Ch 9, 11-12, 3, 13/14 Quizzes (Exam 2 Material)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
In gene families, not all duplicated genes will
become functional members
Whole-genome duplication can contribute to the formation of
gene families
Duplicated genes can diverge in both
their regulatory regions and their coding regions
Proteins required for growth, metabolism, and cell division are more highly conserved than those involved in
development and responses to the environment
You isolate a pathogenic strain of E. coli from an individual and discover that the strain is resistant to an antibiotic. Common laboratory strains of E. coli are not resistant to this antibiotic, nor are any other previously isolated pathogenic E. coli strains. However, such resistance has been observed in other species of bacteria in the hospital in which the individual was treated. This newly discovered antibiotic resistance in E. coli is most likely due to
horizontal gene transfer
You discover that the underlying cause of a disease is a protein that is now less stable than the non-disease-causing version of the protein. This change is most likely due to
a mutation within a gene
Porin proteins form
large, barrel-like channels in the membrane
Porin proteins are made primarily of
B sheets
Porin proteins cannot form
narrow channels
Porin proteins have
alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids
Although cholesterol is a hydrophobic molecule, it has a hydrophilic functional group that resembles the
hydrophilic head group of other membrane lipids
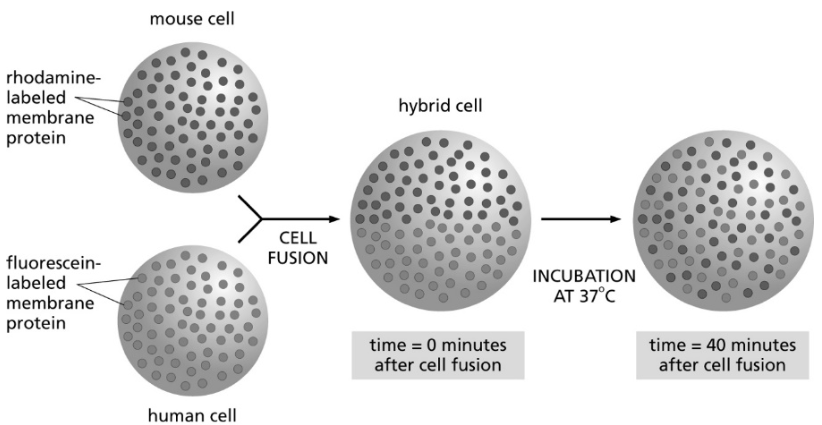
What is demonstrated by the cell fusion experiment depicted in the picture?
lateral diffusion of membrane proteins
We know the detailed molecular structure and mechanism of action of the transmembrane protein bacteriorhodopsin. This protein uses sunlight as the source of energy to pump
H+ out of the cell
Membrane proteins, like membrane lipids, can move laterally by exchanging positions with other membrane components. Which type of membrane protein is expected to be the least mobile, based on its function?
anchors
Viruses reproduce inside a host cell because
viruses use host-cell ribosomes to produce viral coat proteins
HIV is a human retrovirus that integrates into the host cell’s genome and will eventually replicate, produce viral proteins, and ultimately escape from the host cell. What proteins are encoded in the HIV genome?
reverse transcriptase
envelope protein
capsid protein
HIV lacks its own
RNA polymerase and uses the host’s enzyme to transcribe its genes
Horizontal gene transfer is
common in bacteria and has had a major influence on bacterial genomes
What functions are associated with the set of genes found in all organisms on Earth?
DNA replication + cell division
DNA repair
protein production
transcription
translation
New membrane phospholipids are synthesized by enzymes bound to the __________ side of the __________ membrane
cytosolic; endoplasmic reticulum
Yeast cells add
saturated lipids when temperature increases

Consider the apical location of a particular protein expressed in epithelial cells, as illustrated in part A of Figure 11-3. Part B shows the redistribution of this protein around the entire cell. What defects most likely have caused this redistribution?
the deletion of a junctional protein
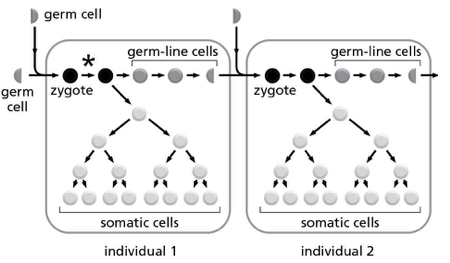
Two individuals are represented in Figure 9-1; individual 1 is one of the parents of individual 2. The asterisk indicates the occurrence of a point mutation on one of the parent’s chromosomes. According to the figure, what is the chance that individual 2 will inherit the mutation that occurs in individual 1?
50%
NADH and NADPH are activated carrier molecules that function in completely different metabolic reactions. Both carry 2 additional __________ and 1 additional __________. This combination can also be referred to as a hydride ion.
electrons; proton
Activated carriers are small molecules that can diffuse rapidly and be used to drive biosynthetic reactions in the cell. Their energy is stored in a readily transferable form such as high-energy electrons or chemical groups. What molecule donates a chemical group rather than electrons?
ATP
ΔG° indicates the change in
the standard free energy as a reactant is converted to a product
most negative ΔG° is most favorable
NADH contains a high-energy bond that, when cleaved, donates a pair of electrons to the electron-transport chain. What are the immediate products of this bond cleavage?
NAD+ + H-
Steps 7 and 10 of glycolysis result in substrate-level phosphorylation. What best describes this process?
the energy derived from substrate oxidation is coupled to the conversion of ADP to ATP
The conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate in step 6 of glycolysis generates a “high-energy” phosphoanhydride bond. What best describes what happens to that bond in step 7?
it is hydrolyzed to drive the formation of ATP
The stimulation of a motor neuron ultimately results in the release of a neurotransmitter at the synapse between the neuron and a muscle cell. What type of neurotransmitter is used at these neuromuscular junctions?
acetylcholine
Although the extracellular environment has a high sodium ion concentration and the intracellular environment has a high potassium ion concentration, both must be neutralized by negatively charged molecules. In the extracellular case, what is the principal anion?
Cl-
Most ion channels are gated, which allows them to open and close in response to
a specific stimulus rather than allowing the constant, unregulated flow of ions
In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced in the
cytosol as glucose is converted into pyruvate
doesnt involve ETC or oxygen
In oxidative phosphorylation, what is the final electron acceptor?
molecular oxygen
In oxidative phosphorylation,
FADH2 and NADH become oxidized as they transfer a pair of electrons to the ETC
The electrons carriers in the ETC of oxidative phosphorylation toggle between
reduced and oxidized states as electrons are passed along