Youngless: Biology Cell Transport (Cell Environments)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
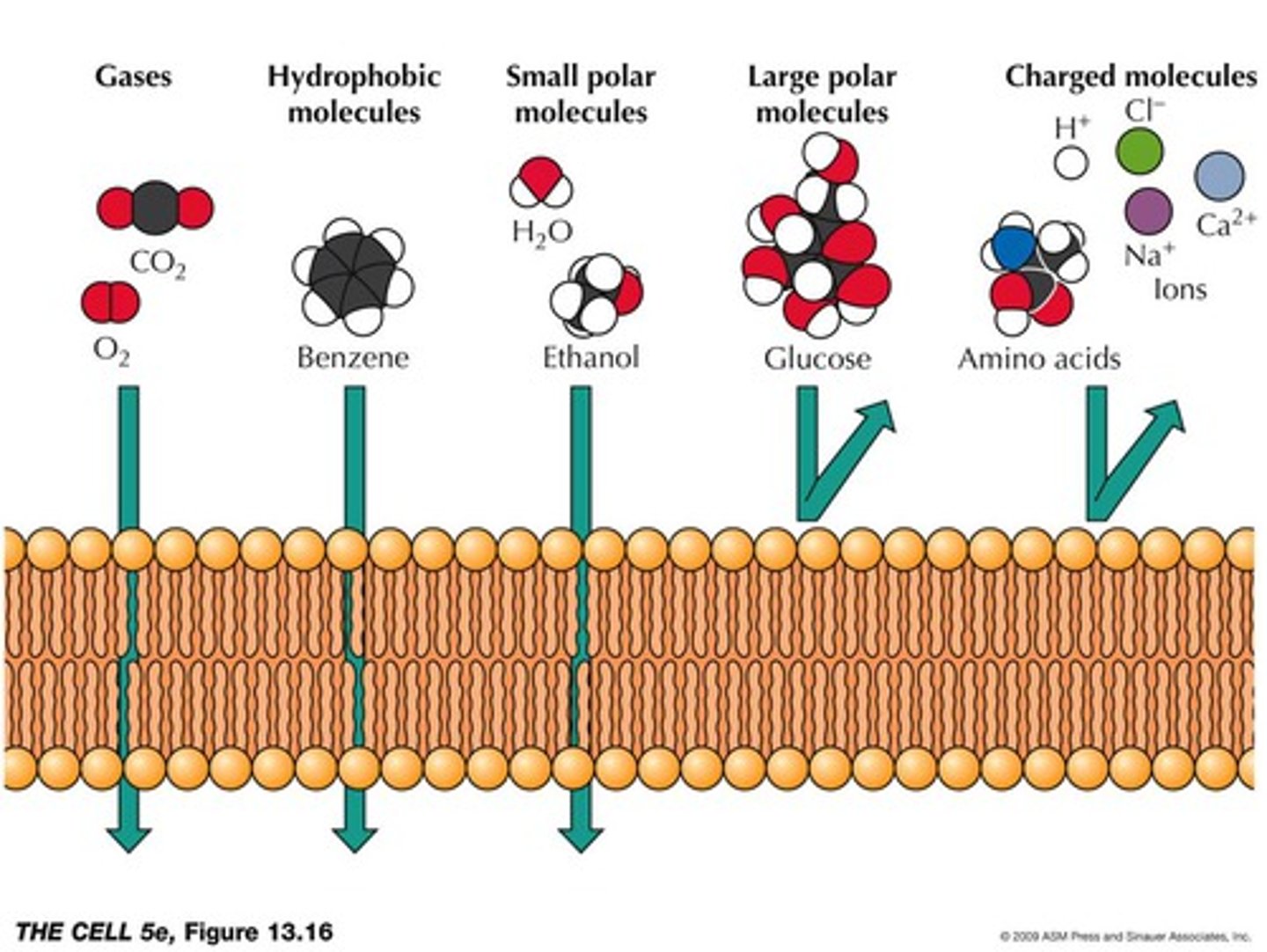
selectively permeable
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
passive transport (energy)
What type of transport Requires NO energy,
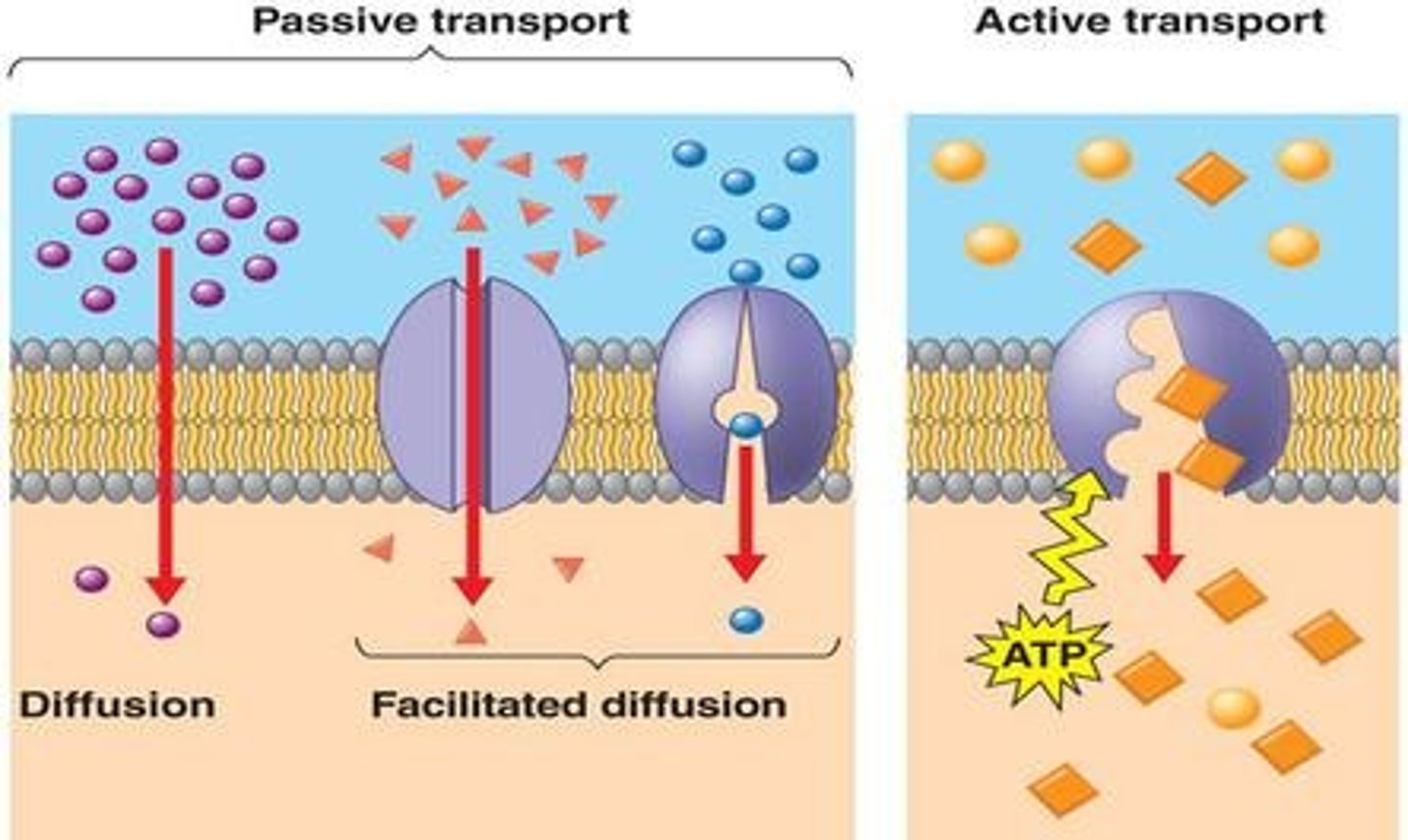
Passive transport (movement)
What type of transport moves molecules from high to low concentration, (Moves down the concentration gradient)
active transport (energy)
What type of transport requires Energy
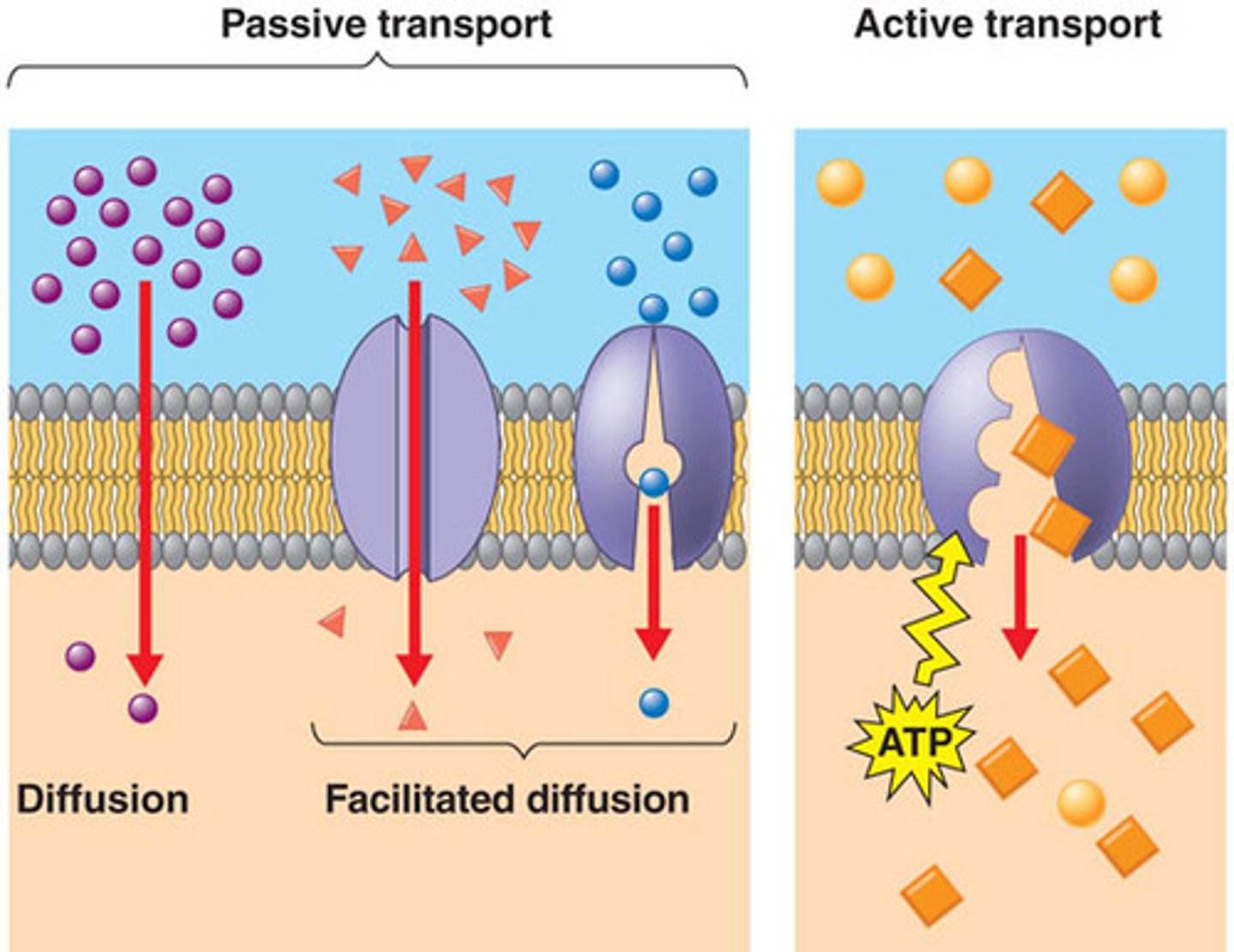
Active Transport (movement)
What type of transport moves material across a cell membrane from low concentration to high concentration.( Moves against a concentration gradient)
Solute
the substance that is dissolved (sugar)
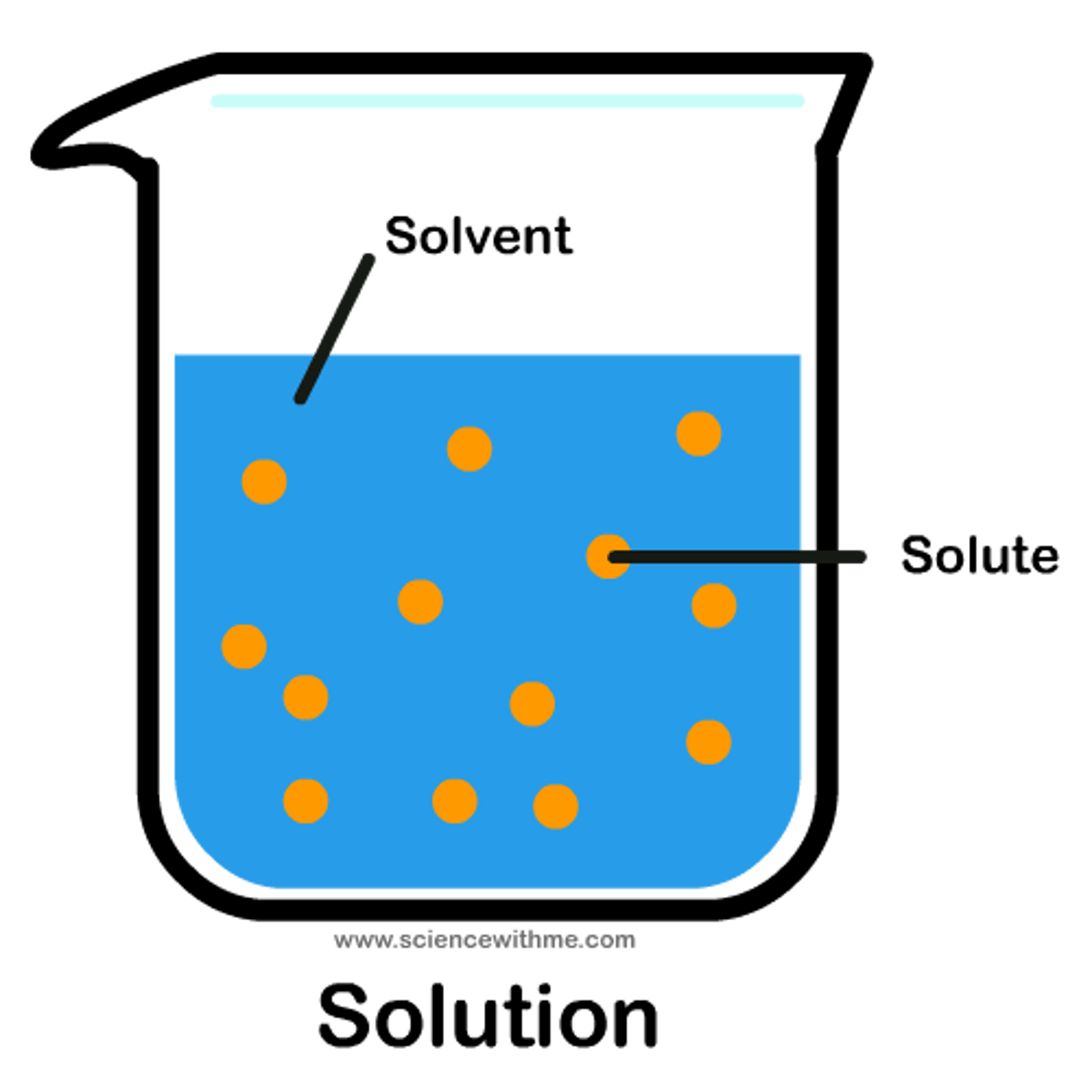
solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves in (water)
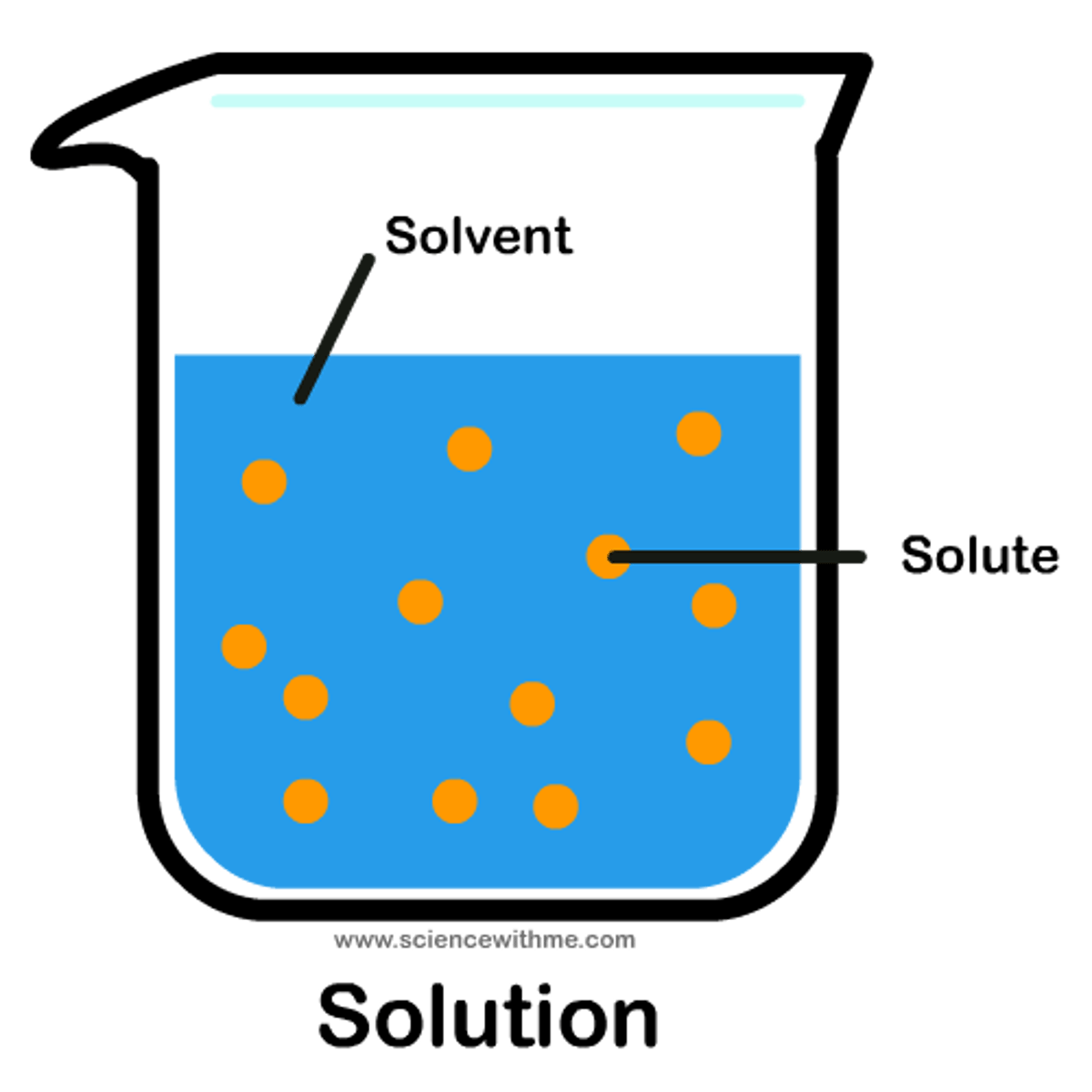
solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another. (solute + solvent = ?)

concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
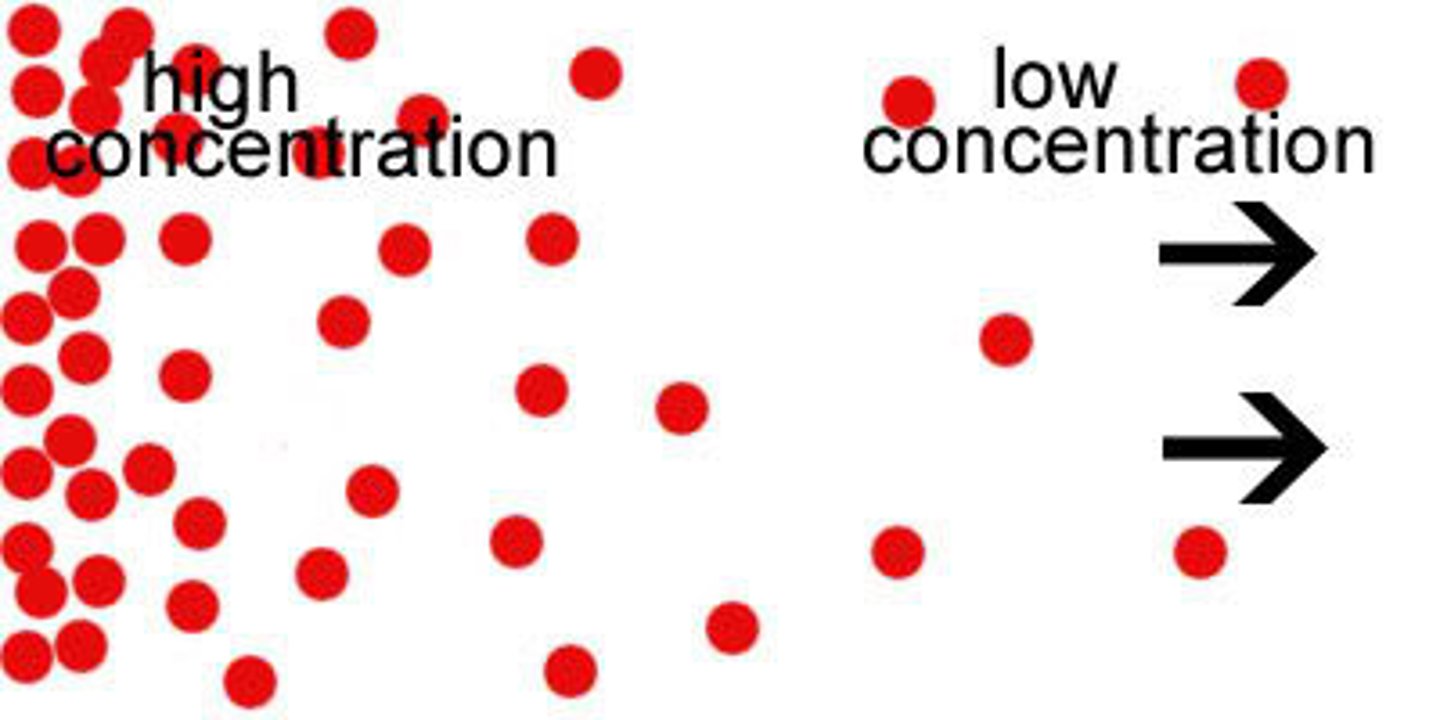
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
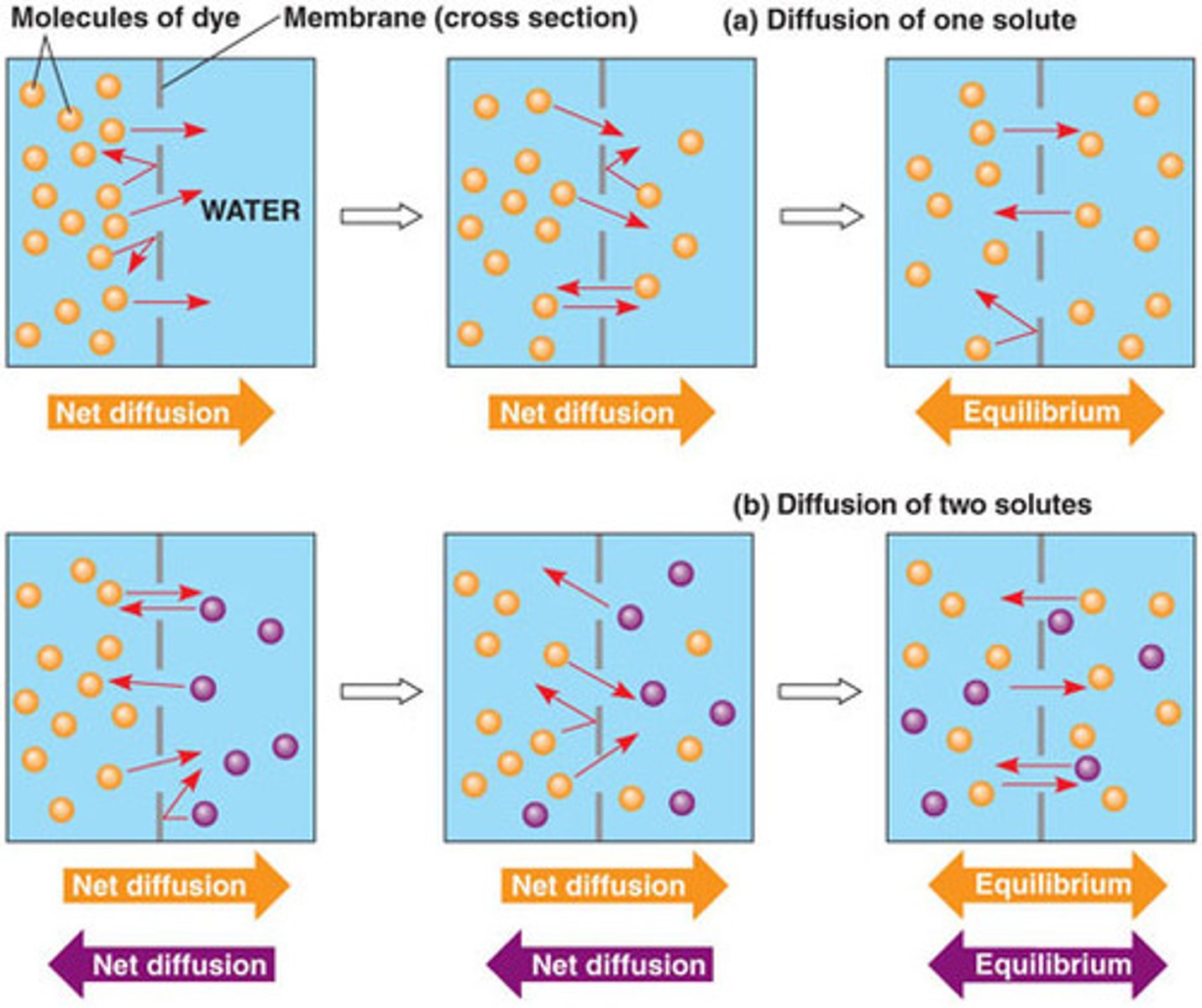
diffusion
osmosis
facilitated diffusion
What are 3 types of Passive Transport.
O2 (oxygen) and CO2 (carbon dioxide)
What molecules can DIFFUSE through a cell membrane?
facilitated diffusion
Passive Transport. Movement of specific molecules (sugar/glucose) across cell membranes through protein channels. Move from high concentration to low concentration. Moves DOWN the concentration gradiant.
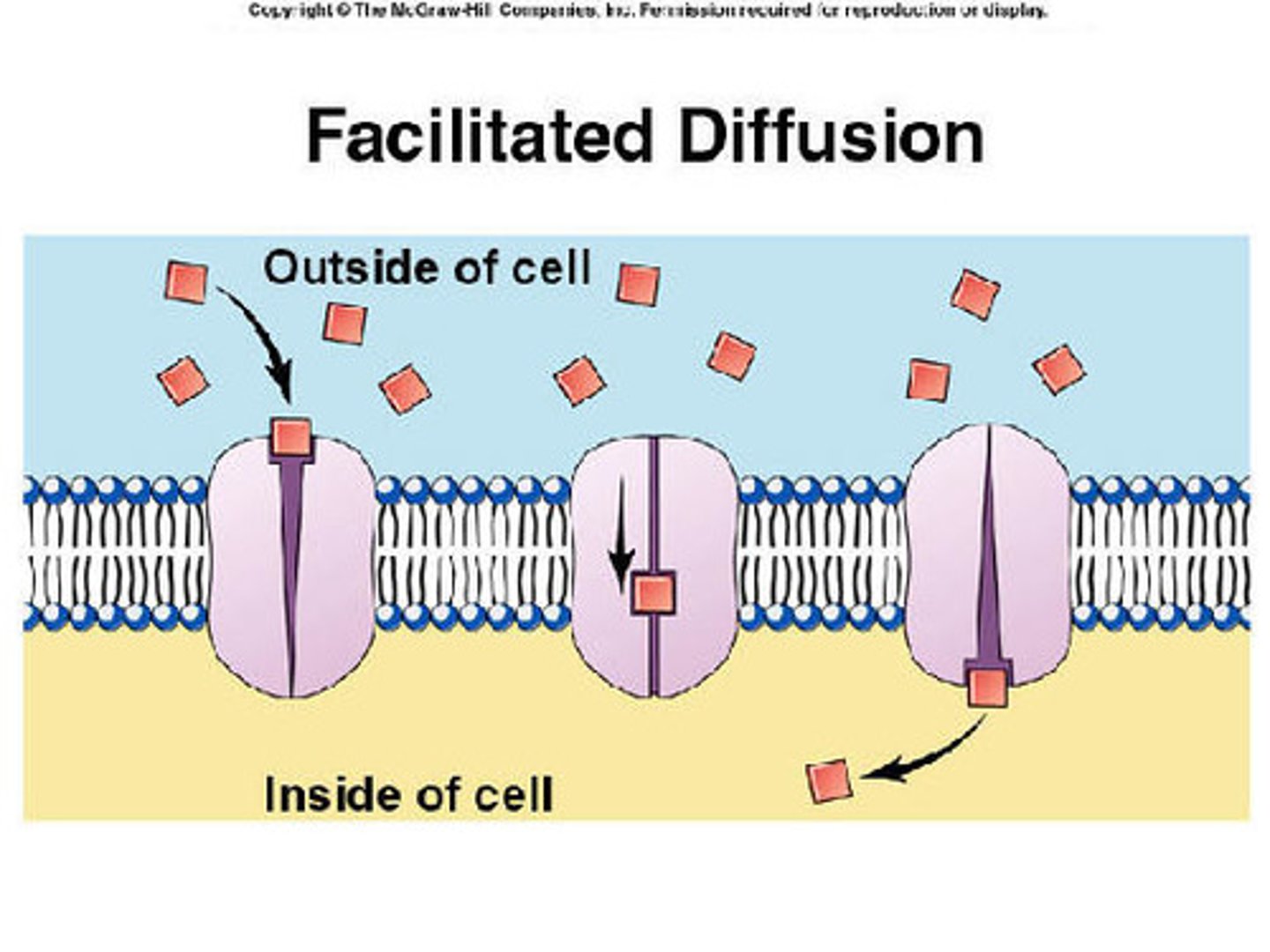
Sugar(glucose)
Salts (Ions)
What types of molecules use FACILITATED DIFFUSION to cross the cell membrane?
Osmosis
Passive Transport. Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Moves from high concentration to low concentration. Moves DOWN the concentration gradiant.
Water
What type of molecule uses OSMOSIS to cross the cell membrane?
hypertonic solution
The water concentration INSIDE the cell is greater then OUTSIDE the cell.
(more solute outside then inside)
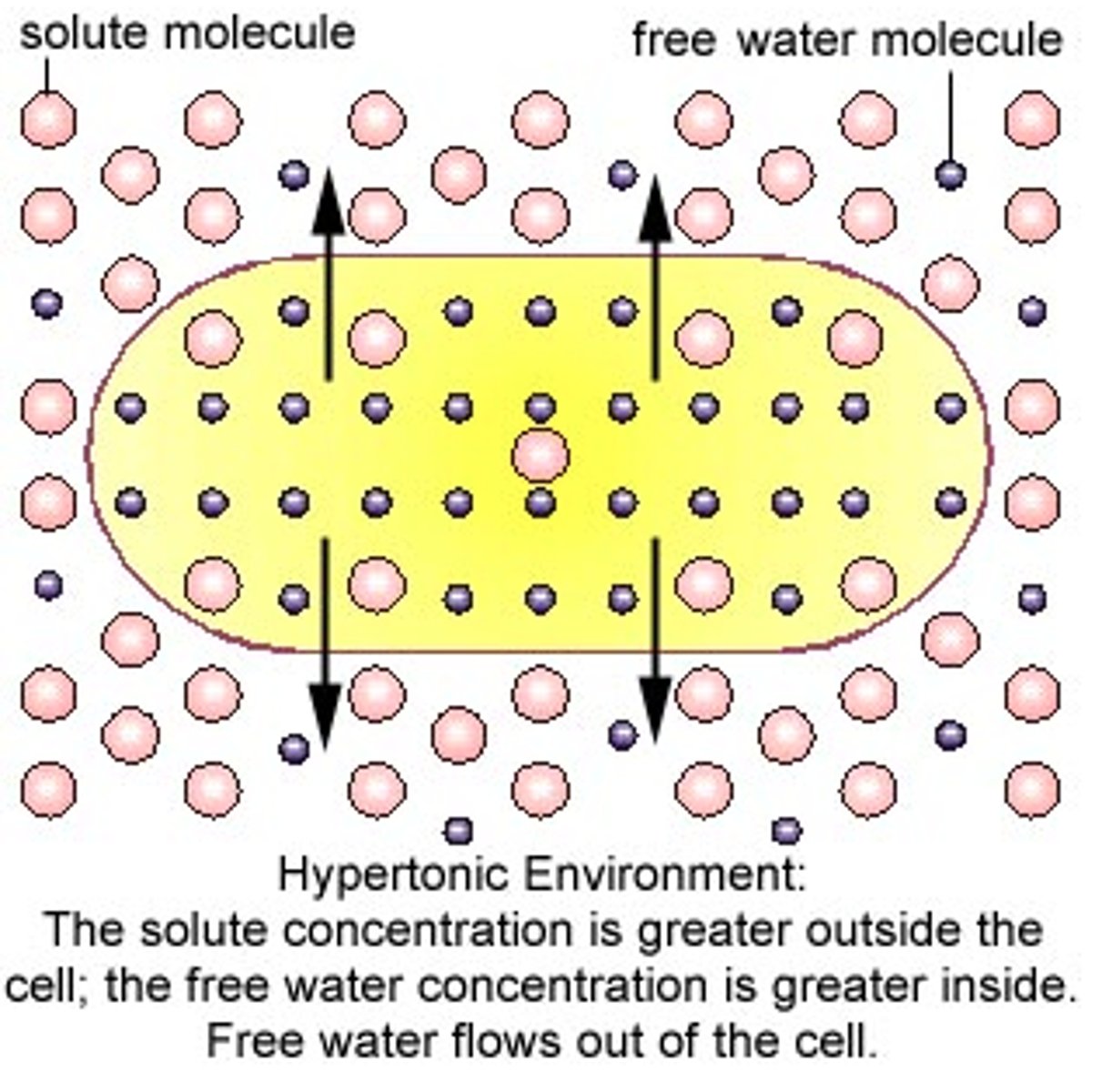
The cell shrinks/shrivels
What happens to the cell shape when placed in a hypertonic solution?
Water moves out of the cell
What will the water do in a hypertonic solution?
Move into the cell
Moves out of the cell
Equal amounts of water moves into and out of the cell (equilibrium)
hypotonic solution
The water concentration OUTSIDE the cell is greater than INSIDE the cell
(more solute inside the cell then outside the cell)
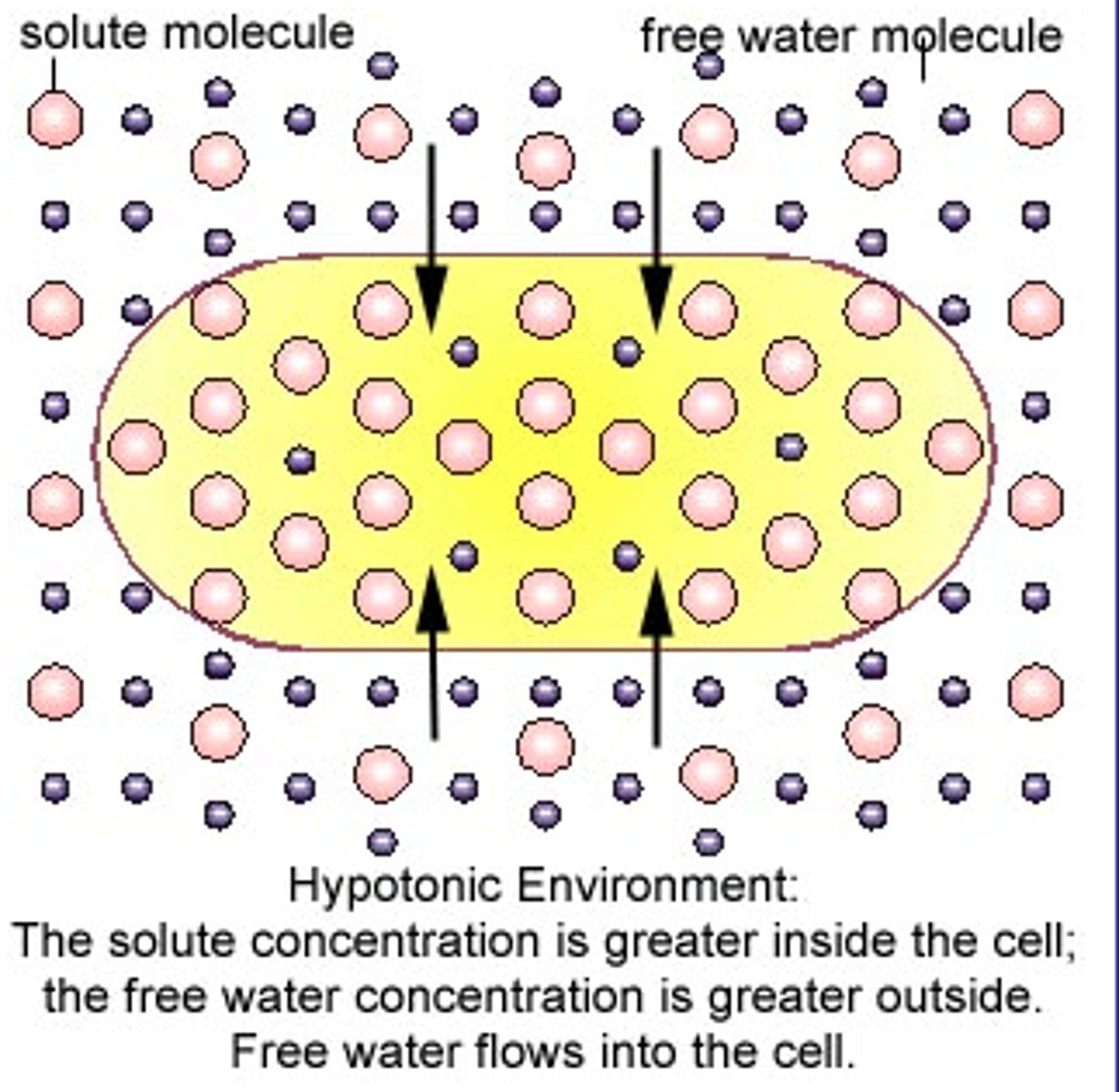
Water moves into the cell
What will the water do in a hypotonic solution?
Move into the cell
Moves out of the cell
Equal amounts of water moves into and out of the cell (equilibrium)
Cell swells
What happens to a cell shape in a hypotonic solution?
isotonic solution
The water concentration OUTSIDE the cell is EQUAL the water concentration INSIDE the cell
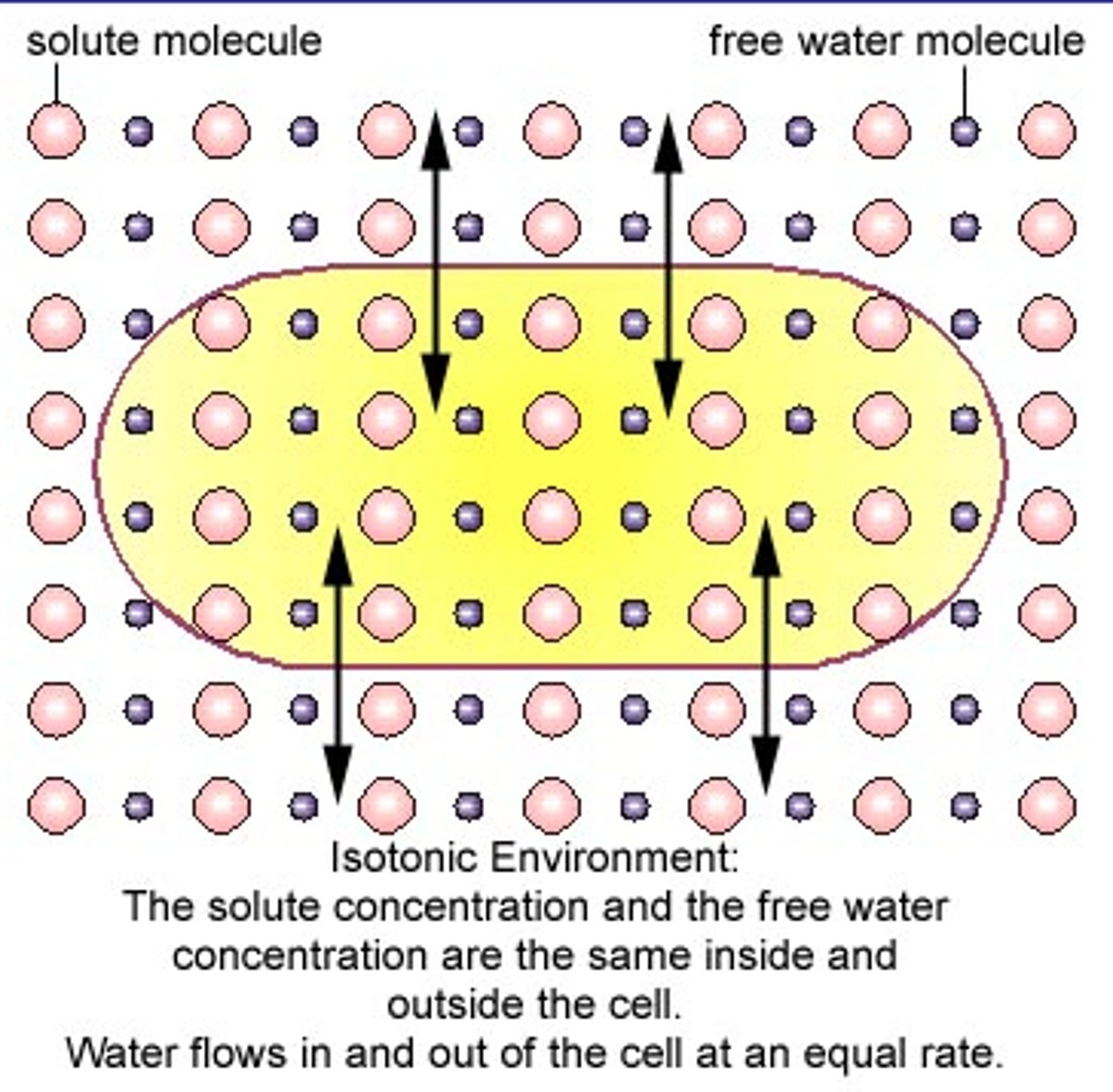
Equal amounts of water moves into and out of the cell (equilibrium)
What will the water do in a isotonic solution?
Move into the cell
Moves out of the cell
Equal amounts of water moves into and out of the cell (equilibrium)
Cell stays the same size
What happens to the cell shape in an isotonic solution?
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Sodium - Potassium Pump (molecular pumps)
What are the 3 types of Active Transport?
Swells
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
Shrinks
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
Stays the same size
What happens to a cell in a isotonic solution
Hypotonic
What type of solution has more water outside the cell than inside the cell?
Hypeprtonic
What type of solution has more water inside the cell than outside the cell?
Isotonic
What type of solution has equal amounts of water inside and outside the cell?