4. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Receptors & Pharmacology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Outline the divisions of the nervous system.
There is the CNS (brain & spinal cord) & PNS -(peripheral nervous system) (cranial, spinal and peripheral nerves)
The PNS is divided into somatic & autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system: innervates part of body under voluntary control e.g. skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system: innervates structures of body except skeletal muscles. e.g. blood, heart vessels
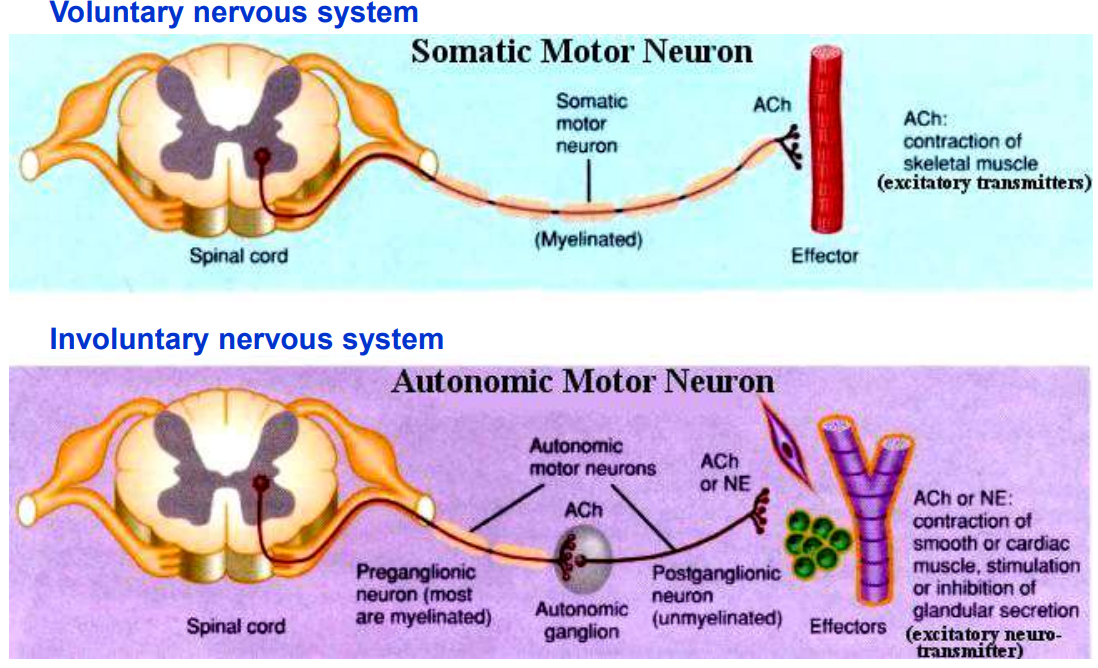
which parts of the neurones are myelinated?
Motor nerves to skeletal muscles and preganglionic autonomic nerves are always myelinated, whereas postganglionic autonomic nerves are generally non-myelinated.
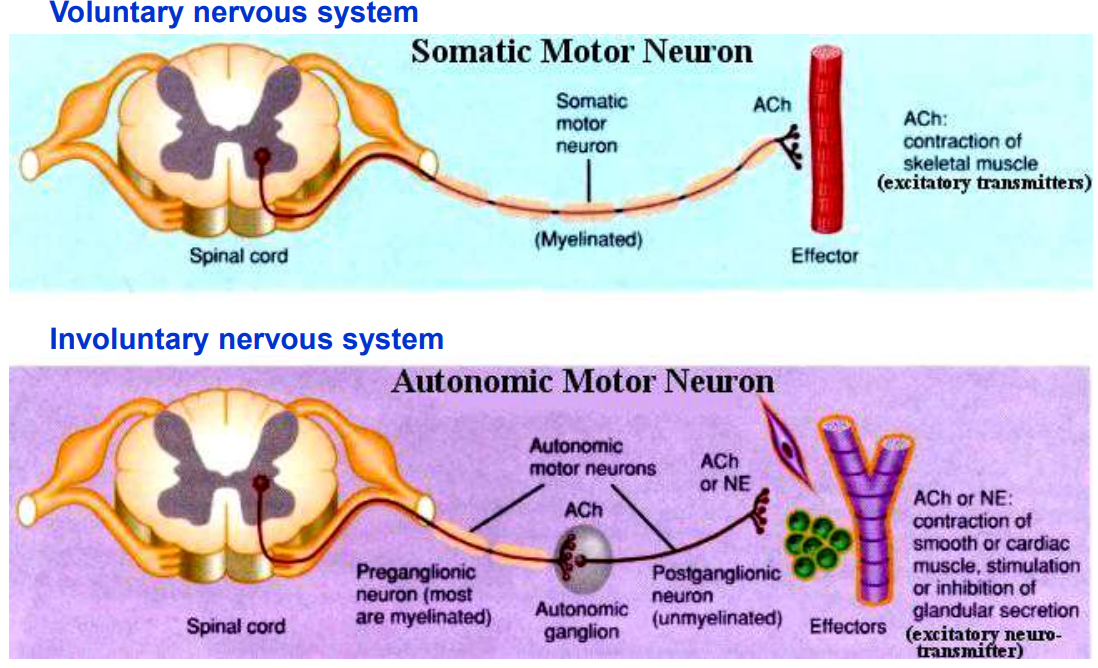
Outline the location & function of arterial baroreceptors.
Found in the walls of the carotid sinus & aortic arch
Detect changes in BP by sensing stretch in the arterial walls & send signals to the medulla oblongata to regulate BP
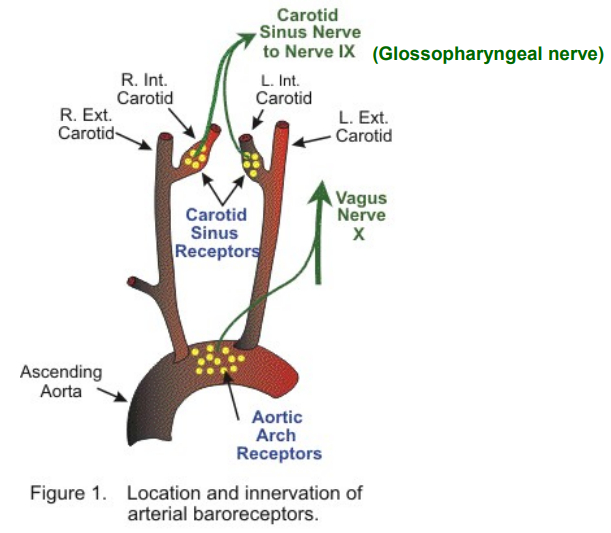
Outline the location & function of arterial chemoreceptors.
Found in the carotid & aortic bodies.
Detect changes in PP of O₂ & CO₂/pH in the blood & send signals to the medulla oblongata to regulate respiratory rate.
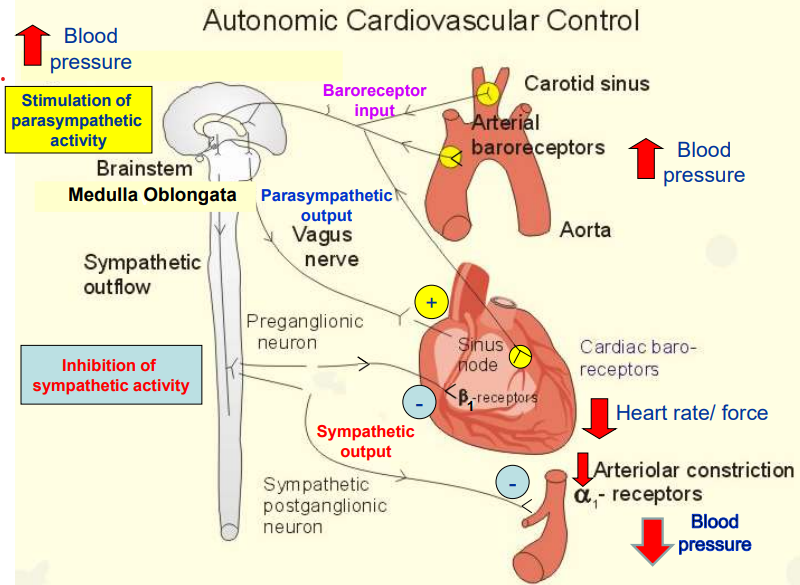
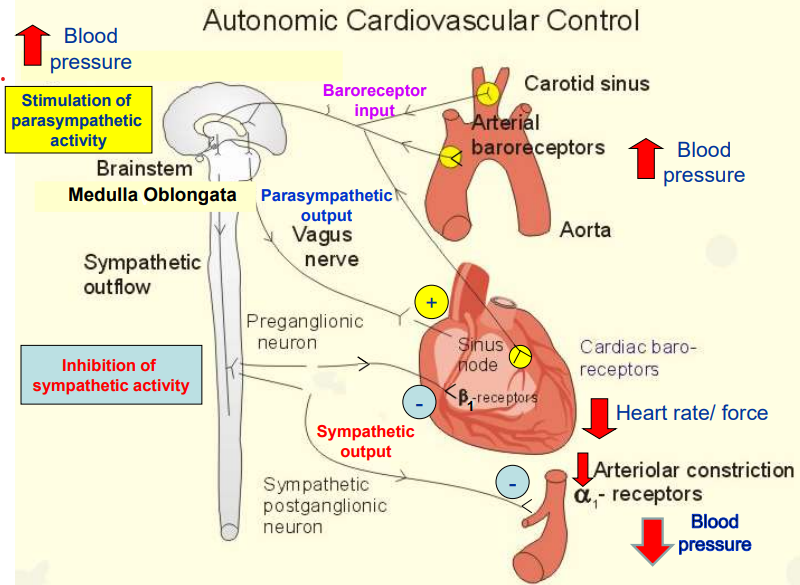
Outline how the ANS controls the cardiovascular system.
Increase in BP (Red Arrow Up)
Baroreceptors in the carotid sinus & aorta detect arterial stretch and send signals to the medulla oblongata.
Medulla Oblongata Response
Inhibits sympathetic activity, ↓ing heart rate, contraction force, and vasoconstriction.
Activates parasympathetic activity via vagus nerve, further slowing heart rate (ACh → M₂ receptors = ↓ SA node firing).
Effects on the Heart and Blood Vessels
Heart: Reduced β₁-receptor stimulation = ↓ed heart rate & contraction force.
Blood Vessels: ↓ed α₁-receptor activation = Vasodilation = Lower blood pressure (Red Arrow Down).
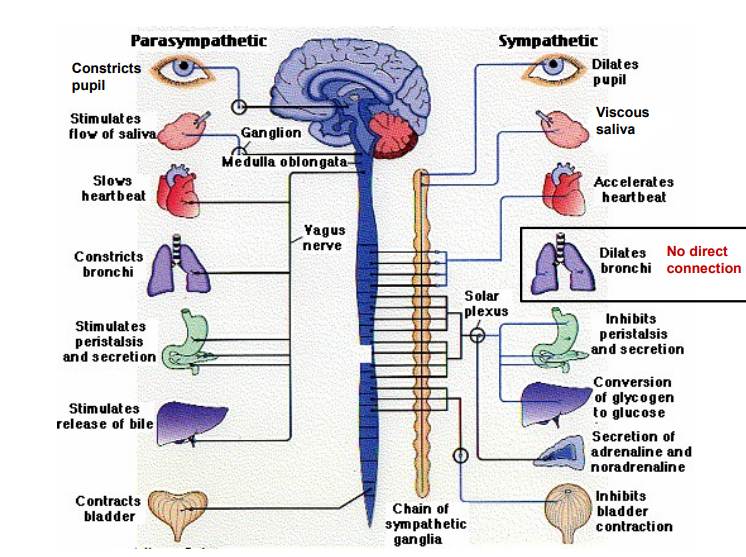
Outline what this diagram represents.
ANS controls involuntary body functions
Parasympathetic Nervous System ("Rest & Digest") → Conserves energy, slows heart rate, promotes digestion, and relaxes the body.
Sympathetic Nervous System ("Fight or Flight") → Increases heart rate, dilates pupils, enhances airflow, inhibits digestion, and prepares the body for stress.
What does noradrenaline act on?
a1 receptors on peripheral arteriole smooth muscle, causing vasoconstriction.
What is the neurotransmitter released at all autonomic ganglia & what type of receptor is then activated on the ganglionic neurones?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
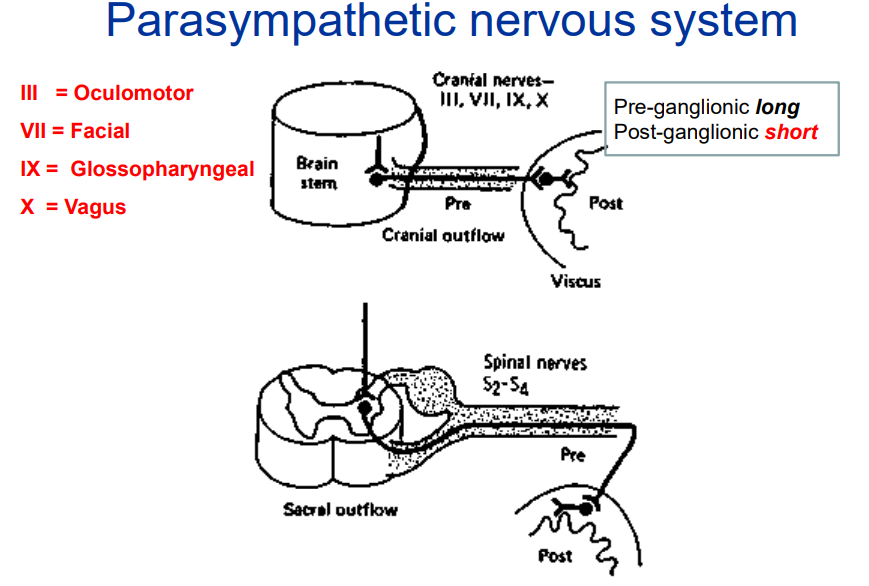
What are the key characteristics of the parasympathetic nervous system, & the ganglionic fiber lengths?
Cranial Nerves Involved:
III (Oculomotor) – Controls eye movements and pupil constriction.
VII (Facial) – Controls facial expressions and salivation.
IX (Glossopharyngeal) – Involved in swallowing and salivation.
X (Vagus) – Regulates heart rate, digestion, and respiratory function.
Pre- and Post-Ganglionic Nerve Features:
Pre-ganglionic fibers are long (travel far before synapsing).
Post-ganglionic fibers are short (synapse close to the target organ).
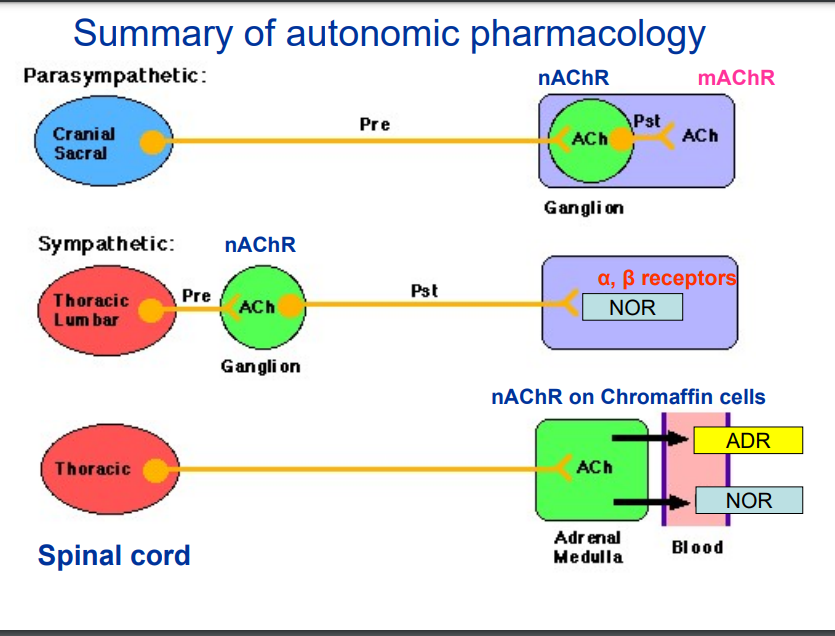
Summarise the pharmacology of the ANS.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (Cranial & Sacral)
Pre-ganglionic neuron releases ACh.
ACh binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) in the ganglion.
Post-ganglionic neuron also releases ACh, which binds to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR) on the target organ.
Sympathetic Nervous System (Thoracic & Lumbar)
Pre-ganglionic neuron releases ACh, which binds to nAChR in the ganglion.
Post-ganglionic neuron releases noradrenaline (NOR), which binds to α and β adrenergic receptors on the target organ.
Sympathetic Nervous System & Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal medulla acts as a modified sympathetic ganglion.
Pre-ganglionic neuron releases ACh, which binds to nAChR on chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla.
The adrenal medulla releases adrenaline (ADR) and noradrenaline (NOR) into the bloodstream, activating α and β adrenergic receptors throughout the body.
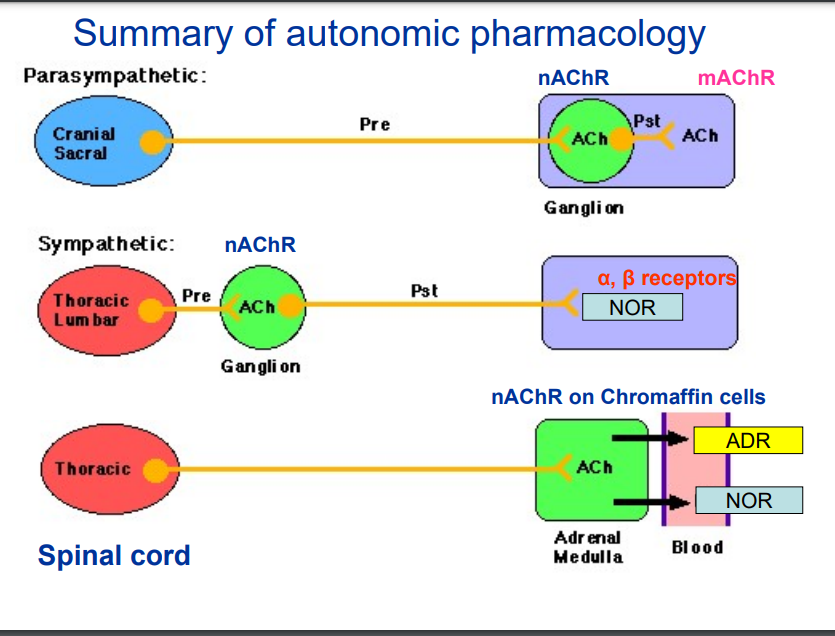
Outline autonomic control of pupil diameter.
Miosis (Constricted Pupil):
Circular muscle contracts (radial muscle relaxed) (parasympathetic).
Pupil becomes smaller.
Caused by bright light, near vision, or parasympathetic drugs.
Mydriasis (Dilated Pupil):
Radial muscle contracts (circular muscle relaxed) (sympathetic).
Pupil becomes larger.
Caused by low light, stress, or sympathetic drugs.
There is no direct parasympathetic ___________ of our blood vessels.
There is no direct parasympathetic innervation of our blood vessels.
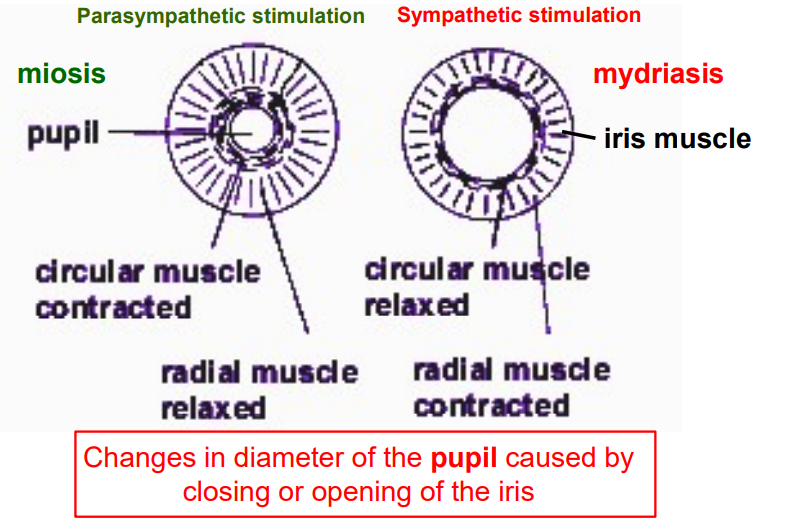
Outline autonomic control of lens thickness.
far vision (sympathetic): ciliary body relaxes, pulling on suspensory ligaments, lens becomes thinner, focusing on far objects.
near vision (parasympathetic): ciliary body contracts, relaxing suspensory ligaments, lens becomes fatter & focused on near objects.
Outline how the ANS controls cardiac rhythm.
sympathetic: NOR activates b1 receptors on the heart, activates Gs protein, which activates adenylyl cyclase, = ↑ cAMP = modulation (↑) of If
parasympathetic: Ach activates M2 receptors on heart, activates Gi (inhibitory G protein complex), inhibits adenylyl cyclase, = ↓ cAMP = modulation (↓) of If
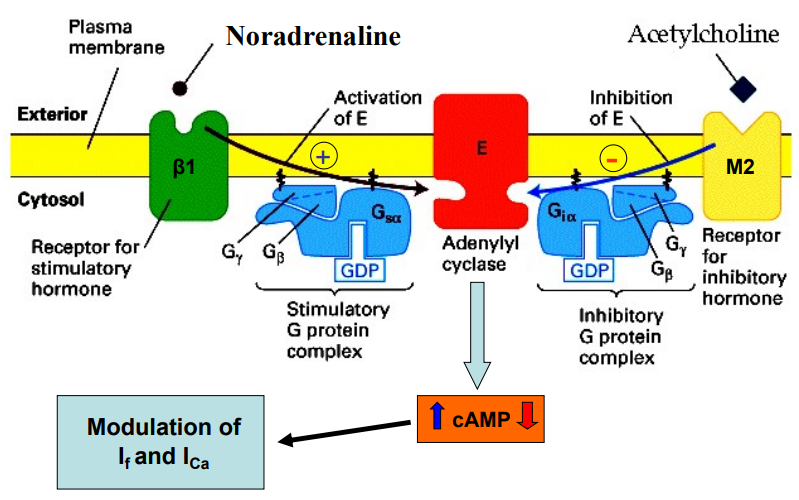
Outline the main mechanism Ach modulates the heart.
Ach activates M2 (muscarinic Ach receptor) = splitting of GB component
GB component activates GIRK K+ channel = membrane hyperpolarisation

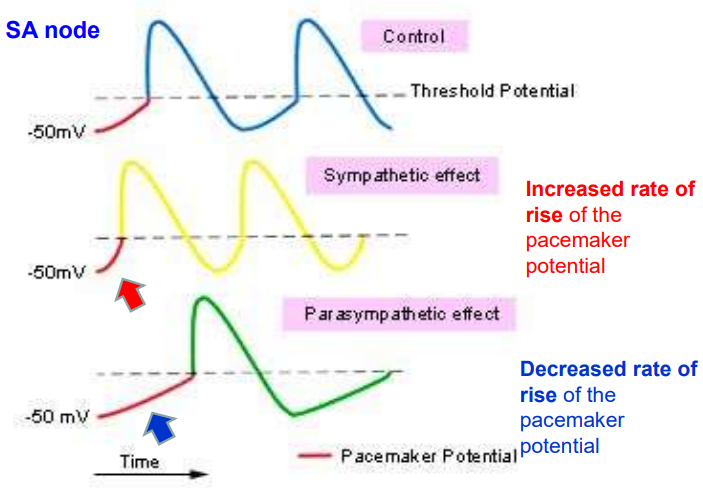
What happens to the SA node AP when we activate the sympathetic nervous system?
A rate in rise of the pacemaker potential.
Outline the efects of the sympathetic nervous system on tissues with α-adrenoreceptors.
Blood vessels (skin, abdomen) (α₁) → Vasoconstriction
Radial iris muscle (α₁) → Pupil dilation
Gut sphincters (α₁) → Contraction
Gut wall smooth muscle (α₁, α₂) → Relaxation
Salivary glands (α₁) → Thick, sparse saliva
Male sex organ (vas deferens) (α₁) → Ejaculation
Outline the effects of the sympathetic nervous system on tissues with β-adrenoreceptors.
Heart (β₁) → ↑ Heart rate & contractility
Gut wall smooth muscle (β₁, β₂) → ↓ Motility & tone
Skeletal muscle arterioles (β₂) → Vasodilation
smooth muscle of bronchioles & trachea (β₂) → Relaxation
Salivary glands (β₁) → Thick, sparse saliva
Bladder detrusor muscle (β₂) → Relaxation
Fat cells (β₃) → Lipolysis
Outline the effects of the parasympathetic nervous system on tissues with M-receptors (muscarinic).
Iris or sphincter muscle (M₃) → Contraction; miosis
Ciliary muscle of eye (M₃) → Contraction; near vision accommodation
Heart (M₂) → ↓ Heart rate
Arterioles → No direct effect (no innervation)
Lungs (M₃) → Bronchoconstriction
Salivary glands (M₃) → Copious salivation
Intestine (M₃) → ↑ Motility, sphincters relaxed
Urinary bladder (detrusor muscle) (M₃) → Contraction
Male sex organs (M₃) → Erection (mediated by NO)
all M₃ except the heart.
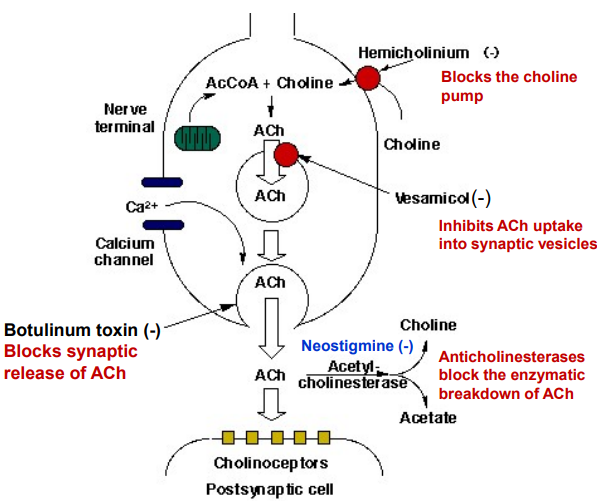
In a cholinergic nerve terminal, how does Botulinum toxin work? What is it used for?
Botulinum toxin blocks acetylcholine (ACh) release at cholinergic nerve terminals by cleaving SNARE proteins, preventing vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter exocytosis, leading to muscle paralysis.
cosmetic reduction of wrinkles by relaxing muscles.
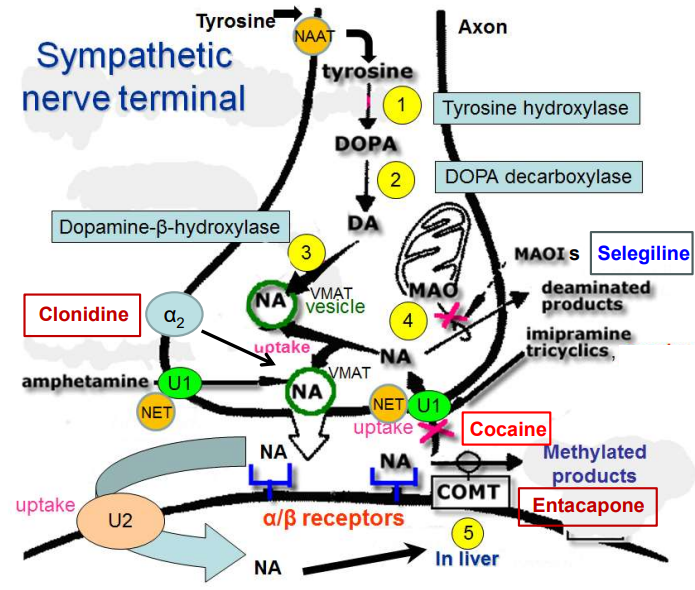
Outline how NOR is synthesised in the sympathetic nerve terminal.
Tyrosine Hydroxylase (1) converts Tyrosine → DOPA
DOPA Decarboxylase (2) converts DOPA → Dopamine (DA)
Dopamine-β-hydroxylase (3) converts DA → NA in vesicles
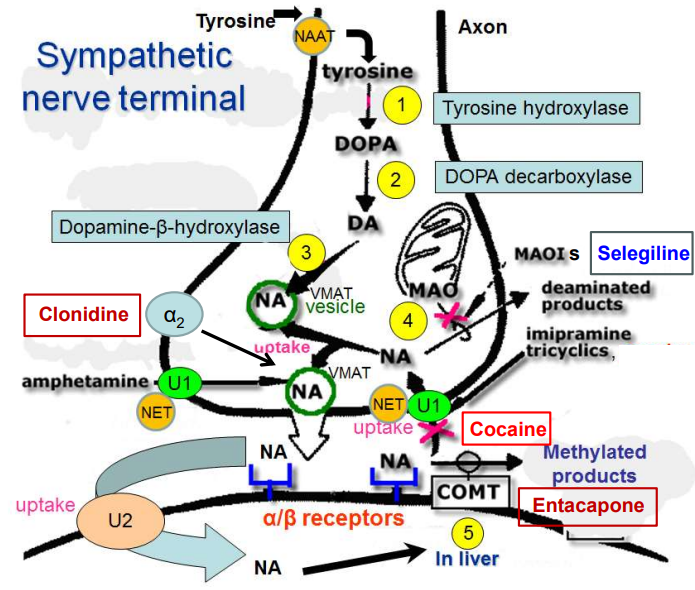
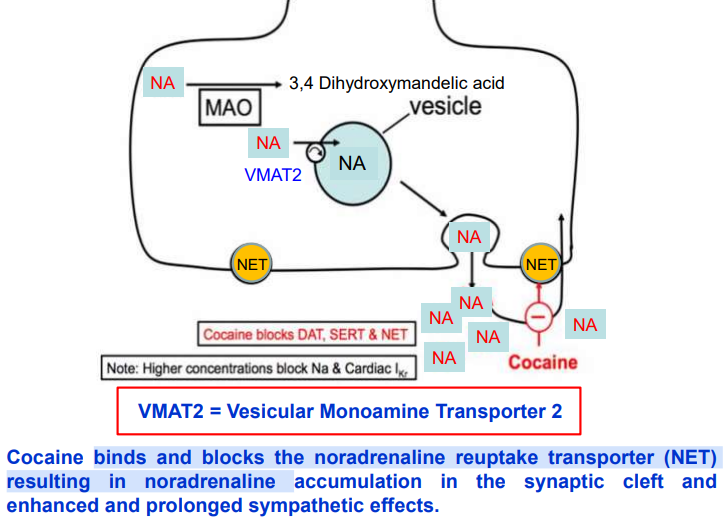
How does cocaine act as a sympathomimetic (class of drugs that mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system) & prevent NA uptake?
Cocaine blocks the norepinephrine transporter (NET), preventing NA reuptake, leading to prolonged noradrenaline action at α/β receptors.
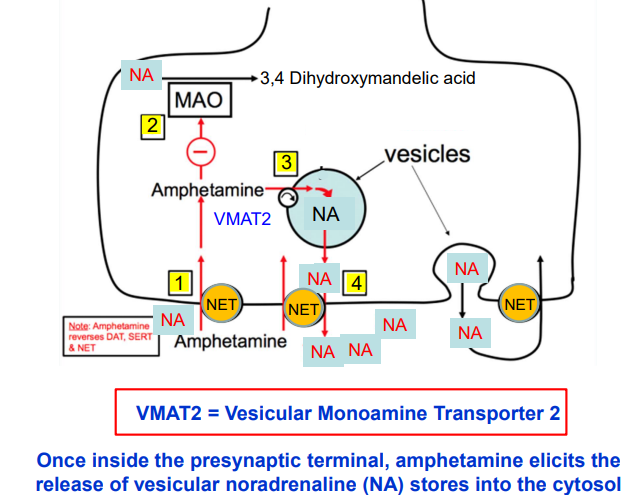
How does amphetamine increase release of noradrenaline?
Amphetamine enters neurons via NET (norepinephrine transporter).
Stimulates VMAT2 (vesicular monoamine transporter), releasing noradrenaline into cytosol.
Increased NA conc triggers NET to work in reverse.
NA pumped into the synaptic cleft, enhancing receptor activation.
How does cocaine increase release of noradrenaline?
Cocaine blocks NET, DAT (dopamine transporter), & SERT (serotonin transporter).
This blockage causes neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin) to accumulate in the synaptic cleft.
Accumulation leads to increased activation of receptors, causing peripheral sympathetic effects (e.g., increased heart rate & BP) and stimulant effects in the brain.
What are noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors?
Drugs that inhibit the noradrenaline uptake process (NET) enhance sympathetic nerve activity.
Tricyclic antidepressants are the main drugs with this property
e.g. imipramine, clomipramine, nortriptyline
What is the issue with classical MAOIs (Monoamine oxidase inhibitors)?
MAOIs (e.g., tranylcypromine, phenelzine) block the breakdown of norepinephrine, but have little effect on nerve stimulation.
They increase the effects of indirect sympathomimetics (e.g., amphetamine, tyramine).
Eating tyramine-rich foods can cause a dangerous blood pressure spike.
More selective MAO-B (Monoamine Oxidase B) inhibitors (e.g., selegiline) don’t have these side effects.
What do COMT inhibitors (Entacapone, Tolcapone) do and what are their side effects?
COMT inhibitors (Entacapone, Tolcapone) prevent the breakdown of levodopa, improving Parkinson’s treatment.
Side effects: Dyskinesias, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, vivid dreams, reddish-brown urine.
Tolcapone can cause liver toxicity.