electromagnetic waves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
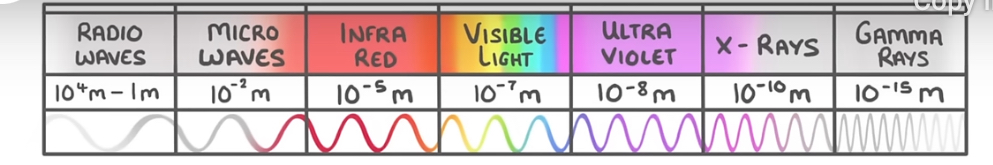
State order of electromagnetic waves going from long to short wavelength
radio, microwave, infrared, visible light (red to violet), ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays.
What type of waves are all electromagnetic waves
Transverse- oscillate perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
What speed do all electromagnetic waves travel as through a vacuum or air
3×10^8m/s
What part of the spectrum can our eyes only detect
Visible light
Where can gamma rays be found
During radioactive decay
Where does visible light, UV and x rays come from
When electrons drop down energy levels
What waves can be used in communication
Radio and microwaves
Which waves are considered ionising
X rays and gamma rays
Radio waves
Longest wavelength and lowest frequency
How can we produce radio waves
Using electricity in the form of alternating current as AC are made up oscillating charges
What determines the frequency of the wave we are going to produce
Frequency of alternating current
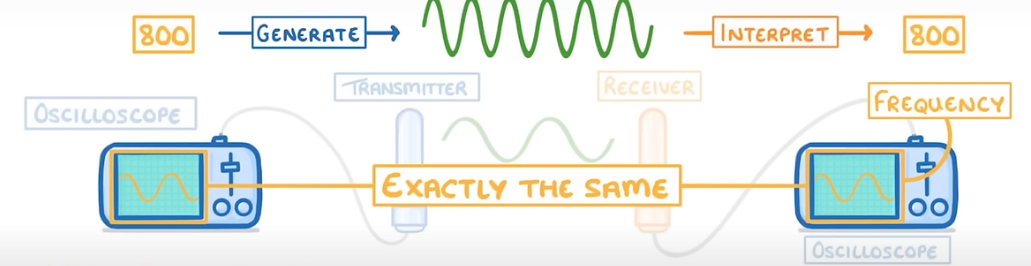
What equipment is needed to generate radio waves
Oscilloscope-see the freq if AC
transmitter
Receiver-absorbs energy and generates AC on another oscilloscope which has the exact same frequency on first oscilloscope
Types of waves for radio wave communication
Long wave-huge distances and bend around the curved surface of earth
Short wave-long distances but can’t be curved instead reflected
Very short waves-TV and FM radio so have to be transmitted directly, not always clear
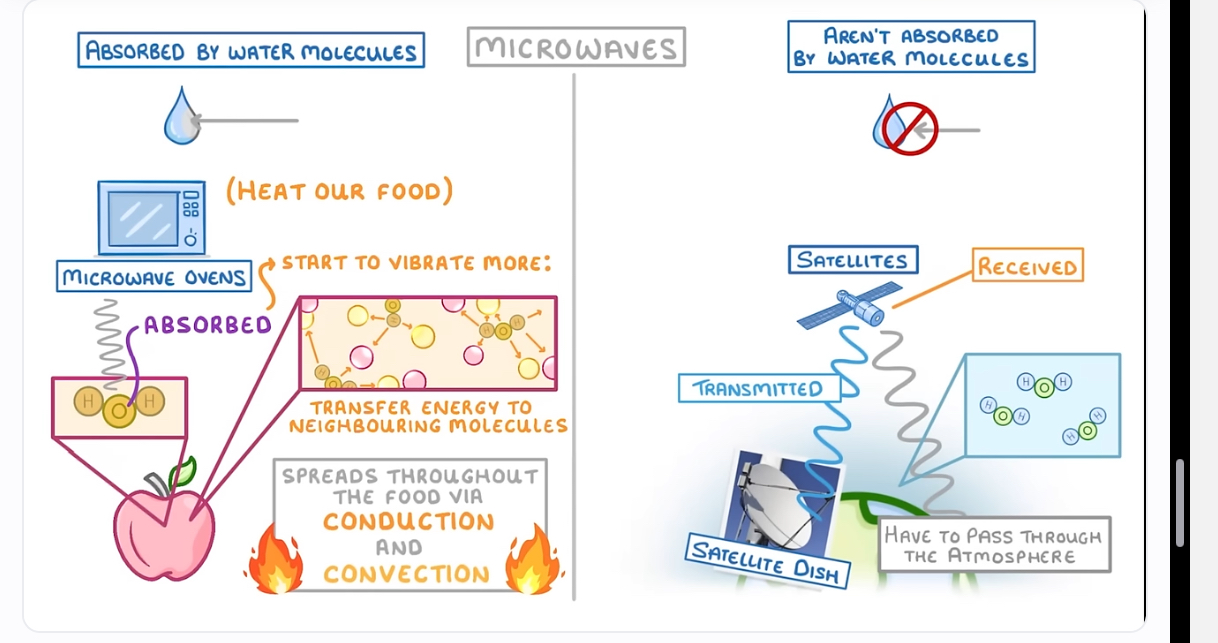
Two groups of microwaves
1)aren’t absorbed by water molecules I.e for satellites
2)absorbed by water molecules I.e microwave ovens
Infrared radiation
Emitted by all object that have thermal energy
Hotter the object=more IR radiation
IR cameras
Infrared radiation camera-see in dark
Can spot living organisms as they will lighter as emit more radiation
Cooking with IR
Oven and grills-metal emits lots of IR radiation which heats our food and heats our food by transferring the heat energy
Doesn’t penetrate the surface of food
Electric heaters with IR
Use electrical energy to heat metal which heats up surrounding I.e in our rooms
Visible light
Appears different colours depending on wave length
Red=longest wavelength
Violet=shortest wavelength
ROYGBIV
How is visible light used for communication
Using optical fibres that are thin glass or plastic fibres that can transmit pulses of light over long distances as light is reflected every time it hits a surface
Transmits data really quickly over long distances
Must have specular reflection
Ultraviolet uses
From sun or sun beds for tan or burns
Fluorescence=ultraviolet is absorbed and energy is re emitted as visible light
Security pens-detect writing when shone
Sterilise water
X rays main use
View internal structure of object I.e our body’s
Firing x-rays through body where rays are absorbed by bones but pass through parts that are mostly air I.e lungs and partially pass through fleshy parts
Dense areas=white like bones
Detect broken bones
Low dose so not too harmful and cheap and quick test
What is radiation measured in
Sieverts
Gamma rays for sterilisation
Medical equipment and food-kill microorganisms without causing other damage
Pros and cons of using gamma, X-rays in medicine
-both ionising radiation so can damage cells and potentially lead to cancer
-but help us to diagnose and treat diseases so worth the risk