Cellular and Molecular Biology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
G proteins are an example of multi-domain proteins. (T or F)
False
2
New cards
In signaling through G proteins and GPCRs, which one of the following is true:
- The GPCR is very rigid and cannot change its shape
-all of these are correct
-the extracellular signal molecule passes through the plasma membrane to activate the G protein
-the GDP is part of the chemical structure of the G protein
-none of these are correct
- The GPCR is very rigid and cannot change its shape
-all of these are correct
-the extracellular signal molecule passes through the plasma membrane to activate the G protein
-the GDP is part of the chemical structure of the G protein
-none of these are correct
none of these are correct
3
New cards
Put the following steps regarding GPCR/G-protein signaling in the correct sequence:
(1) The G protein dissociates into an alpha subunit and a beta gamma complex
(2) The GTP molecule binds the G a subunit
(3) The GPCR undergoes a conformational shape change
(4) A signal molecule binds the GPCR
(5) The GDP leaves the G a subunit
4 - 5 - 3 - 1 - 2
2 - 4 - 5 - 3 - 1
4 - 3 - 2 - 5 - 1
1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5
none of the above
(1) The G protein dissociates into an alpha subunit and a beta gamma complex
(2) The GTP molecule binds the G a subunit
(3) The GPCR undergoes a conformational shape change
(4) A signal molecule binds the GPCR
(5) The GDP leaves the G a subunit
4 - 5 - 3 - 1 - 2
2 - 4 - 5 - 3 - 1
4 - 3 - 2 - 5 - 1
1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5
none of the above
none of the above
4
New cards
Secondary structure is stabilized primarily by hydrogen bonds between the amino acid side groups (True or False)
False
5
New cards
Protein domain is the term used to describe structurally stable independent regions within one polypeptide chain, which are usually connected to each other by relatively short and unstructured polypeptide segments. (True or False)
True
6
New cards
The alpha helix and beta sheet are two examples of regular folding patterns that are often found in parts of proteins. These patterns result from hydrogen-bonding between the N-H and C=O groups in the polypeptide backbone and do not involve the side groups. (True or False)
True
7
New cards
Protein secondary structure elements such as α helices and β sheets constitute the major regular folding patterns in proteins. With regard to these elements,
-the folding patterns result from hydrogen-bonding between the N-H and C=O groups in the polypeptide backbone
-only a few specific amino acid sequences can adopt these repetitive structures.
-hydrogen-bonding between the amino acid side chains defines the type of secondary structure.
-a certain short amino acid sequence always adopts the same secondary structure.
-All of the above.
-the folding patterns result from hydrogen-bonding between the N-H and C=O groups in the polypeptide backbone
-only a few specific amino acid sequences can adopt these repetitive structures.
-hydrogen-bonding between the amino acid side chains defines the type of secondary structure.
-a certain short amino acid sequence always adopts the same secondary structure.
-All of the above.
the folding patterns result from hydrogen-bonding between the N-H and C=O groups in the polypeptide backbone
8
New cards
Which of the following is NOT true regarding the members of a protein family in general?
-Over evolutionary time scales, the family has expanded mainly through gene duplication events.
-They have similar three-dimensional conformations.
-They can functionally replace each other.
-Their gene sequence is less well conserved than their structure.
-They share an ancestry; i.e. they are homologs.
-Over evolutionary time scales, the family has expanded mainly through gene duplication events.
-They have similar three-dimensional conformations.
-They can functionally replace each other.
-Their gene sequence is less well conserved than their structure.
-They share an ancestry; i.e. they are homologs.
They can functionally replace each other.
9
New cards
Many viruses have large capsids in the form of a hollow sphere, made of hundreds of identical protein subunits. What are the advantages of having coats made of several copies of only a few subunits?
-It requires a smaller amount of genetic information.
-The effect of mistakes in protein synthesis on the overall assembly is minimized.
-Disassembly can be readily regulated.
-All of the above.
-Assembly can be readily regulated.
-It requires a smaller amount of genetic information.
-The effect of mistakes in protein synthesis on the overall assembly is minimized.
-Disassembly can be readily regulated.
-All of the above.
-Assembly can be readily regulated.
All of the above.
10
New cards
Stable β-sheet aggregates can form from many proteins, forming intertwined cross-beta strands that have the potential to kill cells or damaged tissues. Which of the following is NOT true regarding these aggregates?
-Different types of such aggregates can form from the same protein.
-Some healthy cells form these aggregates to store their secretory proteins.
-Their formation is associated with conditions such as Parkinson's disease
-They form almost exclusively in the cells of the nervous system.
-They can form spontaneously, but also can be triggered to form by an infection with the same aggregate.
-Different types of such aggregates can form from the same protein.
-Some healthy cells form these aggregates to store their secretory proteins.
-Their formation is associated with conditions such as Parkinson's disease
-They form almost exclusively in the cells of the nervous system.
-They can form spontaneously, but also can be triggered to form by an infection with the same aggregate.
They form almost exclusively in the cells of the nervous system.
11
New cards
The enzyme lysozyme catalyzes the cutting of a polysaccharide chain through hydrolysis. Which of the following is NOT true regarding the catalytic cycle for this enzyme?
- It involves base catalysis.
- It involves acid catalysis.
- It involves strain catalysis.
- It involves covalent catalysis.
- It involves metal ion catalysis.
- It involves base catalysis.
- It involves acid catalysis.
- It involves strain catalysis.
- It involves covalent catalysis.
- It involves metal ion catalysis.
It involves metal ion catalysis.
12
New cards
Phosphorylation of a protein by a protein kinase ...
- can create a binding site for other proteins.
- requires the hydrolysis of two molecules of ATP per phosphorylated residue.
- deactivates the protein.
- adds two positive charges to the protein.
- activates the protein.
- can create a binding site for other proteins.
- requires the hydrolysis of two molecules of ATP per phosphorylated residue.
- deactivates the protein.
- adds two positive charges to the protein.
- activates the protein.
can create a binding site for other proteins.
13
New cards
Many macromolecular complexes in the cell contain scaffold proteins. What do these proteins do that benefit the cell?
- They can hold the many subunits of a large complex together.
- They can confine and concentrate a specific set of interacting proteins to a particular cellular location.
- They can enhance the rate of critical cellular reactions.
- They can provide a large macromolecular complex with either flexibility or rigidity.
- All of the above
- They can hold the many subunits of a large complex together.
- They can confine and concentrate a specific set of interacting proteins to a particular cellular location.
- They can enhance the rate of critical cellular reactions.
- They can provide a large macromolecular complex with either flexibility or rigidity.
- All of the above
All of the above.
14
New cards
which group of organic compounds includes the enzymes?
- Starches
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Carbohydrates
- Starches
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Carbohydrates
Proteins
15
New cards
Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by:
- combining with excess hydrogen to form gaseous wastes
- absorbing water released when polymers are formed
- providing the substrate required for the retain to occur
- affecting the rate at which reactions occur
- combining with excess hydrogen to form gaseous wastes
- absorbing water released when polymers are formed
- providing the substrate required for the retain to occur
- affecting the rate at which reactions occur
affecting the rate at which reactions occur
16
New cards
Which chemical is classified as an enzyme?
- Manganese dioxide
- Galactose
- Lipid
- Protease
- Manganese dioxide
- Galactose
- Lipid
- Protease
Protease
17
New cards
In enzyme regulation, phosphorylation is an example of
Covalent modification
Product inhibition
All of the above
Allosteric regulation
Covalent modification
Product inhibition
All of the above
Allosteric regulation
Covalent modification
18
New cards
Enzymes that are allosterically regulated have multiple active sites. When an allosteric inhibitor binds to an enzyme, all active sites on the protein subunits are changed and work less well. (True or False)
True
19
New cards
Vitamins are essential to the survival of organisms because vitamins usually function as:
- Substrates
- Coenzymes
- Nucleotides
- Nucleic acids
- Substrates
- Coenzymes
- Nucleotides
- Nucleic acids
Coenzymes
20
New cards
Enzymes can catalyze cellular reactions through various mechanisms. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding enzymes?
- They can provide the chemical groups necessary for simultaneous acid and base catalysis.
- They accelerate a cellular reaction by destabilizing the transition state.
- They can form covalent bonds with the substrate during catalysis.
- They can strain a substrate to force it toward a specific transition state.
- They have a higher affinity for the transition state of the substrate than for its stable form
- They can provide the chemical groups necessary for simultaneous acid and base catalysis.
- They accelerate a cellular reaction by destabilizing the transition state.
- They can form covalent bonds with the substrate during catalysis.
- They can strain a substrate to force it toward a specific transition state.
- They have a higher affinity for the transition state of the substrate than for its stable form
They accelerate a cellular reaction by destabilizing the transition state.
21
New cards
Which of the following enzymes would digest fat?
- lipase
- nuclease
- sucrase
- protease
- lipase
- nuclease
- sucrase
- protease
lipase
22
New cards
Competitive inhibitors:
- bind to the active site of an substrate and compete with the enzyme
- none of the above
- bind to another part (NOT the active site) of an enzyme, causing enzyme shape to change
- bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
- bind to the active site of an substrate and compete with the enzyme
- none of the above
- bind to another part (NOT the active site) of an enzyme, causing enzyme shape to change
- bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
23
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitors:
- none of the above
- bind to another part (NOT the active site) of an enzyme, causing enzyme shape to change
- bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
- bind to the active site of an substrate and compete with the enzy
- none of the above
- bind to another part (NOT the active site) of an enzyme, causing enzyme shape to change
- bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
- bind to the active site of an substrate and compete with the enzy
bind to another part (NOT the active site) of an enzyme, causing enzyme shape to change
24
New cards
Allosteric regulation
- occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects protein's function at another site
- may inhibit enzyme activity
- may stimulate enzyme activity
- all of the above
- occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects protein's function at another site
- may inhibit enzyme activity
- may stimulate enzyme activity
- all of the above
all of the above
25
New cards
What do antibodies look like?
- Each antibody structure consists of two heavy chains and two light chains
- antibody forms a Y-shaped molecule
- each antibody is shaped differently
- antibody has a different amino acid sequence at the tips of the "Y"
- All of the above
- Each antibody structure consists of two heavy chains and two light chains
- antibody forms a Y-shaped molecule
- each antibody is shaped differently
- antibody has a different amino acid sequence at the tips of the "Y"
- All of the above
All of the above
26
New cards
A carbohydrate layer is present on the inner leaflet of cell membranes. (True or False)
True
27
New cards
The actions of a protein kinase to modify a protein can be reversed by a:
- protein phosphatase
- protein dephosphorylase
- protein kinase
- protein GTPase
- protein phosphatase
- protein dephosphorylase
- protein kinase
- protein GTPase
protein phosphatase
28
New cards
Because the lipid bilayer is thicker and the lipid composition is specialized in lipid rafts, specific membrane proteins can accumulate there. This enables membrane proteins, which are normally highly mobile, to function together. (True or False)
True
29
New cards
Which of the following is not true of the plasma membrane.
- The lipid layer is fluid
- The plasma membrane is a continuous double layer of lipid molecules
- Phospholipids in the lipid bilayer are free to flip back and forth from one layer to there other.
- Lipid bilayer fluidity depends upon the layer's composition
- The lipid layer is fluid
- The plasma membrane is a continuous double layer of lipid molecules
- Phospholipids in the lipid bilayer are free to flip back and forth from one layer to there other.
- Lipid bilayer fluidity depends upon the layer's composition
Phospholipids in the lipid bilayer are free to flip back and forth from one layer to there other.
30
New cards
Which of the following is not a class of membrane lipid molecules:
- Proteins
- Cholesterol
- Glycolipids
- Phospholipids
- Proteins
- Cholesterol
- Glycolipids
- Phospholipids
Proteins
31
New cards
What do all β-barrel transmembrane proteins have in common?
- The number of β strands.
- The diameter of the barrel.
- The general function, i.e. membrane transport.
- The structural rigidity compared to α-helical transmembrane proteins.
- The number of β strands.
- The diameter of the barrel.
- The general function, i.e. membrane transport.
- The structural rigidity compared to α-helical transmembrane proteins.
The structural rigidity compared to α-helical transmembrane proteins.
32
New cards
Transmembrane proteins:
- can be released from the membrane by a gentle extraction procedure such as salt treatment.
- are sometimes covalently attached to a fatty acid chain that inserts into the membrane.
- cannot contain β sheets in the part of their structure that interacts with the membrane interior.
- are often further attached to the membrane via a GPI anchor.
are typically exposed only to one side of the membrane.
- can be released from the membrane by a gentle extraction procedure such as salt treatment.
- are sometimes covalently attached to a fatty acid chain that inserts into the membrane.
- cannot contain β sheets in the part of their structure that interacts with the membrane interior.
- are often further attached to the membrane via a GPI anchor.
are typically exposed only to one side of the membrane.
are sometimes covalently attached to a fatty acid chain that inserts into the membrane.
33
New cards
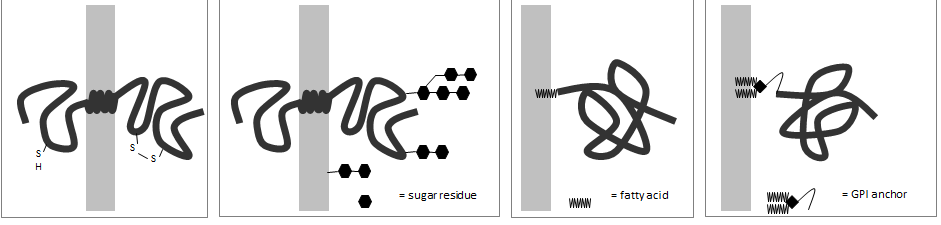
For each membrane protein in the following schematic drawings, indicate whether the cytoplasmic side of the membrane is more likely to be on the left (L) or on the right (R). Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters L and R only, e.g. RRRR.
- LRLR
- RRLR
- LLRL
- RLLR
- LRLR
- RRLR
- LLRL
- RLLR
LLRL
34
New cards
While examining the crystal structure of a membrane protein, you find several phospholipid molecules bound to the protein. You know that these lipids ...
- are thought to help stabilize many membrane proteins.
- may enhance the crystallization of the bound membrane proteins.
- All of the above.
- can have head groups of various sizes and charges depending on the protein.
- interact specifically with the protein.
- are thought to help stabilize many membrane proteins.
- may enhance the crystallization of the bound membrane proteins.
- All of the above.
- can have head groups of various sizes and charges depending on the protein.
- interact specifically with the protein.
All of the above.
35
New cards
Glycolipids such as gangliosides ...
- are found in the extracellular leaflet (facing away from the cytosol) in the cellular membranes.
- All of the above
- are found to constitute about 10% of the total lipid mass in the plasma membrane of neurons.
affect the electrical environment of the membrane.
- may contain oligosaccharide chains with negatively charged residues.
- are found in the extracellular leaflet (facing away from the cytosol) in the cellular membranes.
- All of the above
- are found to constitute about 10% of the total lipid mass in the plasma membrane of neurons.
affect the electrical environment of the membrane.
- may contain oligosaccharide chains with negatively charged residues.
All of the above
36
New cards
The motion of lipid molecules in a synthetic bilayer can be studied by various techniques. Which of the following has been observed in these systems?
- The flip-flops are very rare for phospholipids but cholesterol molecules flip-flop more often.
- Within a bilayer, lipid molecules rarely rotate about their long axis, but diffuse laterally at very high rates.
- All of the above.
- Phospholipids diffuse rapidly within and between the two leaflets of a bilayer.
- The flip-flops are very rare for phospholipids but cholesterol molecules flip-flop more often.
- Within a bilayer, lipid molecules rarely rotate about their long axis, but diffuse laterally at very high rates.
- All of the above.
- Phospholipids diffuse rapidly within and between the two leaflets of a bilayer.
The flip-flops are very rare for phospholipids but cholesterol molecules flip-flop more often.
37
New cards
The two monolayers of the plasma membrane in a human red blood cell ...
- both contain glycolipids.
- have the same abundance of phosphatidylinositol.
- have different overall electrical charges, with negatively charged phospholipids (e.g. phosphatidylserine) normally enriched in the inner monolayer.
- exchange phospholipids only through spontaneous flip-flops.
- both contain glycolipids.
- have the same abundance of phosphatidylinositol.
- have different overall electrical charges, with negatively charged phospholipids (e.g. phosphatidylserine) normally enriched in the inner monolayer.
- exchange phospholipids only through spontaneous flip-flops.
have different overall electrical charges, with negatively charged phospholipids (e.g. phosphatidylserine) normally enriched in the inner monolayer.
38
New cards
Many cells store lipids in droplets of varying sizes. These droplets ...
- are enclosed by a phospholipid monolayer (instead of a bilayer).
- are produced by and released from the Golgi apparatus.
- have mostly protein-free bilayer membranes.
- are composed primarily of charged amphiphilic lipids.
- mostly store cholesterol and phospholipids.
- are enclosed by a phospholipid monolayer (instead of a bilayer).
- are produced by and released from the Golgi apparatus.
- have mostly protein-free bilayer membranes.
- are composed primarily of charged amphiphilic lipids.
- mostly store cholesterol and phospholipids.
are enclosed by a phospholipid monolayer (instead of a bilayer).
39
New cards
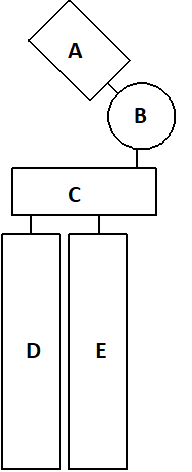
In the following schematic drawing of an abundant plasma membrane phosphoglyceride, which part is positively charged?
- C
- B
- A
- D
- E
- C
- B
- A
- D
- E
A
40
New cards
Which of the following is correct regarding the molecule Cholesterol in cell membrane?
- It is a sterol.
- All of the above
- It is an amphiphilic molecule
- It makes the membrane less permeable to small hydrophilic molecules.
- It affects the fluidity of the lipid bilayer.
- It is a sterol.
- All of the above
- It is an amphiphilic molecule
- It makes the membrane less permeable to small hydrophilic molecules.
- It affects the fluidity of the lipid bilayer.
All of the above
41
New cards
In contrast to transporters, the channel proteins in cellular membranes ...
- interact strongly with the solute(s) that they transport.
- form pores that are always open.
- can only mediate passive transport.
- undergo a conformational change every time they transport a solute.
- interact strongly with the solute(s) that they transport.
- form pores that are always open.
- can only mediate passive transport.
- undergo a conformational change every time they transport a solute.
can only mediate passive transport.
42
New cards
Which of the following types of proteins do not extend into the bilayer?
- Monolayer-associated proteins
- Peripheral proteins
- Transmembrane proteins
- beta-barrels
- Monolayer-associated proteins
- Peripheral proteins
- Transmembrane proteins
- beta-barrels
Peripheral proteins
43
New cards
Which of the following describes membrane protein function?
- They transport ions, nutrients and other substances across the membrane
- They anchor cells to each other
- They transduce external signals to the inside of the cell
- All of the above
- They transport ions, nutrients and other substances across the membrane
- They anchor cells to each other
- They transduce external signals to the inside of the cell
- All of the above
All of the above
44
New cards
Transmembrane alpha helices have side chains that are:
- Charged
- Hydrophobic
- Hydrophilic
Amphipathic
- Charged
- Hydrophobic
- Hydrophilic
Amphipathic
Hydrophobic
45
New cards
Which of the following terms describes transmembrane proteins?
- They are amphipathic with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions
- None of the above
- They have alpha helices with hydrophilic side chains
- They associate with only one side of the phospholipid bilayer
- They are amphipathic with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions
- None of the above
- They have alpha helices with hydrophilic side chains
- They associate with only one side of the phospholipid bilayer
They are amphipathic with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions
46
New cards
Which intermolecular process primarily drives the formation of a bilayer when phospholipids are added to water?
- Lipids cause water to arrange in an ordered, unfavorable cage-like structure. Forcing lipids into a bilayer reduces this effect.
- The ordered arrangement of a bilayer is more favorable than the disordered state of individual free-floating phospholipids
- Phospholipid self-assemble into a bilayer due to the strong affinity they have for each other
- A bilayer arrangement maximizes the strength of Van der waals forces among phospholipids
- Lipids cause water to arrange in an ordered, unfavorable cage-like structure. Forcing lipids into a bilayer reduces this effect.
- The ordered arrangement of a bilayer is more favorable than the disordered state of individual free-floating phospholipids
- Phospholipid self-assemble into a bilayer due to the strong affinity they have for each other
- A bilayer arrangement maximizes the strength of Van der waals forces among phospholipids
Lipids cause water to arrange in an ordered, unfavorable cage-like structure. Forcing lipids into a bilayer reduces this effect.
47
New cards
Why do cells not have membrane transport proteins for O2?
- Because oxygen is transported in and out of the cell in special oxygen-carrying proteins such as hemoglobin.
- Because oxygen can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and diffuse in and out rapidly without the need for a transporter.
- Because oxygen transport across a membrane is energetically unfavorable.
- Because they need to keep the oxygen concentration low inside the reducing environment of the cell.
- Because oxygen is transported in and out of the cell in special oxygen-carrying proteins such as hemoglobin.
- Because oxygen can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and diffuse in and out rapidly without the need for a transporter.
- Because oxygen transport across a membrane is energetically unfavorable.
- Because they need to keep the oxygen concentration low inside the reducing environment of the cell.
Because oxygen can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and diffuse in and out rapidly without the need for a transporter.
48
New cards
An ion channel ...
- always mediates passive transport.
is usually gated.
- All of the above.
- is typically several orders of magnitude faster than a transporter.
- is ion-selective.
- always mediates passive transport.
is usually gated.
- All of the above.
- is typically several orders of magnitude faster than a transporter.
- is ion-selective.
All of the above.
49
New cards
ATP is required in the transport of
- molecules to areas of higher concentrations
- all molecules across a membrane
- molecules through a protein channel
- molecules to areas of lower concentrations
- molecules to areas of higher concentrations
- all molecules across a membrane
- molecules through a protein channel
- molecules to areas of lower concentrations
molecules to areas of higher concentrations
50
New cards
The net movement of uncharged, polar molecules across a semipermeable membrane from a low concentration to a high concentration occurs by facilitated diffusion. (True or False)
False
51
New cards
Red blood cells have a characteristic concave shape because of
- hemocyanin
- hemoglobin
- iron
- cytoskeletal spectrin
- hemocyanin
- hemoglobin
- iron
- cytoskeletal spectrin
cytoskeletal spectrin
52
New cards
Principal classes of membrane proteins include all of the following except
- cell surface markers
- Spectrins
- receptors
- transport proteins
- cell surface markers
- Spectrins
- receptors
- transport proteins
Spectrins
53
New cards
A, B, and O blood groups are marked by surface
- glycerol
- glycoproteins
- glycocarbohydrates
- glycolipids
- glycerol
- glycoproteins
- glycocarbohydrates
- glycolipids
glycolipids
54
New cards
Transmembrane proteins are
- none of the above
- always abundant
- never abundant
- always fixed in position
- none of the above
- always abundant
- never abundant
- always fixed in position
none of the above
55
New cards
In each cycle the sodium-potassium pumps transfer
- two potassium ions in and two sodium ions out
- one sodium ion out and one potassium ion in
- three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in
- one potassium ion out and two sodium ions in
- two potassium ions in and two sodium ions out
- one sodium ion out and one potassium ion in
- three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in
- one potassium ion out and two sodium ions in
three sodium ions out and two potassium ions in
56
New cards
There are several levels of protein structure, the most complex of which is
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Quaternary
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
- Quaternary
Qauternb
57
New cards
In the formation of a macromolecule, what type of bond would join two amino acid subunits?
- Hydrophobic reaction
- Hydrolysis reaction
- Dehydration reaction
- Denaturation reaction
- Hydrophobic reaction
- Hydrolysis reaction
- Dehydration reaction
- Denaturation reaction
Dehydration reaction
58
New cards
What happens during a hydrolysis reaction?
- Protein coils into a secondary structure
- The bond between two subunits of a macromolecule is broken
- Saturated fats become unsaturated
- A bond is formed between two subunits of a macromolecule
- Water breaks ionic bonds
- Protein coils into a secondary structure
- The bond between two subunits of a macromolecule is broken
- Saturated fats become unsaturated
- A bond is formed between two subunits of a macromolecule
- Water breaks ionic bonds
The bond between two subunits of a macromolecule is broken
59
New cards
Proteins are mainly composed of..
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- All of the above
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- All of the above
All of the above