G Chem Unit 5 - Acids and Bases
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a bronsted base/acid?
Base: accepts H+ (proton)
Acid: donates H+ (proton)
What is a lewis base/acid?
Base: donates electrons, nucleophiles
Acid: accepts electrons, electrophiles
What is special about lewis bases?
They are ligands and chelates
Donate the electrons in a coordinate bond
How do you recognize lewis acids?
More electronegative atoms bonded to H
Atoms without H can be acids if electron deficient or large positive charges
How do you recognize lewis bases?
Less EN atom with lone pair
Atoms without lone pairs are not usually basic
What are amphoteric compounds?
Have both acid and base characteristics
What are rules for acid/base strength?
More positive charge = more acidic
More electronegative = more acidic
Larger atoms = more acidic
More negative charge = more basic
Less EN = more basic
Small atom = more basic
What are strong acids?
H2SO4, HClO4, HClO3, HNO3, HCl, HBr, HI
What are strong bases?
O2-, OH-, OR-, NH2-, NR2-, H-, R-
How do acids dissociate?
HA (acid) dissociates into H+ and A- (conjugate base)
How do bases dissociate?
A- (base) associates with water into HA (conjugate acid) and OH-
What is Ka for strong acids?
> 1
Usually produce salts upon dissociation (not bases)
What is Kb for strong bases?
> 1
Conjugate acids are usually salts, not acids
What is Kw? pKw?
1.00 × 10-14 = Kw
14.00 = pKw
What is the relationship between Kw, Ka, and Kb? pKa, pK, and pKw?
Kw = Ka*Kb
pKw = pKa + pKb
What is the equation for Kw?
[H3O+][H+]
What is ph and pOH?
pH = - log [H+]
pOH = - log [OH-]
How are pH and pOH related to pKw?
pOH + pH = pKw = 14
How do you find pH or pOH of strong acids/bases (or do logs in general)?
Convert to scientific notation
Separate terms and take -log of each
log 10^x = x
log 1 = 0, log 10 = 1 → estimate the remaining term
How do you find pH and pOH of weak acids/bases?
Use ICE table
Initial
Change
Equilibrium
Plug into Ka equation
x is negligible in the denominator
What is the pH of a weak acid? Found using Ka
pH = - ½ log (Ka[WA])
No difference for diprotic acids
Use pOH, Kb, and WB for bases
What are buffers?
Mix of conjugate acid/base pairs
What is the pH of a buffer?
pH = pKa + log [WB]/[WA]
What buffer should you use?
Equal concentrations on WA and WB
With pKa ± 1 from pH
Larger net concentrations of WA and WB
When is an acid protonated/deprotonated?
pH > pKa → deprotonated
pH < pKa → protonated
What is a neutralization reaction?
Exothermic
Form salt and water
Complete if moles OH- = moles H+
What is equivalence point?
Moles OH- = moles H+
If at 7 → strong base and strong acid
What are indicators?
Used to determine concentrations
Weak acids of one color when protonated and another when deprotonated
Changes color when pH of solution = pKa of indicator
Change color at equivalence point
What will a titration curve of a weak acid and strong base look like?
Equivalence point with pH > 7
What is the half equivalence point?
Where pH = pKa of weak acid or weak base
Volume of titrant needed to reach equivalence point / 2
The flat part
What will a titration curve of a weak base and strong acid look like?
Equivalence point with pH < 7
What are acidic and basic salts?
Contain an ion that is a weak acid/base
For acid → look at cation → group I or II will never be acidic
For bases → look at anion → Cl-, Br-, and I- are never basic
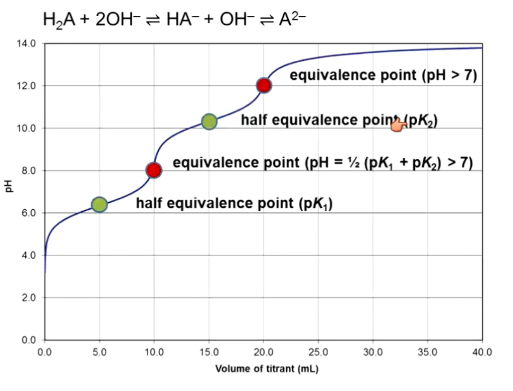
How do you make a titration curve of a diprotic acid?
1st equivalence point = pH = average of pK1 and pK2 = isoelectric point
2nd ep = find like normal
Must fully titrate one proton before moving on to the second