3) Nuclear and electronic structure of atoms and their stability
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
how to find atomic mass
add the number of protons and neutrons
what is mass deficiency
amount of mass converted to energy when the nucleus was formed
theoretical – actual mass of nucleus
theoretical = mass of nucleus = mass of proton x # of protons) + (mass of neutron x # of neutrons)
actual = atomic mass – mass of electrons
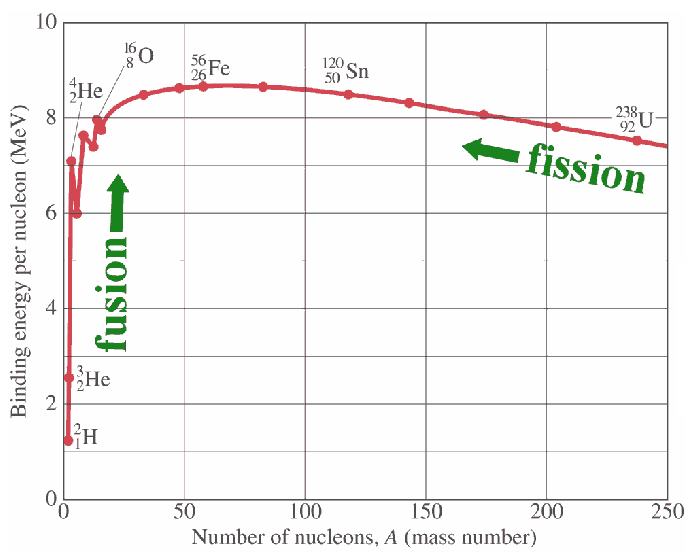
what is NBE? details about it for elements (iron)?
nuclear binding energy = ∆Mc2, ∆M = mass deficiency
iron at mass 56, has the highest NBE of all elements, it’s the strongest, most energy released per nucleon, strongest nucleus
implications of NBE (fusion and fission)
fusion: combining two atoms, cannot fuse elements heavier than iron, you’d have negative energy gain
fission: splitting an atom into other, two fragments you produce are higher on the curve than uranium, that’s why you gain energy (iron is the lower limit)
iron is the largest element you can fuse, and the smallest element you can fission
fusion is going right on graph (bigger), fission is going left (smaller)
what are isotopes
horizontal
atoms of the same element, same protons, different number of neutrons, different atomic mass
toPes = P = proton
what are isobars?
diagonal
same atomic mass, different protons, different neutrons
slight differences in mass, but mass numbers are the same
bars = gold bars = mass
what are isotones
vertical
different atomic mass, different protons, same neutron number
toNes = N = neutrons
stable and unstable nuclides?
stable: nucleus is stable and does not change
unstable/radioactive: nucleus spontaneously transforms into a different nucleus, making a different element
what is the band of stability
the stable nuclides in the middle of the unstable ones
This band follows the neutrons = protons line in the beginning (20 first). After this, it becomes more neutron-rich, because protons repel each other, causing instability
most stable configuration is when atom occupies __? what is radioactive decay
low energy state
radioactive decay is atom trying to get to a more stable configuration
majority of stable nuclides have even number of protons and even number of neutrons. only 4 with both odd
electron in an orbital can be described by four quantum numbers, what are they?
principal quantum number (n=1,2,3,4)
asimuthal quantum number (l = n-1)
magnetic quantum number (m= -1 to 1 including 0)
spin quantum number (describes the spin of electron)
what are the rules of the aufbau princple
electrons enter orbitals with lowest energy, and minimize energy of atom
max number of elecs that can occupy orbital is two
orbs are singly occupied first before they are paired with opposite spins (hunts rule of max multiplicity)
no two elecs can have the same values for all four quantum numbers (paulii exclusion principle)
what makes elements reactive
atoms try to attain a state of filled orbitals by donating, accepting, or sharing electrons with other atoms
only electrons in the outermost shells are typically involved in these transactions
what are two important atomic properties
nuclear stability: determined by proton/neutron number ratio in the nucleus
reaction affinity: determined by the electronic config of the atom