5.6 Photosynthetic Pigments
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
autotrophic
organisms that make complex organic compounds from simple compounds in their environment
photosynthesis
the process by which living organisms, particularly plants and algae, capture the energy of the sun using chlorophyll and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars
heterotrophic
organisms obtain complex organic molecules by feeding on other living organisms or their dead remains
envelope of a chloroplast
is the outer and inner membranes along with the intermembrane space
grana
stacks of thylakoid membranes within a chloroplast
thylakoid
a membrane disc found in the grana of a chloroplast
Lamellae
extensions of the thylakoid membranes which connect two or more grana, acting as a supporting skeleton in the chloroplast, maintaining a working distance between the grana so that they get the maximum light and function as efficiently as possible
stroma
the matrix which surrounds the grana and contains all the enzymes needed to complete the process of photosynthesis and produce glucose
chlorophyll a
a blue-green photosynthetic pigments found in all green plants
Chlorophyll b
a yellow-green photosynthetic pigment
Carotenoids
photosynthetic pigments made up of orange carotene and yellow xanthophyll
Phaeophytin
a grey pigment which is a breakdown product of the other photosynthetic pigments
absorption spectrum
a graph of the amount of light absorbed by a pigment against the wavelength of light
action spectrum
a graph demonstrating the rate of photosynthesis against the wavelength of light
Photosystem I (PSI)
a combination of chlorophyll pigments which absorbs light of wavelength 700 nm and is involved in cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
Photosystem II (PSII)
a combination of chlorophyll pigments which absorbs light of wavelength 680 nm and is involved only in non-cyclic photophosphorylation
what does the absorption spectrum describe?
describes the range of amount of light of different wavelengths that a photosynthetic pigment absorbs . Usually represented as a graph
how is the absorption spectrum found?
measuring the different photosynthetic pigments absorption of light of different wavelengths
diagram of Absorption spectrum
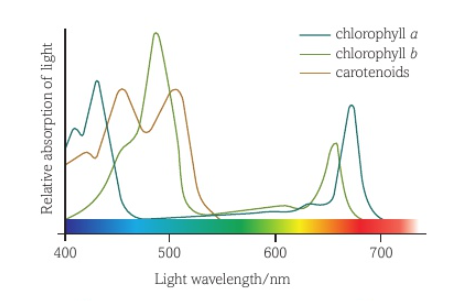
diagram of action spectrum
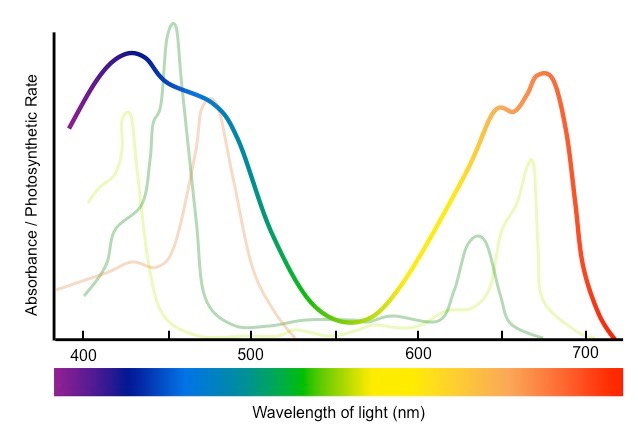
what does the action spectrum show?
the effect of light wavelength on the rate of photosynthesis. the rate of photosynthesis is very closely related to the combined absorption spectrum of all the photosynthetic pigments in a plant
what does the modern action spectrum use?
electronic data logging rather than bacterial movements to measure the rate of photosynthesis to the wavelength of light
how can the rate of photosynthesis be measured?
rate of O2 production
why are leaves green?
the pigment present in leaves absorb a range of wavelengths of light but they absorb very little green light