Neurophysiology (Test 2)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
action potential is a _____ event
membrane
transport of materials in the neuron is a _____ event
axonal
microfillament diameter
6-7 nm
microtubules diameter
25 nm
intermediate filaments diameter
8-12 nm
which microtubule associated (MAP) protein transports substances in an anterograde manner?
kinesin
which microtubule associated protein (MAP) transports substances in an retrograde manner?
dynein
what rate is fast transport in a neuron
2-40 cm/day
which parts of the neuron are transported in a retrograde manner?
synaptic vesicles, axoplasmic substances, some viruses and toxins
what rate is slow transport in a neuron
.2-4mm/day
which type of transport is responsible for repairing/regenerating tips of damaged axons?
slow
what are the two properties of neurons
irritability, conductivity
true/false: unmyelinated axons allow for faster conduction velocity
false
what dictates the electrical activity of a membrane
ion fluxes
what are the three major things to be considered in neurophysiology
membrane potential, intracellular transport, ion fluxes
which has a higher ECF concentration, Na or K?
Na
which has a higher ICF concentration, Na or K?
K
on which side of the cell membrane is Cl concentration the highest?
ECF
which membrane potential is the threshold for an action potential
-55mV
what are the two types of graded non-propagating post-synaptic potentials?
excitatory and inhibitory
true/false: IPSP and EPSPs always result in an action potential
false (must be graded to threshold)
what ion rushes in to the cell following a threshold stimulus and where does it rush in to?
Na, initial segment
which ion rushes out of the cell during repolarization?
K
action potentials will continue to fire multiple times across a neuron until what happens
acetylcholine esterase removes ACH from the receptor causing EPSPs
in what period can no impulse be fired along a neuron
absolute refractory period
in which period could an impulse still be fired if the stimulation was great enough?
relative refractory period
about how fast is an action potential
3 milliseconds
about which charge is the overshoot part of the action potential
40 mV
definition of internal and external mesaxon
where the myelin sheath starts and stops wrapping around
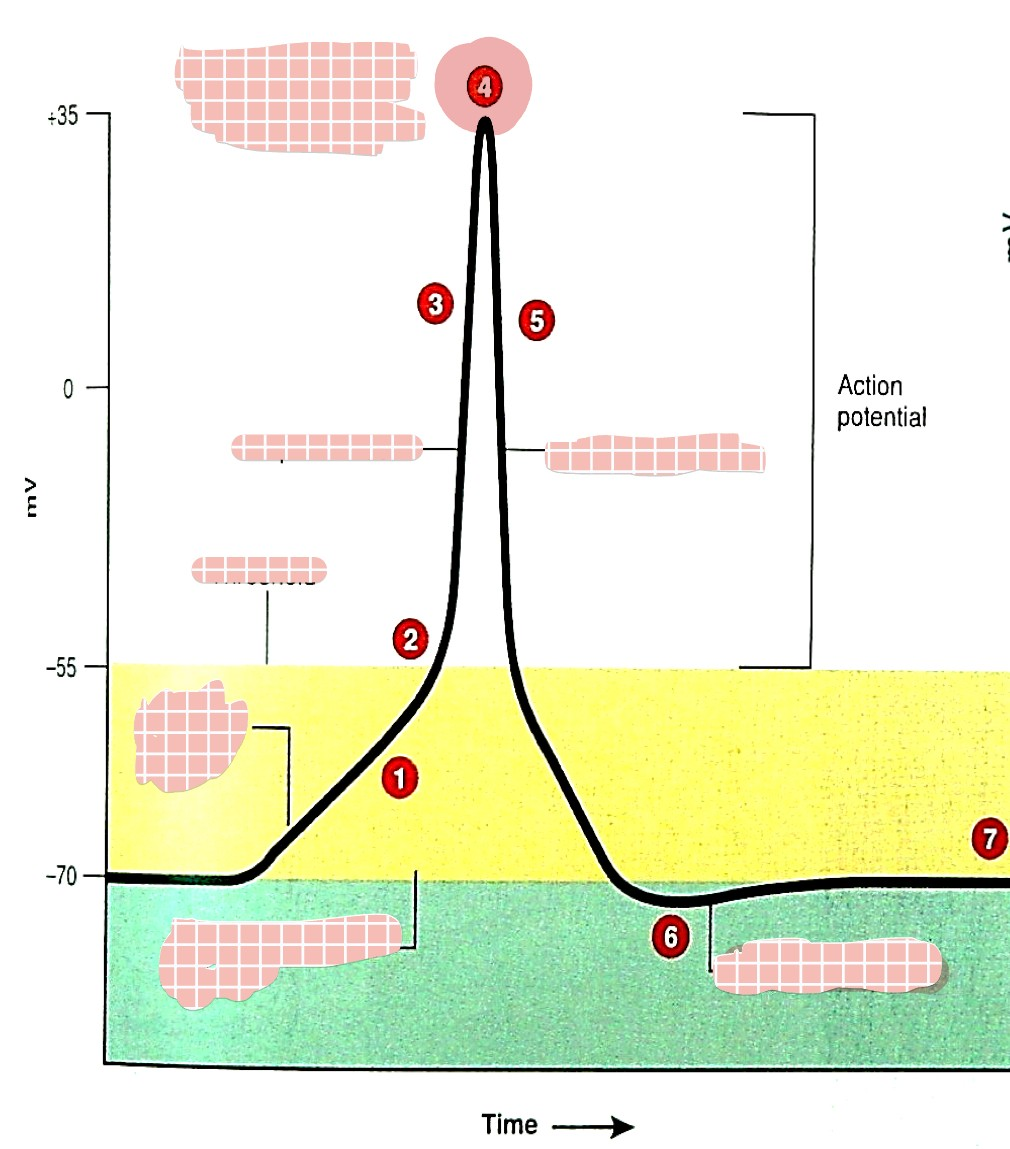
what is 1
generator (graded) potential
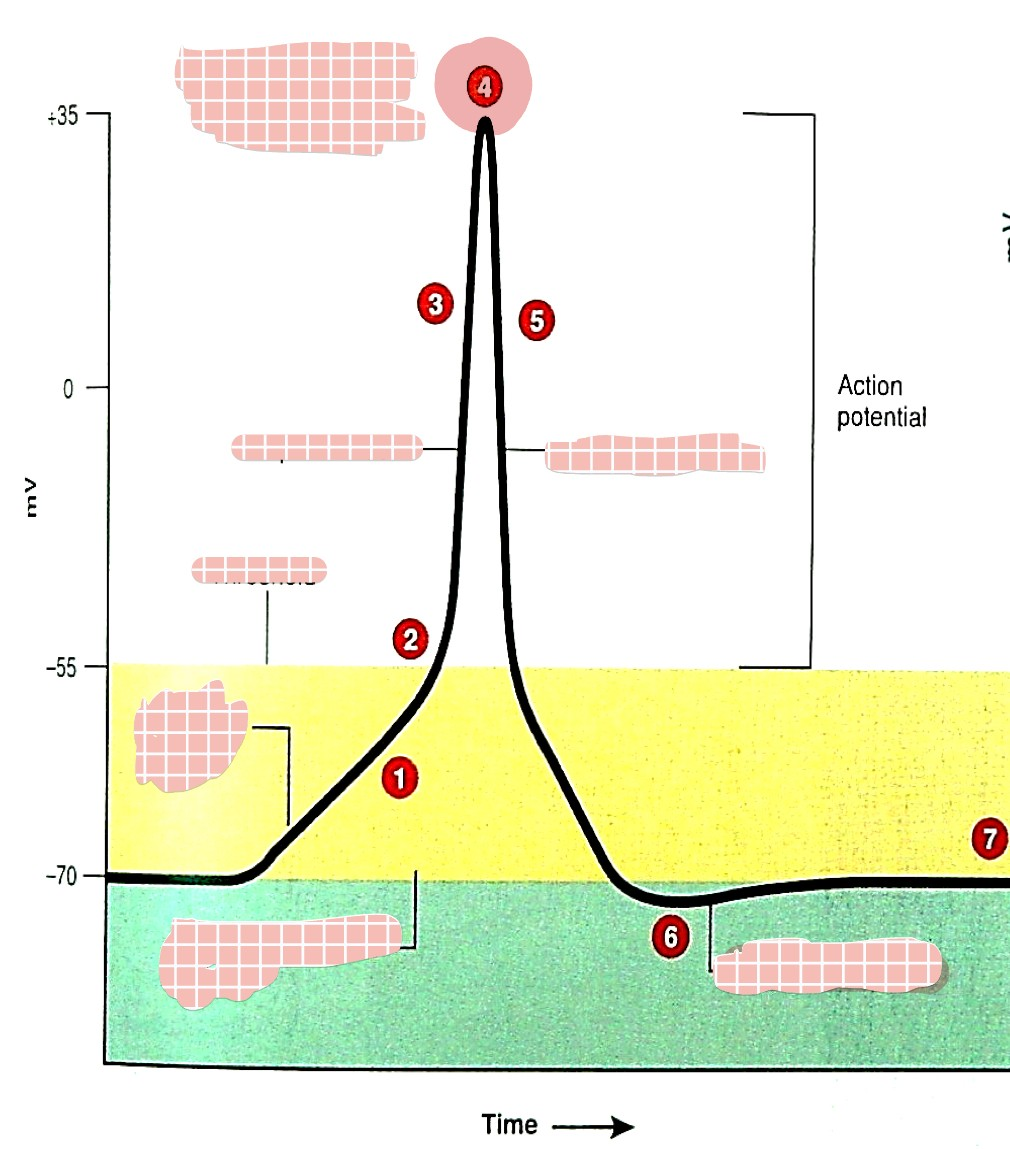
what is 2
threshold
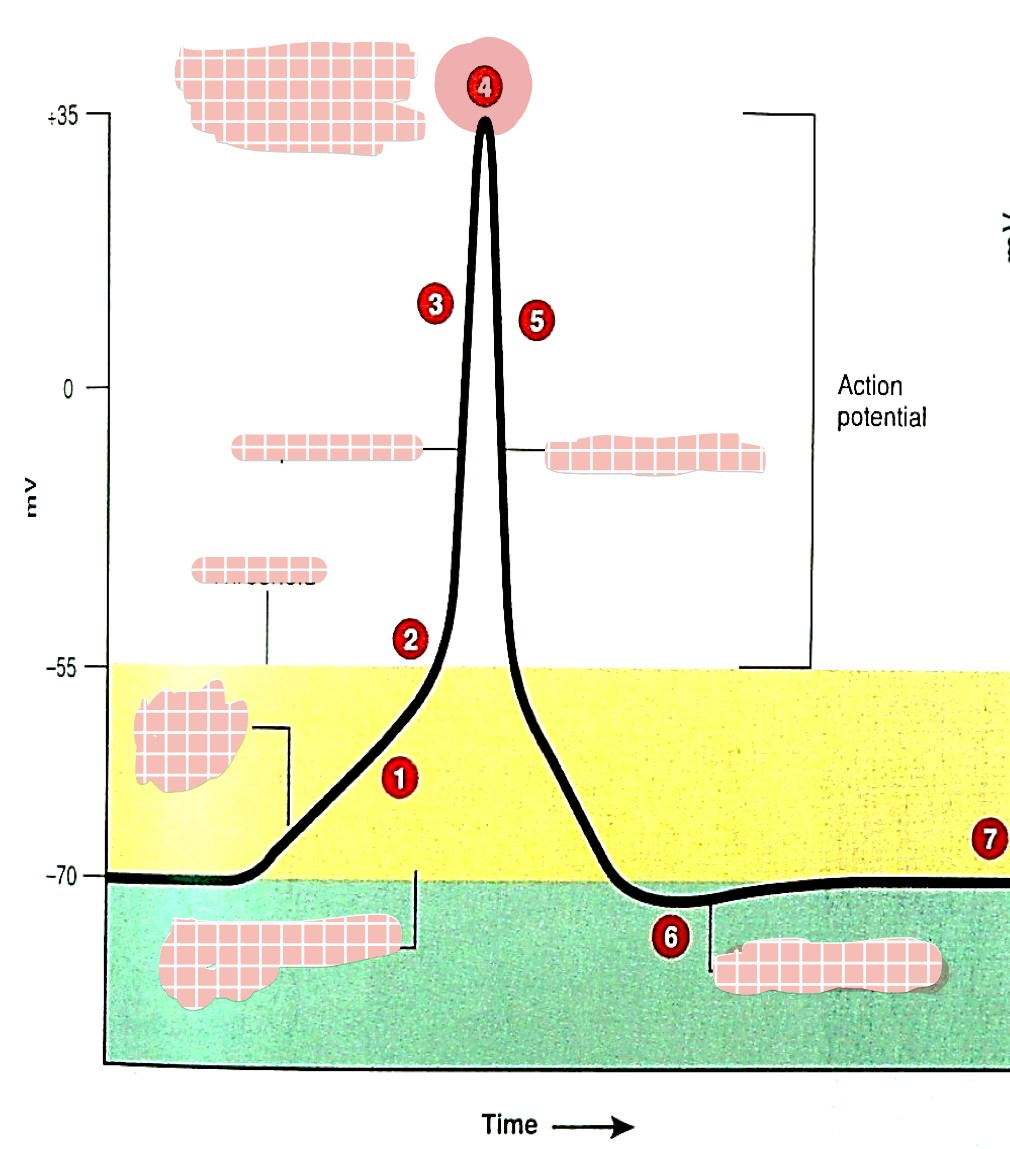
what is 3
depolarization
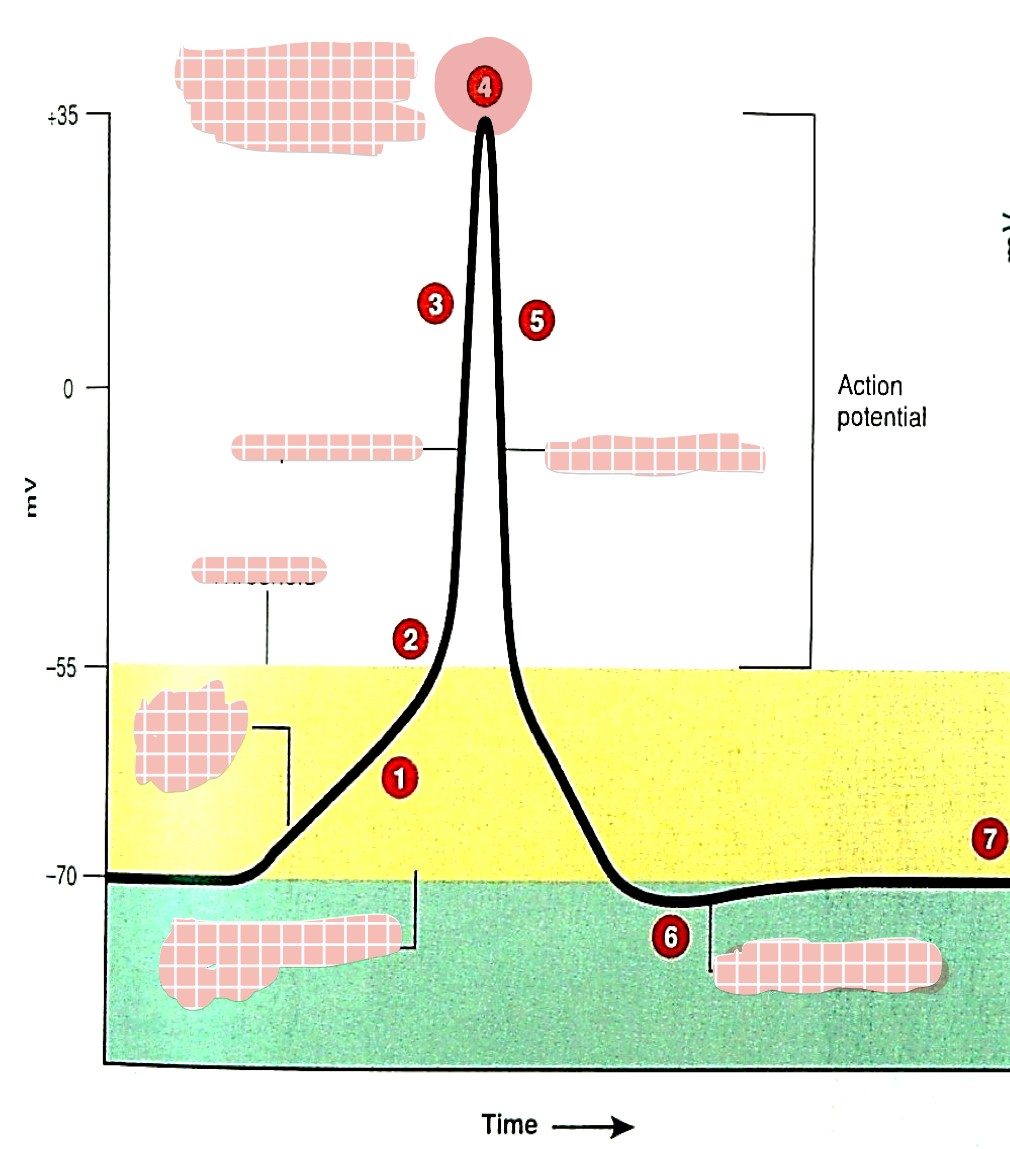
what is 4
overshoot
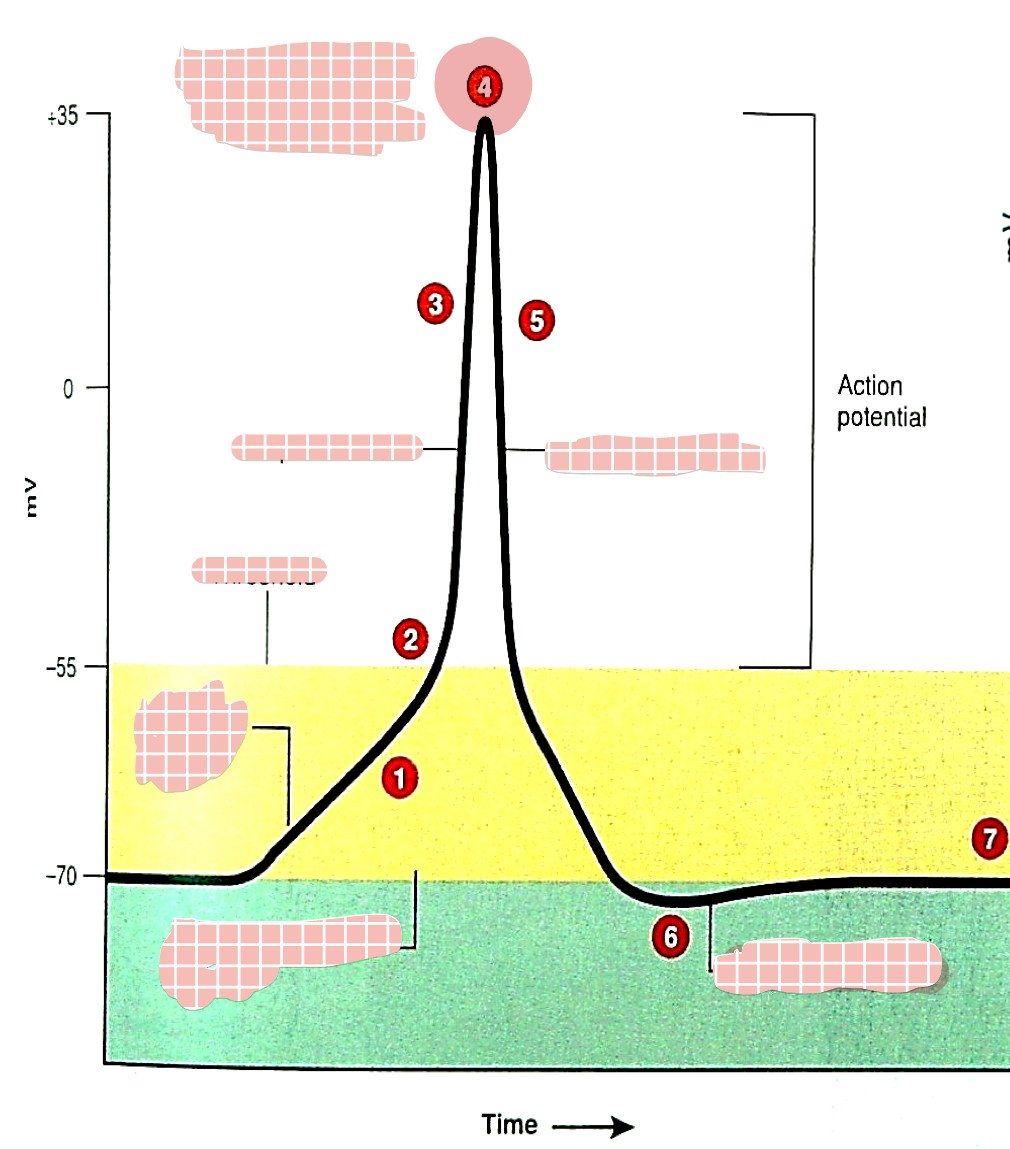
what is 5
repolarization
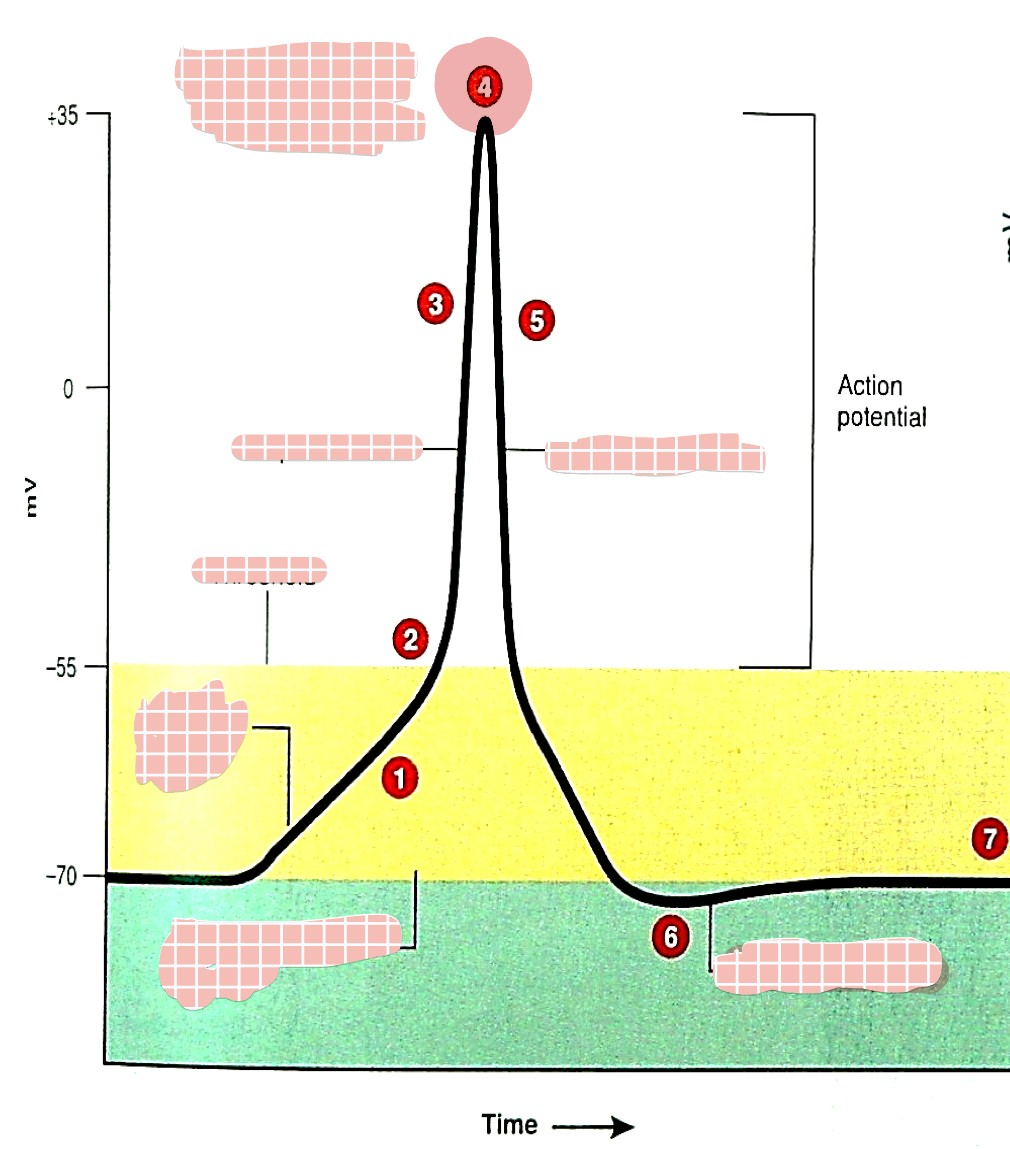
what is 6
hyperpolarization
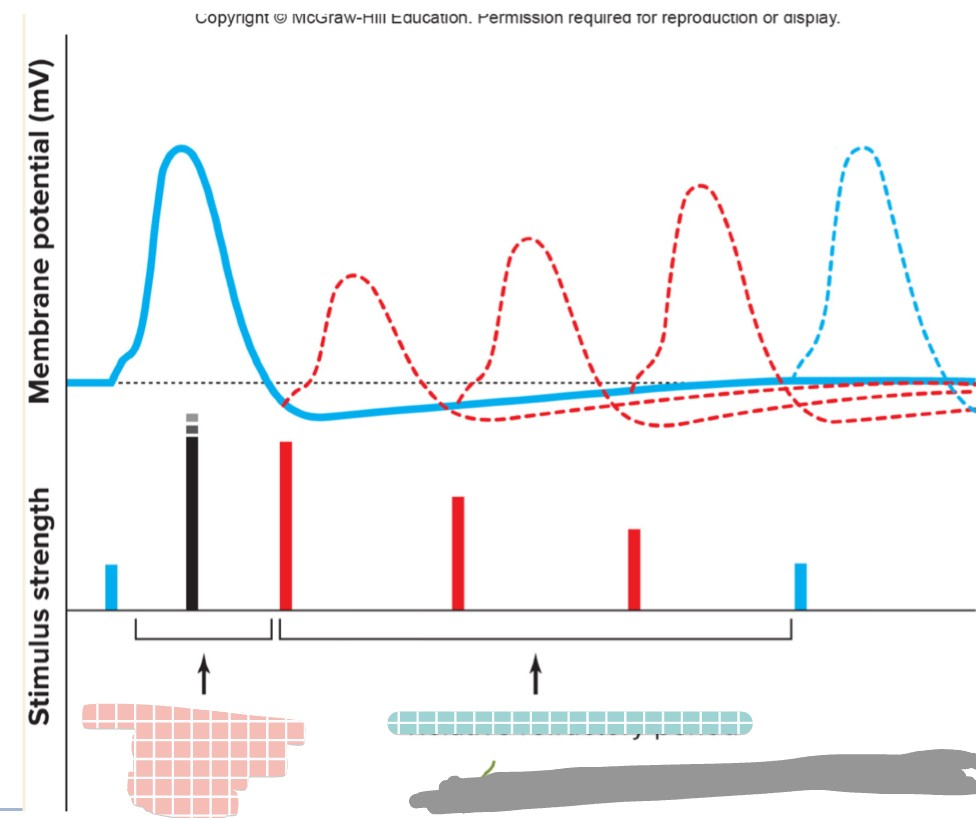
which one is the absolute refractory period (pink/blue)
pink
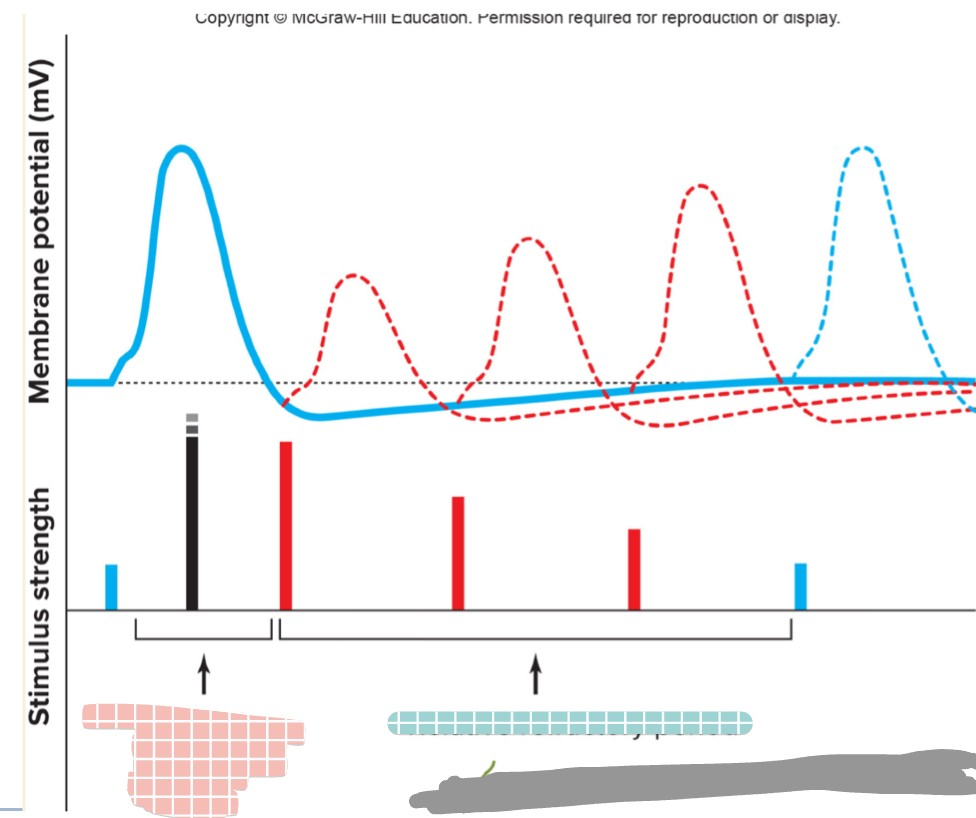
which one is the relative refractory period (pink/blue)
blue