EEMB 116 LAB PRACTICAL #1
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
dorsal
upper side/back of an organism
ventral
lower side/belly of an organism
what phylum has segmentation and an exoskeleton with jointed appendages?
Phylum Arthropoda
what phylum lacks segmentation and no exoskeleton and no jointed appendages?
phylum Annelida
what groups are under phylum annelida?
Phylum Annelida
C. Polychaeta “bristle worms“
F. Nereididae
Neanthes sp. “rag worm”
F. Sabellariidae
Phragmatopoma californica “sand castle worms”
C. Clitellata “leeches and earthworms”
SC. Oligochaeta
F. Lumbriculidae
Lumbricus terrestris
SC. Hirudinomorpha “leeches”
homonomous
body plan with uniformed segments
heteronomous
body plans with different segments w/ specialized functions
dioecious
separate sexes
hermaphroditic
both sex organs on the same individual
direct development
immatures look like adults
indirect development
immatures go through metamorphosis to become adults
coelom
fluid filled body cavity
hydrostatic skeleton
using the pressure from water to apply force or change shape
cuticle
outermost layer of the annelid body
epidermis
bottom layer containing gland cells
metameres
linear series of segments separated by septa
septa
the dividing walls of metameres
prostomium
first body part (before mouth) with sensory structures
peristomium
surrounds the mouth— bears the tentacles or palms
pygidium
bootyhole
parapodia
paddle-like appendages for movement or respiration
chaetae
annelid bristles
acicula
chitinous chaetae inside parapodia to support them
ocelli
simple eyes
opperculum
a structure that covers or closes an openings
sorting grooves
groove that sorts food into the mouth, found on some polychaete
caudum
“tail” of segmented worms
pharynx
anterior(front) part of digestive tract, usually eversible in annelids
trochophore
larval stage of indirect-developing annelids
clitellum
a thickened section of the body of Clitellates which creates sacs for eggs to be stored
radiole
heavily ciliated feather-like structures on head used for feeding and respiration
like a filter fan
cirri
tentacle-like structures for feeding and/or respiration
elytra/elytron
dorsal scale like structures that are modified dorsal cirri
class polycheata
mostly marine
segmented
separate sexes with external fertilization (release eggs) and indirect development with a trochophore larva
have a pharynx
dorsal blood vessel caries the blood to the butt and the ventral vessel carries blood to the head
class clitellata
no parapodia
reduced or absent chaetae
hermaphroditic with internal fertilization and direct development
clitellum present
family Lumbriculidae
under class Clitellata, phylum annelida
freshwater and terrestrial environments
segmented
burrowers but some are tube dwellers or parasites
chaetae used for burrowing
locomotion depends on peristalsis and the chaetal manipulation to make up for the lack of parapodia
well developed musculature
Subclass Hirudinomorpha
mostly freshwater
reduced coelom
reduced septa (heteronomous)
some are blood suckers or carnivorous
thick body wall
oral and anterior sucker
fixed # of segments (33)
dorsoventrally flattened
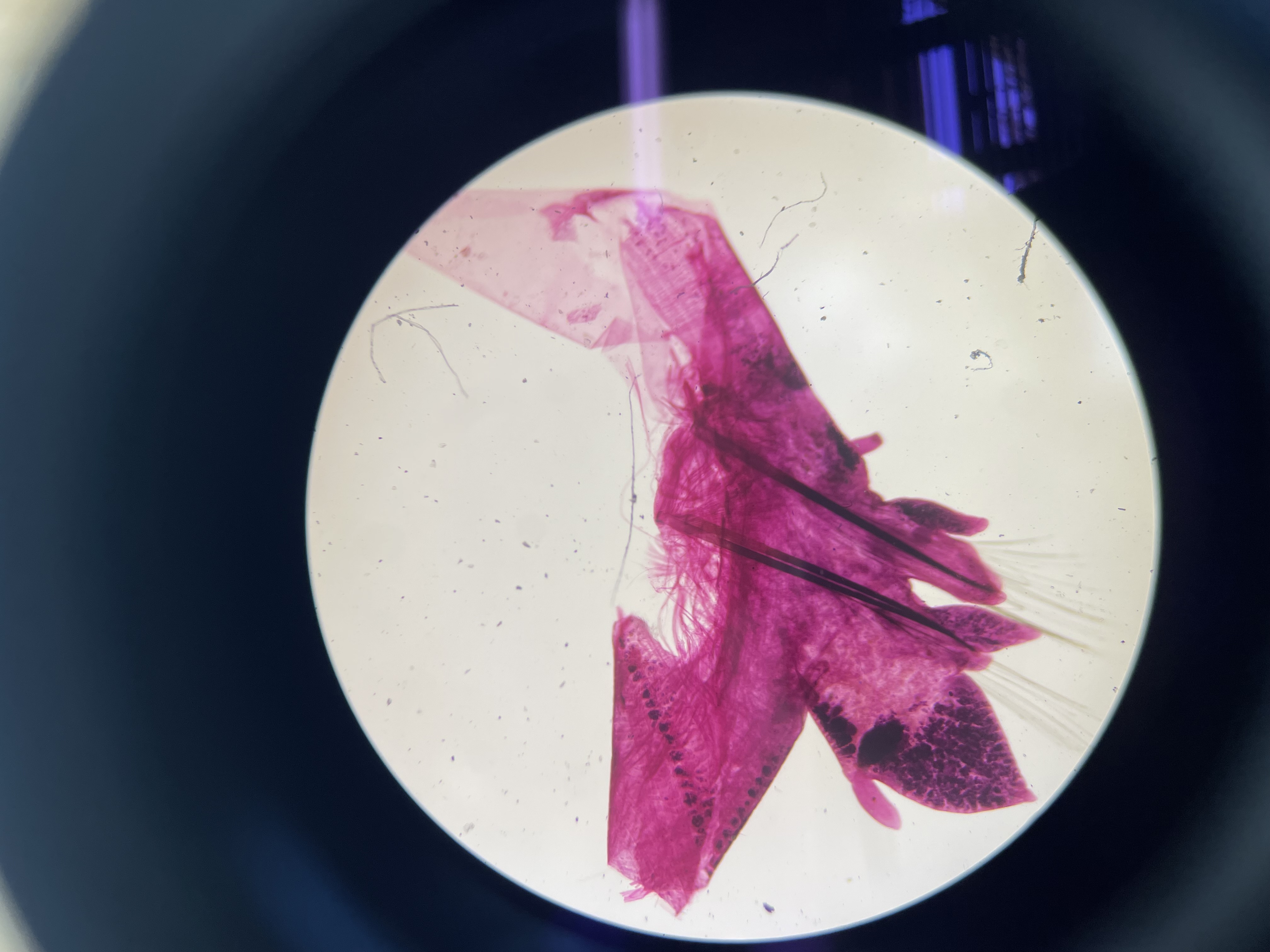
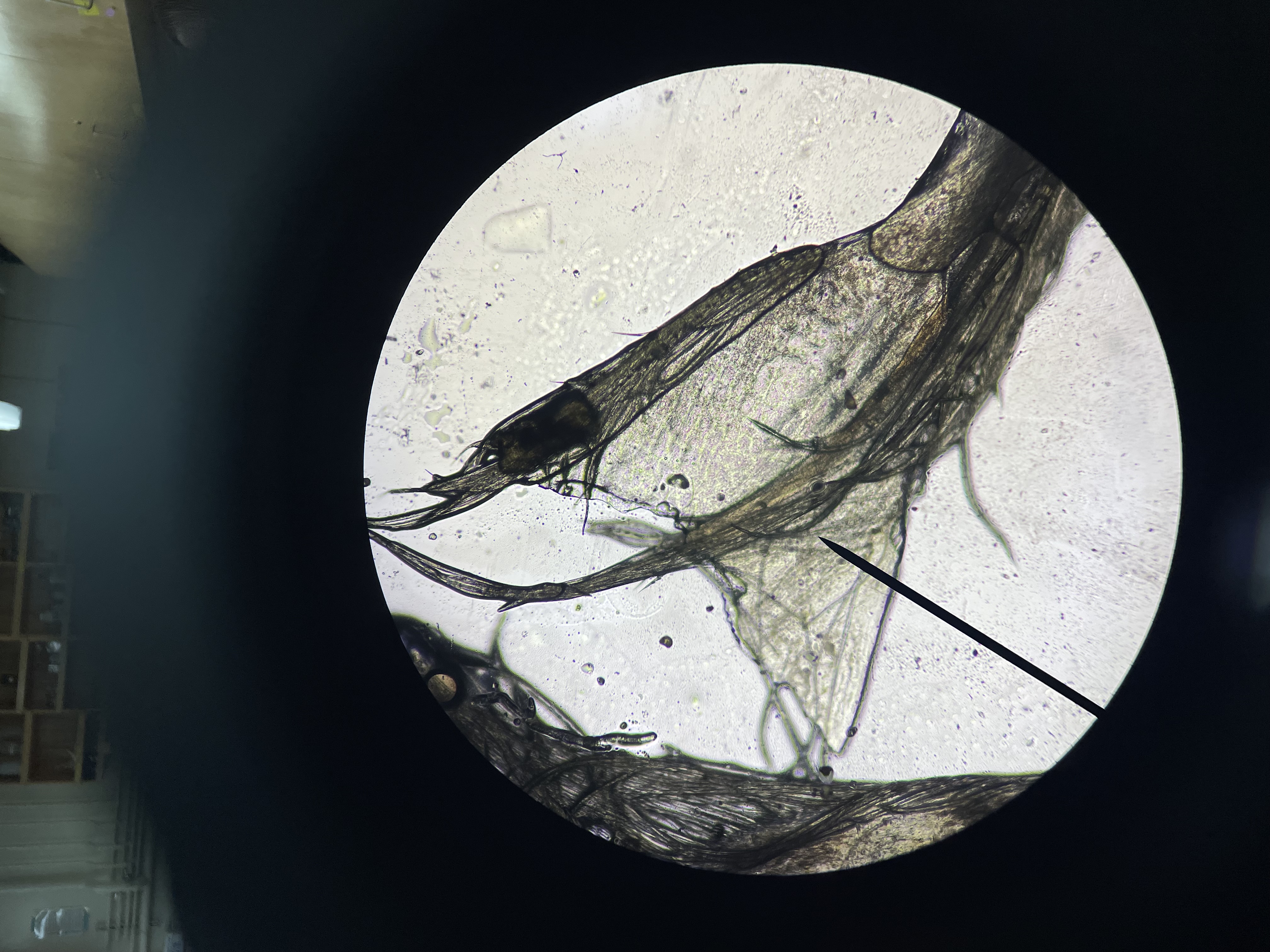
what is the name of the dark lines?
which class of annelids would possess this structure?
acicula in parapodia of Neanthes
sp. Neanthes, F. Nereididae, C. Polychaeta, P. Annelida

what is this?
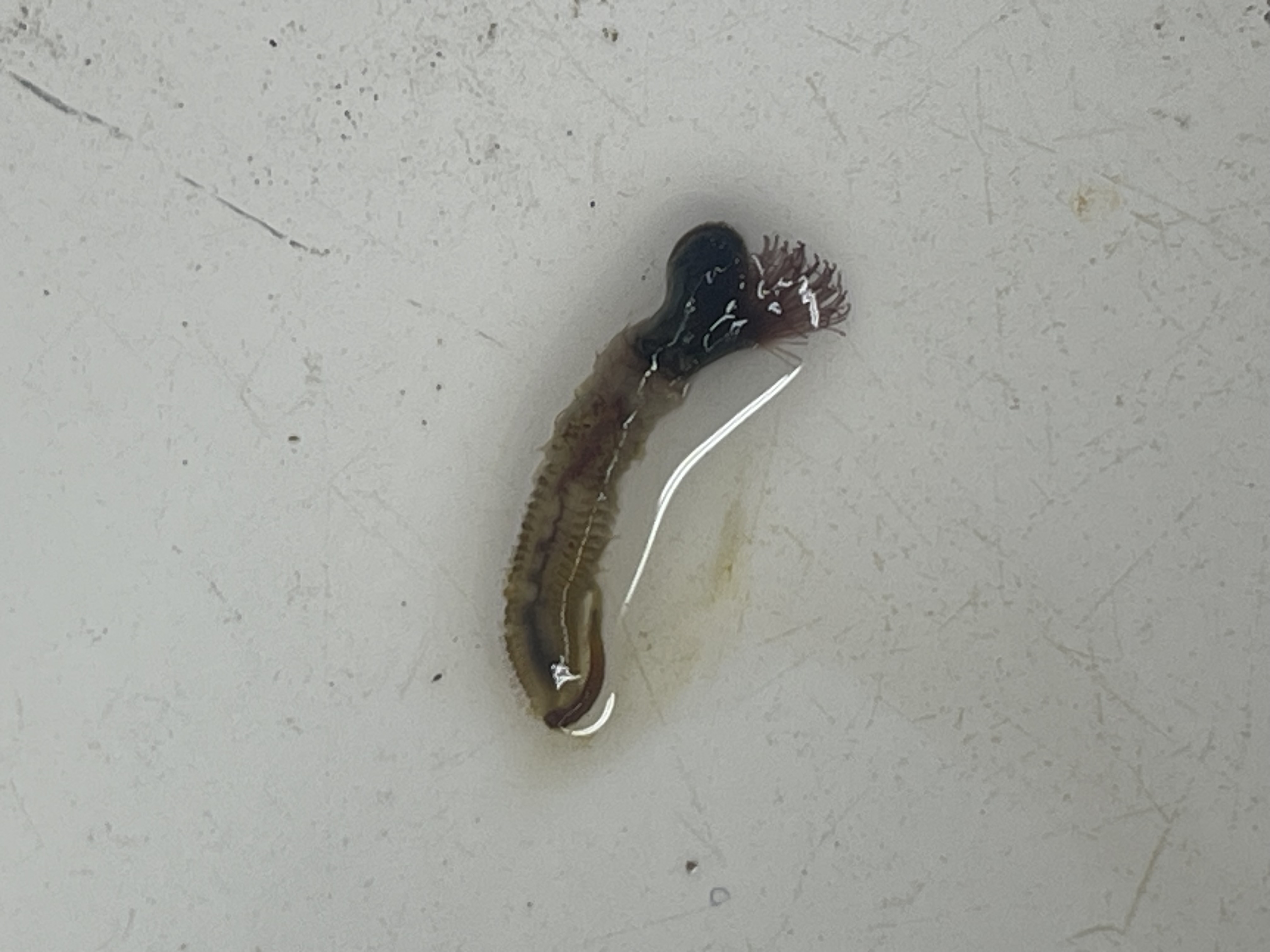
sp. Phragmatopoma californica, F. Sabellariidae, C. Polychaeta, P. Annelida
known as “sand castle worms”
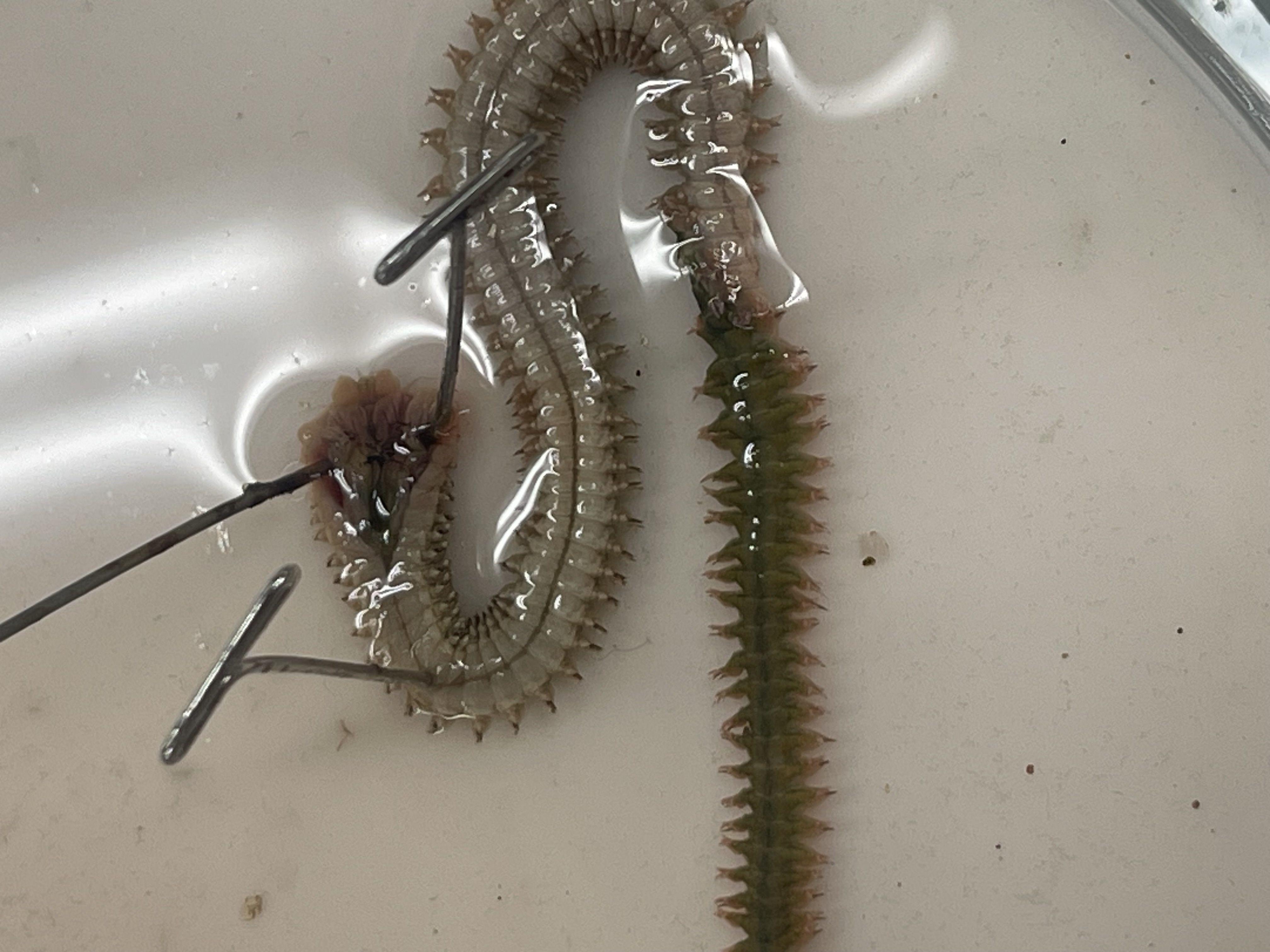

what is this and find the ocelli, parapodia, acicula
sp. Neanthes, F. Nereididae, C. Polychaeta, P. Annelida
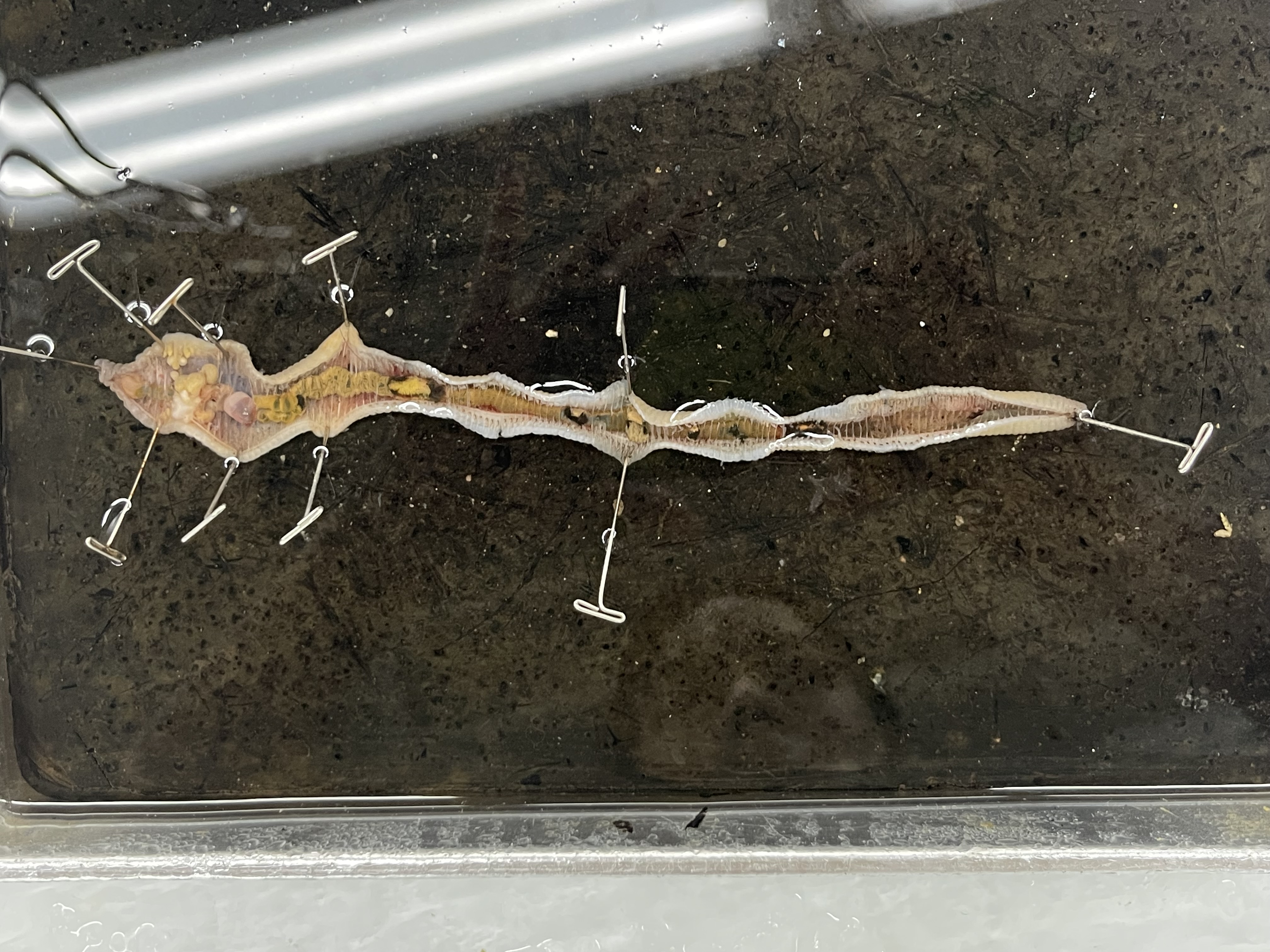

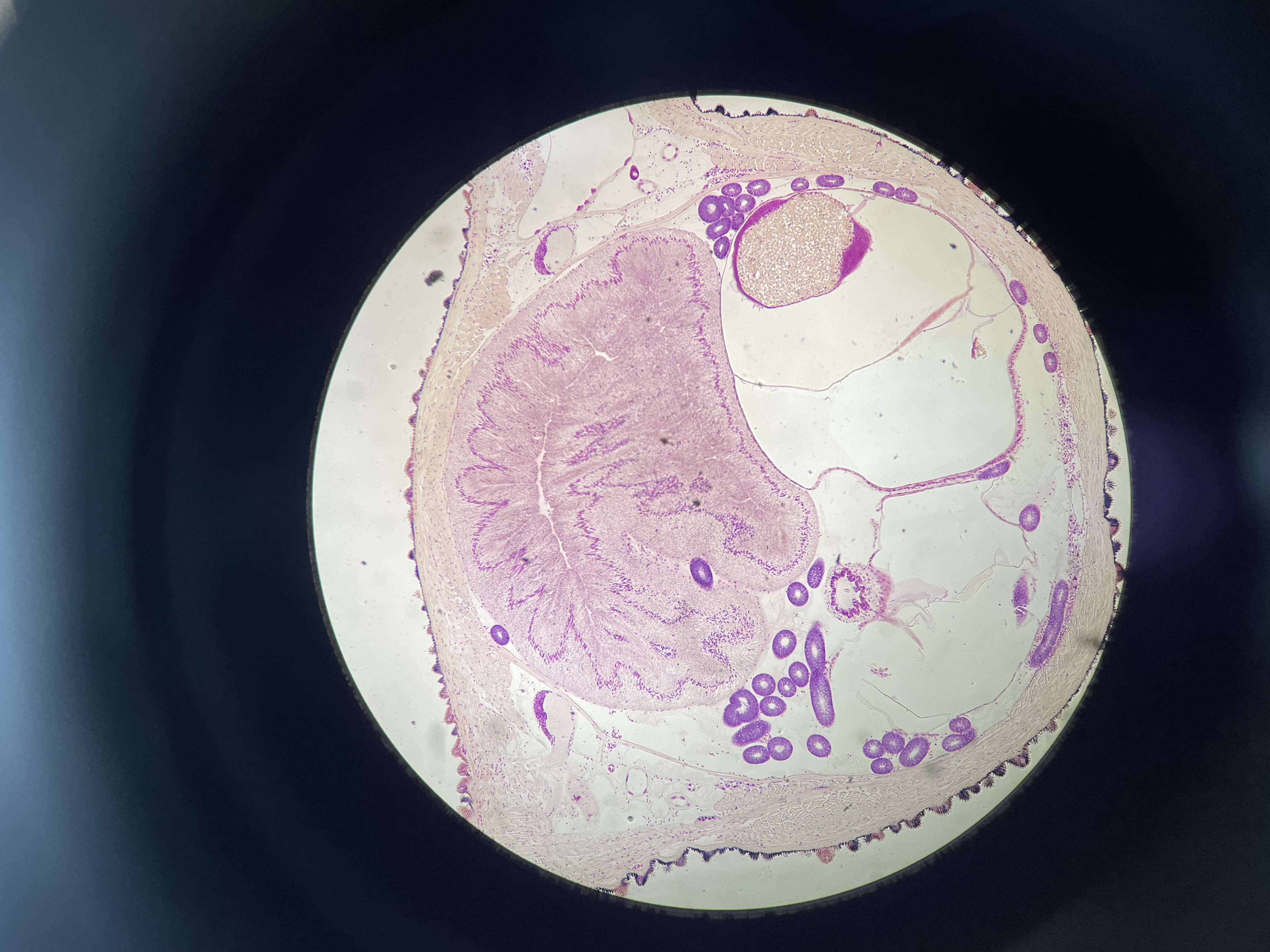
what is this and find the septa, buccal cavity, pharynx, crop, gizzard, spermatheca, lobes of seminal vesicle, nerve cord, and peritoneum
sp. Lumbricus terrestris, F. Lumbriculidae, SC. Oligochaeta, C. Clitelatta, P. Annelida
what are the types of feeding strategies?
active predatory: free-living, seeking out large prey (PF)
deposit feeders: eat organic matter in sediment (DF)
suspension feeders: eat from water column (SF)
who is under subclass errantia?
F. Onuphidae
F. Nereididae
F. Glyceridae
F. Polynoidae
F. Hesionidae
F. Phyllodocidae
F. Aphroditidae
who is under subclass Sedentaria?
F. Opheliidae
F. Maldanidae
F. Terebellidae
F. Cirratulidae
F. Flabelligeridae
F. Sabellariidae
F. Sabellidae
F. Serpulidae
F. Chaetopteridae
O. Sipuncula
SC. Echiura
cephalo
head
ped-/pod-
foot
cuticle
protective outer layer of epidermis
tagmata
morphologically distinct regions like the abdomen
endopodite
inner branch on biramous structure
exopodite
outer branch on biramous structure in crustacean
podites
limb segments
hemocoel
body cavity containing circulatory fluid (like coelom, but reduced)
cryptobiosis
a state when metabolism is undetected
tardigrades
rostrum
anterior projection of the carapace
mandibles
jaws used to crush food
maxillae
mouthparts for sorting food and delivering it to mandibles
thoracopods
appendage on the thorax
maxillipeds
appendages on thorax for food handeling
pereopods
appendages used for walking and often for swimming forward
chelipeds
pincers/claws
coxae
base of pereopods
dactyl
end of the pereopods
pleopods(swimmerets)
appendages on the abdomen used for swimming
uropods
last abdominal appendages
telson
where the abdomen ends, has the anus
kinda like center fin
who is under the super phylum Panarthropoda?
p. Onychophora
p. Tardigrada
p. Arthropoda
Subphylum Crustacea
how is the crustacean body divided?
two tagmata: head and abdomen
Phylum Onychophora
hydrostatic skeleton
most are dioecious
spray slime glands like spiderman to capture and eat food
ancestral to both annelids and arthropods
what features do Onychophora have in common with Annelids?
external/internal segmentation
what features do Onychophora have in common with Arthropods?
chitinous cuticle has papillae, cuticle molted, hemocoel, tracheal tube for respiratory, chitin lined pharynx & esophagus
Phylum Tardigrada
8 lobopods
have claws, spines, external plates, cirri
resistant eggs and cyst
can undergo cryptobiosis
body has a cuticle that is molted
what is this? find the gut, body wall layers, slime gland, heart, and hemocoel
cross section of velvet worm Peripatus
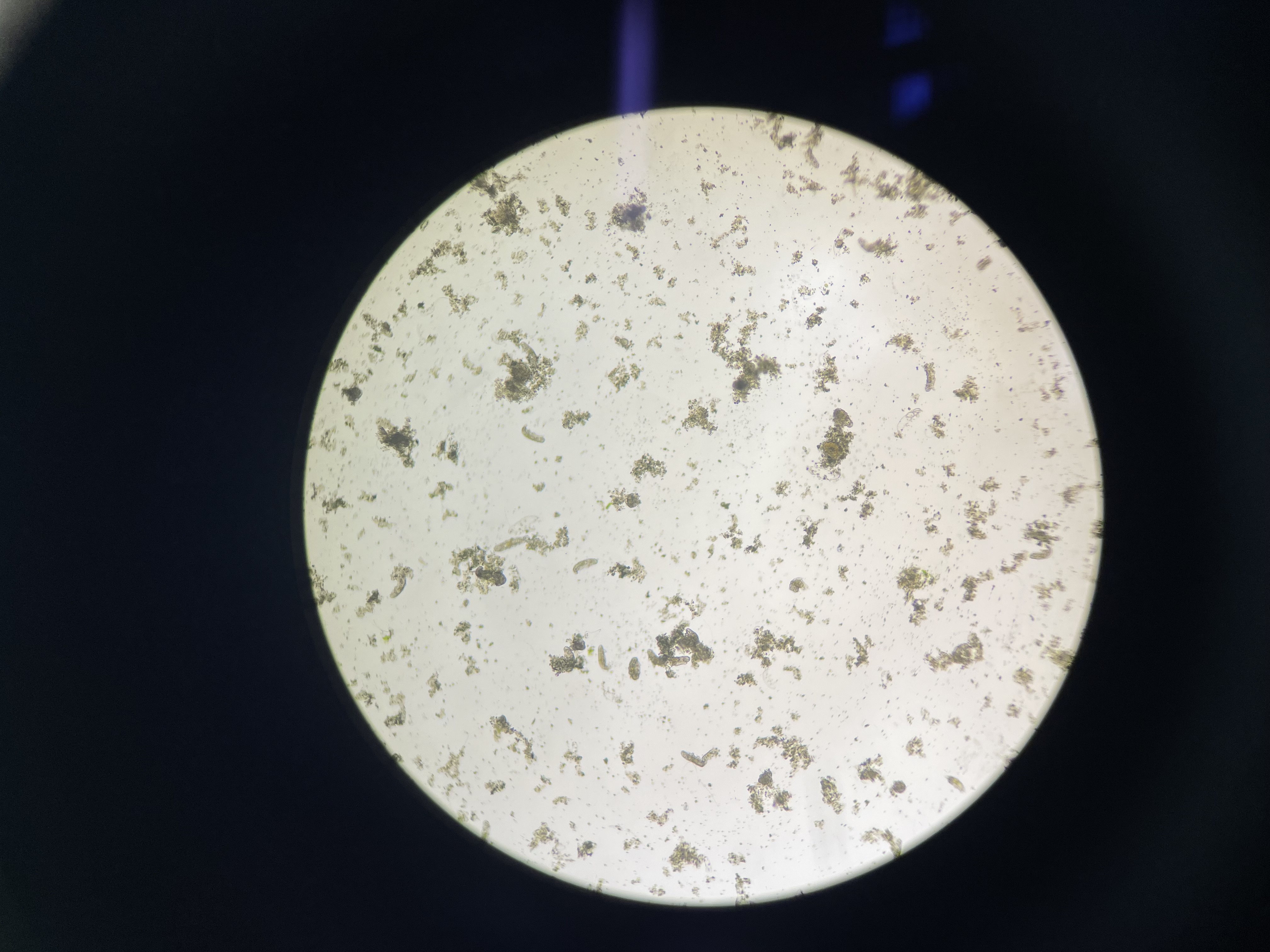
what is this showing?
tardigrades

name each of these parts of a crayfish?
starting from top of tray:
telson
uropods
pleopods
pereopods
mandible
maxilla
maxillipeds
antenna
antennule
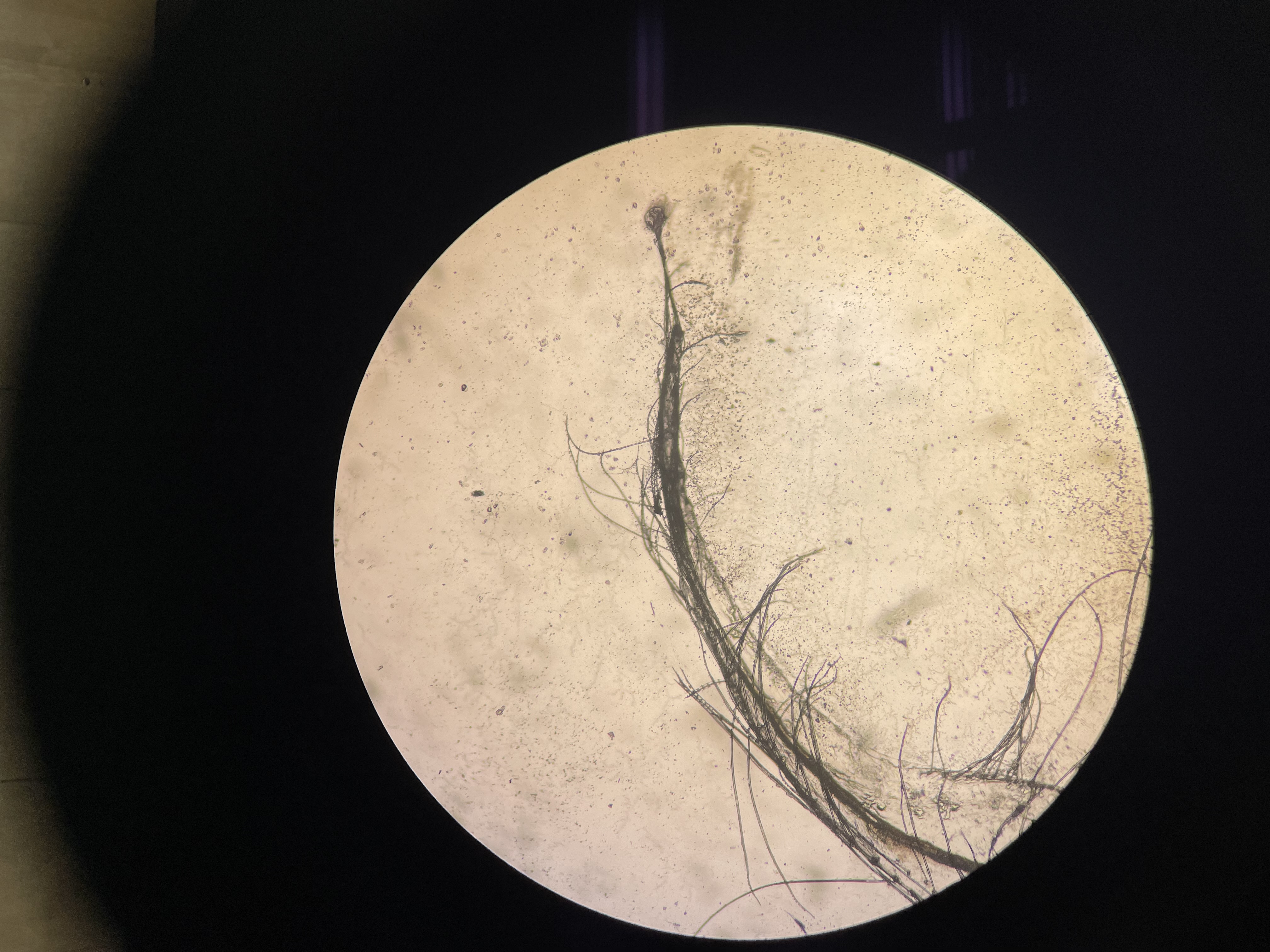
what stage of molting is this?
post molt
no apolytic space, flesh inside is right up against the cuticle, no new setae
seen in Pachygrapsus sp (lil crab i killed)
what stage of molting is this?
pre molt
apolytic space is obvious, flesh is pulled back and old setae folded. new setae can be seen
seen in Pachygrapsus sp (lil crab i killed)
marsupium
a pouch to protect eggs
thoracopod
any appendage attached to the thorax
nauplius
first larval stage of crustaceans
taxonomy list for phylum arthropoda
SP Crustacea
C. Copepoda
C. Ostracoda
C. Branchiopoda
O. Diplostraca
O. Mysida
SC. Cirripedia
O. Thoracica
Superorder Peracarida
O. Amphipoda
O. Isopoda
O. Decapoda
IO Achelata
IO Anomura
IO Brachyura
IO Caridea
meroplankton
spend portion of lives as plankton, like spiny lobsters and barnacles
holoplankton
planktonic throughout their life, like copepods and krill
epitoke
posterior sexual portion of polychaetes that are specialized to swim to find mates and reproduce through spawning
in polychaetes
zoea
first planktonic larval stage of many Decapods
IO Anomura have long dorsal and anterior spines
crabs brood eggs past the nauplius stage and release planktonic Zoea
in crustacea
megalopa
second and last planktonic larval stage of some Decapods
in crustacea
phyllosoma
a larval stage unique to Achelata (spiny lobsters)
some stay in this stage for years
in crustacea
cypris
second larval stage unique to barnacles
both ends of carapace are pointed
elytra
modified dorsal cirri on F. Polynoidae
used for respiration
gnathobases
found at base of legs, grind up food and move towards mouth in the middle
coxa
basal most article of pereopods
how can you tell the sex of a Pachygrapus sp. (crab)?
female= U shape abdomen
male= V shape abdomen
branchial chamber
gill chamber
pericardial sac
walled sac containing heart and vessels. take up water to assist in ecdysis
cardiac stomach
large anterior foregut that keeps food from coming back up the esophagus
pyloric stomach
2nd stomach containing the gastric mill
gastric mill
rows of “teeth” in the pyloric stomach used for digestion and auditory signaling
hepatopancreases
after both stomachs, food goes here to be absorbed and stored
chromatophores
pigment sacs that become more visible as small muscles pull sac to surface of skin
ecdysis
process of shedding the old cuticle
exuvia
the old, shed cuticle