Chemistry Spring Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/58
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
Avogadro's Number
6.02 x 10^23
2
New cards
Mole
The standard SI base unit for an amount of a substance.
3
New cards
Physical change
When the chemical composition is not changed.
4
New cards
Chemical Change
Energy is transformed from one form to another in what type of change?
5
New cards
Gay-Lussac's Law
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature if the volume and moles of gas are kept constant.
6
New cards
P₁/T₁\=P₂/T₂
What is Gay-Lussac's equation?
7
New cards
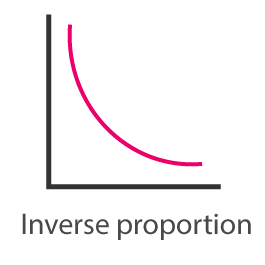
Inverse relationship
The variables change in opposite directions: one increases while the other decreases, and vice versa.
8
New cards
Compound
Composed of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds.
9
New cards
Percent Composition
The percent by mass of each element in a compound. Can be used to help identify an unknown compound.
10
New cards
Stoichiometry
The study of the quantitative relationships that can be derived from chemical formulas and equations.
11
New cards
Excess reactant
The reactant that is not completely used up in a chemical reaction.
12
New cards
Ideal Gas
A gas that obeys the gas laws under all conditions of temperature and pressure.
13
New cards
Element
Pure substance that only contains one kind of atom.Ex: Copper (Cu) and Bromine (Br)
14
New cards
Absolute Zero
Theoretically the lowest attainable temperature.
15
New cards
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance.
16
New cards
Boyle's Law
States that the volume of a sample of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure if the temperature and the amount of gas are kept constant
17
New cards
P₁V₁ \= P₂V₂
What is Boyle's Law equation?
18
New cards
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
At a constant temperature and volume, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture.
19
New cards
P(total)\= P₁+P₂+P₃...
What is Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure equation?
20
New cards
Gas Stoichiometry
1 mole of a gas is equal to 22.4 L
21
New cards
Kelvin Scale
K \= *C + 273
22
New cards
Empirical Formula
The formula which gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
23
New cards
Mole ratio
The ratio obtained from the balanced equation that indicates the proportions of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
24
New cards
Percent yield
Actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
25
New cards
Molar Volume
22\.4 Liters = 1.0 moles
26
New cards
Charles's Law
The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature if the pressure and the amount of gas are kept constant.
27
New cards
V₁/T₁\=V₂/T₂
What is Charles's Law equation?
28
New cards
Avogadro's law
Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules
29
New cards
V₁/n₁ \= V₂/n₂
What is Avogadro's Law equation?
30
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
Combines Boyle's law, Charles’s Law, Gay-Lussac’s Law, and Avogadro’s Law to show the relationship for the four variables of pressure,volume, temperature, and number of molecules.
31
New cards
PV \= nRT
What is the Ideal Gas Law equation?
32
New cards
Combined Gas Law
combination of Boyle and Charles’s Lawsr
33
New cards
P₁V₁/T₁ \= P₂V₂/T₂
What is the Combined Gas Law equation?
34
New cards
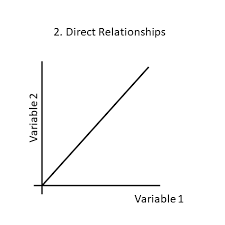
Direct relationship
Both variables increase together or both decrease together.
35
New cards
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined.
36
New cards
Atom
The smallest units of an element that maintain the properties of that element.
37
New cards
Celsius
Of or denoting a scale of temperature on which water freezes at 0° and boils at 100° under standard conditions.
38
New cards
Limiting Reactant
The reactant or reagent that controls the amount of product that can be formed in a chemical reaction.
39
New cards
Real Gas
Deviates from ideal behavior under conditions of high pressure and low temperature because it is no longer a gas.
40
New cards
General Chemistry
Examines the structure of matter and the reaction between matter and energy. It is the basis for the other branches of chemistry.
41
New cards
Astrochemistry
The study of composition and reactions of the chemical elements and molecules found in the stars and in the space and of the interactions between this matter and radiation.
42
New cards
Electrochemistry
Considered to be the study of electron transfer, particularly within an electrolytic solution.
43
New cards
Green Chemistry
Is concerned with processes and products that eliminate or reduce the use or release of hazardous substances.
44
New cards
Nuclear Chemistry
Branch of chemistry associated with nuclear reactions and isotopes.
45
New cards
Physical Chemistry
Applies physics to the study of chemistry. Quantum mechanics and thermodynamics are examples.
46
New cards
Thermochemistry
Involves the study of thermal effects of chemical reactions and the thermal energy exchange between processes.
47
New cards
Agrochemistry
This branch of chemistry may also be called agricultural chemistry. It deals with the application of chemistry for agricultural production
48
New cards
Biochemistry
Branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical reactions that occur inside living organisms.
49
New cards
Environmental Chemistry
The chemistry associated with soil, air, and water and of human impact on natural systems.
50
New cards
Inorganic Chemistry
Is the branch of chemistry that deals with the structure and interactions between inorganic compounds, which are any compounds that aren't based in carbon-hydrogen bonds.
51
New cards
Organic Chemistry
Deals with the chemistry of carbon and living things.
52
New cards
Polymer Chemistry
Examines the structure and properties of macromolecules and polymers and finds new ways to synthesize these molecules.
53
New cards
Theoretical Chemistry
Applies chemistry and physics calculations to explain or make predictions about chemical phenomena.
54
New cards
Analytical Chemistry
Branch of chemistry involved with studying the properties of materials or developing tools to analyze materials.
55
New cards
Chemical Engineering
Involves the practical application of chemistry to solve problems.
56
New cards
Geochemistry
The study of chemical composition and chemical processes associated with the earth and other planets.
57
New cards
Medicinal Chemistry
Chemistry as it applies to pharmacology and medicine.
58
New cards
Photochemistry
Branch of chemistry concerned with interactions between light and matter. Including bioluminescence.
59
New cards
Spectroscopy
Examines the interactions between matter and electromagnetic radiation as a function of wavelength.