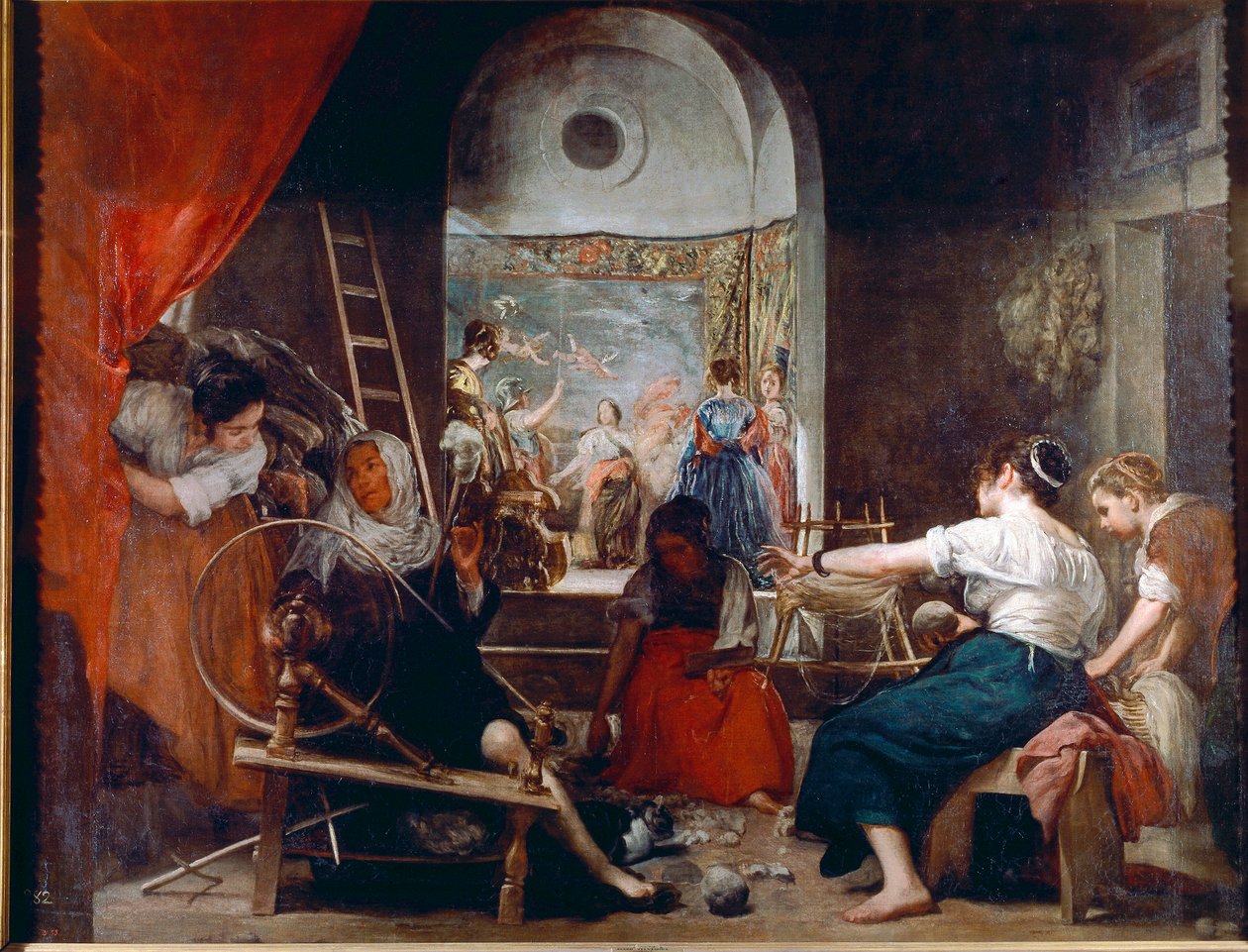
Velázquez, The Fable of Arachne, 1655-60.
Women spinning wool in foreground
In background, Athena with helmet, telling story of Arachne
Paying tribute to Rubens and Titian mythology artwork, recognizing masters and continuing tradition, Zeus transformed into bull, taking Europe
Movement of wheel
Influence of Michelangelo, posture
Possibly destroyed in fire, needed addition, or unfinished (Women’s faces blurred)

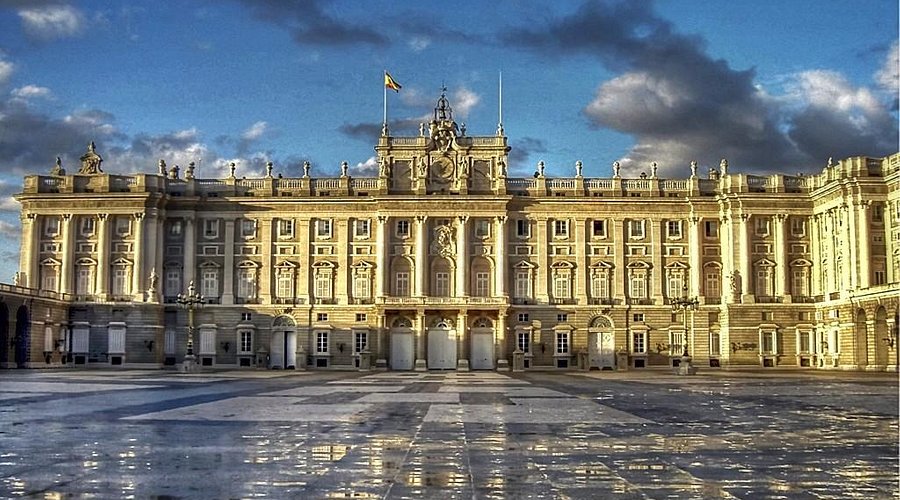
Royal Palace
Neoclassical outside
Geometry, repetitive
Rooms have been remodeled at different times
Philip V brought Italian architects
Originally Alcazar, burned down in 1734 Christmas Eve, rebuilding took two decades

Royal Academy of Fine Arts
Opened mid 18th century
King can decide what is taught
Students have better education, more students and instructors
Instructors for anatomy, color, composition, etc.
Technically superior
Lacked originality, one way to be artist, “proper” art
History painting (past history, present message) encouraged
Handed out medals to history paintings, art needs to teach people

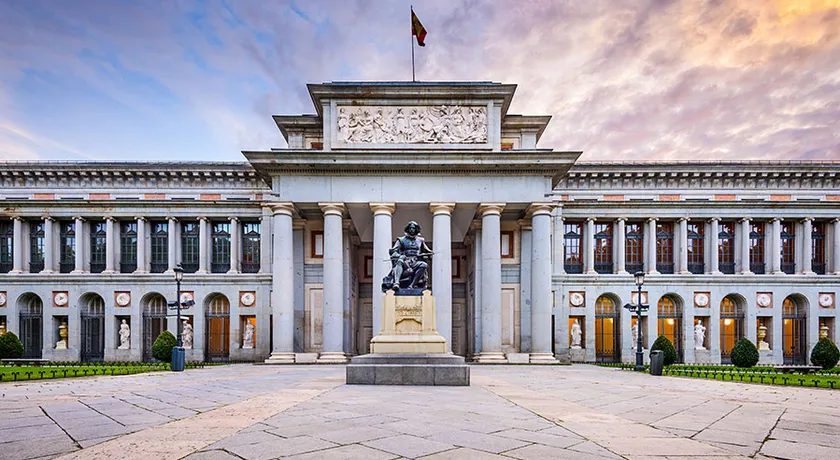
Prado Museum, 1785-1808, architect Juan de Villanueva
Opened in 1819
Originally supposed to be a natural history museum
Round arches, proportions, columns, Roman
Classical columns, repetition of same motifs, proportions and balances, the idea of making the museum a place to study
Founded by Queen Maria Isabel de Braganza, husband King Ferdinand VII, second wife and niece of him, granddaughter of Charles IV, exceptional art promoter, convinced Ferdinand VII to show the royal collection to the public
Botanical gardens located nearby
Neoclassicism

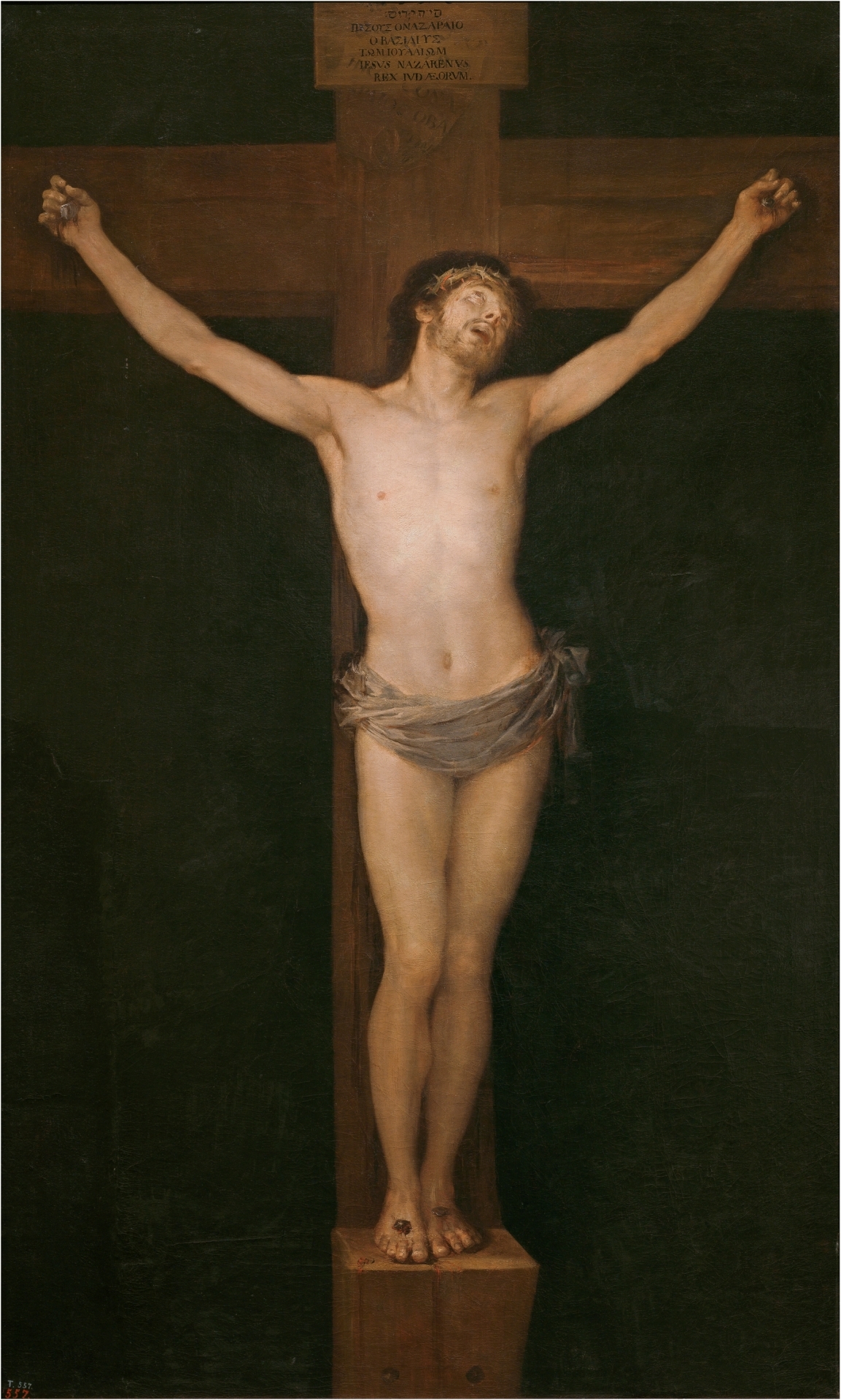
Goya, Christ Crucified, 1780, Prado Museum
Presented to the Academy as his entry work
Neoclassical / Rococo style
Spanish iconography
Soft modeling using sfumato

Goya, Dance on the Riverbanks of the Manzanares River, 1778
Past times and amusements of Madrilenians
Very nicely dressed, not high people, Sunday clothes
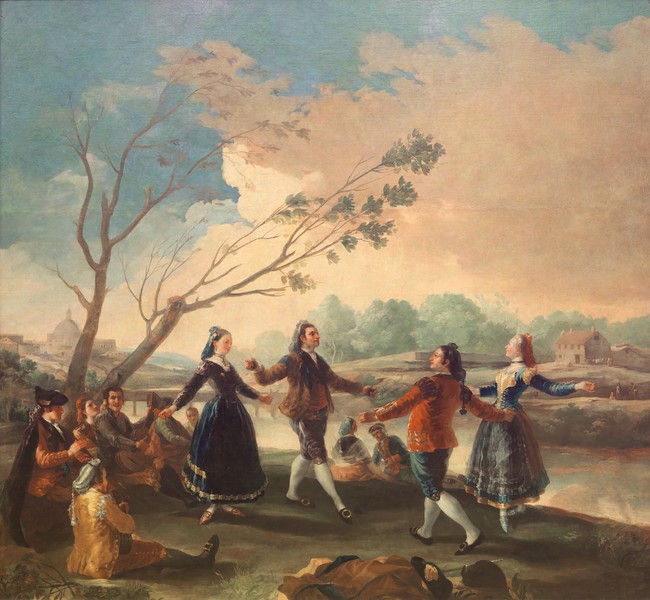
Goya, The Crockery Vendor, 1778
September fair
Cartoon for the bed chamber of the Princess of Asturias
Important event because of clothing, person from Valencia because of shoes
Complex narrative (outside the frame)
Class division
Old lady and off canvas gesture are a reference to prostitution

Goya, The Wedding, 1791-92
For Charles IV’s office
Cynical outlook
Satyrical view of society
Moratín “Little Maidens consent” (1801) Novel criticized women for getting married to first person who asks
Goya has been appointed court painter in 1789 (“Principal Painter of the King” in 1799) and was already the official portraist of Madrid’s society
Groom related to guy in green
Priest smiling, got money
People gossiping
Goya interested in gender roles, gender sterotypes

Goya, The Inquisition Tribunal, 1812, Royal Academy of Fine Arts
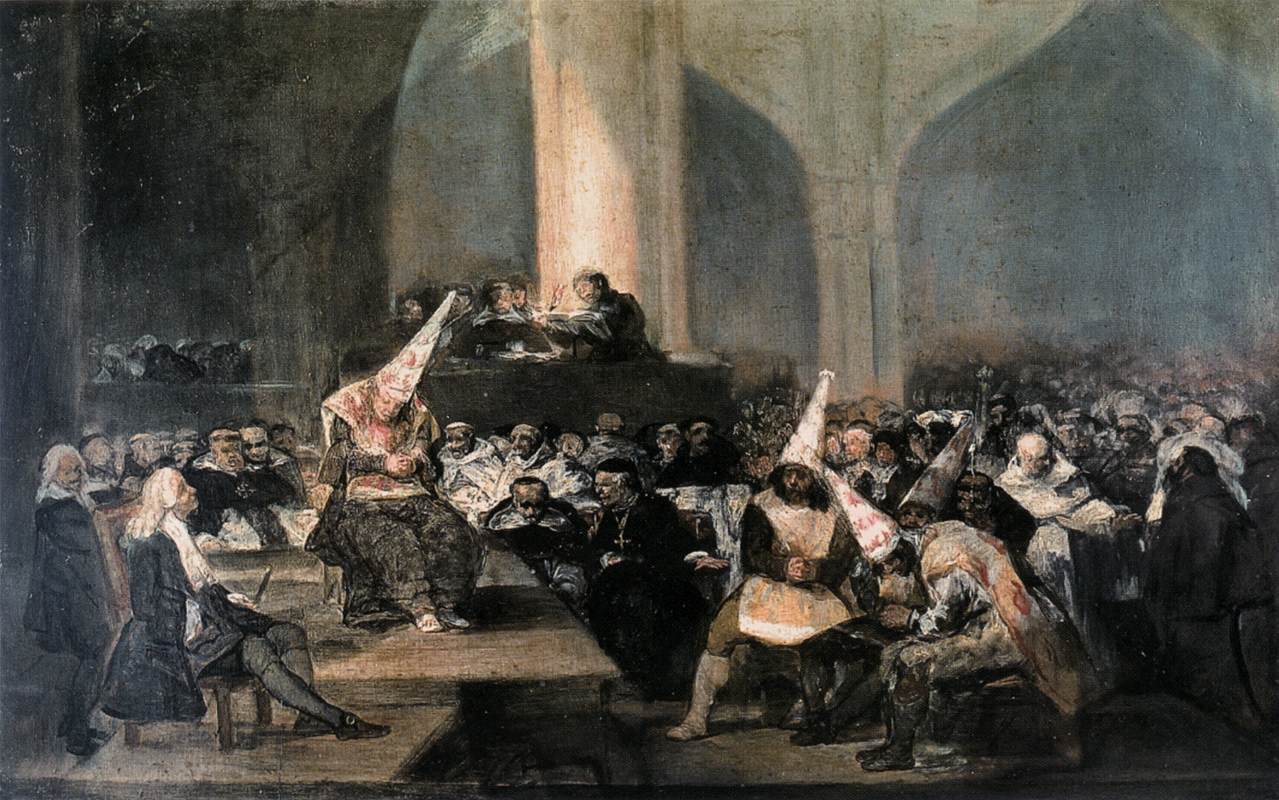

Goya, Procession of Flagellants, 1812, Royal Academy of Fine Arts

Goya, The Madhouse, 1812, Royal Academy of Fine Arts

Goya, The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters, 1799
“Los Caprichos” 1799: The censorship of human errors and vices
Main subjects: The decline of reason, anticlericalism, superstition

Goya, The Family of Charles IV, 1800
Highlighting Spanishness of Royal Family because cousins in France were getting executed due to the French Revolution.
Did not paint everyone together, spent summer painting individual portraits. Some people passed during this creation but are included in the group portrait.
Reference to Hercules in left painting, Maria Lucia is the strong one, foreigner, good mother, raising children, does not have a good reputation because she is having an affair.
Ferdinand VII future king, forced parents to abdicate, ends up abandoning country and takes the royal guard, appointed brother Joseph I as new King of Spain.
People felt abandoned.
Lady looking away did not exist, future wife to Ferdinand VII

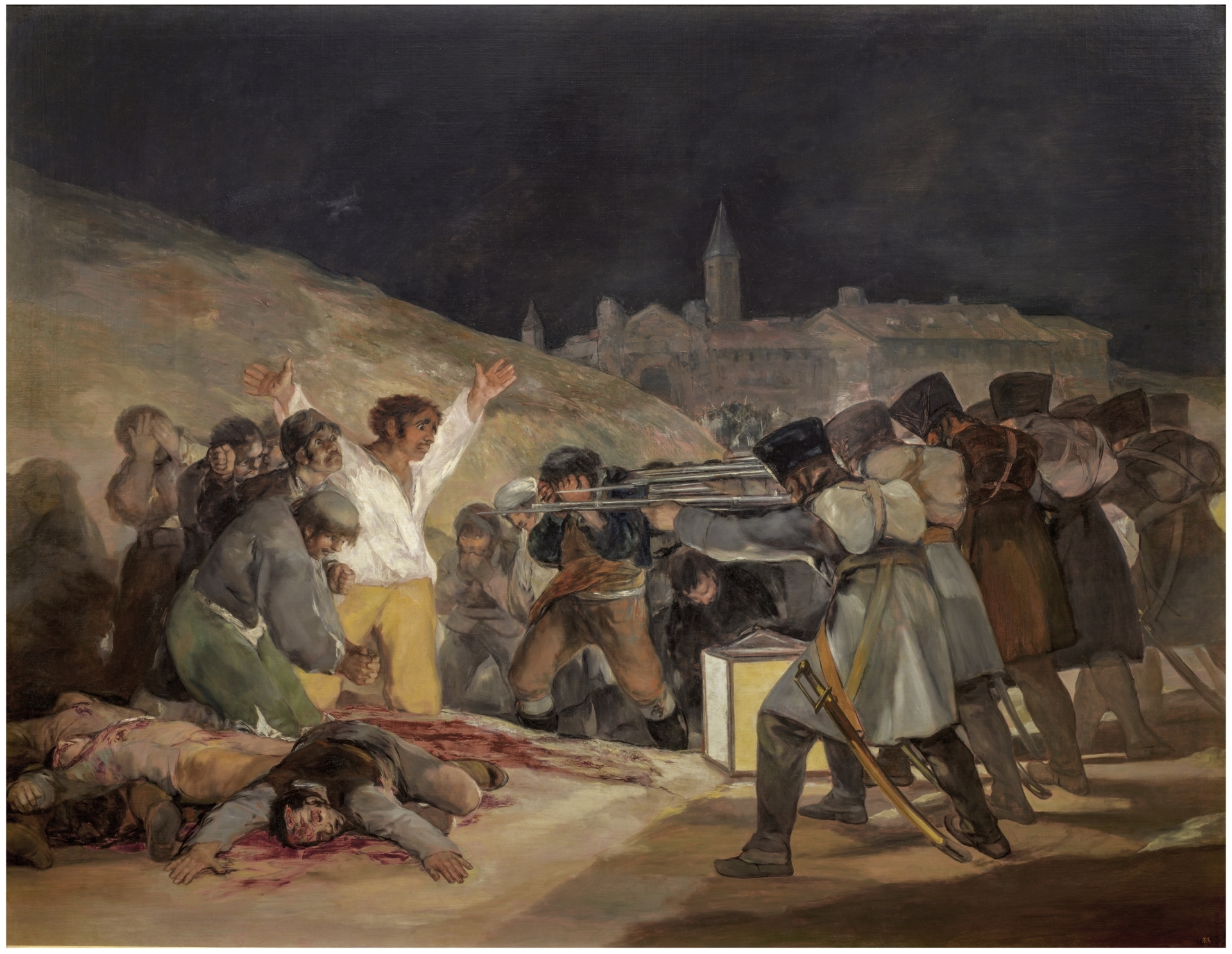
Goya, Second of May, 1814
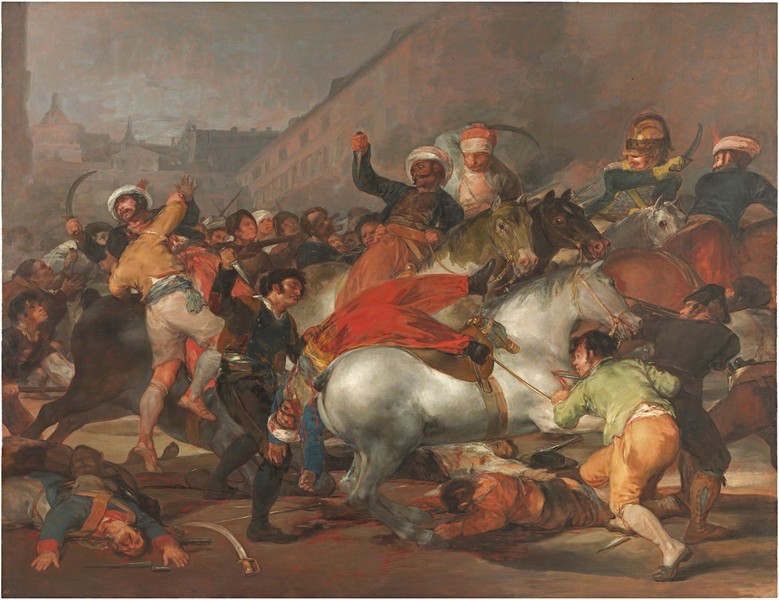

Goya, Third of May, 1814
Everyone is a victim of the war
Victims show emotions, soldiers show nothing, can’t see faces
White and yellow colors of the Vatican
Arms up like cruxifixction, marks in palms of hands

Goya, Saturn Devouring his Son, 1820-23
Black painting
Making reference to Saturn, prophecy that son will dethrone him
Chronos in Greek, time, no one is immortal, can’t escape prophecy
Reference to Goya’s age, passing of time, King of Spain, Napoleon, how men treat women, wife having miscarriages

Goya Witches Sabbath, 1820-23
Women getting together means witches
Believed in witches, women living alone, not without men supervision
“[Black paintings] are a romantic model for the romantics; an impressionist for the impressionists; Goya leader became an expressionist for the expressionists and a forerunner of surrealism for the surrealists.” —Nigel Glendinning
Modern painter
Distorted faces, superstitious

Goya, Half-Drowned Dog, 1820-23
Black painting
Most human gaze, other paintings show monsters
Not popular to idealize animals / dogs at this time, modern thinking

Pascual Colomer, Spanish Congress, Mid 19th century,
Neoclassical style to show power, even in the US
Democracy born in Athens
Pure, simple, stable architecture provides a clear ideology

Alberto del Palacio, Atocha Station, 1889
Built with iron and glass
Outskirts of city

Ricardo Velázquez Bosco, Glass Palace, 1887
Colonial exhibition
Wanted to build structure that would function as a greenhouse, brought plants from Philippines (and people), showcased in building
In Retiro park
Used iron and glass, neogothic atmosphere (round arches, thin columns, pointed arches, base made out of brick, tiles Islamic influence)
Art exhibitions now

Ponciano Ponzano, 1864, Pediment of the Congress
Marble
Allegories
Symbols of abstract concepts (progress, justice)
Not mythological sculptures
Proportions, idealized

José de Madrazo, Death of Viriatus, 1808, Prado Museum
Resistance of the Iberians against Roman domination
Patriotic spirit (French invasion)
Contained dramatic influence of classical sculpture
Vibrant colors, Roman subjects, technique is polished, makes painting neoclassicism
History painting, past is used as a metaphor for the present
Linear perspective, composition
Viriatus: lived in Iberian Peninsula at the time of Roman invasion, worked his way up to general, betrayed by two “friends”
Resonated among Spaniards who are resisting Napoleon, French
Madrazo was student, then director of Royal Academy, studied in Rome
Reality no outfits, tents, shields, banners, etc.
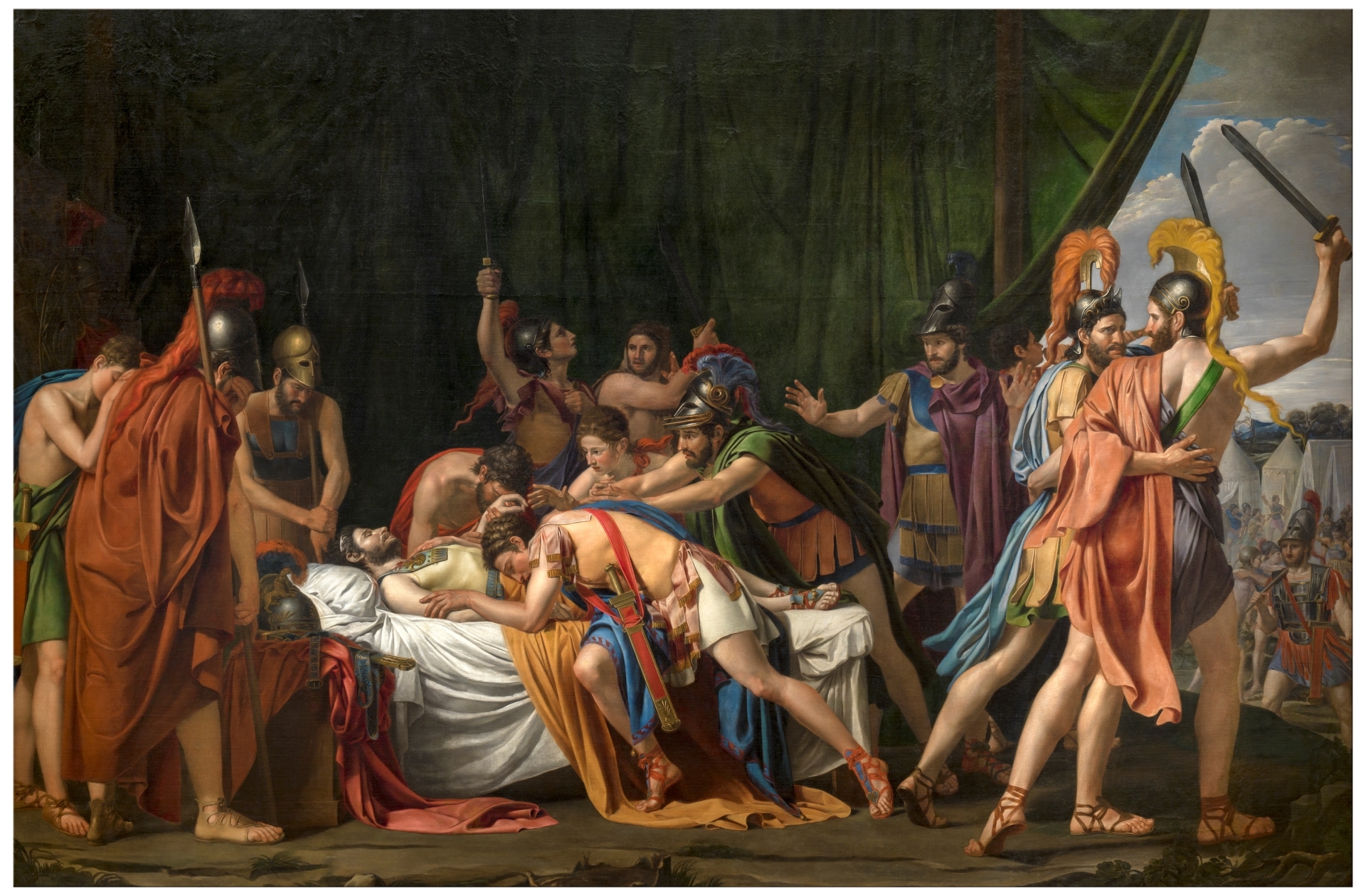

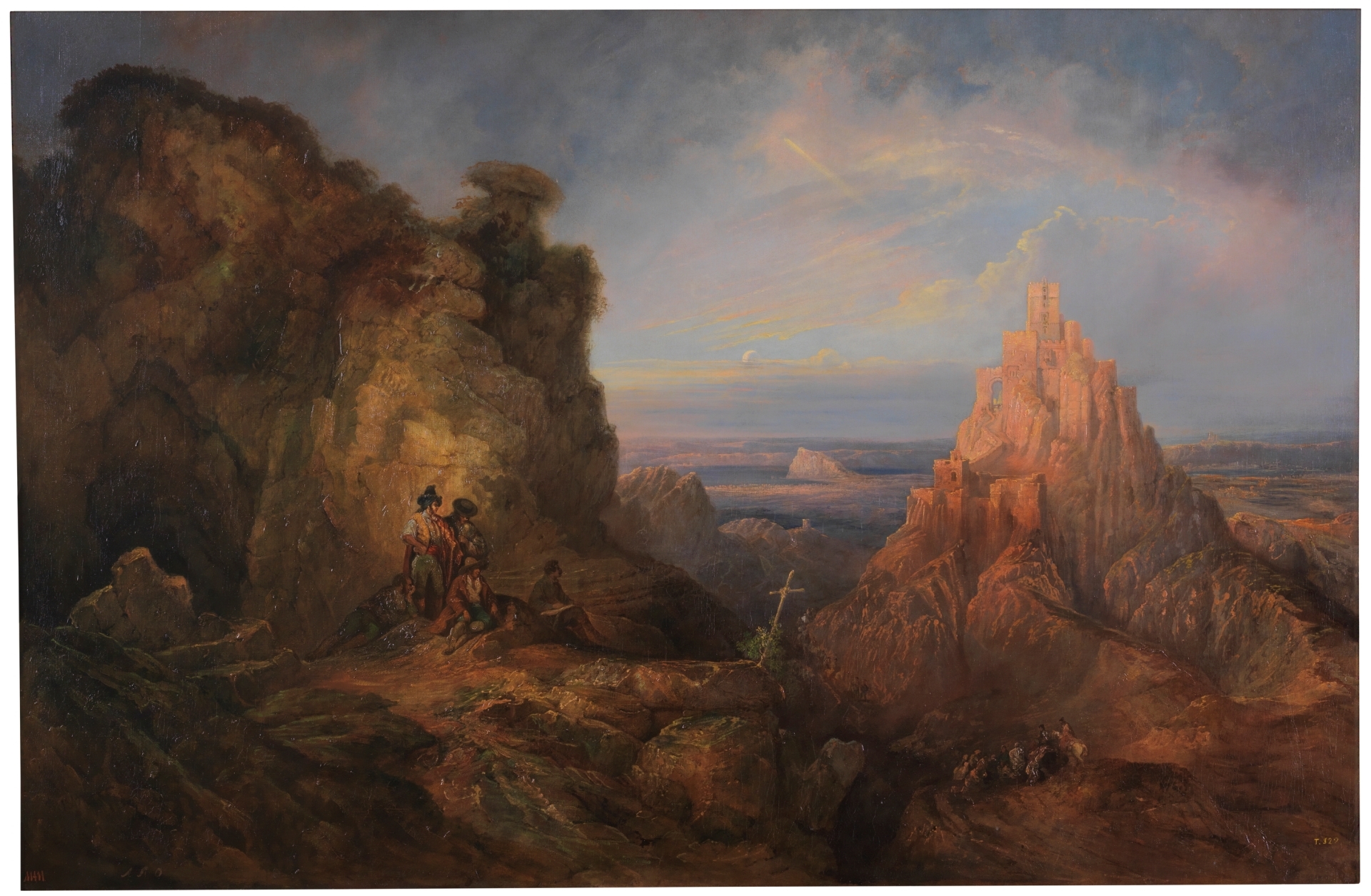
Jenaro Pérez Villaamil, View of the Castle in Gaucín, 1849, Prado Museum
Romanticism
Movement that reacts against classicism, focuses on nature and feeling, art is medieval or Islamic, nature in its pure form (storm, mountains, volcanoes), nature is bigger than us and is the center of the universe
Emphasis on individualism, intuition, emotion, (an idealized) past, and (wild) nature
Reaction to the Enlightenment (Age of Reason)

Eduardo Rosales, Queen Isabella Dictating her Last Will, 1864, Prado Museum
Realism
Authentic, carpet isn’t perfect
Isabella I, very pale
Won many prizes, awards, symbol of the time
Artist was early/mid twenties
Her and king unified the country, the Reconquest
Last will, wants to keep country and territories together
1864, before Mexico gains independence, other countries, Spain losing its influence
Woman standing on the left married Philip the Handsome, loved her husband, jealous of mistresses, nicknamed “The Mad One” for getting upset at affairs, locked in tower
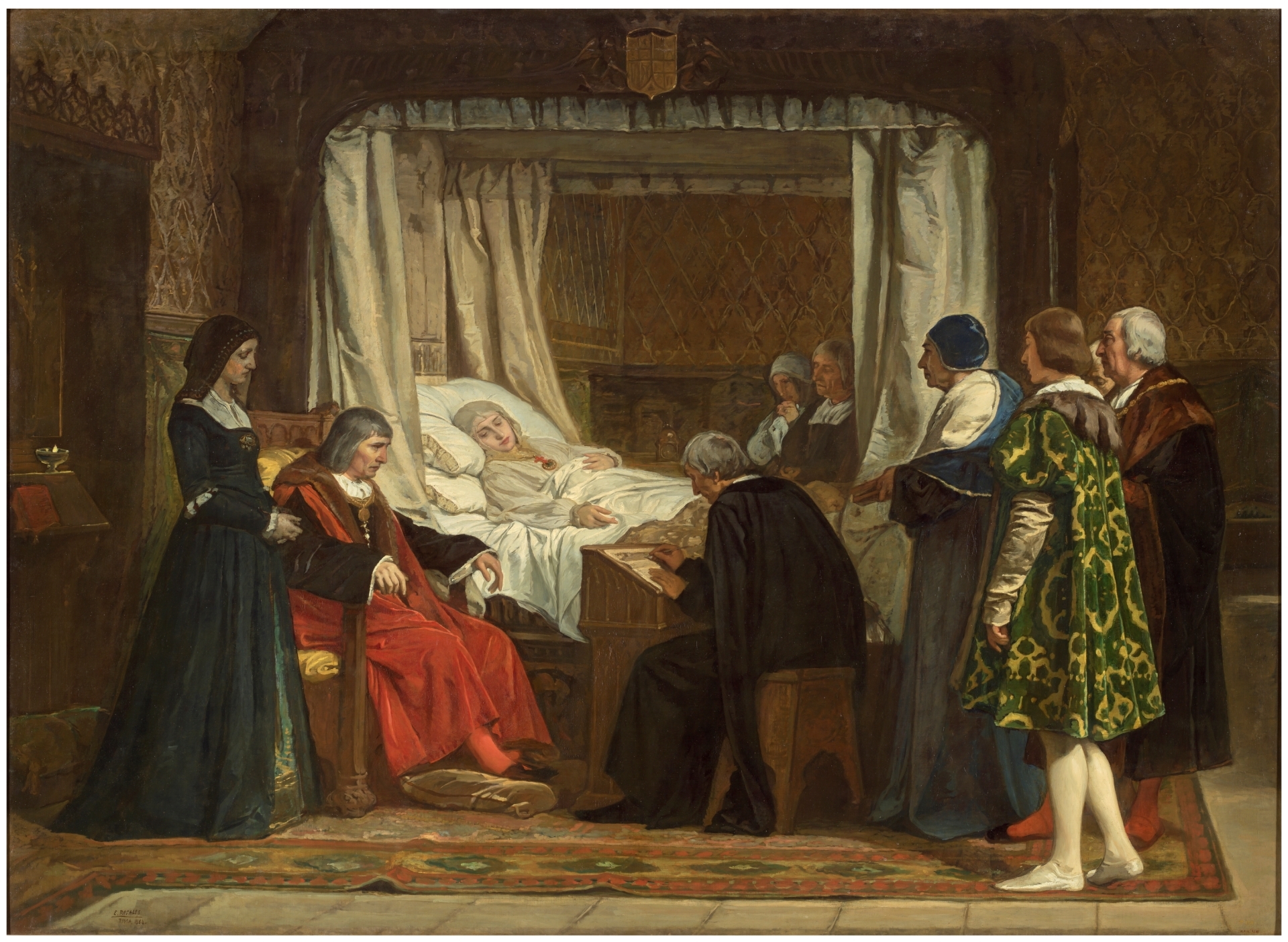
Francisco Pradilla, Queen Joanna "the Mad", 1877, Prado Museum
Joanna the Mad, after Philip dies
Procession, buries him near her parents Catholic Kings
Walked to Granada while pregnant
Dressed as widow
Influences of realism, tire tracks, emotions, dirt
Romanticism: themes of unrequited love, death
History painting

Antonio Gisbert, Executions of the General Torrijos and his Companions, 1886-88
Isabella II ruling, under regency of mother
People fighting against Napoleon and Ferdinand VII, went to London
Told they would be safe, went back to Spain, killed as soon as they got off boat
Priests offering comfort
Could choose to be blindfolded or not
Individuality through facial features, body language, clothing, hair, costumismo
Attention on victims
Went to beach where it happened, interviewed relatives of victims
Similar to painting men being executed with hands like crucifixion by Goya, Third of May

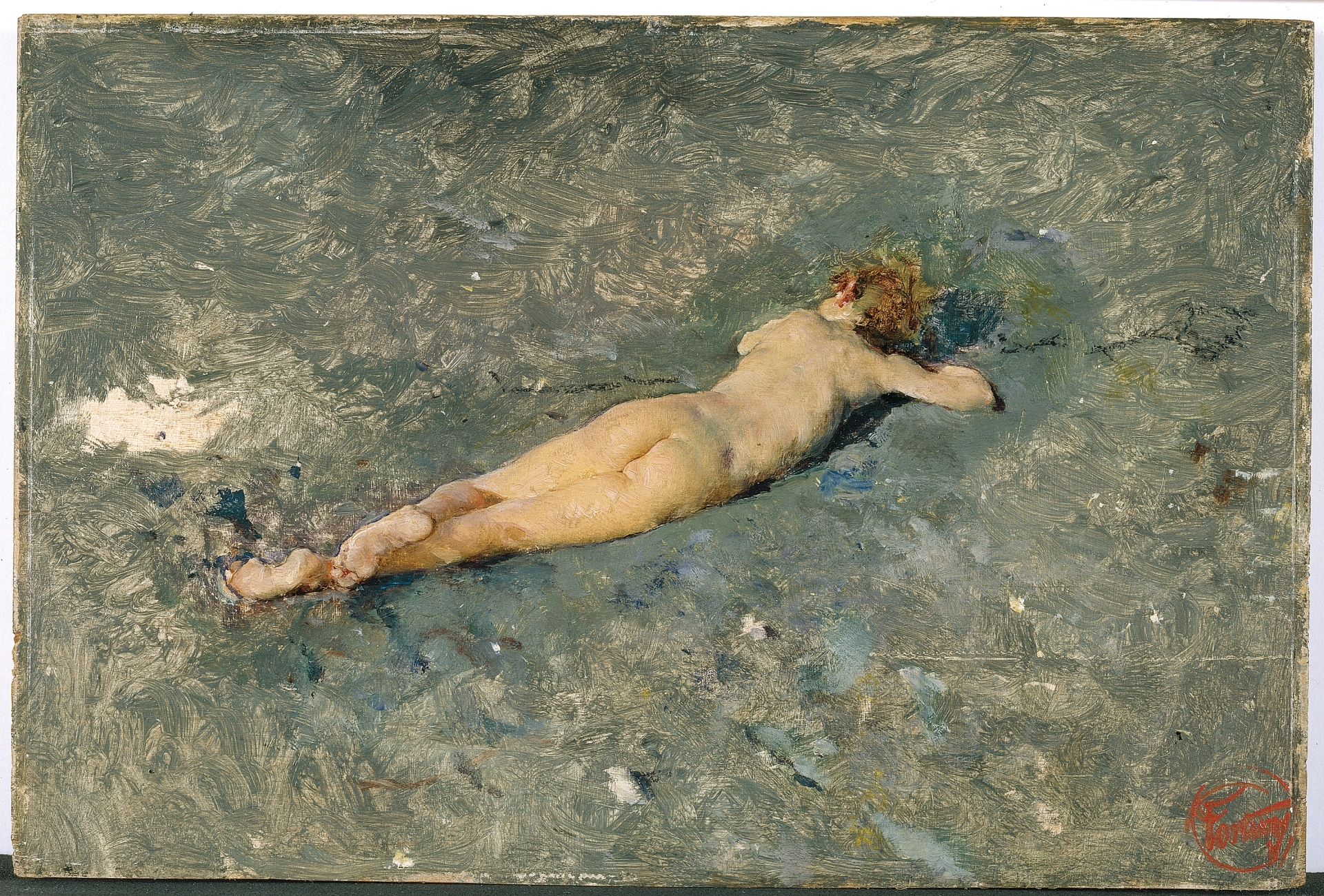
Mariano Fortuny, Nude on the Beach, 1874
Brushstrokes are loose, sketchy, bold
Light and color, green, blues, purples, mixed on canvas

Mariano Fortuny, The Painter's Children in the Japanese Room, 1874, Prado Museum
Painting left unfinished
Very nice room, very wealthy
Two children playing, bored during nap time, boy wearing Japanese No Theater mask, girl with fan
Influence of Japan and photography
Cherry tree branch, golden butterflies
Painter Madrazo’s daughter marries Fortuny, created artwork for his father-in-law

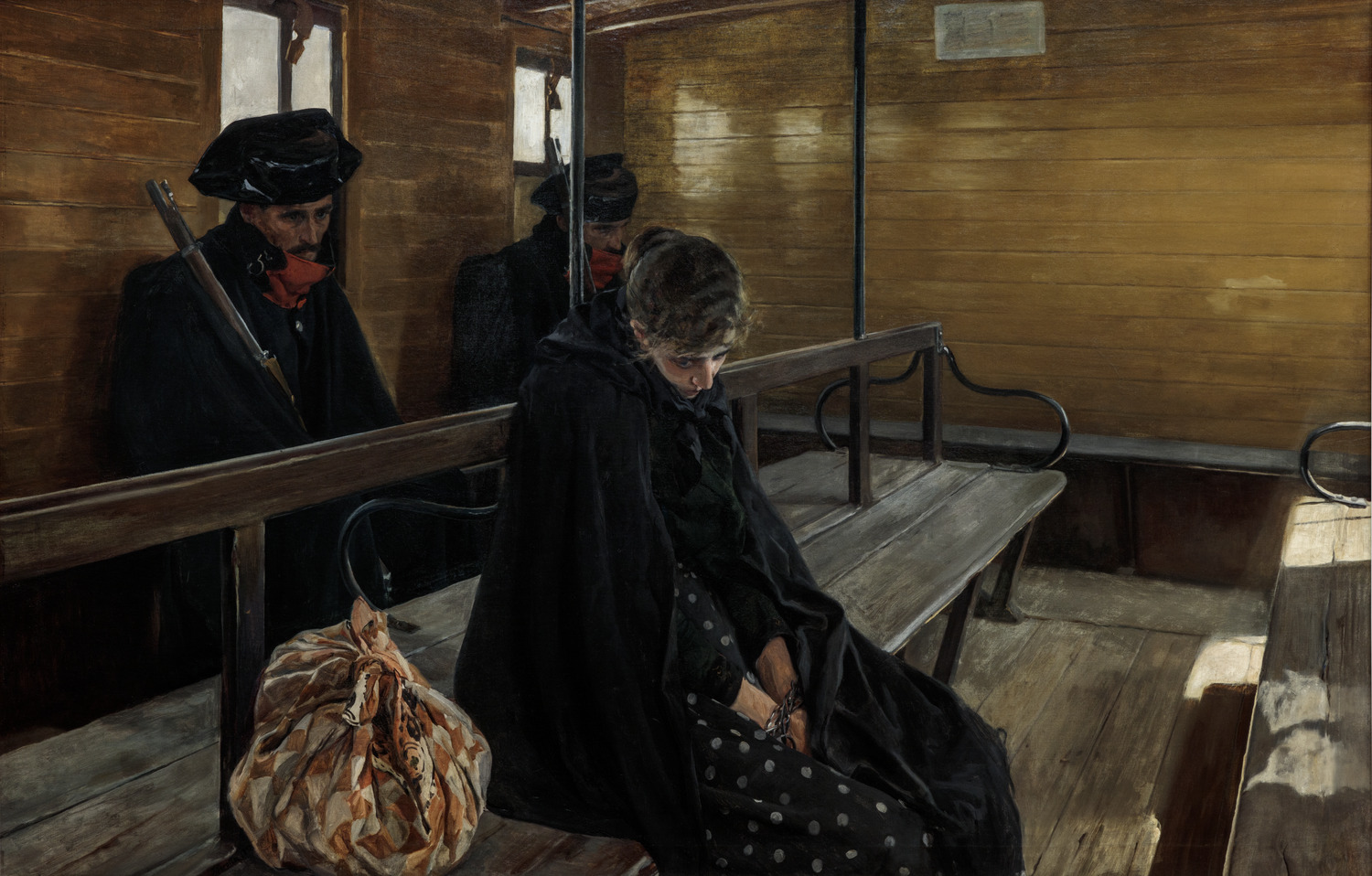
Sorolla, Another Marguerite, 1892
Woman’s face: uncomfortable, disassociating
Homeless, bag indicator
Hands are tied
Marguerite, famous criminal at the time, another woman who committed a crime
Realism

Sorolla, Sad inheritance, 1899
Last painting covering social issues
Saw boys going to water in Valencia, supervised by a priest, many needed crutches to walk, learned they were orphans and taken in by church, many had polio because they had gotten sick from their parents
Realism, but outdoors, colors lighten, many colors in sand, light is shining
People interested in lighter palette, subjects

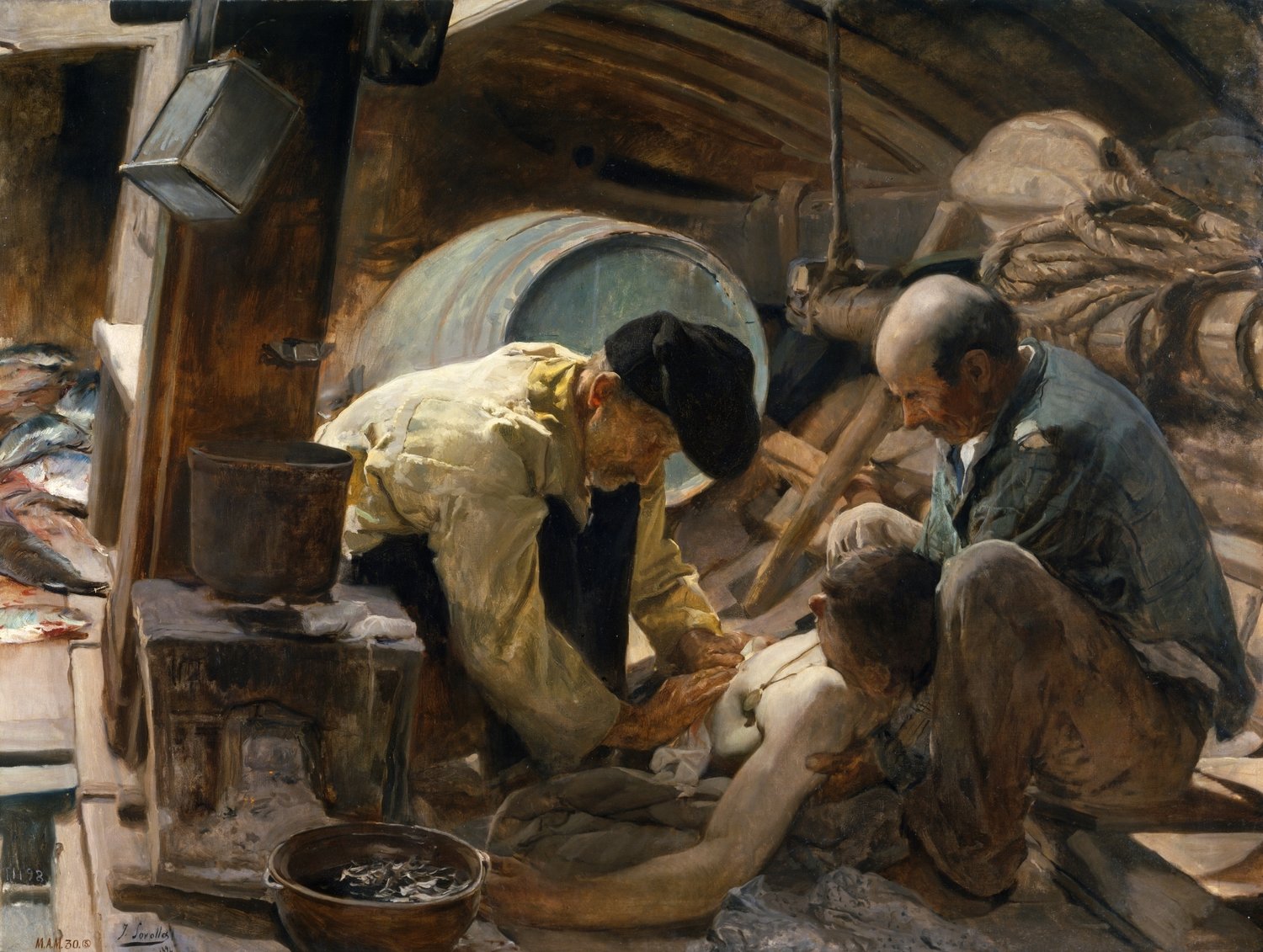
Sorolla, And They Still Say Fish is Expensive, 1894
Below deck on a boat, man is seriously hurt
Fishermen, three generations, one family connected
Costumismo: black hat, Basque country
Locket, given by family?
People who complain about prices, actually hard work
Realism, melodramatic vision

Sorolla, A Walk on the Beach, 1909
Wife and daughter
Uses color in white dresses
Flat paintings, 3 dimensional for academic paintings
Using angle of photograph

Darío de Regoyos, Good Friday in Castille,1904, Bilbao Museum of Fine Arts
Impressionism
Procession
Bright colors: modern; Black colors: tradition
Two lines: people and train
Mixing black and white Spain, tradition and modern

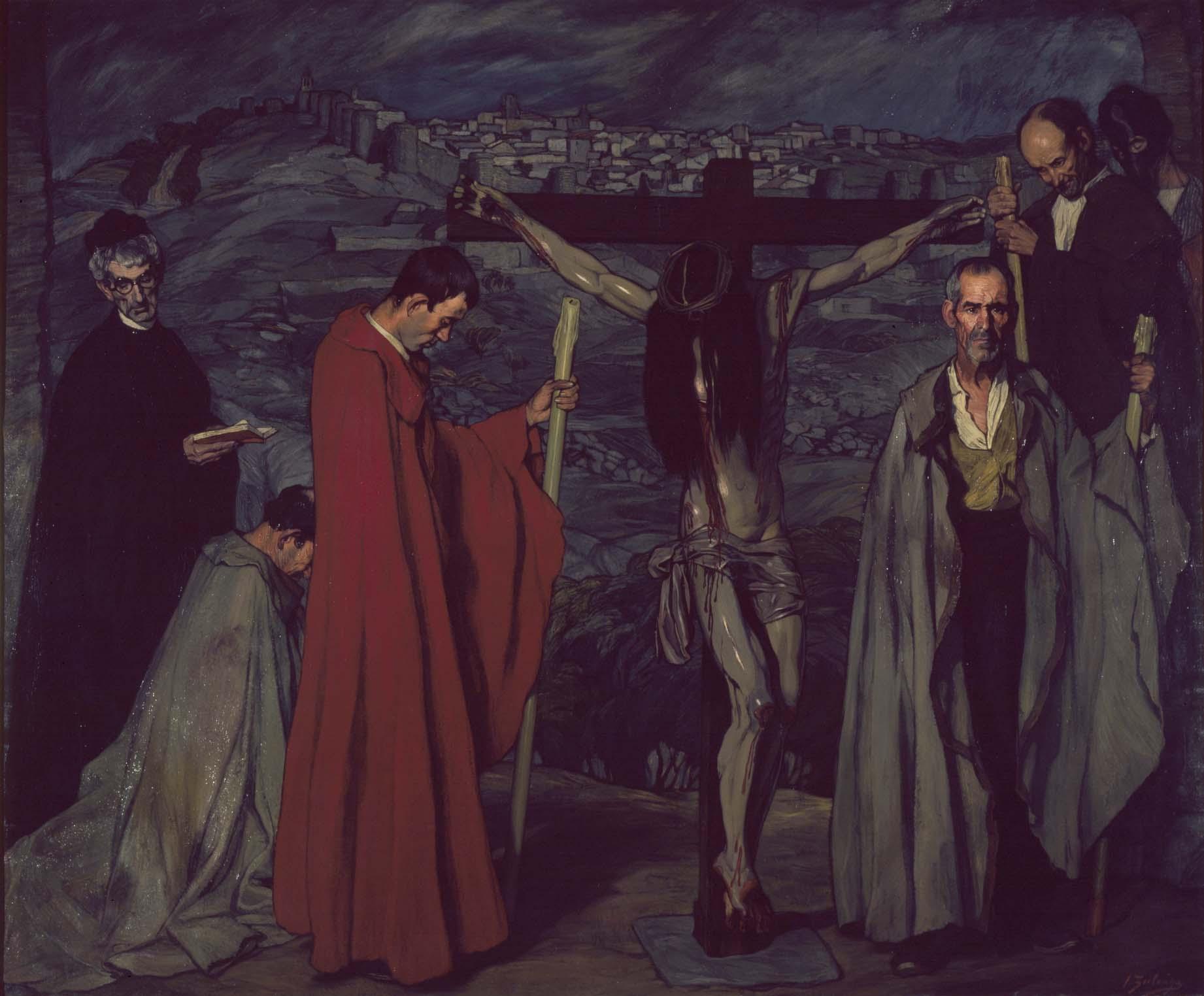
Zuloaga, The Christ of the Blood, 1911, Renia Sofia Museum
Commoners, sculpture of cruxifixction, theatrical
Reminder of El Greco, elongated figures
A true emblem of Generation ‘98

Zuloaga, Dwarf Gregorio, 1907, The State Hermitage Museum, Saint Petersburg
Reminder of Goya characters, expression looks a little unhuman
Carrying pot and pig skin, used to contain wine
Black Spain, forced, trying to find odd character and situation
In disarray
Gaze
Reminder of Velazquez, painted those who served the monarchy
Reminder of El Greco, sky, color, brushstrokes

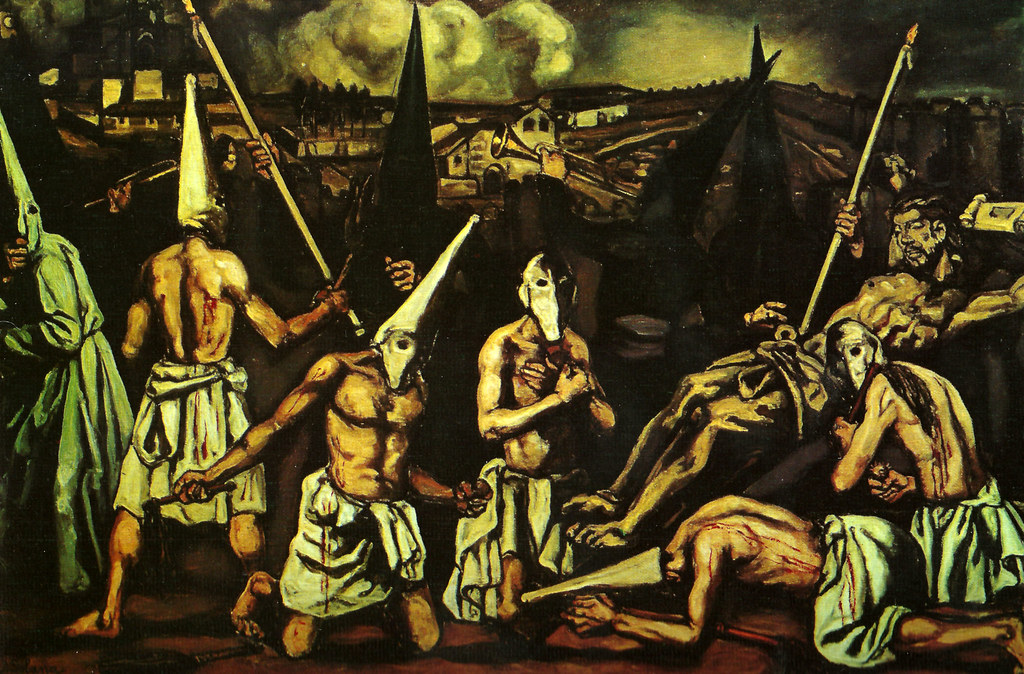
Gutierrez Solana, The Flagelants, 1910
Paint is thick, many layers
Artist entered academy at 14 years old
Similar to Goya’s paintings

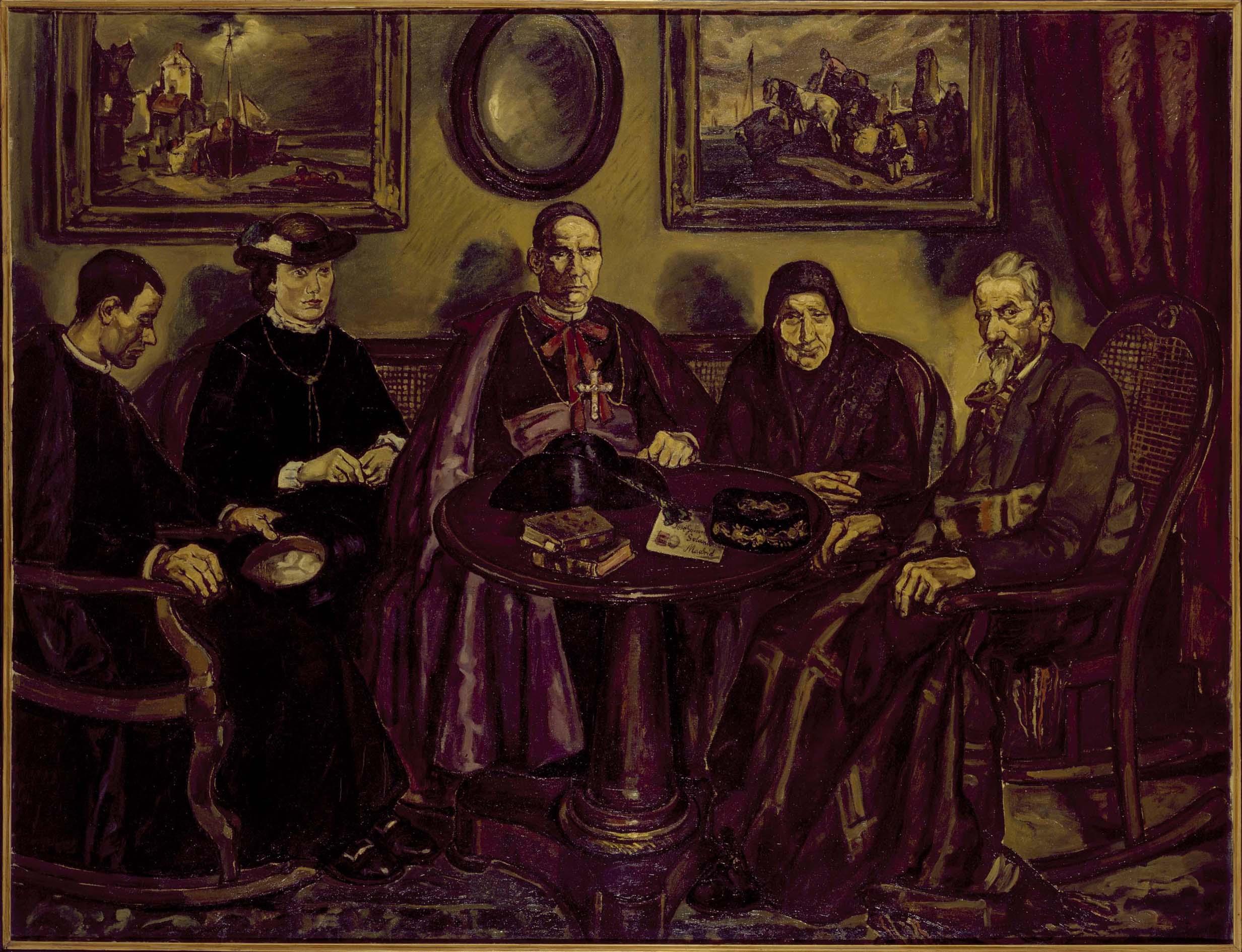
Gutierrez Solana, The Bishop's Visit, 1926, Reina Sofia Museum
Stuck in past
Strangeness

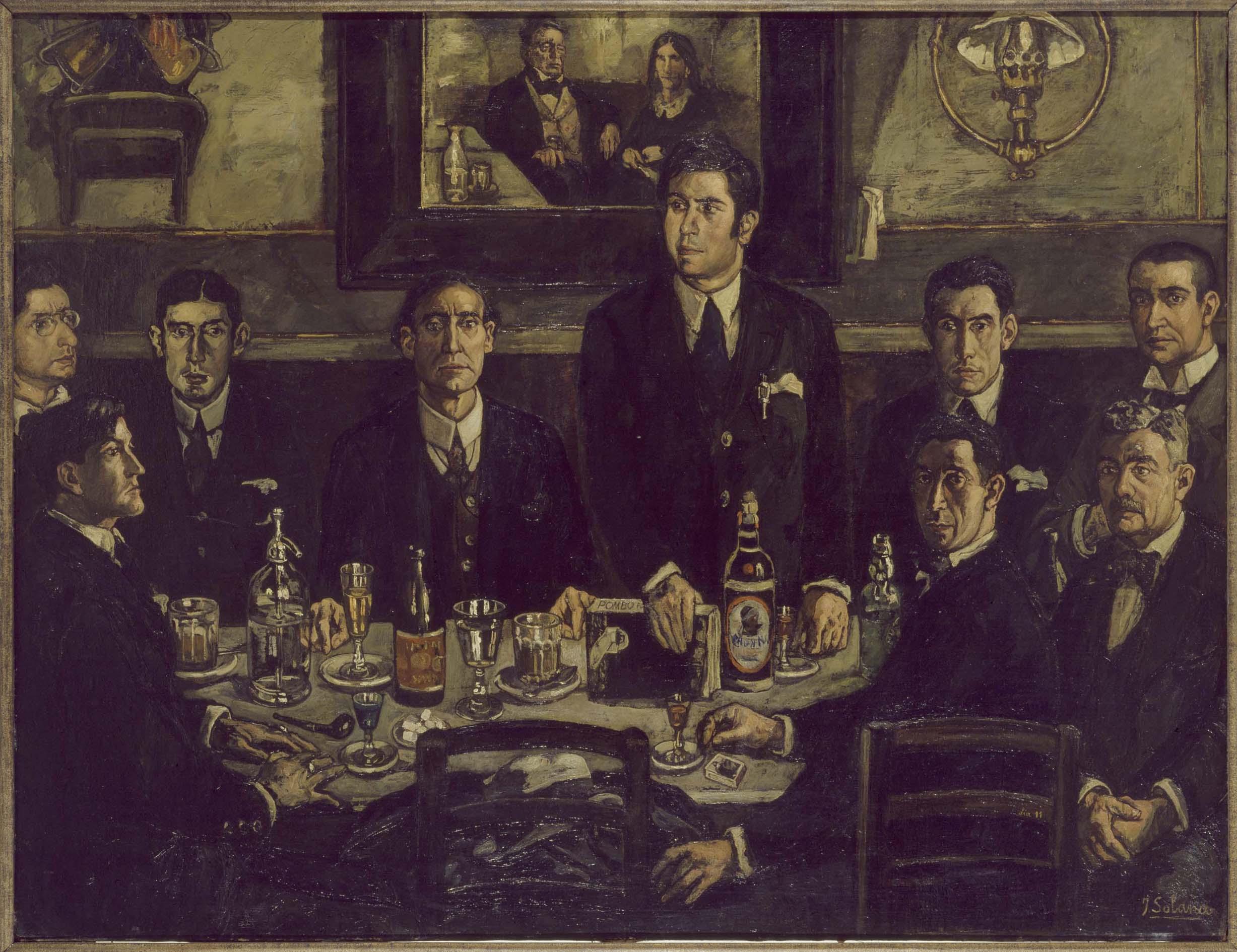
Gutierrez Solana, Gathering at Cafe Pombo, 1920, Reina Sofia Museum
Tertulia: a gathering that is very long and things are discussed, cultural, similar to book club, will debate literary things, etc.
The man in the middle: Ramon Gomez de la Serna, modern person introducing modernity in Madrid, poet, Museum of Madrid recreated his office, collector, surrealist, loved El Rastro, left Spain for war and took things with him

Describe the art produced in the court of Philip III, who were the painters he
favored? Which constructions did he sponsor?
Juan Pantoja de la Cruz was a favored artists, as he created a portrait of him and was the royal painter. He was creating at the beginning of the baroque period. Philip III sponsored the construction of the Plaza Mayor, as it was originally designed during Philip II’s reign with architect Juan de Herrera, but architect Gomez de Mora built it while Philip III was ruling.
Which artists exerted an influence on Velázquez?
Titian and Reubens influenced Velázquez’s work because once he began to work for the King Philip IV he had access to the royal collection. His portrait of Martinez Montañes is similar to Titian’s because of the subject, fancy clothing, and the iconography of a sculpture, or in Titian’s case, a paintbrush, referencing their work. In his mythological paintings, specifically The Fable of Arachne, he is referencing both artists because of the subject matter. Also, his use of naturalism is inspired by both artists.
Who were the “people of pleasure” in Velázquez’s paintings? Why were their
depictions so relevant?
Velázquez created paintings of people who were entertainers for the royal court in his paintings Calabacillas, Pablo de Valladolid, Don Diego de Acedo, and Barbarroja. These people were jesters or actors/singers and some had physical and/or mental disabilities. These depictions were relevant because it was moving away from religious, mythological, or royal paintings and instead focusing on people who would not have been recognized without the artwork.
Explain the significance of Las Meninas. Why is said painting so important for Art
History?
Las Meninas is a portrait of the royal family, but also includes Velázquez as the artist. Princess Margaret is being waited on by two adults with dwarfism, two other mentors are in the room, along with a butler, two ladies in waiting, and then the King and Queen are seen in the mirror. Since Kings and Queens could not have portraits together, there is a mirror reflecting them, so they are standing behind the perspective the painting is shown at. The large canvas Velázquez is working on is this exact painting. It places the viewer in an active role and it is important to art history because Velázquez is breaking protocol by placing himself in the piece.
Describe the artistic changes introduced by the Bourbon dynasty in Spain. Please
provide examples of works.
The Bourbon dynasty in Spain introduces the art style of Rococo. The Royal Palace is one example of this because after the original Alcazar burned down, they rebuilt the palace to what it is today. While the outside resembles neoclassicism and baroque architecture, the inside has elements of rococo because of the use of nature in rooms like the Porcelain Room, and its theatrical style.
What were Goya’s intellectual and artistic influences?
Artist Francisco Bayeu was Goya’s teacher and painted in the late baroque, early rococo style. Once in Madrid, Goya studied Velázquez’s artwork and was inspired by him and Anton Raphel Mengs. Velázquez’s use of space was seen in Goya’s work, Duke and Duchess of Osuna. Lived during the French Revolution (1789-99) and the absolute monarchy of Ferdinand VII (1813-1833) inspiring the subjects of his paintings that showed commoners, not just the royal family. He was also inspired by Titian, specifically for his painting La maja desnuda.
Who were Goya’s patrons?
Goya worked under four Spanish Kings, Charles III, Charles IV, Ferdinand VII, and Joseph I. He did not get along with the Kings, but he was the closest to Charles III. However, he was not political, so he would create internal and political problems with his artwork. Such as his portrait May 2nd was commissioned by the monarchy but paints the people of Madrid and the crown in a lesser light.
Why is Goya considered one of the first modern painter?
Goya is considered a modern painter because of technicality and intellectually because of his reflection of contemporary events as he would paint for himself. He would paint works reflecting subjects such as gender, war, and religion.
How is Goya’s work on prints different from his creations on canvas? Explain the
themes, formal style, and significance of his prints.
On the prints, Goya has to create the work flipped, including the text. Unlike the paintings he was creating at the time, his prints have more of a creepy/scary theme, like in Here Comes the Bogeyman and So They Carried Her Off!. They were also significant because they were of commoners, not anyone involved with the monarchy or of religion or mythology.
What is History painting? When does it develop? By whom and with which
purposes?
In the 19th century, history painting became important as the Fine Art Royal Academy began to celebrate it. When they hosted competitions, the artwork that always won gold were history paintings. They were so important because the artwork told a story and had a moral. It was something people could learn from and with the influence from the academy, they were able to set the precedent of what art is and what matters when it comes to art.
Is there any impressionist painting in Spain? Please explain.
There is not really any impressionism in Spain, however, when it did occur it was a later arrival, during the second half of the 19th century. Belgium impressionism painter Carlos de Haes was a teacher at the Fine Art Royal Academy. Then the two artists Fortuny and Sorolla paint in the impressionism style and after travel in Europe, they bring that style to Spain.
Briefly explain the main characteristics of the 1898 Generation specifying the artists
who best represent it.
During the Spanish-American (The Cuban War) and the whole generation is disappointed and have a “tragic sense of life.” Goya influenced this along with the style of baroque and realism. Photographs and films pushed the “realism” style. They began to reinterpret what “Spanishness” is.
Describe José Gutierrez Solana’s depiction of Madrid
Inspired by Goya, Solana portrays Spain with brutality and crude realism. “The black color of life.”