serotonin related pharmacology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
drugs that are used in behavioral pharmacotherapy work by...
alteration of neurotransmission activity in the brain (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin)

what behavior problems can we use pharmacotherapy to treat in animals?
-separation anxiety
-fears and phobias
-hyperactivity
-compulsive disorders
-cognitive dysfunction in older dogs
-house soiling in cats
what are the neurotransmitters of clinical importance in behavioral pharmacotherapy?
serotonin
dopamine
norepinephrine
(these are all monoamine neutrotransmitters, transmit the control and expression of emotions)
serotonin is especially important in what behaviors?
mood
feeding
reproductive behavior
norepinephrine is associated with what type of emotion?
alertness and focus
which neurotransmitter is related to mood, feeding, and reproductive behaviors?
serotonin
what neurotransmitter is important in regulating alertness and focus?
norepinephrine
which neutrotransmitter has a big role in cognitive functions, motivation, and awakeness?
dopamine
what type of functions does dopamine regulate?
Cognitive functions or brain activities: attention, memory, processing speed, and executive functions (i.e., reasoning, planning, problem solving, and multitasking).
motivation
awakeness
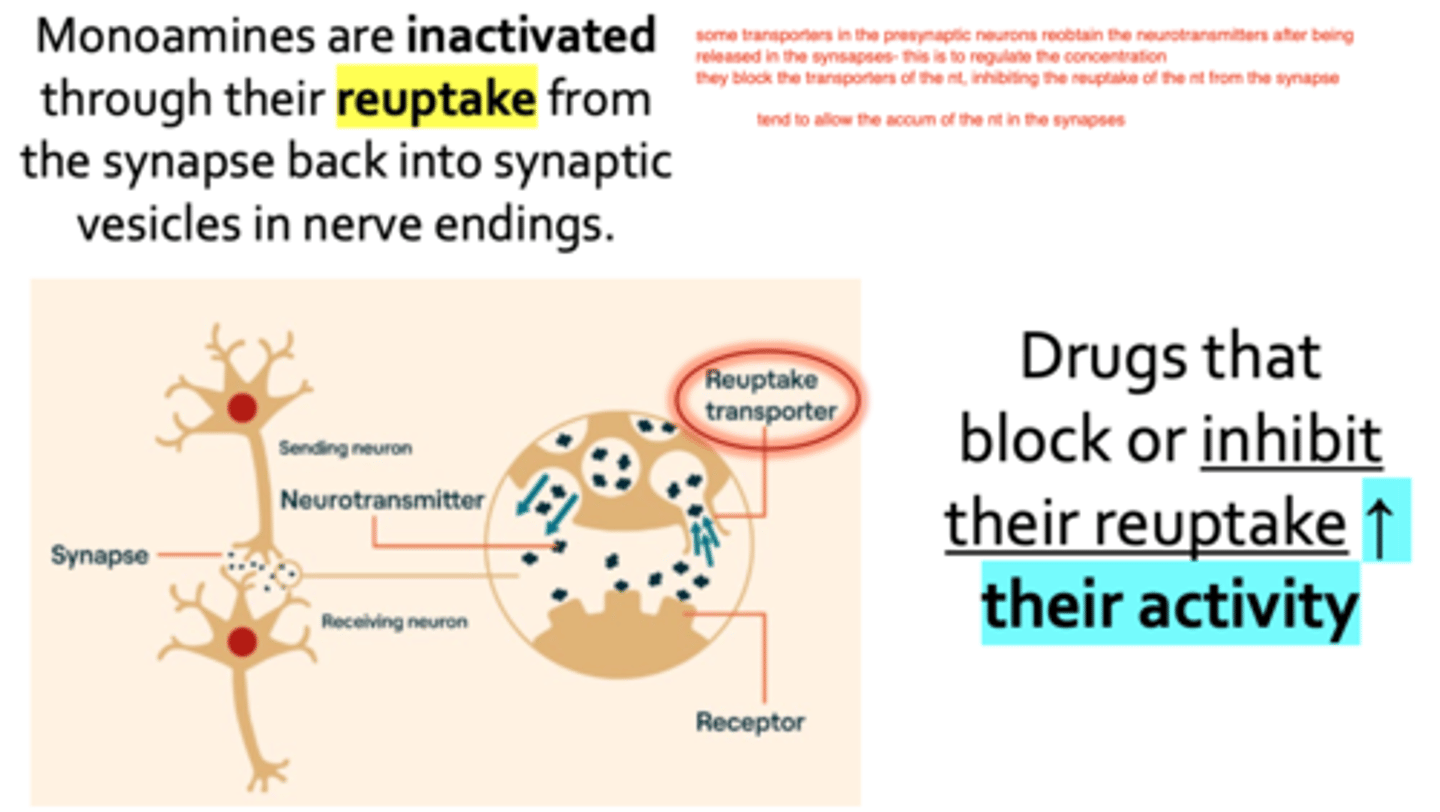
how do drugs increase the activity of monoamines (dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine)?
they block their reuptake, allowing their accumulation in the synapses
what are the most common drugs in treating behavioral problems in veterinary medicine?
antianxiety and antidepressant medications
serotonin (5-HT) is involved in the regulation of:
-mood
-feeding behavior
-sleep/wakefulness
-control of sensory pathways (including nociception)
-control of body temperature
-vomiting
-emotional behaviors (including aggression)
where in the body are serotonin receptors found?
enteric nervous system
CNS
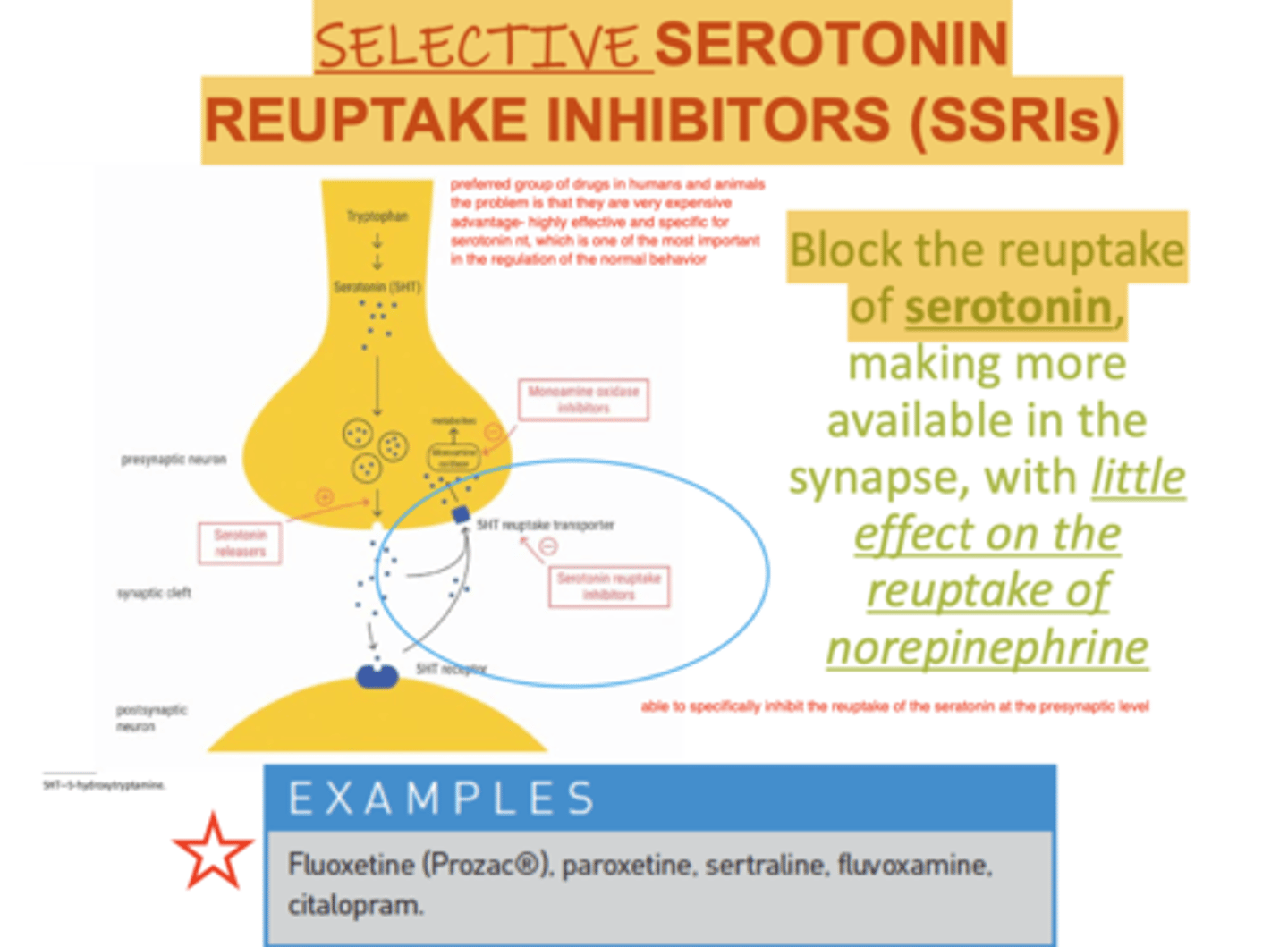
how do selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) work?
block the reuptake of serotonin, making more available in the synapse
they have little effect on the reuptake of norepinephrine
what drugs do we use in vet med that are in the category of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)?
Fluoxetine (prozac)
Paroxetine
Sertraline
Fluvoxamine
Citalopram
what type of drug is Fluoxetine (prozac)?
SSRI
what type of drug is paroxetine?
SSRI
what type of medication is sertraline?
SSRI
what type of drug is fluvoxamine?
SSRI
what drug is Citalopram?
SSRI
what are the clinical uses of SSRIs (Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Sertraline, Fluvoxamine, Citalopram) in veterinary medicine?
obsessive disorders
phobias
aggression
separation anxiety
cats- fluoxetine and paroxetine are used for treating urine spraying, inappropriate urination, anxiety disorders, aggression, obsessive compulsive disorders
dogs- fluoxetine, sertraline, and citalopram are used to treat acral lick dermatitis, anxiety disorders, and obsessive compulsive disorders
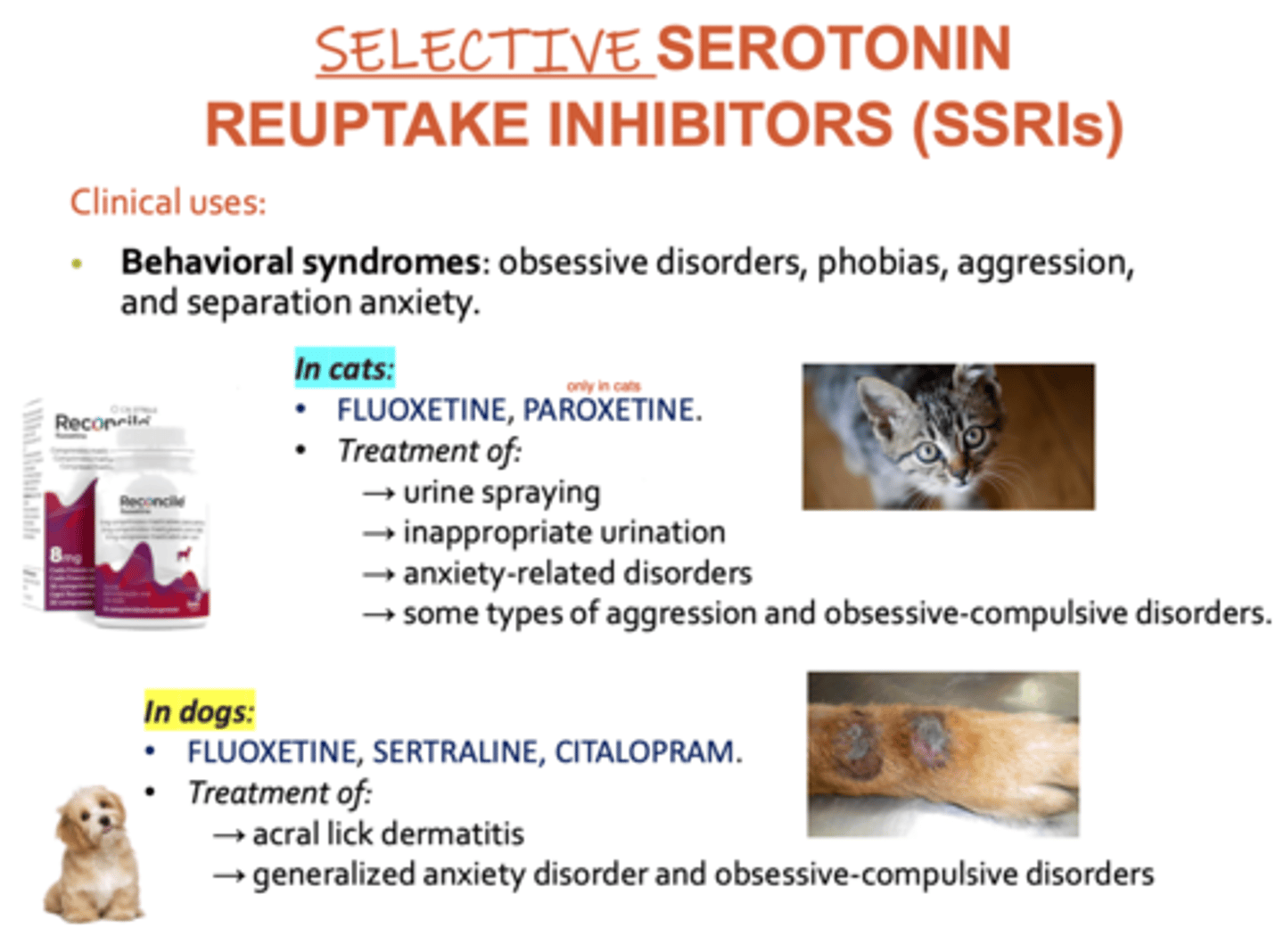
what SSRIs are used in dogs?
fluoxetine
sertraline
citalopram

what SSRIs are used in cats?
fluoxetine
Paroxetine

what are the possible side effects of SSRIs in animals?
-mild sedation
-temporary lack of appetite
-anorexia
-increased anxiety
-decreased sexual motivation
-nausea and vomiting
the side effects are mild because these drugs are selective for serotonin receptors
why are SSRIs not commonly used in veterinary medicine?
because they are expensive, so we tend to use tricyclics instead
do SSRIs have severe side effects?
yes but mild. their side effects are mild because they are selective for serotonin receptors

which is the first choice and second choice in behavioral pharmacotherapy in vet med?
first- SSRIs
second- TCAs
but a lot of owners choose TCAs because they are cheaper
how do TCAs (tricyclic antidepressants) work?
inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, potentiating their effects in the brain
which drugs only inhibit the reuptake of serotonin?
SSRIs
which drugs inhibit the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine?
TCAs (tricyclic antidepressants)
which TCA is the most selective for serotonin?
clomipramine
what is the most used TCA in veterinary medicine?
Clomipramine
what is the use of Clomipramine in veterinary medicine?
used as an adjunct to behavior modification programs, especially in longstanding and severe anxiety
Cats: treatment of urine spraying, aggression, obsessive compulsive disorders
Dogs: treatment of separation anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorders, and to modify owner-directed dominance aggression

what type of drug is Clomipramine?
TCA
what is the main pharmacological effect of Clomipramine?
antidepressant (it inhibits the reuptake of serotonin)
what are the adverse reactions we can see with Clomipramine treatment?
anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, appetite changes, hepatobiliary disturbances
what medication is considered an "atypical" antidepressant?
Trazodone
what is Trazodone?
an "atypical" antidepressent that works as an agonist and antagonist for serotonin receptors- it is a weak serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a serotonin 5HT2A receptor antagonist
which antidepressant works as both a serotonin antagonist and agonist?
Trazodone
how do we administer Trazodone?
orally
which antidepressant has high binding to plasma proteins so has a risk of drug interactions?
trazodone
how is trazodone excreted?
urine
what are the adverse reactions possible with Trazodone?
Sedation, GI issues, Serotonergic syndrome (hyperthermia,
agitation, ataxia, hypertension, convulsions and
coma) when combined with other drugs that facilitate serotonin activity
what is serotonergic syndrome?
a result of elevated serotonin levels in the body
clinically, it presents as hyperthermia,
agitation, ataxia, hypertension, convulsions and
coma. it can even result in death if untreated.
the symptoms tend to appear quickly- within 10 min to 4 hours of taking the drug
this can be caused by high doses, mixing drugs that effect serotonin, high sensitivity to the drugs, and interaction with certain foods (cheese, turkey, red meat, bananas, peanut butter, anything with L-tryptophan)

what are the therapeutic applications of Trazodone?
dogs: treatment of mild thunderstorm phobia, as an adjunct to TCA or SSRI treatment (increases calmness, decreases agitation, and aids sleep), facilitating behavioral calming in dogs following
elective orthopedic surgeries
cats: treatment of travel anxiety and during veterinary examinations
what antidepressant can be used to calm cats during veterinary examinations?
Trazodone
what antidepressant can be used with TCA or SSRIs to increase the calming effect, decrease agitation, and aid with sleep?
Trazodone
what antidepressant is prescribed for treating mild thunderstorm phobia in dogs?
Trazodone
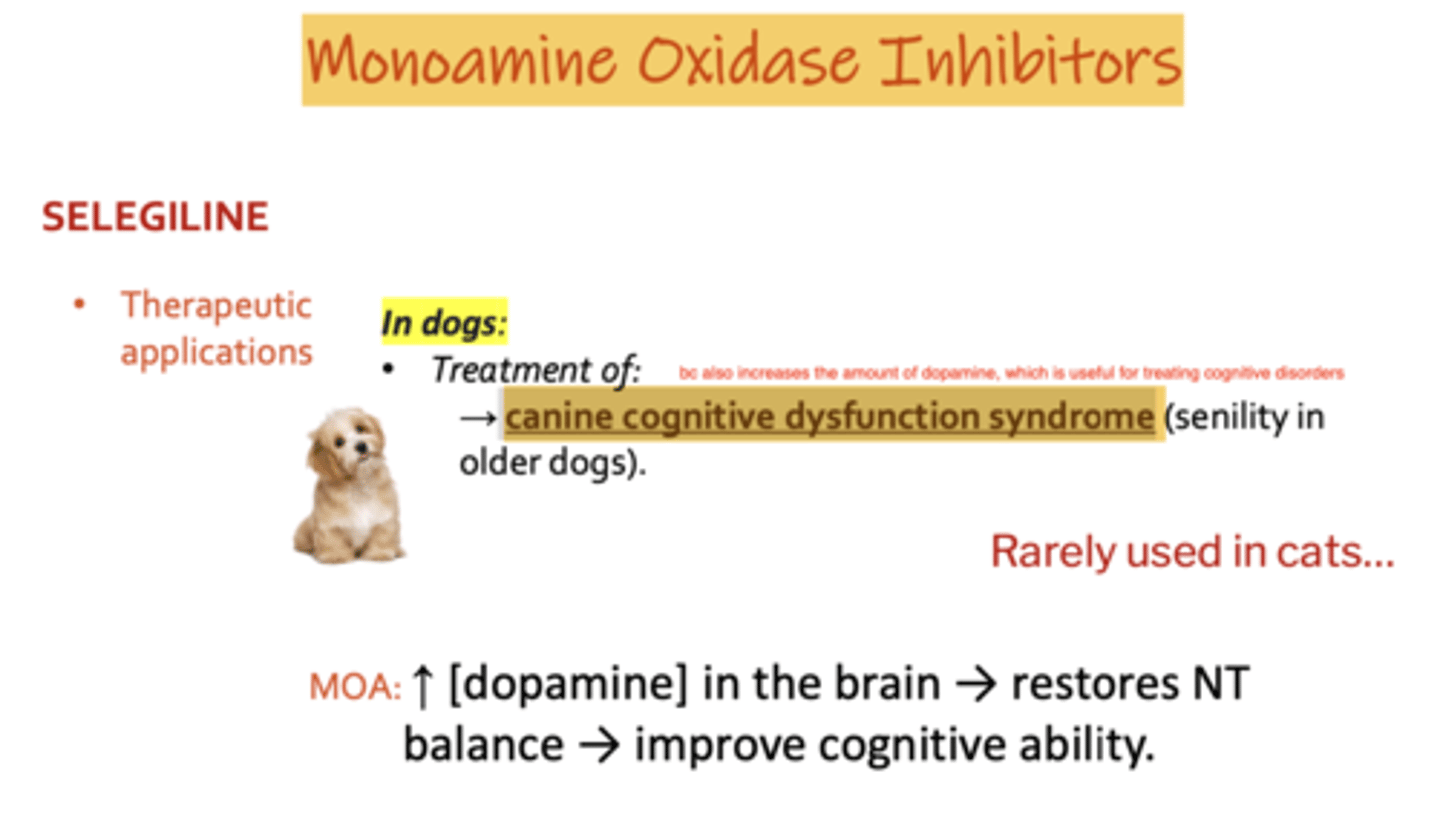
which drugs are monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
selegiline
how does selegiline work?
it is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, so inhibits the metabolism of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. this increases the levels of all 3 neurotransmitters
what are the therapeutic applications of selegiline?
dogs: treatment of canine cognitive dysfunction syndrome (senility in older dogs)
not used in cats
which drug is useful for treating canine cognitive dysfunction syndrome?
selegiline
because it increases the amount of dopamine, which is useful for treating cognitive disorders