Psych Stats quiz 1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Scientific Method steps
observation
question
hypothesis
prediction
test the prediction
interation time or it is successful!
operationalization
way to measure variables
reliability
degree to which independent measurements of a behavior under the study are consistent - are you getting the same response if tested repeatedly?
validity
degree to which it measures what it is intended to measure - are you measuring what you say you’re measuring
how to study development? list
cross-sectional
longitudinal
microgenetic
cross-sectional study
compares children of diff ages on a give behavior, ability, or characteristics - studied within the same time period
longitudinal
follwing the same children over a substsantial long period + observing the changes/development
microgenetic
track ages, focus on a small point in the target age range and do an in-depth depiction of the processes that produce change
cohort effects (threat to study)
When a group of people who were born around the same time are similarly exposed to historical experiences, that influence the dependent variable of interest - ex) smoking in the 90s vs now
causation or correlation
correlation doesn’t equal causation - threat to study
methods for studying development
naturalistic observation
structure observation
interviews and questionnaires
correlational
experiemntal
naturalistic observation
examination of ongoing behavior in an environment not controlled by the researcher.
structured observation
a method that involves presenting an identical situation to each participant and recording the participants behavior.
interviews and questionnaires
Structured interview: a research procedure in which all participants are asked to answer the same questions.
- Clinical interview: experimenter can go off-script.
Questionnaires: When you’re lucky enough to work with kids who can read
correlational
comparison of existing groups of children or examination of relations among children’s scores of different variables.
experimental
Random assignment of children to groups and experimental control of procedures presented to each group.
ethical consideration
Do no harm
Informed consent
Parental consent
Coercion
Deception
Anonymity vs. confidentiality
Known & unknown risks
periods of prenatal development
zygote —> embryo —> fetus —> baby
germinal —> embryonic —> fetal
conception 3-8 weeks 9weeks-birth
~ 2weeks
germinal period
zyogote
conception-2weeks
cells split
forms placenta
“stem cells” forms embryo
amniotic sac + fluid
hawthorne effect
people may alter behavior if they know they are being observed
embryonic period
3-8 weeks
from this period, areas near the ehad develop earlier than those furhter away
cephalocaudal developement
brain development - Neurogenesis, Cell migration/differentiation, Myelination, Synaptogenesis, Pruning
Neurogenesis
the proliferation of neurons through cell division
Synaptogenesis
the process by which neurons form synapses with other neurons.
fetal period
By 9 weeks, a fetus has…
A giant head
All of its internal organs
Begun the process of sexual differentiation
Nails!
teratogens
A potentially harmful agent
•Dose–response radiation: Potential problems depend on how the mother is exposed to the teratogen and for how long. The more exposure, the more at risk the fetus becomes.
hazards to prenatal period
cigarettes, alcohol, maternal factors, occupational hazards, environmental pollution
chromosomes
Molecules of DNA that transmit genetic information
genotypes
the exact genetic material that an individual inherits (i.e., the pairing of the alleles)
phenotype
the observable expression of the genotype, including both physical characteristics and behavior
genetic transmissions issues
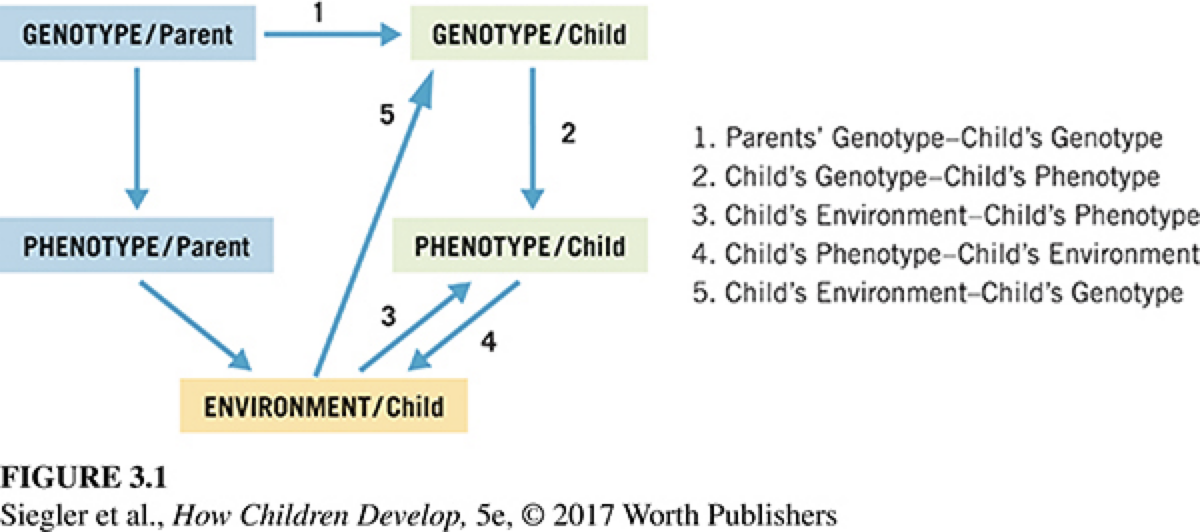
The field of epigenetics
the study of mechanisms that will switch genes on and off without changes to the DNA sequence itself
plasticity
process that helps brain adapt to things
experience-expectant processes
expect taht we will encounter experiences in the world around us; our brain is ready for it
Creates vulnerability. If that experience isn’t encountered, then the neural circuits won’t be fine-tuned and developed
gneerally occurs early during development
generally universal - we all expect visual stimuli
sensitive periods
experience-dependent plasticity
what you learn/how your brain develops is dependent on the experience we live
can occur over the life span in response to complex stimuli
more unique to individuals + their experiences
no optimal period
sensation
The processing of basic information from the world through the sense organs (eyes, ears, skin, etc.)
perception
The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information about objects, events, and the world around us.
taste for fetus
Amniotic Fluid contains a variety of flavors, and prefers some more than others
Some mothers with Polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid)
smell for fetus
Amniotic fluid contains odorants
Food and drink with strong odors (e.g., curry, coffee) can be detected in amniotic fluid during childbirth
hearing for fetus
can hear - soap opera example
habituation
A simple form of learning that involves a decrease in response to repeated or continued stimulation
dehabituation
The introduction of a new stimulus rekindles interest following habituation to a repeated stimulus.
preferential looking technique
A method for studying visual attention in infants that involves showing infants two patterns or two objects at a time to see if the infants have a preference for one over the other.
visual acuity
sharpness of visual discrimination.
Poor at birth but adult-like by 8 months
Deficits are in infants’ contrast sensitivity (the ability to detect differences in light and dark areas in a visual pattern) because of the spacing of cones in the eye
early visual processing
1 month: perimeters, focus on high contrast features
2 months: perimeters, plus details (focus on eyes)
4+ months: focus on mouth
Object segregation:
The identification of separate objects in a visual array.
cues to depth perception
Around 1 month:
Optical expansion:
closer objects are bigger
Around 4 months:
Binocular disparity:
Differences in retinal images between the two eyes.
Around 6-7 months:
Monocular depth cues emerge:
Examples include: interposition, convergence of lines in the distance, relative size.
Stereopsis:
How the brain corrects for and interprets binocular disparity to perceive depth.