HAN312 lec6 nervous system & special senses
1/283
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
284 Terms
nervous system functions
carries impulses between the brain, neck, head, and spinal nerves
releases chemicals called neurotransmitters
controls voluntary and involuntary bodily functions
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PSN)
nerves throughout the body, cranial nerves, spinal nerves, autonomic nervous system (ANS)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
involuntary bodily functions, sympathetic vs parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
part of ANS, influence bodily functions during times of stress
parasympathetic nervous system
part of ANS, heart rate, breathing, GI tract muscles
cerebrum
largest and uppermost portion of the brain, divided into right and left halves (cerebral hemispheres) and subdivided into lobes, cerebral cortex, gyrus, sulcus
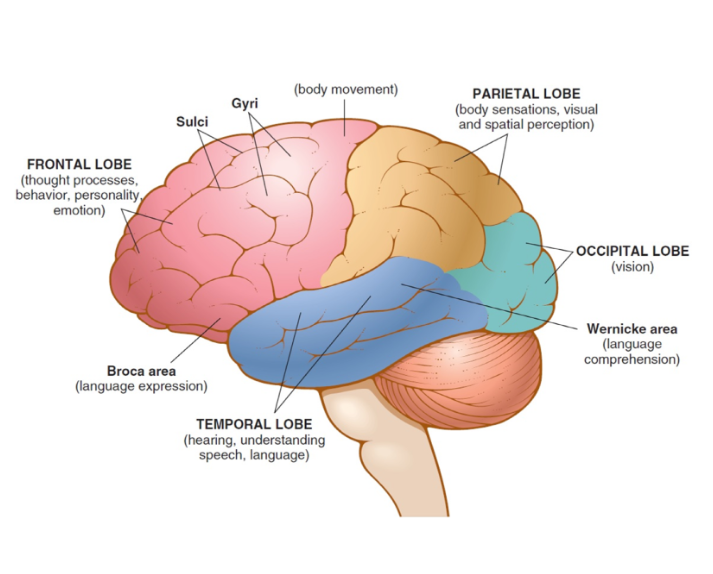
cerebral cortex
surface nerve cells, gray matter, controls higher mental functions (speech, vision, smell, movement, hearing, and thought)
gyrus
raised convolution on the surface of the cerebrum
sulcus
groove or fissure on the surface of the brain
frontal lobe
front portion of the cerebrum that controls voluntary muscle movement and is involved in emotions, Broca area
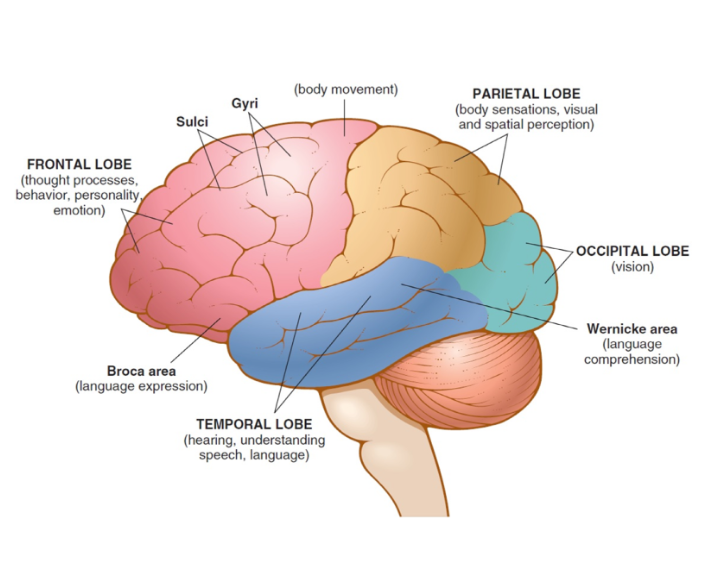
occipital lobe
back portion of the cerebrum that control vision
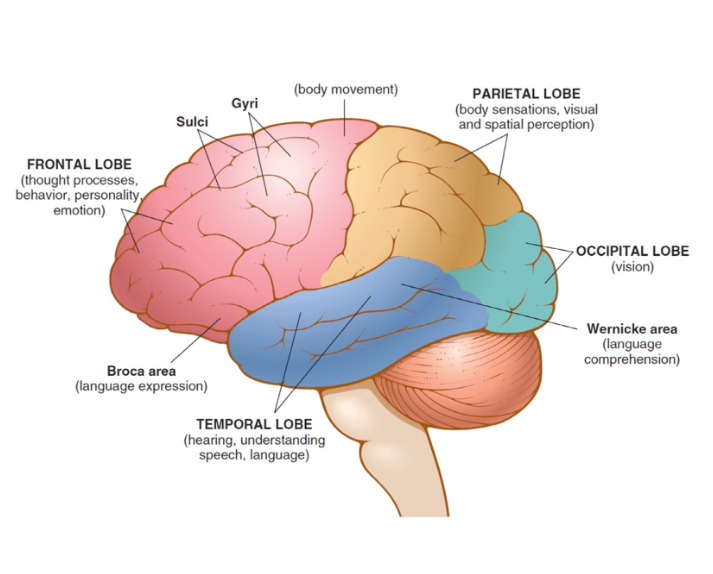
parietal lobe
middle-top portion of the cerebrum involved in perception of touch, temperature, and pain
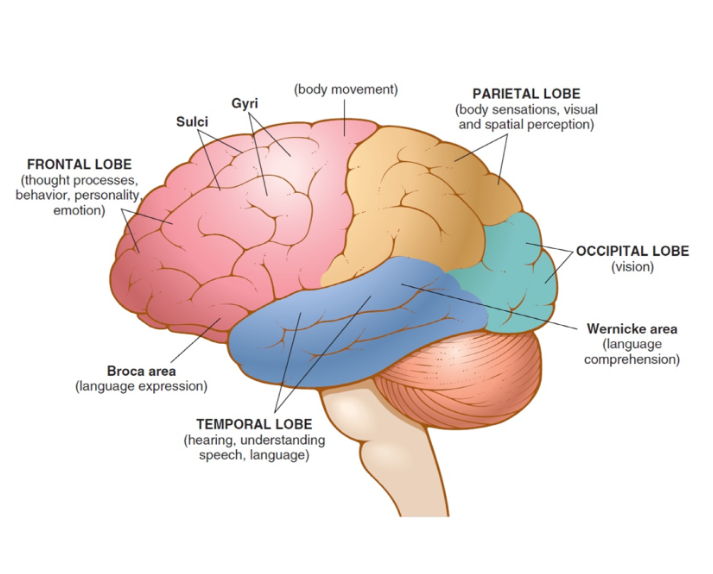
temporal lobe
portion of cerebrum below the frontal lobe, controls senses of hearing and smell as well as memory, emotion, speech and behavior, Wernicke area
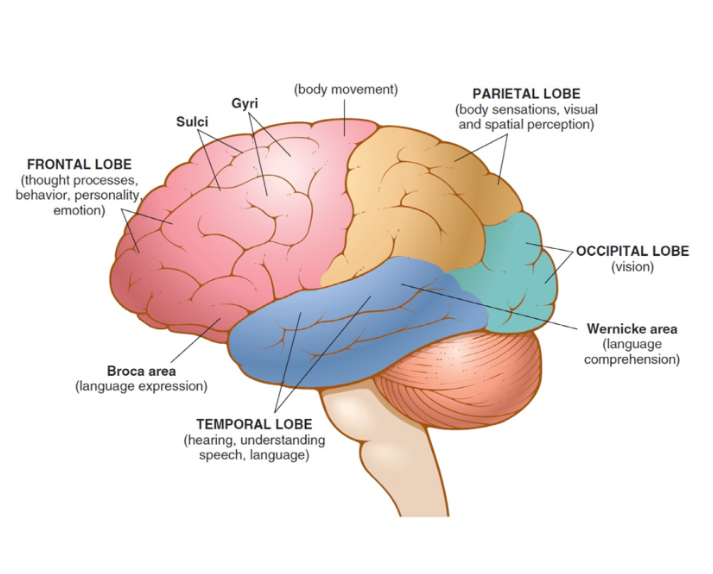
diencephalon
hypophysis, responsible for directing sensory information to the cortex, area deep within the brain that contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland
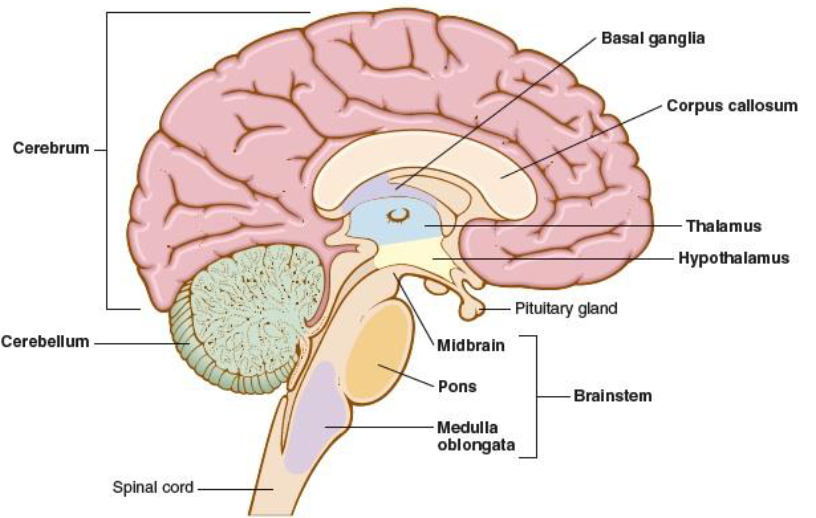
thalamus
integrates and monitors impulses from the skin, i.e. pain
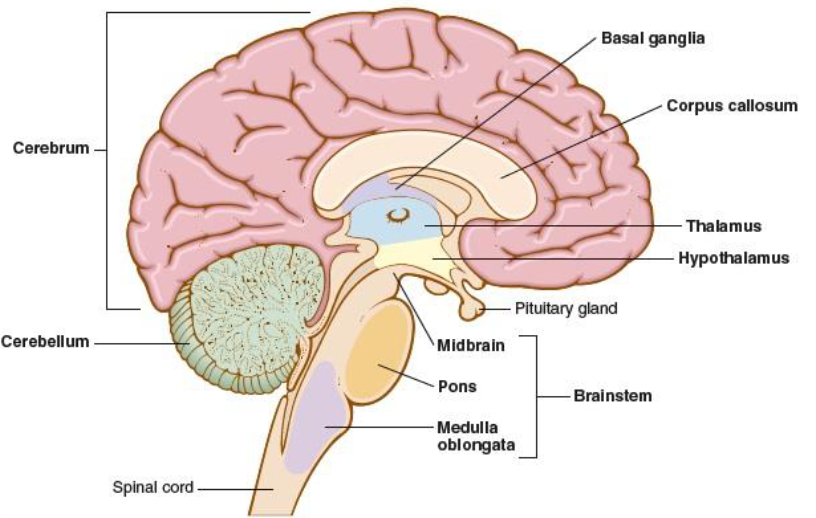
hypothelamus
controls body temp, sleep, appetite, sexual desire, and hormones (released from the pituitary gland)
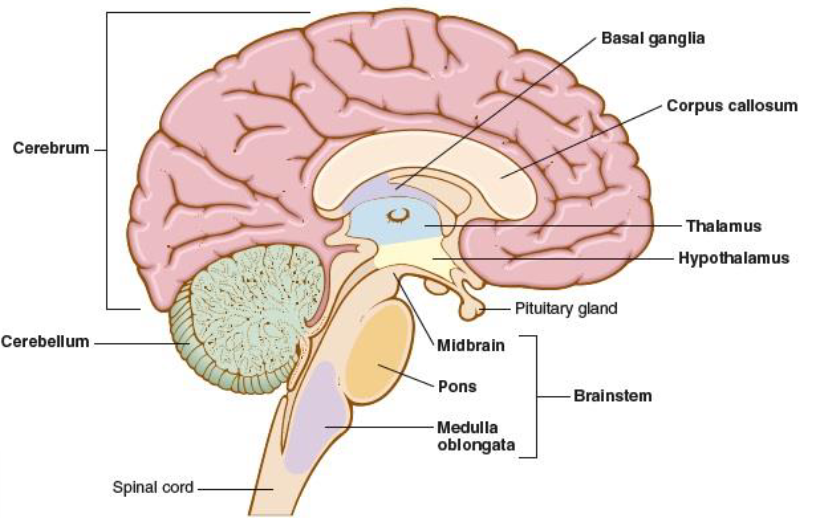
cerebellum
hindbrain, posterior portion of the brain, coordinates the voluntary muscles and maintains balance
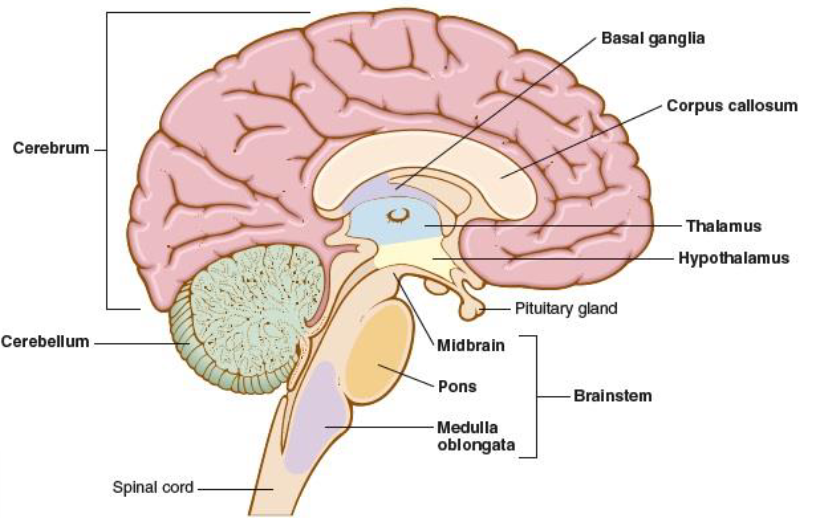
brainstem
connects the brain to the spinal cord, assists in breathing, heart rhythm, vision, and consciousness, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
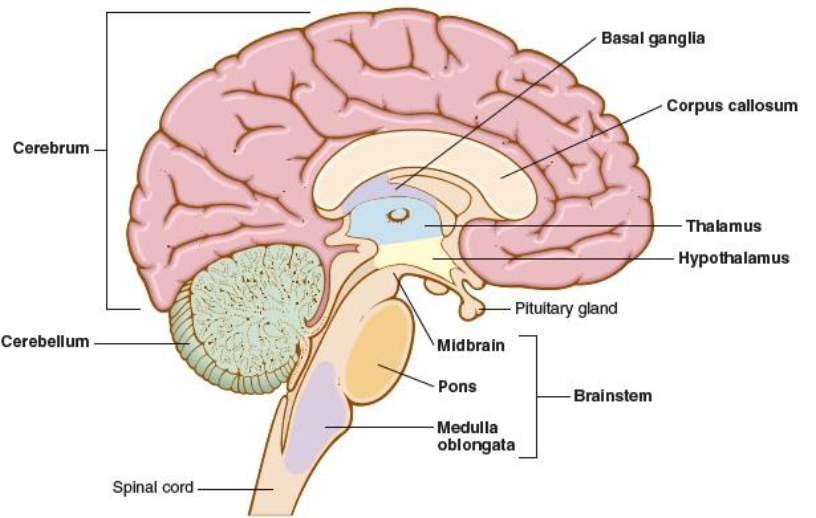
midbrain
mesencephalon, uppermost part of brainstem that connects the brainstem to the cerebellum, controls sensory processes
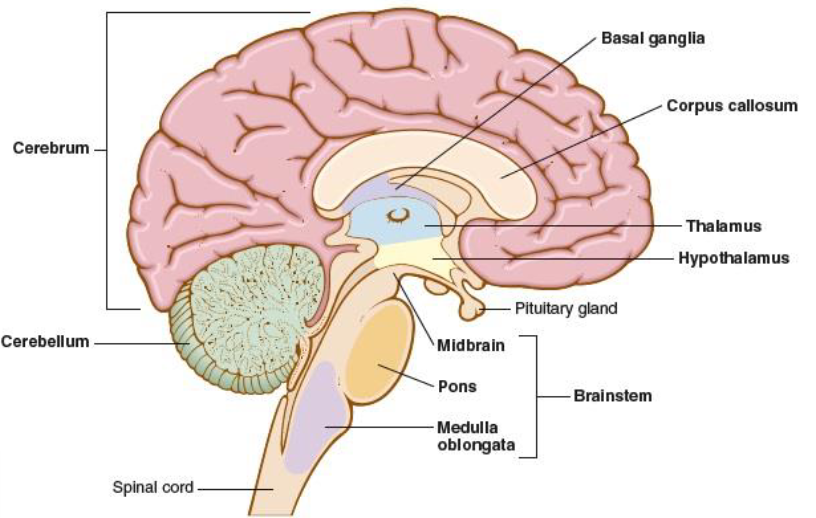
pons
bridges cerebrum and cerebellum with the rest of the brain, houses nerves for face and eyes
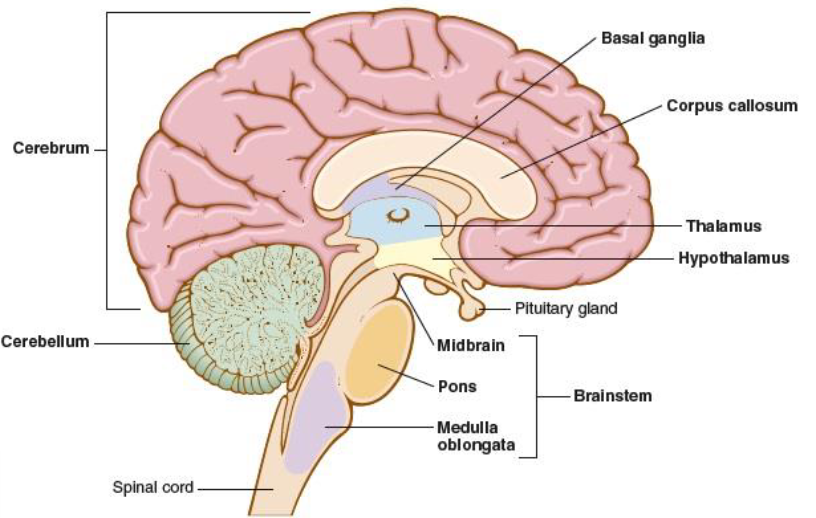
medulla oblongata
part of the brainstem that connects the brain and the spinal cord, controls respiration, heartbeat, and blood vessel size
ventricle
one of the 4 interconnected cavities within the brain that contain and secrete cerebrospinal fluid
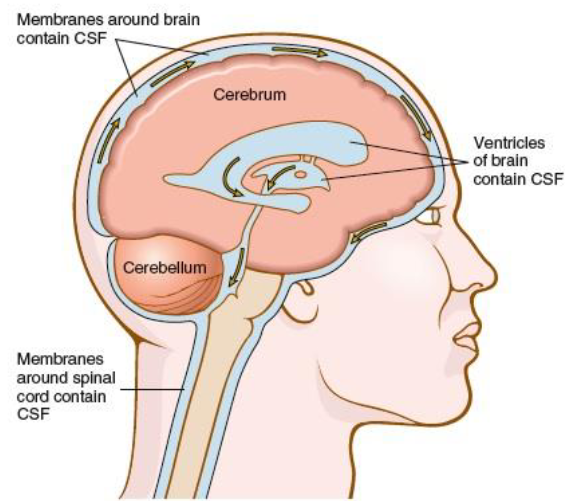
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
colorless fluid that circulates in and around the brain and spinal cord, acts as a protector and transports nutrients
meninges
membranous covering of the brain and spinal cord, dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
dura mater
strong fibrous outermost layer of the meninges, subdural space under
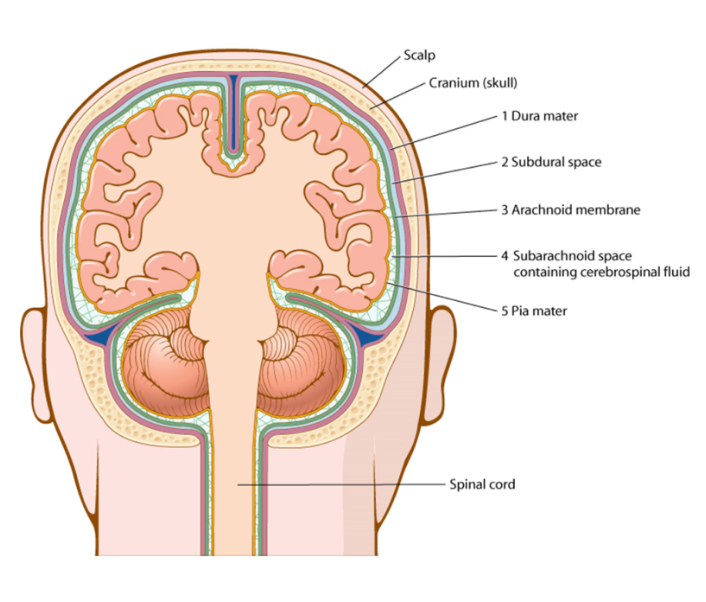
arachnoid
delicate fibrous membrane forming the middle layer of the meninges, subarachnoid space under
pia mater
thin inner layer of the meninges that attaches directly to the brain and spinal cord
spinal cord
portion of the CNS contained in the spinal or vertebral canal, responsible for nerve conduction to and from the brain and the body, begins at the brainstem and ends at the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae, culminating in the cauda equina (horse tail)
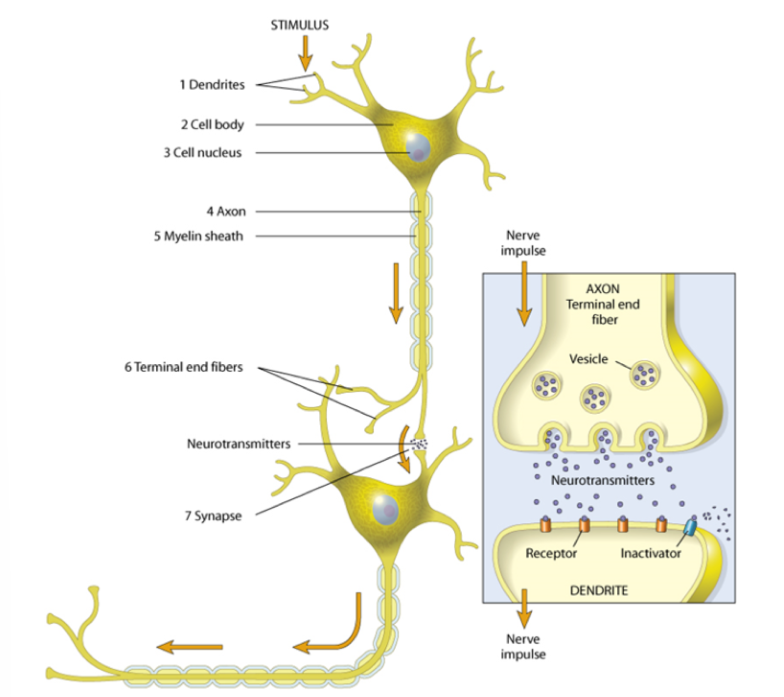
neurons
individual nerve cells that make up the basic structure of the nervous system and conduct impulses
anatomical portions of a neuron
dendrite, cell body, nucleus, axon (myelin sheath), terminal end fibers (secrete neurotransmitters across synapse)
ganglion
group of nerve cell bodies located along the pathway of a nerve
plexus
interlacing network of nerves
neurotransmitters
chemical messenger released into a synapse by a neuron, either stimulates or inhibits another cell
sensory nerves
afferent, carry messages toward the brain
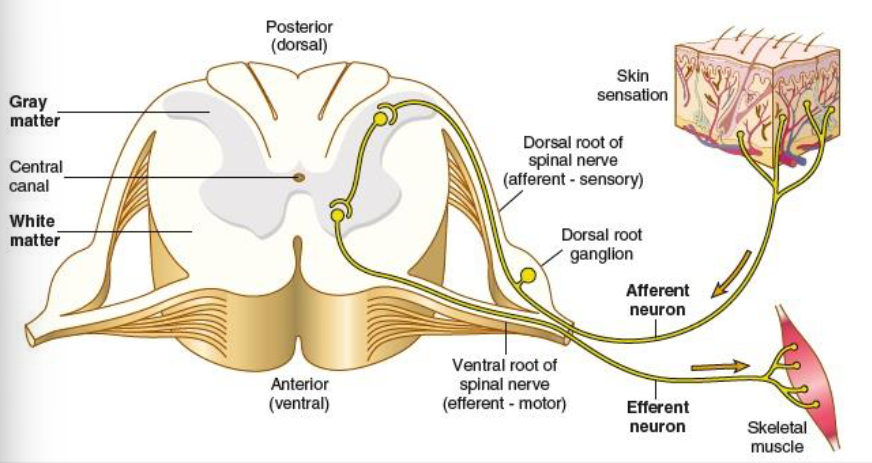
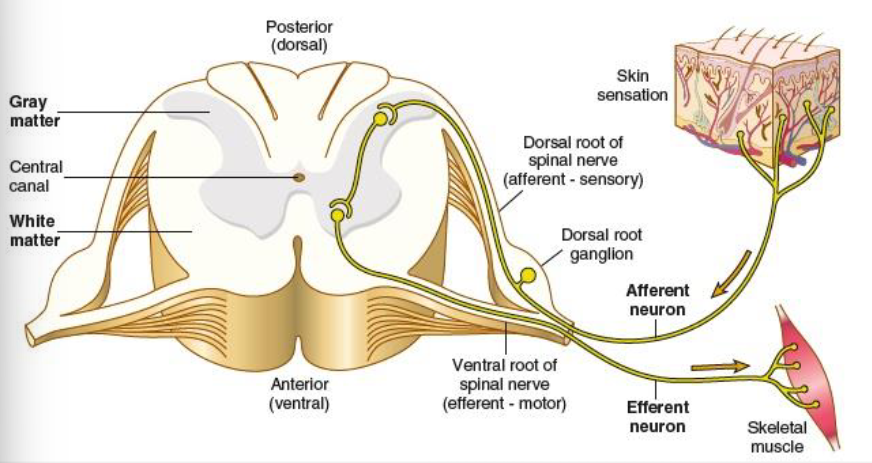
motor nerves
efferent, carry messages away from the brain
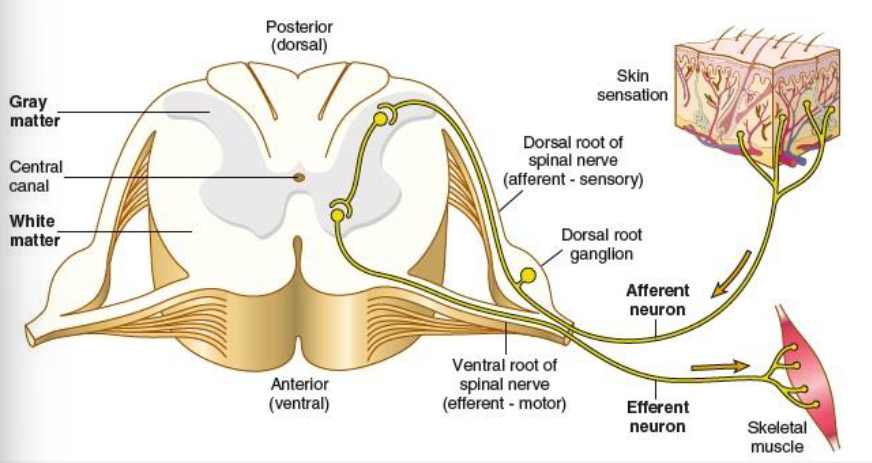
mixed nerves
carry both sensory and motor fibers
dorsal root
carry sensory impulses toward the spinal cord/brain
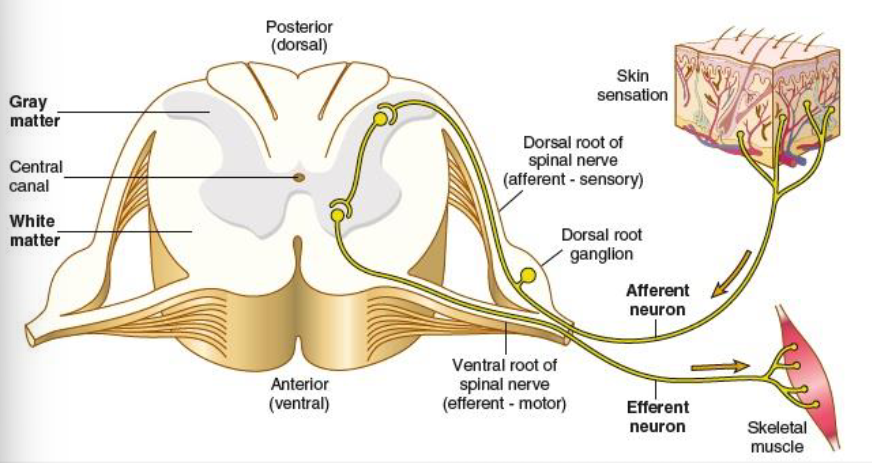
ventral root
carries motor impulses away from the spinal cord/brain to muscles or glands
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that emerge from the cranium, olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal
olfactory nerve
I, sense of smell
optic nerve
II, vision
oculomotor nerve
III, controls eye movement (up, down, medial, and pupil constriction)
trochlear nerve
IV, controls superior oblique eye movement (downward and outward eye movement)
trigeminal nerve
V, sensory (face, teeth, sinuses) and motor (chewing muscles)
abducens nerve
VI, controls lateral rectus eye muscle (outward eye movement)
facial nerve
VII, facial expressions, taste, and tear and salivary gland function
vestibulocochlear nerve
VIII, hearing and balance
glossopharyngeal nerve
IX, taste, swallowing, salivation
vagus nerve
X, controls heart rate, digestion, speech
accessory nerve
XI, controls neck and shoulder muscles
hypoglossal nerve
XII, controls tongue movements
spinal nerves
31 pairs that emerge from the spine
neuroglia/glia cells
cells that support and protect nervous tissue, do not transmit impulses
glia cells CNS
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia
glia cells PNS
satellite cells, Schwann cells
astrocytes
provide structural (blood brain barrier) and metabolic support, repair cells
oligodendrocytes
myelinate axons and insulate electrical impulses
ependymal cells
produce and moves cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)

microglia
defense and immune response
satellite cells
provide structural and metabolic support for cell body of neurons
Schwann cells
myelinate axons and insulate electrical impulses
combining form gray
poli/o
combining form sensation, perception
esthesi/o
combining form speech
phas/o
combining form word, phrase
lex/o
combining form muscle
my/o
combining form movement
kines/o
combining form order, coordination
tax/o
combining form entire brain
encephal/o
combining form skull
crani/o
combining form head
cephal/o
combining form cerebrum
cerebr/o
combining form cortex
cortic/o
combining form thalamus
thalam/o
combining form cerebellum
cerebell/o
combining form pons
pont/o
combining form meninges
mening/o, meningi/o
combining form sheath (referring to meninges)
thec/o
combining form hard, dura mater
dur/o
combining form ventricle
ventricul/o
combining form spine
spin/o
combining form vertebra
spondyl/o
combining form spinal cord, bone marrow
myel/o
combining form ganglion
gangli/o, ganglion/o
combining form glue, neuroglia
gli/o
combining form few, scanty
olig/o
combining form nerve
neur/o
combining form nerve root
radicul/o
combining form vagus nerve
vag/o
prefix half
hemi-
prefix on, following
epi-
prefix above, excessive
hyper-
prefix below, deficient
hypo-
prefix beside
para-
prefix many, much
poly-
prefix four
quadri-
suffix mind
-phrenia
suffix speech
-phasia
suffix movement
-kinesia, -kinesis, -kinetic