Biology - Unit 3: Deuterostomes
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Deuterostomes
embryonic development of the anus before the mouth


Phylum Echinodermata, Class Crinoidea
Feather stars, sea lilies

Phylum Echinodermata, Class Asteroidea
Sea stars
Phylum Echinodermata, Class Ophiuroidea
Basket stars, brittle stars

Phylum Echinodermata, Class Echinoidea
Sea urchins, sand dollars

Phylum Echinodermata, Class Holothuroidea
Sea cucumbers
Endoskeleton
Bony and/or cartilaginous structures within the body that provide support
Water vascular system
A system of fluid-filled tubes and chambers that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton
Tube feet
One of the many small, mobile, fluid-filled extensions of the water vascular system
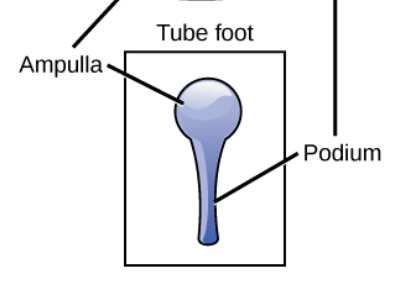
Ampulla
balloon-like part of the tube foot that is inside the body
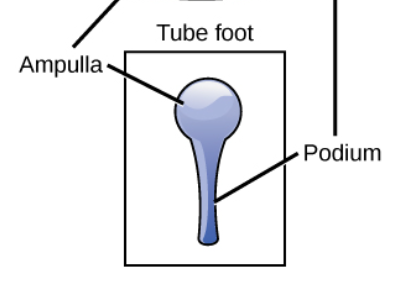
Podium
tube-like part of the tube foot that is outside of the body
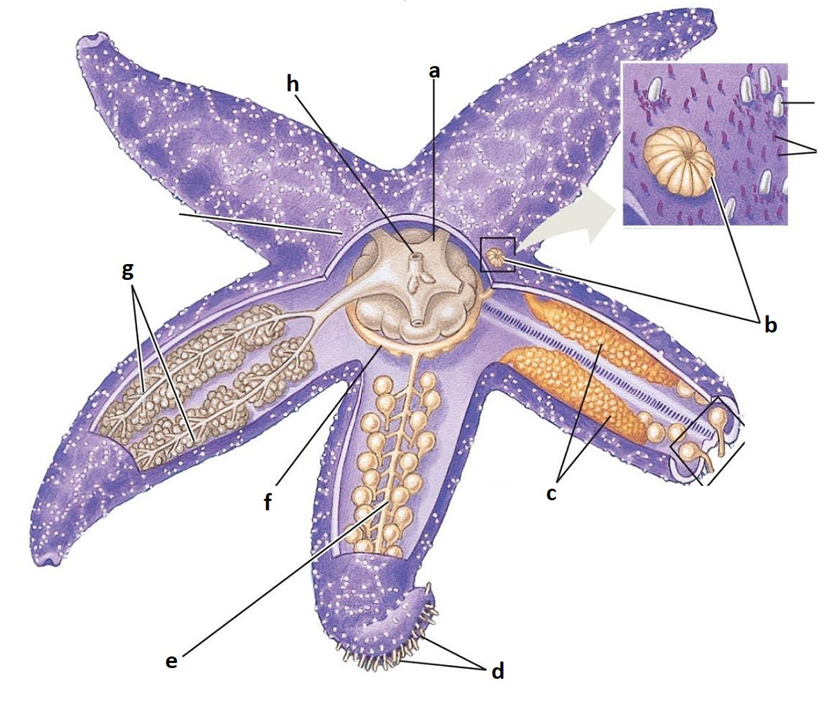
A
Stomach
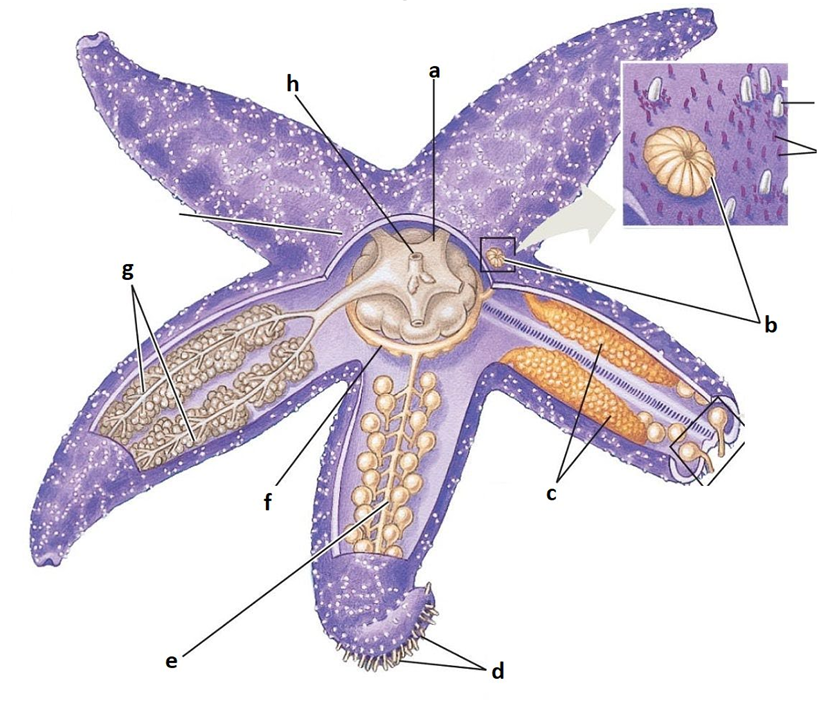
B
Madreporite
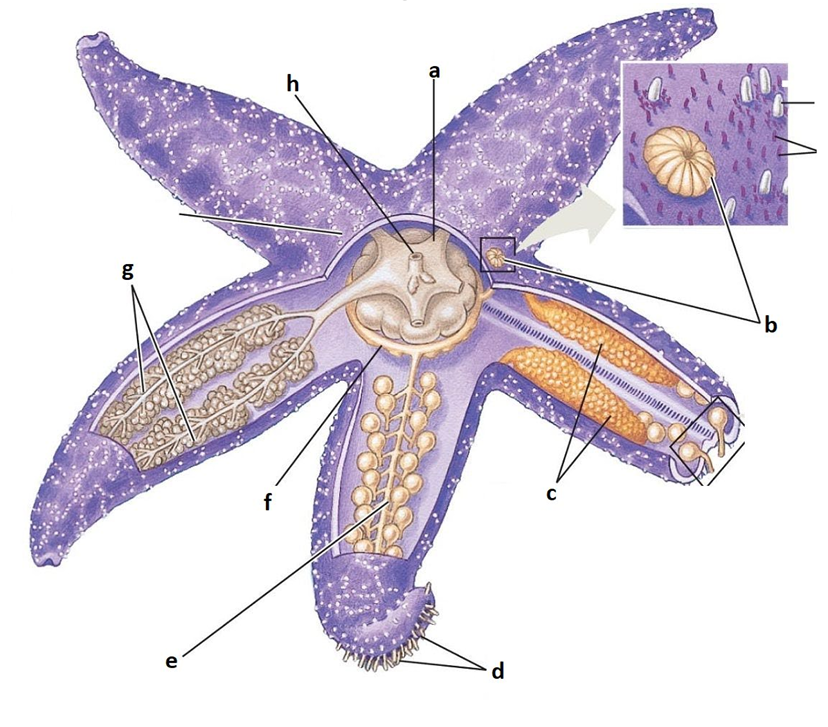
C
Gonads

D
Tube feet
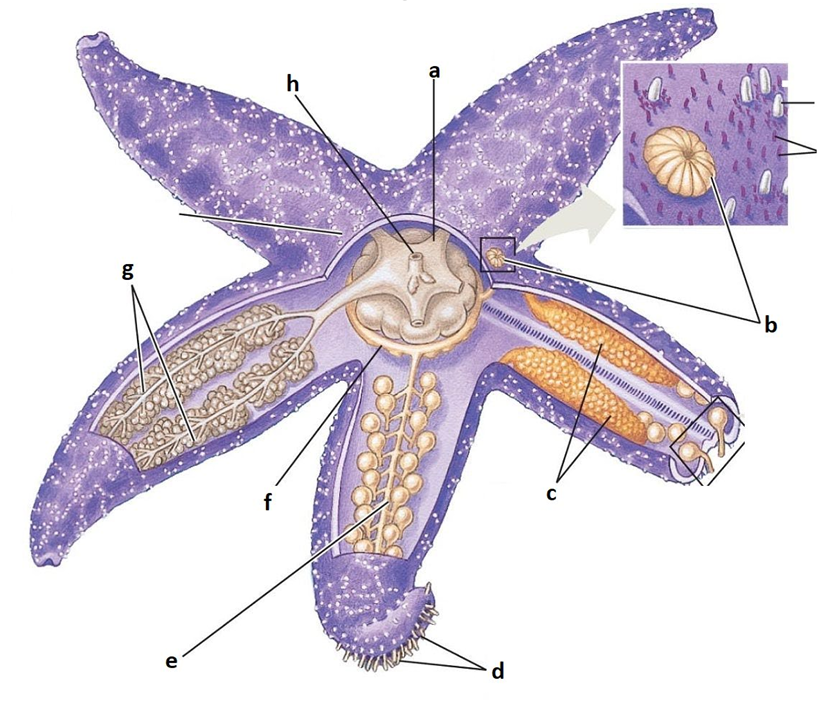
E
Radial canal
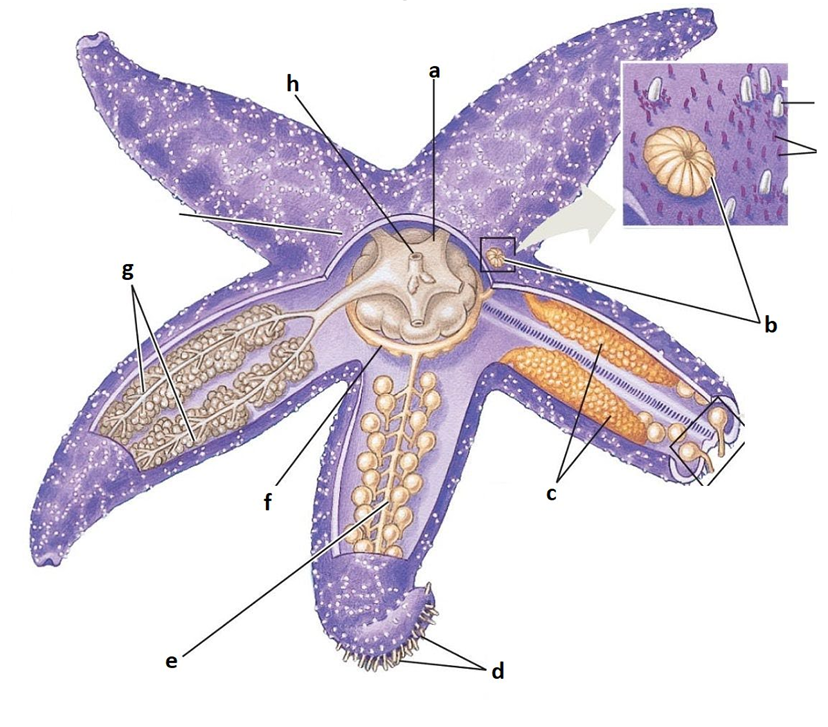
F
Ring canal
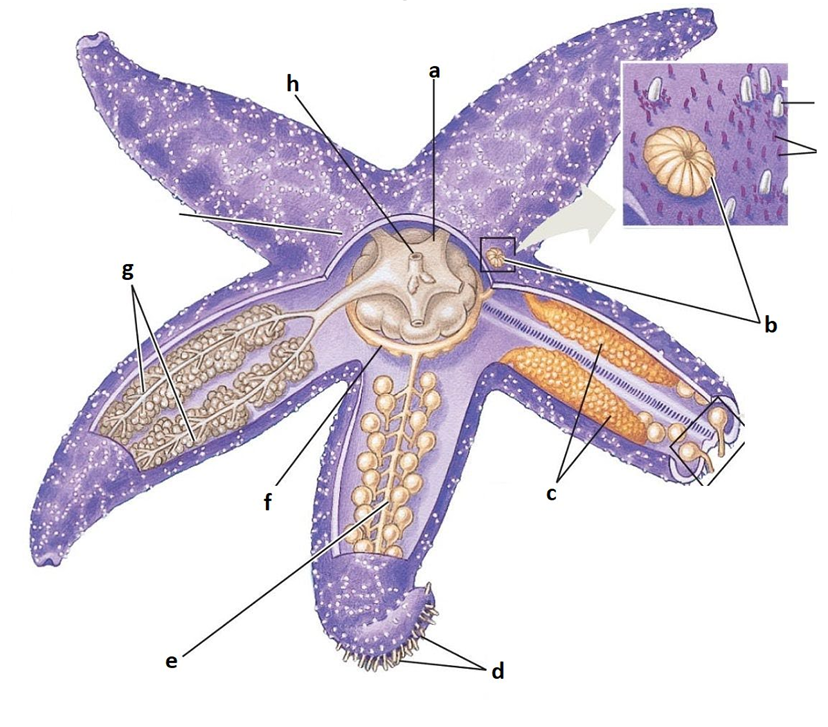
G
Digestive glands
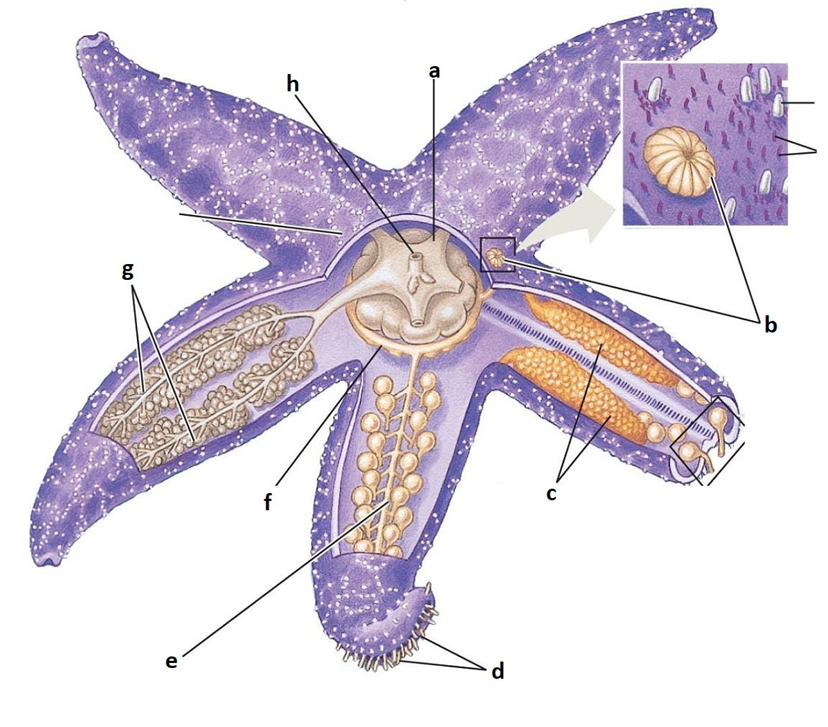
H
Anus
4 features of Phylum Chordata:
pharyngeal slits or pouches, dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, post anal-tail
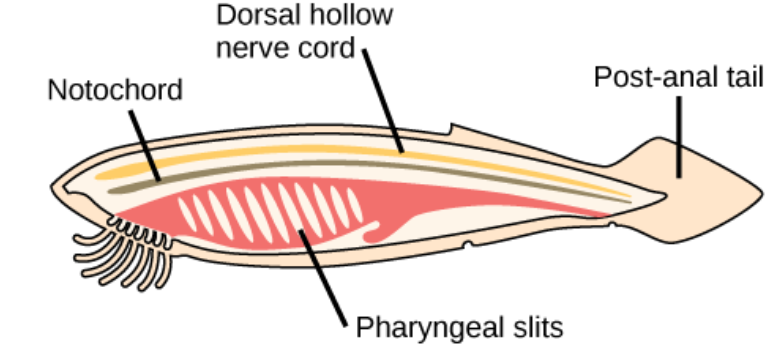
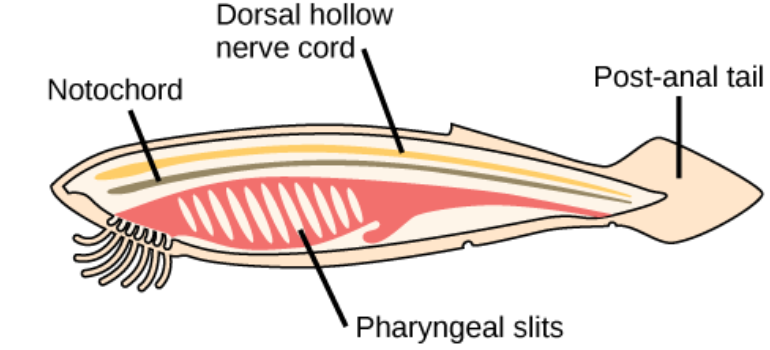
Pharyngeal slits or pouches
A set of parallel openings from the throat to the outside that function in feeding and/or gas exchanges.
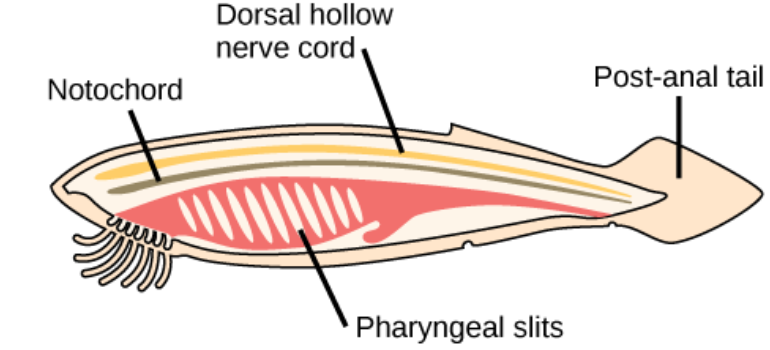
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
A bundle of nerves running the length of the body
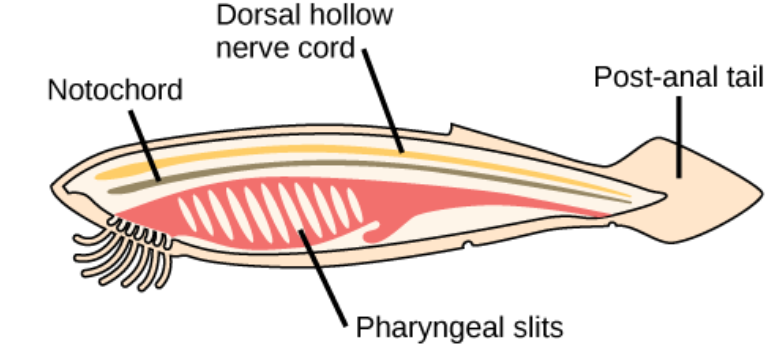
Notochord
A supportive, flexible rod that occurs in the back of a chordate embryom ventral to the developing spinal cord

Subphylum Cephalochordata
Lancelets

Subphylum Urochordata
Sea squirts and salps
Subphylum Vertebrata
Fish and tetrapods
Amniotic egg
An egg that has a watertight shell or case enclosing a membrane-bound water supply, food supply, and waste sac
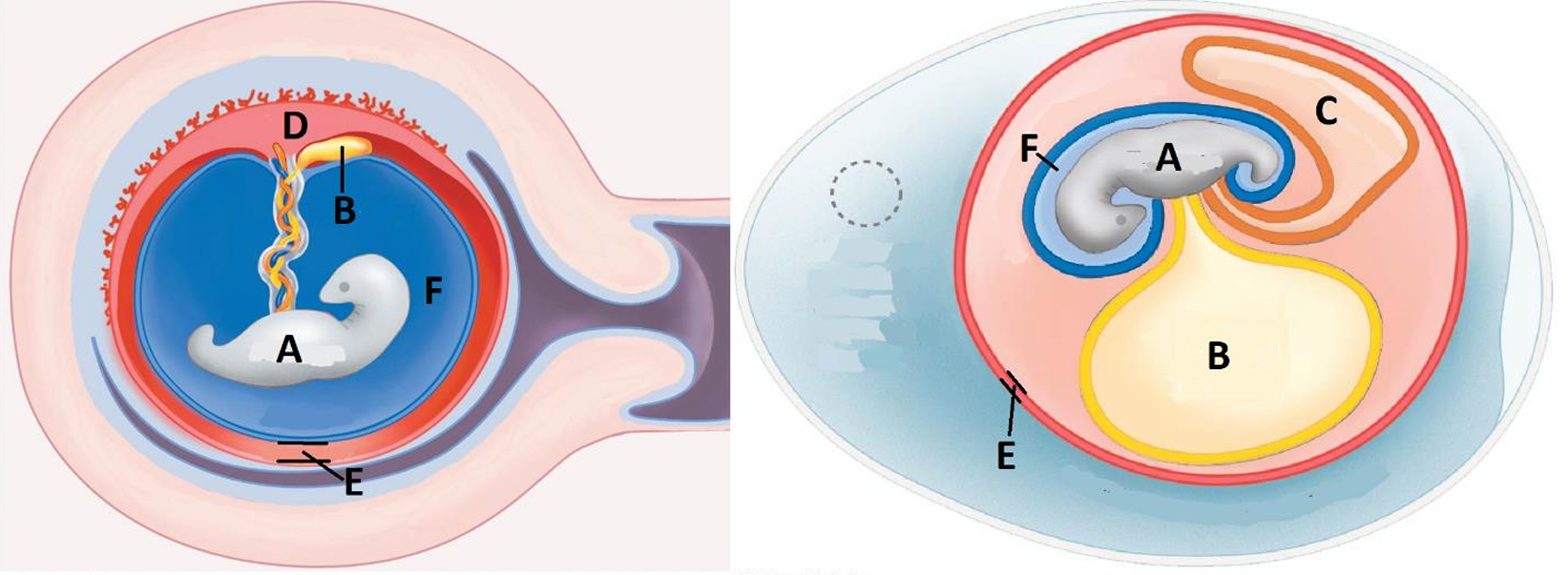
A
Embryo
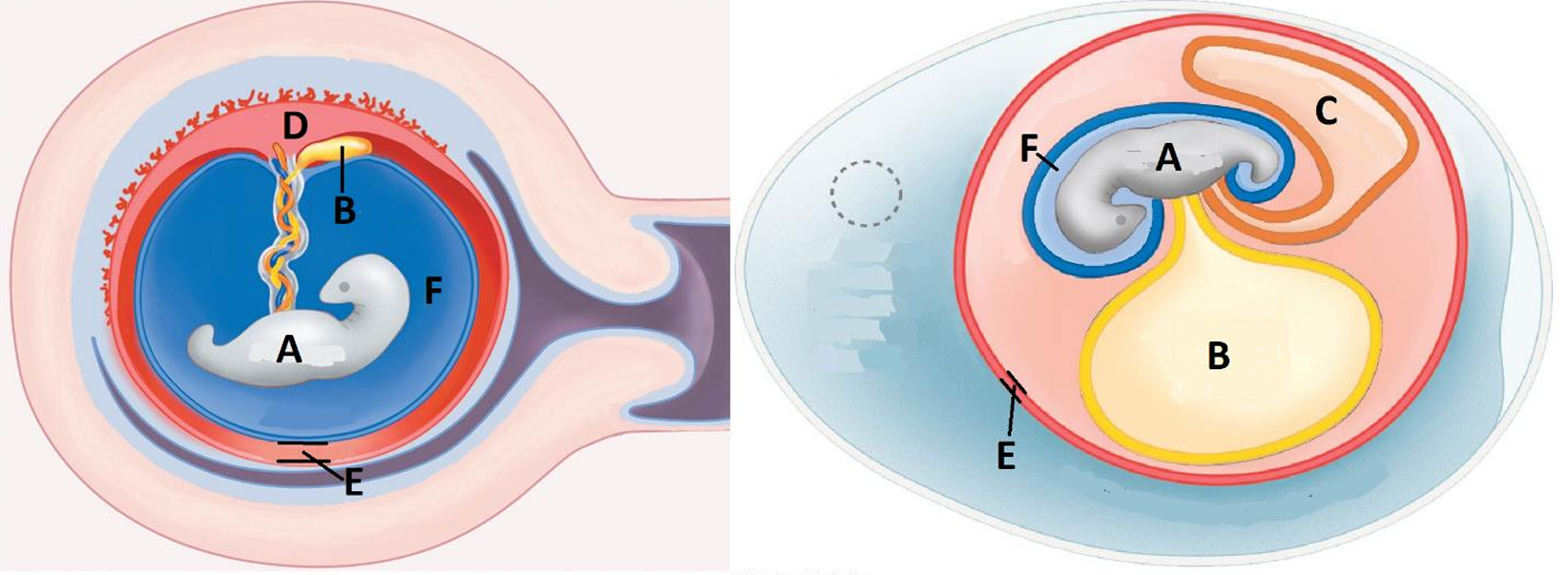
B
Yolk sac
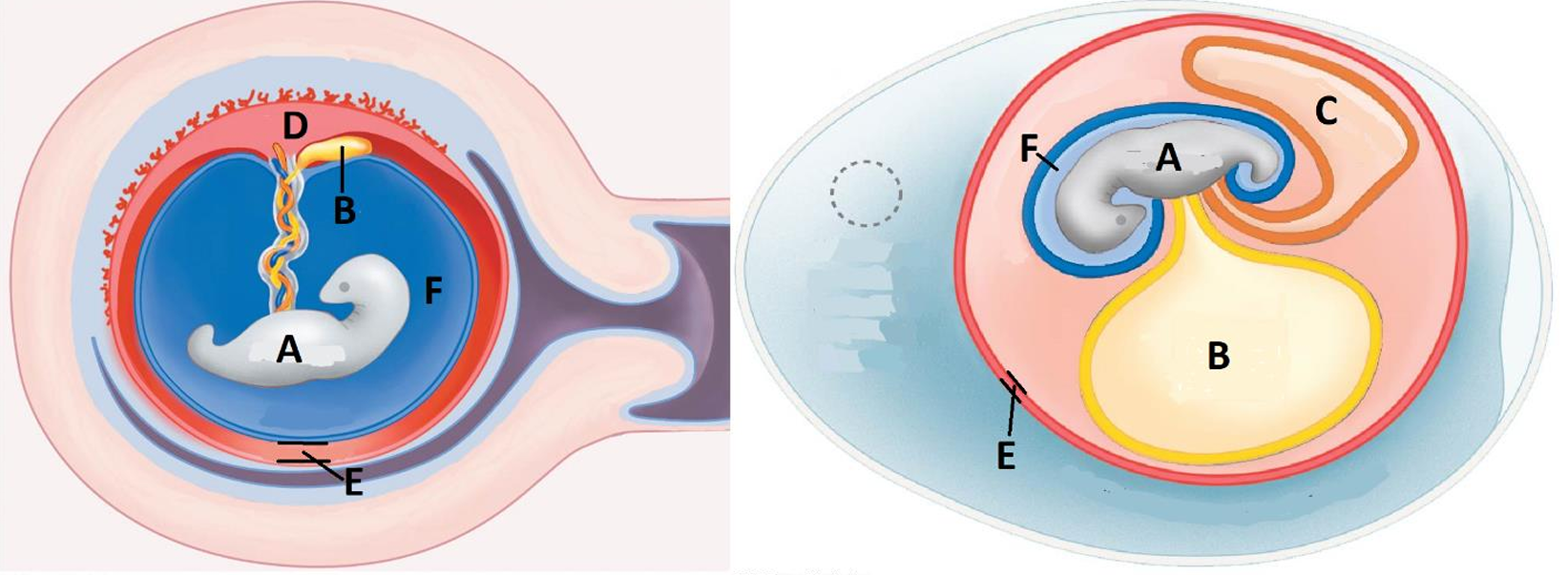
C
Allantois/waste sac
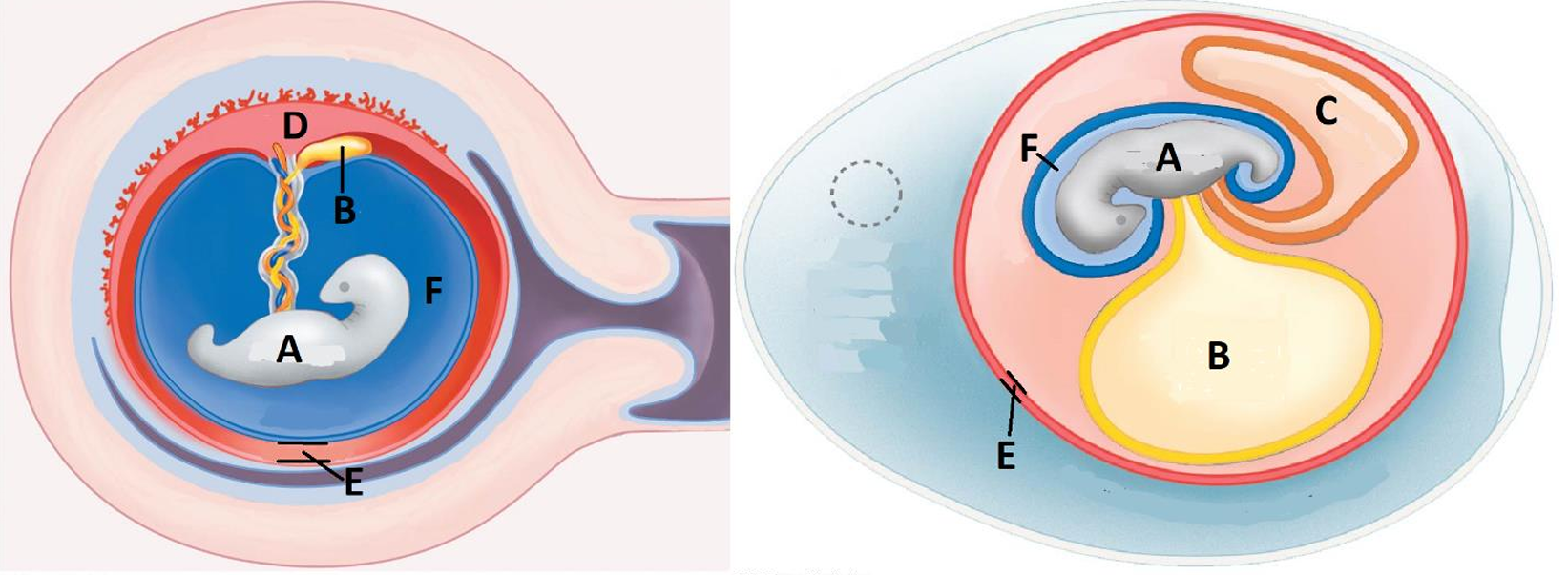
D
Placenta
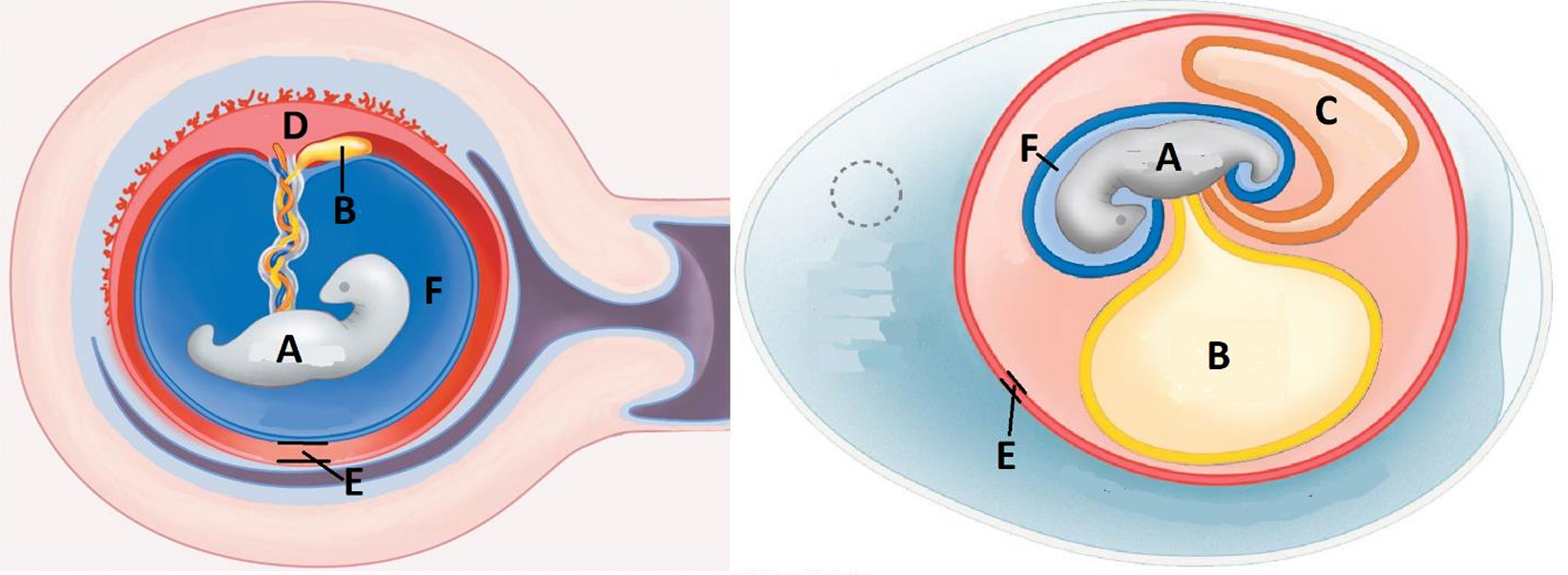
E
Chorion
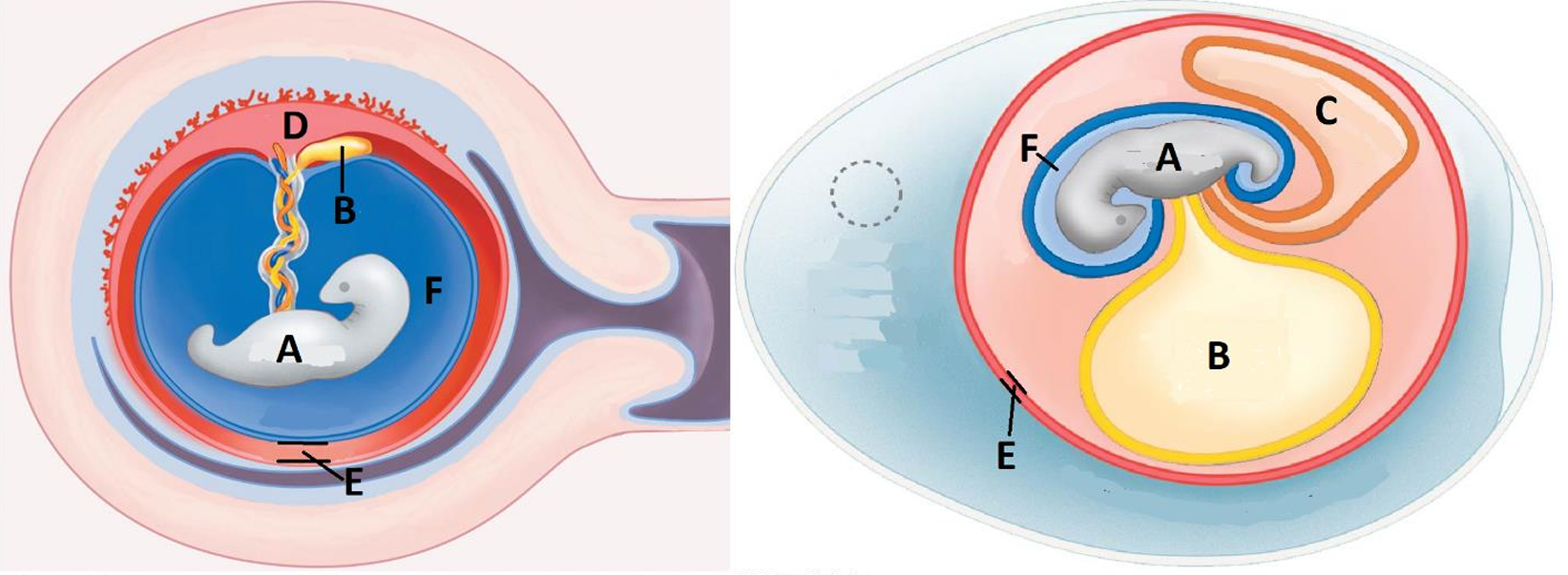
F
Amnion

Agnathans
“Jawless fish”, lampreys, hagfish
Gnathostomata
Jawed vertebrates

Phylum Chordata, Class Chondrichthyes
“cartilaginous fish”, sharks, rays
Class Osteichthyes
“bony fishes”, ray-finned fishes, coelacanths, lungfish

Phylum Chordata, Class Amphibia
Frogs, toads, salamanders, caecilians
Phylum Chordata, Class Mammalia
Platypus, echindnas, marsupials, placental mammals

Phylum Chordata, Class Mammalia, Order Monotremata
Platypus, echidnas

Phylum Chordata, Class Mammalia, Order Marsupiala
Marsupials

Phylum Chordata, Class Mammalia, Order Eutheria
Placental mammals
Amniotes
Lineage of vertebrates that reproduce with amniotic eggs; mammals, birds, reptiles

Phylum Chordata, Class Reptilia
lizards, snakes, turtles, crocodiles, alligators, birds

Phylum Chordata, Class Reptilia, Lepidosauria
Lizards, snakes

Phylum Chordata, Class Reptilia, Order Testudinia
Turtles

Phylum Chordata, Class Reptilia, Order Crocodilia
Crocodiles, alligators

Phylum Chordata, Class Reptilia, Aves
Birds
Oviparous
depositing fertilized eggs outside the body, where they develop and hatch
Ovoviviparous
producing eggs that are retained inside the body (nourished by yolk) until they are ready to hatch and released via live birth
Viviparous
producing live young (instead of eggs) that develop within and are nourished by the body of the female parent, typically via a placenta, before birth
Neoteny
the retention of juvenile features in the adult animal
Hemimetabolous
(of an insect) having no pupal stage in the transition from larva to adult
Homometabolous
complete metamorphosis
Homeothermy
relatively uniform body temperature maintained nearly independent of the environmental temperature
Poikilothermy
variable body temperature that is usually only slightly higher than the environmental temperature
Endotherm
An animal that gains most of its body heat from internal metabolic processes
Ectotherm
An animal that gains most of its body heat from external sources as opposed to metabolic processes

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Coleoptera
“sheath-winged”, beetles

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Lepidoptera
“scale-winged”, butterflies, moths

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Diptera
“two-winged”, flies, mosquitoes, gnats, midges

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Hymenoptera
“membrane-winged”, ants, bees, wasps

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Hemiptera
“half-winged”, bugs

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Orthoptera
“straight-winged”, grasshoppers, crickets

Phylum Arthropoda, Class Insecta, Order Odonata
“toothed”, dragonflies, damselflies
Lateral Line
A pressure-sensitive sensory organ found in many aquatic vertebrates
Ampullae of Lorenzini
Structures on the heads of sharks that contain electroreceptors