evolution grade 11 bio uni
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Leclerc (1700)
Species may change over time
and that’s humans are similar to apes
Mary anning (early 1800s)
Discovery of the fossil
Georges Cuvier (early 1800s)
Acknowledged annings work
Developed palaeontology
Proved that species go extinct
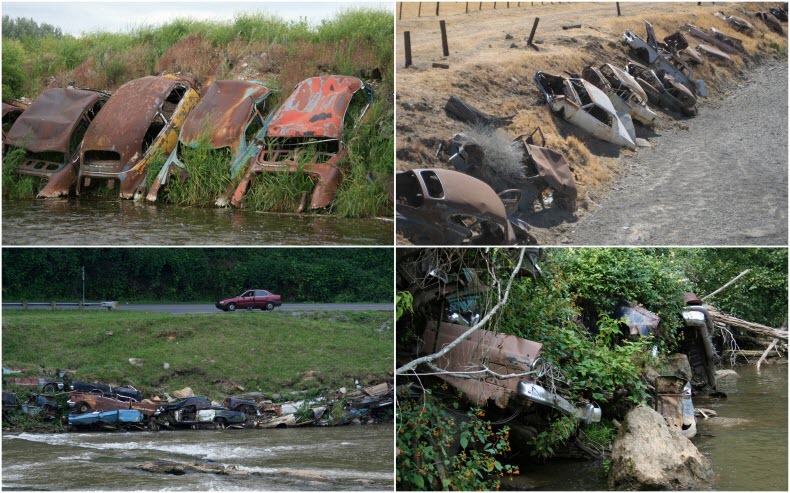
Charles lynell (mid 1800s)
Uniformitarianism— geological changes occur slowly and continuously (erosion of mountains)

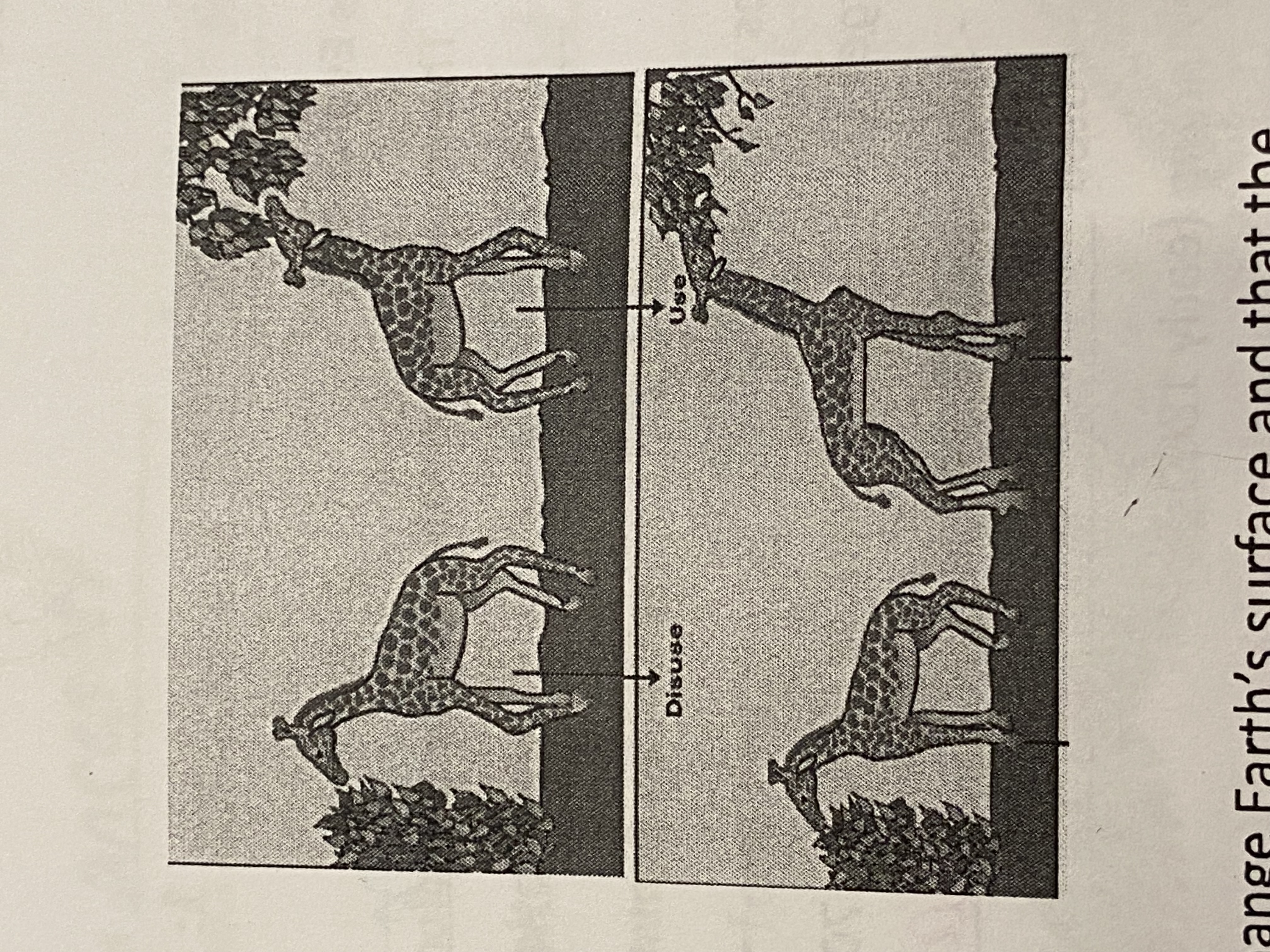
Jeans baptiste Lamarck (early 1800s)
Inheritance of acquired characteristics
Characteristics passed to offspring
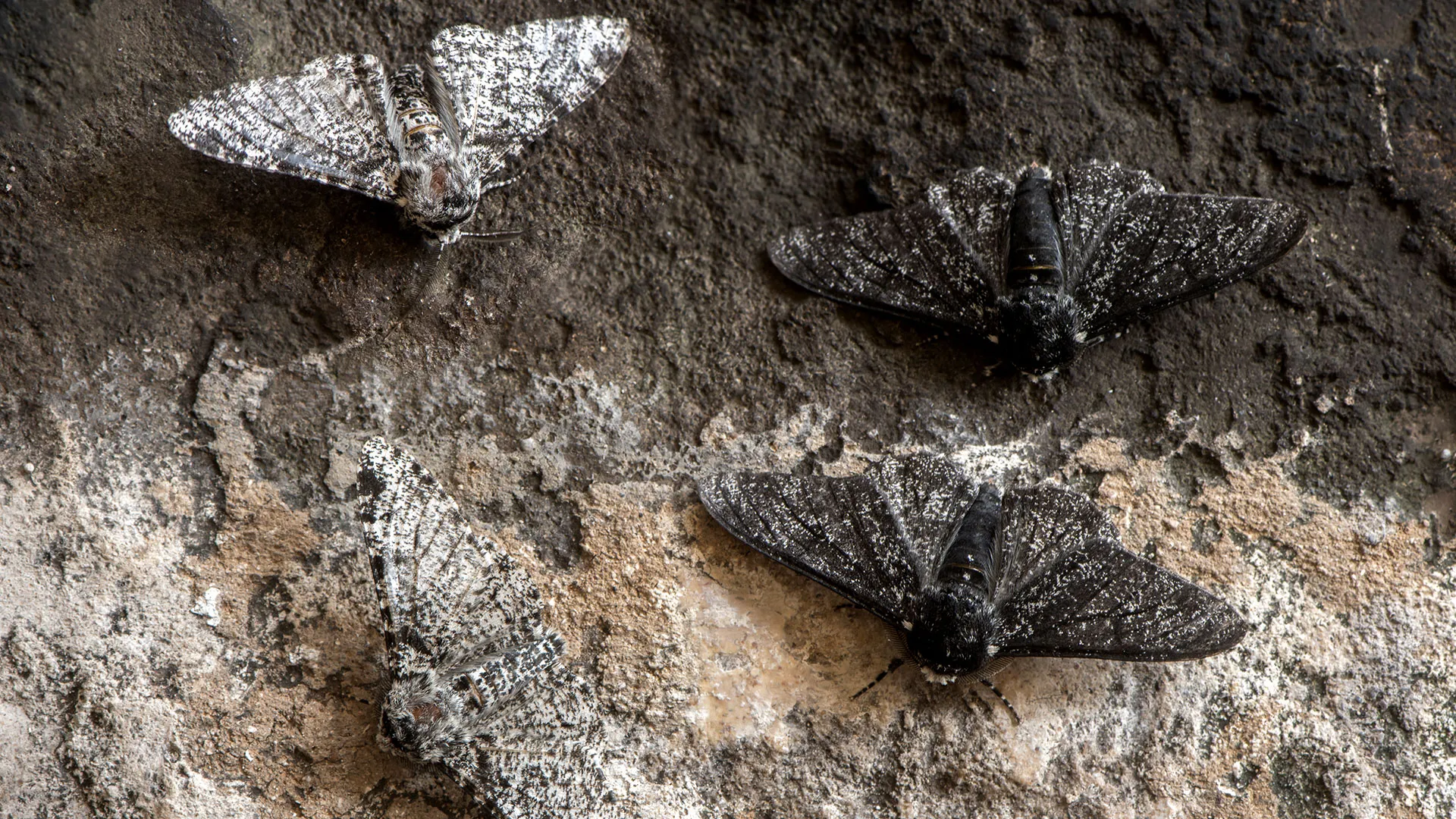
Charles Darwin (mid 1800s)
1: species were not created in their present form— but evolved from ancestral species
2: proposed that natural selections was the mechanism for evolution
Natural selection
Over time— life has changed— and will continue to change. Individuals with favourable traits are more likely to leave more offspring better suited for their environment

Wallace agreed with Darwin’s 4 main theories
1) organisms can produce more offspring than can survive— organisms compete for limited resources
2) individuals of a population vary, variations are inheritable
3) individuals that are better suited for local conditions survive to produce more offspring
4) processes for changes are slow
What term did Darwin hate and why?
Evolution— which implies progress. Instead he used “descent with modification”
Artificial selection
Selective breeding of domesticated organisms by humans
what are the 5 sources of evidence of evolution?
1) Fossil record
2) Biogeography
3)comparative anatomy
4) comparative Embryology
5) molecular biology
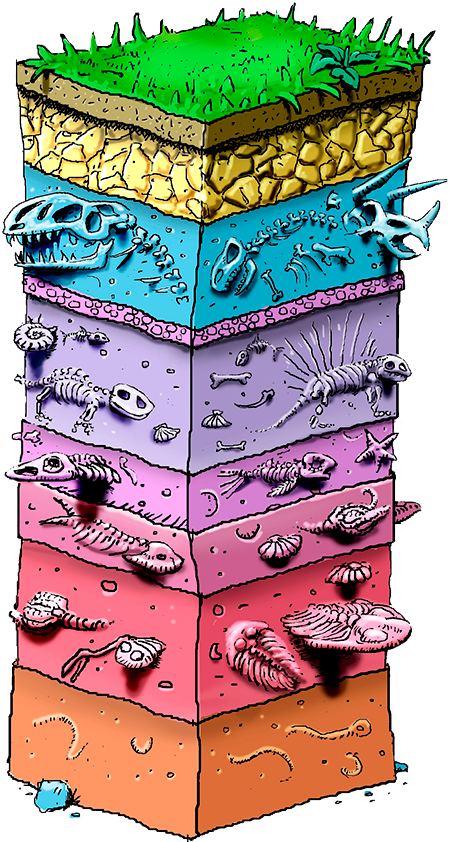
what is fossil record?
fossils appear in the soil in chronological sedimentary layers
(shows how animals may have evolved over time and how different species relate to one another. )
Ice allows for _____ analysis
Amber hardened ______ of pine
DNA
Resin
what is biogeography?
When there are geographical changes which influence a species evolution according to Continental or plate tectonics
Comparative Anatomy
structures that are similar because of common ancestry
what are the three types of structures?
Homologous, Analogous and vestigial structures.
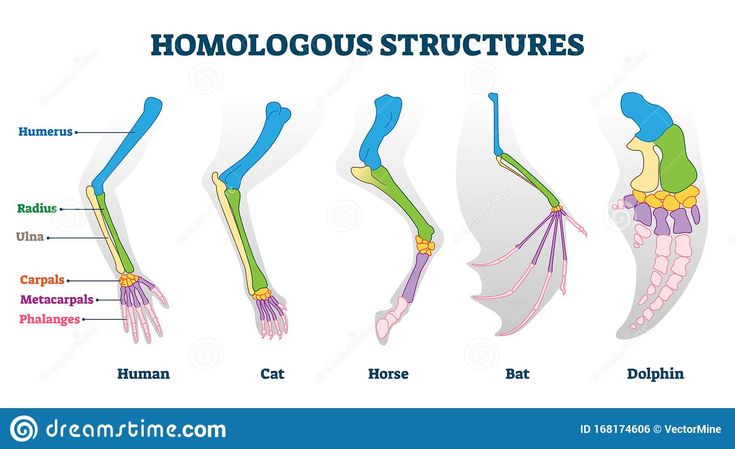
Homologous structures
are anatomical features that share a common origin but may serve different functions in different species.
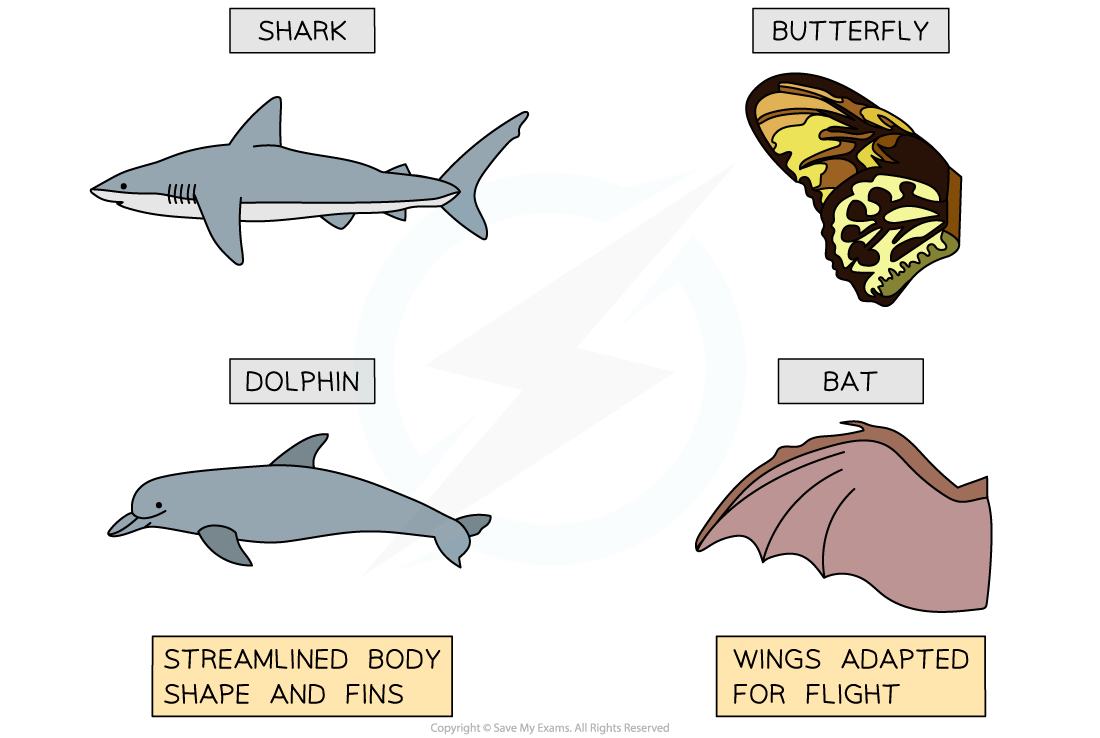
Analogous structures
are anatomical features that perform similar functions in different species but do not share a common evolutionary origin.
what is a vestigial structure?
is an anatomical feature that has lost its original function through evolution, often remnants of structures that were functional in ancestral species.
comparative embryology
is the study of the similarities and differences in the embryonic development of different species, providing insight into evolutionary relationships.
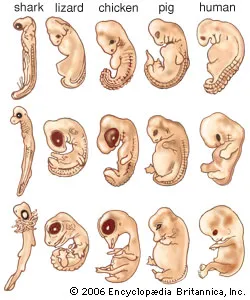
molecular biology
genomes can now be studied to reveal sim and diff. helps us better understand mutations
microevolution
is the small-scale evolution that occurs within populations, leading to changes in allele frequencies over time and often resulting in adaptation to local environments.
macroevolution
is the large-scale evolutionary change that occurs over geologic time, resulting in the emergence of new species.
what are the five mechanisms of evolution?
natural selection, sexual selection, artificial selection, genetic drift, gene flow
what is natural selection
envm increases frequency of alleles which provides a reproductive advantage. the envm will place a selective pressure on certain phenotypes
what are the three variations of natural selection?
A) stabilizing selection (somewhere right in the middle (skinny, medium, fat mouse)dfff