Module 4b - Stress I
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the 3 ways to Conceptualize Stress?
Stressor = the stressful stimulus
Strain = the bodies response
Transaction = the process
What is Stress?
The circumstance in which transactions lead a person to perceive a discrepancy between the physical or psychological demands of a situation and the resources of their biological psychological or social systems
Cognitive Appraisal Model
Primary Appraisal
Secondary Appraisal
Cognitive Appraisal
Mental process by which people assess two factors
Primary Appraisal
Whether the demand threatens them (psychologically or physically)
What is at stake
Secondary Appraisal
Whether they have the coping resources to meet the demand
What can be done?
Judgments of Primary Appraisal
Irrelevant - stressor unlikely to impact you (being ill in the past has not hurt you)
Benign-positive - stressor might work to your advantage (being ill can let you skip a test)
Stressful - stressor might harm you (being ill could lead to death)
Primary Appraisal - under stressful categories
Stressful:
Harm-loss: damage that has already been done
Threat: expectation of future harm
Challenge: opportunity for growth, mastery, profit
Secondary Appraisal
What can be done?
Comparing primary appraisal to the resources we have to determine if we can cope with the stressor
Especially if we appraise something as stressful
Draw out Nervous system
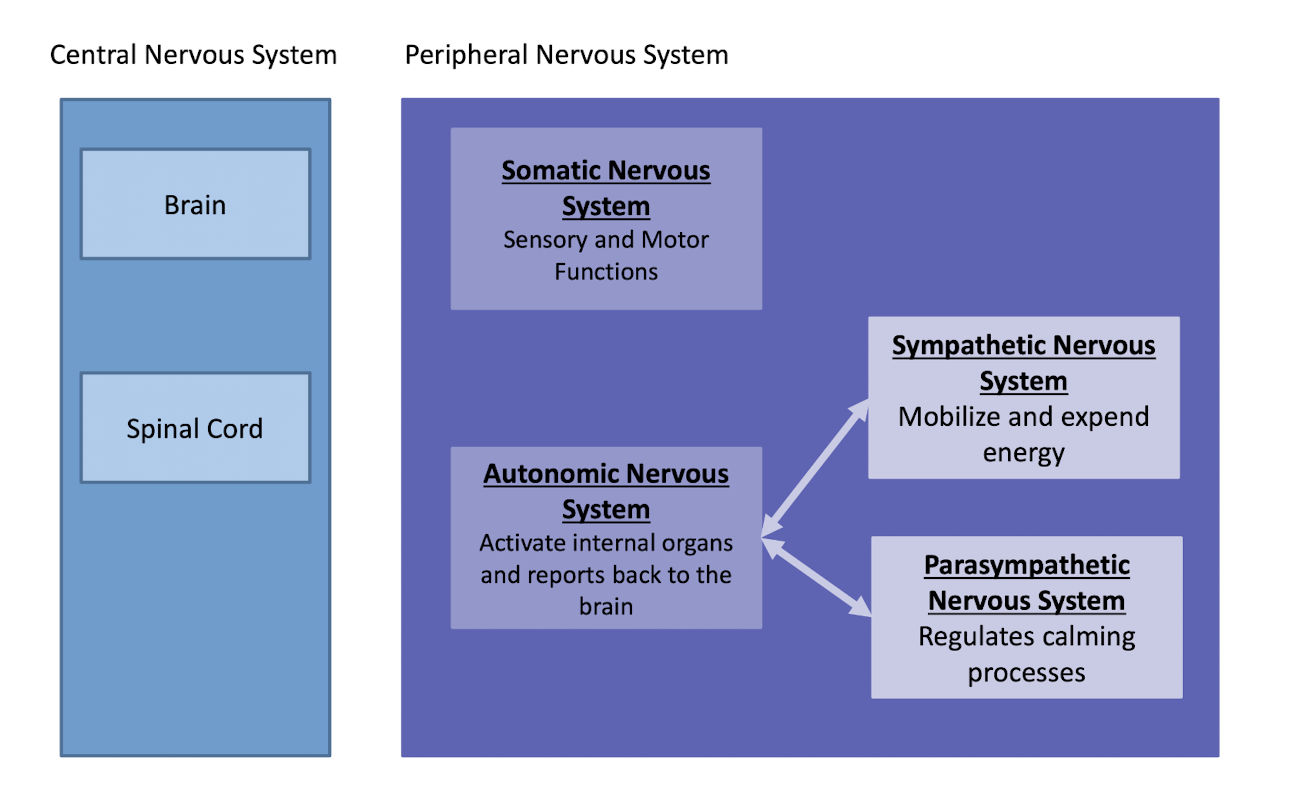
Fight or Flight
Fight: aggressive response to stress
Flight: withdrawal
What happens to you nervous system when in fight or flight?
Sympathetic NS activations (organs and stimulated)
Endocrine system and adrenal glands activate
Adrenaline (epinephrine) secreted
Physiological changes happen to prepare body for stress
Fight or Flight today
Fight: aggressive response to stress
Flight: social withdrawal
General Adaption Syndrome
Sequence of physiological reactions to stress
Response is identical regardless of stressor
What are the three phases of General Adaption Syndrome
Alarm
Resistance
Exhaustion
Alarm Phase
Mobilized bodies resources to meet the stressor
Similar to fight or flight
What does a Fast Acting Alarm phase look like?
Sympathetic activation, epinephrine released into blood stream
What does slow acting Alarm phase look like?
Hypothalamus-pituatary-adrenal (HPA) axis stimulates response that lead to the release of cortisol to further prepare body for mobilization
Resistance
Effort to cope/adapt with a strong stressor that has continued
However, continued physiological arousal might lead to inability to cope with new stressors
Fasting acting Resistance
Physiological processes diminish
Slower acting Resistance
HPA activation predominates
Exhaustion
Depleted physiological resources
Caused by severe long-term repeated stress
Weaken immune system
If continues, disease and internal damage likely
Allostatic Load
The effect of the body adapting repeatedly to stressors that accumulate over time
High load = poor health
Cumulative stress > degree of activation
What are the four factors impacting physiological stress?
Exposure
Reactivity
Recovery
Restoration
Do all stressors create the same physiological reactivity
Yes - general adaptation syndrome is the same regardless of stressor
What are the psychosocial factors related to stress?
Cognitions
Marginalization
Emotions
Cognition and stress
Thoughts can prolong stress response
Stress can interfere with memory
Emotions and Stress
Emotions tend to accompany stress
Used to evaluate their stress
Fear is a common emotional reaction to a stressor
Fear
Psychological discomfort and physical arousal during threat
Phobias
Anxieties
Marginalized populations and stress
Generally report increased stressors
Intergenerational Trauma
Trauma that is transferred from the first generation of trauma survivors to the second and further generations of offspring of the survivors