CHILD GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms

NURSING CARE OF A FAMILY WITH an infant
physical growth
weight
height
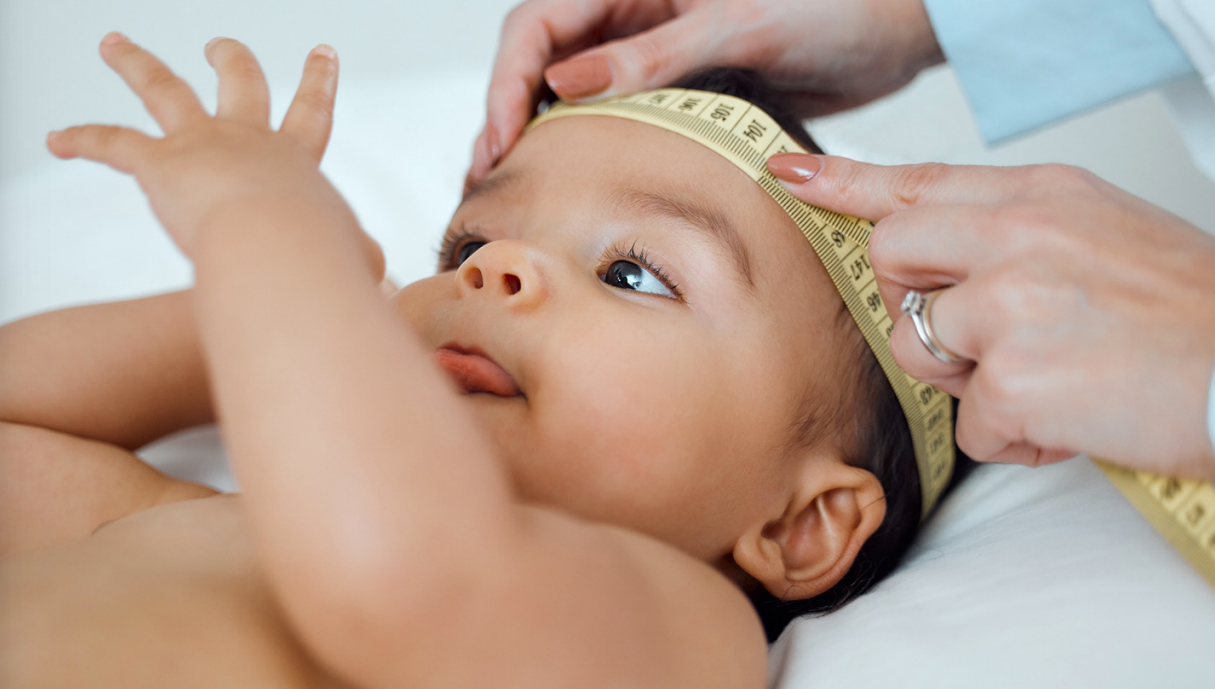
head circumference
body proportion
body systems
teeth
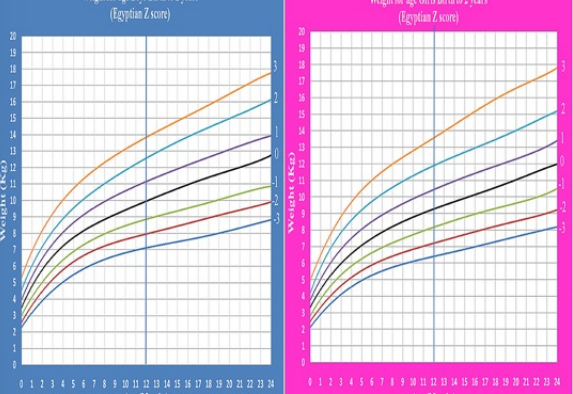
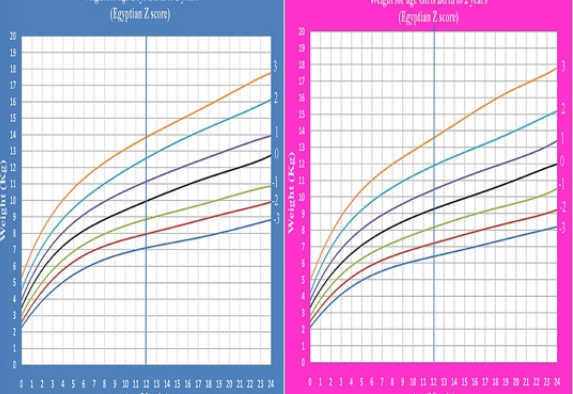
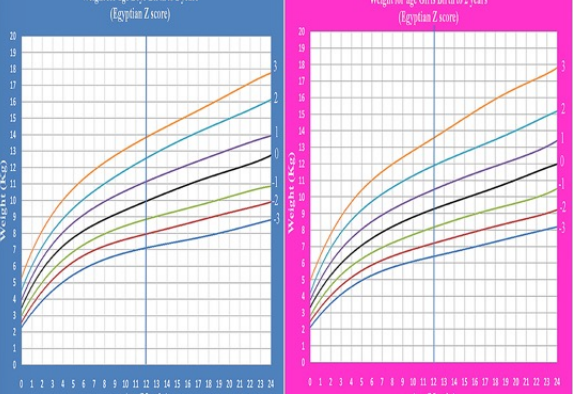
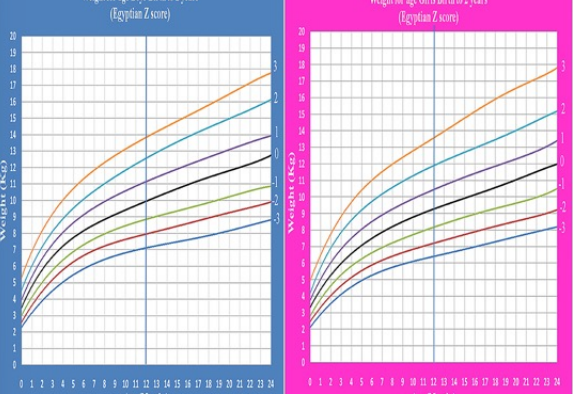
anthropometric measurements
weight is doubled by 4-6 months and tripled by the first year
length increases by 50% during the first year
by 1 year, brain is 2/3 the adult size
weight is doubled by ___ months and ___ tripled by the first year
4-6, tripled
length increases by ___ during the first year
50%
by 1 year, brain is ___ the adult size
2/3
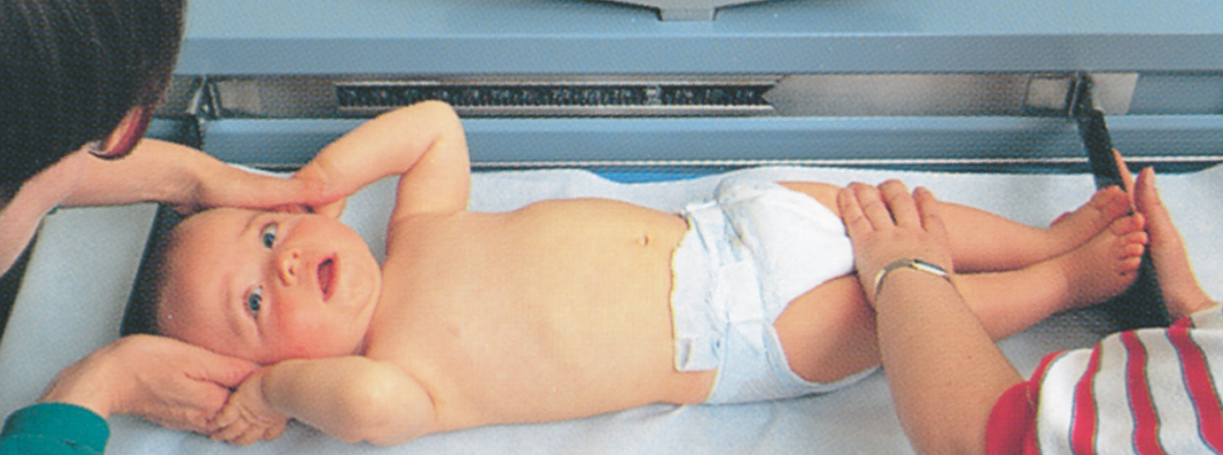
measuring an infant head to heel, from the top of the head to the base of the heels
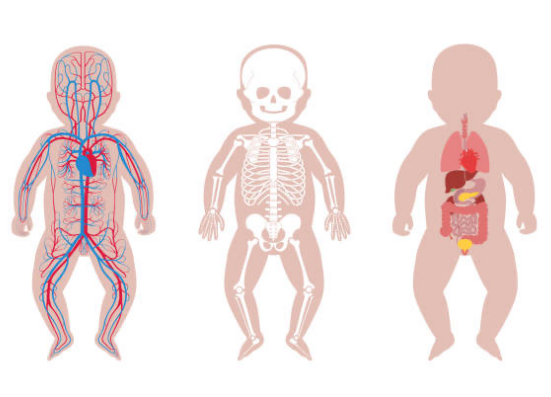
body systems
HR 100-120 bpm to 120-160 bpm
BP 80/40 to 100/60 mmHg
physiologic anemia at 2-3 months of age
RR 20-30 bmp to 30-60 bpm
GIT, liver, renal remains immature
immune system functional by 2 months
thermoregulation matures by 6 months
HR ______ bpm to ______ bpm
100-120, 120-160
BP ____ to ____ mmHg
80/40, 100/60
Physiologic anemia at ___ months of age
2-3
RR ____ bmp to ____ bpm
20-30, 30-60
GIT, liver, renal remains ___
immature
Immune system functional by ____
2 months
Thermoregulation matures by ____
6 months
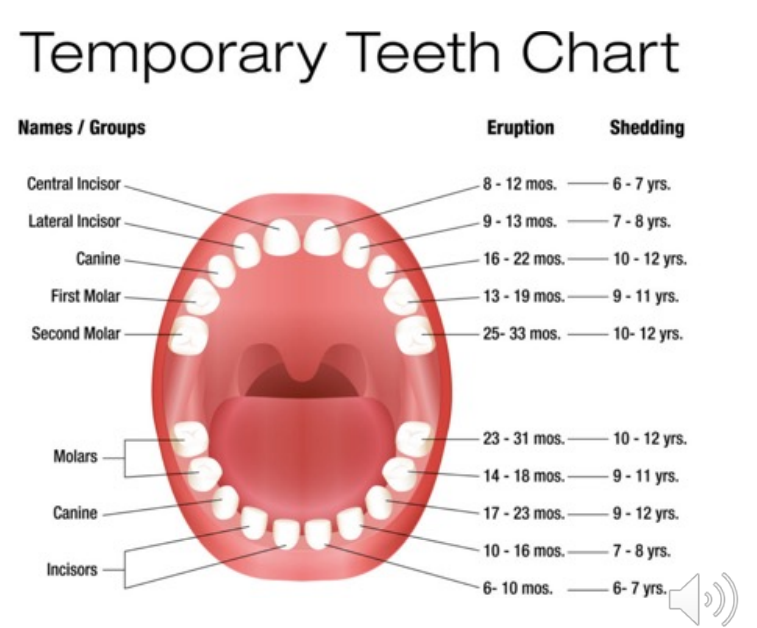
teeth
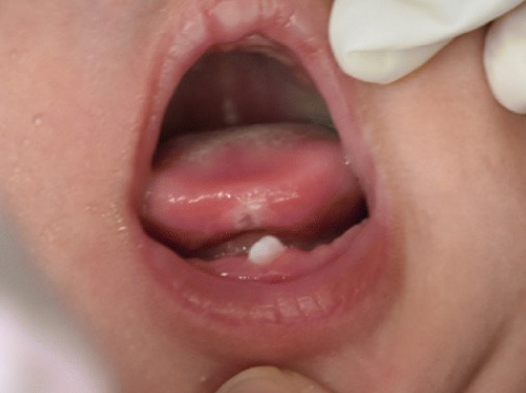
natal/neonatal teeth
born with teeth (natal teeth)
teeth erupt in the first 4 weeks of life (neonatal teeth)

motor development
gross motor development
ventral position
prone position
sitting position
standing position
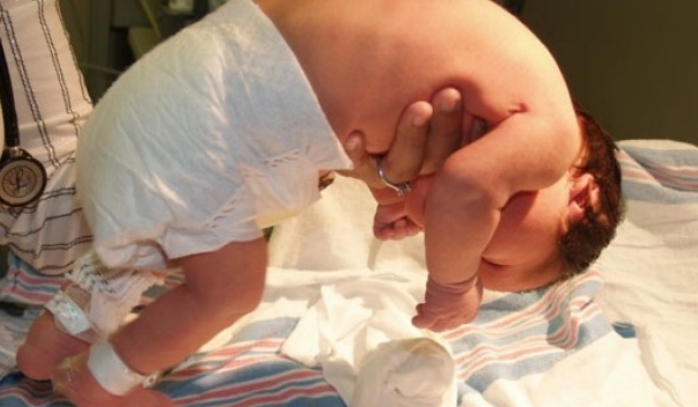
ventral position
1 month: lift their head momentarily and then drop it again.
2 months: hold their head in the same plane as the rest of their body, a major advance in muscle control.
3 months: infants lift and maintain their head well above the plane of the rest of the body in ventral suspension.
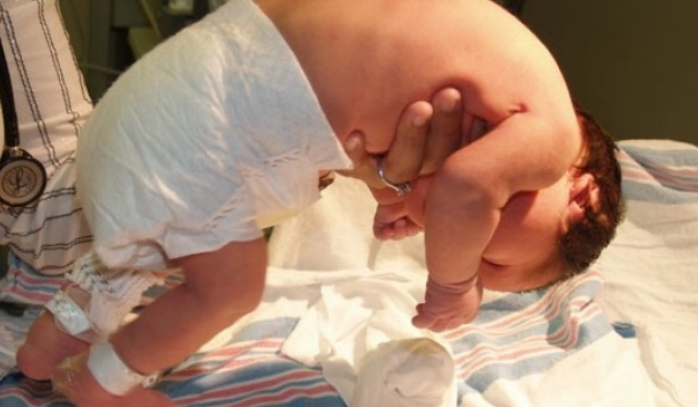
lift their head momentarily and then drop it again
1 month
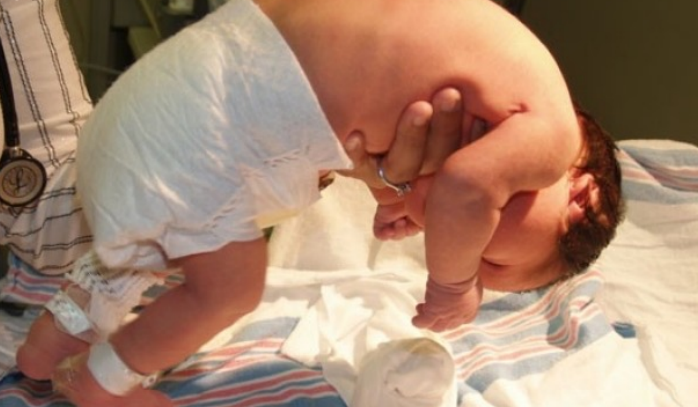
hold their head in the same plane as the rest of their body
2 month
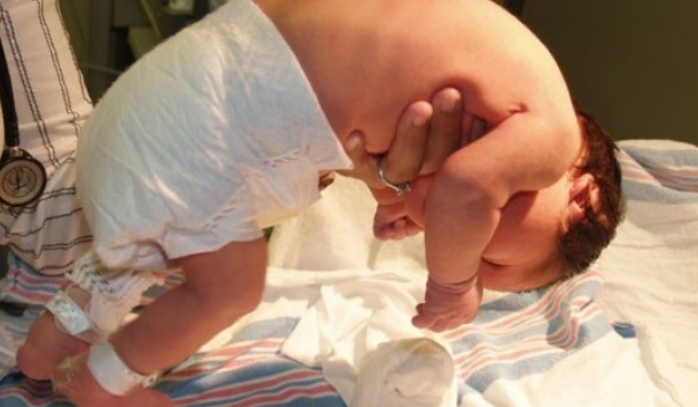
infants lift and maintain their head well above the plane of the rest of the body in ventral suspension
3 months
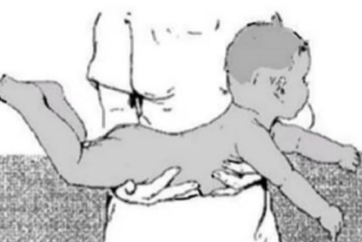
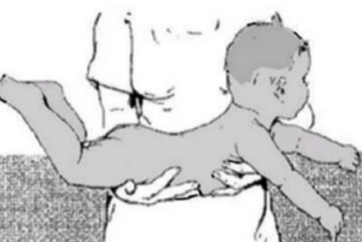
landau reflex
stimulation: newborn were made to lie in a prone position with the nurse’s hand supporting the trunk
normal response: the head will extend and the back and hips will extend in sequence (superman)
age of disappearance: appears in 3 months, disappears at 12-24 months
function: absence of reflex occurs in hypotonia, hypertonia or mental abnormality
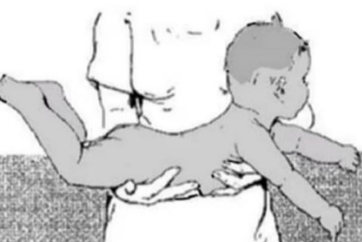
landau reflex stimulation
newborn were made to lie in a prone position with the nurse’s hand supporting the trunk
landau reflex normal response
the head will extend and the back and hips will extend in sequence (superman)
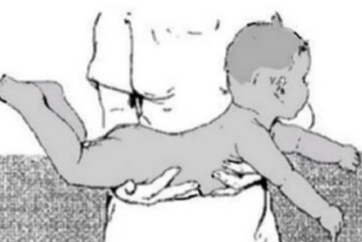
landau reflex age of disappearance
appears 3 months, disappears at 12-24 months
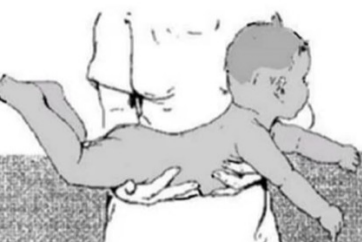
landau reflex function
absence of reflex occurs in hypotonia, hypertonia, mental abnormality
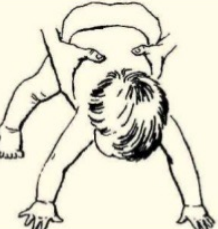
parachute reflex
appears about 6-9 months and persists thereafter
elicited by holding the child in ventral suspension and suddenly lowering him to the couch
arms extend as a defensive reaction
clinical significance
absent or abnormal in children with cerebral palsy
would be asymmetrical in spastic hemiplagia
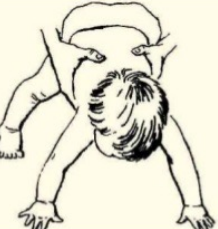
reflex appears at about ___ months and persists there after
6-9
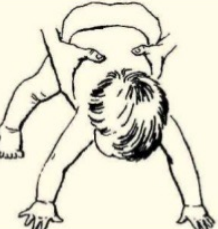
elicited by holding the child in _____ and suddenly lowering him to the couch
ventral suspension
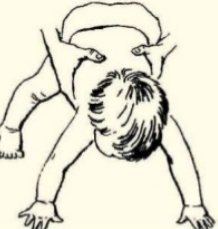
arms extend as a ____ reaction
defensive
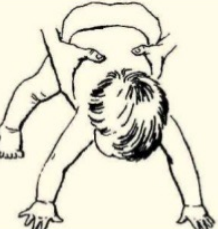
parachute reflex clinical significance
absent or abnormal in children with cerebral palsy
would be asymmetrical in spastic hemiplagia

prone position
1 month: lift head and turn it easily to side
2 month: can raise head and maintain position but cannot raise chest high enough to look around yet
3 months: lifts head and shoulders well off the table and looks around when prone
4 month: lift their chest off the bed and looks around actively, turning their head from side to side. they can turn from front to back
5 month: able to rest weight on their forearms when prone; can turn completely over, front to back and back to front
6 months: can raise their chest and the upper part of their abdomens off the table
9 months: can creep from the prone position

lift head and turn it easily to side
1 month: prone position

can raise their head and maintain the position but they cannot raise their chest high enough to look around yet
2 month: prone position

lifts the head and shoulders well off the table and looks around when prone
3 month: prone position

lift their chests off the bed and look around actively, turning their head from side to side. They can turn from front to back.
4 month: prone position

able to rest weight on their forearms when prone; can turn completely over, front to back and back to front
5 month: prone position

can raise their chests and the upper part of their abdomens off the table
6 month: prone position

can creep from the prone position
9 month: prone position
sitting position
1 month: extreme head lag
2 month: can hold head fairly when sitting up
4 month: no more head lag
6 month: can sit momentarily without support
7 month: may sit alone with hands held forward for balance
8 month: can sit securely without support (major milestone)
9 month: sit so steadily that they can lean forward and regain their balance
extreme head lag
1 month sitting position
can hold head fairly when sitting up
2 month sitting position
no more head lag
4 month sitting position
can sit momentarily without support
6 month sitting position
may sit alone with hands held forward for balance
7 month sitting position
can sit securely without support (major milestone)
8 month sitting position
sit so steadily that they can lean forward and regain balance
9 month sitting position
standing position
1 month: stepping reflex
3 month: try to support part of their weight on their feet
4 month: able to support their weight on their legs
6 month: nearly support their full weight when in a standing position
7 month: bounces with enjoyment in a standing position
9 month: can stand holding onto a coffee table if they are placed in that position
10 month: can pull themselves to a standing position by holding onto the side of a playpen or low table, but cant let themselves down again yet
11 month: learns to “cruise” or move about the crib or room by holding onto objects such as crib rails, chairs, walls, and low tables,
12 months: can stand alone at least momentarily
stepping reflex
1 month standing position
try to support part of their weight on their feet
3 month standing position
able to support their weight on their legs
4 month standing position
nearly support their full weight when in a standing position
6 month standing position
bounces with enjoyment in a standing position
7 month standing position
can stand holding onto a coffee table if they are placed in that position
9 month standing position
can pull themselves to a standing position by holding onto the side of a playpen or a low table, but they cannot let themselves down again yet
10 month standing position
learns to “cruise” or move about the crib or room by holding onto objects such as the crib rails, chairs, walls, and low tables
11 month standing position
can stand alone at least momentarily
12 month standing position

fine motor development
grasp reflex (1 month)
holds object (2 month)
reach for objects (3 month)
thumb opposition(4 month)
grasping objects with both hands (5 month)
holds objects with both hands (6 month)
transfer toys from one hand to the other (7 month)
pincer grasp (10 month)
hold crayon and draw semi-straight line (10 month)
development milestones 1
month 0-1: coos at the end of first month
play: enjoys watching face of primary caregiver; needs play time in prone position
month 2: makes cooing sounds; differentiates cry
time reflexes fade: grasp reflex fading
play: enjoys bright- colored mobiles
month 3: smiling face, nodding and squeal with pleasure or laugh out loud
time reflex fade: landau reflex is strong
play: spends time looking at hands; “tummy time” important during the day
month 4: very talkative, cooing, babbling, and gurgling when spoken to
time reflex fade: stepping, tonic neck, extrusion reflexes are fading
play: needs space to practice turning
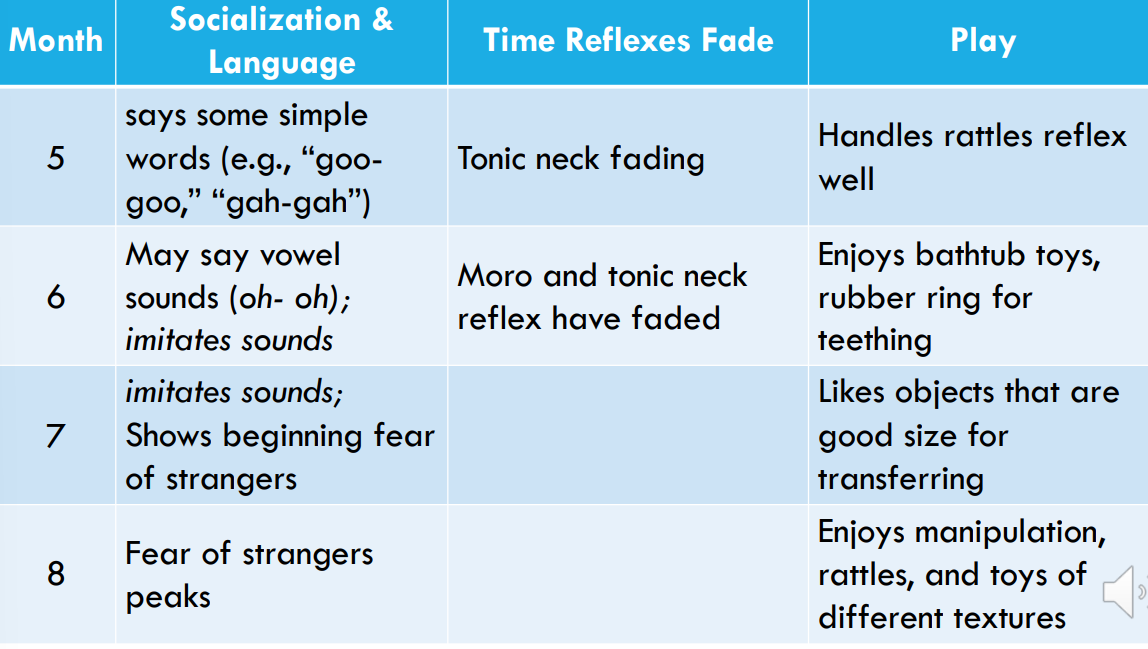
development milestone 2
month 5: say some simple words (e.g., “googoo,” “gah-gah”)
times reflexes fade: tonic neck reflex
month 6: may say vowel sounds (oh- oh); imitates sound
moro and tonic neck reflex have faded
month 7: imitates sounds; shows beginning fear of strangers
play: likes objects that are good size for transferring
month 8: fear of stranger peaks
play: enjoys manipulation, rattles, and toys of different texture
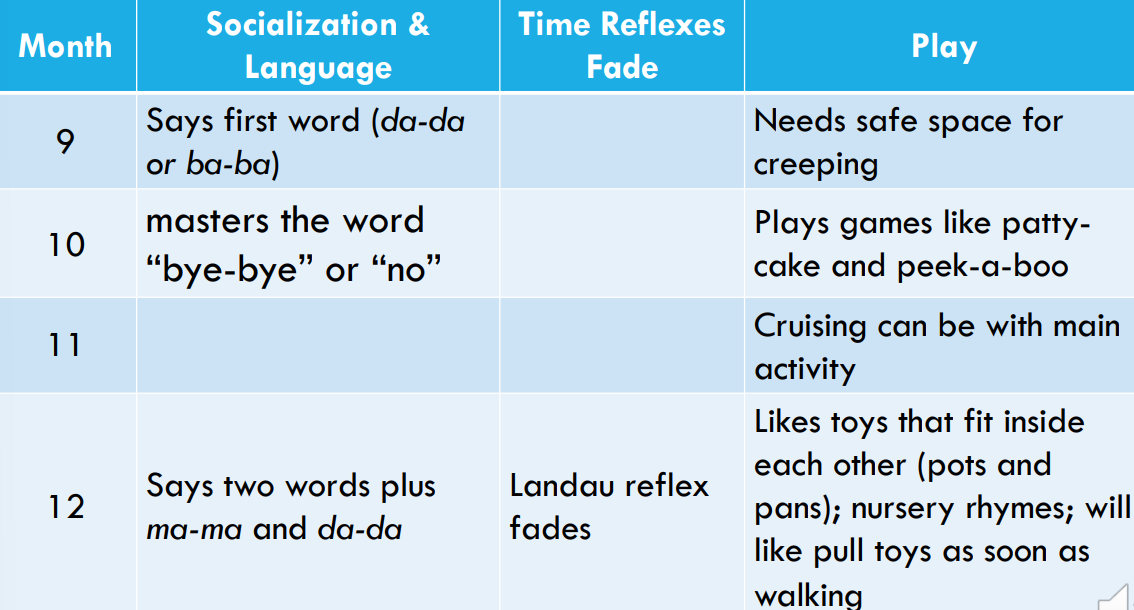
development milestones 3
month 9: Says first word (da-da or ba-ba)
play: needs safe space for creeping
month 10: masters the word “bye-bye” or “no”
play: Plays games like pattycake and peek-a-boo
month 11:
play: Cruising can be with main activity
month 12: says two words plus ma-ma and da-da
time reflexes fade: landau reflex fade
play: Likes toys that fit inside each other (pots and pans); nursery rhymes; will like pull toys as soon as walking
development of vision
Babies start to focus at 6-8 weeks “Binocular Vision”
Hand regard at 3 months
Recognize familiar objects at 4 months
Depth perception at 6 months.
Pat their own image in a mirror at 7 months
Object permanence begins to surface at 10 months.
Babies start to focus at 6-8 weeks ______
“Binocular Vision”
______ at 3 months
Hand regard
development of hearing
hearing awareness at 2 months
turns head to locate sound at 3 months
turns and looks in the direction of a distinctive sound at 4 months
localizes sound at 5-6 months
recognizes name and listen when spoken to at 10 months
development of touch, taste, smell
infant need to be touched so that they can experience skin to skin contact
infants have acute sense of taste. solids are to be introduced at 6 months
infants-paced complementary feeding
infants can accurately smell within 1-2 hours after birth
emotional development
social smile at 6-8 weeks
fear of strangers start at 6 months but peaks at 8 months
very aware of changes in tone of voice at 9 months
overcome the fear of strangers at 12 months
cognitive development
primary circular reaction at 3 months: explores objects by grasping them with the hands or by mouthing
secondary circular reaction at 6 months: reach for a mobile above the crib, hit it, and watch it move, they realize it was their hand that initiated the motion, and so they hit it again
discover object permanance at 10 months: ready for peek-a-boo
1 year of age: they are capable of reproducing new events (they deliberately hit a mobile once, it moves, and they hit it again)
primary circular reaction at 3 months:
explores objects by grasping them with the hands or by mouthing
secondary circular reaction at 6 months:
reach for a mobile above the crib, hit it, and watch it move, they realize it was their hand that initiated the motion, and so they hit it again
discover object permanence at 10 months:
ready for peek-a-boo
1 year of age:
they are capable of reproducing new events (they deliberately hit a mobile once, it moves, and they hit it again)
nursing diagnoses
ineffective breastfeeding r/t maternal fatigue
disturbed sleep pattern (maternal) r/t babies need to nurse every 2 hours
imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements r/t infants difficulty sucking
health seeking behaviors r/t adjusting to parenthood
social isolation r/t lack of adequate social support
ineffective role performance r/t new responsibilities within the family
promoting infant safety
aspiration prevention
fall prevention
car safety
safety with siblings
bathing and swimming safety
childproofing
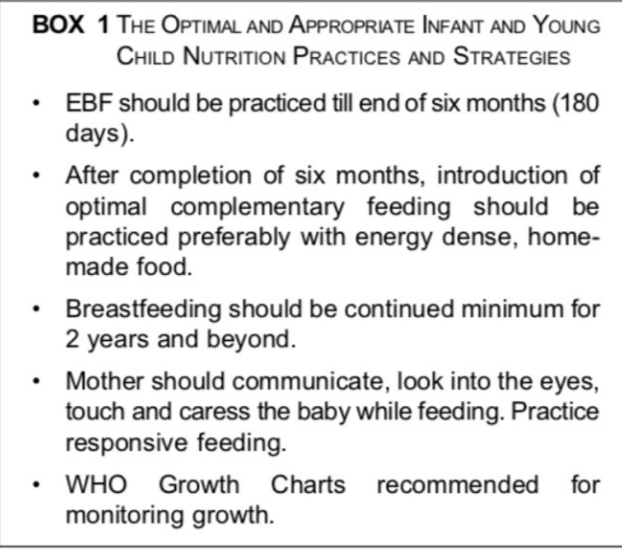
promoting nutritional health of an infant
only breastmilk for the first 6 months
breastfeeding up to 2 years and beyond
complementary feeding at 6 months

promoting infant development in daily activities
bathing
diaper-area care
dental care
dressing
sleep
exercise
parental concerns and problems r/t normal infant development
ü Breastfeeding
ü Teething
ü Thumb-sucking
ü Use of Pacifiers
ü Head banging
ü Sleep Concerns
ü Constipation
ü Loose Stools
ü Colic
ü Spitting up
ü Diaper Dermatitis
ü Miliara
ü Baby-Bottle Tooth Decay
ü Obesity in Infants

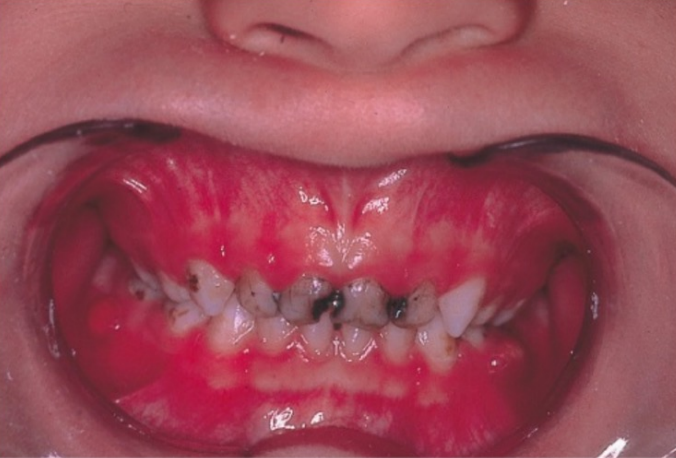
extensive decay in the upper teeth
baby-bottle syndrome
NURSING CARE OF A FAMILY WITH A TODDLER
TODDLER PHYSICAL GROWTH
gains 5-6 Ibs and 5 inches a year
head circumference increases by 2 cm at a second year 20 decidous teeth at 2.5 year
pouchy abs
chest circumference bigger than head at 2 years
noticeable lordosis
baby fat begin to disappear
wide-base gait
HR 90-110 bpm
RR slow slightly
BP 99/64 mmHg
brain develops 90% of adults size
GIT become less common
bowel and urinary control
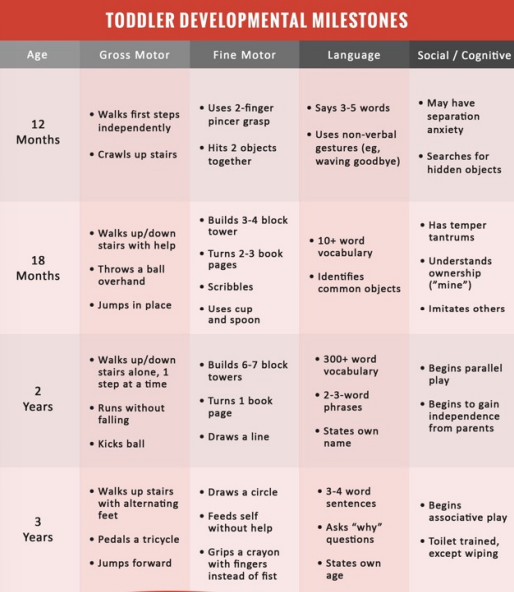
toddler development milestones
toddler safety
accidents are the major cause of death
lead screening
nutritional health
a toddler’s appetite is usually less than a infant’s
allow self-feeding
toddlers usually prefer to eat the same type of food over and over
daily food consumption may vary greatly, energy needs are generally met when sufficient food is supplied in a positive environment
toddler activities of daily-living
dressing
sleep
bathing
dental care
parental concerns in toddlerhood
toilet training
ritualistic behavior
negativism
discipline
separation anxiety
temper tantrums
nursing diagnoses toddlerhood
health seeking behavior r/t normal toddler development
deficient knowledge r/t best method of toilet training
risk for injury r/t impulsiveness of toddler
interrupted family process r/t need for close supervision of a toddler
readiness for enhance family coping r/t parents ability to adjust to need of child
risk for imbalanced nutrition
disturbed sleep pattern
nursing care of a family with a preschool child
nursing diagnoses preschooler
health seeking behaviors r/t developmental expectations
risk for injury r/t increased independence outside the home
delayed growth and development r/t frequent illness
risk for poisoning
parental anxiety r/t lack of understanidng of childhood development
growth and development preschooler
vocabulary increases markedly
tonsils appear enlarged
growth is only 2-3.5 inches per year
no new teeth develops
pulse rate decreases to about 85/min
body contour changes to be more childlike
genu valgus may be evident
increased coordination
summary of preschool growth and development

emotional development
play
initiative
imitation
fantasy
oedipus and electra complex
gender roles
socialization
preschool cognitive, moral, and spiritual development
children learn by asking
intuitional thought
magical thinking to rational beliefs
right or wrong based on parent rules
do good out of self interest
preschooler safety
keeping children safe, strong, and free
motor vehicle and bicycle safety
falls
drowning
animal bites
poisoning
burns
community safety
preschooler activity of daily living
dressing
sleep
exercise
hygiene
dental care
discipline
parental concerns with the preschool period
common health concerns
common fears of the preschooler
behavioral variations
sex education
choosing a preschool or child care center
preparing child for school
broken fluency
bathroom language
developmental skills for 3-4 years
