Biophysics Module 5: Electric and Magnetic Fields of Life
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What are the distinct characteristics of electric forces in electro magnetism (2)
Attraction and Repulsion
What does attraction and repulsion depend on
The charge of the body
Just like gravity, electric forces (diminish/ increases) as the __ of separation distance between a pair of interacting charges
Diminish, as the square of separation distance between a pair of interacting charges
Difference between gravity and electromagnetism
Gravity is only attraction, electromagnetism has attraction and repulsion
Scientists used to think that __ and _ were two separate issues before electromagnetism
Electricity and Magnetism
Who helped establish elecctromagnestism?
Maxwell
Magnetism is associated with electricity when __
2 bodies move relative to each other
Maxwells theory encompasses what?
Electricity, Magnetism, and Light
Property of particles with long range interaction depend on what (according to Maxwell)
Charge
Electromagnetic waves are waves like sound waves but the difference is that they are __
Transverse
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum (y/n)
Yes
Electromagnetic waves travel at what speed through a vacuum
C = 300, 000, 000 m/s
Electromagnetic waves can be __ from one force to another
Transferred
Like sound waves, electromagnetic waves can be ___ or _ after hitting a surface
Reflected or Refracted
Force and Magnetic Field is __ to each other
Perpendicular
In the hand rule what is the thumb, pointer, and middle finger
Thumb = Force
Pointer = Magnetic Field
Middle = Electric Current
Equation of electromagnetic Force
F = qE(electric force) + qv x(cross not times) B(Magnetic Force)
3 Properties of electricity
Charge (q)
Electric Field (e)
Electric Potential or Voltage (A)
What is charge (q)?
Unit of electricity used to describe the size of force an object feels when exposed to other charged objects
Charge is measured in what?
C or Coulombs
What is an electric field
Where the electric force is transfered
Can be thought of as invisible lines
What are electric fields created by
Charged Bodies
What is the electric field expressed in?
N/C, Newtons Per Coulumb
What is Electric Potential/Voltage
Term used to describe the potential energy of electric attraction/repulsion
What is the unit of Electric Potential/Voltage
J/C, Joules per Coulumb
What is coulumbs law formula?
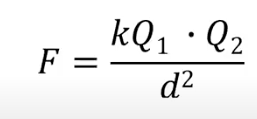
The electromagnetic force of two objects gets weaker or stronger dependent on what 2 factors? What are the relationships of these factors to force?
Charge and Distance
Higher the charge the more repelling/attractive force
The more the distance the less repelling/attractive force
k constant in the coulomb equals what?
9X10^9 N*m²/C²
A proton and an electron have a set charge of __
Proton = 1.6×10^-19
Electron = - 1.6×10^-19
If the force is negative then the objects are (attracting/repulsing)
Attracting
1 Armstrong = How many meters?
1×10^-10
Ohms Law formula
V = I R
Ohms law tells us that the current flowing through a conductor is __ to its resistance
Proportional
Series Circuit
Numerous resistances linked one after another
Parallel circuit
Numerous resistances linked across one another
How many current pathways are in a parallel circuit
More than 1
For series pathways, all the __ are similar and _ is cumulative
Current (because one current), Voltage is cumulative
For parallel pathways, all the __ are similar and _ is cumulative
Voltage are similar, current is cumuative
Humans have __ charge but we still use electricity in biochemical and molecular processes
Neutral
Electric fields line up from the __ to _ side
Positive to Negative
What is electrophysiology
The branch of physiology dealing with electric phenomena associated with living bodies or/and their function
What are the two major points of focus for electrophysiology
CNS and Membrane and ion channels
What is Patch Clamping? (method i electrophysiology)
Uses a micropipette to make contact with the cell, introduces a circuit to measure the membrane potential and analyzes the cell from there
Why is studying ion channels important?
Shows the the membrane potential or separation of charge between 2 environments
Resting membrane potential of Neuron
Has a negative concentration gradient with more potassium inside while theres more sodium outside
Concentration gradient is negative inside the cell so there must be more positive ions outside the cell
What happens when neurotransmitters are released?
Initiates Depolarization causing the neuron to become more positive by allowing for the influx of Sodium ions into the neuron through the opening of sodium channels
Increase in millivolts (MV)
Usage of ion channels can lead you to creating pain medication such as __
Vioxx
Electrocephalograph (EEG)
Records auto electrical activity in the skull and skin, is able to check for seizures, and deep thinking.
Skin voltages have a range of 10-100mV
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Records the activity of the heart by measuring cutaneous electrical potential across the thorax
This is where the muscles of the heart cells depolarize (contract)
Atrium muscle cells contract in unison due to the electrical signal of __
Sinoatrial node
Defibrilator
Employs a pulse or current to reestablish rhythmic and coherent contraction of heart muscles
Electroshock therapy
Bone growth
Bone growth seems to be faster when the bone has negative charge,
This is associated with the creation of material stress known to produce bone strengthening
For Magnetic Fields, how can the visualization of magnetic force be shown
Arrow heads
Given a magnet with north and south poles, the magnetic field lines of the magnet will be __ on the outside
North to South
Given a magnet with north and south poles, the magnetic field lines of the magnet will be __ on the inside
South to North
How to visualize magnetic fields in real life?
Buying iron fillings and looking where they face
How to measure magnetic force (magnetism)?
Magnetometer
SI units of magnets is __, the force applied to a charge by moving through a magnetic field
Tesla T, or Gauss T = 1×10^4 G
That is the Lorentz Force law ?
Determining the magnetic force (seperate from maxwells law because that was electromagnetic force)
Lorentz force law formulas
F = qV x B
F = qvB sin (theta)
Charge moving across a wire
F = BIL sin (theta)
Right hand rule of magnetism
F = thumb
I (Electric Current)= hand (direction of the wire)
Curling the finger would give you the B (magnetic field)
Amperes Law
Given a current flowing, and given an imaginary loop circling the wire, and given the radius R from the loop to the midpoint.
Then the magnetic field at the edge is weaker than those closer to the current
Magnetic Force which is farther from the current = weaker
Magnetic Flux
Summation of the magnetic field lines given an enclosed area
Si Unit of Magnetic flux is _
Weeber wb
In an enclosed space, the magnetic flux value always equals __
0
Electromagnetic Induction: Galvanometer Experiment
Galvanometer was stationary, magnet was stationary = No deflection
Magnet moved closer = deflection in that direction
Magnet was stationary but it was nearer = no deflection
Magnet was moved further away = deflection
Electromagnetic induction happens due tot he fact that magnetic force is the __
Movement of two objects relative to one another
Faradays 1st Law
EMF (electromagnetic force) changes when magnetic force within a circuit by moving the magnetic field (Property of magnetic induction)
How to move the magnetic field?
Moving the magnet towards or away from the coil
Moving the coil into or out of the magnetic field (closer to the field)
Changing the area of the coil placed in the magnetic field (magnetic flux?)
Rotating the field relative to the magnet
Faradays 2nd Law
The magnitude of the electromotive force is proportional to the rate of flux linked by the coil
Magnetic flux impacts electromagnetic force
Flux linkage is given by __
Flux * Number of turns in the coil
What is a by product of faradays law?
AC generator
What is the AC generator?
Machine that turns mechanical energy into electrical energy
AC is based on what principle
Electromagnetic Induction
AC has what parts?
Armature, shaft, magnets, slip rings, brushes
Graph of an AC is _
sinusoidal (oscillating)
When the Armature is horizontal with A B going down, flemmings right hand rule directions are
Thumb (motion of conductor) = Up
Index (Magnetic Field) = Right
Middle (Current) = Outward
When the Armature is vertical with A B going down flemings right hand rule directions are
Thumb (motion of conductor) = Down
Index (Magnetic Field) = Right
Middle (Current) = Inward
Electron Spin Resonance
Electrons have a spin which gives it a movement, it acts as a mini bar magnet
Because it has a movement, when it encounters a magnetic field it can spin in 2 ways
Two ways an electron can spin when theres a magnetic field
Parallel
Anti Parallel
This changing of energy levels in an applied magnetic field is called the __
Zeeman effect
Electron spin resonance or the electron paramagenetic resonance is the __
Spin flip of an electron in a magnetic field
What kind of electrons are affected by electron paramagnetic resonance
Unpaired electrons
What does ESR Spectroscopy do
Using a magnetic field, it can find unpaired electrons due to its changes in spins.
It can not find paired electrons because the two spins cancel each other out
Whether parallel or antiparallel is dependent on
Energy state of the electron
Why is ESR Spectroscopy useful
Can identify free radicals like specific oxygen and nitrogen species
As well as transition metal ions and other paramagnetic species
Concentration of free radicals is normally too low to calculate with magnetism alone, _can help elucidate the size
Uv radiation
Another thing that can help identify characteristics of a molecule with paramagnetic electrons (like a free radical) are __
Spin probes
What is used as a spin probe that was synthesized by us
Nitroxide (has its own unpaired electrons and can interact with other species to tell us information)
Why study free radicals?
Measure of health or disease state
Too much free radicals is instability
Free radicals make more free radicals causing disease and cancer
Nuclear resonance spin spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance uses large magnets in order measure the interactions between the radio frequency (rf) electromagnetic radiations with the nuclei of molecules placed in a magnetic field.
What do the measurement between the interactions between radio frequency electromagnetic radiation to nuclei help us do
map out the structures, dynamics, reaction state, and environment of the molecules
Map out chemical or protein structure
NMR in Biology
Essentially it maps out protein structures which can be useful when the disease you have missfolds a protein.
Proteins have native states but under specific diseases this can change which would give you different values when you do NMR
Examples of diseases that have missfolded proteins
Type 2 Diabetes, Alzhimers’s, Parkinsons, Cancer, etc.
What is made in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A detailed illustration of organs and tissues, it can show you if you have cancer or tumors or other problems
How does MRI Work?
To create a magnetic resonance image, the body is moved through a strong magnet with a gradient(field inreasing in a direction), radio frequency pulses passing through the body as well
What do radio frequency pulses help check?
Absorbing Protons
MRI is saved for (live/dead) tissue?
Alive
Rationale behind Magnetic Nano Particles
Nano particle delivery is hard
Concept behind Magnetic Nano Particles
There is a drug that is ingested, it is guided by a magnet to reach the desired tumor