12 Acid-Base Equilibria
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
A proton donor
What do H+ ions always form in water?
Hydroxonium ions- H3O+
What are Bronsted-Lowry bases?
Proton acceptors
What do Bronsted-Lowry bases form in water?
A compound with an H+ ion, leaving OH-
What is the difference between strong and weak acids?
Strong acids dissociate almost completely in water and nearly all H+ ions will be released.
Weak acids dissociate slightly in water and only a small number of H+ ions are released.
What is the difference between strong and weak bases?
Strong bases dissociate almost completely in water, releasing many OH- ions.
Weak bases dissociate slightly in water, releasing a small number of OH- ions.
Give examples of strong, monoprotic acids.
HCl, HNO3
Give an example of a strong base.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), (most group ½ hydroxide compounds except magnesium and beryllium)
Give an example of a weak base.
Ammonia
What are conjugate pairs?
Species linked by the transfer of a proton. The species that has lost the proton is the conjugate base and the species that has gained a proton is the conjugate acid.
What happens when an acid is added to water?
A= acid
B= base
The equilibrium is set up: HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻
The equilibrium HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻ is set up. How does A act in the forward and reverse reaction?
In the forward reaction, HA acts as an acid as it donates a proton.
In the reverse reaction, A- acts as a base and accepts a proton.
The equilibrium HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻ is set up. Which is the conjugate pair?
HA and A- as HA is the conjugate acid of A- and A- is the conjugate base of HA.
A base dissolves in water. What equilibrium is set up?
B + H₂O ⇌ OH⁻ + BH⁺
What are the two conjugate pairs in the equilibrium B + H₂O ⇌ OH⁻ + BH⁺?
B is the conjugate base of BH+, in the backward reaction BH+ is the conjugate acid of B
H2O and OH- also form a conjugate pair.
What is the enthalpy change of neutralisation?
The enthalpy change when solutions of an acid and a base react together, under standard conditions, to produce 1 mole of water.
What conditions are needed in a neutralisation reaction to produce a neutral solution?
The concentration of H+ ions from the acid must be equal to the concentration of the OH- ions in the base.
How does the standard enthalpy change of neutralisation change when using weak acids and bases?
It includes enthalpy to do with the reaction between H+ and OH- ions and enthalpy of dissociation because in weak acids and bases, they originally only dissociate slightly but then must constantly dissociate more to replace the H+/OH- ions in solution and maintain equilibrium.
What is the pH scale?
A logarithmic scale that is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration.
Why is [H+] equal to acid concentration in strong monoprotic acids?
They dissociate fully and each mole of acid produces one mole of H+ ions, and therefore the H+ concentration is the same as the acid concentration.
What is the equation involving pH and H+ ion concentration?
pH = -log₁₀[H⁺]
Give an example of strong polyprotic acids.
H₂SO₄, H₃PO₄
Give an example of weak monoprotic acids.
Ethanoic acid- CH₃COOH
Give an example of weak polyprotic acids.
CH₂(COOH)₂
How do you find the pH of a weak acid?
Use the acid dissociation constant- k. This is because as the acids do not dissociate fully in solution, the [H+] concentration is not the same as the acid concentration.
You can assume that (with equilibrium HA⇌H⁺ + A⁻) [HA] at the start = [HA] at equilibrium as only a tiny amount of HA dissociates.
This creates the equation Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
You can assume that all the ions come from the acid, so [H+] = [A-].
Ka= [H+]²/[HA]
Why does the assumption ‘[HA] at the start = [HA] at equilibrium’ only work for weak acids, not strong acids?
In weak acids, only a tiny amount of HA dissociates whereas in strong acids HA dissociates more and so the difference in concentrations at the start and at equilibrium are more significant.
Calculate the pH of 0.02 moldm⁻³ propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH). Ka = 1.30 × 10⁻⁵.
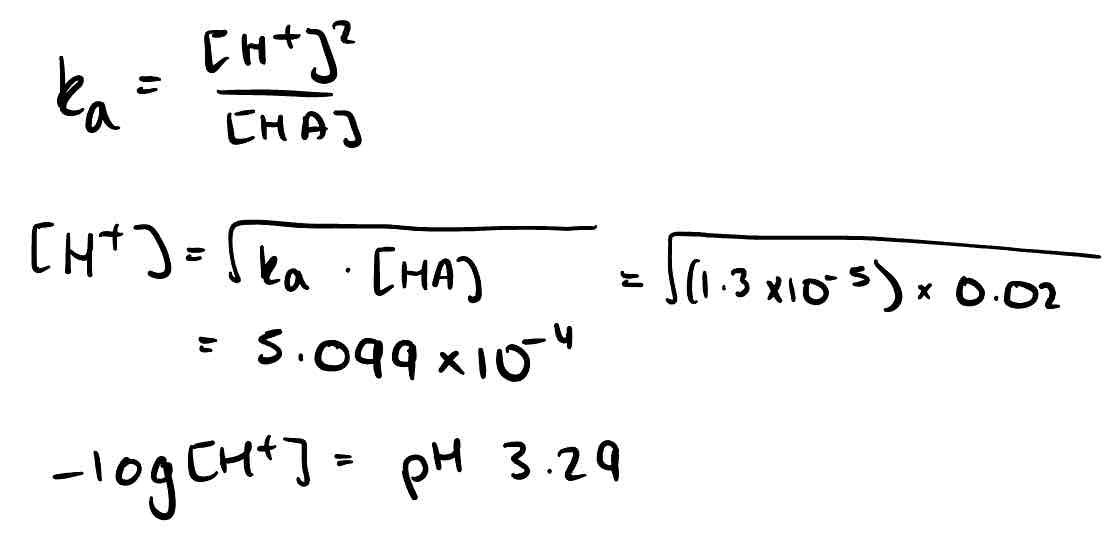
The pH of ethanoic acid solution was 3.02 at 298K. Calculate the concentration. Ka = 1.75 × 10⁻⁵.
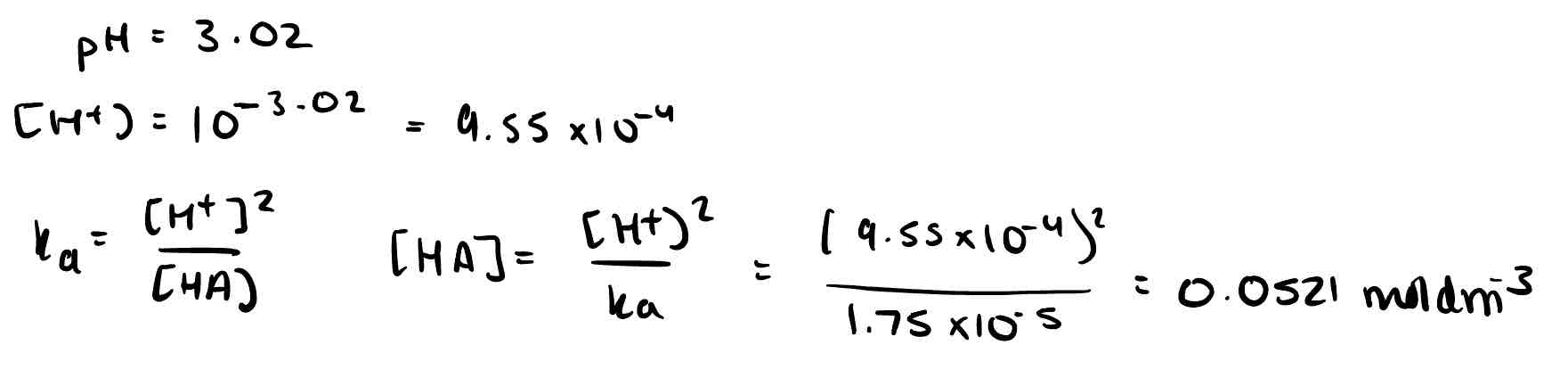
Why, in water, is there always both hydroxonium and hydroxide ions?
Water can act as both an acid and a base
What is kw?
The ionic product of water. Water only dissociates a little, so the equilibrium is over to the left and there are so few ions that the concentration of water is considered constant.
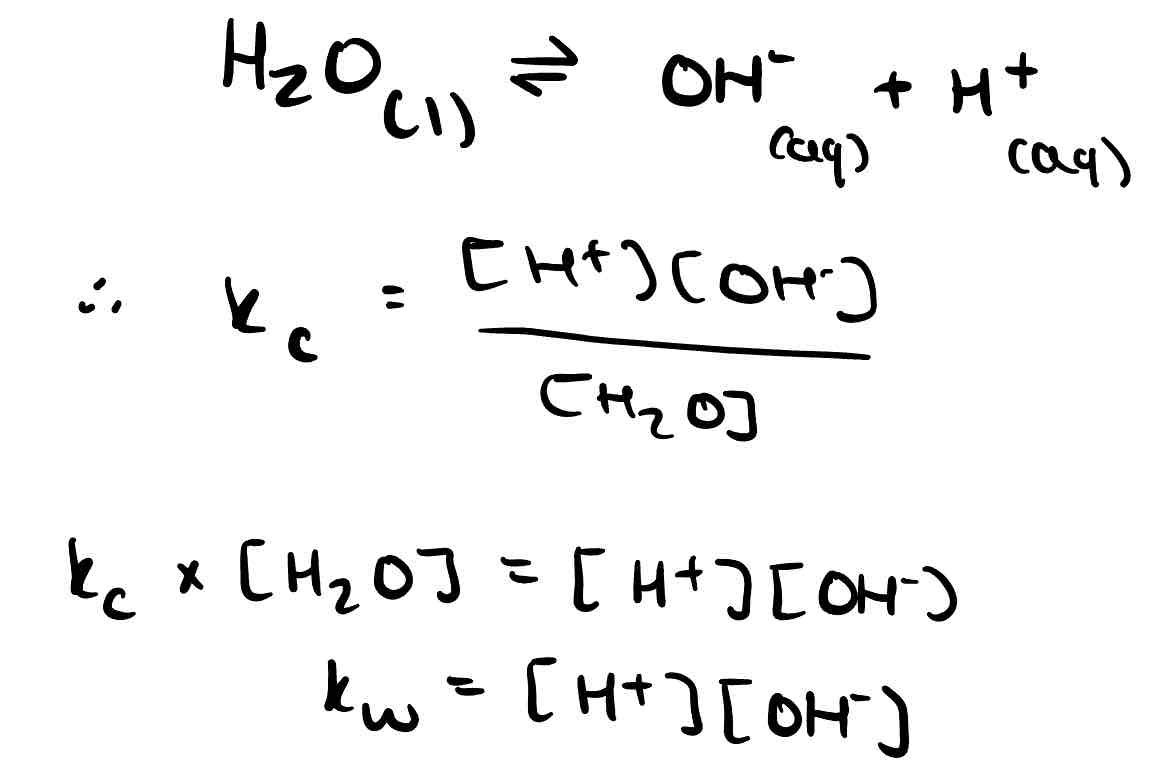
How can Kw be used to find the pH of a strong base?
Kw = [H⁺][OH⁻] ; with Kw and [OH⁻] of a strong base you can find [H⁺] and therefore pH.
Find the pH of 0.1 moldm⁻³ NaOH at 298K. Kw = 1 × 10⁻¹⁴.
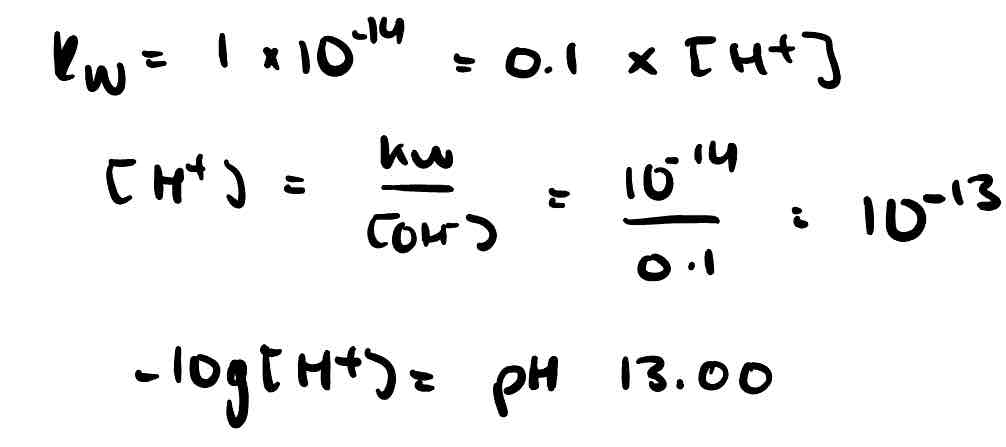
What is pKa?
-log Ka
What is used to measure pH in an experiment?
A pH probe
1.31g of ethanoic acid are dissolved in 250cm³ of water. The solution has a pH of 2.84; calculate the acid dissociation constant.
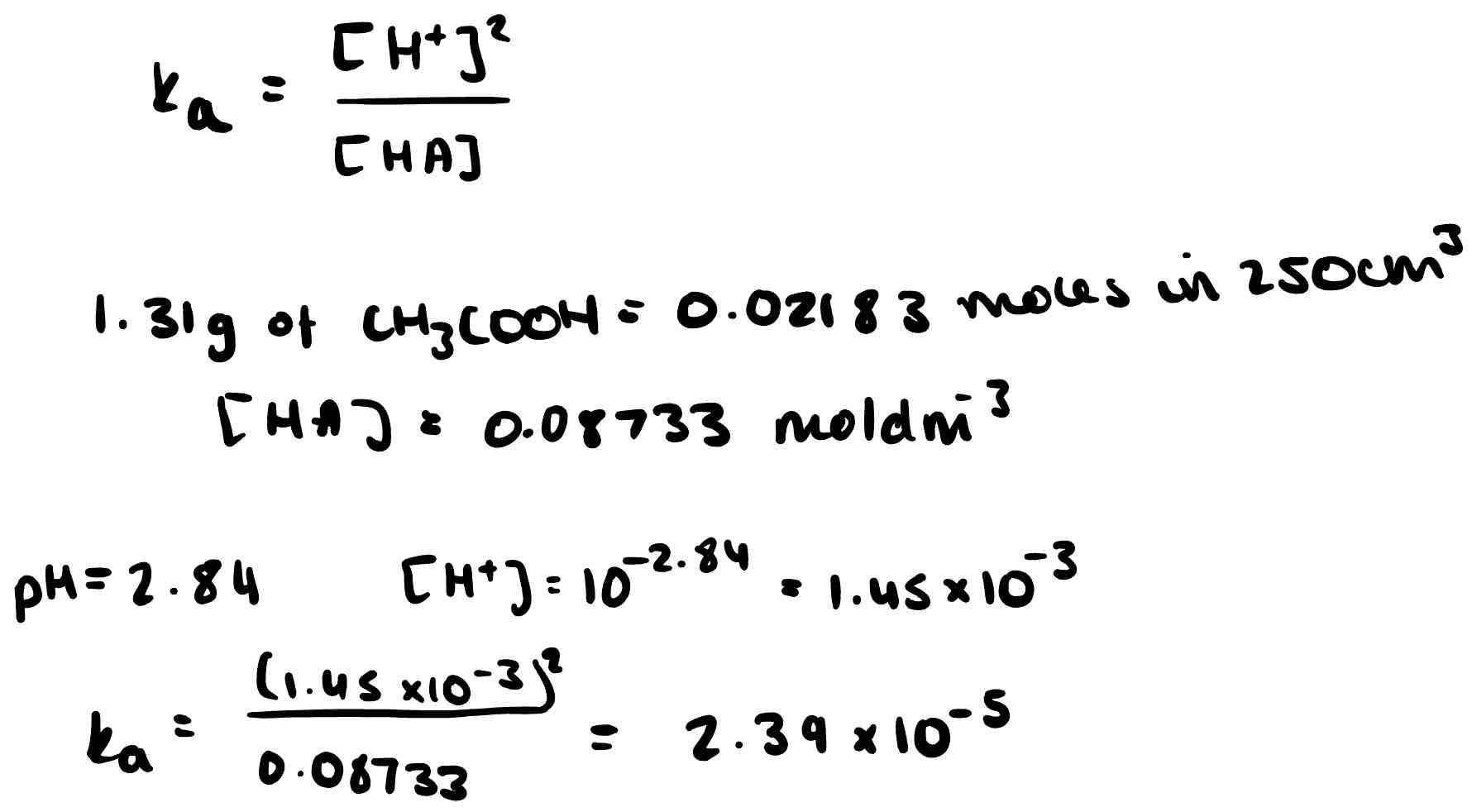
How much does diluting a weak acid by a factor of 10 increase the pH by?
0.5
Draw the titration curve of a strong acid and strong base.
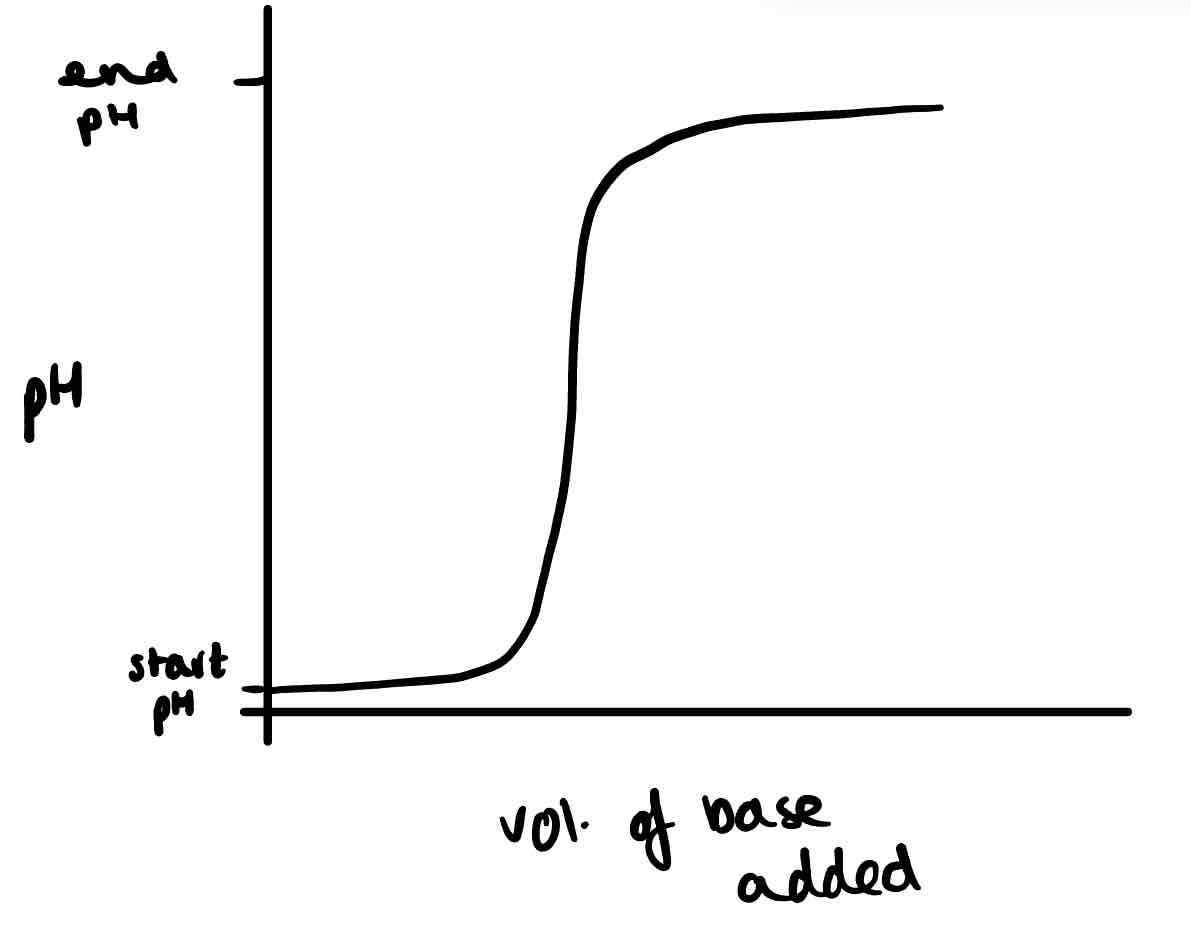
Draw the titration curve of a strong acid and weak base
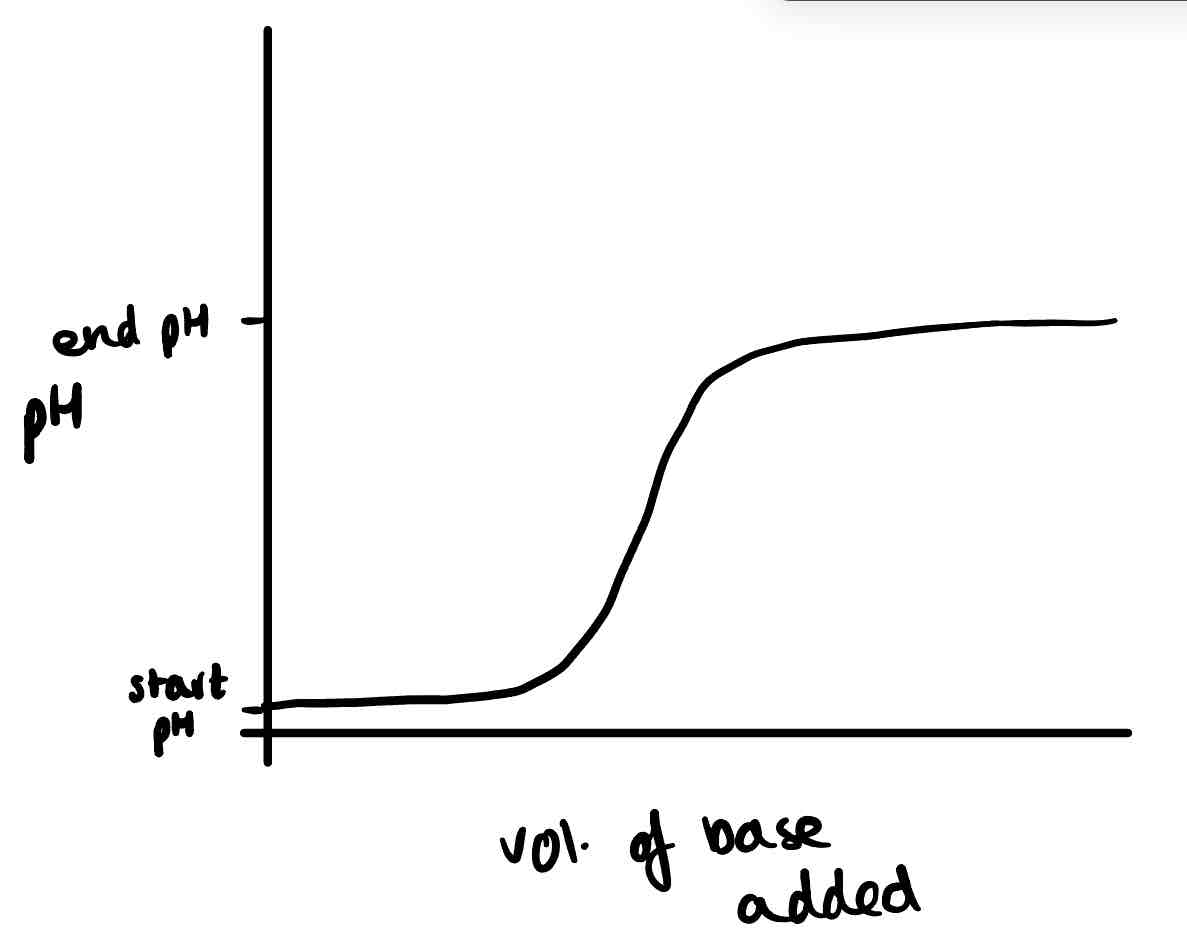
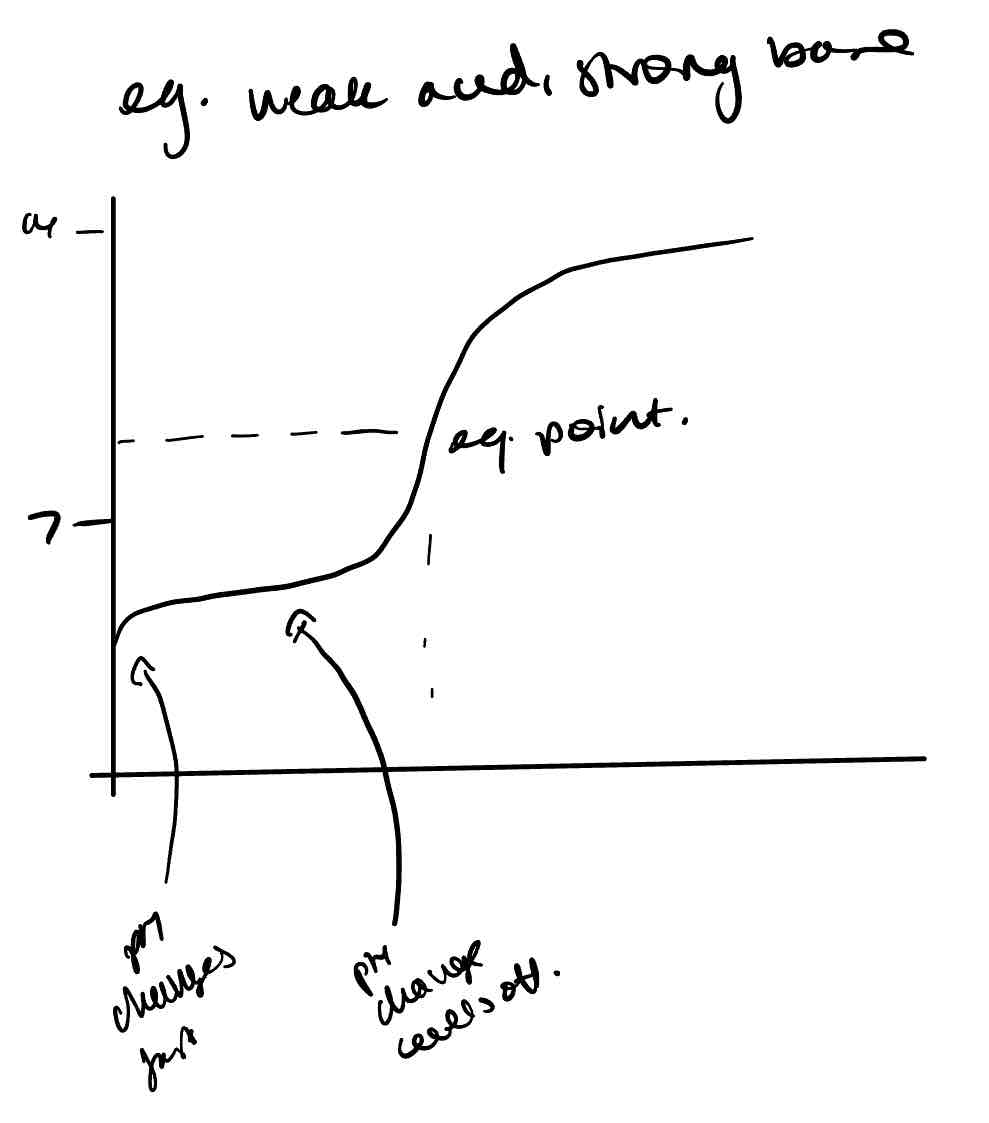
Draw the titration curve of a weak acid and strong base
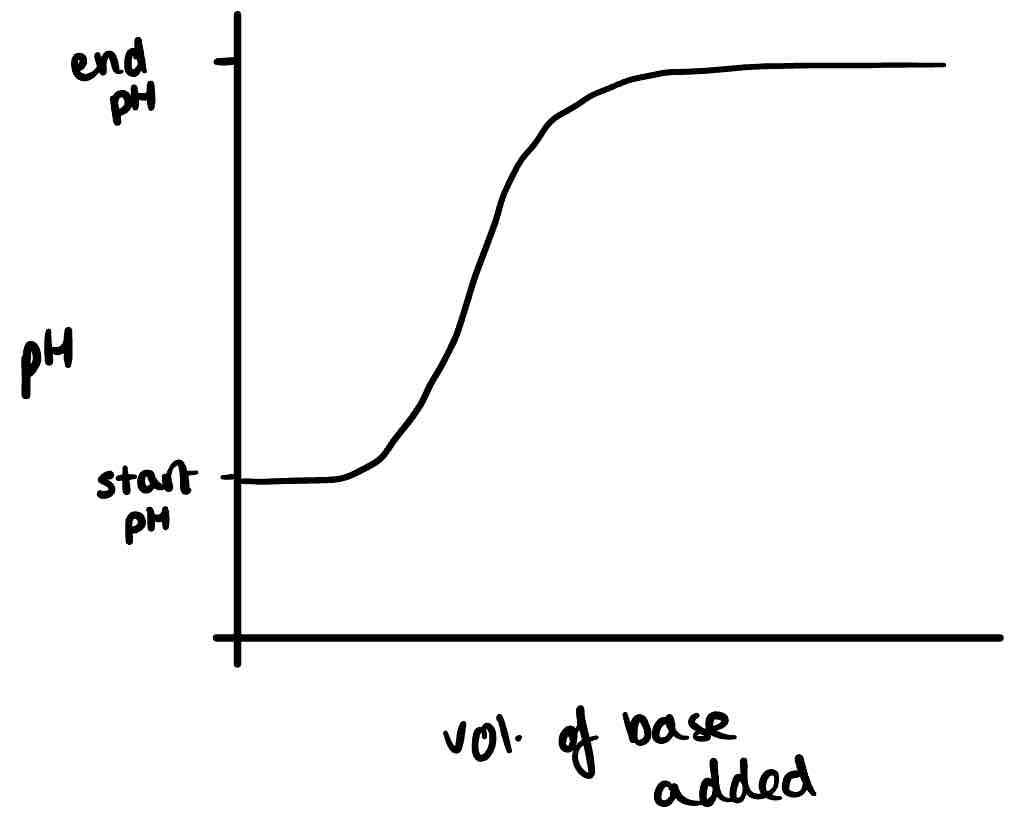
Draw the titration curve of a weak acid and weak base.
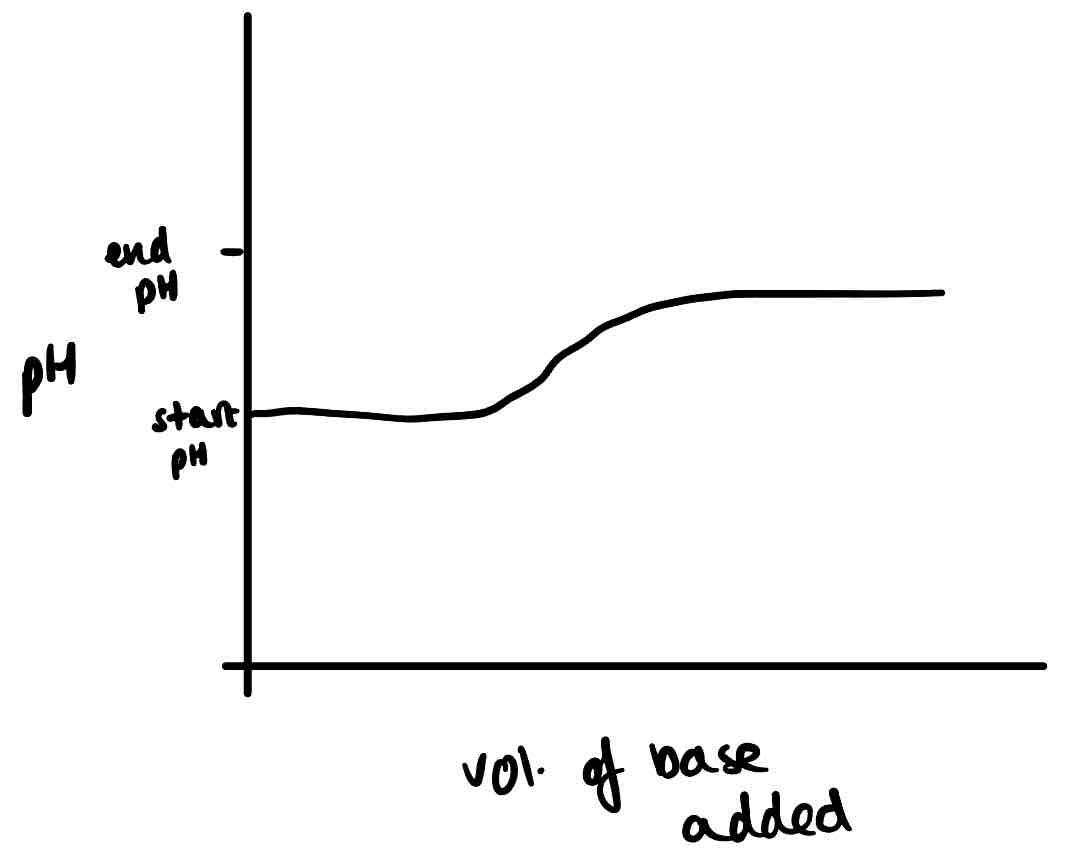
Why do the lines of a titration curve begin straight horizontal?
Addition of small amounts of acid /base have little impact on pH
What is the vertical line on a titration curve?
The equivalence line. The point at the centre of this is the equivalence point or end point. Here, [H⁺] = [OH⁻] and a tiny amount of acid or base causes a sudden, big change in pH.
How can titration curves be used to find pKa of a weak acid?
At the half equivalent point of the titration curve of the weak acid with a strong base, [HA] = [A⁻], so Ka = [H⁺] and pKa = pH.
![<p>At the half equivalent point of the titration curve of the weak acid with a strong base, [HA] = [A⁻], so Ka = [H⁺] and pKa = pH.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/132468cf-9d82-4352-9017-e617b7f22559.jpg)
What is a buffer?
A solution that minimises changes in pH when small amounts of acid/base are added.
What are acidic buffers?
Buffers containing a weak acid and its conjugate base. They have a pH of less than 7. The following equilibrium is set up and the conjugate pair controls the pH of solution: the conjugate base reacts with any H⁺ and the conjugate acid releases H⁺ if there is an excess of base.
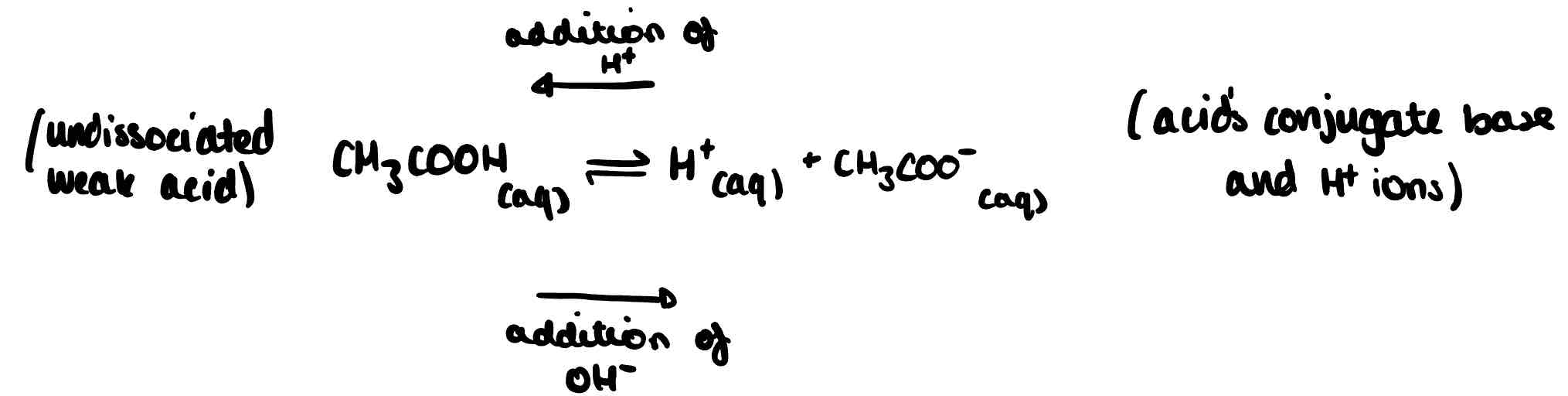
How can acidic buffers be made?
Mixing a weak acid with the salt of its conjugate base.
the salt dissociates into its ions and the acid only slightly dissociates.
Eg. Ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate.
or
Mixing an excess of weak acid with a strong base.
all the base reacts with the acid.
The weak acid is in excess, so there is some leftover to slightly dissociate.
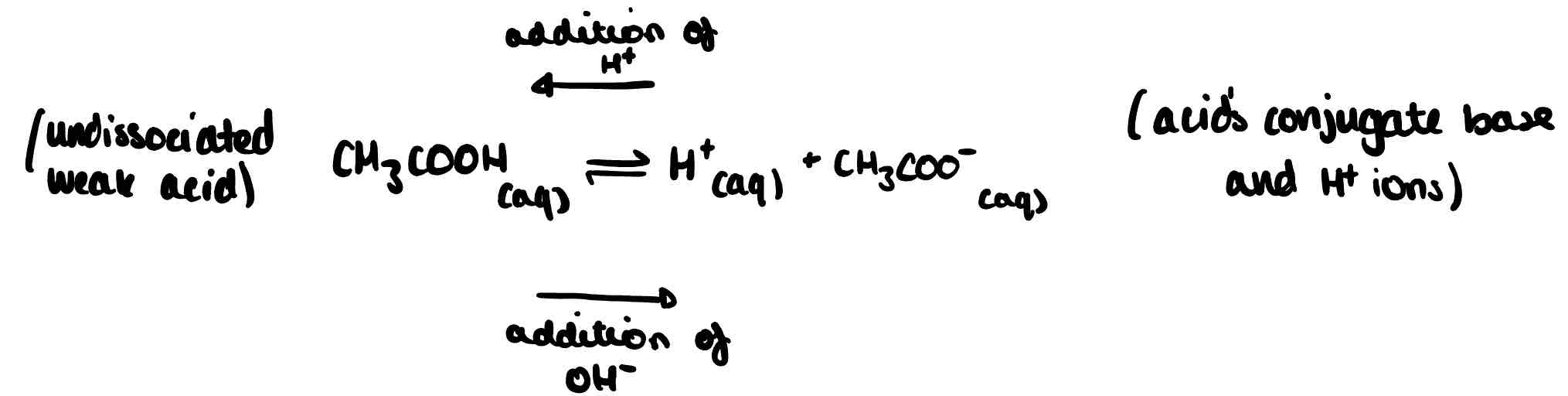
Describe what would happen if a small amount of acid was added to the following buffer equilibrium.
H⁺ concentration increases. Extra H⁺ reacts with CH₃COO⁻ to form CH₃COOH. Equilibrium shifts to the left, reducing H⁺ concentration to close to its original value.
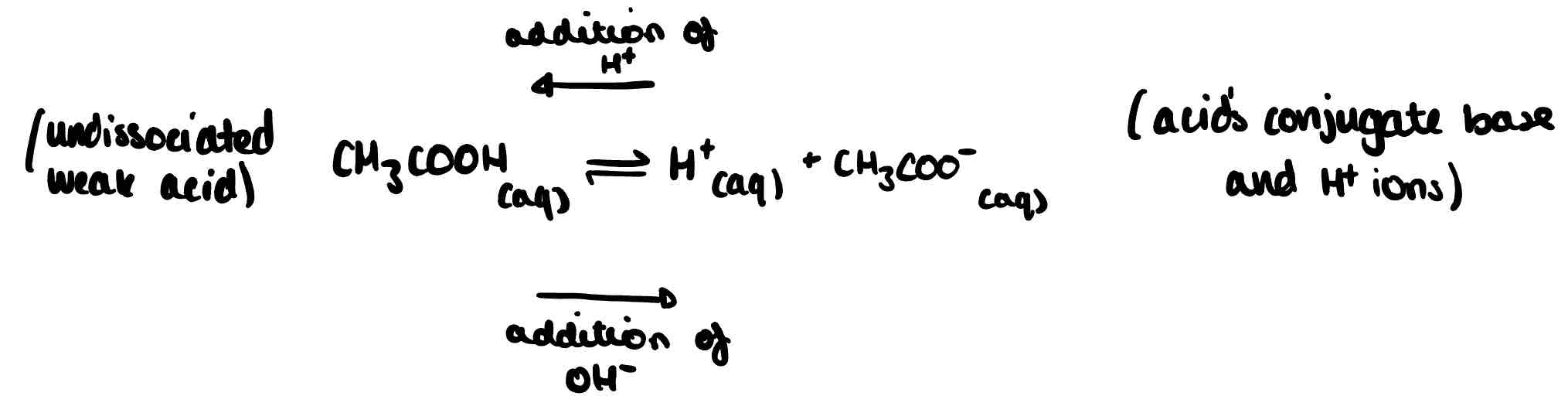
Describe what would happen to the following equilibrium concentration if a small amount of base is added.
OH⁻ concentration increases. These react with the H⁺ ions to form H₂O, removing the H⁺ from equilibrium. More CH₃COOH dissociates to replace the H⁺ ions as equilibrium shifts to the right and the H⁺ concentration increases until it is close to its original value.
How are alkaline buffers made?
From a weak base and one of its salts.
Why does the curve of the titration curves of weak acids and strong bases and strong acids and weak bases level off?
The formation of buffer solutions as the reaction proceeds.
What assumptions must be made to calculate the pH of buffer solutions?
the salt of the conjugate base is fully dissociated, so concentration of A⁻ is the same as the original concentration of salt.
HA only slightly dissociates, so equilibrium concentration is the same as initial concentration.
A buffer solution contains 0.4 moldm methanoic acid and 0.6 mol sodium methanoate. Ka = 1.8 × 10⁻⁴. What is the pH?
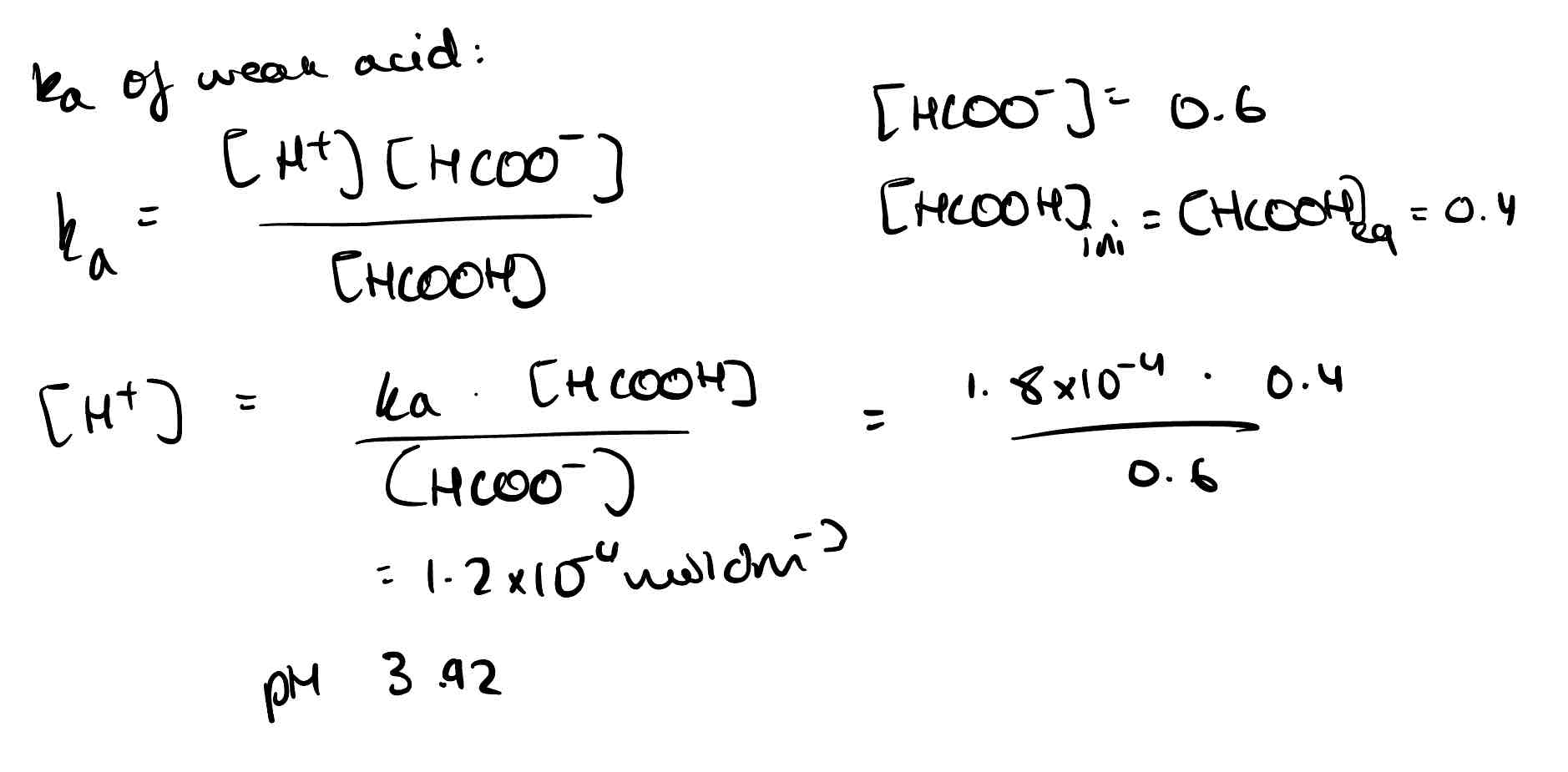
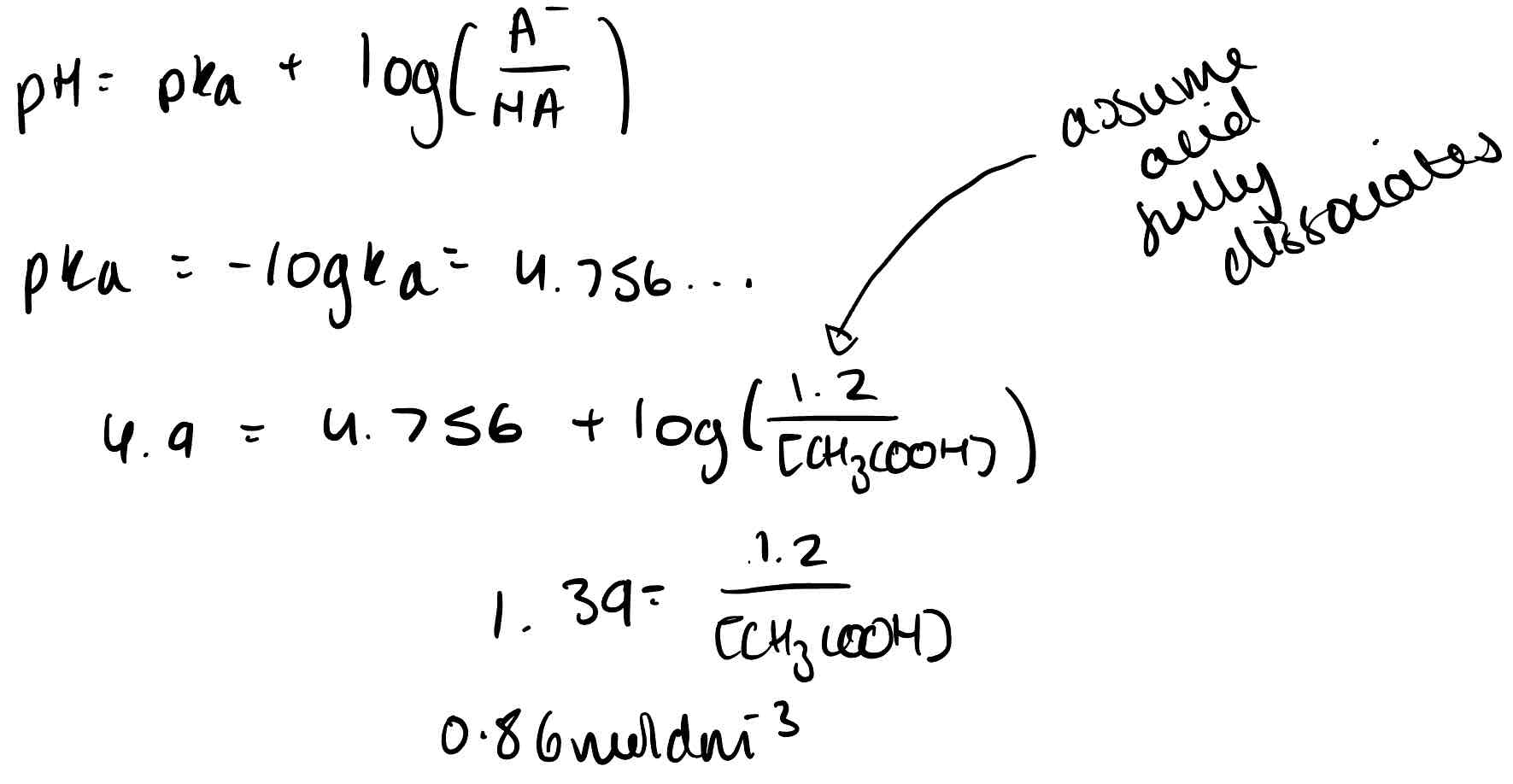
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log (A⁻/HA)
A buffer contains ethanoic acid and an ethanoic acid salt. 1.2 moldm³ salt is used. The buffer has a pH of 4.9 and Ka of the acid is 1.75 × 10⁻⁵. What concentration of ethanoic acid is needed? Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.