Day 8: Case Study - and mechanisms
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are coleoptiles
the first part of the shoot to emerge in monocot seedlings
What was the case study example
coleoptile bending
Who investigate the location of light perception in coleoptiles
Charles Darwin and his son Francis
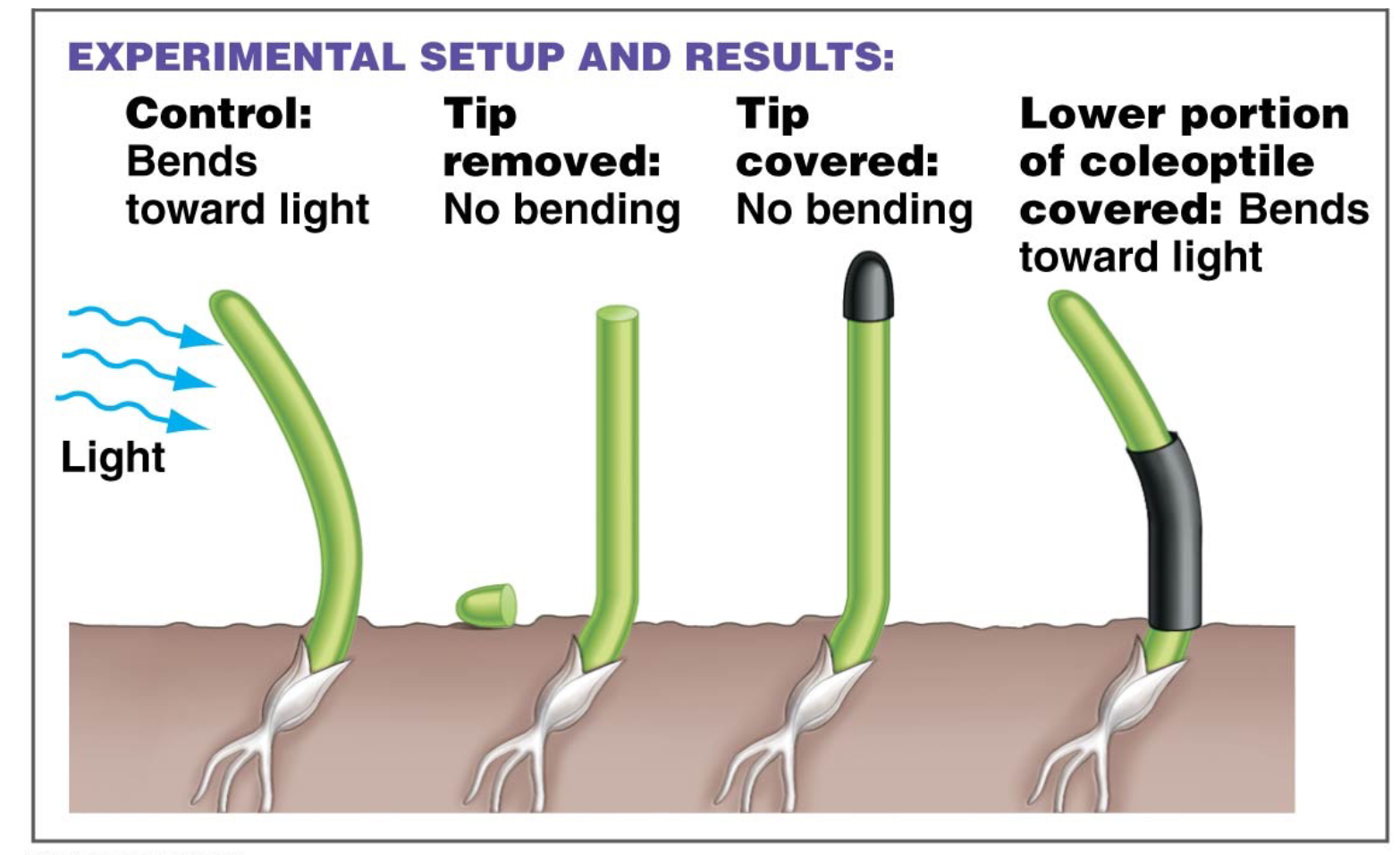
Question of perception of light in coleoptiles
where is light sensed by coleoptiles to allow phototropism
Conclusion of perception of light in coleoptiles
light is sensed by coleoptile tips only
Peter Boysen-Jensen
investigated possible pathways for messages
What possible pathways for messages did Peter Boysen-Jensen investigate
water-soluble (hydrophilic) chemical
lipid-soluble (lipophilic) chemical
electrical signal
How did Peter Boysen-Jensen test message pathways
control - block all possible message types
hydrophilic chemical - used permeable agar
lipophilic chemical - used butter
electrical signal - used foil
Peter Boysen-Jensen’s conclusion on chemical pathways
a water-soluble chemical carries the message from the tip to the growing cell
Arpad Paal
hypothesized differential distribution of messenger
Conclusion of Arpad Paal on differential growth
light causes the accumulation of the chemical on the shaded side of the coleoptile
What does the name auxin mean
to grow
How does auxin affect cells elongation
it influences growth in shoots and roots - but in opposite ways
differential accumulation controls direction of growth
Frits Went
looked at the effect of messenger concentration
How is degree of response controlled
auxin diffuses into agar block
more time or more tips on agar = greater chemical concentration
agar block placed on one side of coleoptile
angle of bending increased with greater concentration of messenger
Conclusion of how degree of response controlled
concentration of messenger affects strength of response
How does auxin move in shoots and type of transport
moves down the shoot from the tip, polar transport
Effect of increased auxin in shoots
increased auxin causes increased cell elongation in shoots
Does auxin create greater growth on sunny or shady side
shady side
How does auxin move and type of transport
auxin moves from the sunny side to the shady side, lateral transport
Result of auxin moving from sunny side to shady side
differential concentration
Current hypothesis for cell elongation
acid-growth pathway
How do roots perceive gravity
by using amyloplasts known as statoliths
What doe statoliths control
the distribution of auxin
How do statoliths create unequal distribution of auxin
by pressing the “sides” of cells
In roots lower auxin leads to
more cell elongation
Does lower of higher auxin levers create more cell elongation
lower levels
What are the two possible hypotheses to explain why more auxin is on the dark side
shoot tips make more auxin on the dark side than on the light side
auxin is made equally by all cells, but transported from the light side to the dark side
Conclusion for why more auxin on dark side
auxin is made at equal rates throughout the tip but transported to shaded side
Does phototropism occur for all wavelengths(colors)
no
What is light sensed by
PHOT1 and PHOT2
What are PHOT1 and PHOT2
they are membrane-bound receptors called phototropins