2: lipids + carbohydrates
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
simplest carbohydrates
monosaccharides
polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones (and their derivities)
carbohydrates
empirical formula of carbohydrates
(CH2O)n
monosacharides (simple sugars) contain ____—___carbons and _____ hydroxyl groups
3-7 carbon
2 or more hydroxyl groups
can monosaccharides exist in many isometric forms?
YES
dihydroxyacetone
d-glyceraldehyde
L-glyceraldehyde
are all ..
monosaccharides
monosacharide nomenclature is based on what two characteristics?
number of carbons (triose- heptose)
most oxidized group (ketose vs aldose)
are ribose and glucose aldoses or ketoses?
how many carbons does each have?
aldose
ribose= 5 = pentose
glucose = 6 = hexose
are fructose, ribulose, and dihydroxyacetone ketoses or aldoses?
how many carbons does each have?
ketose
dihydroxyacetone = 3 = triose
ribulose = 5 = pentose
fructose = 6 = hexose
dihydroxyacetone and glyceraldehyde are both
triose
glucose and fructose are both hexoses that can be used for what process?
glycolysis
molecules that have identical molecular formulas that differ in how the atoms are ordered
constitutional isomers
glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone both have the empirical formula (C3H6O3) but one is an aldose and the other is a ketose
what is this an example?
constitutional isomers
stereoisomers are molecules that differ in spatial arrangement but not ________ _____
bonding order
how can you figure out how many different stereoisomers exist for a monosaccharide?
2n
n= number of chiral centers (asymmetric carbons)
how can you tell if a monosaccharide has d or l sterochemistry ?
d = if OH farthest from most oxidized carbon is on RIGHT
l= if OH farthest from most oxidized carbon is on LEFT
what is the difference between diastereomers and enantiomers ?
enantiomers = all chiral centers flipped (mirror)
diasteromers = not ALL chiral centers flipped
a carbon bonded to four different substituents
asymmetric carbon
diastereomers differing in configuration only at a SINGLE asymmetric center
epimers
isomers that differ at a new asymmetric carbon formed on ring closure
anomer
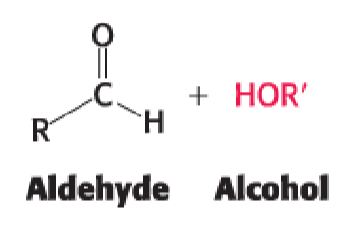
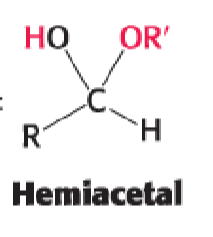
aldehyde + alcohol —>
hemiacetal
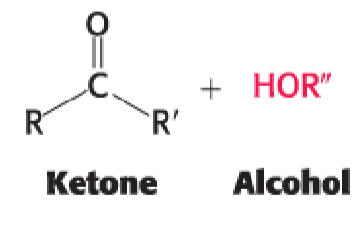
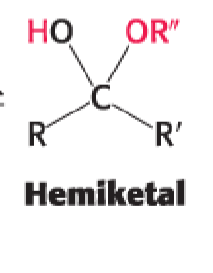
ketone + alcohol —>
hemiketal
monosacharides are predominately in ______ formation inside cells (in solution)
ring
in aquods solutions the aldehyde or ketone group of a sugar molecule tends to react with a _______ group of the SAME molecule closing the molecule into a ring
hydroxyl
glucose (hexose) forms a _________ ring because of its similarity to ______
pyranose
pyran
fructose (hexose) forms a _____ ring because of its similarity to ________
furanose
furan
which carbon of fructose gains chirality once it becomes a furanose in solution?
2 (carbon that used to be ketone— will have OH)
which carbon of glucose gains chirality once it becomes pyranose in solution?
1 (carbon next to the O in the hexagon that isnt methylhydroxy) —- this carbon used to be aldehyde
sugars that contain two or more monosaccharides linked by O-glycosidic bonds
_________ is a disaccharide containing two sugars
sucrose
how are O-glycosidic bonds created?
OH from one sugar combines with OH from another sugar (could be from anomeric carbon) come together and create water —- one O remains
what is meant by a reducing ends when monosacharides form glycosidic bonds?
when monosaccharides don’t use up the OH from their anomeric carbons in the glycosidic bond they can unfold iinto their open-chain form from their ring shape
what is meant by non- reducing ends when monosacharides form glycosidic bonds?
anomeric carbon is used up in glycosidic bond so it is locked into its ring form and won’t be able to go back into its open chain form
what is the difference between alpha and beta glycosidic bonds?
if OH that is participating in bond formation is on the bottom than it is alpha and if it on top it is beta
the disaccharide sucrose is formed from _______ and _________
glucose (aldose) and fructose (ketose)
in the formation of the sucrose the anomeric carbon of glucose (C1 -a ) and the anomeric carbon of fructose (C2 - b) form a glycosidic link
is sucrose a reducing or non-reducing sugar?
with this information, what is the name of their glycosidic linkage?
non-reducing
sucrose is locked in its position
a-1, b-2 - glycosidic linkage
maltose is a disaccharide made of two glucose molecules
the bond forms from C1 of one glucose and C4 of another glucose
is maltose a reducing or non-reducing sugar?
what type of bond is present?
reducing because the C1 carbon of one glucose is free to turn back into its open chain
1,4 glycosidic bond
disaccharide resulting from the hydrolysis of large oligosaccharides that consist of two linked glucose molecules
joined by 1,4- glycosidic linkage
maltose
maltose can be hydrolyzed to glucose by _________ (_____________)
maltase (a-glucosidase)
disaccharide that consists of galactose linked to glucose
lactose (milk-sweet cow in the galaxy)
lactose can be hydrolyzed by _________ in human beings and by __ -_______ in bacteria
lactase
beta galactoses
is lactose a reducing sugar? how do you know?
1,4 bond between galactose and glucose
C4 is not using up its anomeric carbon and can be reduced
which monomers have useful functions on their own while their polymers are simply used for storage?
monosaccharide and fatty acids
which monomers are more useful once they have formed polymers?
nucleotides and amino acids
what is glycogen?
long chains made of glucose that are used for storage
glucose is stored as the MACROmolecule ________ to provide _________
glycogen
energy
________ (_____) : large polymeric oligosaccharides formed by the linkage of multiple monosaccharides
plays roles in energy storage and structural integrity
polysaccharides (glycans)
what is the difference between polysaccharides and homopolymers?
polysaccharide made up on multiple different monosaccharides formed for storage
homopolymer = large chain of SAME monosaccharide formed for storage
where can glycogen be found, where is it stored?
granules can be found in the cytoplasm of liver cells
what is the most common homopolymer is animal cells?
glycogen (made only of glucose)
most of the glucose units of glycogen are linked by _______ glycosidic linkages while BRANCHES are formed by _____ glycosidic linkages
1,4
1, 6
glycogen can be hydrolyzed by
a-amylase
___________ increases the surface area to allow for between access for enzymes to rapidly break down glycogen
this is possible through which types of bonds?
branching
1,6 glycosidic linkages
are alpha or beta 1,4 glycosidic linkages within polysaccharides favor bent helical structures more suitable for MAMMALIAN storage
what are examples of polysaccharides composed of these 1,4 glycosidic bonds between monosacharides?
ALPHA
starch and glycogen
are alpha or beta 1,4 glycosidic linkages within polysaccharides favor straight chains optimal for structural purposes in PLANTS?
what are examples of polysaccharides composed of these 1,4 glycosidic bonds between monosacharides?
BETA
cellulose
what is the difference between alpha and beta 1,4 glycosidic linkages between monosaccharides to make polysaccharides?
alpha = mammalian storage = glycogen + starch
beta = plant structure= cellulose
when cells need more ATP then they can generate from ______ molecules taken in from the bloodstream they break down ________
food
glycogen
where do each of these steps of glycogen conversion take place?
polysacharide —> sugars —> glucose—>—> pyruvate
pyruvate —> acytelcoA
cytosol
mitochondria
where does the following conversions take place to create ATP?
fats—> fatty acids
fatty acids —> acytel CoA
cytosol
mitochondria
glycogen is considered a short/long term storage of energy and has the largest stores in _____ and ______
short
liver and muscle
Even though both muscle and the liver store glycogen what is different about the release from both?
muscle will only supply glucose to itself
liver will supply glucose through the bloodstream to any organ requiring energy
on average a human stores enough GLYCOGEN for only about _______ of normal activities (energy demands) but enough FAT to last for nearly a ______
1 day
month
which enzyme breaks down glycogen into glucose when ATP is low?
glycogen phosphorylase
glycogen phosphorylase breaks down glycogen into
_____________ first which is then converted to ___________
glucose -1 -phosphate
glucose -6 - phosphate
what is the difference between amylase and
explain the difference in the breakdown of glycogen when released by the liver vs the muscle
muscle= glycogen phosphorylase convert glycogen to glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate which then undergoes glycolysis
liver= glucose-6-phosphate is further converted into glucose using glucose phosphotase before going through glycolysis and being released into the blood stream
4 physiological roles off FATTY ACIDS:
_____ molecules
building blocks of _____ lipids and _________lipids
many proteins are modified by the _______ attachments of fatty acids, which function to target proteins to membrane locations
fatty acid derivatives serve as _______ and intracellular messengers
fuel
phospholipids and glycolipids
covalent
hormones
all fatty acids have a ________ group at one end and a long __________ tail at the other
carboxlyl
hydrocarbon
fatty acids that have double bonds are considered to be uunsaturated/saturated
UNSATURATED with hydrogen bonds
triaglycerols (TAGs) are the storage form of fatty acids as _________ _______ with ______
uncharged esters and glycerol
fatty acids are stored in cells as an energy reserve (fats and oils) through an _______ linkage to _______ to form _____________ (____________)
ester
glycerol
triglycerides / triglycerides
how can you identify the chemical composition of fatty acids within the lipid molecules?
the number of carbons (starting from ester carbon!) and number of double bonds
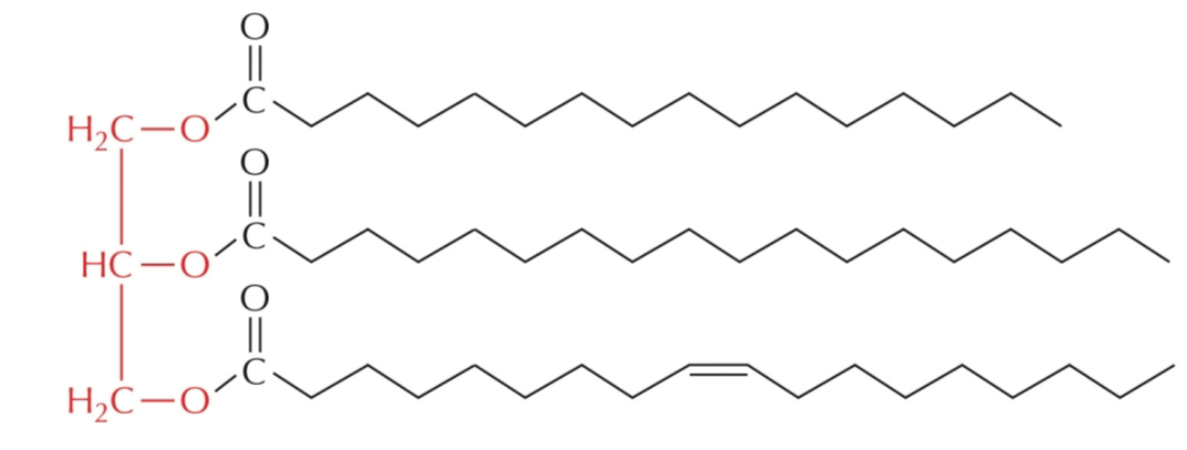
identify the following fatty acids within this triglyceride
C16:0
C18:0
C18:1
triglyceride structure is determine by _______ _______ composition
fatty acid
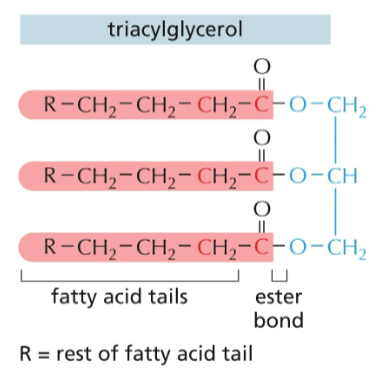
which color represents glycerol ?
light blue
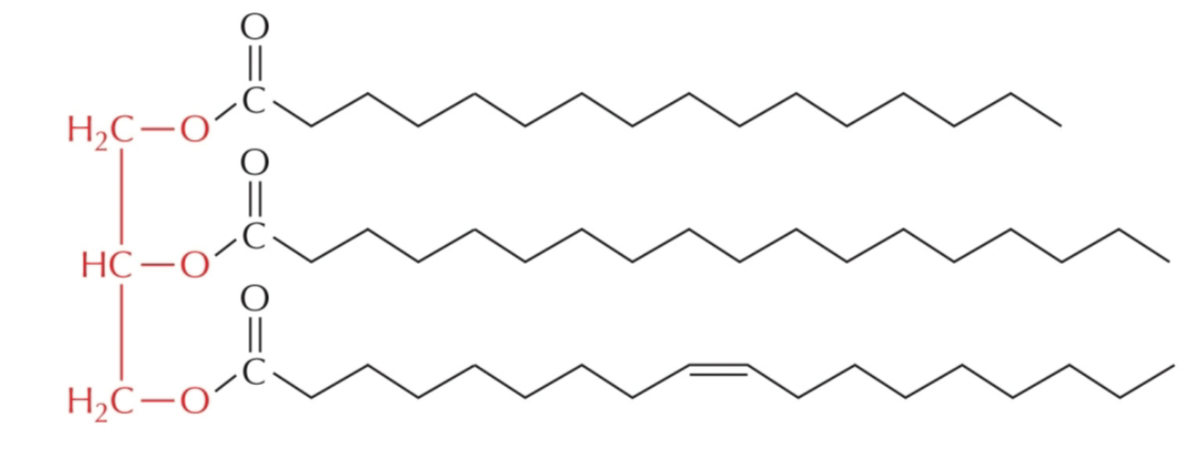
is the following a simple triglyceride?
why or why not?
NO bc/ all of the fatty acids are not identical
do lipids with saturated or unsaturated fatty acids have higher energy density and why?
saturated
they are linear and able to be stacked ontop of each other for storage
lipids with saturated/unsaturated fatty acids are solid at room temp (fats)
saturated (linear + compact)
lipids with saturated/unsaturated fatty acids are liquid at room temperature (oil)
unsaturated
___________ are highly concentrated energy stores
where are they stored?
triaglycerols (TAGs)
adipose tissue and muscle
fuel-rich white tissue that is located throughout the body notably under the skin (subcutaneous fat) and surrounding internal organs (visceral fat)
adipose tissue
fat cells that makeup adipose tissue
major site of triaglycerol accumulation
specialized for triaglyceral synthesis, storage, and mobilization into guel
adipocytes
what occupies most of the adipocyte volume within adipose tissue?
what are they surrounded by that allows them to undergo lipid metabolism?
lipid droplets— made of triacylglycerols
surrounded by phospholipid monolayer and proteins
triaglycerol degredation from a triacylglycerol to a diacylglycerol to a monoacylglycerol is made possible by intestinal _______ secreted by the ___________
lipases
pancreas
in _______ cells:
triacylglycerol —> glycerol + fatty acids
in _______cell:
glycerol + glycolysis —> pyruvate
glycerol + gluconeogenesis —> glucose
in other tissues (ENERGY)
fatty acid __________ ——> acytelCoA —> ____ ____ _________ —> CO2 + H2O
fat
liver
oxidation citric acid cycle
glycerol from triacylglycerol is converted to a _______ _____________ in the ______
glycolytic intermediate in the liver
glycerol is absorbed by the _______
phosphorylated and oxidized to __________ ____________
isomerized to _________________
liver
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate
fatty acids are transported via _________ for energy (ATP) supply in tissues
low glucose levels in the blood trigger the _________ of triacylglycerol molecules in fat droplets to ______ ______and _______
these fatty acids enter the ________ where they bind to _______ protein
fatty acid transporters in the plasma membrane of cells that __________ fatty acids such as muscle cells then pass these fatty acids into the cytosol
moved into the ____________ for energy production
bloodstream
hydrolysis
fatty acids and glycerol
blood albumin
oxidize
mitochondria
______ is the most efficient energy source
_______ of one gram of fat releases twice as much energy as the ________ of _____________
fat
oxidization oxidation glycogen
fatty acids provide energy to all tissues in the body except the _______
the ________ relies of circulating _______ or ________bodies when available because fatty acids are poorly utilized in this organ
brain
brain glucose ketone
in phospholipids, two of the OH groups in _______ are linked to fatty acids while the third OH group is linked to ______ _______ which carries a negative charge which is further linked to a small _______ group
glycerol
phosphoric acid
polar
what are the 5 polar groups found in phospholipids?
Serine
Ethanolamine
Choline
Glycerol
Inositol
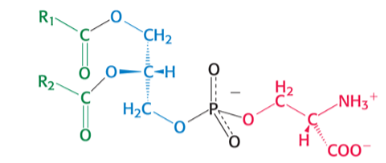
which phospholipid is pictured ?
phosphatidylSERINE
SUPER has COO- AND NH3+
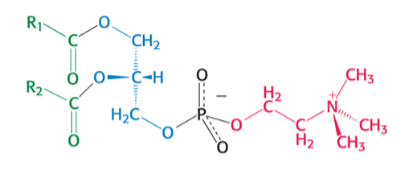
which phospholipid is pictured ?
phosphatidylCHOLINE
choline is crazy for methylated nitrogen
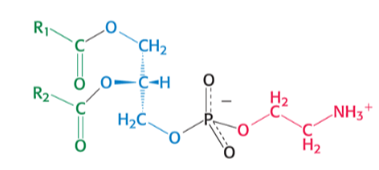
which phospholipid is pictured ?
phosphatidylETHANOLAMINE
ethan chill he only got one NH3+
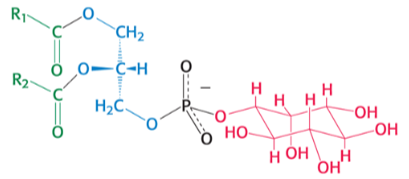
which phospholipid is pictured ?
phosphatidylINOSITOL
complicated chair like its name
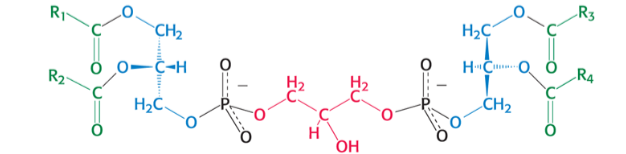
which phospholipid is pictured ?
diphospatidylglycerol (cardiolipin)
we knowww glycerol from triacyylglycerides (3 OH 3 Cs)
lipid _______ based on chemical properties of fatty acids are critical in biology
fatty acids have hydrophilic ____ and hydrophobic _______
in water they can form surface ______ or spherical _______
their derivatives can form from larger aggregates held together by _______ forces
aggregation
head
tail
hydrophobic
_______ form large, spherical fat droplets in the cell cytoplasm
_______ and _______ form self-sealing lipid bilayers which are the basis for all cell membranes
triacylglycerides
phospholipids and glycolipids
_______ are a common class of lipidsi that have a common multi-ring structure
steroids