Herpetology Exam 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
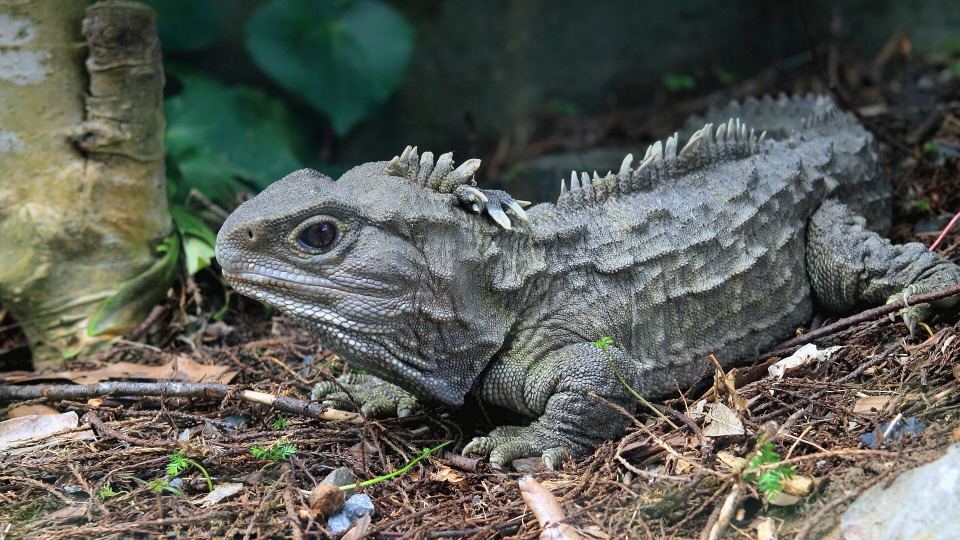

tuatara
found in a few islands off New Zealand
Rynchocephalia
beaked head
Sister group to lizards and snakes (squamata) - closest relatives
Common as fossils, 2 species living
Looks like a lizard but many primitive characteristics
primitive amniote skull
Large, heterodont teeth
Paired outpockets in posterior wall of cloaca, precursors to hemipenes?
Eggs laid in burrows, 12-15 month development!
Long lived animals, >70 years in captivity
Uses burrows, seabird burrows
Mostly nocturnal, optimal temp 63-68oF (likes colder temps)
Insectivorous, bird nestlings/eggs also
sort of endangered
Alligators and crocs
•Crocodylians belong to an archosaur lineage that dates back to the late Triassic, extensive fossil record.
•Only ~26 species worldwide, endangered
•Skin, meat, “dangerous”
heavily armored with osteoderms
osteoderm
bone skin
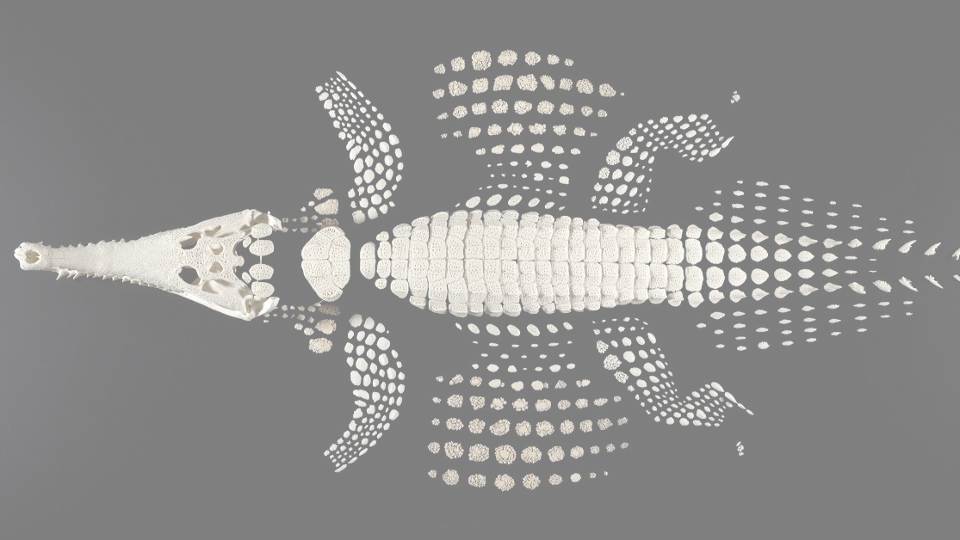
crocodylians
Aquatic, Freshwater & some saltwater
Nostrils at tip of snout with valves
Secondary palate, can breathe with prey in mouth
Advanced respiratory system, 4 chambered heart
oviparous
Temperature-dependent sex determination
Social behavior often complex
Parental care- build nests and mothers protect, then transport babies to water
Vocalizations
Body postures, head slapping
mating sensory organs on mouth
Eat anything
Often drown larger prey, gulpers not chewers
can’t eat huger things, drown it/hide it to rot, then rip apart
great digestive systems, disolve bones
“spin move” aka “death roll”
Around world in tropical, subtropical regions
3 families, ~26 species
2 species in the U.S.
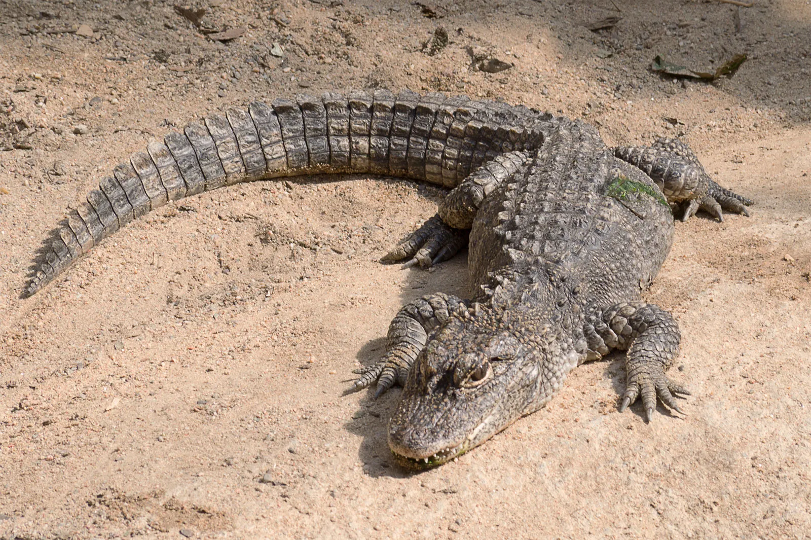

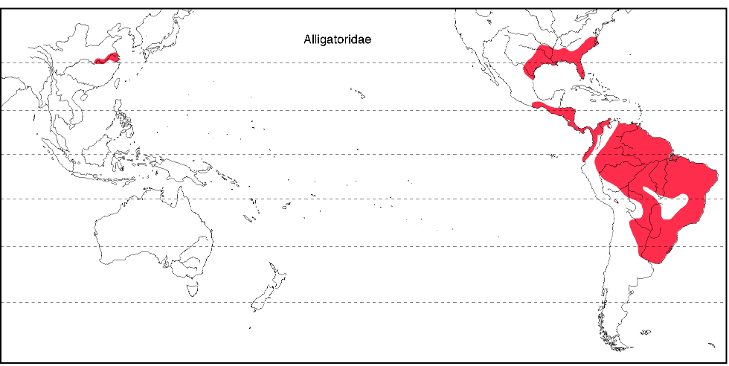
alligatoridae
•2 Alligators and 6 Caiman
American and chinease alligator (short snout)
•Teeth in lower jaw fit in pits in upper jaw
•Large rivers, swamps, lakes, lagoons
•El lagarto (the lizard in spanish)
Male American alligators can weigh 1,000 pounds (454 kilograms), 11.2 feet (3.4 meters) long. Female alligators are on average 8.2 feet (2.6 meters)
crocodylidae
•2 genera, 13 species
•4th tooth in lower jaw in notch in upper jaw
•Largest= Saltwater croc, 7m (20’ 2400 #)
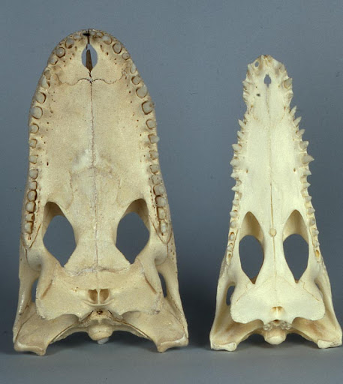
alligator vs croc
left alligator, right croc
american croc
central/south america
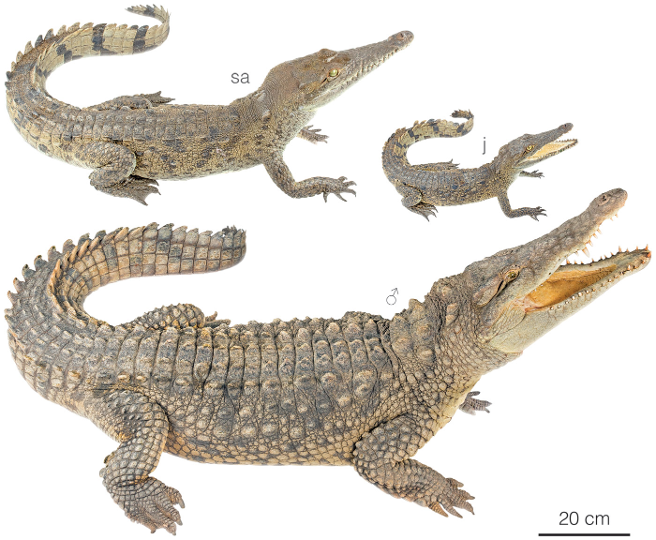

gharial
2 species, garial and false gharial
•Fish eating crocodile, fish specialists- thin snout=fast
long pointy teeth
•Endangered, now just in a few rivers in Nepal, northern India, 2% of historic range
•Big (>19 ft), awkward on land, great in water
•Adult males have a distinct boss at the end of the snout, which resembles an earthenware pot known as a ‘ghara’
could be for vocalization, resonates
•Only crocodilian so sexually dimorphic
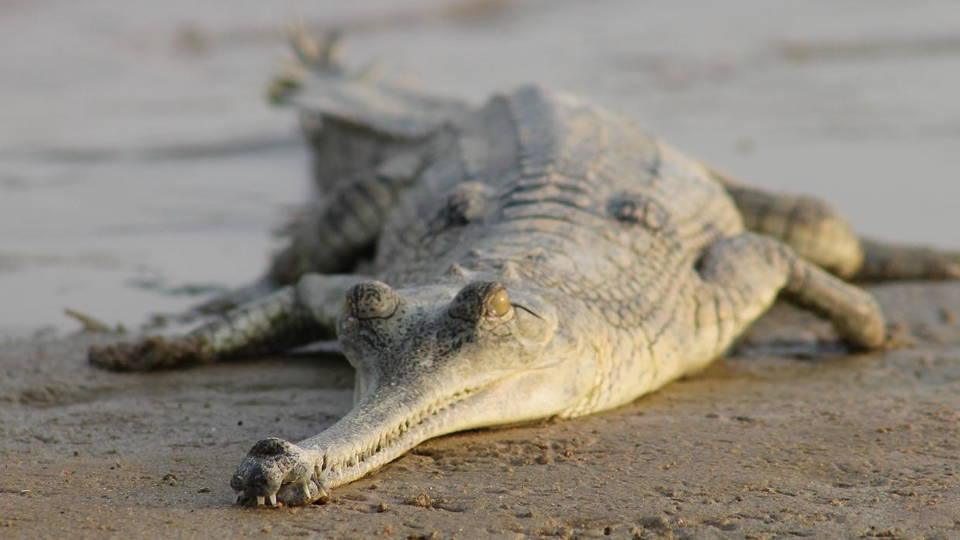

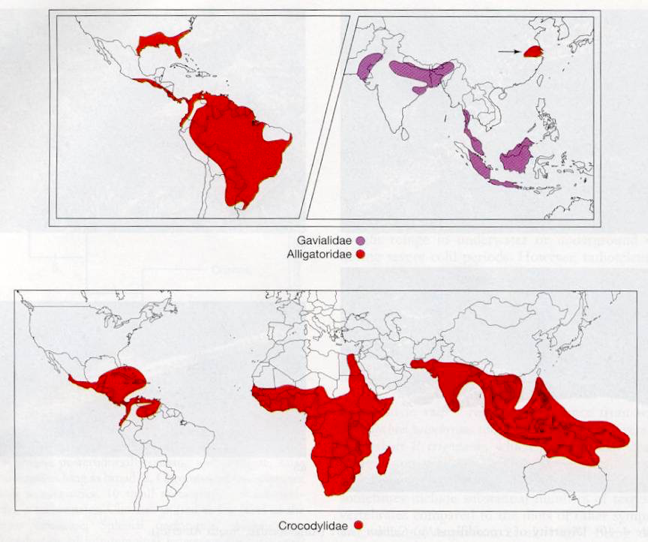
caimens
central south america
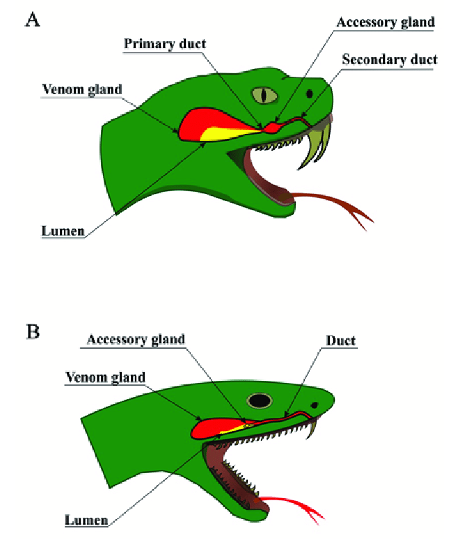
snake venom
It is modified saliva
Complex mix of proteins & enzymes
Has about 20 different enzymes, of which, a species
usually has between 6 and 12Venom’s primary importance is to immobilize its prey,
then to help it digest it.~300/3000 species of snakes
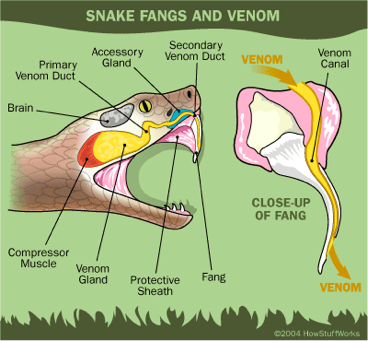
venom anatomy
bites to human
Probably 7000-8000/yr in U.S.
5-6 deaths
E. & W. Diamondbacks most deaths
Males 17-27 years old…alcohol
Mortality rate in developed <1%
snake worshippers- evil, test their faith
Around 5.4 million people are bitten by snakes each year
81,000-138,000 die each year, lots of disabilities
neglected tropical disease that disproportionately affect children, rural communities, and crisis-affected populations
illegitimate vs legitimate bites
legitimate- bit by accident
illegitimate- keep snakes on purpose, get bit
venom
need to subdue large prey with venom
cooperative behavior unlikely, can’t share food
can meter amt of venom, conserve supply - “dry bite”
more venom= quicker dies
will bite, follow, swallow unconcious animal
aglyphous dentition
garter, milk, burmese python etc
recurve teeth
opistogylphous
rear fangs
enlarged, grooved rear fangs, need to chew
pop toads after enlarged

Proterogylphous
Anterior fangs deeply grooved or tubular
front fangs, not very long
Elapidae (cobras, etc.), only 11mm in 4m cobra
Typically seize prey and hang on
solenogylphous
Can fold backwards, tubular, retractable
29mm fangs in 2m Gaboon Viper (3x length of cobra)
Quickly stab & recoil, toxins in deep
vipers, rattlesnake
stab and release
Neurotoxin
have the ability to damage and or destroy nerve tissues
Cobras and Coral Snakes
Ptosis (unable to keep eyes open), lethargic, muscle weakness, paralysis spreads throughout the body causing inability to speak because of difficulty breathing. Salivation occurs followed by vomiting and frothing around the mouth.
Hemotoxins
affects the blood and causes Hemolysis and Hemorrhage
Vipers
western diamodback rattlesnake,
Very painful. Inflammation and oozing occur. Bleeding from the mucous membrane occur at the mouth, anus, and nose and there is hemorrhaging under the skin.
slower and more painful than the neurotoxin. Finally, there is vascular collapse and loss of consciousness.
swellings, bruising
hemo = muscle
Myotoxins
muscle pain and turn urine brown to black because of the protein Myoglobin that is present
sea snakes
yellow bellied sea snake
There are no symptoms really. Just severe upper body pain and urine changes to brown black color.
myo = blood
antivenim
antibodies to venom
inject horses/sheep, suffers immune response
treat envenomation into others
“passive immunity”
expensive

antivenom administration
•Early administration is crucial: The antivenom is most effective when given within 8 hours of the bite.
•Allergic reactions: As with any antivenom, there is a risk of allergic reactions, so patients should be monitored closely.
•Other treatments: In addition to antivenom, supportive care, such as intravenous fluids, pain medication, and respiratory support, may be necessary.
•Not a substitute for prevention: If you are in an area where venomous snakes are present, take precautions to avoid bites.
snakebite management

herpetoculture
The keeping of live reptiles or amphibians in captivity either as a hobby or a commercial breeding operation.
herpetology vs herpetoculture
Often amateurs
Different than pet keeping, don’t give names usually
Emphasis on a few species – artificial selection for certain traits as in domesticated animals
Can be some tension between groups, concern that collection of wild specimens is harmful
Released animals in wild a problem – big snakes
conservation tool, increased reproductive output
insurance policy against catastrophic events
learned behaviors in captivity=decreased survival released in wild
breeding challenges
Inbreeding depression
High costs
Ethical considerations- some oppose bringing into captivity
Perhaps a tool, but not a panacea
complete domestication
significant genetic and behavioral changes through human selection and breeding, making them reliant on humans for survival and reproduction
must be
docile, not panic, breed well in captivity, social structure easy for human management, useful purpose
started domestication = didn’t have to hunter gather, could spend time on war/inventions etc instead of worrying about food
mutations
Genes controlling color and/or pattern
Selective breeding
Valuable at first... then market gets saturated