Functionality
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ppt 1 and 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Superior colliculi
Process visual information
Inferior colliculi
Process auditory information
Tectum
Superior and inferior colliculi make it up.
Substantial nigra
Contains neurons that release dopamine
Red nucleus
Communicates with motor neurons in the spinal cord.
Reticular formation
Involved with sleep and arousal, temperature control, and motor control. The mid brain also gives rise to several cranial nerves.
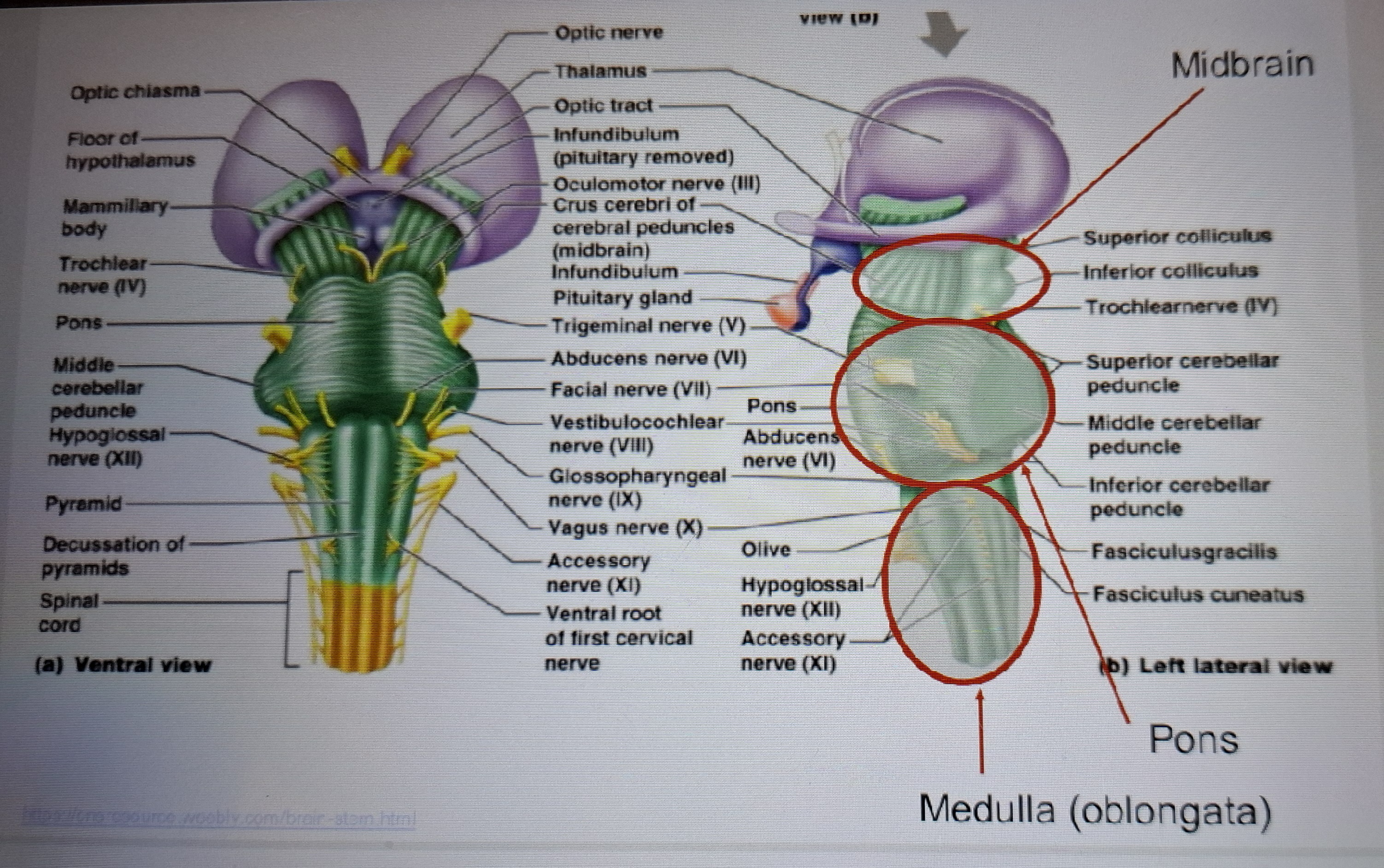
Pons
Attached to the cerebellum and contains motor control and Sensory nuclei and gives rise to cranial nerves.
Medulla
Contains cranial nerves nuclei and marks the transition brain to spinal cord.
Nuclei regulates breathing and heart rate.
All axons from the to the spinal cord run through the medulla.
Brainstem
Contains pons,medulla and cerebellum.
Cerebellum"the little brain”
Elaborated convoluted and densely packed structure involved in motor coordination and learning.
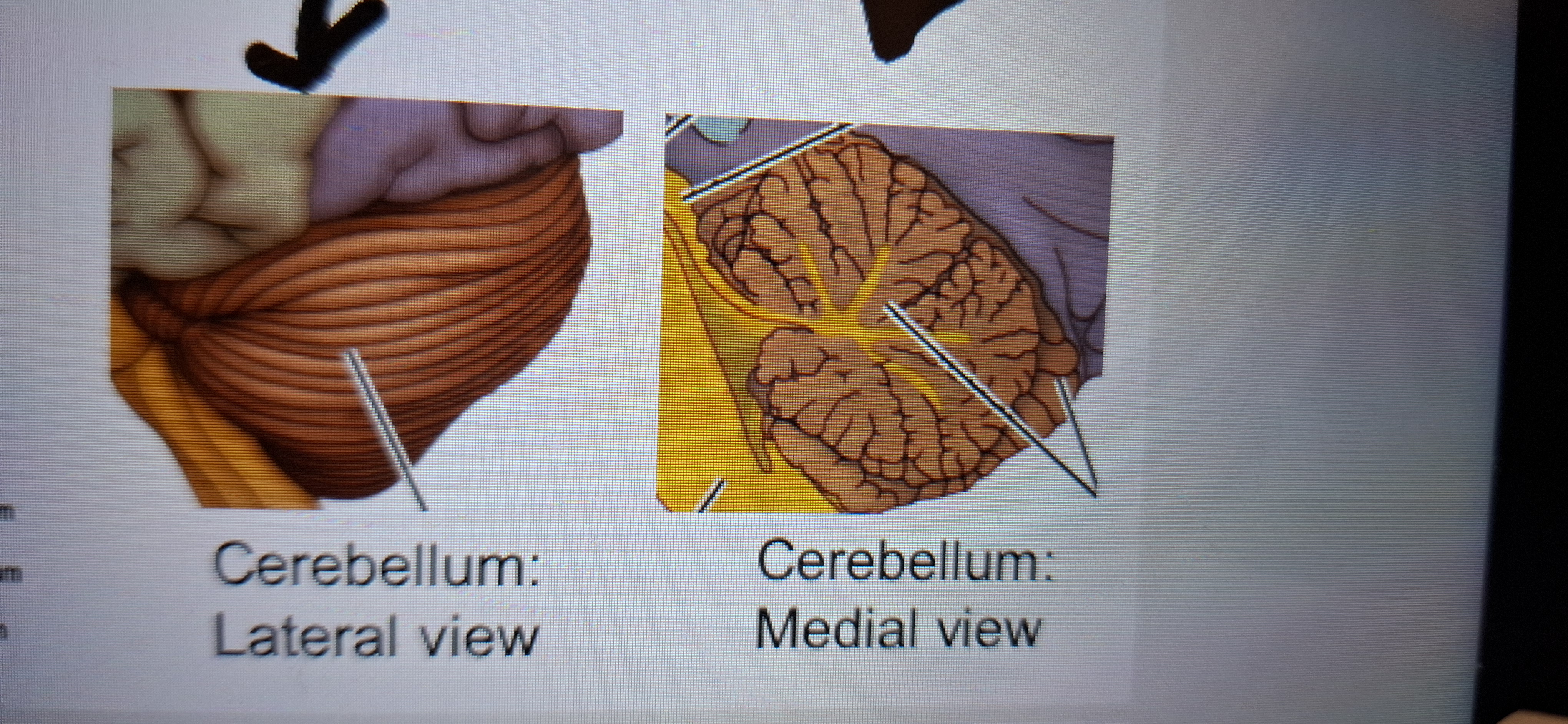
Three developmental parts of medulla
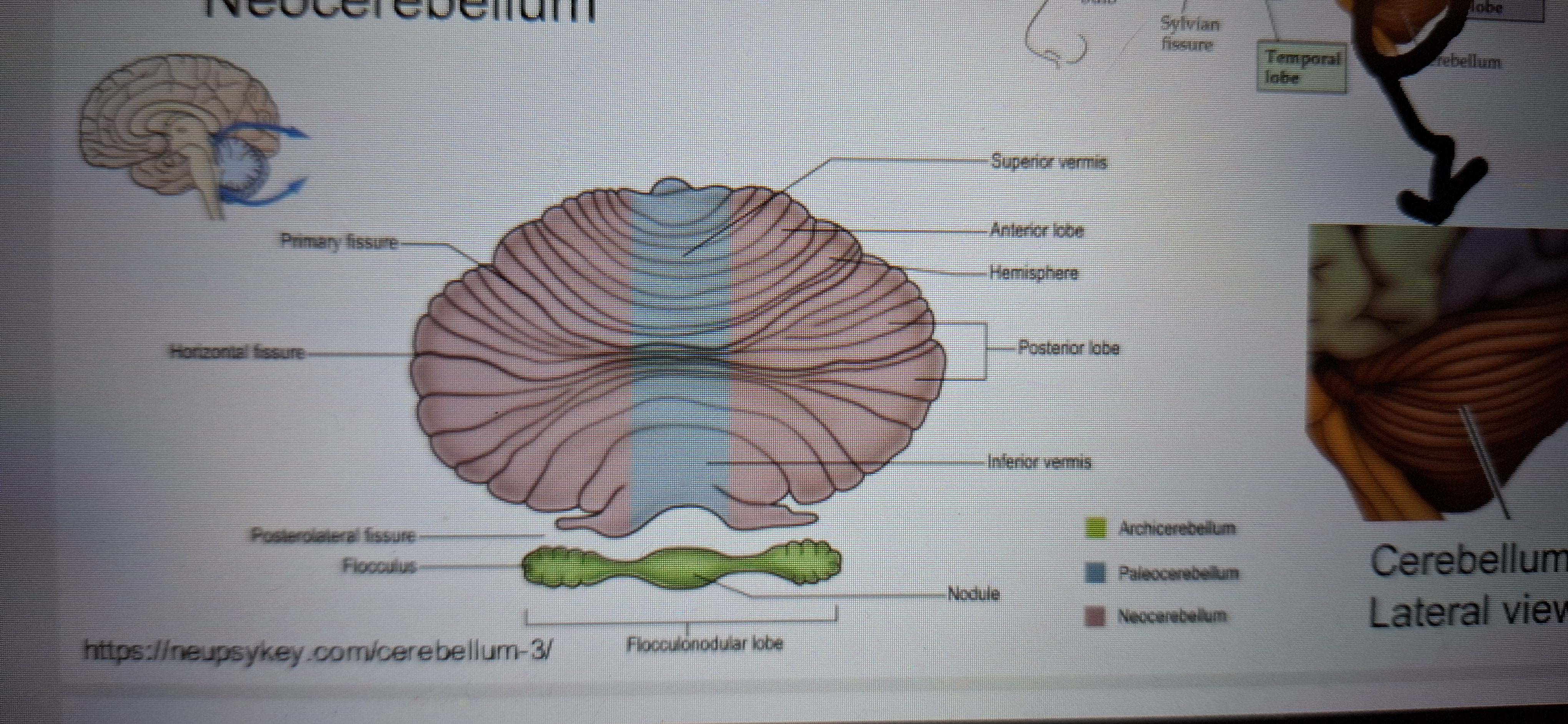
Archicerebellum
Paleocerebellum
Neocerebellum
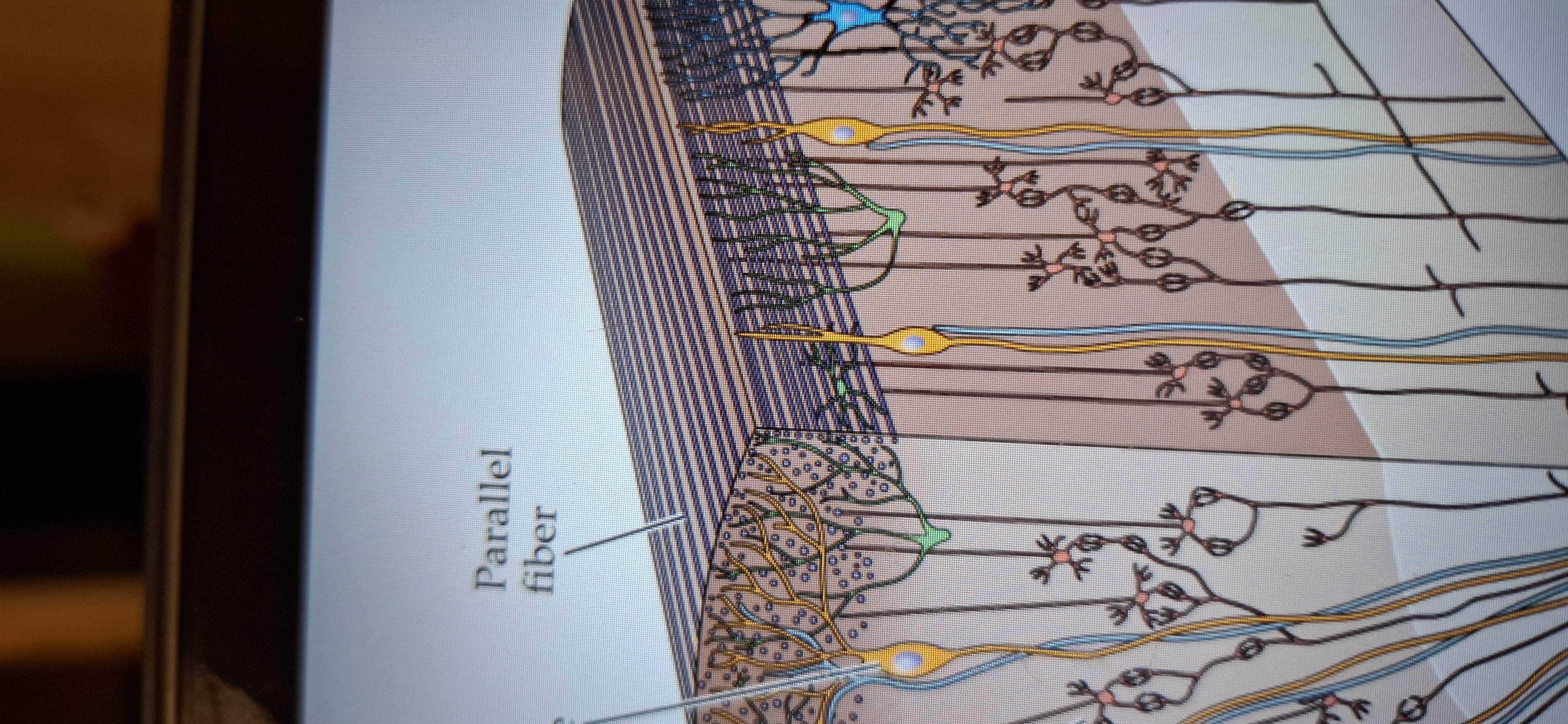
Main components of neocerebellum.
Purkinje cell, granule cell, and parallel fibres.
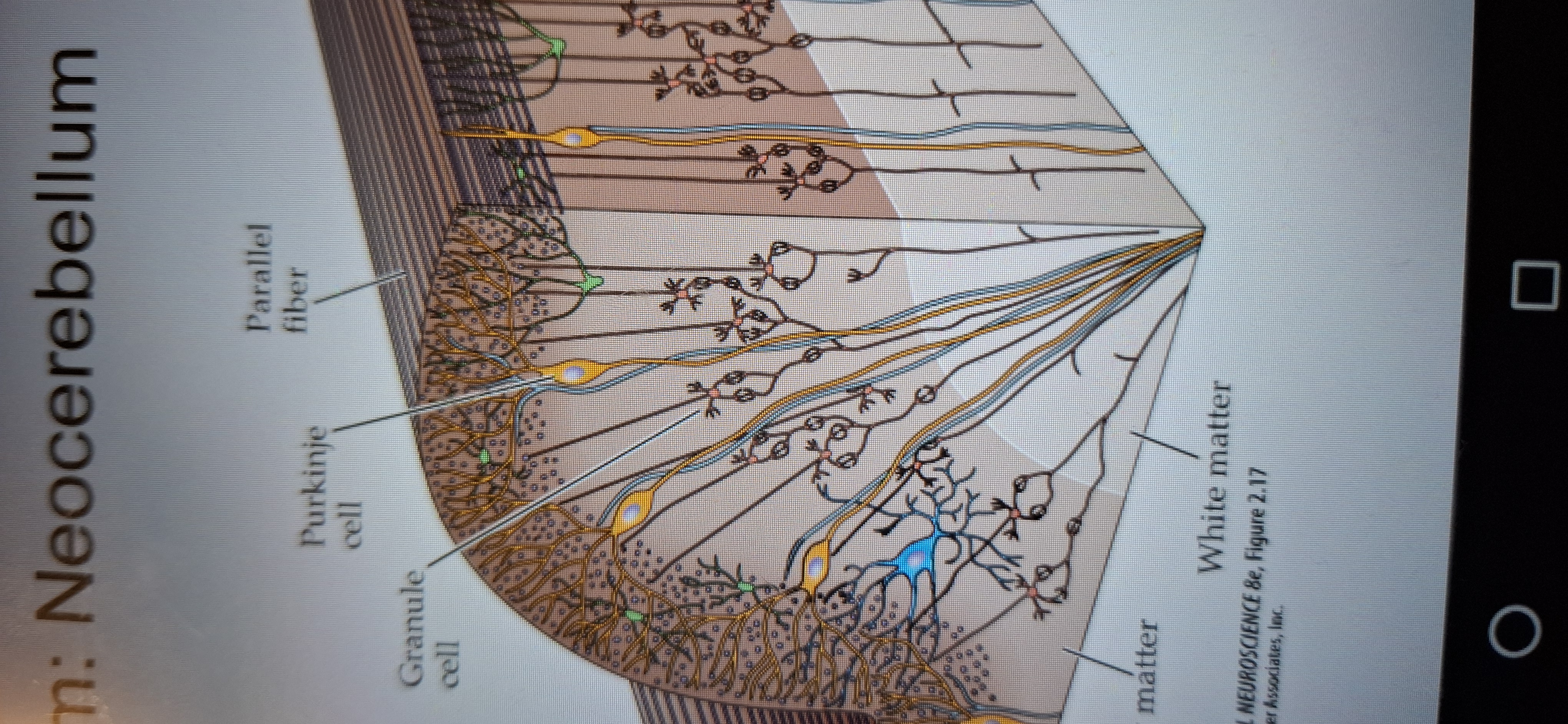
Purkinje cell
The middle layer, it's large cells form a single row.
Granule cell
Layer composed of small neurons whose axons form the third layer.
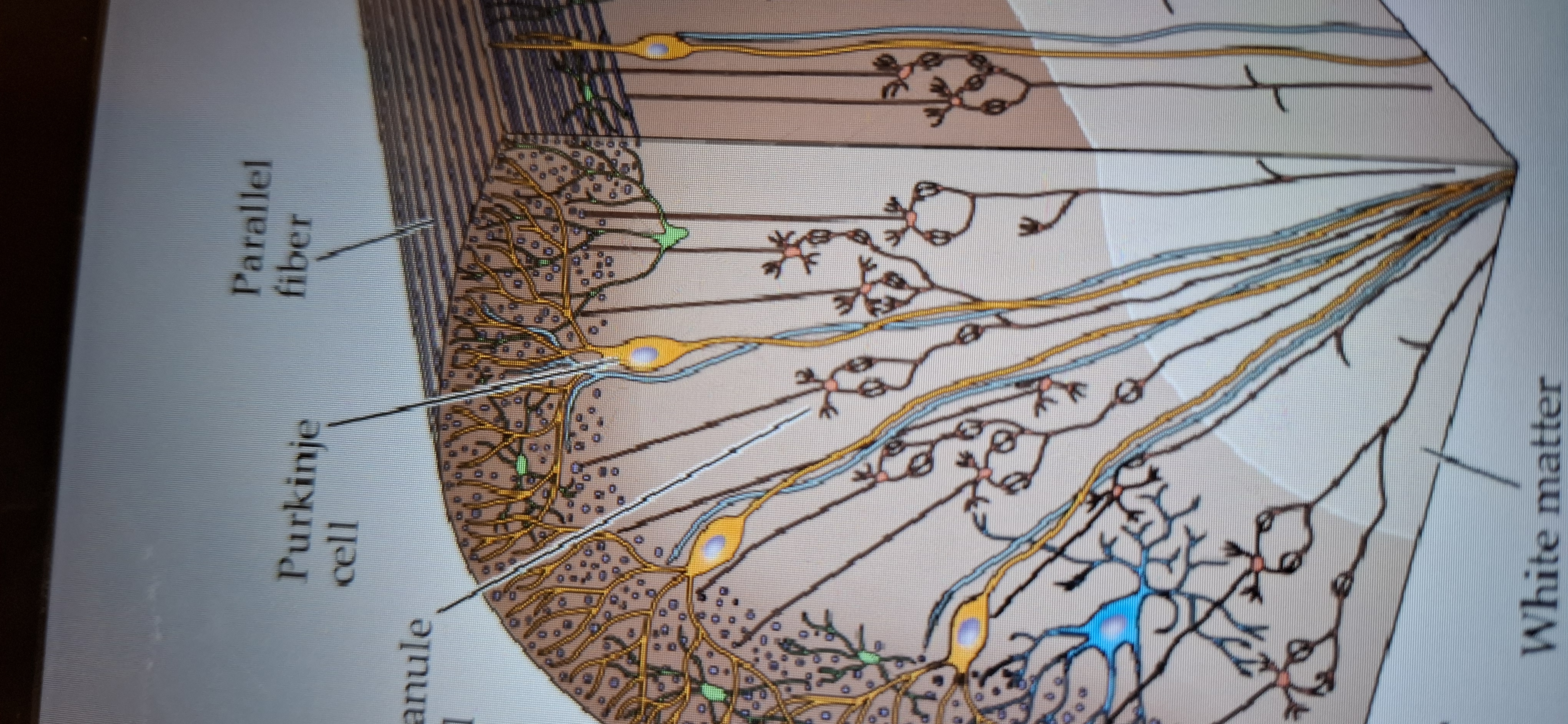

Parallel fibres
Makes up the third outermost layer(also called molecular)
Cortical regions
Communicate via tract of axons(fascicles)
Short-to nearby cortical regions
Longer-to other parts of cortex
Connection between hemispheres via the corpus callosum.
Long multisynaptic chains through subcortical regions.
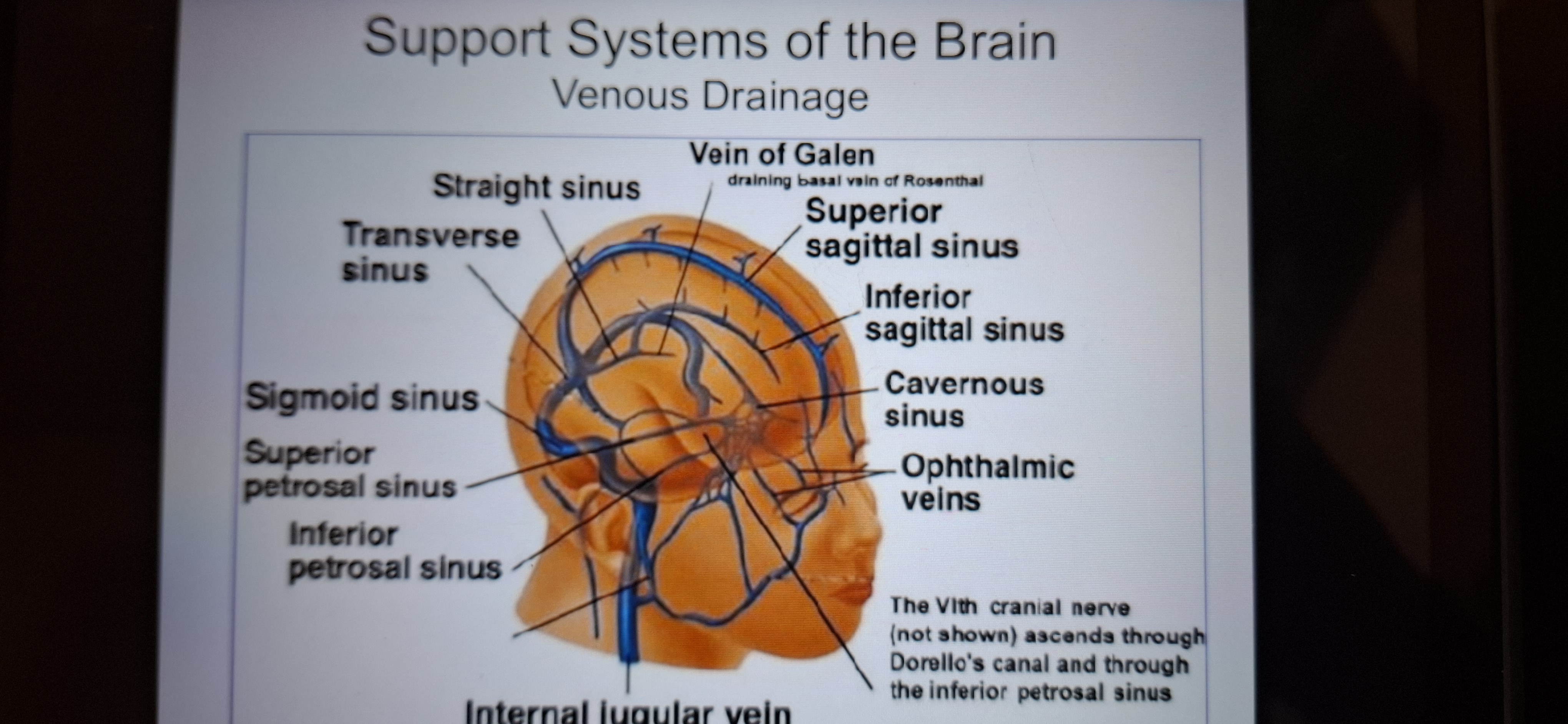
Support systems of the brain
1 Arterial circulation
2.venous drainage
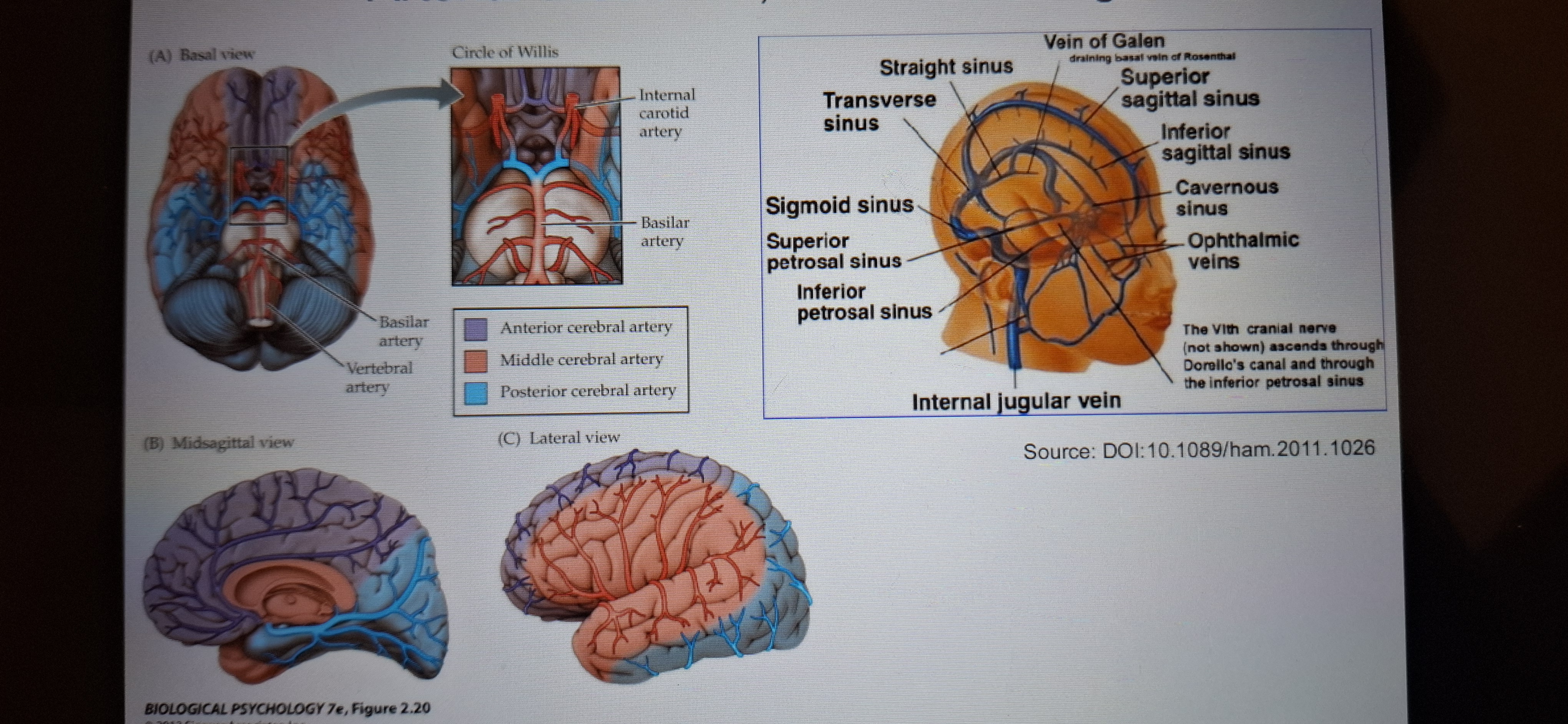
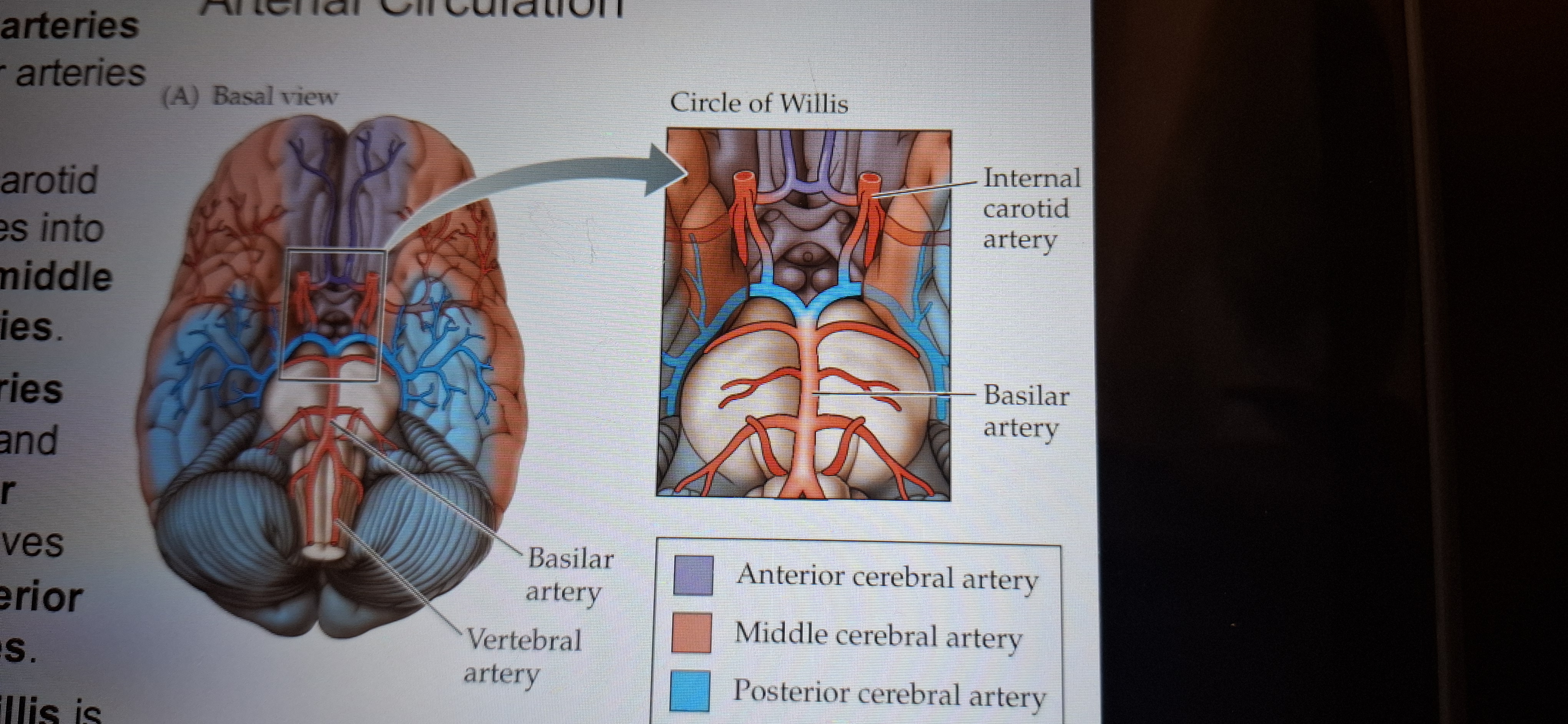
Arterial Circulation
Carotid arteries are the major arteries to the brain.
The internal carotid artery branches into anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
Vertebral arteries enter the skull and form the basilar artery,which gives rise to the posterior cerebral arteries.
Circle of willis
Is a structure formed by the major cerebral arteries.
Support drainage system of the brain.
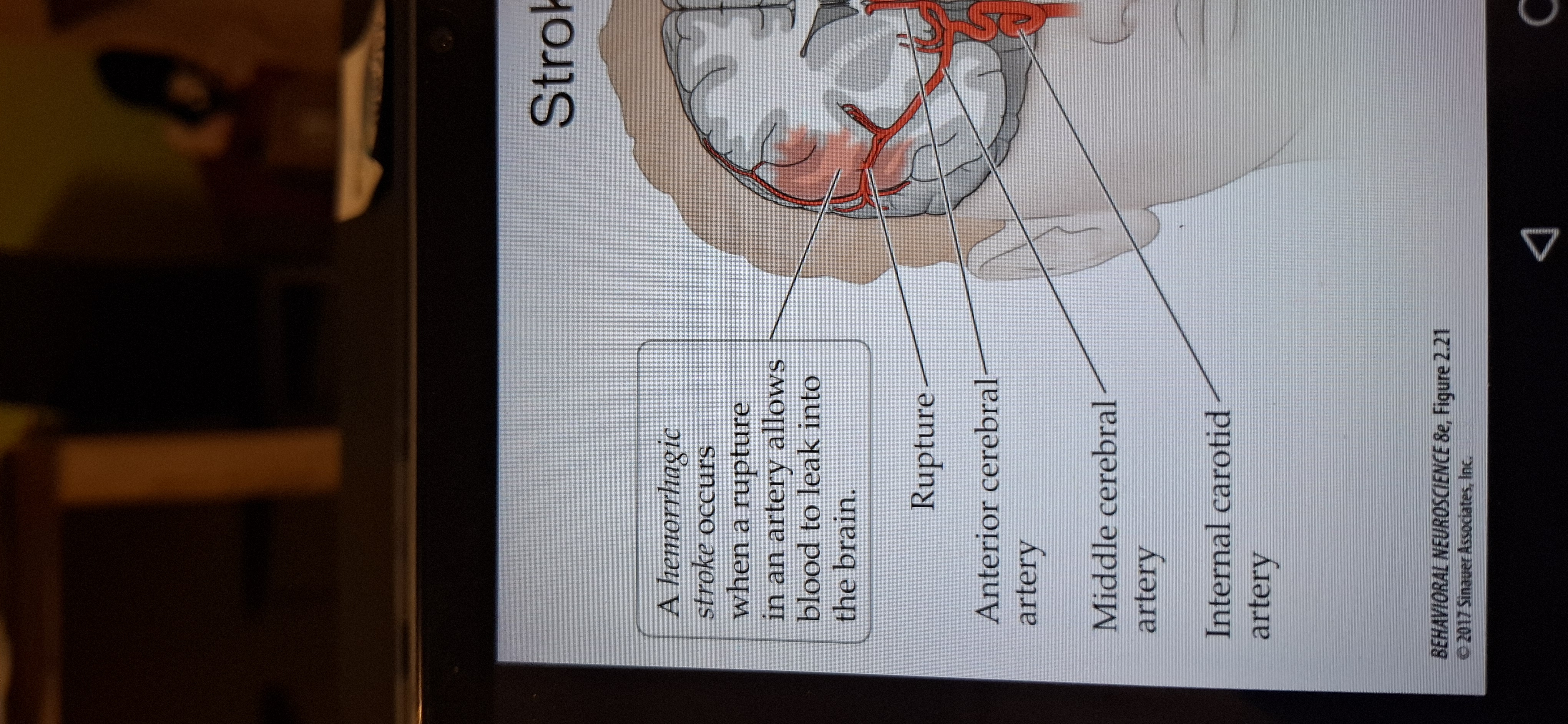
Haemorrhagic stroke
When a rupture in an artery allows blood to leak into the brain (15%)
Mass lesions can displace nervous system structures so severely that they are shifted from one compartment to another. A situation called herniation.
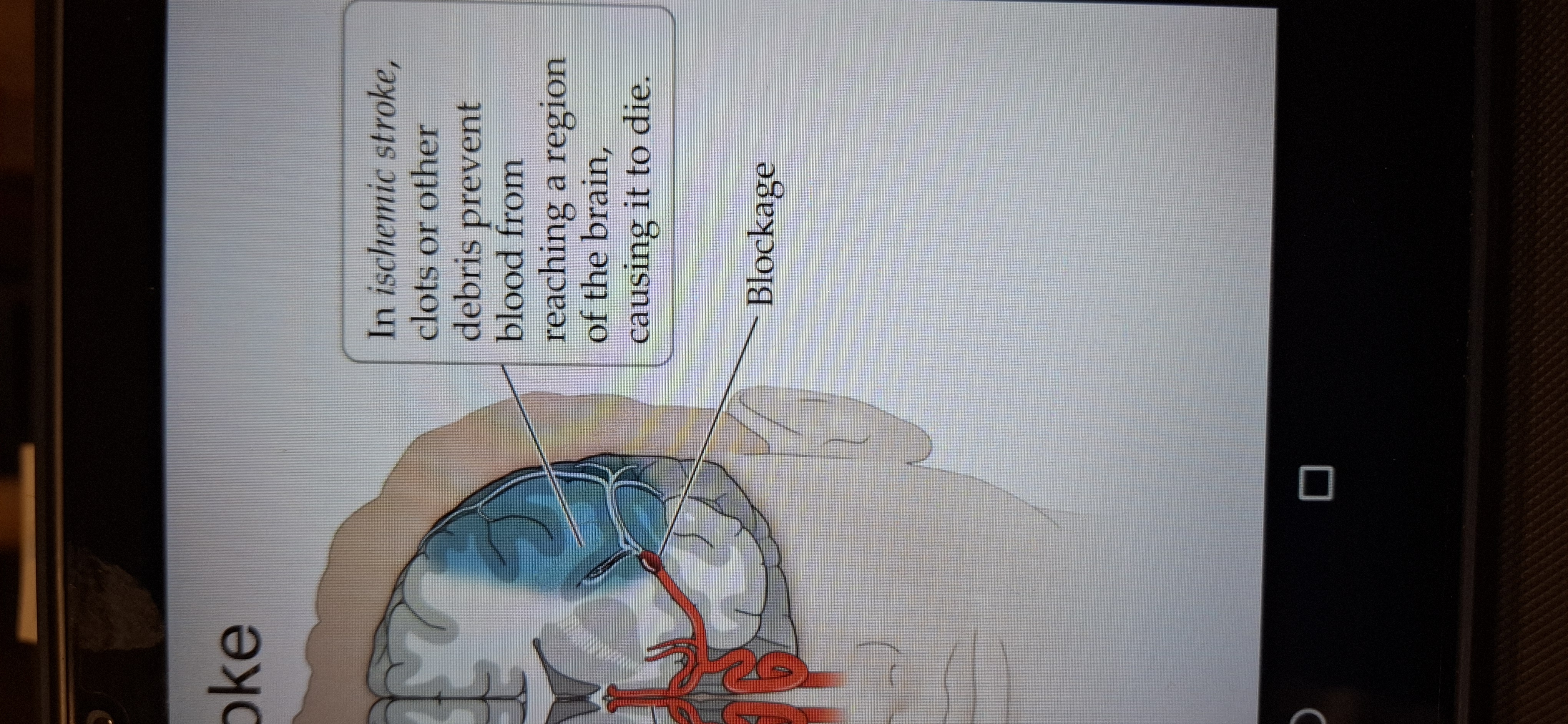
Is Ischemic stroke(brain infarct)
When clots or other debris prevent blood from reaching a region of the brain, causing it to die. 85%
Ventricular system
A series of chambers fills with CSF.
CSF(cerebrospinal fluid) has 2 main functions:
1.Acts as a shock absorber
2.provides an exchange medium between blood and brain.
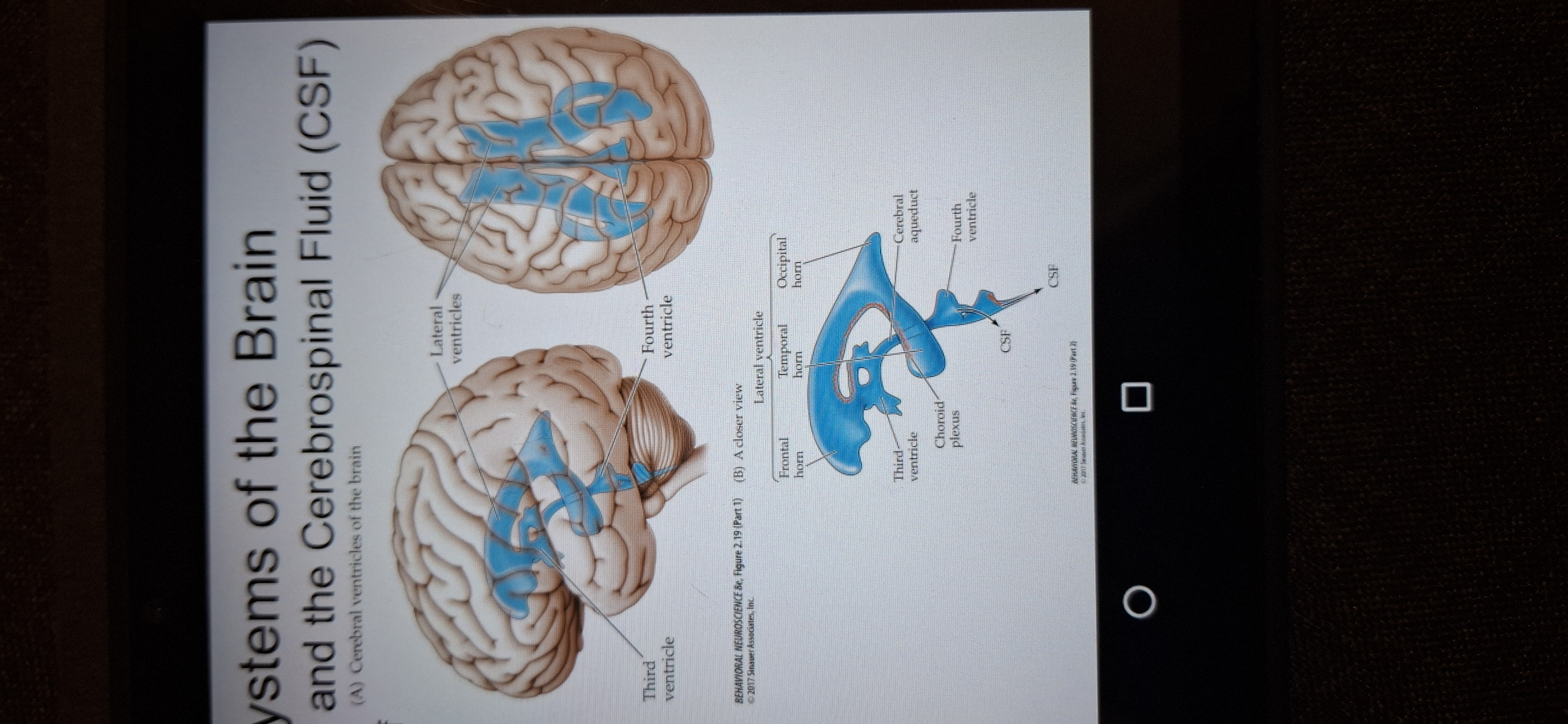
Choroid plexus
Membrane which produces csf.
Flow of csf
From third ventricle to the fourth ventricle whre it exists to circulate in the brain and spinal cord.
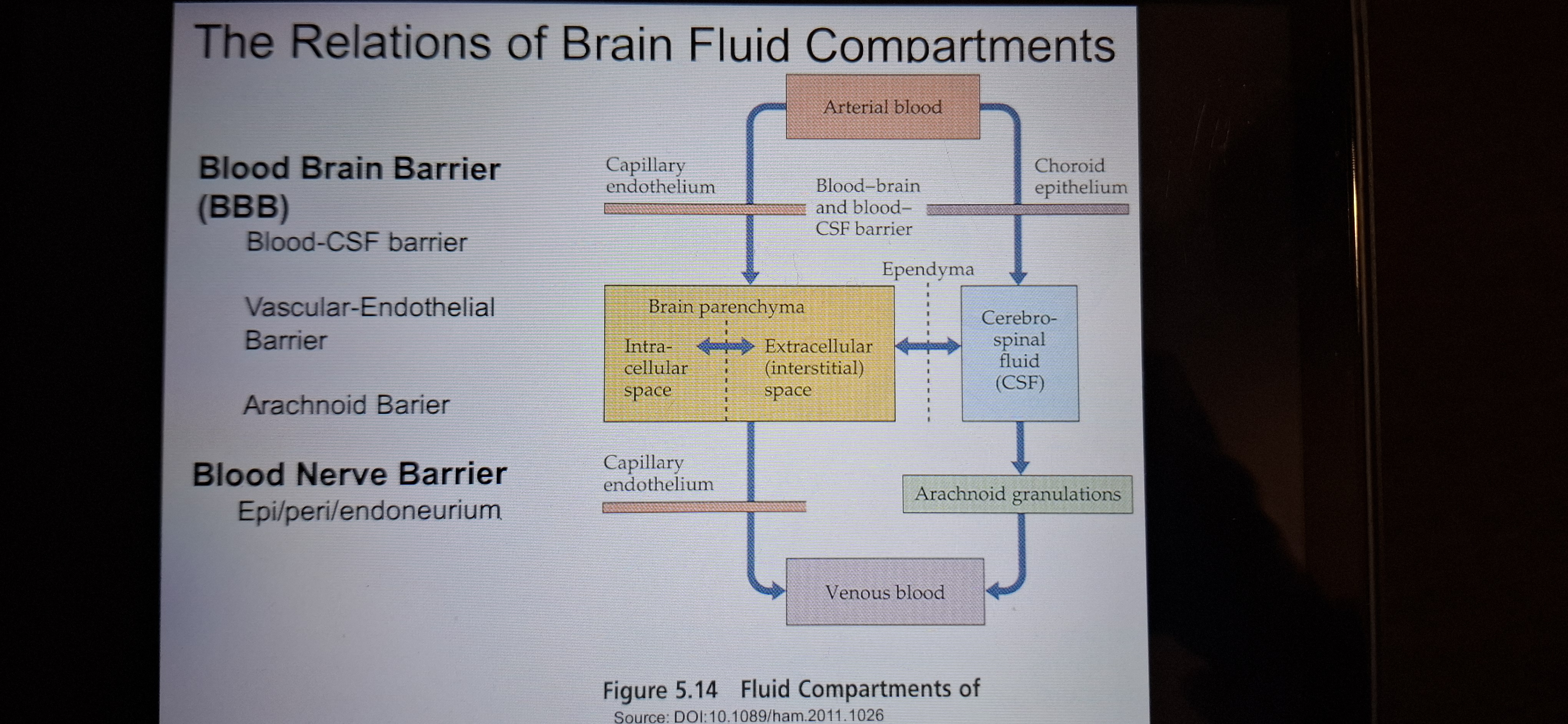
Brain barrier
See figure
Visualising gross brain anatomy.
Usr ct scans,mri,dti,physiology( PET,fMRI)
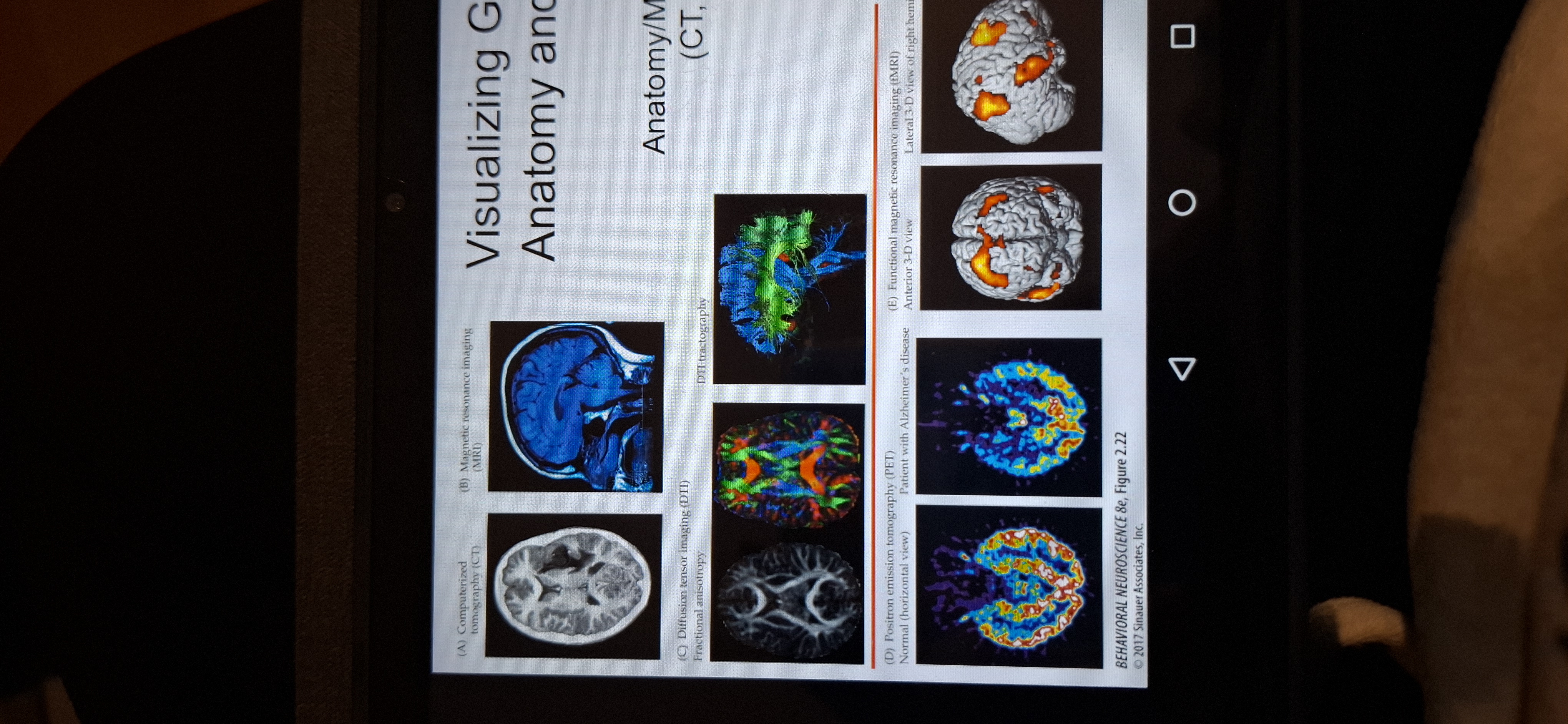
fMRI
Functional MRI detects small changes in brain metabolism such as oxygen use, in active brain areas.
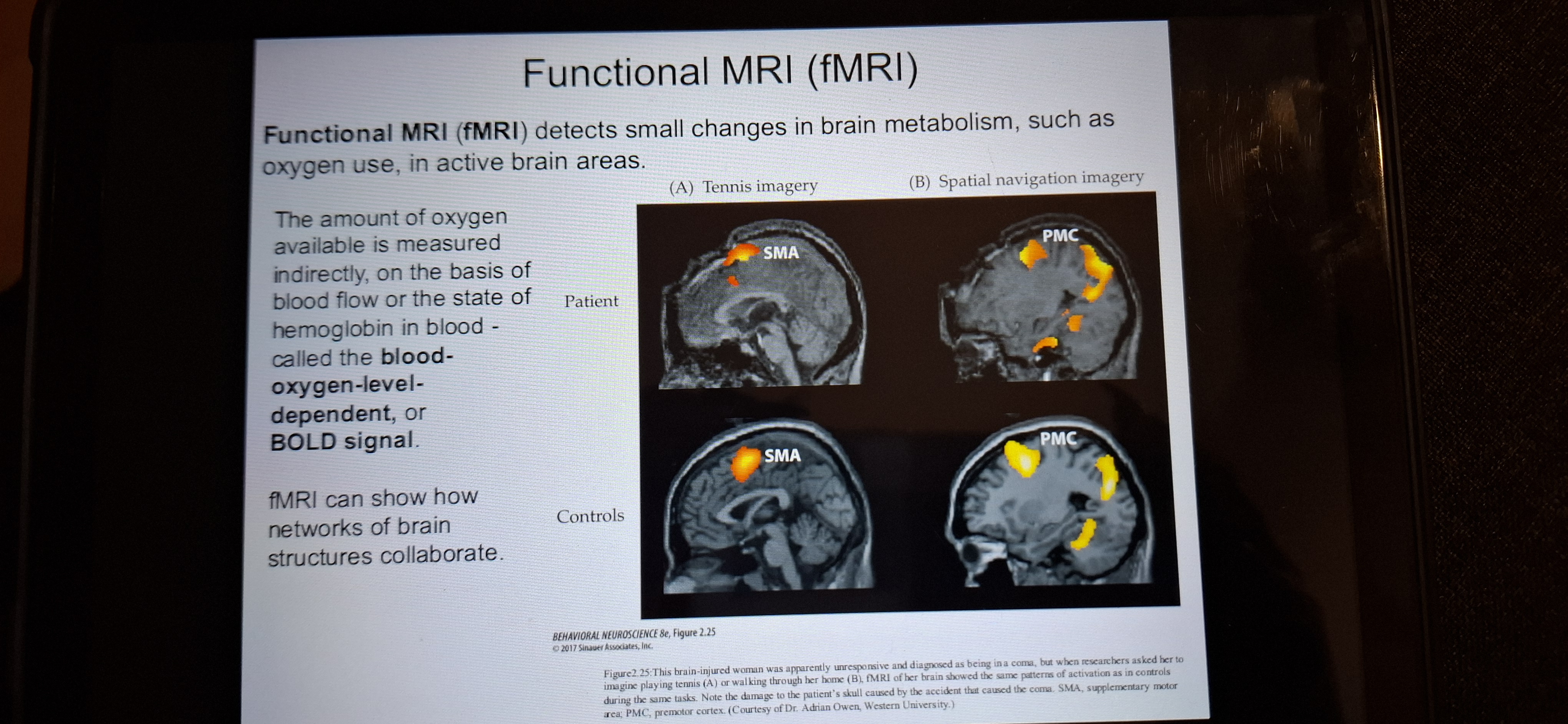
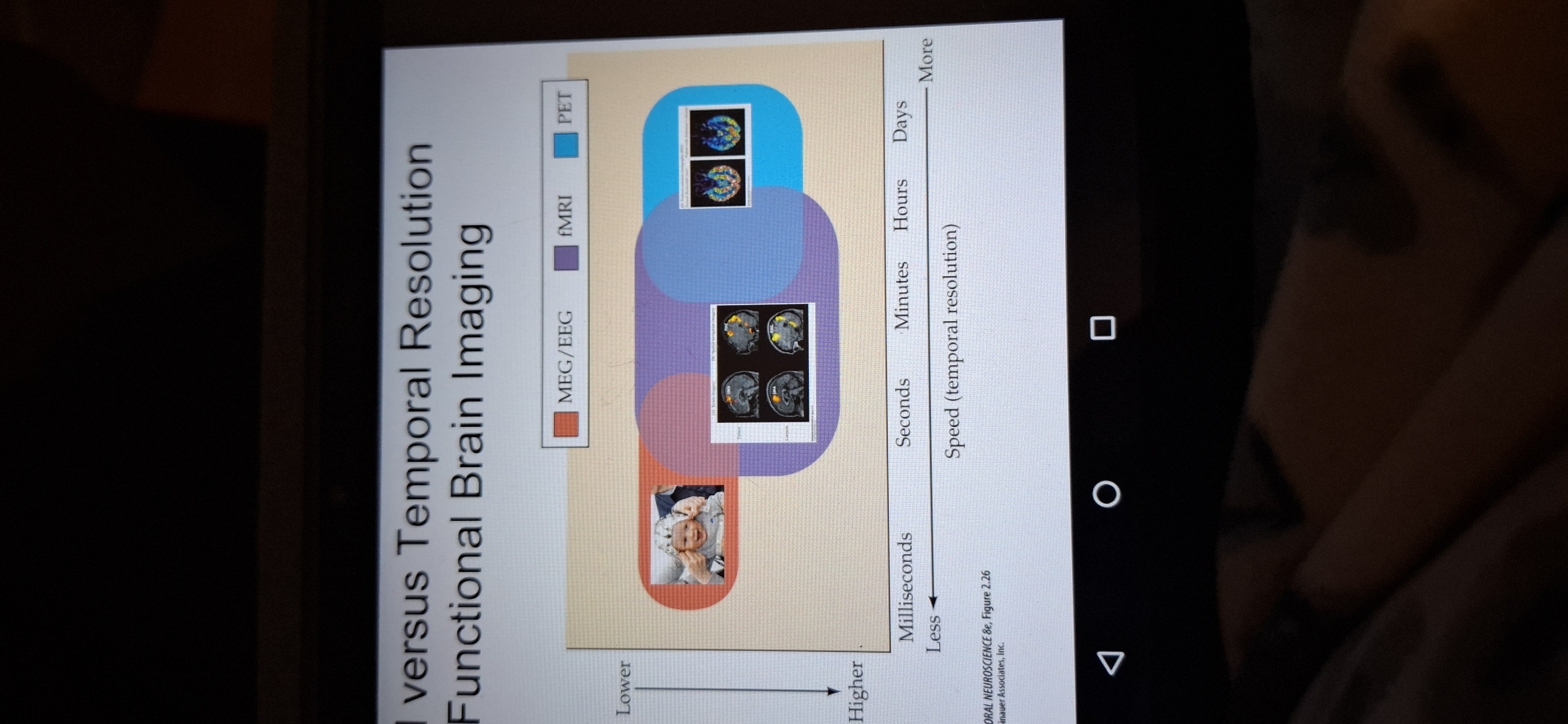
Limitations of brain imaging
Speed accuracy trade off
MEG/EEG milliseconds
fMRI- sec or min
PET- hours or days.