Experiment 7: Cardiac Physiology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
The Heart consists of _ pumps in series
2
Blood flow in the heart is ___-directional
Uni
3 Types of Major Cardiac muscle…
Atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, excitatory and conductive muscles
True or False: Cardiac Muscles are not striated
False

Flow of the Heart (Type 1)
1
True or False: If the SA node loses connection the AV node, purkinje fibers will lose its ability to perform an action potential…
True
____ happens at the P wave
Atrial depolarization
____ happens at the Q wave
Initial depolarization of the interventricular septum
____ happens at the R wave
Ventricular depolarization
________ __________ is the highest depolarization because the strongest contraction of the heart is produced here in order to overcome the pressure of the aorta and peripheral resistance
Ventricular depolarization
____ happens at the S wave
Final depolarization
____ happens at the T wave
Ventricular repolarization
True or False: Ventricular depolarization can still occur in the U wave.
True
Cardiac muscle fibers are arranged in a ___________.
latticework
Cardiac muscle contains ______ and _______ filaments.
actin, myosin
Cardiac muscle cells are separated by ___________.
intercalated discs
Ions move in the ICF of cardiac muscle through ___________.
Gap junctions
Cardiac muscle functions as a ___________, enabling a cascade of events.
syncytium
___________ is the key term in determining where electrical signals should start in a normal beating heart.
Sinus rhythm
When the action potential starts in the ___________, it marks the start of blood flow.
AV node
If backflow occurs, deoxygenated blood will return to the ___________ system.
peripheral blood
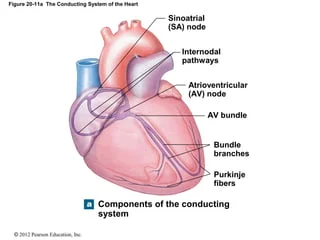
Specialized Excitatory and conductive systems of the heart flow:
__ Node → __________ pathways → __ Node → ________ → ________ → ________ _______
SA, internodal, AV, bundle of HIs, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers,
True or False: Heart rhythmicity would not have a direct effect on one’s BP and HR
False
Parasympathetic stimulation is distributed mainly to the __ and __ nodes.
SA, AV
___ decreases the rate of rhythm of the __ node and decreases _________ of __ junctional fibers.
Ach, SA, excitability, AV
Ach increases the _________ of fiber membranes to ___________ ions, leading to rapid leakage out and causing ____________
permeability, potassium, hyperpolarization
Sympathetic stimulation increases the rate of __ node discharge.
SA
Sympathetic stimulation increases the _____ ___ _______ and excitability of the cardiac muscle.
rate of conduction
Sympathetic stimulation increases the ___________ of contraction.
force
_____________ stimulates ___________ receptors, increasing membrane permeability to Na+ and Ca2+ ions.
Norepinephrine, b1 adregenic
Blood flow through vessels is affected by ___________.
Resistance
The ________ is the pressure exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels.
Blood pressure
The pressure in arteries during ___________ is typically higher than during ________ .
systole, diastole
___________ is a condition that can result from prolonged high blood pressure.
Hypertension
Factors that can affect blood pressure include ___________, heart rate, and blood volume.
cardiac output
True or False: Air temperature, emotions, body size, medication, and body position can all affect heart rate.
True
_______ __________ __________ is the resistance of the “entire” circulation.
Total peripheral resistance
True or False: PRU is computed by-
Total Pulmonary Vascular Resistance
Total Peripheral Vascular Resistance
False
During late diastole, the ___________ and _______ valves are open.
mitral, tricuspid
During late diastole, the ___________ and ________ valves are closed.
aortic, pulmonic
About __% of the blood that flows into the heart is passive.
70
In late diastole, blood flows into the heart passively from the ___________ and pulmonary _____.
superior and inferior vena cava, veins
In late diastole, there is a rise in ___________ as the __ valve cusps drift toward the closed position.
pressure, AV
Ventricular pressure remains ___________ during late diastole.
low
5 Phases of the Cardiac cycle:
1. ________
2.________
3.________
4.________
5.________
Atrial systole, Isovolumetric ventricular contraction, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation, Ventricular filling
Atrial systole places the remaining __% of blood into the __________.
30, ventricles
During Atrial systole, there is some ___________ of blood into the veins due to contraction.
regurgitation
True or False: Regurgitation is possible in Atrial systole
True
During Ventricular systole, the __ valves close.
AV
In Ventricular systole, ventricular muscle initially ___________ a little.
shortens
During ___________ _______ ________, intraventricular pressure rises sharply.
Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
True or False: During isovolumetric ventricular contraction, there is ejection of blood.
False
Isovolumetric ventricular contraction lasts _____ sec.
0.05
Aortic pressure during ventricular systole is ___________ mmHg.
80
Pulmonary pressure during ventricular systole is ___________ mmHg.
10
To overcome aortic and pulmonary pressures, the ventricles need to ___________ the pressure rapidly.
increase