Sustainable Transitions: Past, Present and Future
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
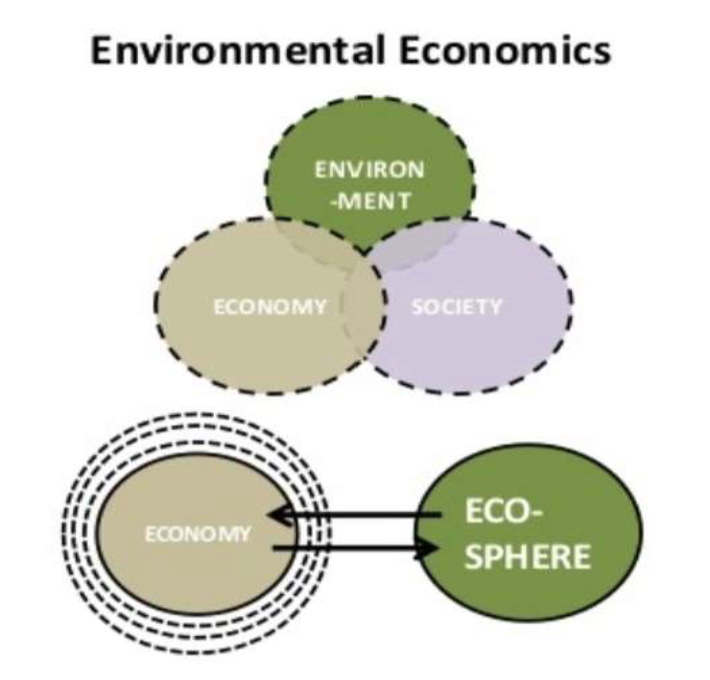
Environmental economics
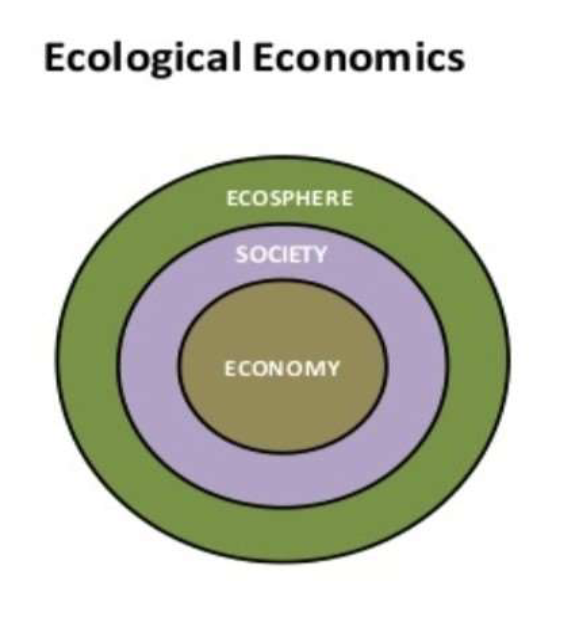
Ecological economics
Kuznets Curve
Club of Rome
Limits to Growth report, 1972
Earth is finite and unlimited growth is not possible
Limits will be reached in 100y
Optimistic - possible to establish sustainable stability where basic needs are met
First use of computer
UN Conference on the Human Environment
Stockholm, June 1972
113 countries
Creation of UN Environment Programme
Emergence of international environmental law
Would later lead to yearly COP meetings with UNFCCC
First mention of the link between environmental degradation and poverty
Earth Summit
Rio de Janeiro, 1992
UN Conference on Environment and Development
Start of UNFCCC and COP
Recognizes the right of all nations to exploit resources without damaging the environment
Common but differentiated responsibility to solving environmental problems
Agenda 21 - plan of action to tackle environmental problems
Our Common Future (Brundtland report)
World Commission on Environment and Development, 1987
Sustainable development = balancing environmental, economical and societal sustainability
Decoupling economic growth and environmental degradation
Including “the needs of future generations”
Basis for Rio Declaration and Agenda 21
Kyoto Protocol
Japan, 1997
industrialized countries must cut their GHG emissions by 5.2% between 2008 and 2012 compared to 1900 levels
common but differentiated responsibilities
US withdrew
covered only about 18% of global emissions
Paris Agreement
2015
limit the avg. global temperature increase to 1.5 C
196 parties
Policy principles for SD
Policy integration
vertical - scale, local→ global
horizontal - sectors (e.g. energy, water, food, housing)
Intragenerational solidarity - equity among groups in society
Intergenerational solidarity - taking into account the interests of future generations
Internalization of externalities - social and environmental costs included in prices
Participatory policy making - stakeholder involvement
Sustainable indicators criteria
Specific, Measurable, Usable, Sensitive, Available, Cost-effective
GDP
gross domestic product
total market value of all finished goods and services produced in a specific area and period
finished product not intermediate, needs to be sold
only counts production, not resale or unpaid work
= consumption + government spending + investment + net export
nominal = measured at current market prices without adjusting for inflation
real = adjusted for inflation
PPP = purchasing power parity = adjusted for differences in price levels across countries (what can be bought for this money)
per capita = per person
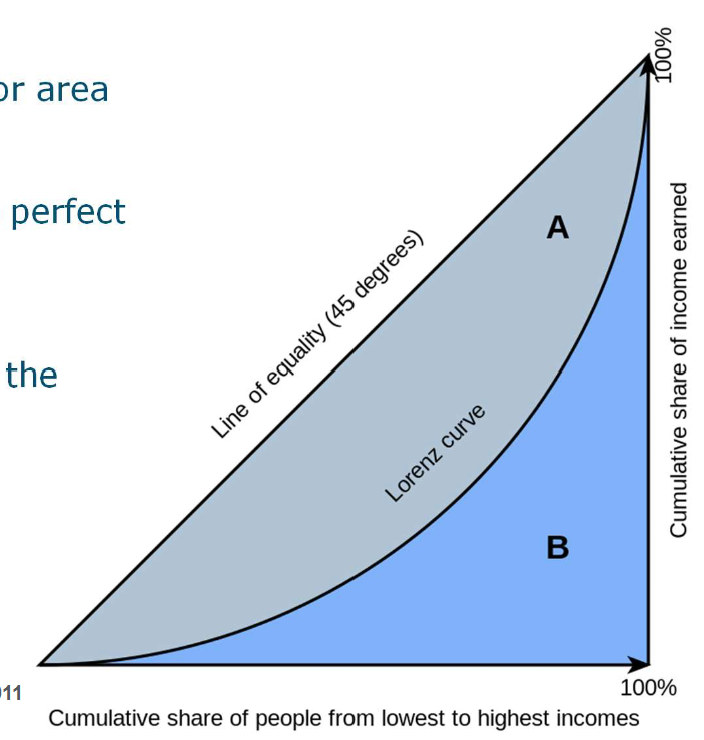
Lorentz curve
shows distribution of wealth in a country or area
Gini coefficient - ratio between perfect equality and inequality (A/A+B)
0=equality, 1=inequality
The Veil of Ignorance
Rawls 1971
what is a fair distribution of wealth
how would you design a society if you didn’t know who you would be born as
Features of environmental indicators
representation
simplification
communication
Single indicator
one parameter representative for the whole issue - simple to understand but can it capture the whole issue?
Aggregate indicator
Combination of parameters - accurate but more work (time and money)
Indexes (indeces)
indicators that do not represent existing quantities, but are relative to a chose value or period in time (usually aggregate)
4 relevat actors (indicators, communication)
sender - conveying the message
receiver - the target group
maker - collector of information
warrant - guarantees trustworthiness
GNP
gross national product
what nationals produce anywhere
Anthropocene
geological epoch in which humans are the primary cause of permanent planetary change
Coal blast furnace
1709
Abraham Darby
charcoal → coal
coal was cheaper, burned hotter and cleaner
higher furnace capacity
higher quality iron (fluid)
Steam engine
1712
Thomas Newcomen
coal driven
used to pump water from the deepening coal mines
Watt steam engine
1763 - 1775
improved Newcomen’s design
rotary motion allowing the piston to pull and push the beam
required less coal
used e.g. in textile factories
steam hammer used the watt steam engine
Steam locomotive
1804
Richard Trevithick
used in coal mines
Locomotive “Rocket”
1825
George Stephenson
stronger locomotive
Used to transport coal from the mines in Darlington to the sea port in Stockton
Reduced the transport costs of coal
→ Rapid expansion of the British railway network (1825-1850) also for passengers and cargo other than coal
North River steamboat
1807
first use of steam engine to drive paddlewheel
SS Normannia
1890
much larger
used a screw propeller
cut down travelling time
Could the industrial revolution happen on charcoal/wood?
No!
1700-1913 - increase in coal production in Britain from 3 to 250 million tons
For this to happen on charcoal/wood a forest the size of England+Wales would be needed
What explains the Industrial Revolution?
property rights, inventions
hard work, ‘Protestant ethic’
innovative mindset
cheap labor, beneficial terms of trade, population outlet, new markets
move to cities, economic diversification
economic and military competition
Location of coal deposits
historian Kenneth Pomeranz compares England and China (Yangzi Delta)
both experience economic growth and technological advancements
both faced wood scarcity
England had better located, more accessible coal deposits enabling it to sustain economic growth
Unique structure: high wage + cheap economy
historian Robert Allen
incentive to innovate to save on the expensive energy (wood) and labor because coal was cheap
why innovate if there is no economic need? (Boserupian argument)
Second industrial revolution
1860-1910 (or much longer?)
Started in Britain, US and Germany
coal → oil
internal combustion
electrification
artificial fertilizers
communication (telegraph, telephone, radio)
Europe + offshoots (US, Canada, New Zealand, Australia)
1990: 30% pop, 95% energy use
1990: 20% pop, 70% of commercial energy use
→ the IR is still diffusing
Organic vs industrial society

Levelized cost of energy
LCOE=sum of costs over lifetime/sum of electrical energy produced over lifetime [$/kWh]
Gielen & Boshell 2023: 5 key areas
energy efficiency
power systems transformation/RE
electrification of end-use sector
bioenergy deployment
CO2 capture, use and storage (CCUS)
Constrains on flow of RE from source to user
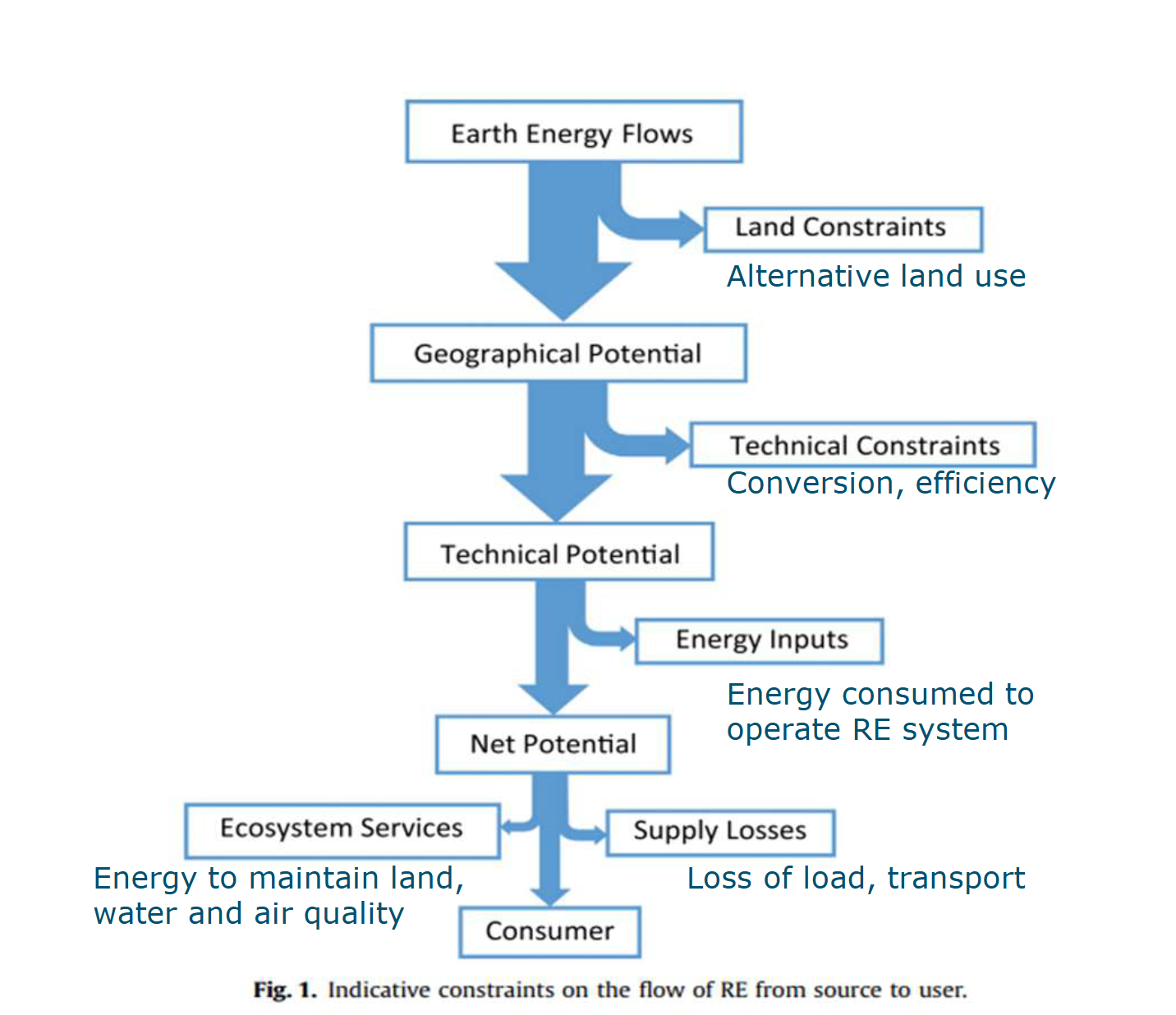
years of fossil fuel reserves
coal: around 135
oil: around 50
gas: around 45
cleaner energy sources
higher H:C ratio
coal>oil>natural gas>hydrogen
Smil 2016
national ET differ in speed
global ET gradual, prolonged
FF dominated world (80%)
ET to RE driven by CC
no evidence of speeding up of ET (has changed)
ET so far mostly electric
global growth of RE not extraordinarily rapid
ET to RE gradual at best
FF based reserve capacities needed for intermittency
even fastest rate falls short of 2050 net-zero target
greening electricity easier that heat, fuel, plastics and construction
current FF infrastructure not rapidly replacable
Fouqet 2016
how much of world’s soy is used as feed?
70-75%
What % of Dutch meat and dairy value is export?
meat: 60%, dairy: 65%
Value chain
series of steps that a product goes through with value added at each step
What % of global agriculture and food exports are traded within GVCs (across multiple countries)?
1/3
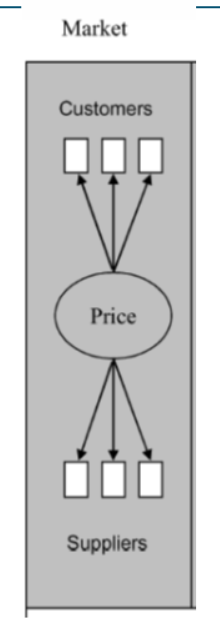
GVC governance: Market
suppliers and lead firms interact through simple transactions
easy to switch partners
exchange mainly driven by price competition
low complexity in product specification, supplier has high autonomy
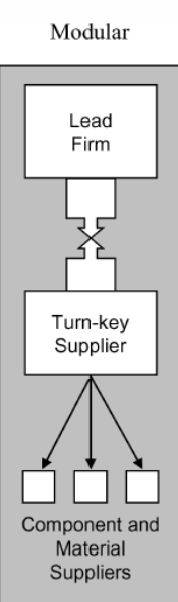
GVC governance: Modular
suppliers make products or provide services to a customer according to detailed specifications, but they have full responsibility for process technology, components and production
the suppliers delivers a ready-to-use or fully assembled products, so the lead firm doesn’t manage the details of production
E.g. Tetrapak
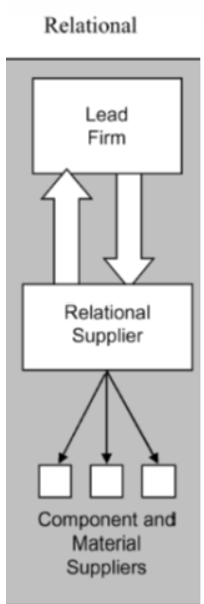
GVC governance: relational
firms rely on complex, long-term relations with suppliers
high mutual dependency between lead firms and suppliers
based on trust, frequent interactions, knowledge sharing
firms participate actively in design, innovation and product planning
relational ties take years to develop and can involve co-investment, training or technology transfer
e.g. Friesland Campina
GVC governance: Captive
independent firm that is highly dependent on a lead firm for contracts, market access and often technical guidance
the lead firm dictates specifications, quality standards, delivery schedules and sometimes pricing
limited autonomy of the supplier
e.g. Nike, Apple
GVC governance: Hierarchy (integrated)
lead firm controls multiple stages of the value chain itself rather than relying (heavily) on independent suppliers
the firm owns production, processing and sometimes distribution
high control and coordination
e.g. Pepsico
Hybrid: contract farming
between captive and integrated
farmers agree to produce a specific quantity and quality of a crop for a lead firm under pre-agreed terms (price, standards, delivery)
allows lead firms to secure supply without owning farms
farmers often get access to inputs, credit, or technical support
Farmers are dependent on lead firm for contracts, market access, and guidance on production
what % of supermarket products contain palm oil
1/3, not only in food
RSPO
sustainable palm oil certification
8 founder crops
einkorn wheat
emmer/durum wheat
barley
lentils
pea
chickpea
bitter vetch
flax
bread wheat
emmer wheat crossed with wild grass
why sedentary farming?
Andrea Matranga (2024)
climate change - seasonality
Why the fertile crescent first?
largest zone of Mediterranean climate
greatest climatic variation
wide range of altitudes and topographies
large mammals suitable for domestication
Jared Diamond’s main thesis
1997
Eurasia - largest pool of domesticable plants and animas
Horizontal continent - easier spread of crops, livestock and technologies
Peasant based societies enhance state centralization
Proximity humans-livestock → disease environment
Columbian exchange
post-1492
Exchange of domesticated animals
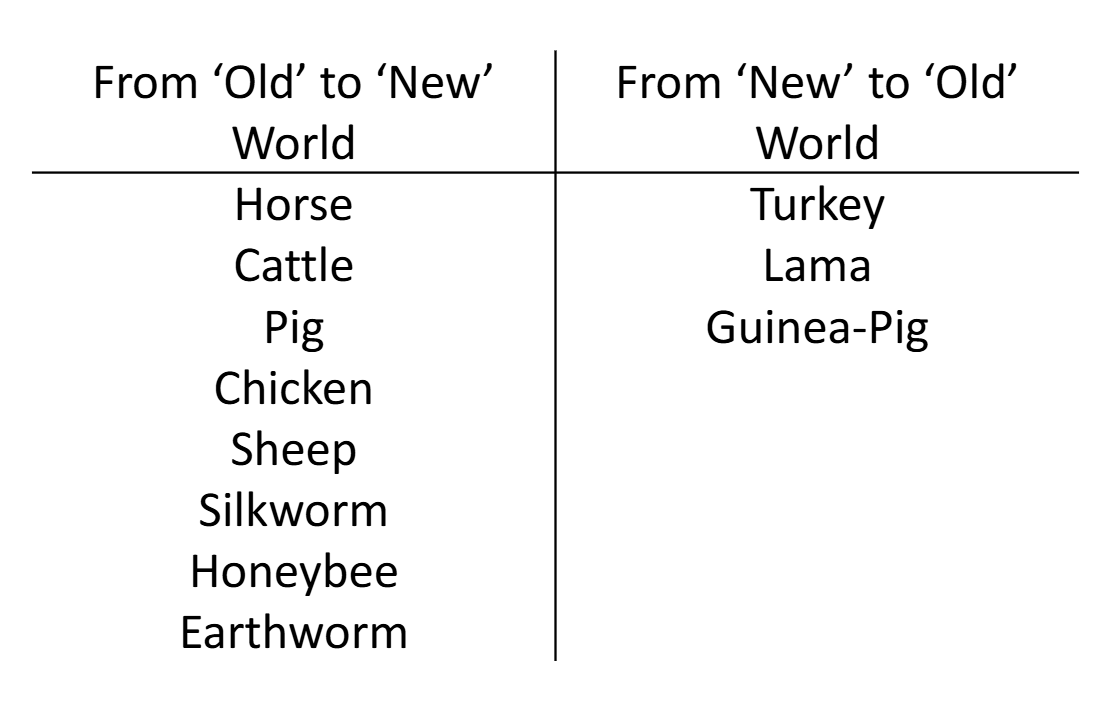
Impacts of animal exchange
bees pollinate new European crops
worms eat forest litter (trees’ food)→ less dense, easier to clear
pigs dig up wild tubers that Native American rely on in case of crop failure
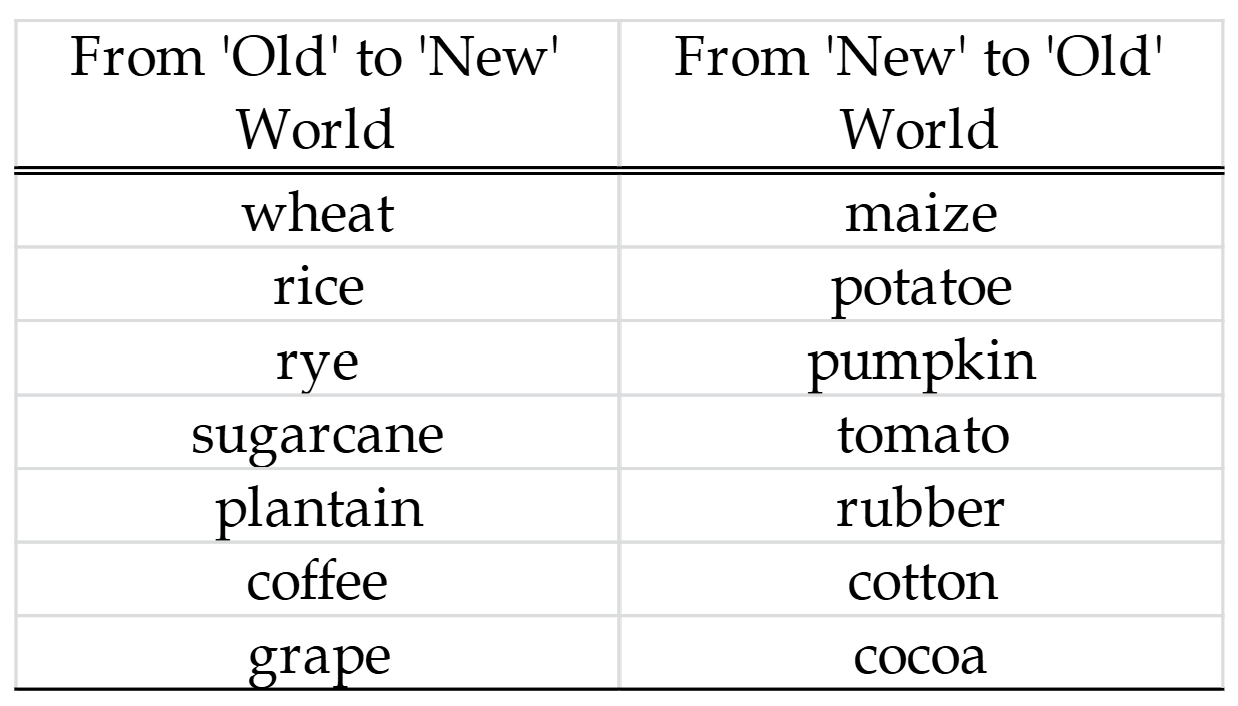
Plant exchange
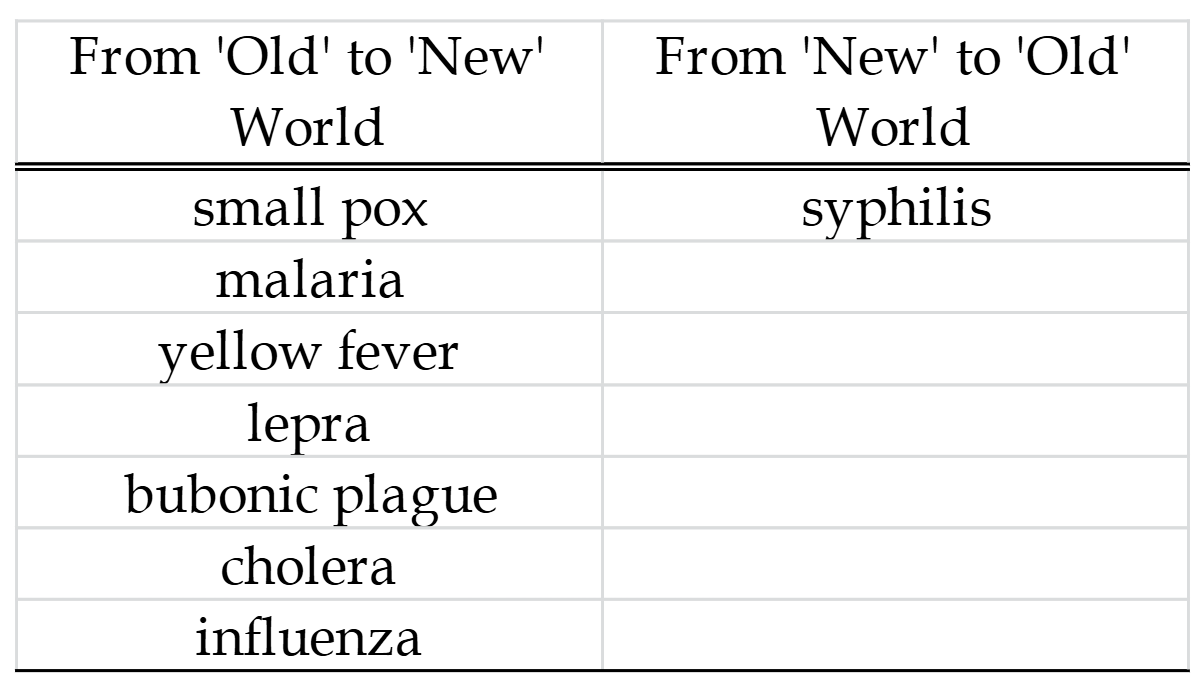
Disease exchange
When was the potato initially introduced in Europe?
1573, by sailors and missionaries
Why didn’t the potato take off until mid-18th century?
people knew similar poisonous plants
they didn’t like its looks and were scared they could get leprosy from it
Marie Antoinette
(1755-1793)
gave prestige to the potato
Benefits of the potato
high yields, high nutritional value (calories), easy to grow
protein deficiency in cassava and maize
maize produces fewer calories/acre of land
What % of pop. growth and urbanization in the Old World between 1700-1900 can be explained by the introduction of potato?
25% of population growth, 30% of urbanization
The Great Irish Famine
1845-1852
illustrates the dangers of dependency on one crop
massive population decline (deaths + emigration (North America))
18th century: agrarian change in Europe gains pace
wider adoption of potato and maize
increased land under cultivation → deforestation
experimentation with crop rotation systems
experimentation with manure (from cities)
UK: enclosure acts, reducing open fields and communal lands → British (Second) Agricultural revolution
19th century: scientific innovation
scientific experimentation with new food plant varieties, use of fertilizers and disease control in US, Europe and Japan
increasing trade in new fertilizers (guano, nitrates from Chilean/Peruvian coastline)
mid 19th C onwards: Atlantic food trade using railroads and steamships (NA wheat floods European market) → agricultural depression
late 19th C: scientific plant breeding + invention of chemical fertilizer as it was predicted that guano and nitrates from tropical islands couldn’t satisfy future demand
EAT-Lancet Commission
2025
Scientific review of what constitutes a healthy diet for both humans and the planet
Norman Borlaug
1914 - 2009
“Father of the Green Revolution”
Nobel Peace Prize in 1970 for his contribution to the world food supply
1944, Mexico: He led a team that crossed wheat varieties to produce new high-yielding, semi dwarf and disease-resistant varieties
Norin 10 (a semi-dwarf wheat variety from Japan) was crossed with Mexican varieties
Expansion to Asia → India became self sufficient and exporting country
IR8
semi-dwarf rice developed by the International Rice Institute at the Philippines (IRRI) in the 1960s that conquers much of Asia
crossing between Peta (Java) and Dee-geo-woo-gen (Taiwan)
Green revolution (narrow definition)
invention and implementation of new high yielding varieties (HYVs) of wheat, maize and rice
1940 - 1970
HYVs have a higher volume of kernels per ear, on shorter stems
Green revolution (broader definition)
complemented by new land and water management techniques
state-coordinated programs of hybridized seed distribution
up-scaled investments in rural infrastructure
the spread of rural credit facilities
intensified use of pesticides and herbicides
global scale of agrarian growth
Increase in wheat yields in England in the 20th century
from 2 to 7 tons per hectare on average
(while it took England nearly 1,000 years to increase wheat yields from 0.5 to 2)
similar increase in many developing countries, especially in Asia and Latin America, but much less so in Sub-Saharan Africa
Why did Africa miss the green revolution?
unique ecology:
highly variable climate
soil heterogeneity → no silver bullet HYV
tropical soil easily exhausted
history of extensive farming
more limited food storage in tropical climate
lack of irrigation infrastructure
post-colonial states not ready
Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD)
EU council adopted May 2024, entering into force in June 2024
to require due diligence for companies to prevent adverse human rights and environmental impacts in the company's own operations and across their value chains
EU Parliament weakened directive’s scope Nov 2025
One Country One Priority (OCOP)
Promote Special Agricultural Products
Develop sustainable and inclusive value chains
Strengthen partnership and capacity building
Ensure environmental sustainability
One Commune One Product
program in Vietnam
to promote local products
Responsible consumption in the UK food sector
6 Revolutions
Neolithic (10,000 BC)
Age of discovery (1492-1800)
Agricultural (1700-1900)
Industrial (1760-1880)
Health and mortality transition (1850-1950)
Green (1950-1980)
Neolithic revolution
domestication of animals
storage of grain
traded surpluses
more control over food crops
% increase of wheat yields in developing countries
200% in 35 years (around 1960-1995)
20th century demographic miracle
80 billion hominids born over 4 million years
Post 1750: 28% of years lived
Post 1900: 20%
Post 1950: 13%
Environmental awareness in the early-modern period (1500-1800)
realization that wood is a finite resource and should be used sustainably
rapid deforestation
philosophers’ optimism in the age of enlightenment - humans will continue to develop as long as the earth exists, population growth might reduce and the earth will be found sufficient to support its inhabitants
Malthus! (1766-1834)
Environmental awareness during the Industrial revolution
coal is a finite resource!
why should we progress and sacrifice the well-being of the planet if it only results in a bigger population, not a happier one
‘Peak Oil’ theory
M. King Hubbert, 1956
oil under the ground is finite so oil extraction will reach a maximum and then decline
world oil production = bell curve
Dust Bowl / ‘Dirty thirties’
1930s
conversion of grassland → cropland
extensive deep ploughing displaced deep rooted grasses that trapped soil and prevented wind erosion
period of draught in the 1930s caused severe erosion, blowing away up to 75% of virgin topsoil
→ government program to conserve soils, soil erosion research exploded worldwide
London’s great smog
1952
High-pressure weather system
created envelope of cold air
preventing dispersion of pollutionthick ground level smog for 5 days → 4000 deaths, rise in asthma in kids exposed to the smog
→ Clean Air Act 1956
Rachel Carson
‘Silent Spring’, 1962
founder and catalyst of environmental awareness
her book warned against the harmful effects of of agrochemical pesticide DDT in agriculture on bird and human life
she accused the chemical industry of spreading disinformation and animal poisoning
she provoked wide spread discussion and DDT ban in the US (1972)
Agent Orange
an herbicide and defoliant chemical used by the U.S. military in the Vietnam War 1961-1971
led to huge environmental damage - destroyed Vietnamese cropland and around 18% of forests, animal species etc.
up to 4 million Vietnamese were exposed to it
around 1 million people disabled or suffering health problems as a result
Acid rain awareness
the term ‘acid rain’ was already coined in 1872 Manchester
in 1960s scientists began widely studying the phenomenon
caused by emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide
transboundary pollution
Critiques of environmental awareness
some predictions of the 1960/70s didn’t come true
early environmentalists were too negative, ‘prophets of doom’
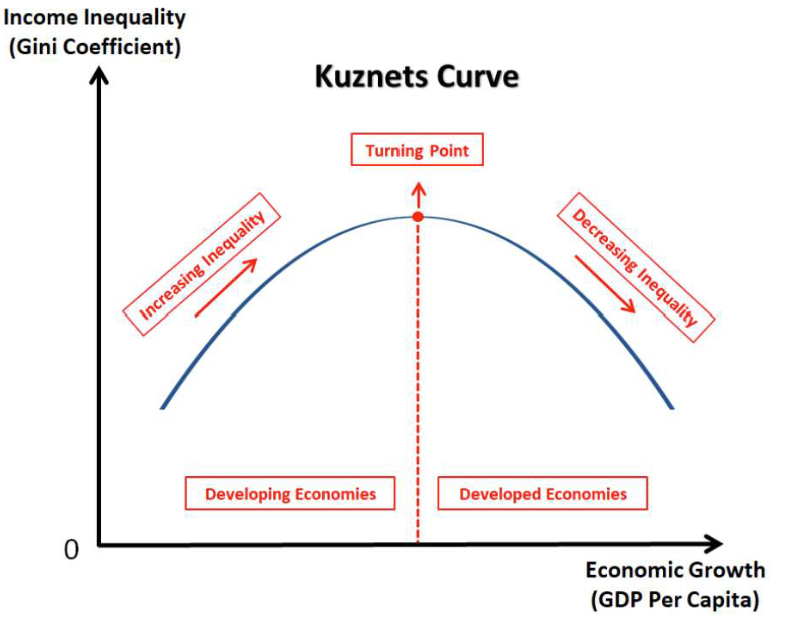
arguably, economies become more sustainable once a high level of GDP per capita is reached (environmental Kuznets curve)
scarcity induces innovation and technological progress
Clear new technology + strong landscape pressure
Technological substitution
Clear new technology + medium landscape pressure
Reconfiguration
Competing niches + strong landscape pressure
De- and realignment
Competing niches + medium landscape pressure
Transformation