Labs 7-10 Exam
1/343
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
344 Terms
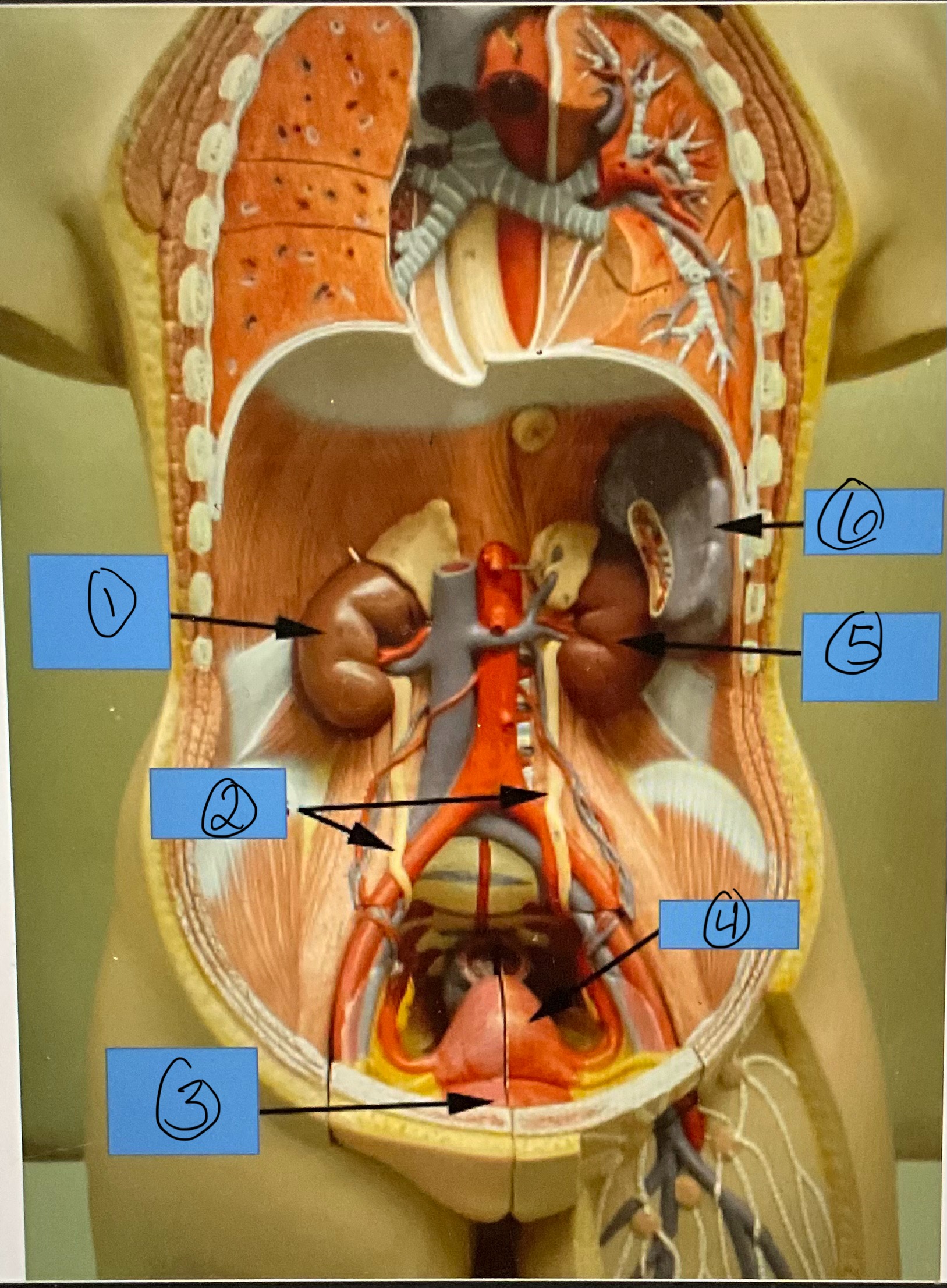
What is 1?
right kidney
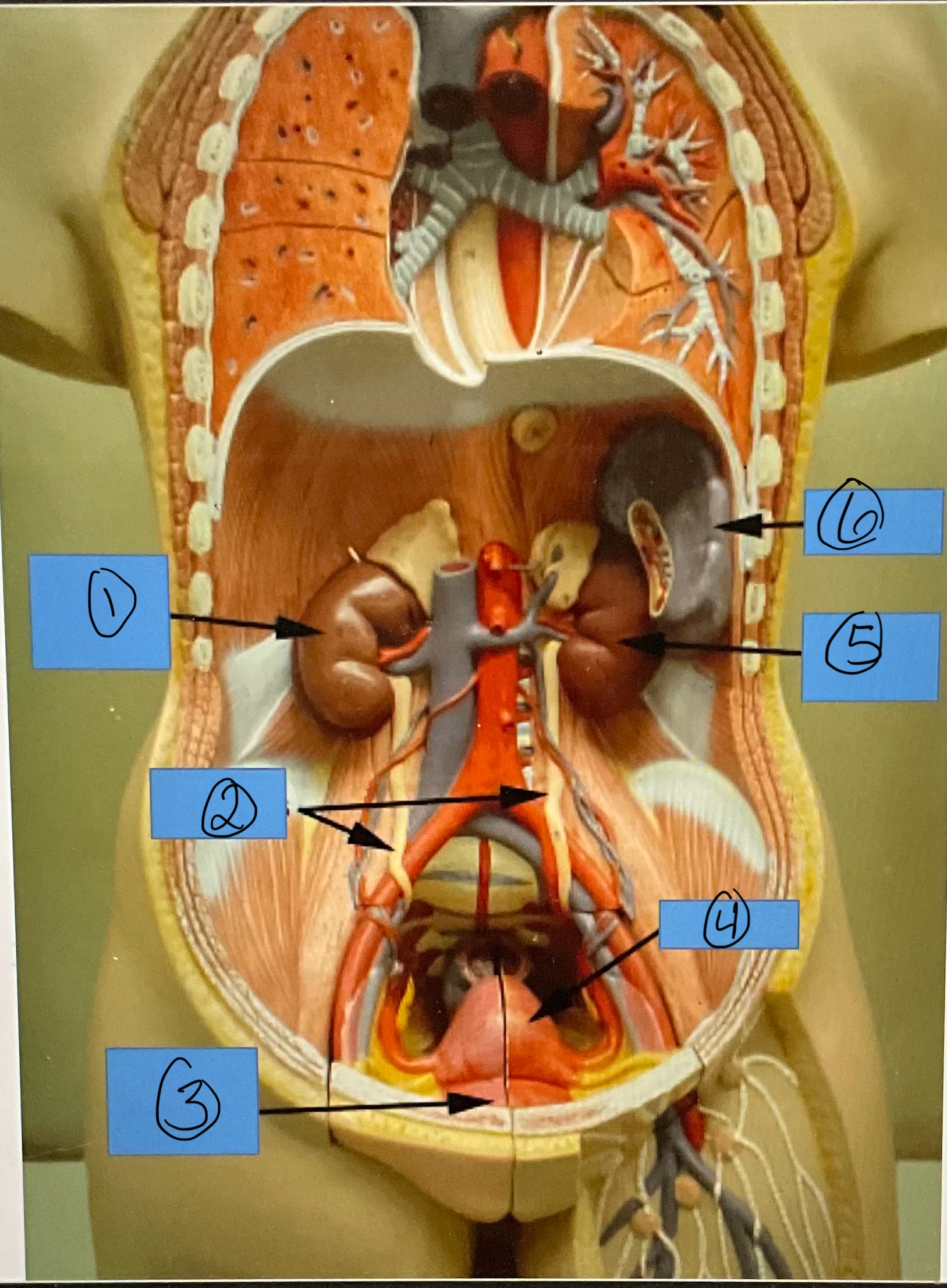
What is 2?
ureters
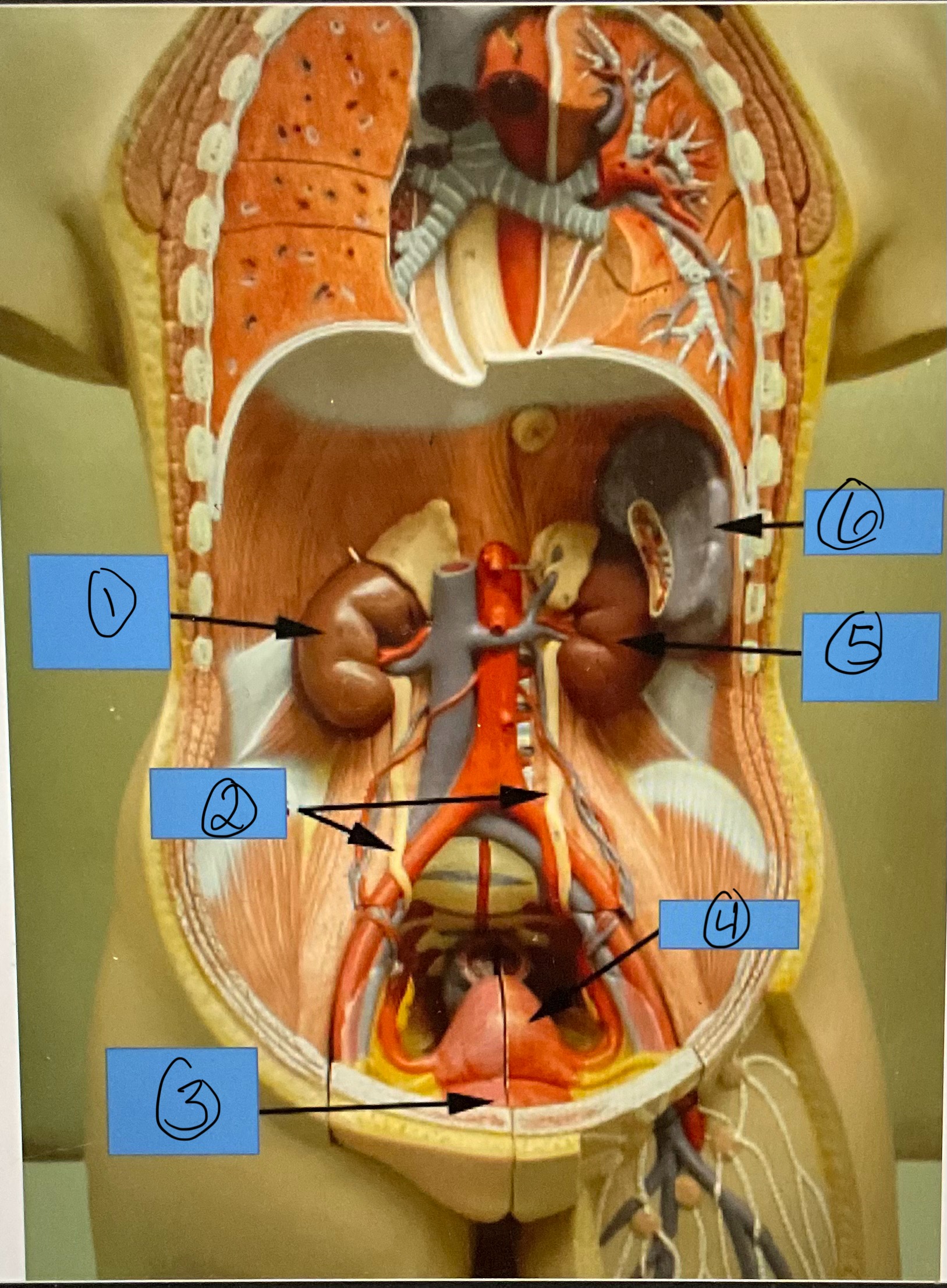
What is 3?
urinary bladder
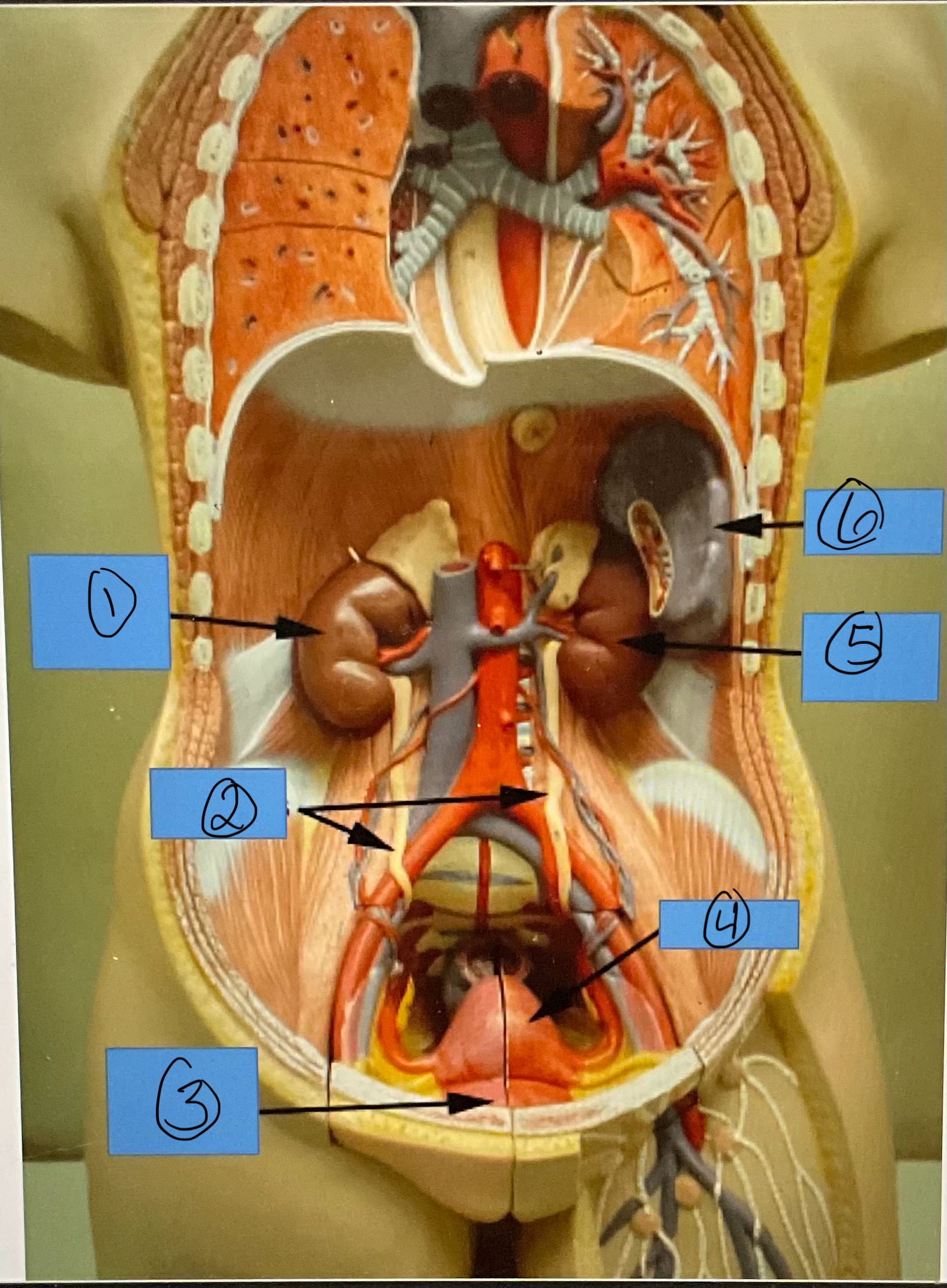
What is 4?
uterus
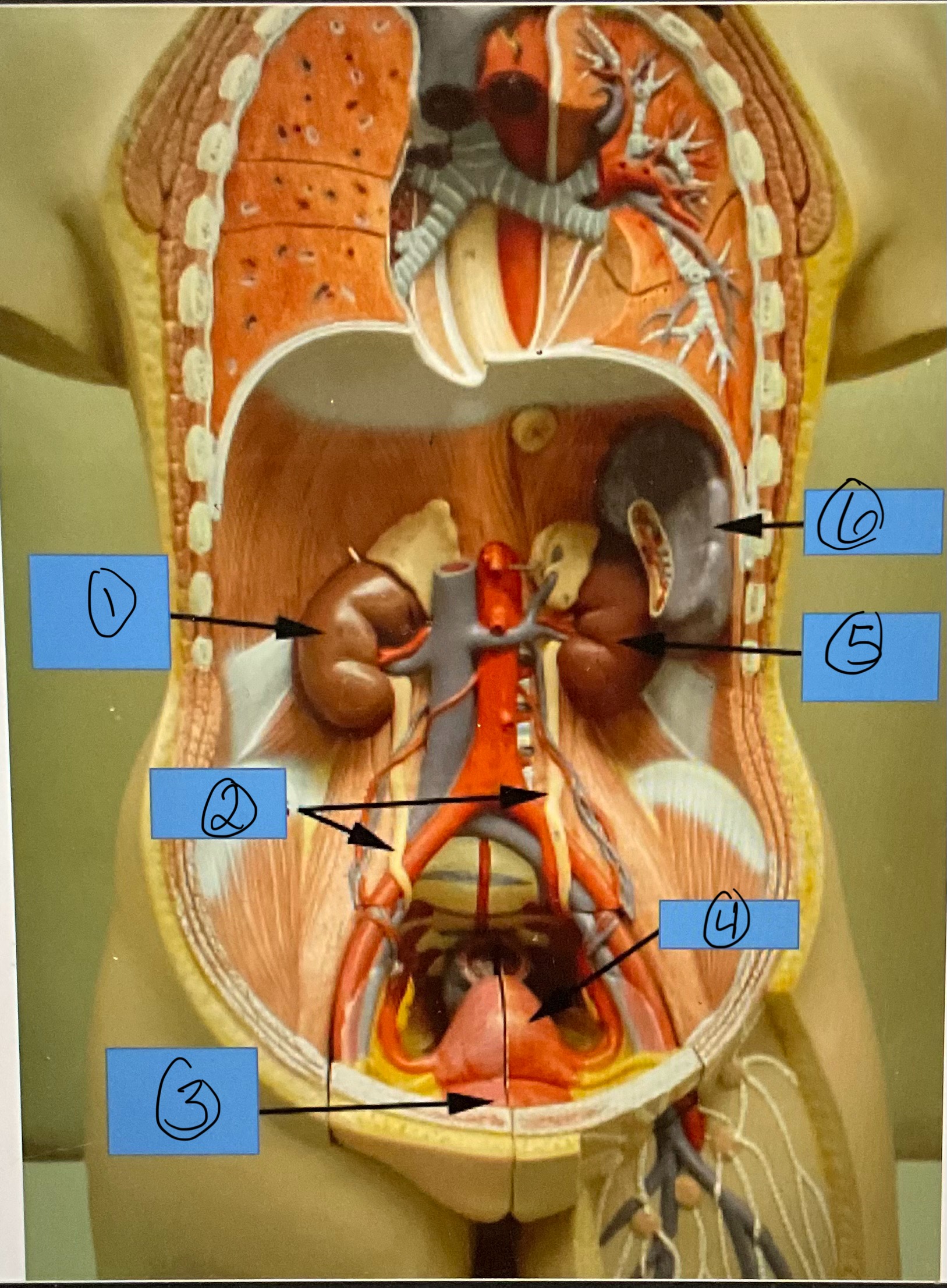
What is 5?
left kidney
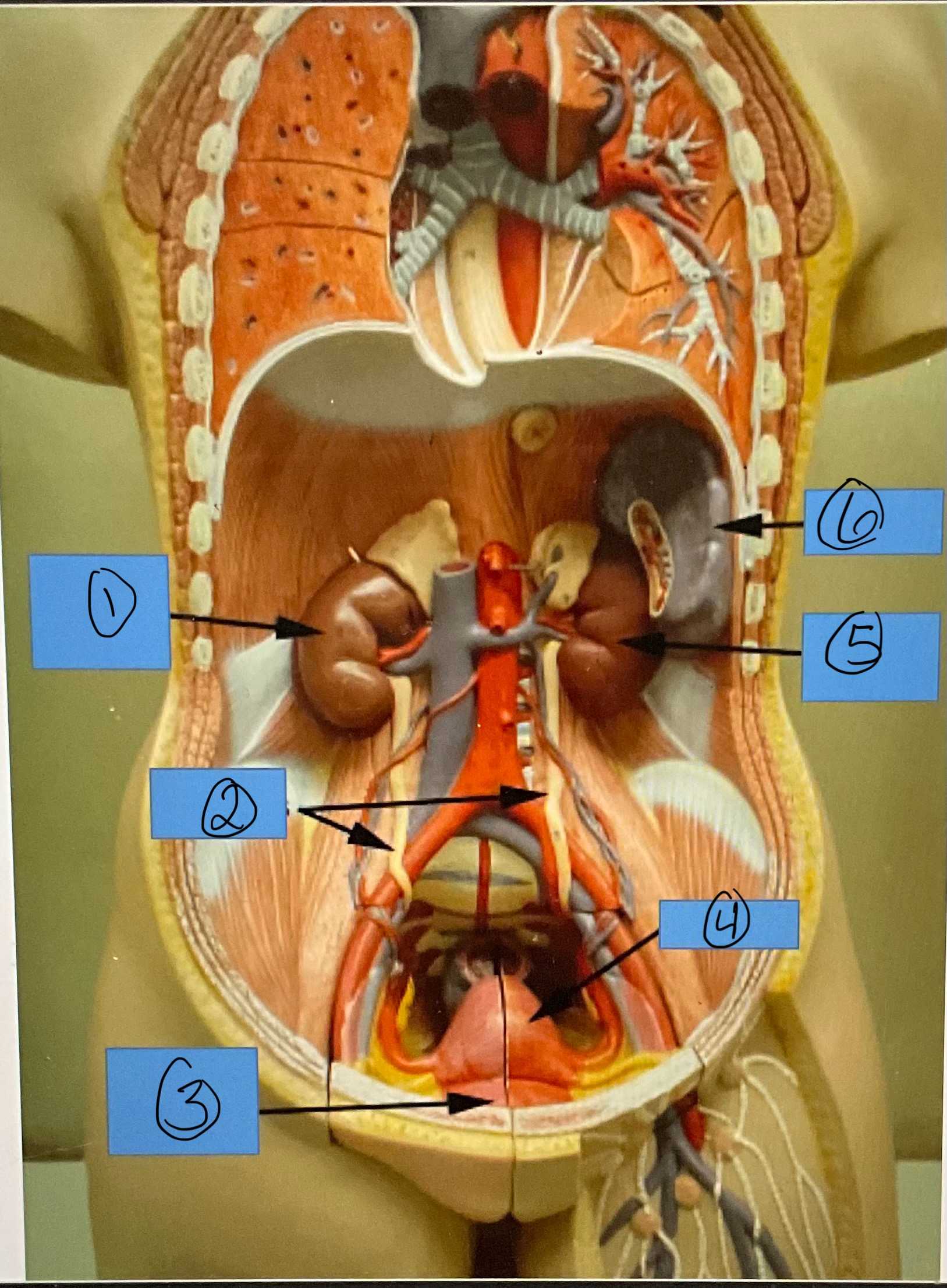
What is 6?
spleen
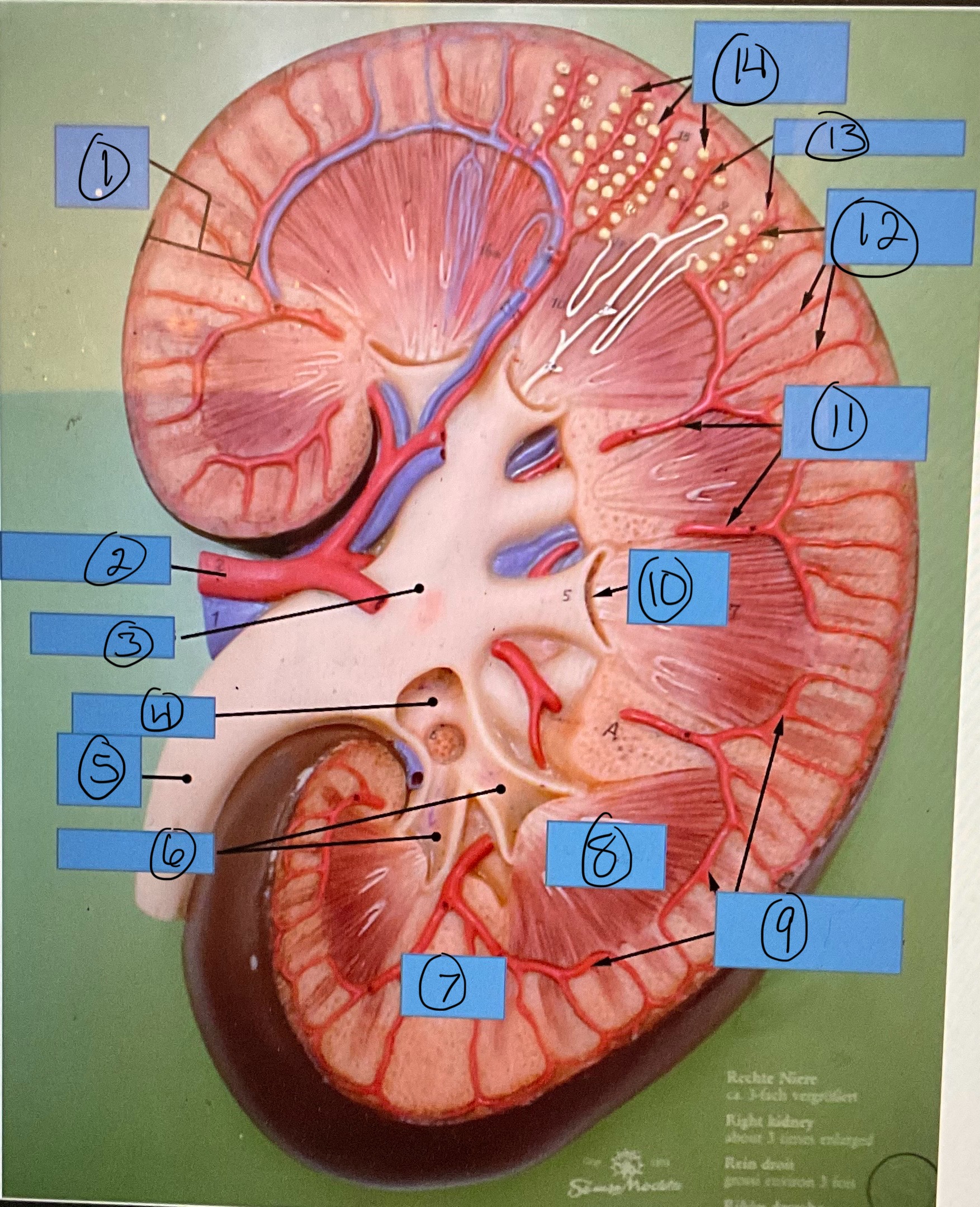
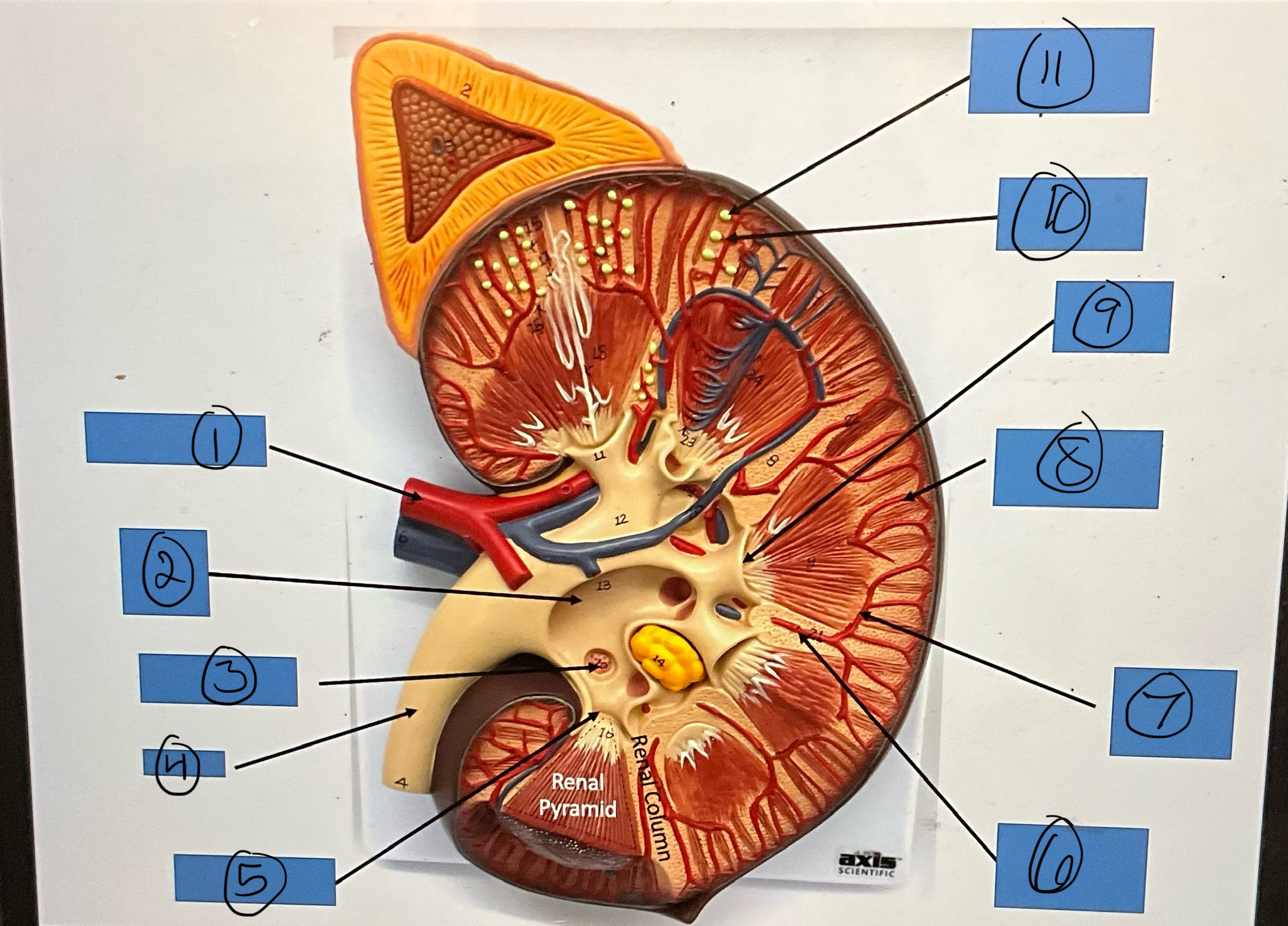
What is 1?
renal cortex
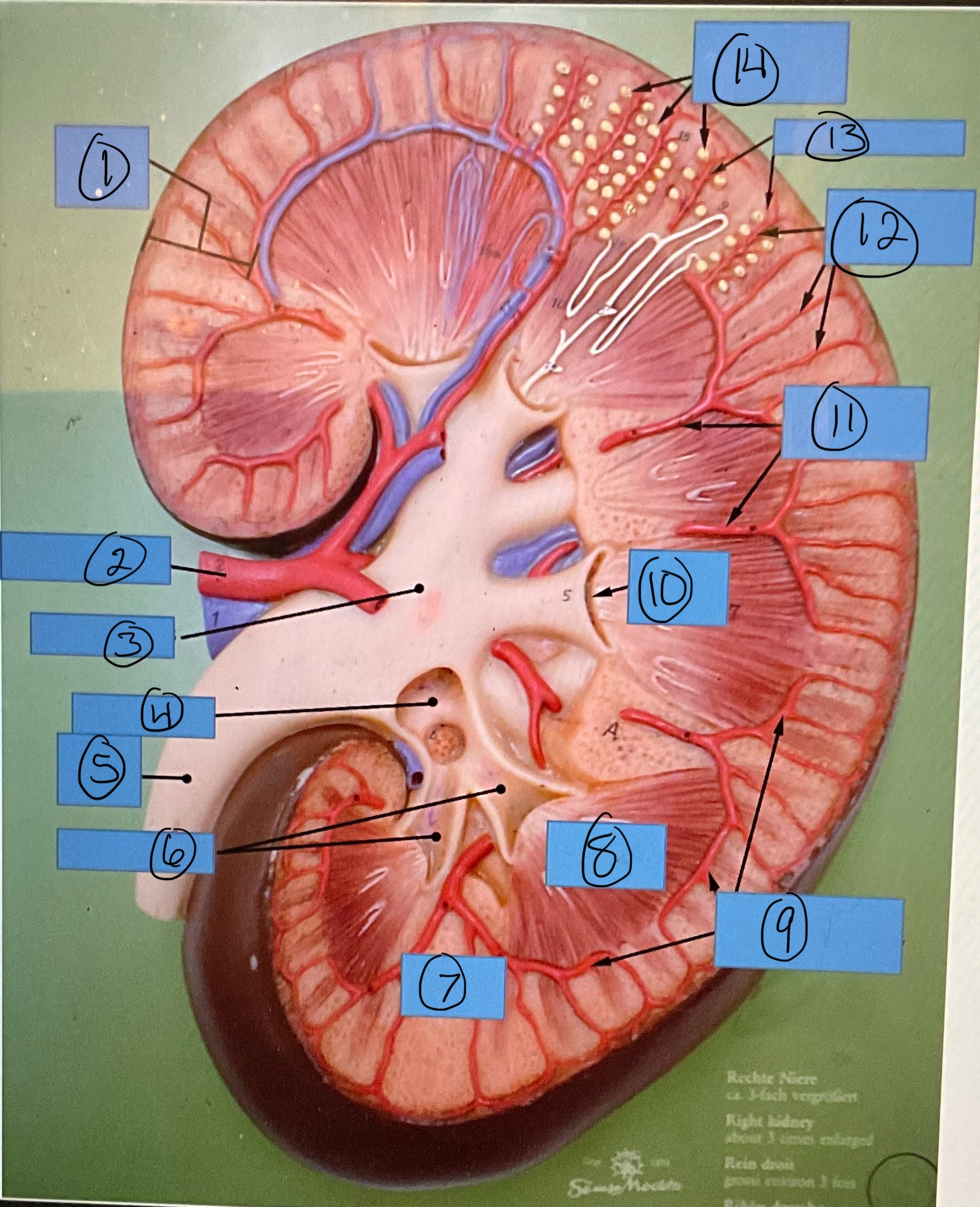
What is 2?
renal artery
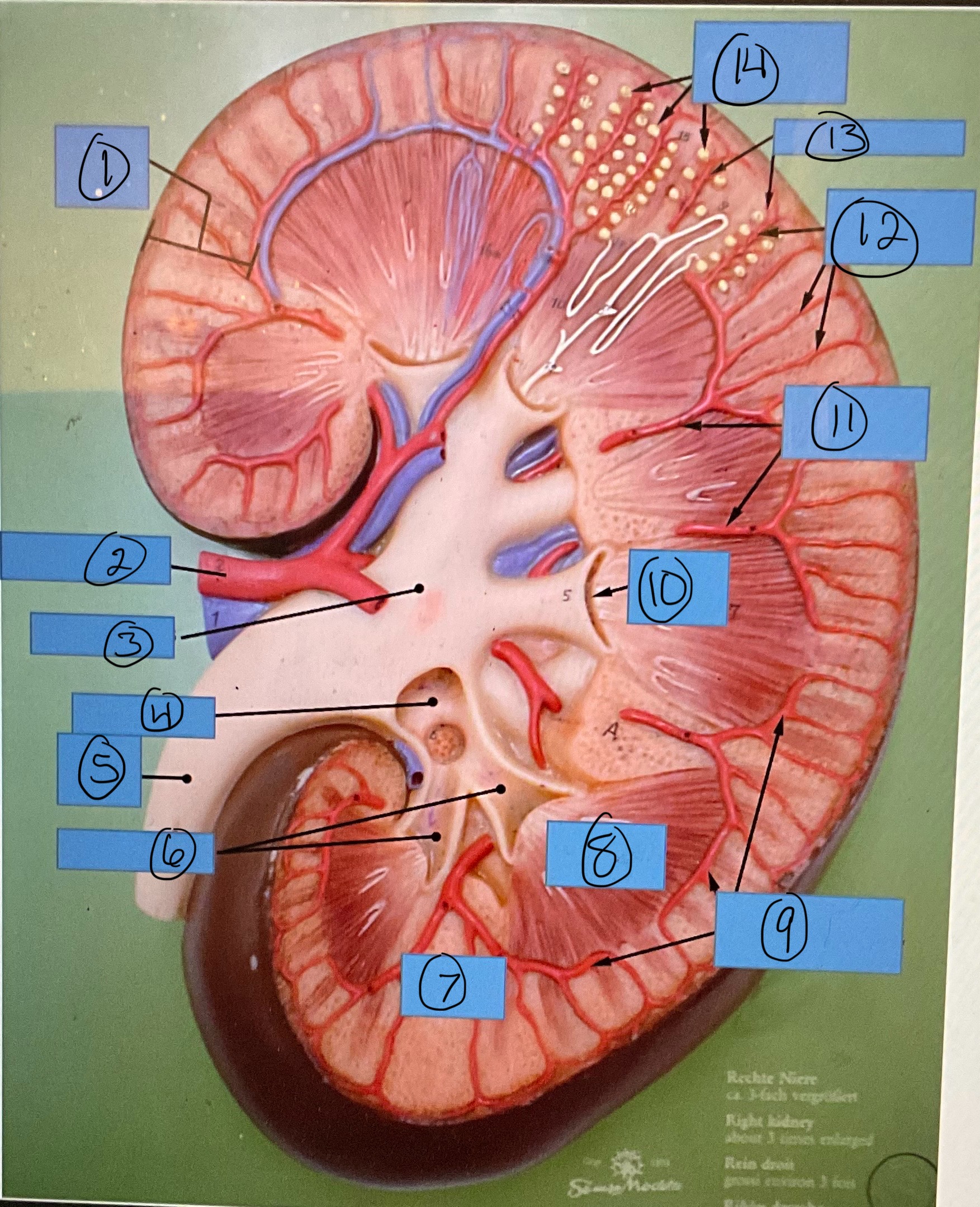
What is 3?
renal pelvis
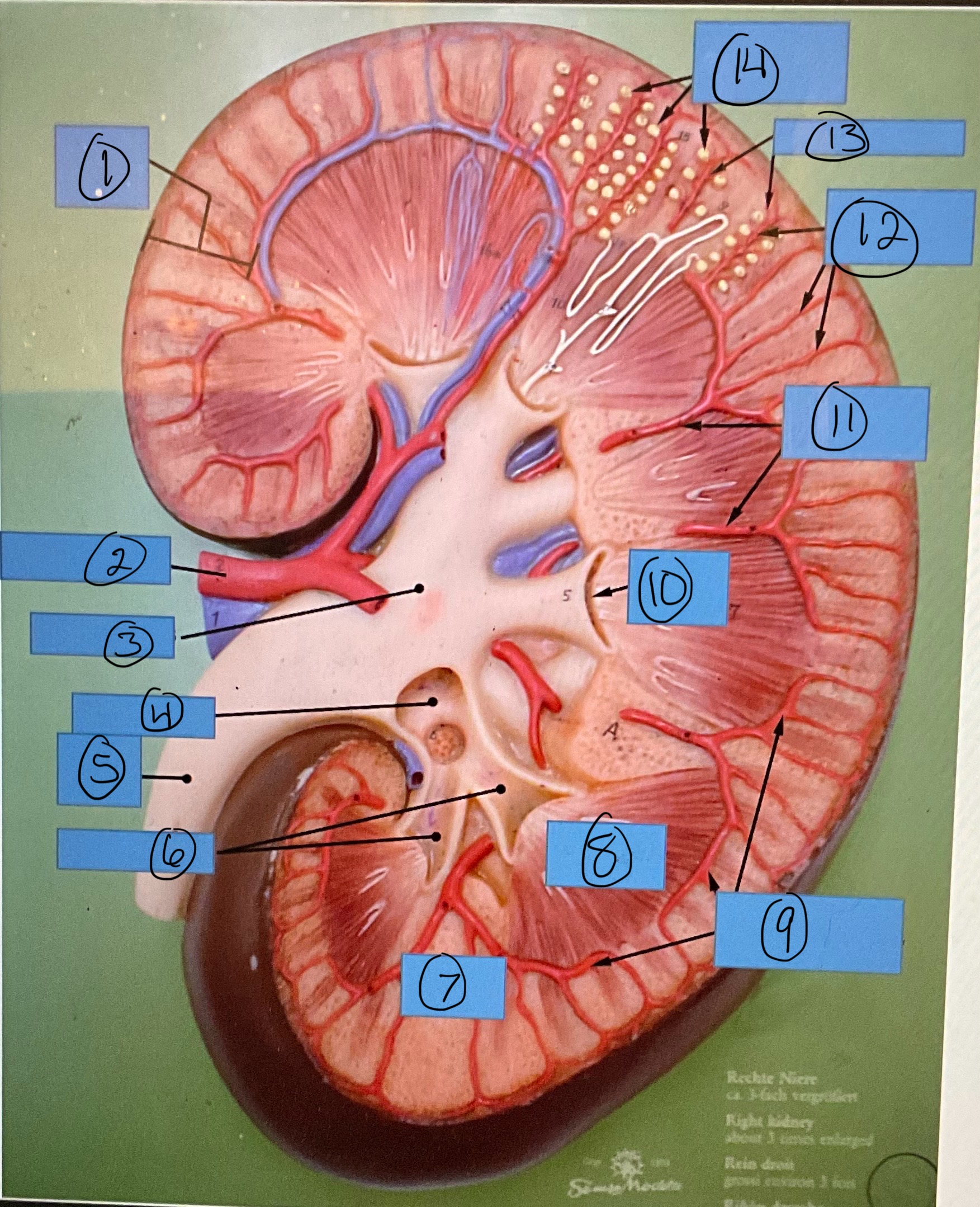
What is 4?
major calyx
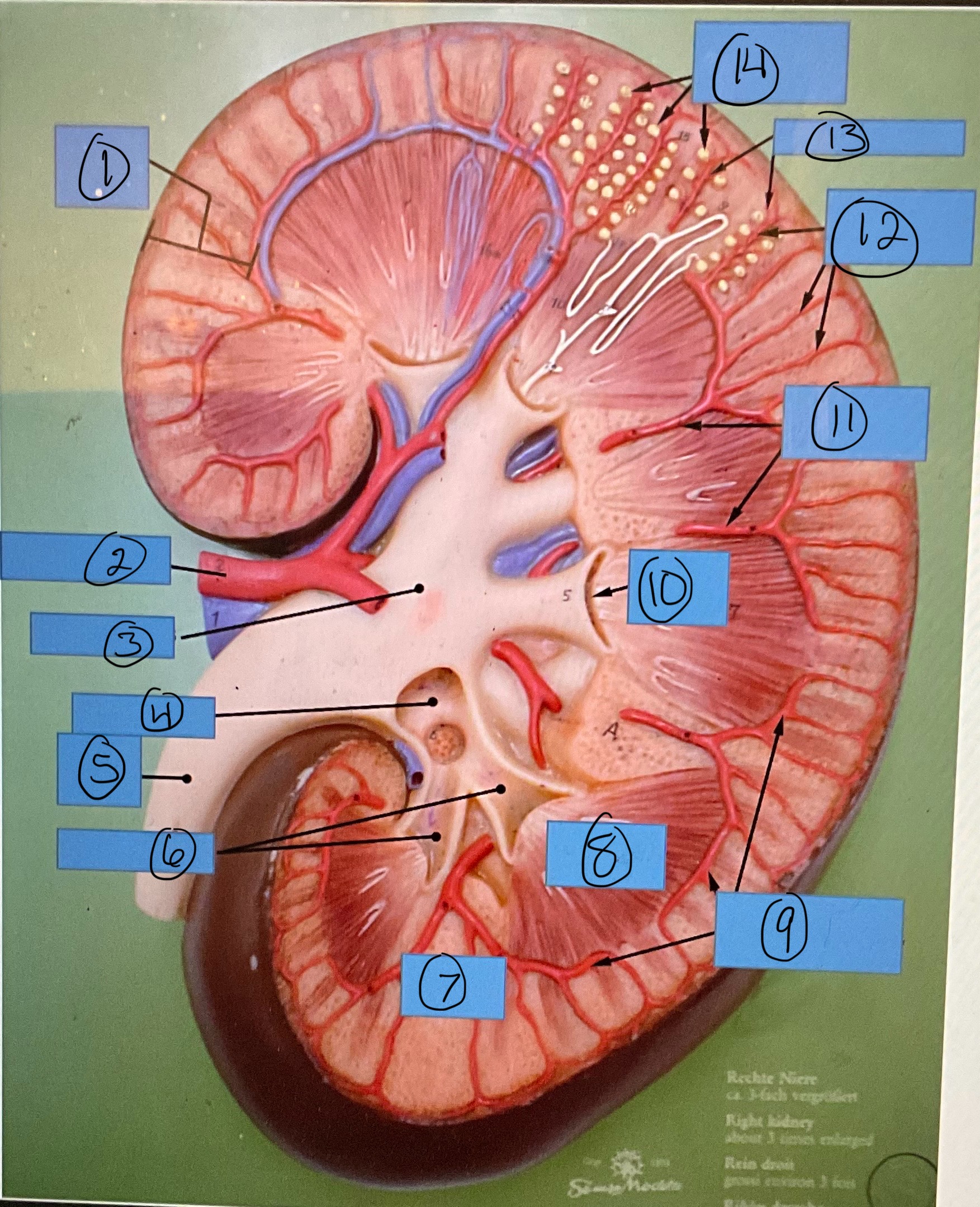
What is 5?
ureter
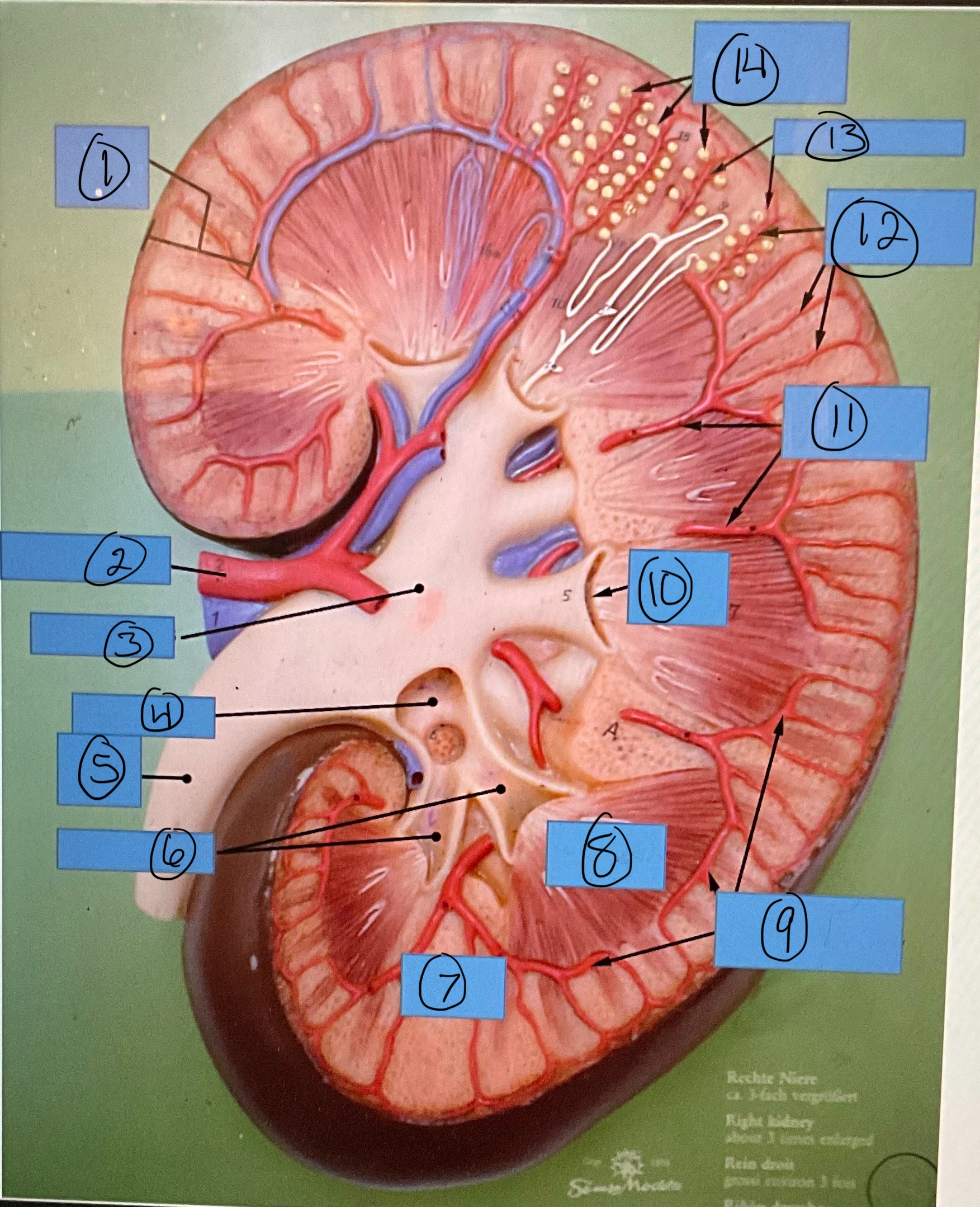
What is 6?
minor calyces
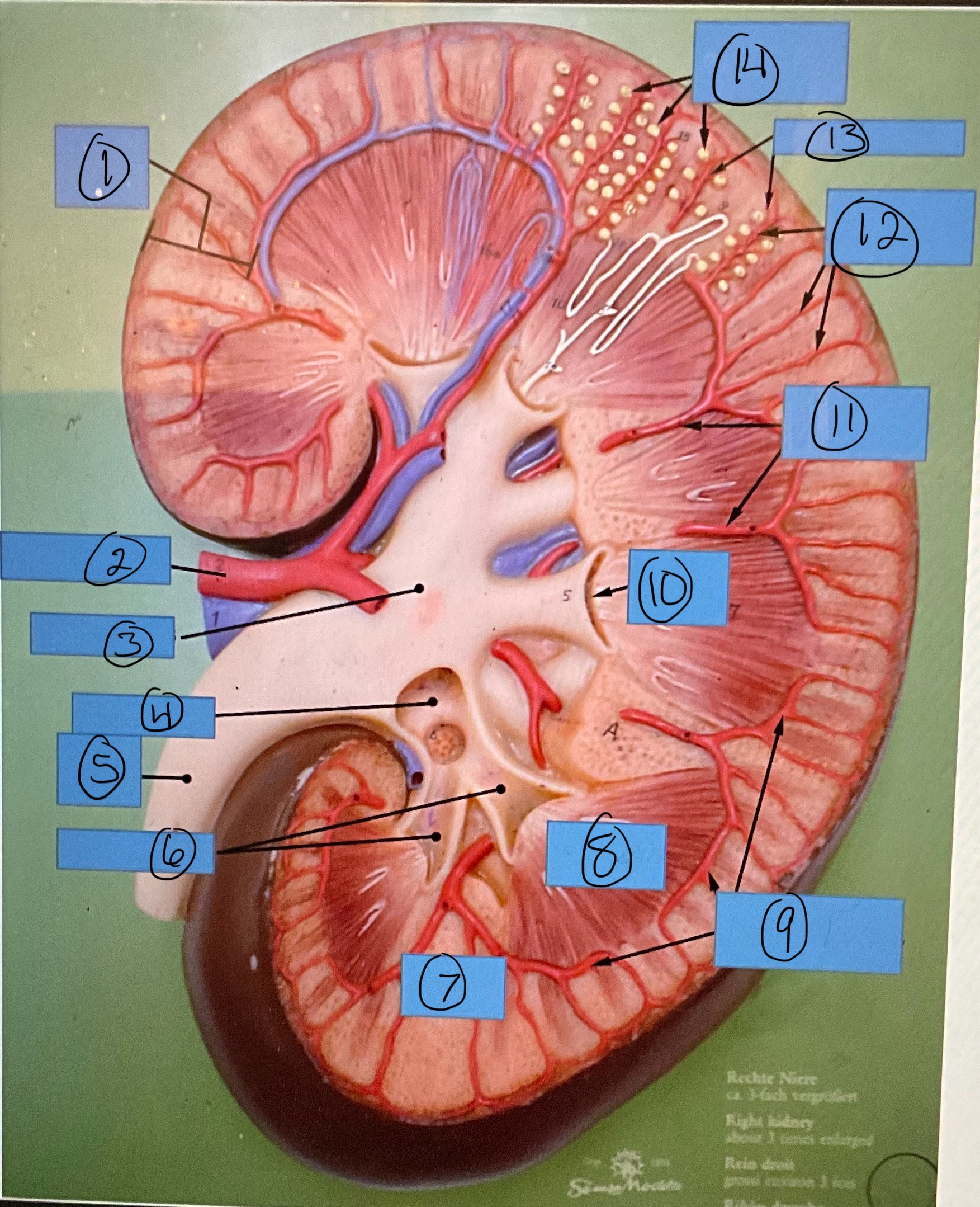
What is 7?
renal column
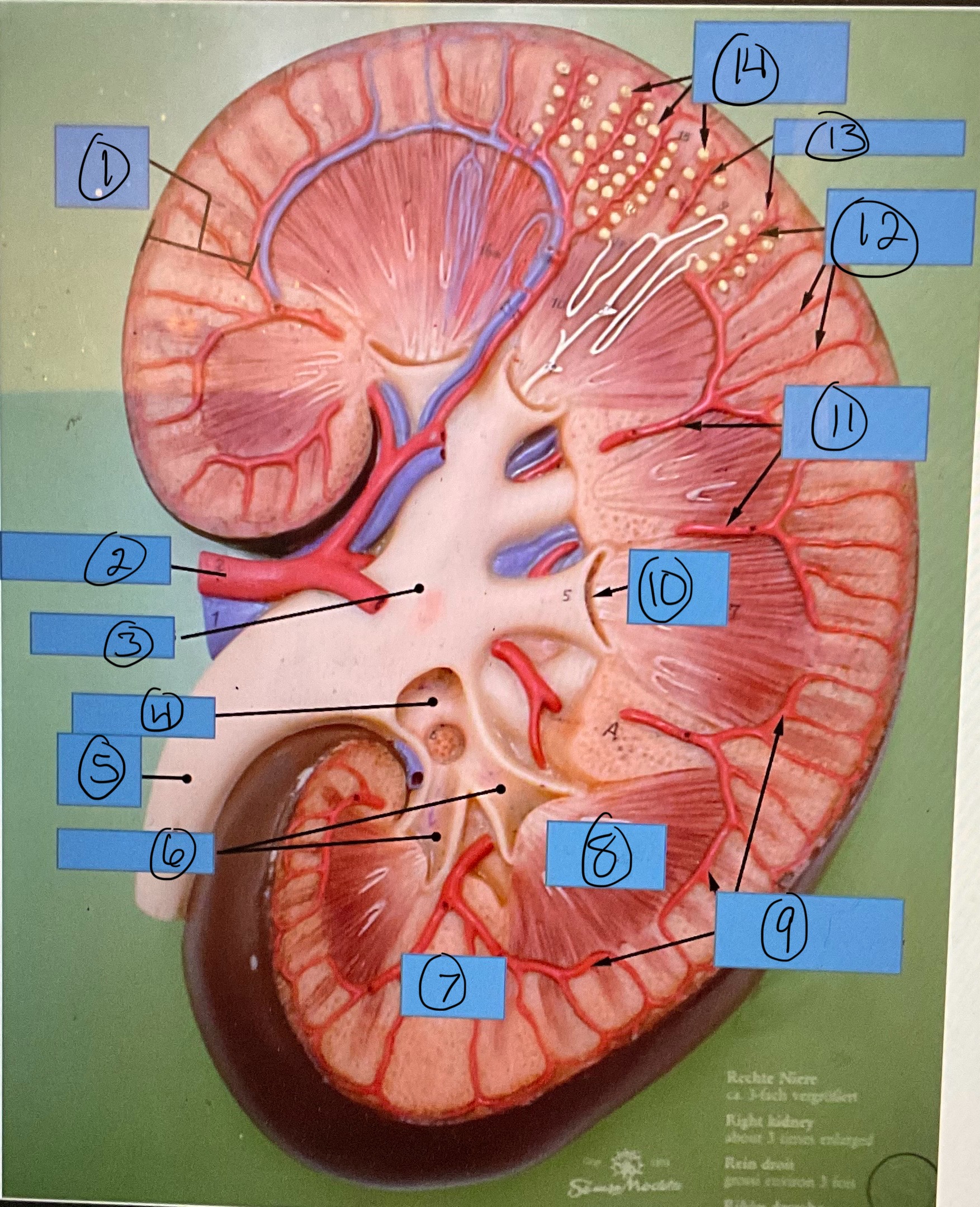
What is 8?
renal pyramid
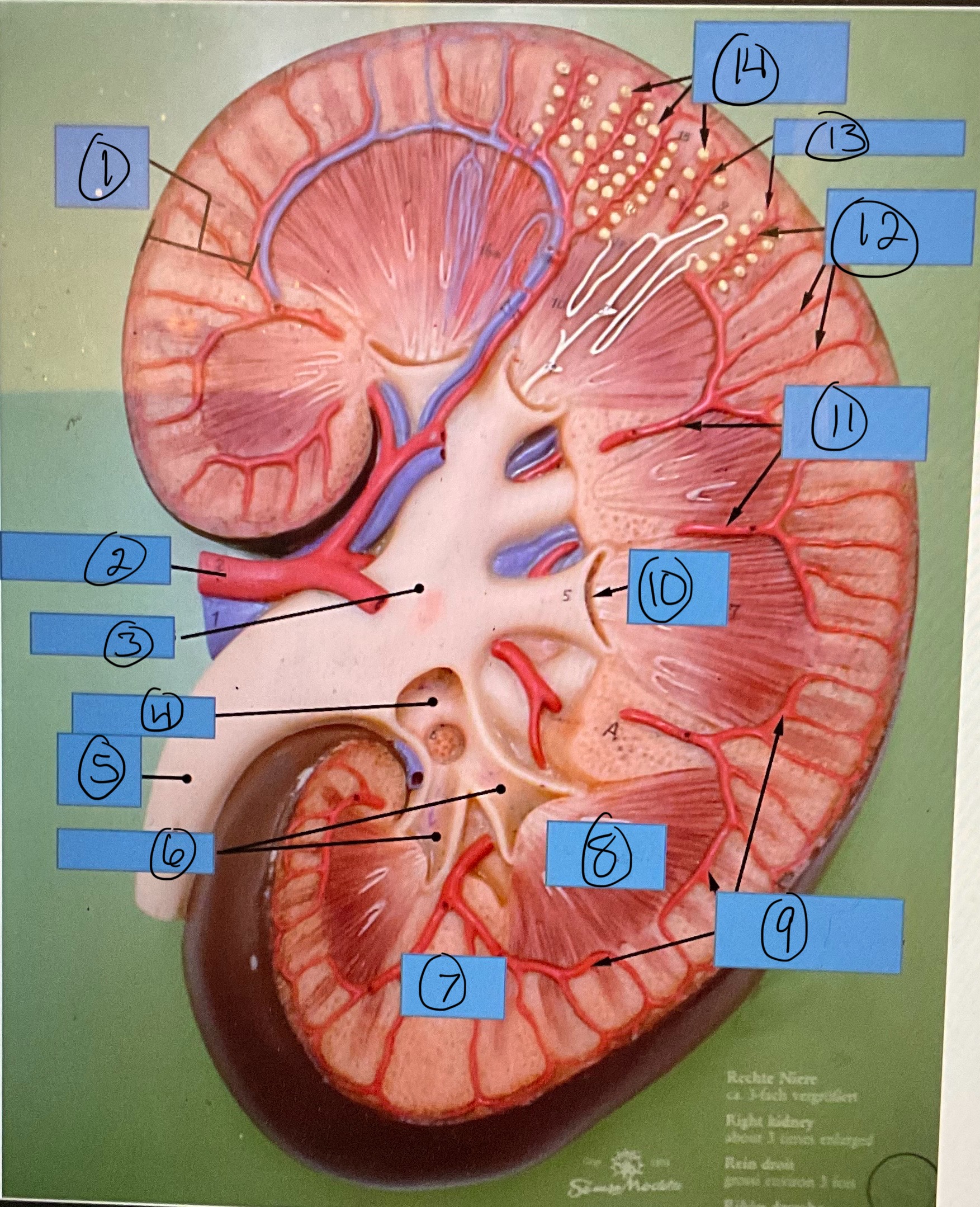
What is 9?
arcuate arteries
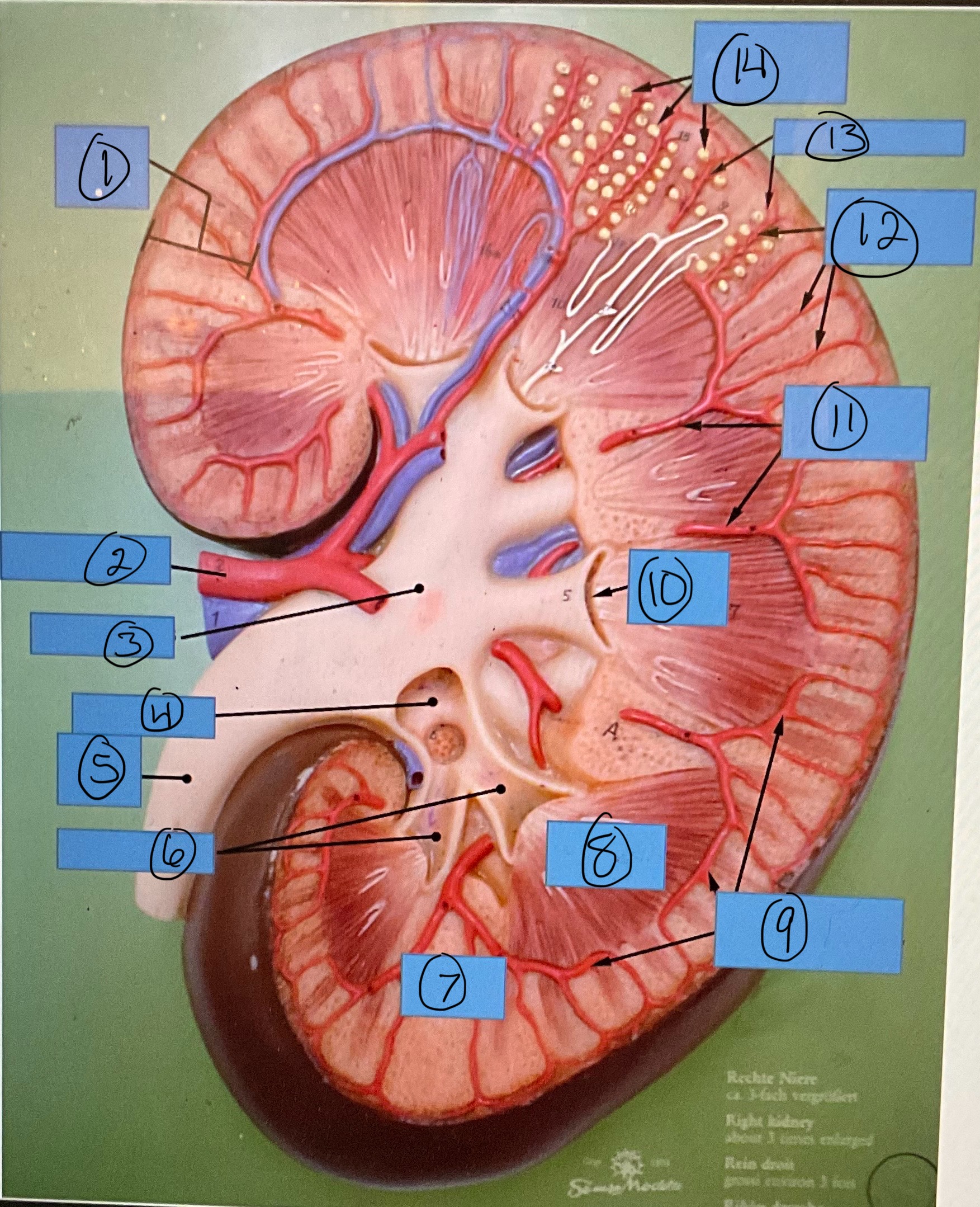
What is 10?
renal papilla
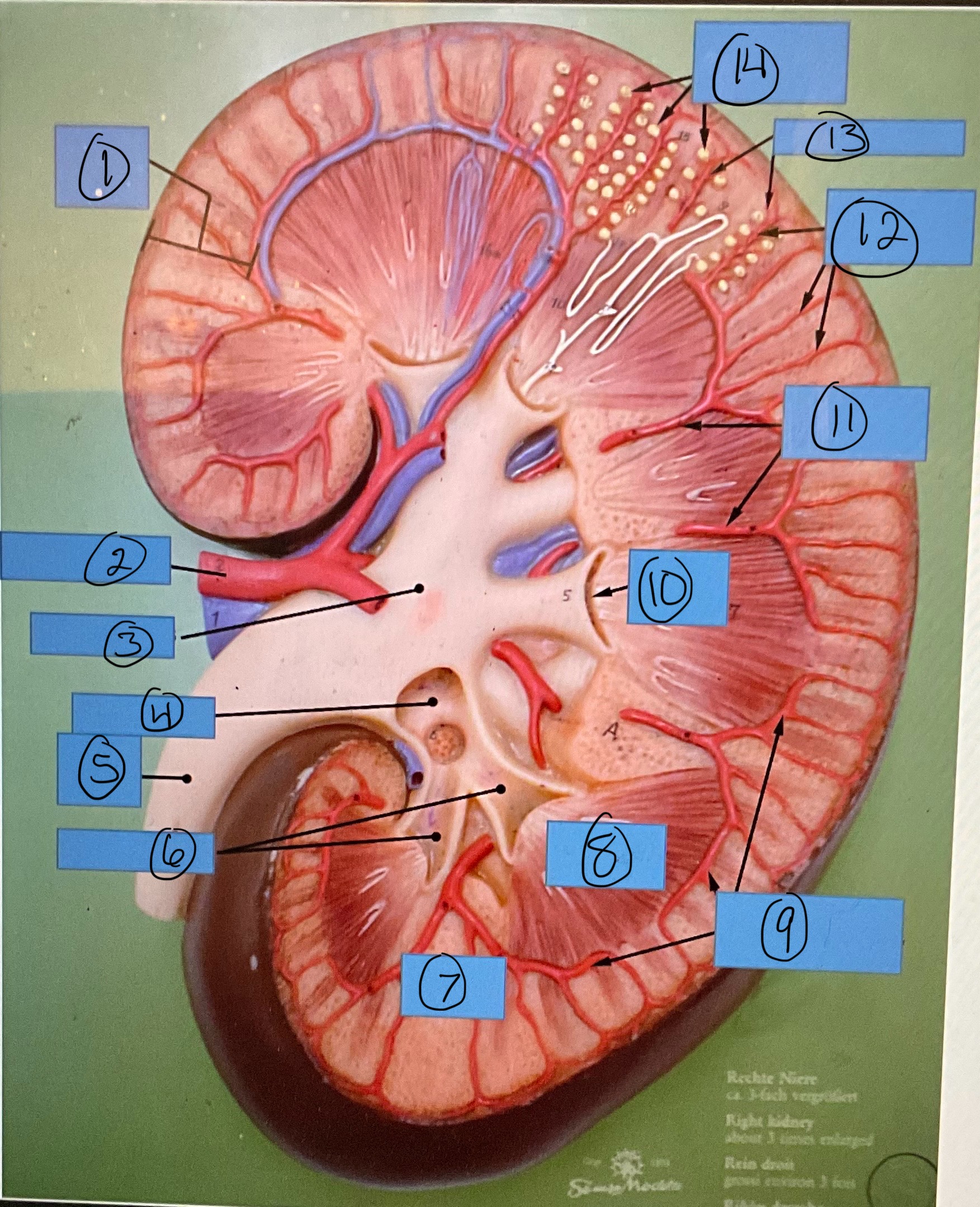
What is 11?
interlobar arteries
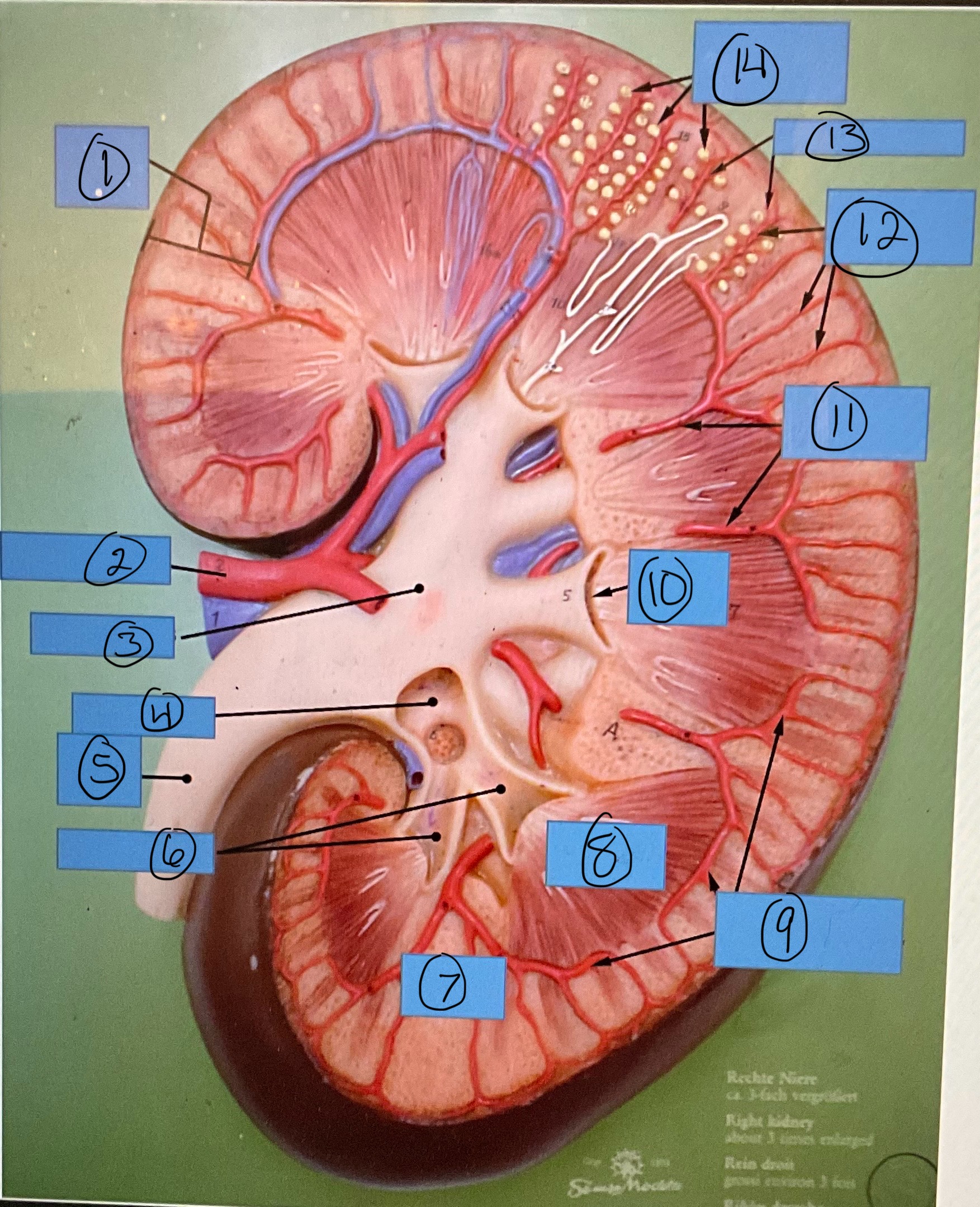
What is 12?
interlobular arteries
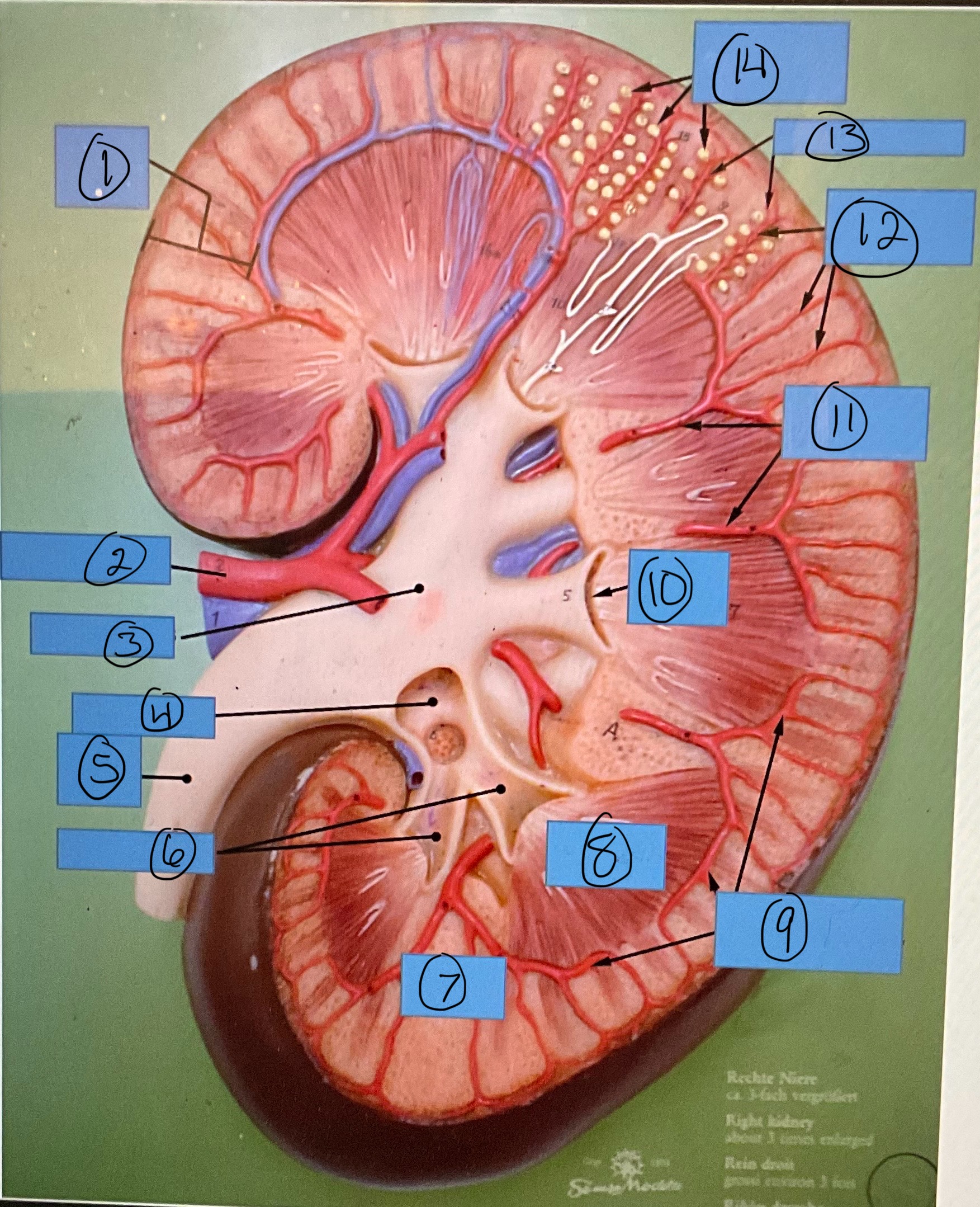
What is 13?
afferent arterioles
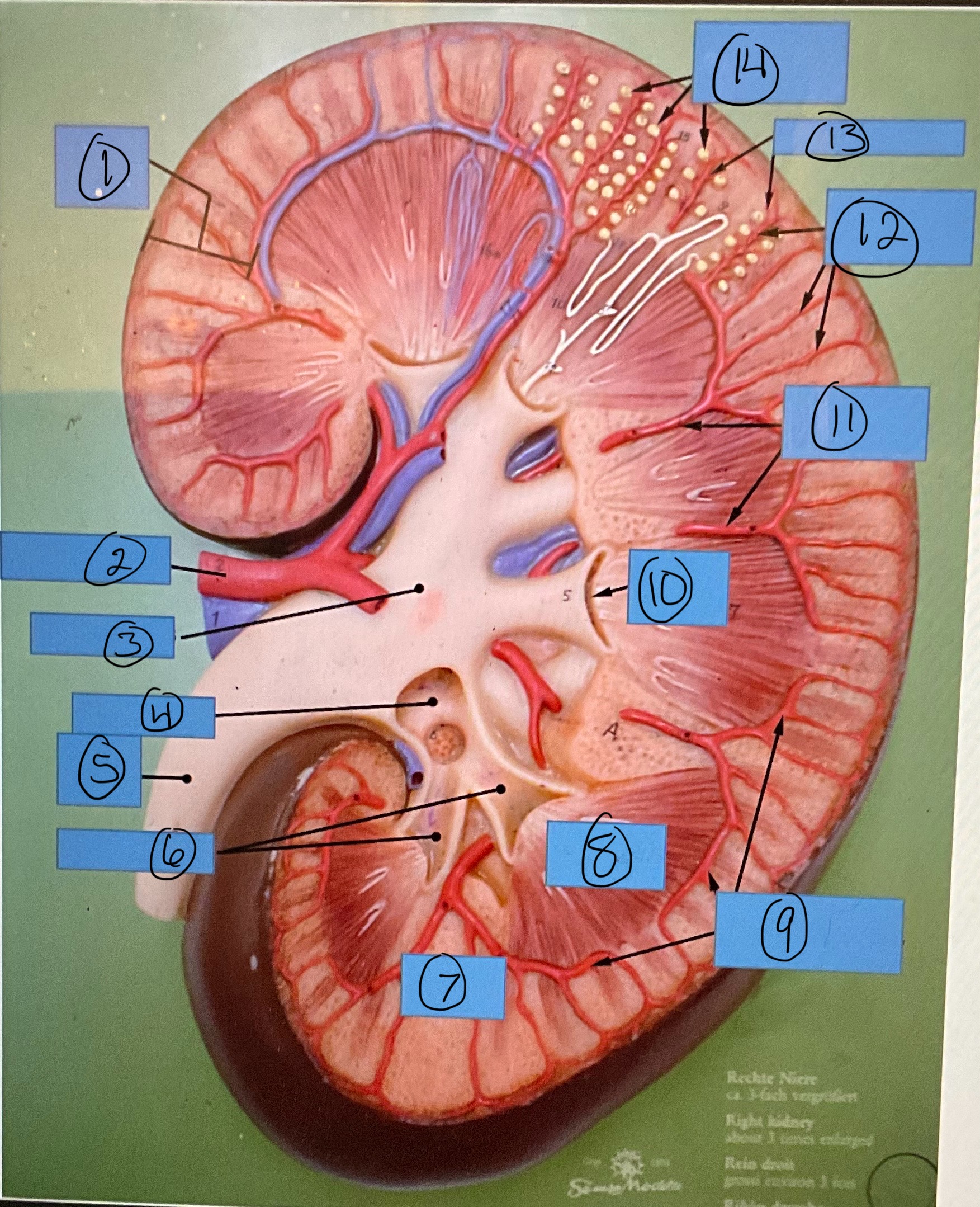
What is 14?
glomerular capsules
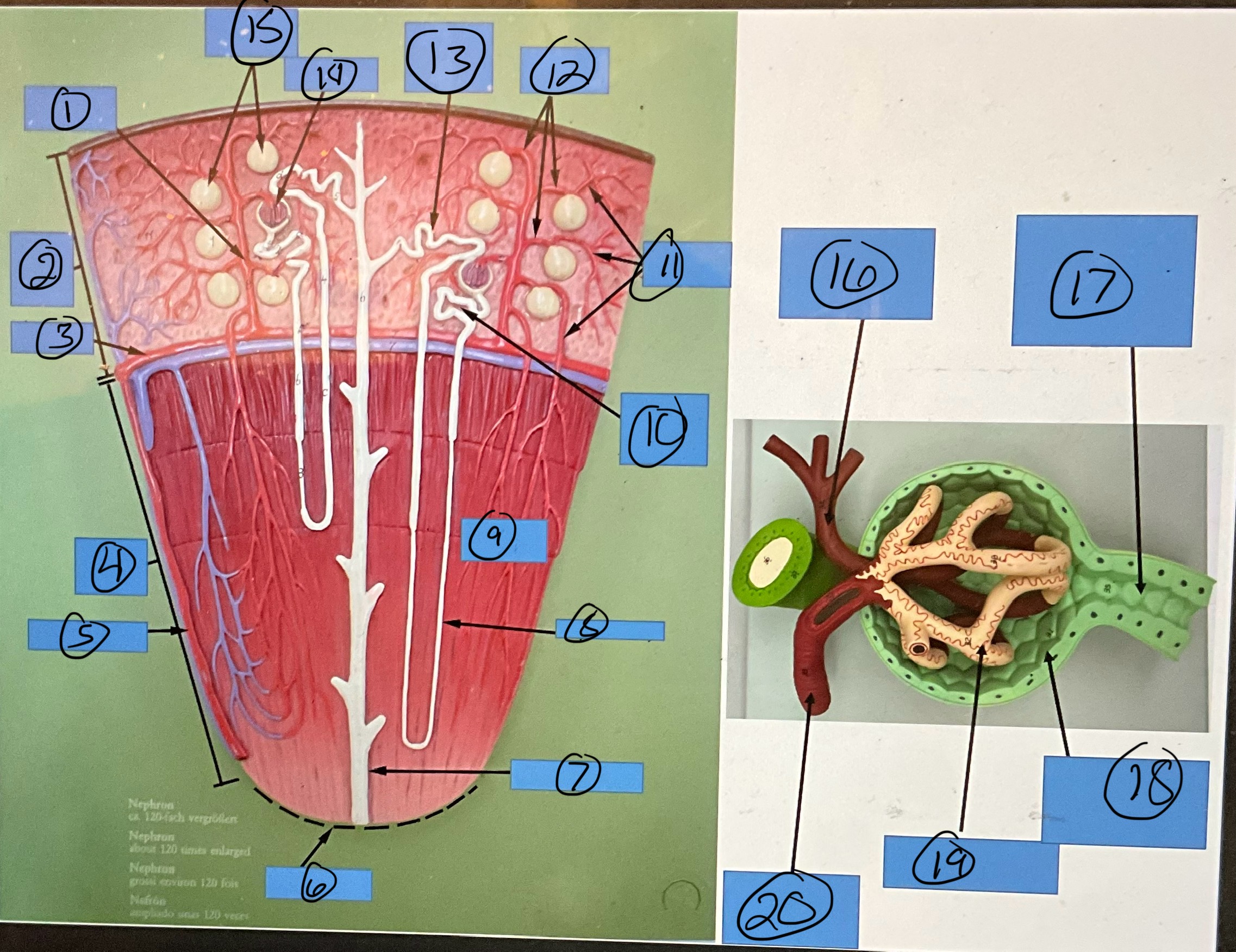
What is 1?
interlobular artery
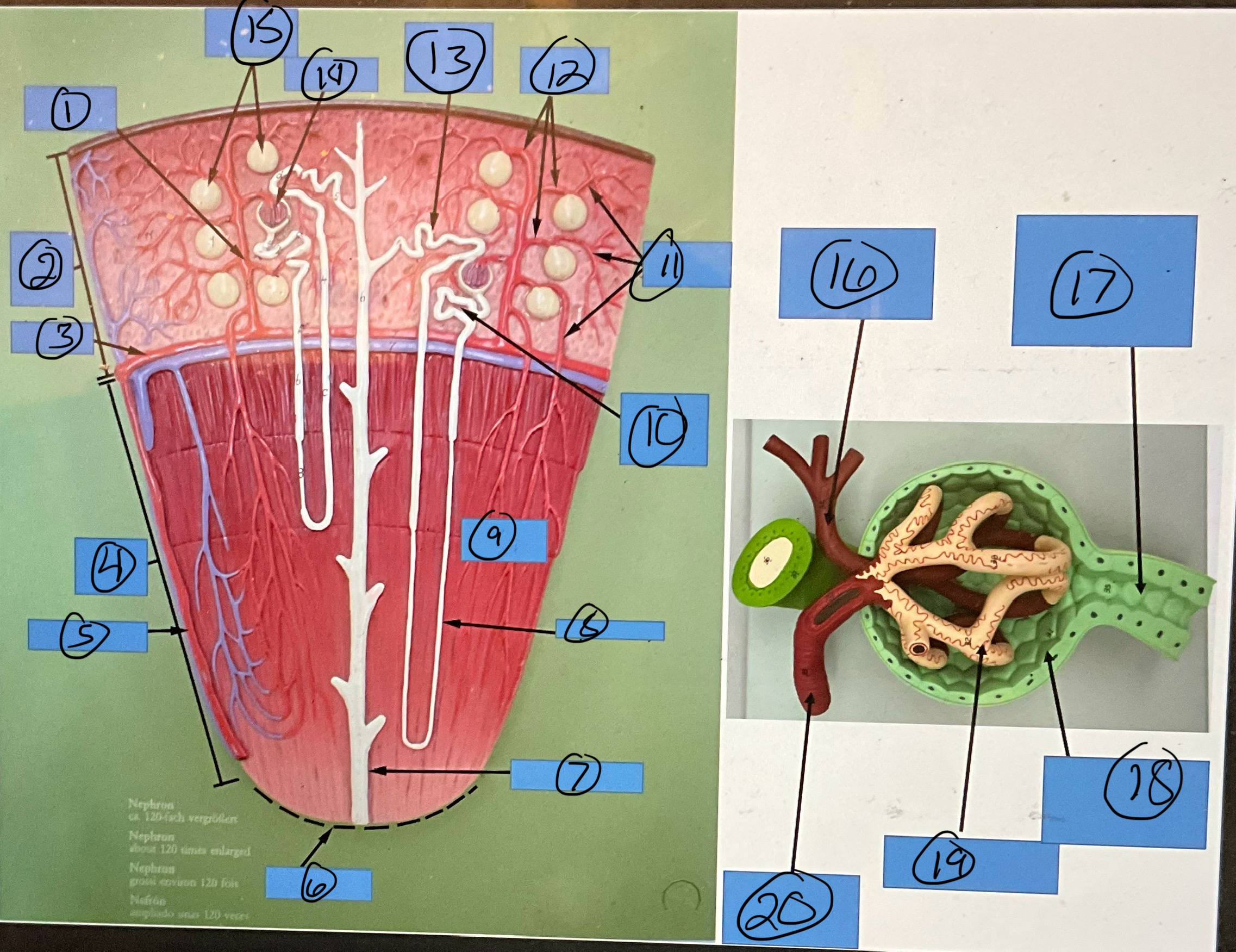
What is 2?
renal cortex
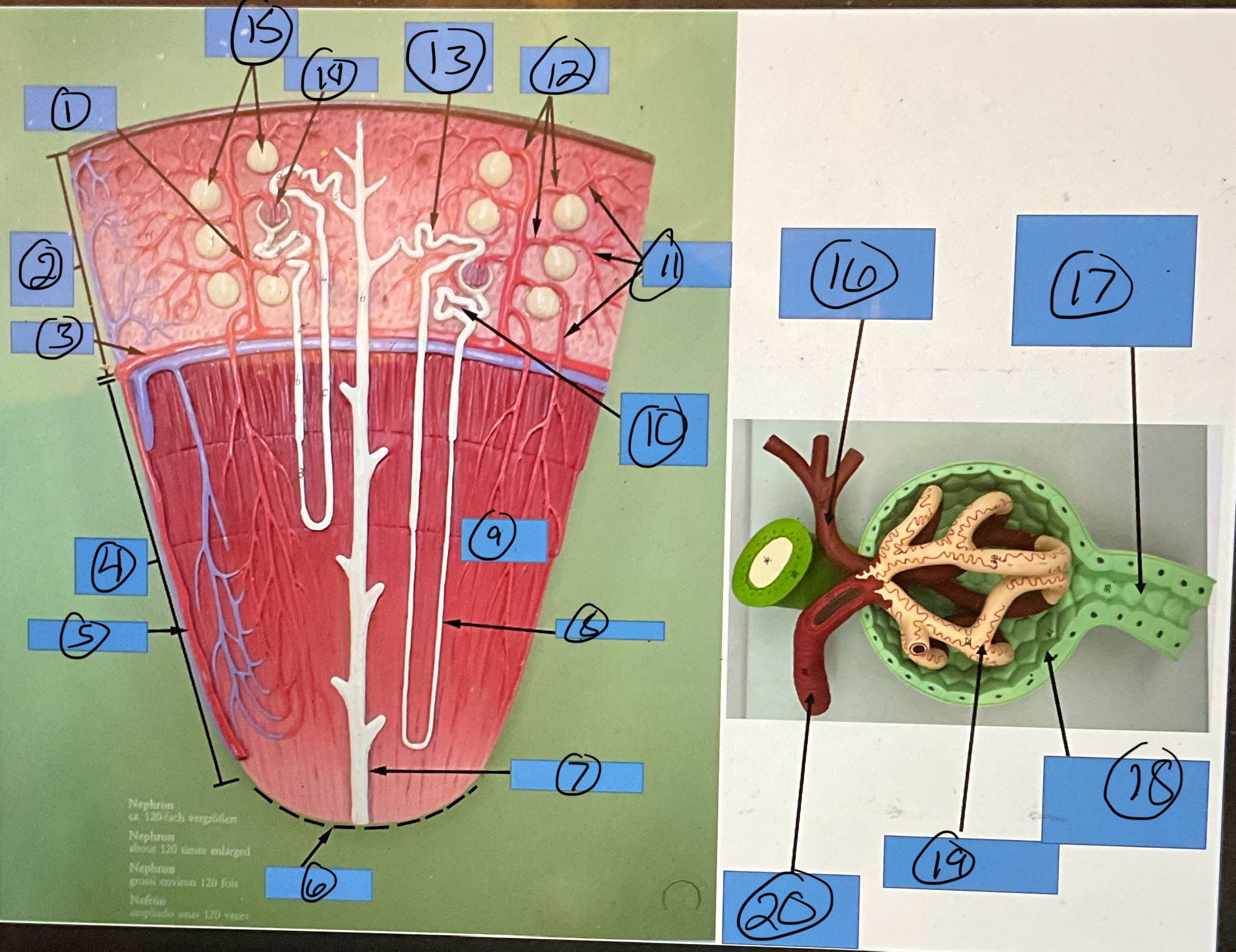
What is 3?
arcuate artery
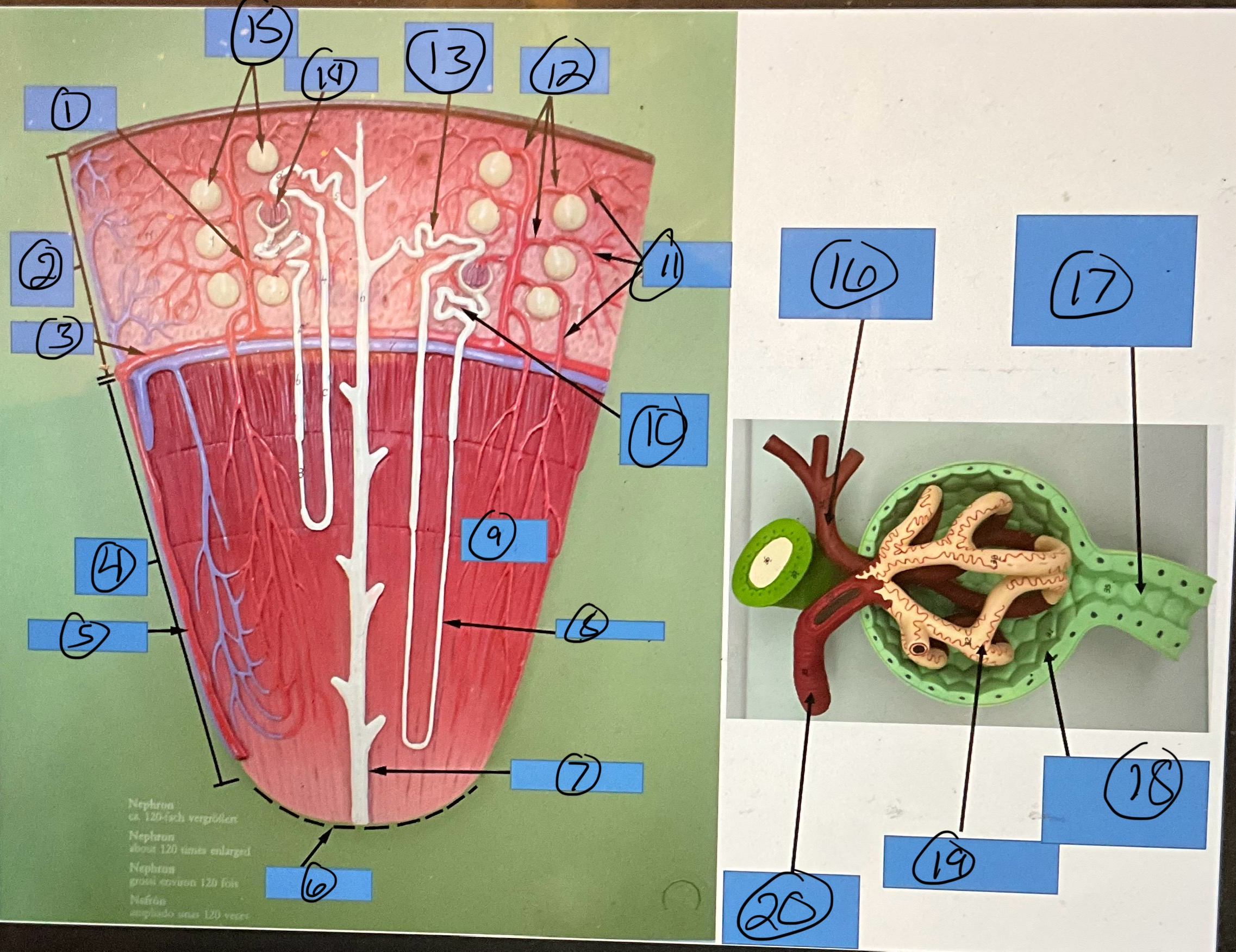
What is 4?
renal medulla
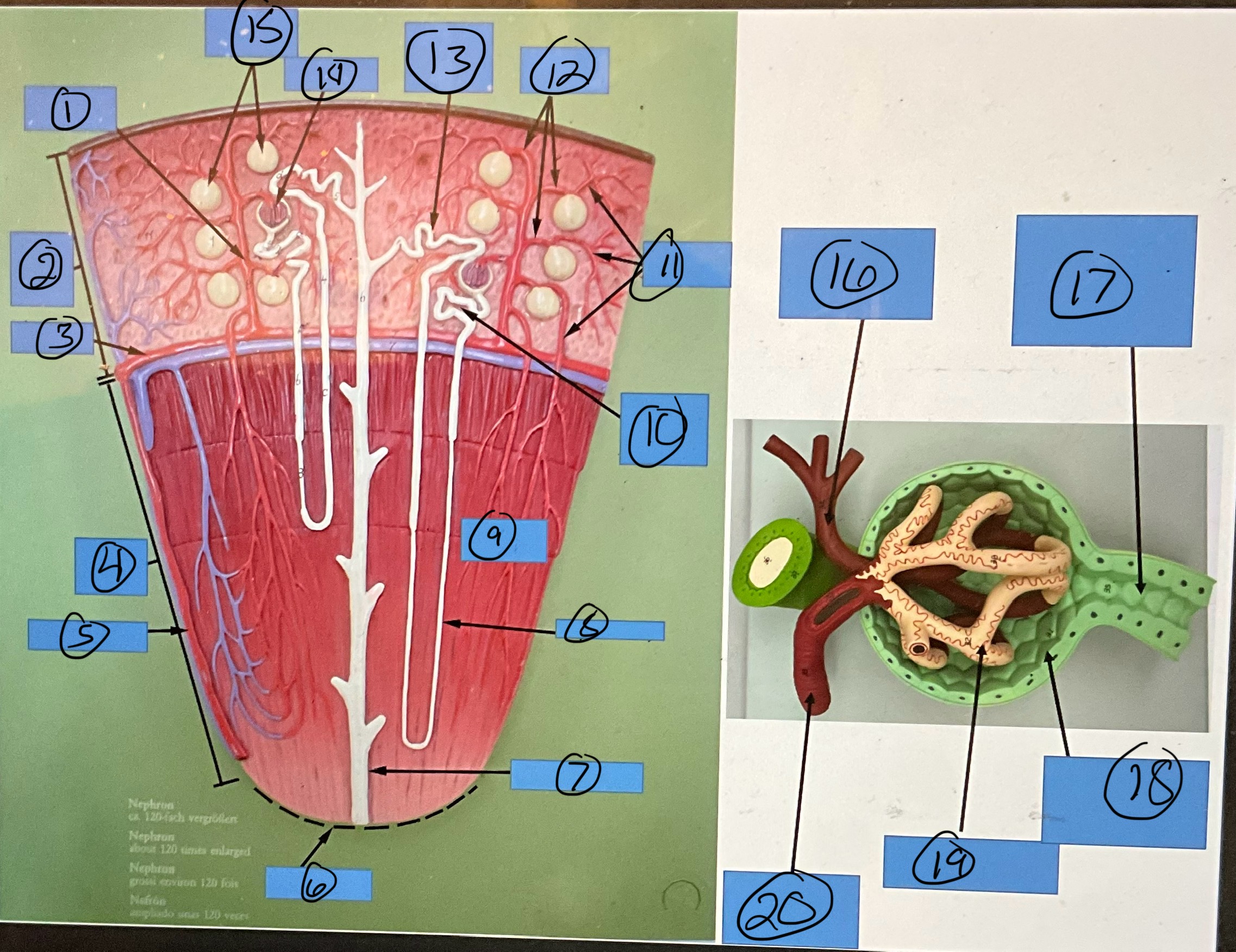
What is 5?
interlobar artery
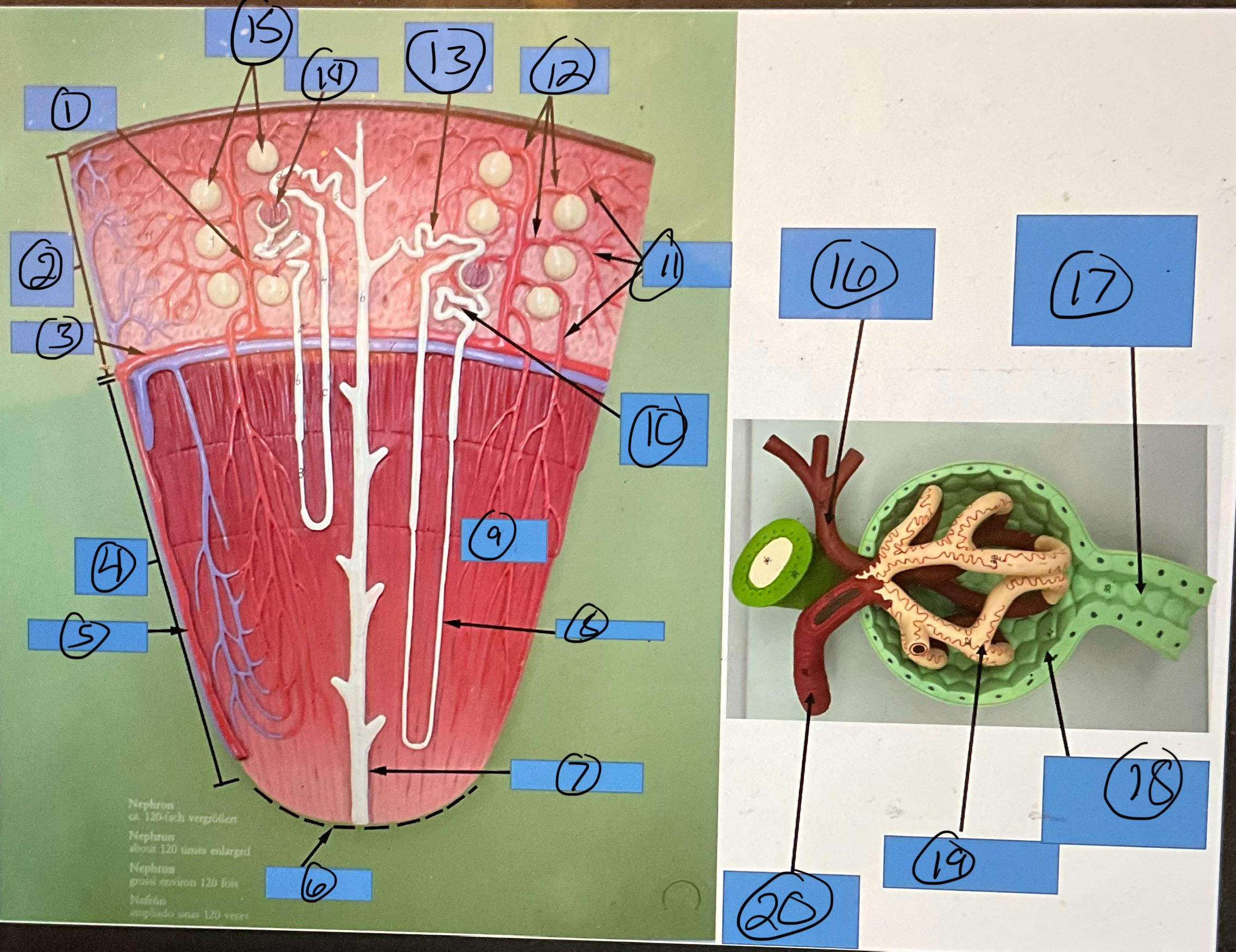
What is 6?
renal papilla
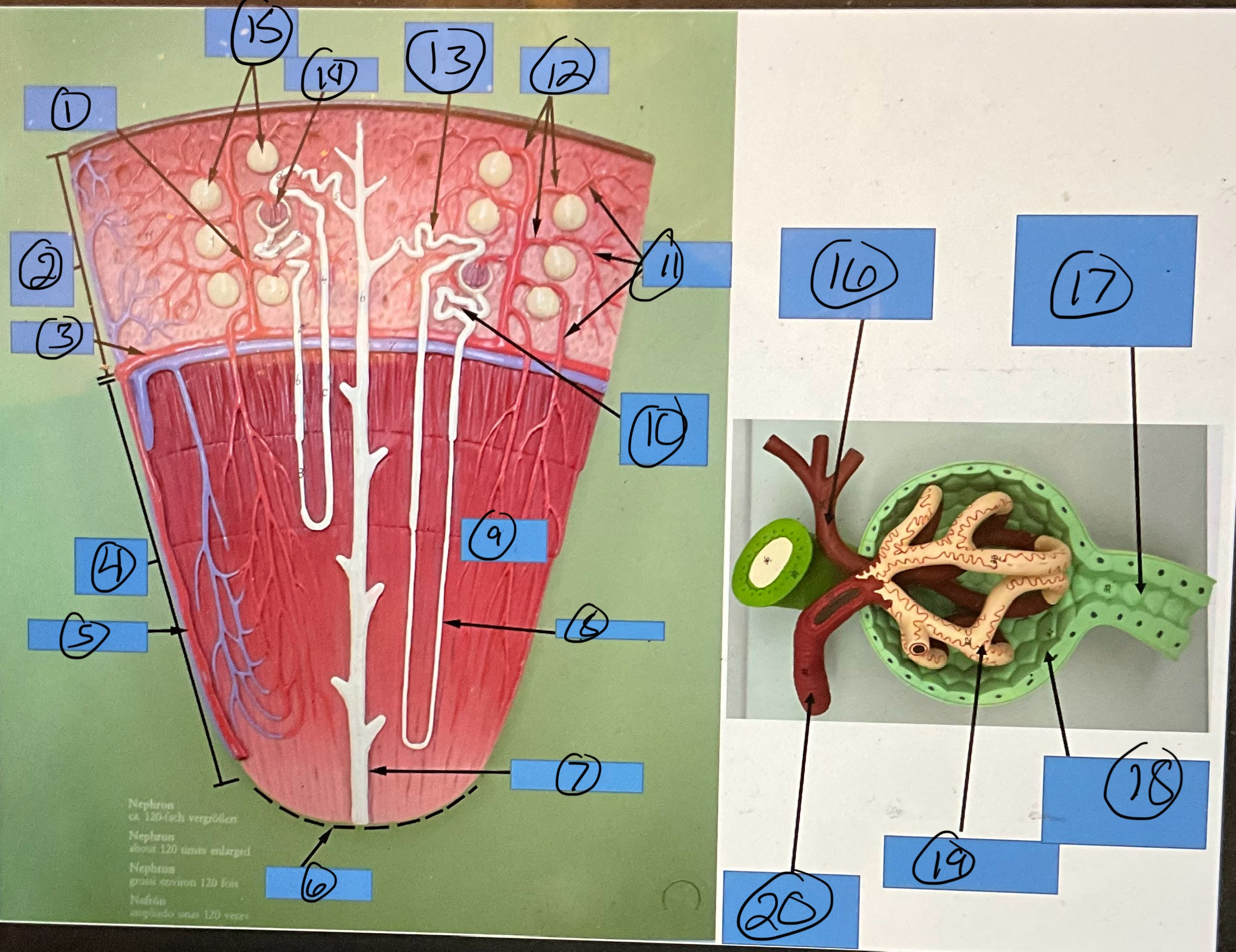
What is 7?
collecting duct
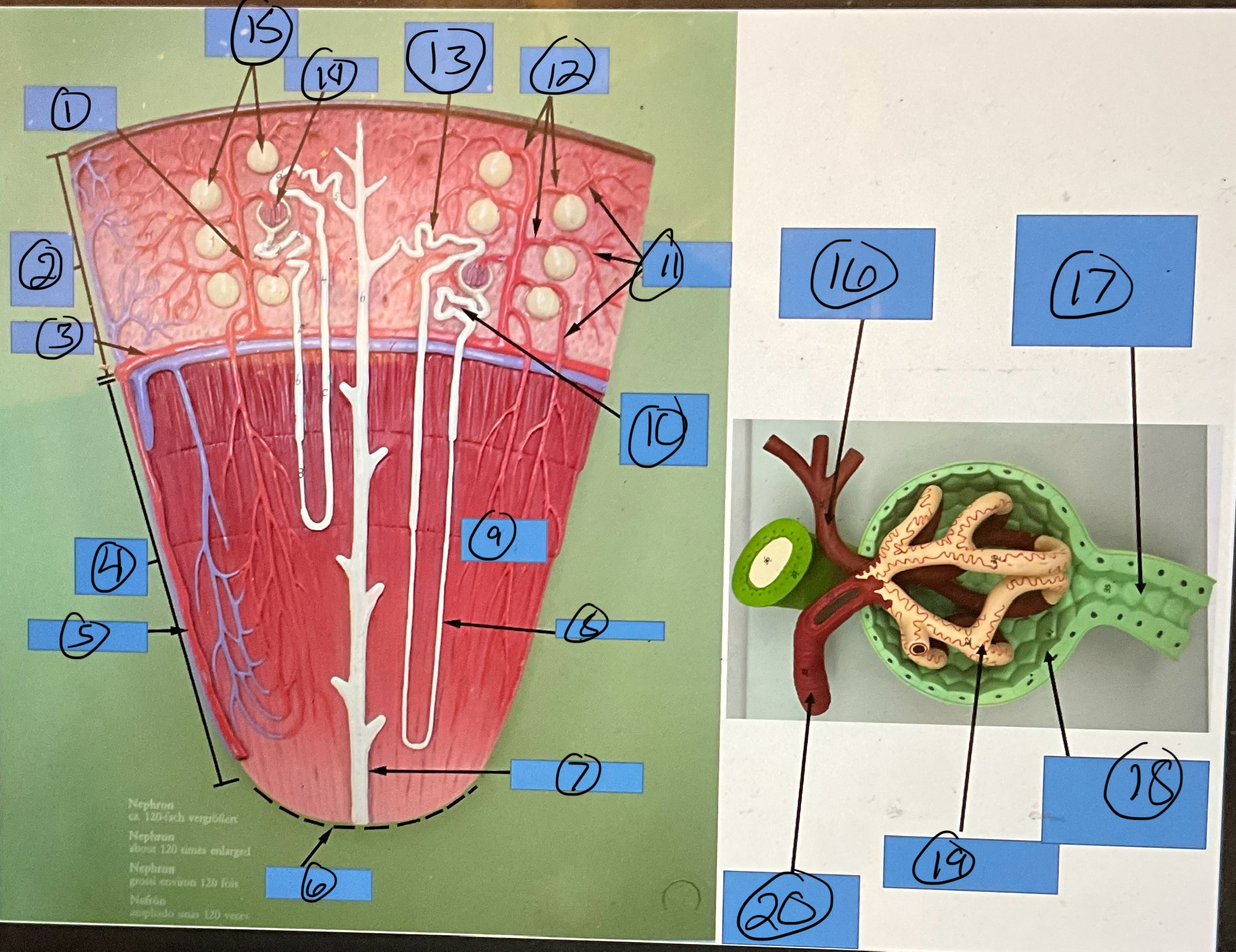
What is 8?
nephron loop
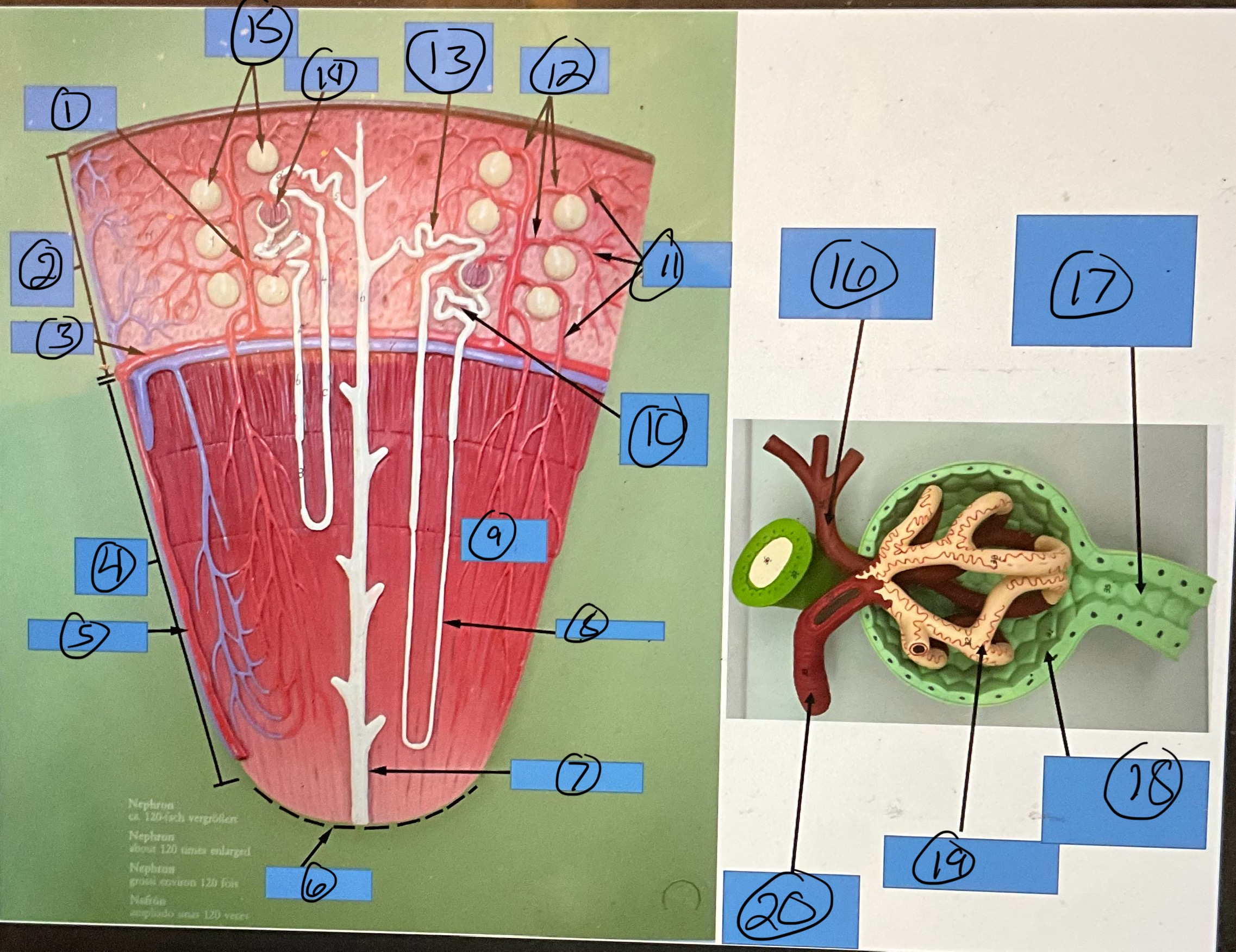
What is 9?
renal pyramid
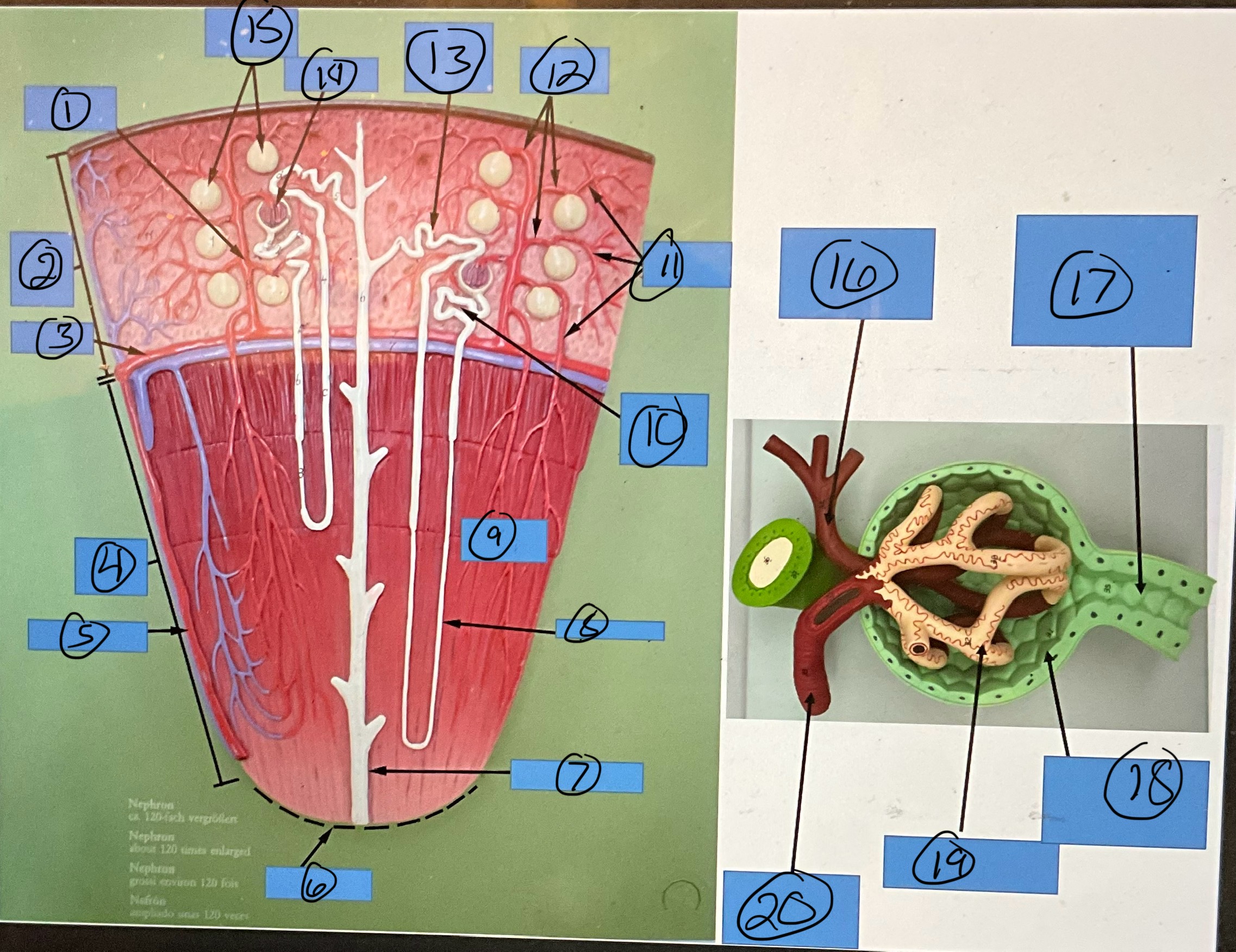
What is 10?
proximal convoluted tubule
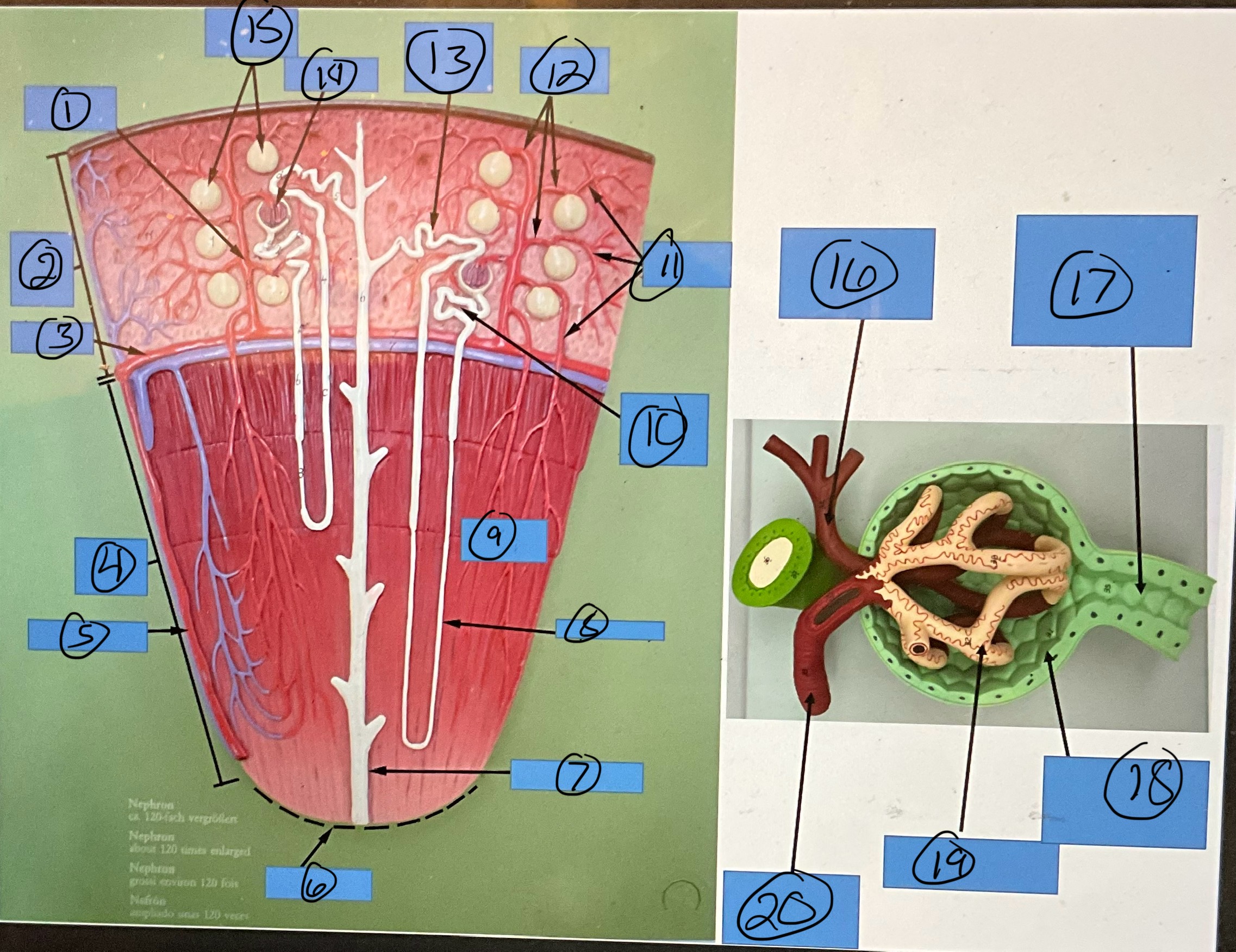
What is 11?
efferent arterioles

What is 12?
afferent arterioles
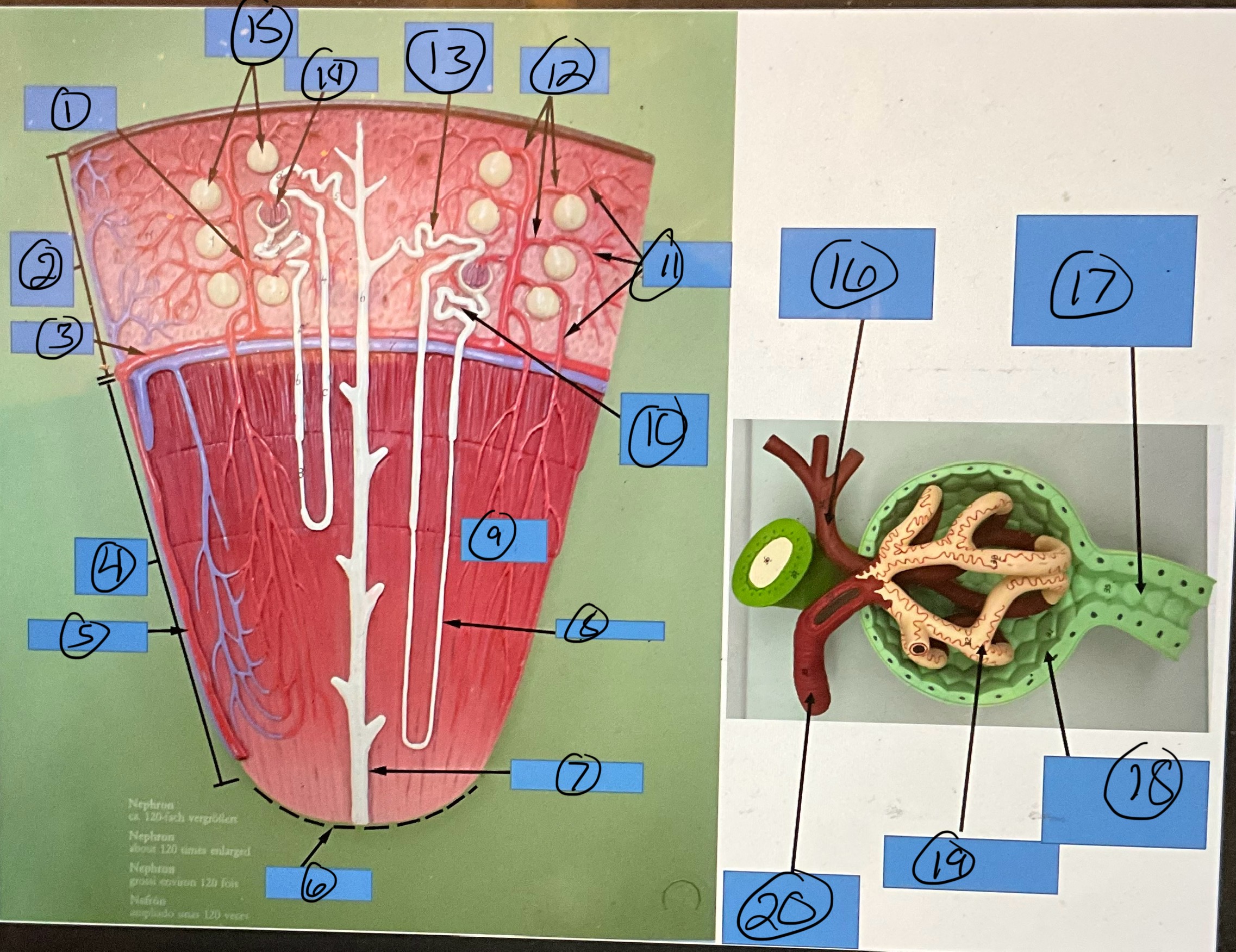
What is 13?
distal convoluted tubule
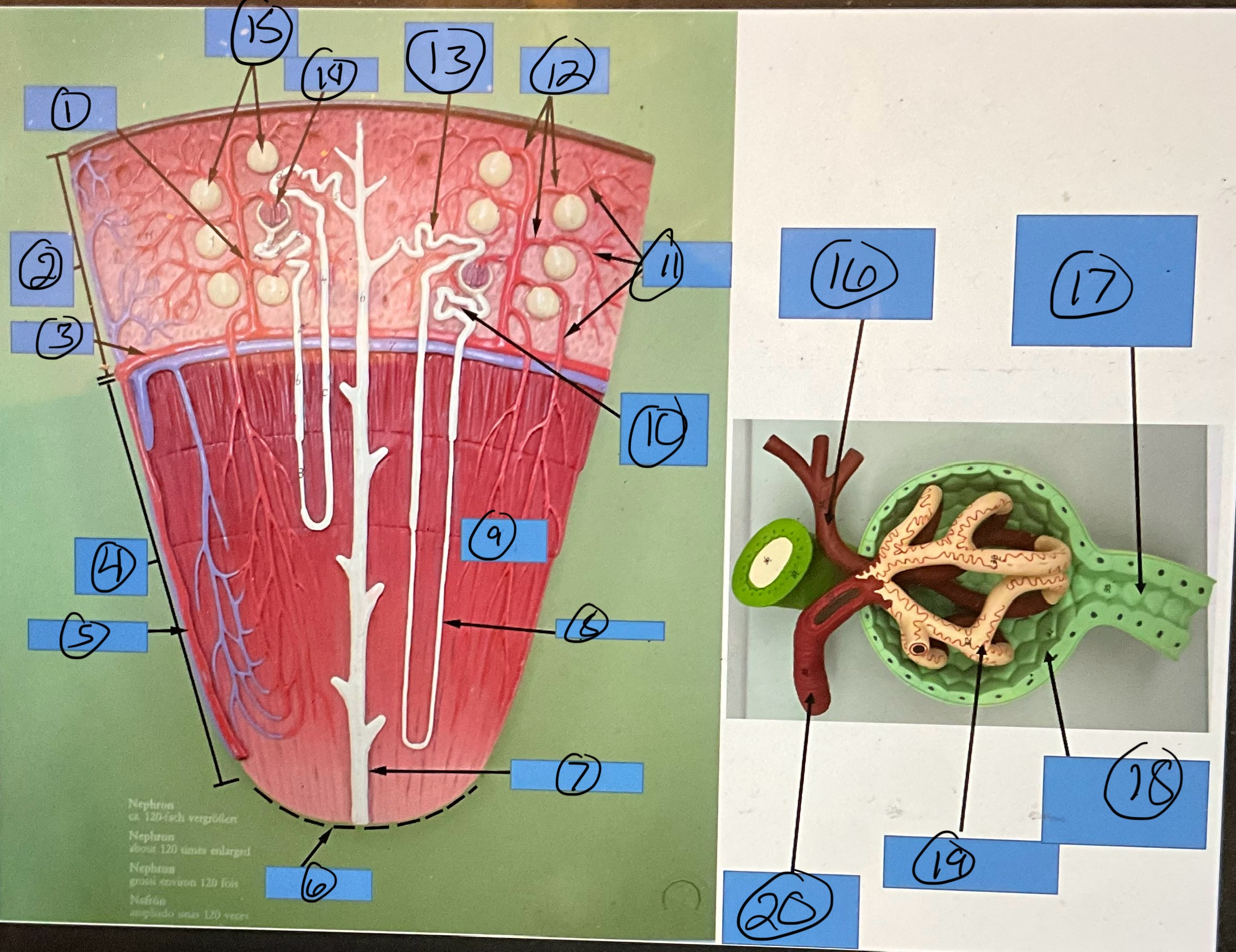
What is 14?
glomerulus
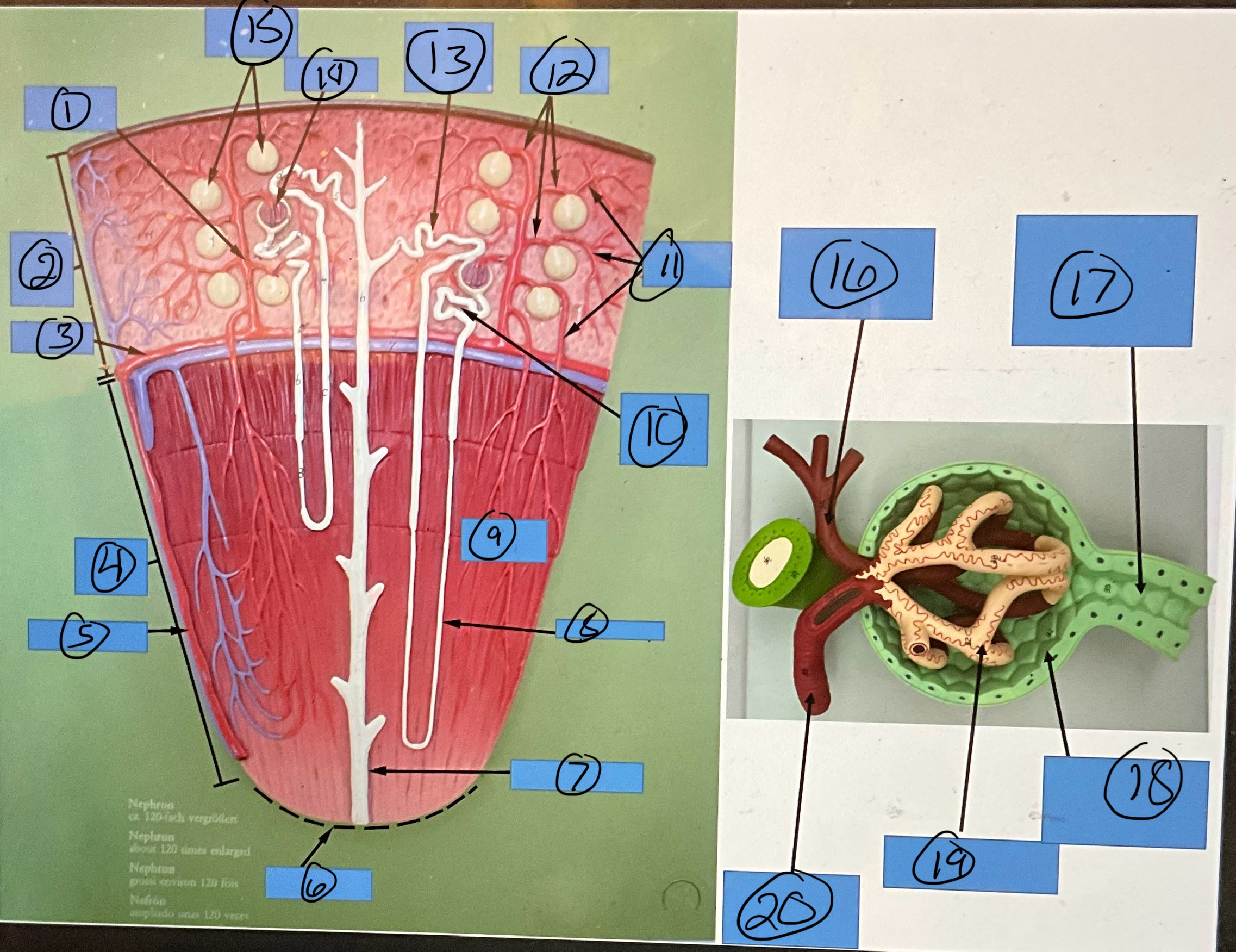
What is 15?
glomerular capsules
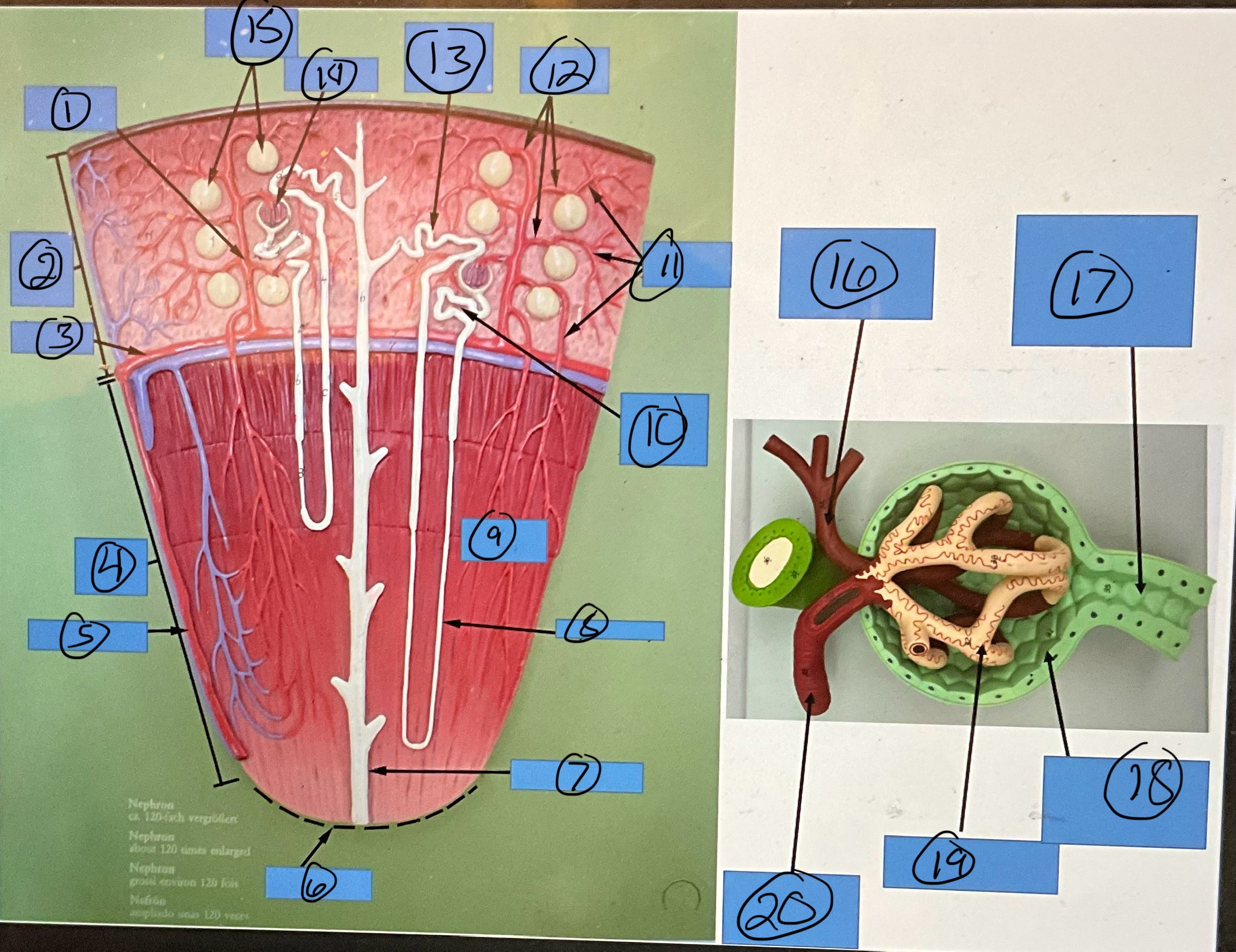
What is 16?
efferent arteriole
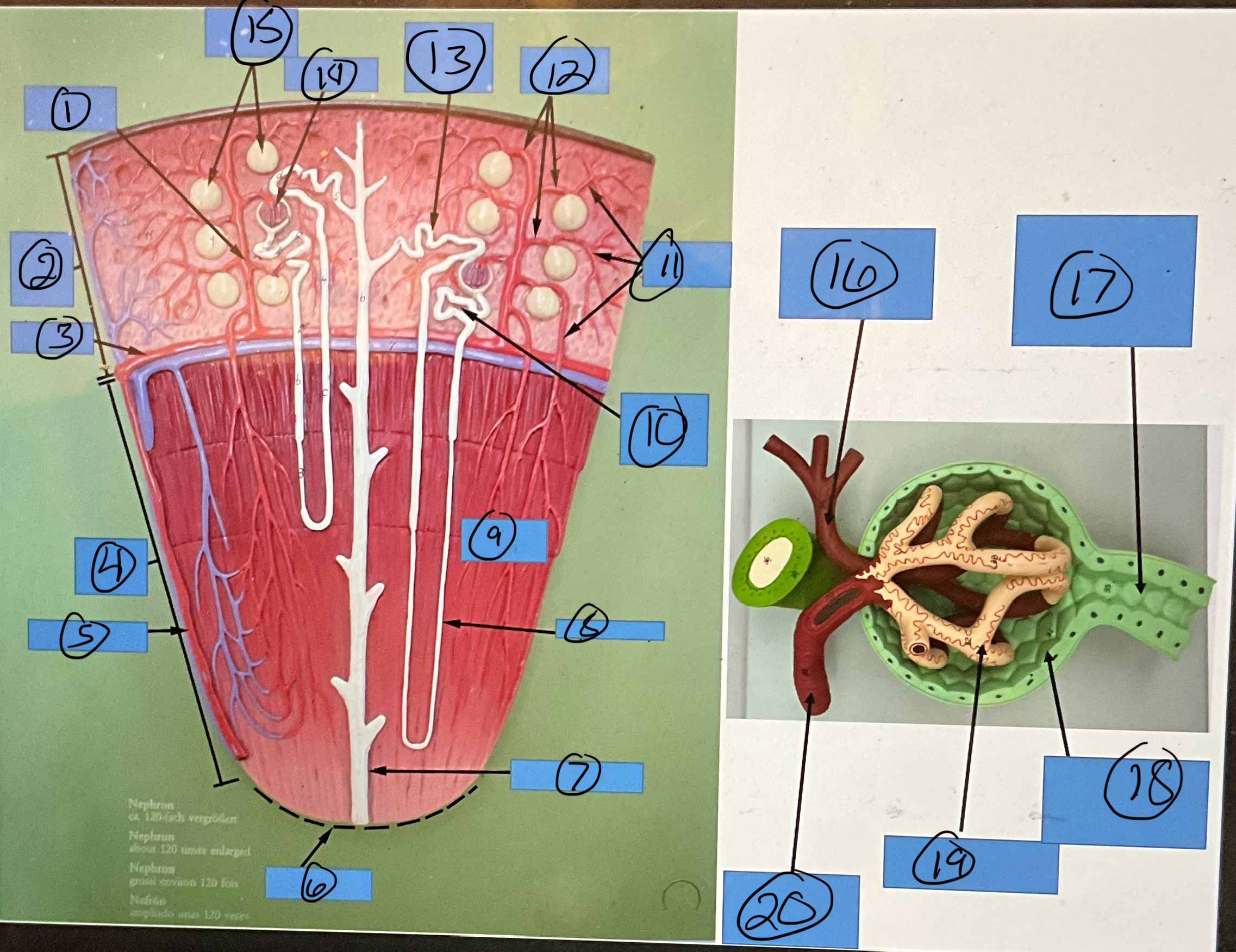
What is 17?
proximal convoluted tubule
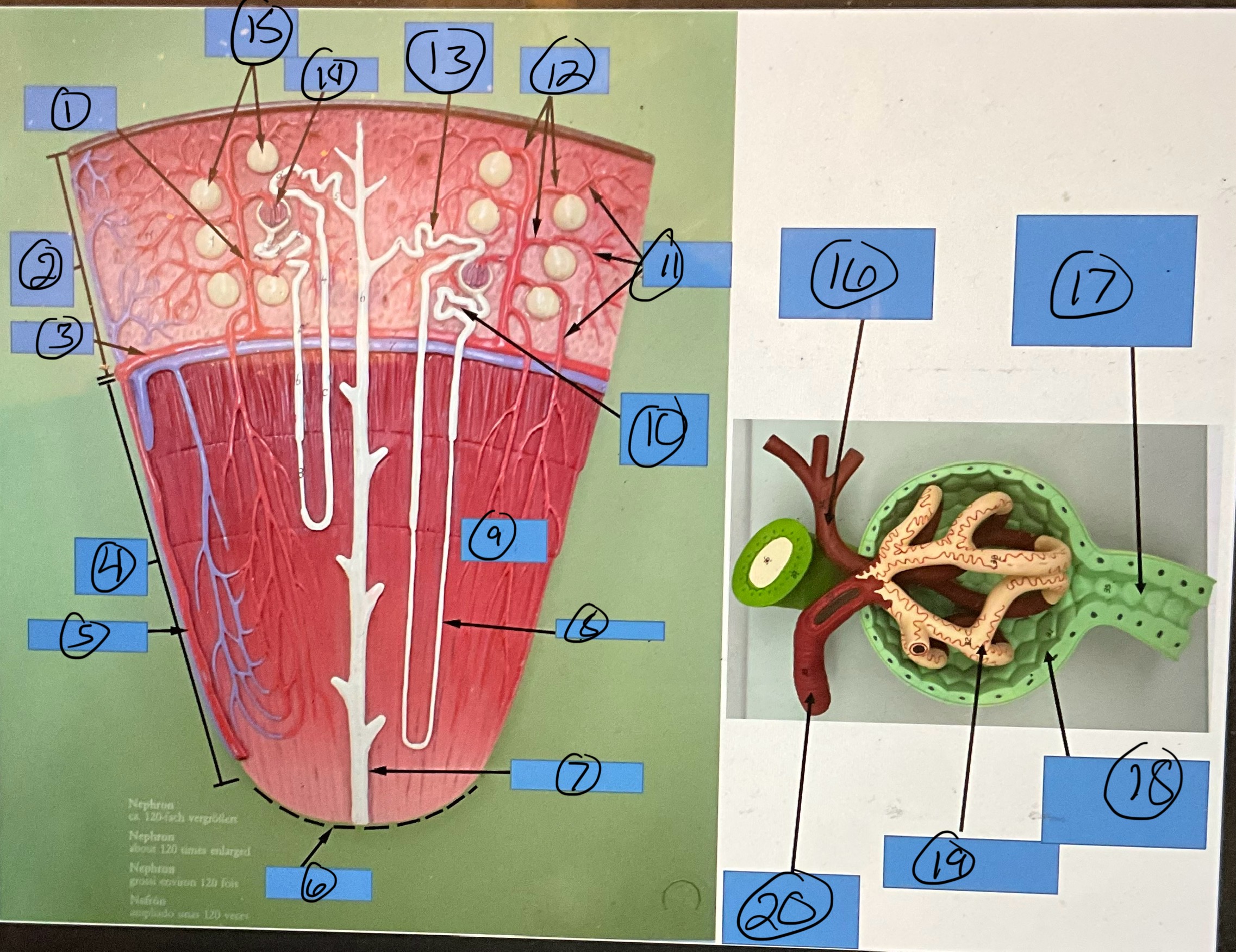
What is 18?
glomerular capsule
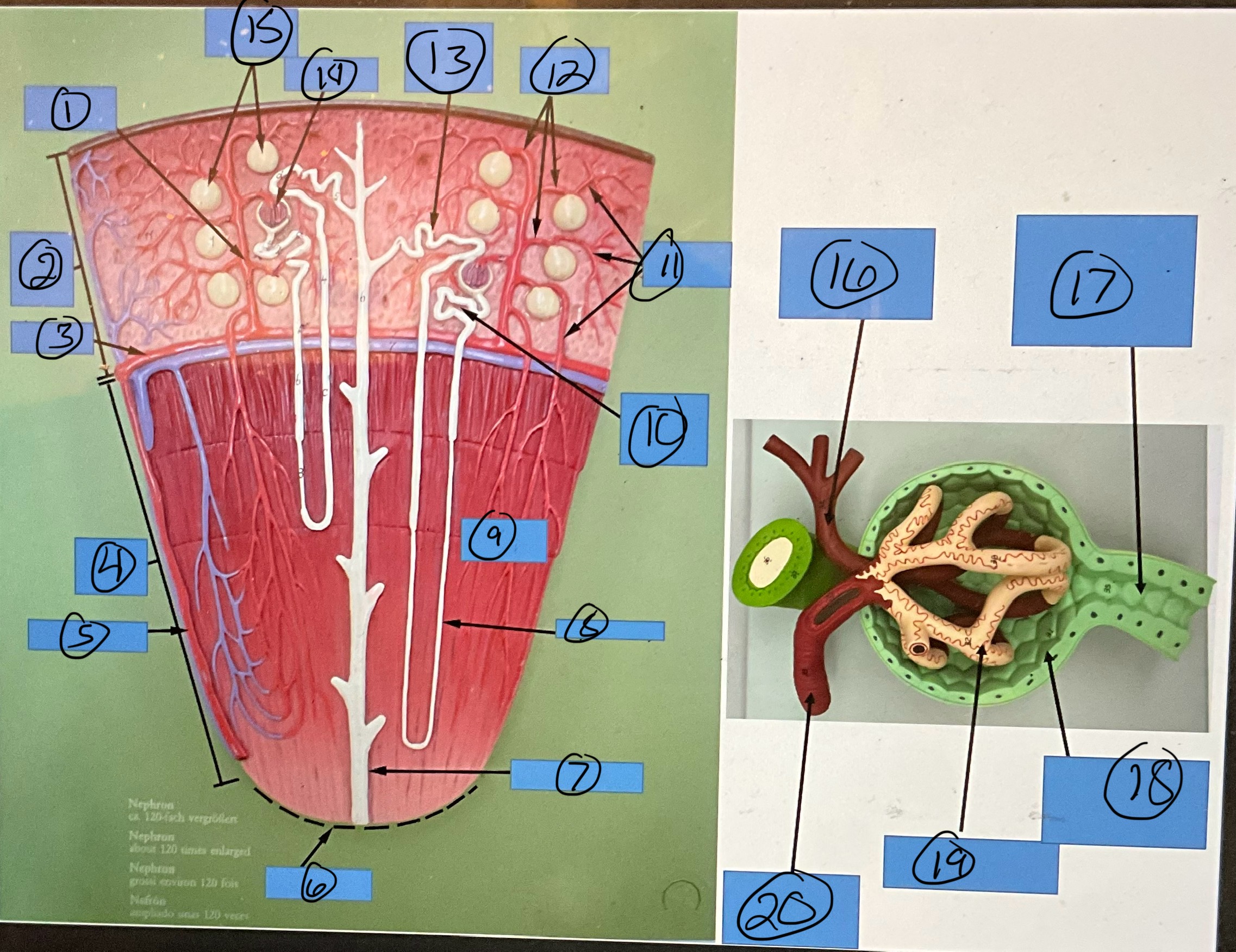
What is 19?
glomerulus
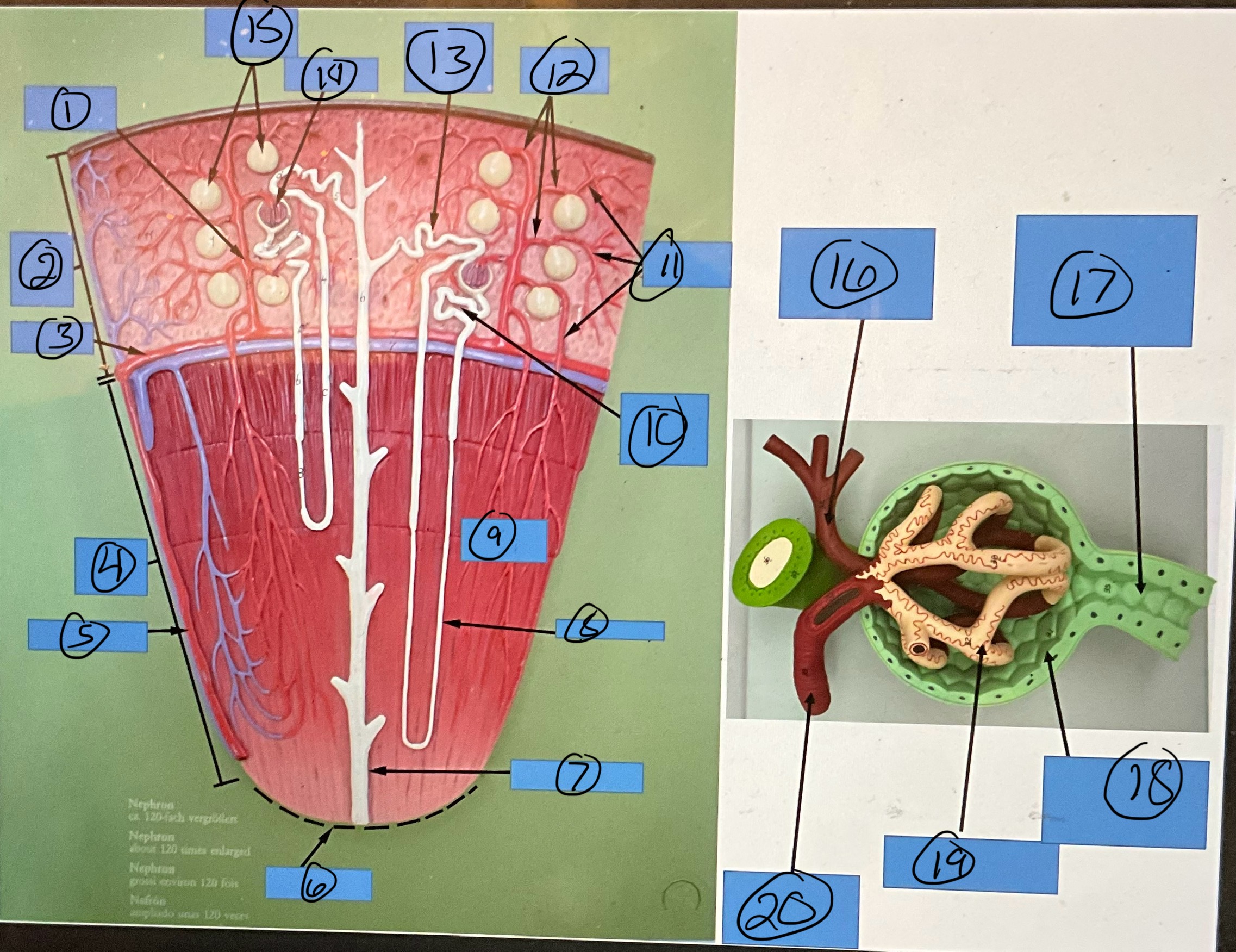
What is 20?
afferent arteriole
What is 1?
renal artery
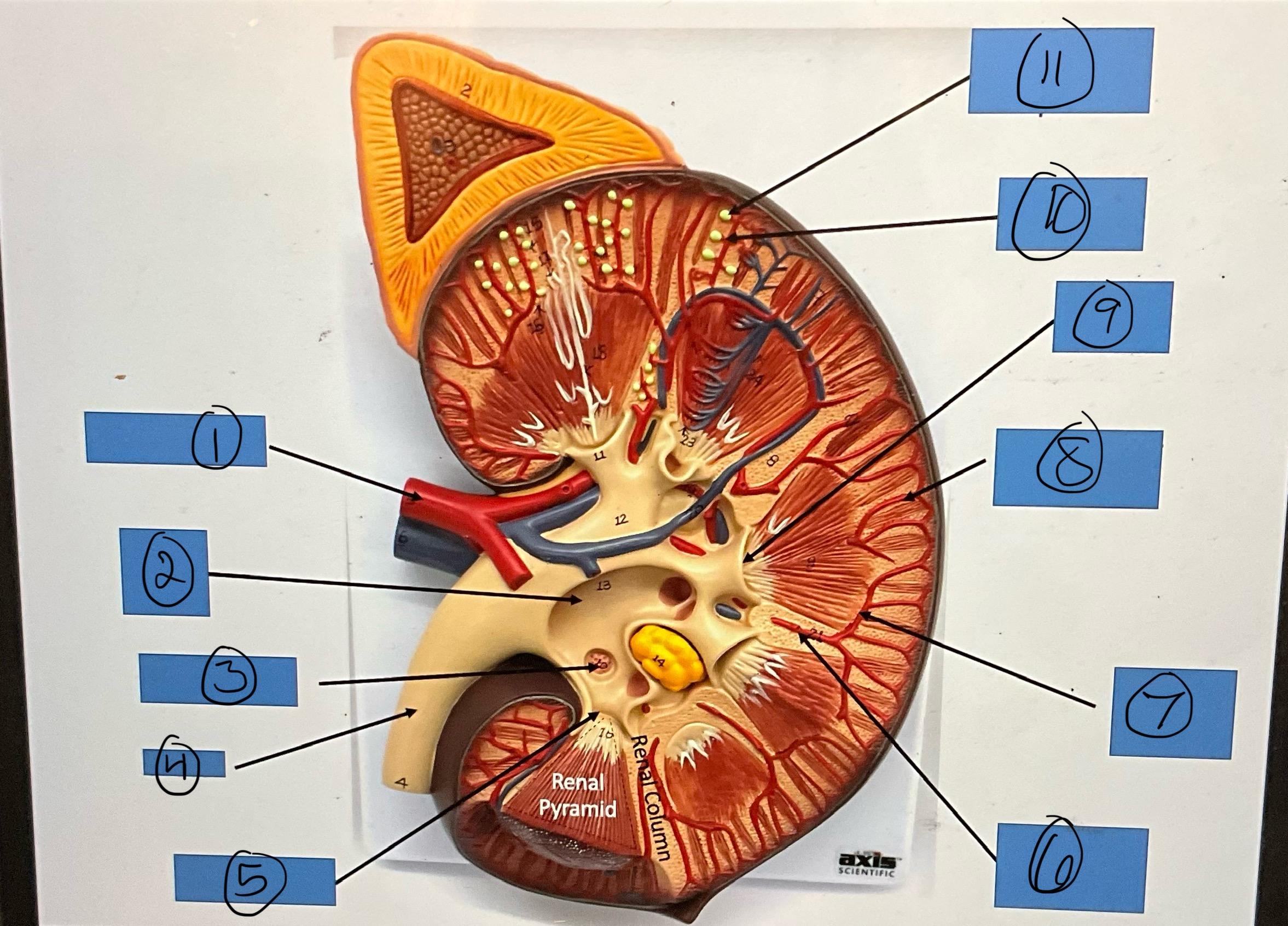
What is 2?
renal pelvis
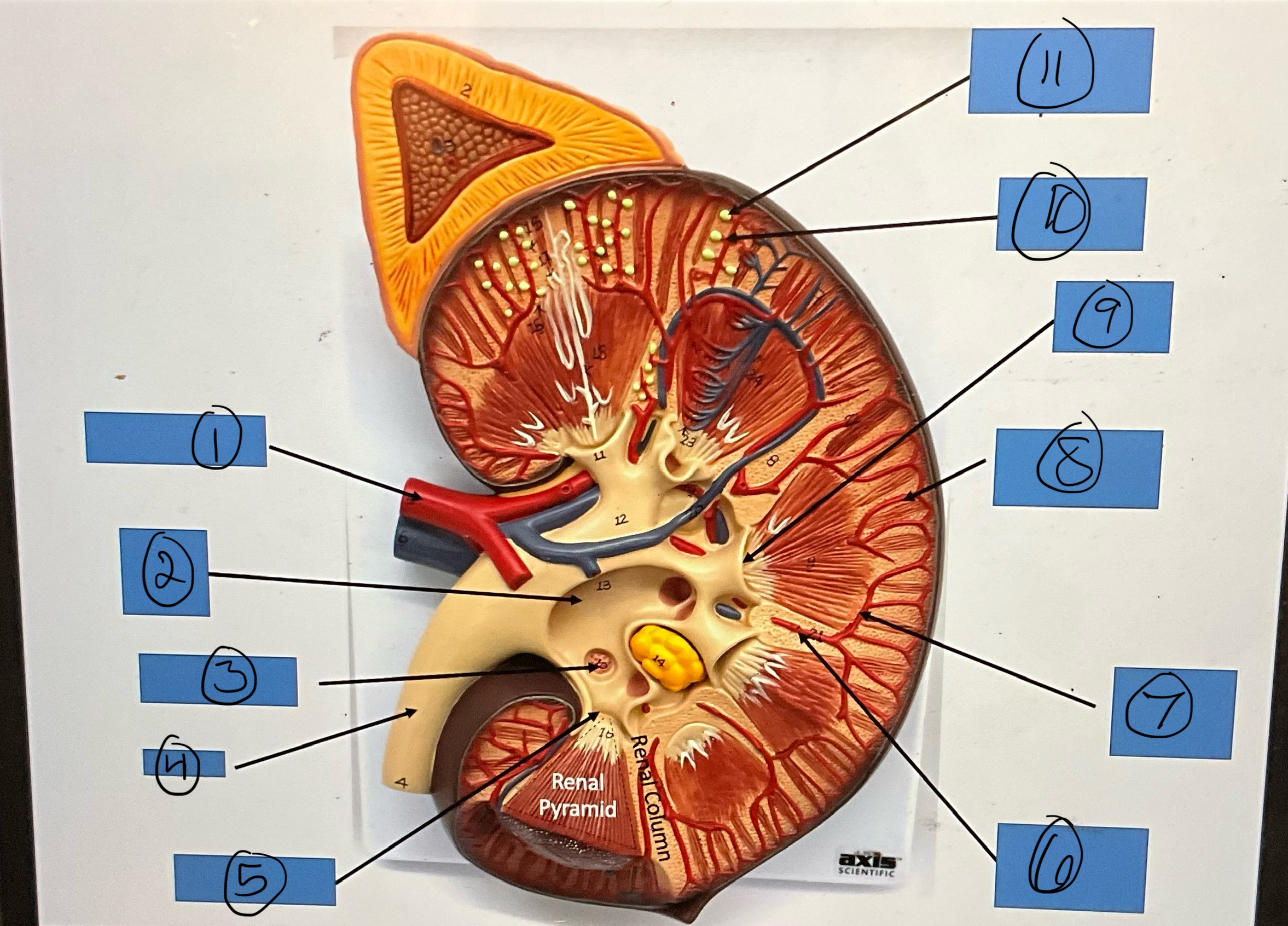
What is 3?
major calyx
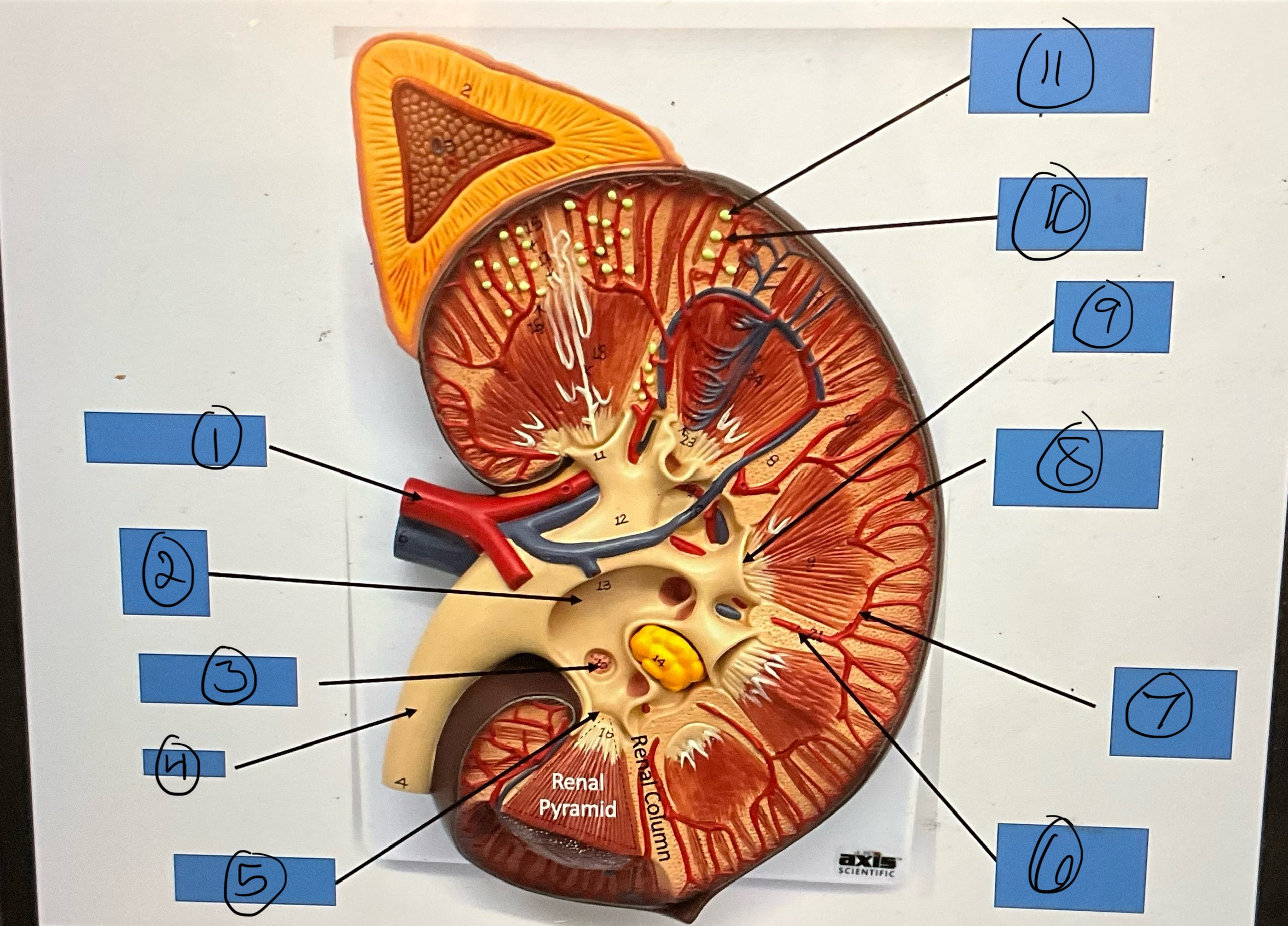
What is 4?
ureter
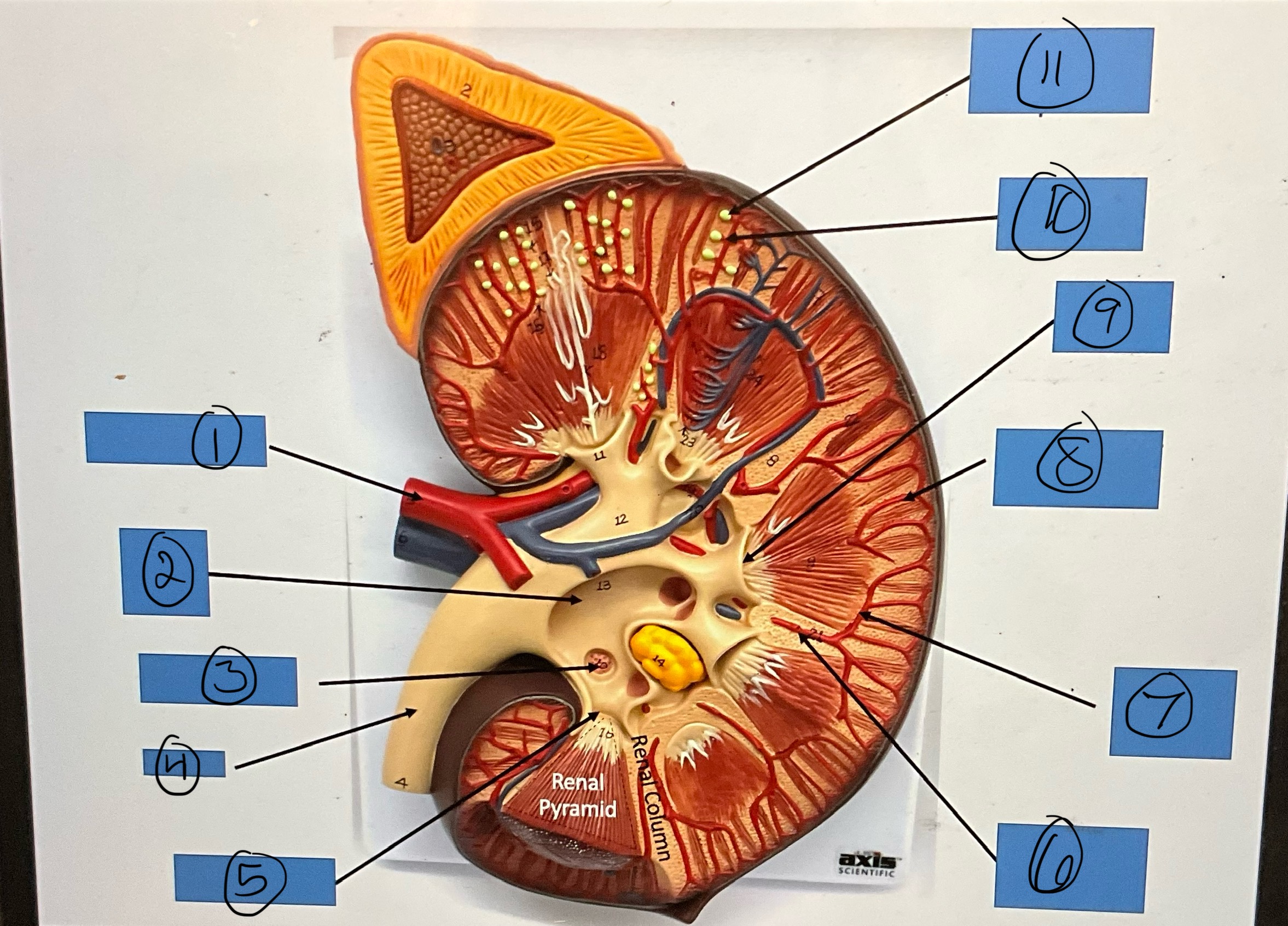
What is 5?
minor calyx
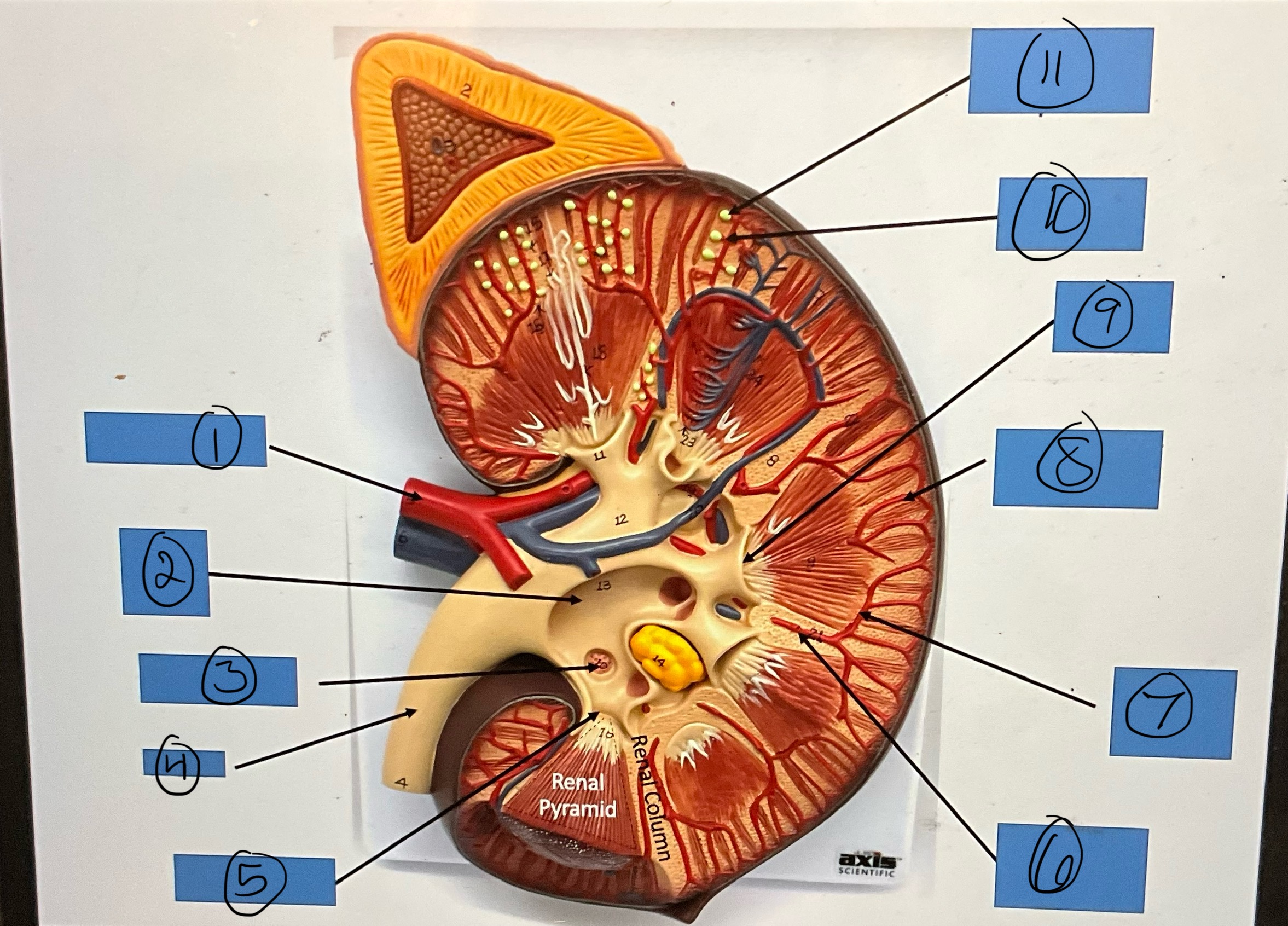
What is 6?
interlobar artery
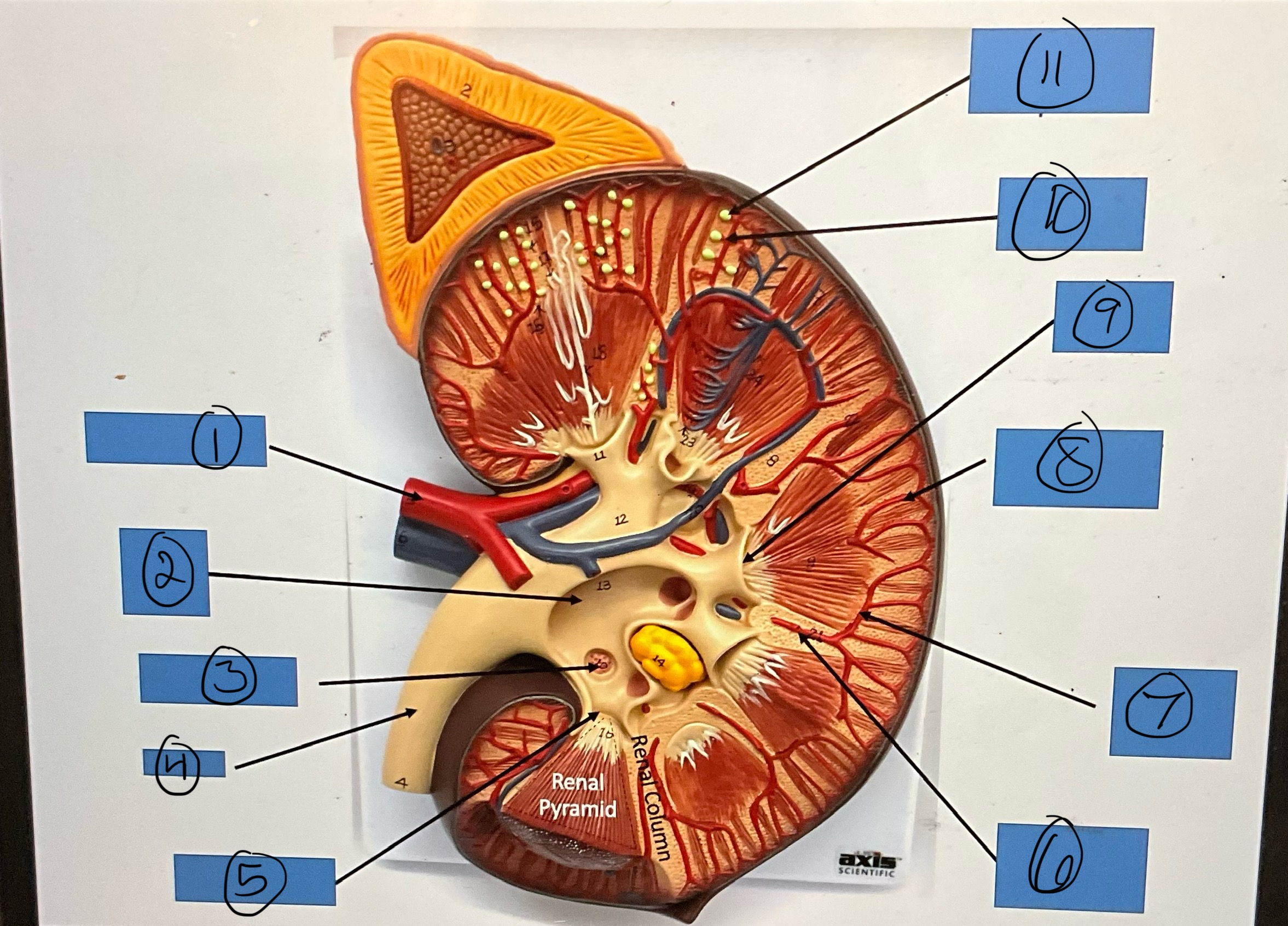
What is 7?
arcuate artery
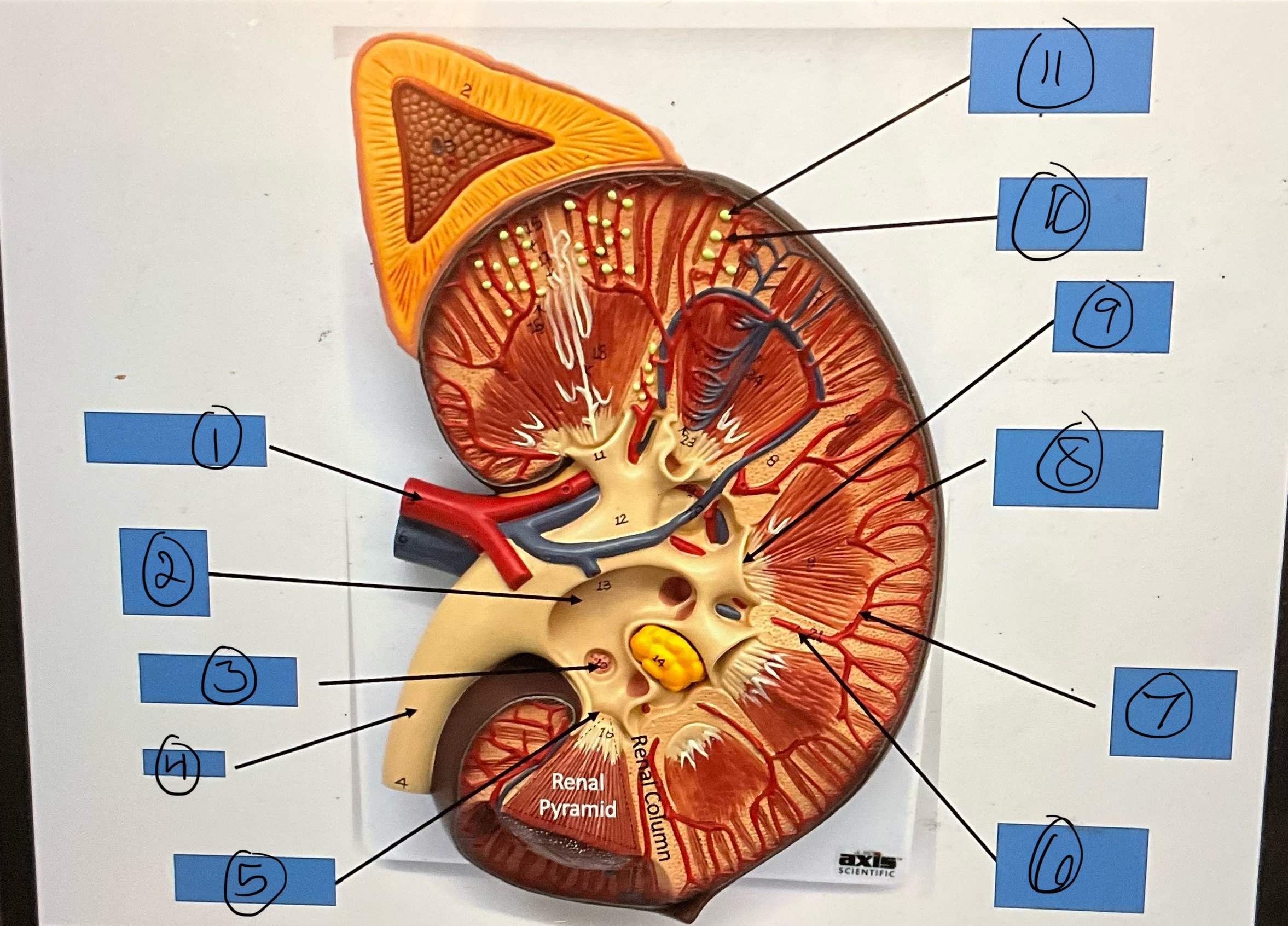
What is 8?
interlobular artery
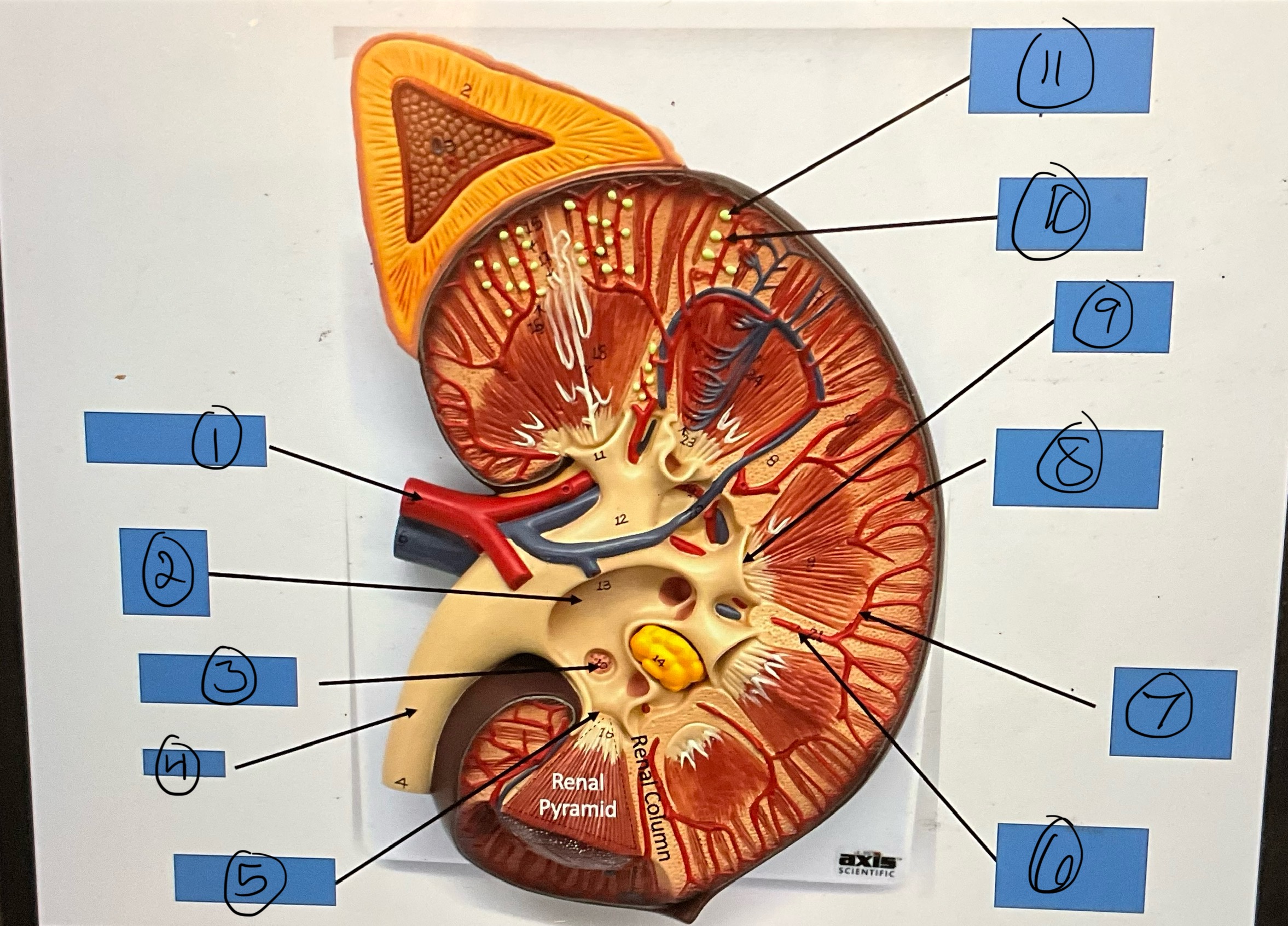
What is 9?
renal papilla
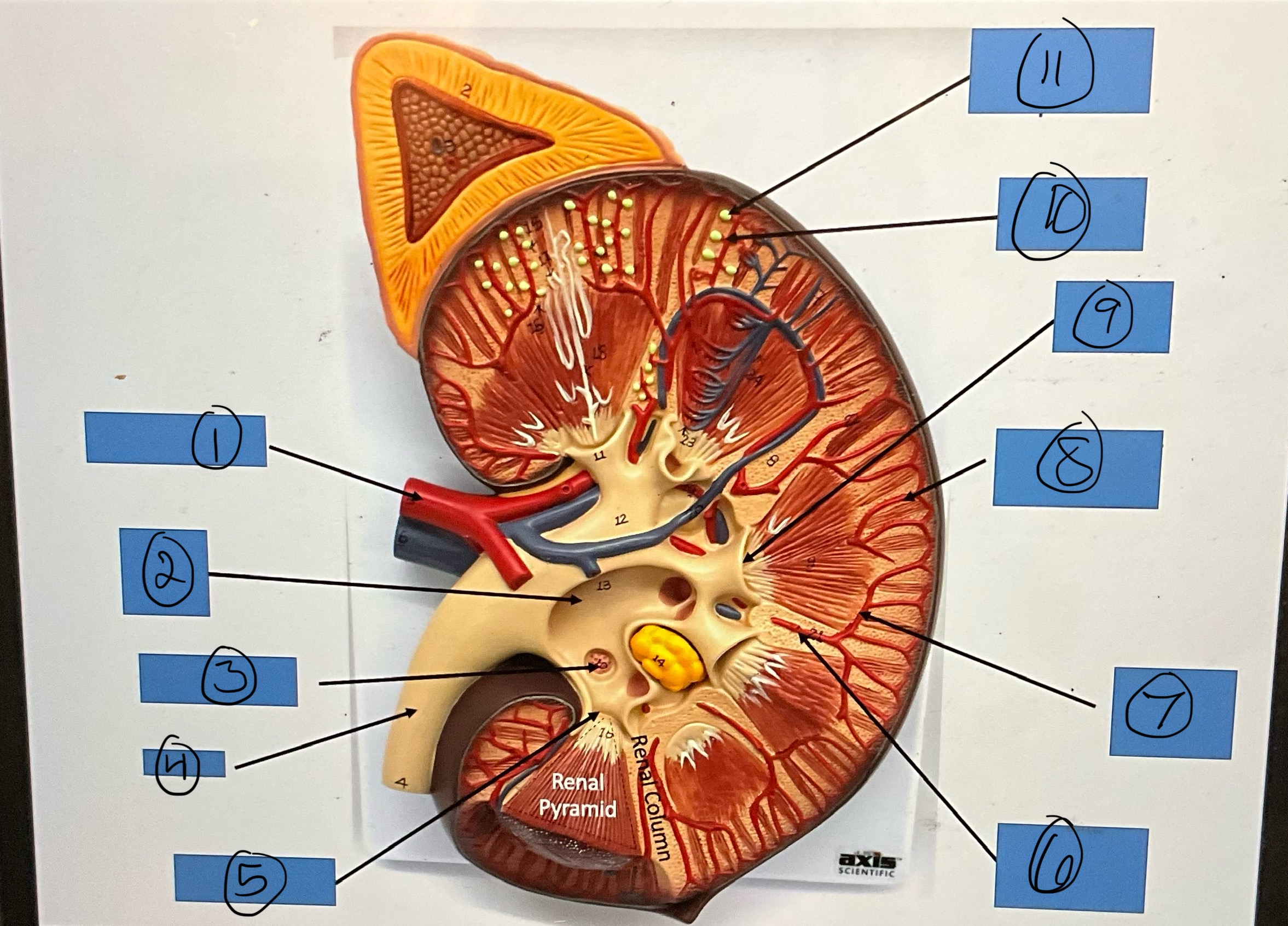
What is 10?
afferent arterioles
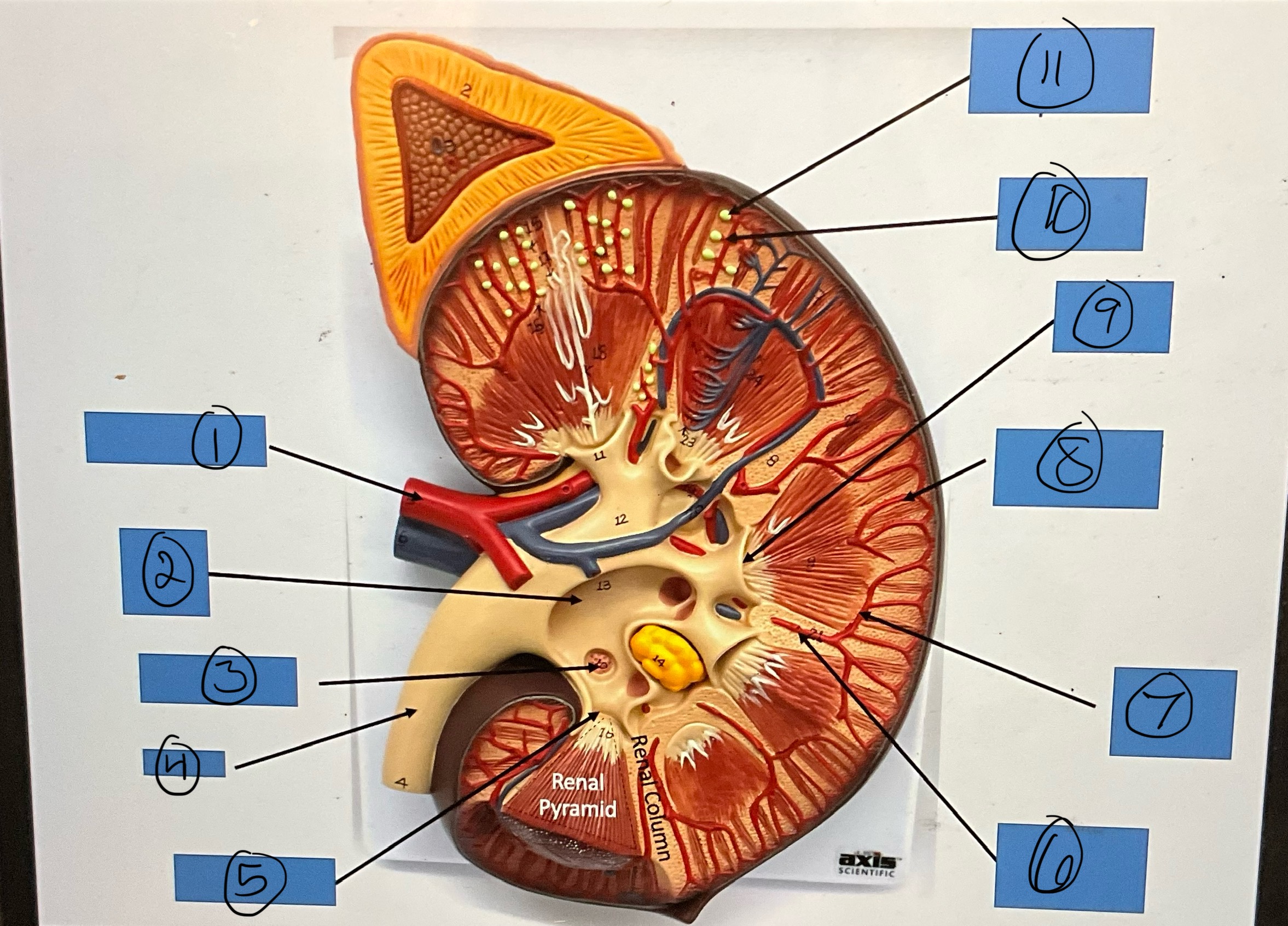
What is 11?
glomerular capsule
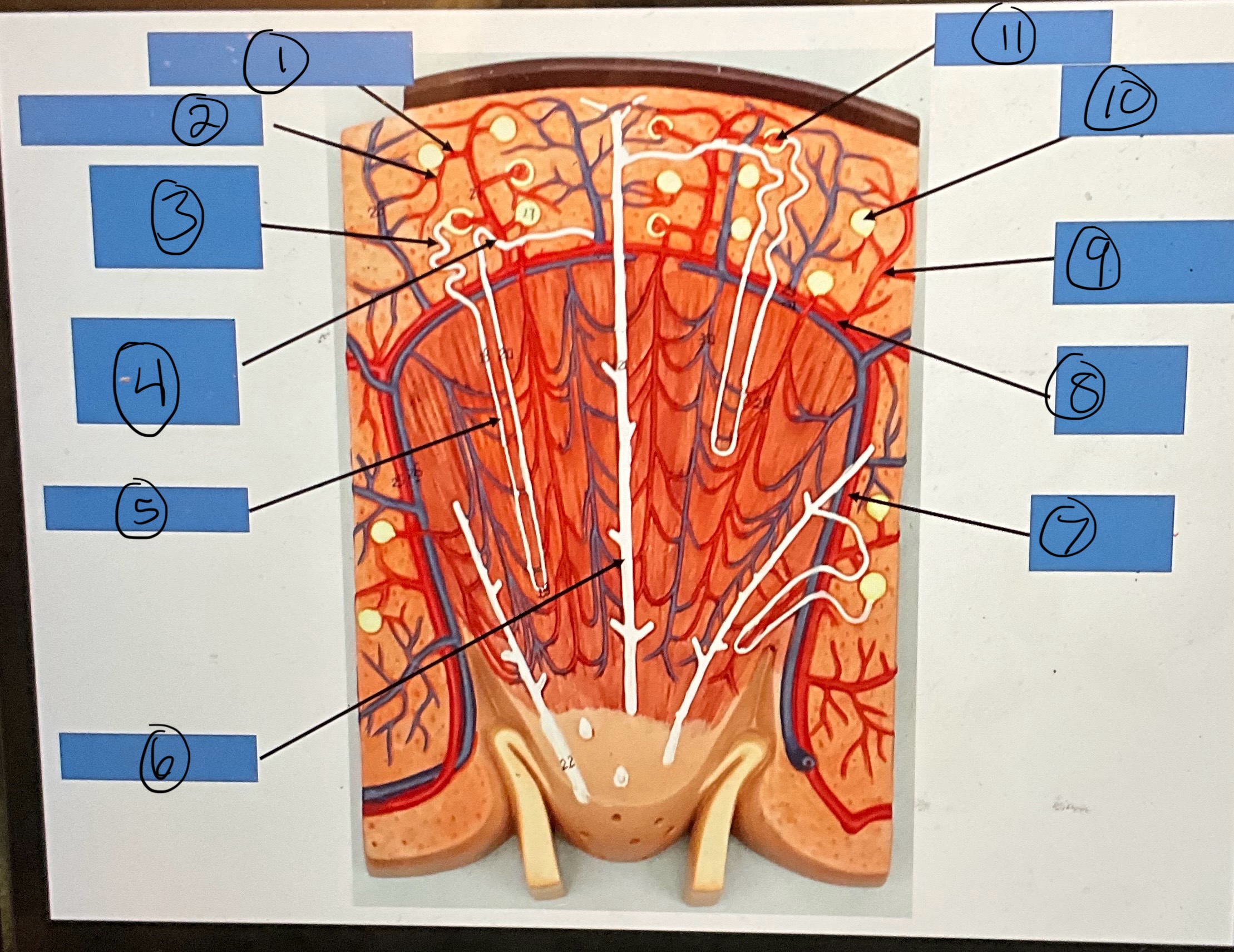
What is 1?
afferent arterioles
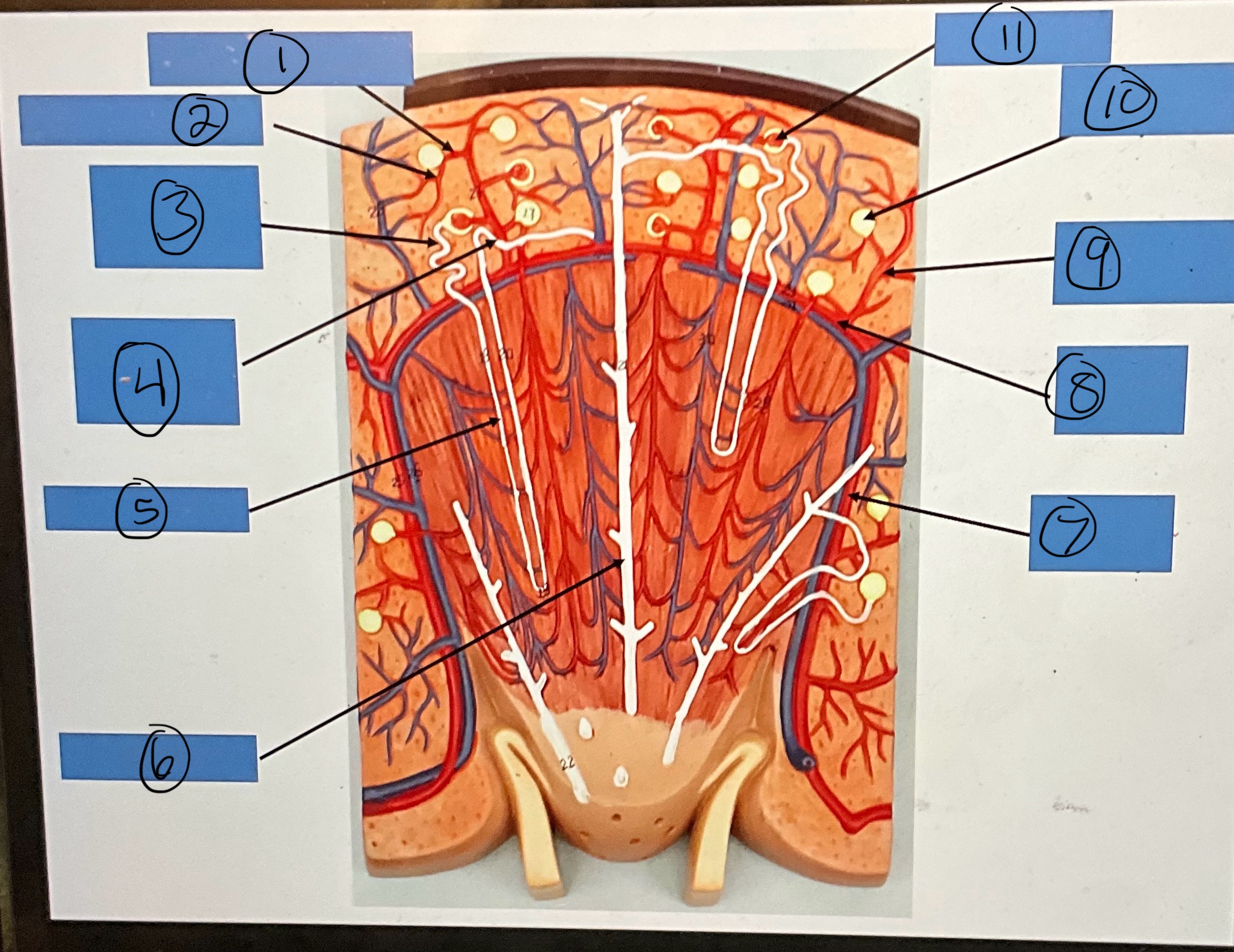
What is 2?
efferent arterioles
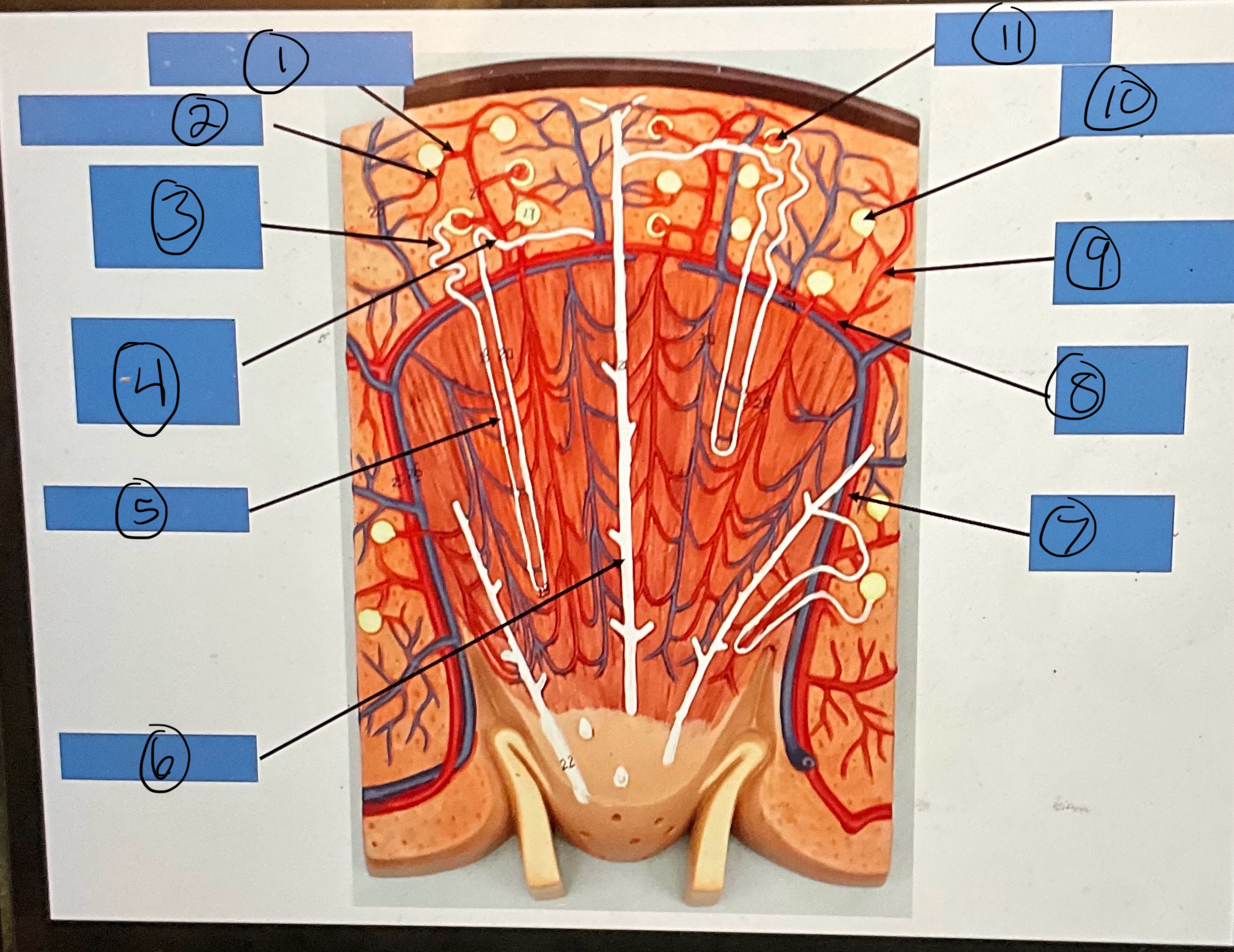
What is 3?
proximal convoluted tubule
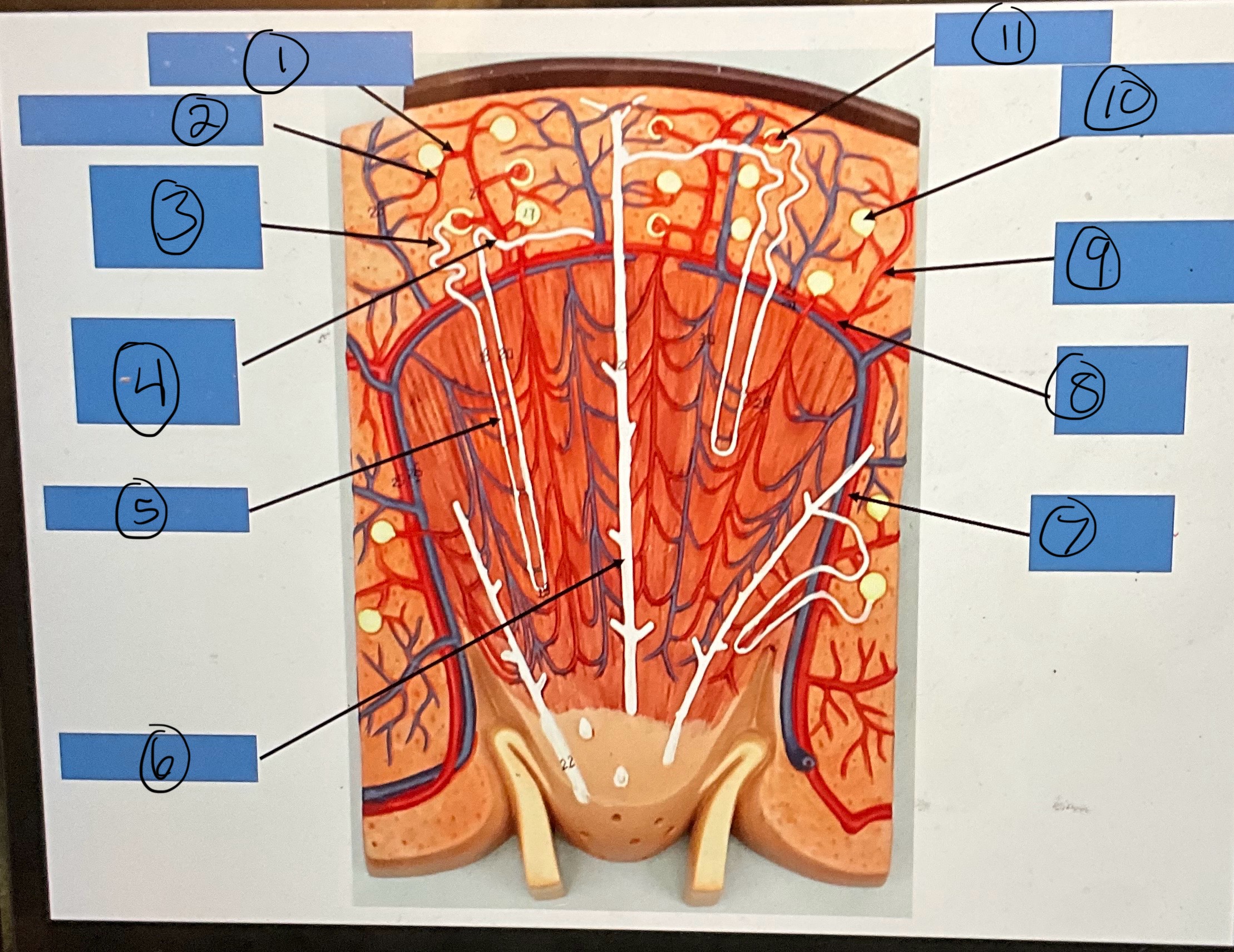
What is 4?
distal convoluted tubule
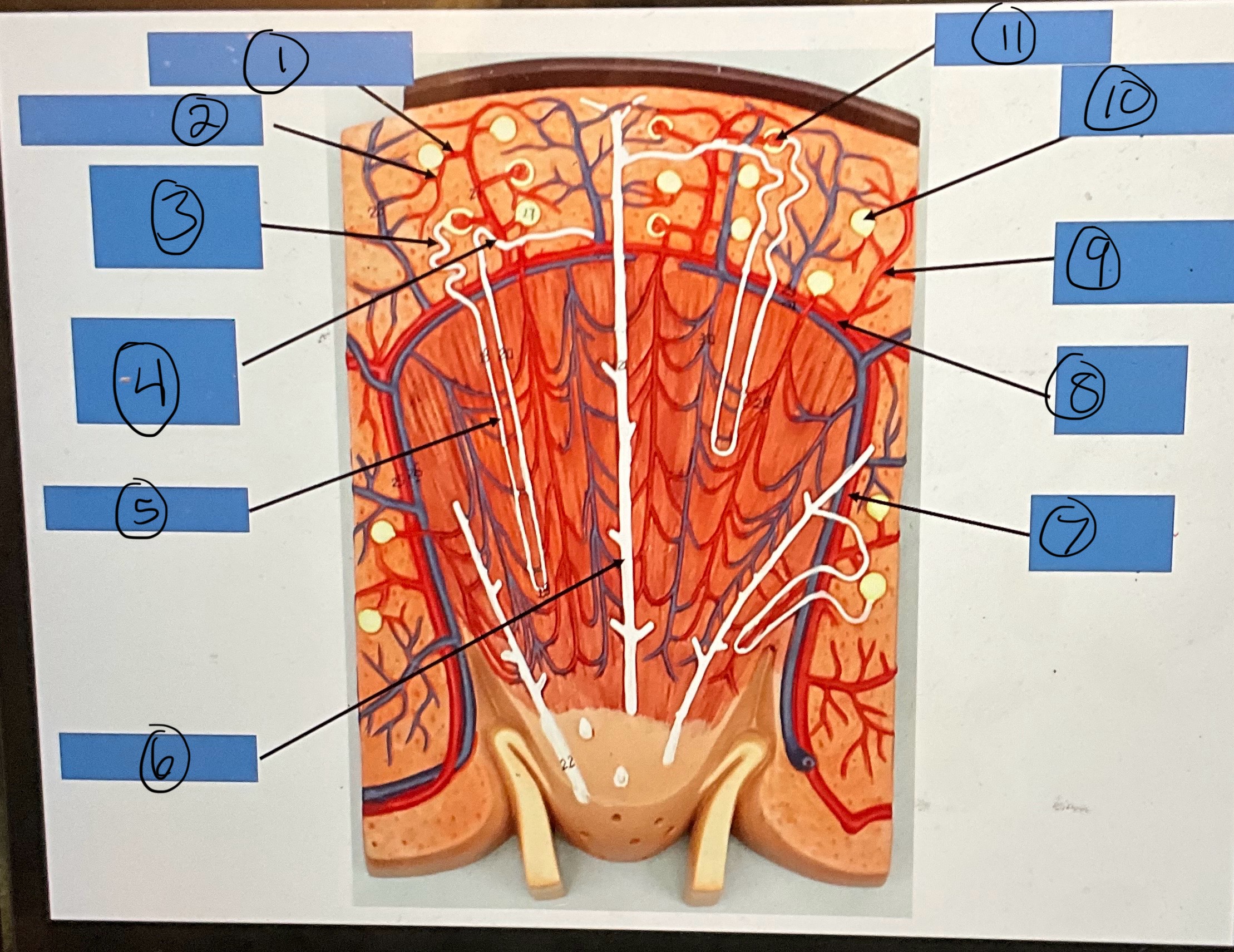
What is 5?
nephron loop
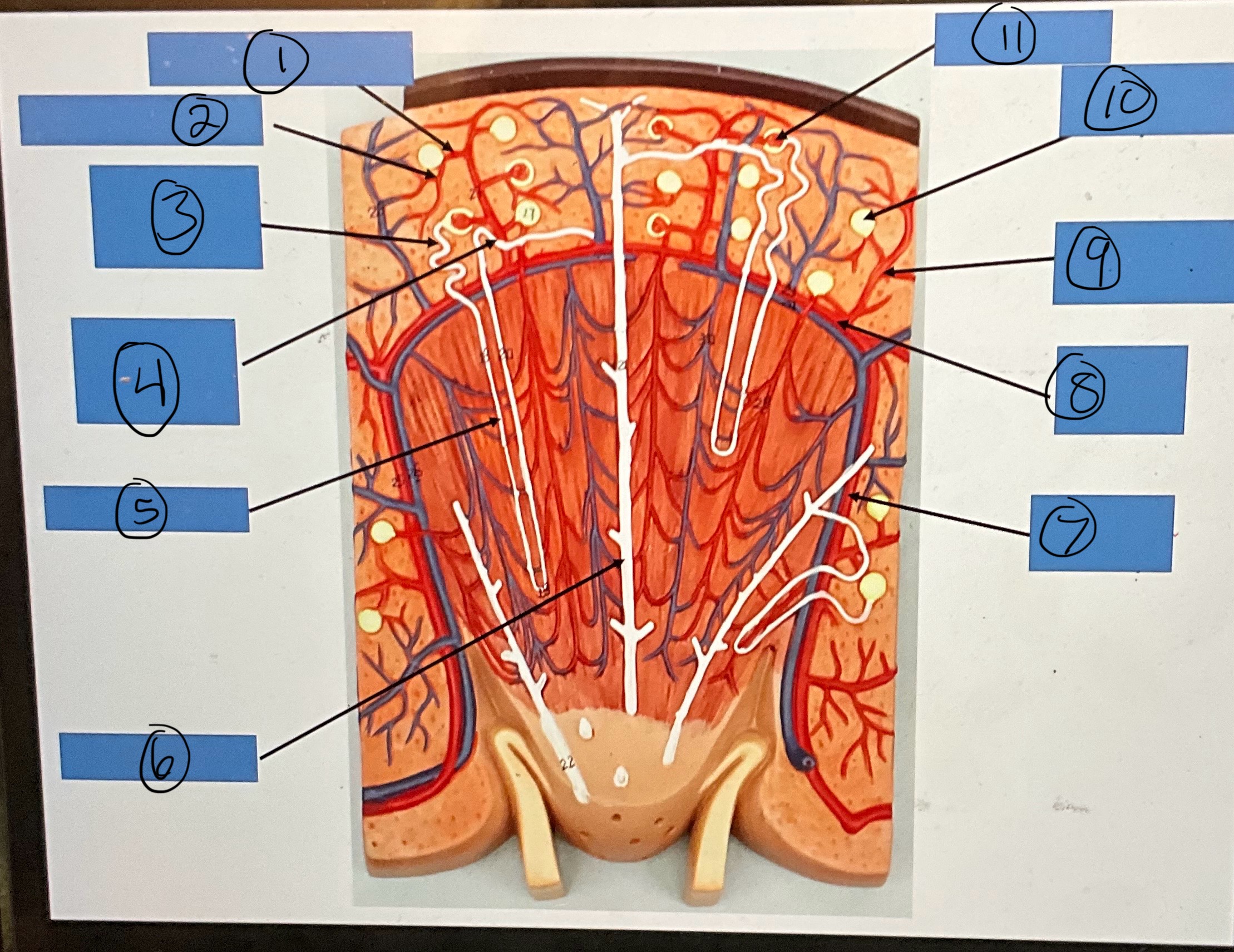
What is 6?
collecting duct
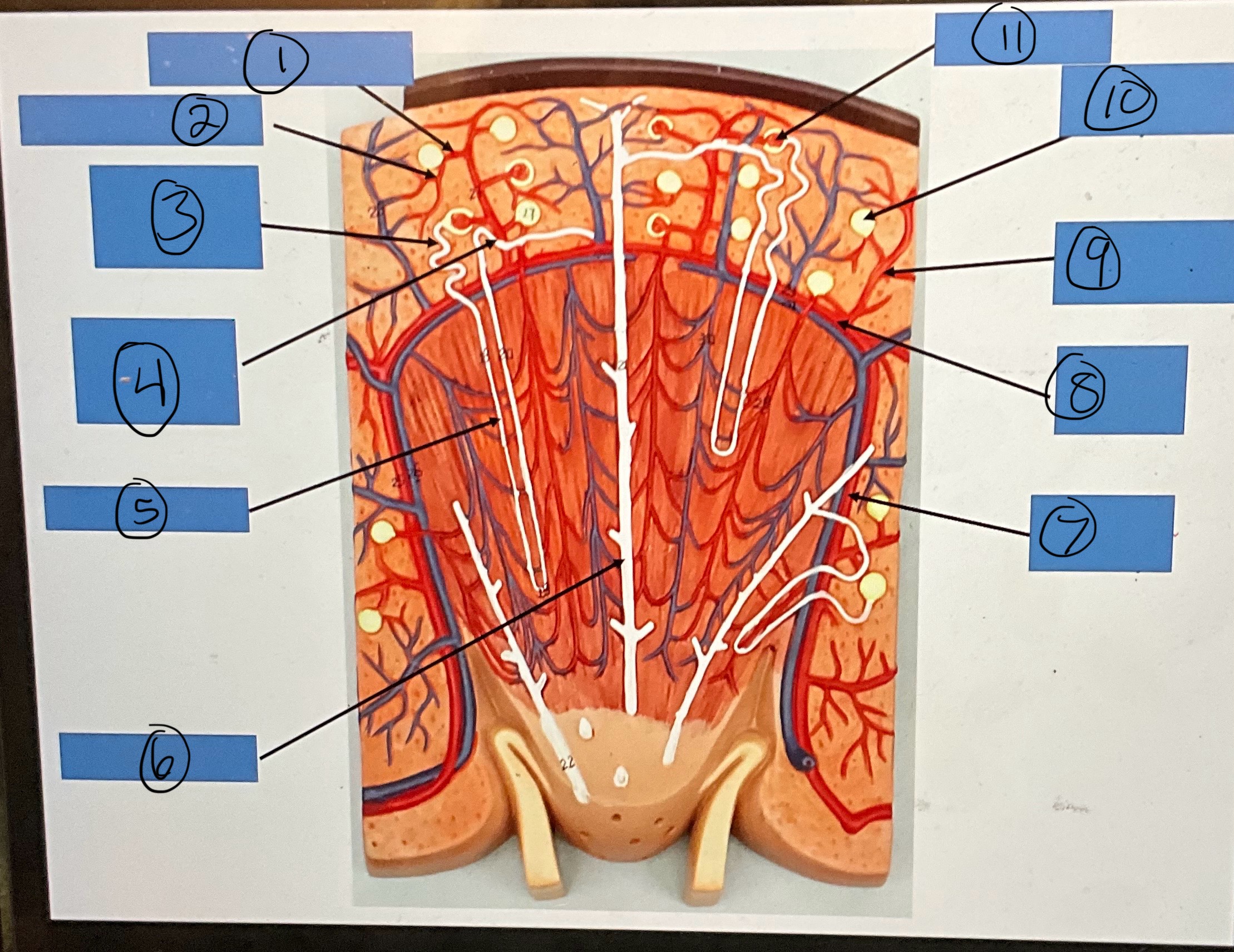
What is 7?
interlobar artery
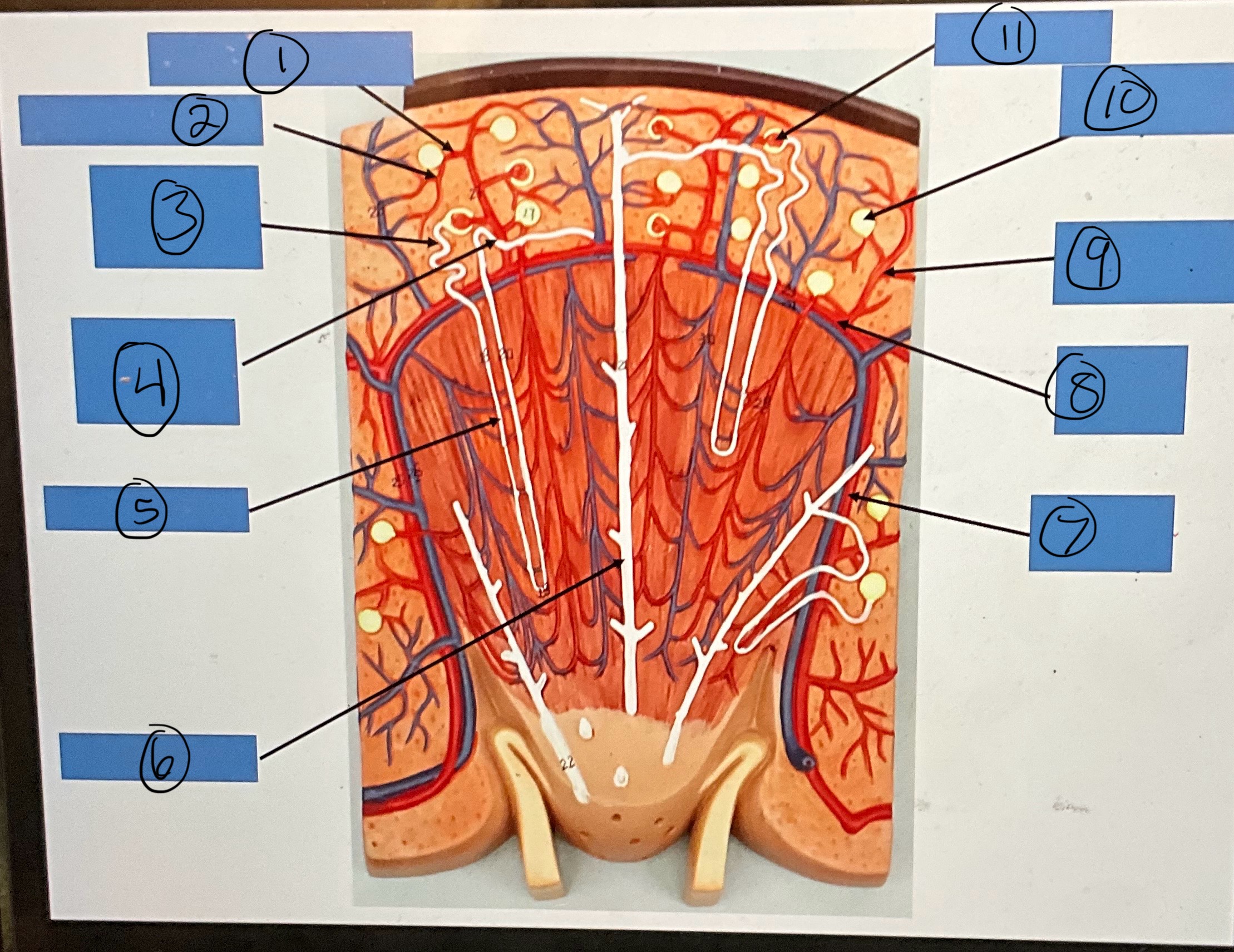
What is 8?
arcuate artery
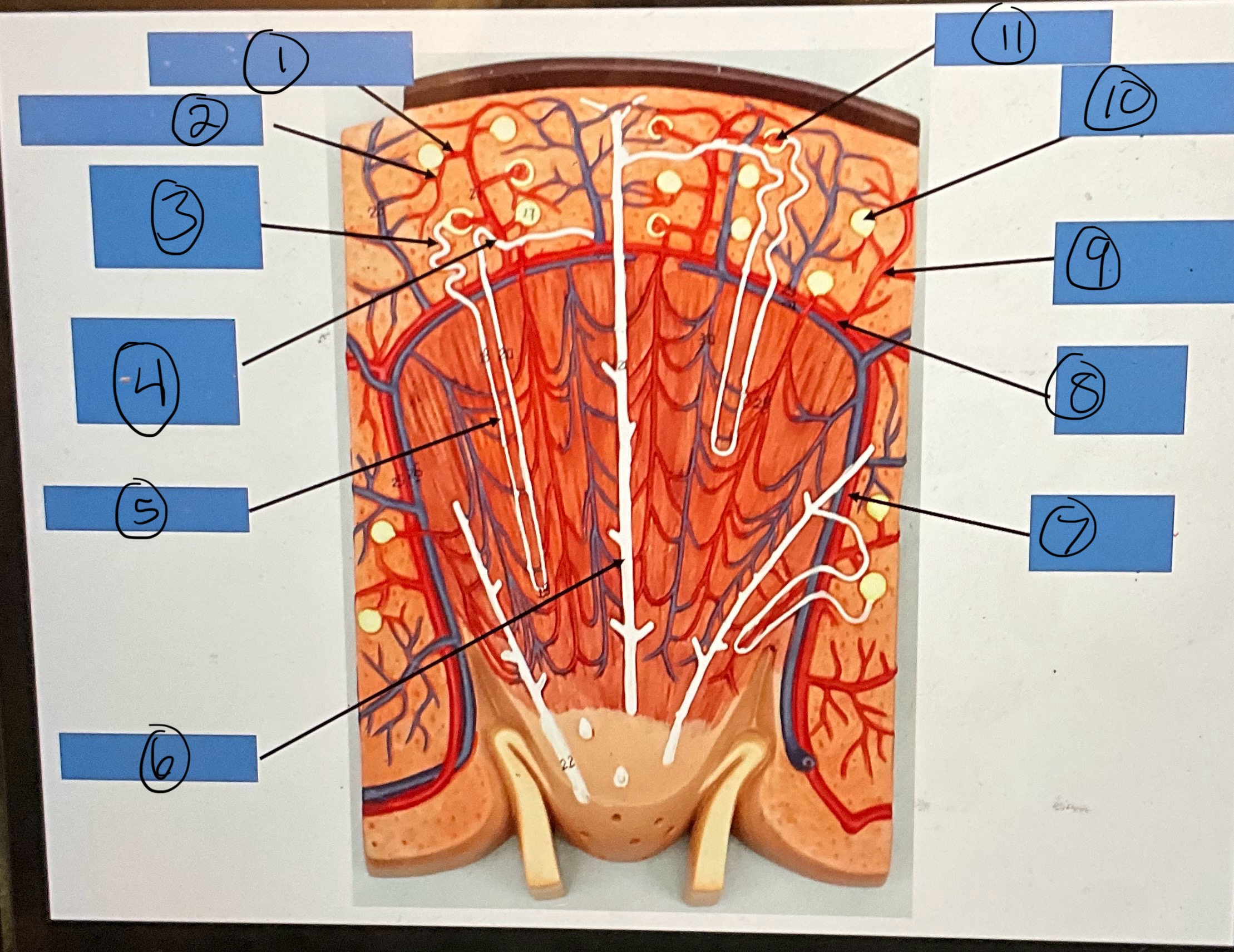
What is 9?
interlobular artery
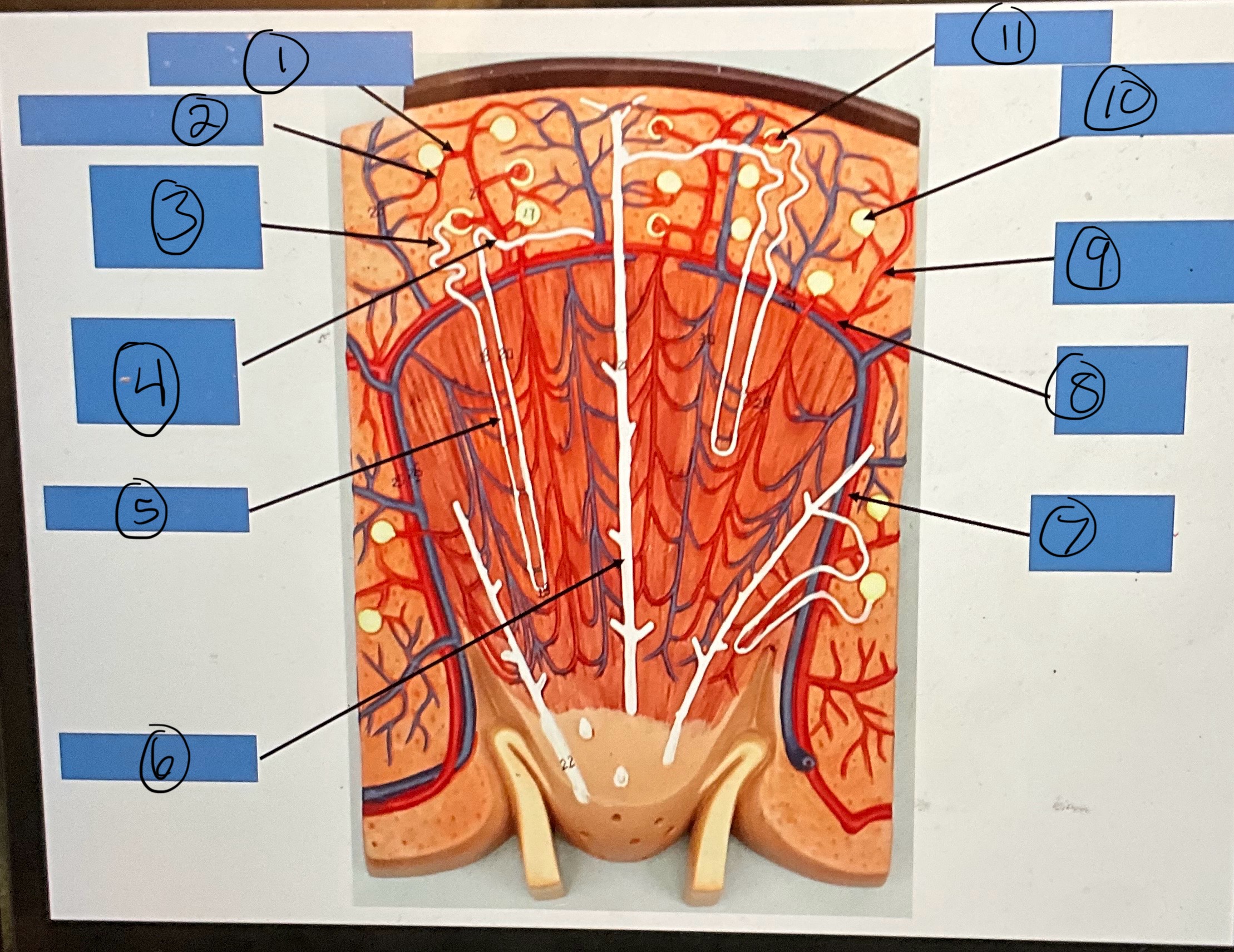
What is 10?
glomerular capsule
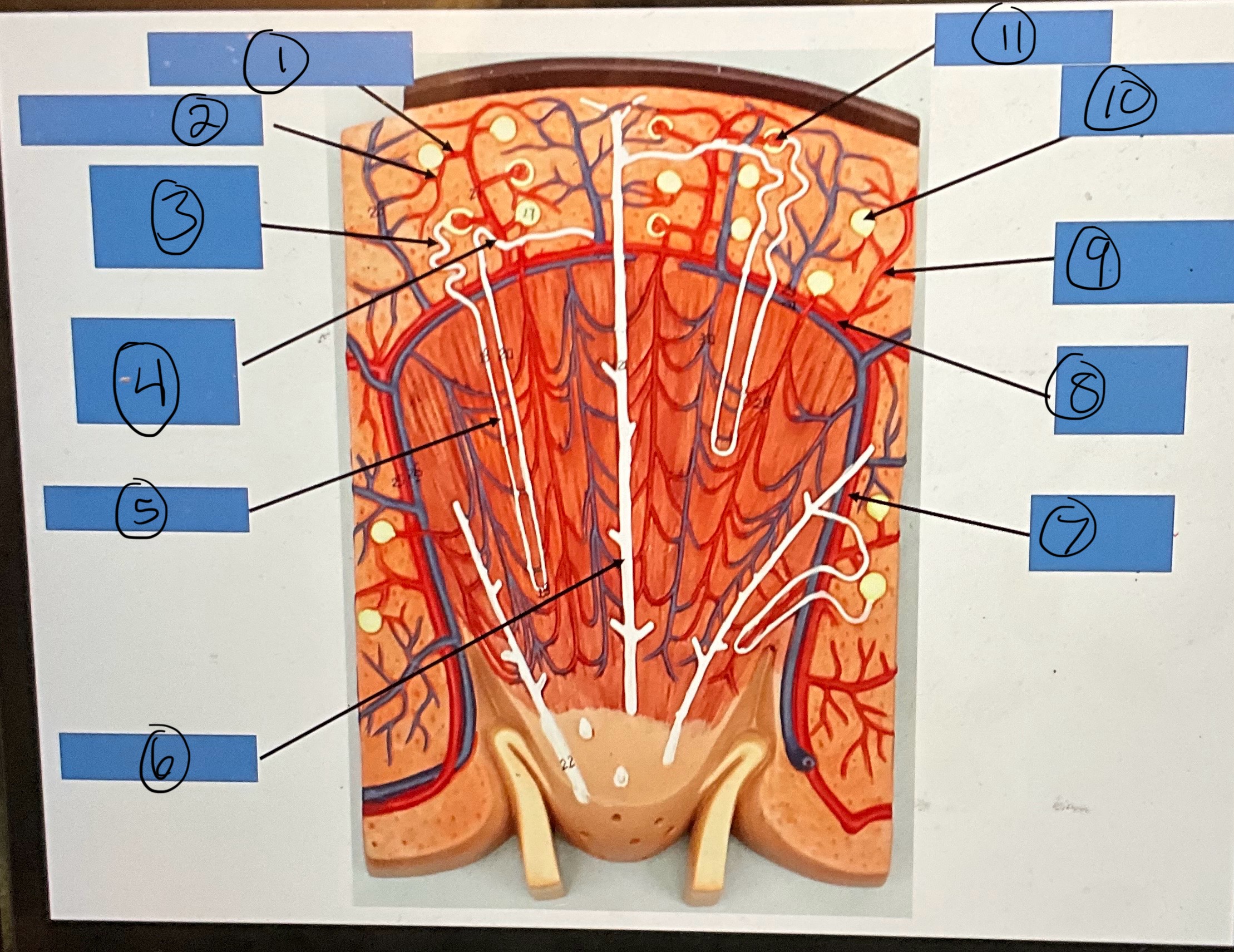
What is 11?
glomerulus
What are the organs of the urinary system?
right and left kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra
Besides waste removal, what are the functions of kidneys?
urine storage, regulation of blood volume, regulation of erythrocyte production, and regulation of acid/base balance
How can the kidneys be divided?
renal cortex (outer region) and renal medulla (inner region)
How does blood flow through the kidney?
renal artery, interlobar artery, arcuate artery, interlobular artery, afferent arteriole, glomerulus, and efferent arteriole
What is the flow of filtrate (urine)?
glomerular capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, nephron loop, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct, minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra
Non-pathologically, what does proteinuria mean?
pregnancy and high protein diet
Non-pathologically, what does urea mean?
high protein intake
Non-pathologically, what does glycosuria mean?
high sugar intake
Non-pathologically, what does ketonuria mean?
low carbohydrate diet
Non-pathologically, what does hematuria mean?
menstrual contamination
Non-pathologically, what does urobilinogenuria (urobilinogen) mean?
small amounts are normal
Non-pathologically, what does pH mean?
4.5-8, high protein intake, and vegetarian diet
Pathologically, what does proteinuria mean?
damage to glomerular membrane
What are two examples of glomerular membrane damage?
hypertension and glomerulonephritis
Pathologically, what does urea mean?
impaired renal function
Pathologically, what does glycosuria mean?
diabetes mellitus, brain injury, and myocardial infarction
Pathologically, what does ketonuria mean?
diabetic acidosis and starvation
Pathologically, what does pyria (leukocytes) mean?
UTI and glomerulnephritis
Pathologically, what does urobilinogenuria mean?
liver disease and hemolytic anemia
Pathologically, what does bilirubinuria mean?
liver disorders and obstructed bile duct
Non-pathologically, what does pyria (leukocytes) mean?
contamination from vaginal discharge
What is urinalysis?
assesses the status of the body and any possible conditions by analyzing the urine for specific levels of proteins, metabolites, or blood
What is the glomerulus surrounded by?
glomerular capsule
What does the glomerular capsule do?
captures filtrate after it leaves the glomerulus
From the glomerulus capsule, where does the filtrate travel to?
nephron
Where is urine stored until it leaves the kidneys?
renal pelvis
After urine leaves the kidneys, where is it stored?
bladder
Where is urine excreted from the body?
urethra
What is the difference of the urethra in male and female reproductive systems?
male: urinary and reproductive systems
female: urinary system
What does the nephron allow?
tubular secretion and tubular reabsorption
What is an example of tubular secretion?
if the body has retained too much of an electrolyte, the body can secrete that metabolite from the blood stream into the nephron for elimination
What is an example of tubular reabsorption?
if too much electrolyte has been filtered, the metabolite can be reabsorbed into the blood stream from the nephron
The kidneys filter waste from our bloodstream to do what?
create filtrate and convert that filtrate into urine
Where are the nephrons located?
cortex
What is the nephron responsible for?
filtering the blood and converting that filtrate into urine
What do renal pyramids house?
nephron loops and collecting ducts
Where do the collecting ducts drain?
renal papilla, minor calyx, major calyx, and renal pelvis
Where does the renal pelvis drain urine?
ureters for delivery to bladder