compsci quiz
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
The following statement ________.
*num3 = *val;
stores the value of the variable pointed to by val into the variable pointed to by num3
Consider the following statements:
int *s;
int m;
int j;
j = 25;
s = &j;
m = j;
After these statements, which of the following statements will change the value of j to 88?
*s = 88;
Use the delete operator only on pointers that were
created with the new operator in dynamic memory
Which of the following statements is NOT valid C++ code?
All of these are invalid
int ptr = int *num1;
int ptr = &num1;
float num1 = &ptr2;
void calc( int* r)
{
* r += 2;
}
int main( )
{
int *a = new int(5);
calc( a );
cout << *a;
}
What is the output of *a?
7
A pointer variable stores a(n) ___________.
address
The amount of memory used by an array depends on the array's data type and the number of elements in the array.
True
In C++, the name of an array is interpreted as
the address of the first element
What will the following code display?
int numbers[] = {99, 87, 66, 55, 101};
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++)
cout << numbers[i] << " ";
87 66 55
Consider the following code segment:
int p = 9, q = 8;
int ptr1 = &p;
int ptr2 = &q;
ptr1 = ptr2;
Which of the following figures correctly illustrates the memory of these variables?
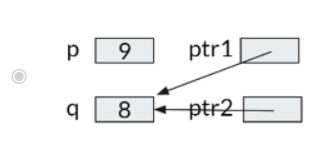
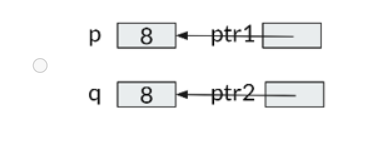
Consider the following code segment:
int p = 9, q = 8;
int ptr1 = &p;
int ptr2 = &q;
*ptr1 = *ptr2;
Which of the following figures correctly illustrates the memory of these variables?
What is the constructor that takes no parameters?
default constructor
It is often a good idea to specify the data members as public to allow the client program to access the data member of a class.
False
A class may contain multiple constructors if
They have distinguishable argument lists
Which of the following creates an object of the "Time" class, and initialize it using a constructor that takes three parameters?
Time t(9, 40, 'A');
When C++ sees a ∆ b, where a is ClassName object and b is <Type> object, and ∆ is overloaded using the member function (internal) method. a ∆ b is equivalent to call.
a.operator∆(b)
Which of the following operators cannot be overloaded?
. :: #
When we define and implement operator overloading in C++:
It may or may not be a class member function
Which operator overloading declaration is "internal"?
bool Time::operator<(const Time & t)
To implement an overloaded binary operator for a class with an external function, two function parameters are required.
True
Insertion to the beginning of an array-based implementation list is generally slower than insertion to its end.
True
Which of the following function is the copy constructor for List ADT
List::List(const List & origList)
C++ compiler does not provide any default copy constructor and assignment operator.
False
The assignment operator for a class must not be a function member.
False
When an object's lifetime is over, the object's _____________ is called automatically
destructor
the next field of the last node in a linked list
holds a null pointer
What are the advantages of using the linked list?
Insert new item without shifting
Can expand/contract as necessary
Delete existing item without shifting
Nodes in a linked list are stored in contiguous memory.
False
What is the operation of the following statements for a linked list?
Node * temp = head;
head = new node;
head->data = 25;
head->next = temp;
insert a node to the start of the linked list
A linked list is a series of connected
nodes
What value does function mystery return when called with a value of number = 4?
int mystery( int number )
{
if (number == 0)
return 1;
else
return ( number * mystery( number – 1 ) );
}
24
When computing Fibonacci numbers, the standard recursive algorithm (based on the definition of the Fibonacci number) is less efficient than iterative algorithms.
True
Consider the following function:
int Func(int x, int y) {
if (x == y) {
return 0;
}
else if (x > y) {
return Func(x - 1, y) + 1;
}
else {
return Func(x, y - 1) + 1;
}
}
What will be the return value of a function call to Func(5,20)? _________
15
To solve a problem recursively, you must identify at least one case in which the problem can be solved without further calling itself.
True
Consider the following function:
void test_a(int n)
{
cout << n << " ";
if (n > 0)
test_a( n - 2 );
}
What is printed by the call test_a(4)?
420
How many times will the following function call itself if 5 is passed as the argument?
void showMessage(int n)
{
if (n>0){
cout << “good day!” << endl;
showMessage(n-1);
}
}
5
how many times will the following function call itself if 5 is passed as the argument?
void showMessage(int n)
{
if (n>0){
cout << “good day!” << endl;
showMessage(n-1);
}
}
An infinite number of times
What is the height of an empty tree?
-1
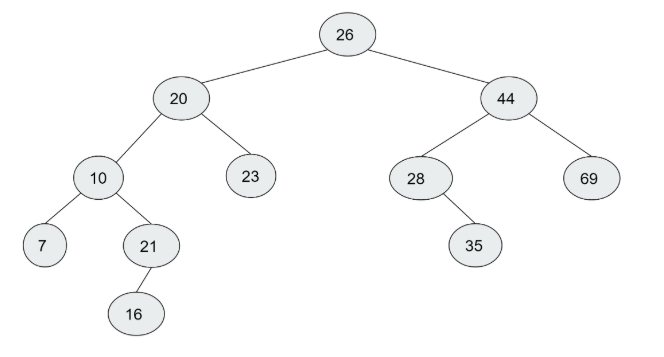
Which of the following is correct about the tree shown below:
It is NOT a binary search tree because we can find a node whose data is smaller than some node in its left sub-tree.
To list all the nodes in a binary search tree in increasing order, what kind of traversal should be used?
inorder
Consider writing a recursive function that computes the sum of the data field of all nodes in a binary tree. The function’s prototype is:
Sum(BinNode * root);
Which of the following is the correct recursive case for this function?
return Sum(root->left) + Sum(root->right) + root->data;
Storing data using a binary search tree uses less space than using a linked list.
False
Consider the following binary search tree.
Consider inserting a new data item 12 into this BST. Then the new node should become the _________ (left child or right child) of the node ______ (write the data value of the node who would become the parent of the inserted node).
right child , 9
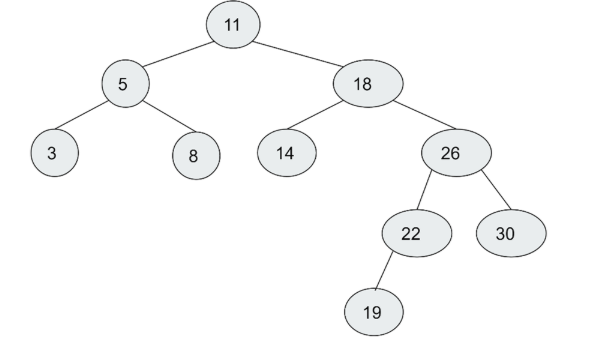
The preorder traversal of the tree shown below should be
11 5 3 8 18 14 26 22 19 30
Quicksort performs better for a sorted list than for a random list.
False
Quicksort on average has computing time
O(n log n)
insertion sort on average has computing time
O(n2)
Which of the following formulas in big-O notation best represents the expression n3 + log(n) + 100n2 + 9020?
O(n3)
What is the running time of the following code segment?
int s = 0;
for(int i=0; i<2n; i++){
s += i*i;
}O(n)
What is the running time of the following code segment?
int s = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n*n; j++){
s += 1;
if(j >= n)
{
break;
}
}
}O(n^2)