3- digestion + absorption physio
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
3 main processes of digestion
secretion: enzymes, mucus, ions into digestive tract + hormones into blood
absorption: water, ions, nutrients
motility: contractions of smooth muscle to crush, mix, propel
what’s the main organ of digestion + absorption
small intestine
what other 2 organs are involved w/ digestion + absorption
pancreas: releases pancreatic juice containing enzymes
gallbladder: releases bile
how many liters of fluid pass though the GI system everyday
9 L
how many liters are ingested each day
2 L, remaining 7 L comes from the GI system
how many liters are eliminated/lost each day to stool
only 100 mL
5 important cell types of small intestine
enterocyte
goblet cell: mucin
enteric endocrine cell: gastrin, CCK, secretin
stem cell
Paneth cell: lysozyme
which small intestine cell is involved with absorption
enterocytes, absorbs amino acids, glucose, monoglycerides, membrane enzymes
4 features of the small intestine that increase its surface area
intestinal folds
villi
microvilli
crypts
T/F: villi only live for a few days, die + shed into lumen
true
which part of the small intestine has the largest amount of digestion + significant amount of nutrient absorption
jejunum
which nutrients are not absorbed in the small intestine
iron
vitamin B12
bile acids
how is vitamin B12 absorbed
intrinsic factor from stomach parietal cells binds to B12 in duodenum → binds to receptor in distal ileum to be absorbed into portal blood
3 types of absorption diffusion mechanisms of GI tract
simple
carrier-mediated
channel-mediated
how is starch/carbs digested
salivary amylase breaks down food → polysaccharides
pancreatic amylase in duodenum breaks down polysaccharides → disaccharides
disaccharidase in small intestine epithelium breaks down disaccharides → monosaccharides (simple sugars)
4 examples of disaccharides
lactose: glucose-galactose
sucrose: glucose-fructose
maltose: glucose-glucose
starch: glucose-glucose
3 examples of monosaccharides (simple sugars)
glucose
fructose
galactose
how are monosaccharides (simple sugars) absorbed
via Na+ dependent transporter: glucose + lactose
via non-Na+ dependent transporter: fructose
in capillaries
once the monosaccharides (simple sugars) are absorbed, where does it go
carried to liver where they’re stored
how are pancreatic proteases (enzymes that cleave peptide bonds) activated
small intestine secretes enterokinase, which cleaves trypsinogen (secreted by pancreas) → trypsin, which allows all other proteases to be activated
how is protein digested
stomach: denatures + partially hydrolyzes proteins using HCl + pepsin
small intestine: proteases breakdown proteins → amino acids
how is protein absorbed
Na+ dependent cotransporters via active transport in small intestine enterocytes
how are lipids digested
bile acids combine w/ fats → emulsion droplets that are degraded by lipase, breaking the fat → monoglycerides
how are lipids absorbed
micelles containing monoglycerides penetrate + release fats into unstirred layer next to small intestine epithelium for absorption
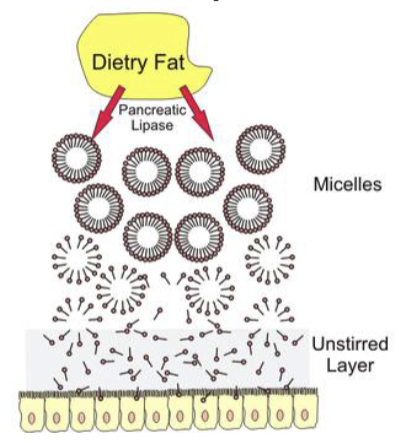
how does pancreatic lipase break down fat
hydrolyzes glycerol-fatty acid bonds in triglyceride → 2 monoglycerides + free fatty acids
how are fats absorbed
after entering the enterocyte, the monoglycerides + fatty acids are reassembled into triglycerides → triglycerides are repackaged into chylomicrons in smooth ER → chylomicrons are secreted from the enterocyte via exocytosis into the lymphatics
main function of colon
reabsorb water via Na+ gradient