Paranasal sinuses and orbits
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What view best demonstrates the basilar foramina?
submentovertex
What is the vertex of the head?
Topmost portion (crown)
What sinus is best visualized by submentovertex view?
sphenoid sinus
What is a mucocele?
Typically benign cyst/white density seen in the sinus
What is a floating palate fracture?
Le Fort I
What is a facial fracture of the maxilla?
Le Fort II - pyramidal
What is the fracture when all the facial bones are coming off the cranium?
Le Fort III
How many bones make up the orbits?
7
What are the holes/foramen of the orbits and what do they contain?
supraorbital fissure - nerves to innervate eye muscles
optic foramen/canal - optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
inferior orbital fissure - nerves to innervate skin of the face
Where is the lacrimal gland located? How many excretory ducts does it contain?
Upper outer quadrant of orbit. 6 - 12 ducts.
Where is the lacrimal sac located?
Inner canthus
Where does the nasolacrimal duct drain to?
inferior nasal meatus (this is why our nose runs when we cry)
What tube able do we need to use to get the orbits clear of the petrous ridges?
25 degrees caudal
Where do we want the petrous ridges to be for a parietoacanthial waters view?
Just below the floor of the maximally sinus
How is the modified waters different from the PA waters? Where will the petrous ridges be seen?
OMBL is 55 degrees to the plane of the IR. Petrous ridges seen mid maxillary sinus.
What view visualizes the optic foramen? How is it done?
Rhese view - Median sagittal 53 degrees to IR. AMBL perpendicular to IR. Enter 1” superior and 1” posterior to ear attachment.
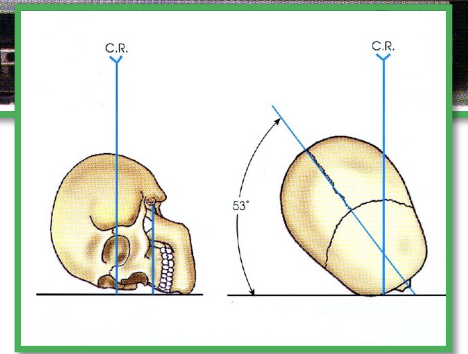
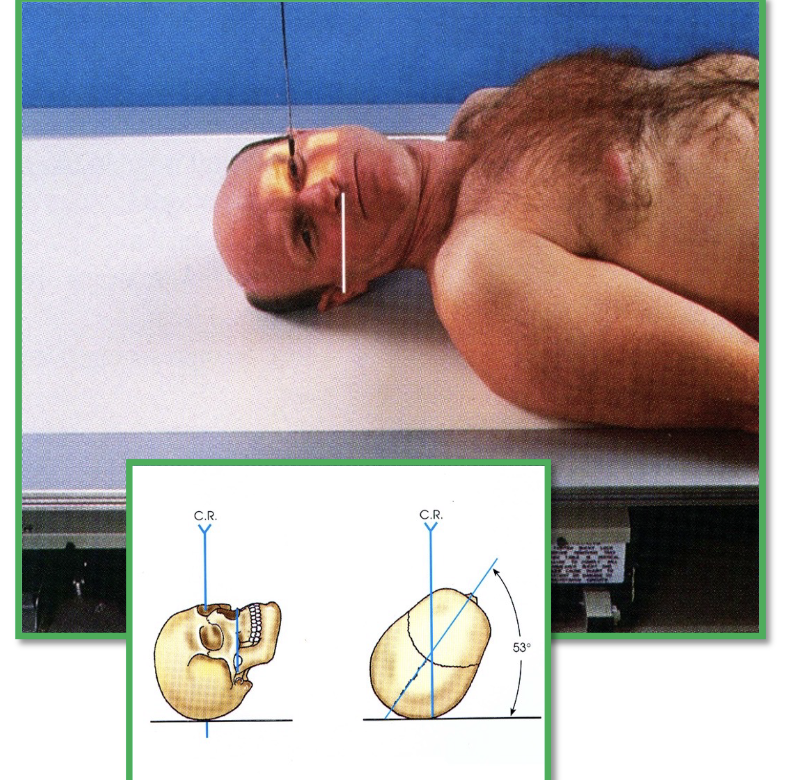
What view is this?
Reverse Rhese
What is downward displacement of the eyeball called?
Proptosis
What is outward/anterior protrusion of the eyeball called?
Exophthalmos
What fracture involves the floor of the orbit?
Blow out fracture
What is a tripod fracture?
Fracture of zygoma away from the face. Three point fracture.
The modified Caldwell horizontal beam best demonstrates which sinuses?
Frontal and ethmoid
The lateral sinus projection best demonstrates which sinus(es)?
Sphenoid
What is the purpose of the paranasal sinuses?
lighten the skull, protect the brain from trauma, add resonance to voice
The antrum of highmore is another name for which sinus?
maxillary
What are the nasal turbinates/conchae?
supreme (very small), superior , middle, and inferior (its own bone)
Drainage from all the sinuses passes through what?
osteomeatal complex
What is the baseline for the parietoacanthial waters view?
OMBL 37 degrees to plane of IR
What is the odontoid seen in the exaggerated waters projection?
2” below the mandible
What is the baseline for the submentovertex?
IOMBL vertical - parallel to the plane of the IR